Structural Characteristics and Anticoagulant Property In Vitro and In Vivo of a Seaweed Sulfated Rhamnan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
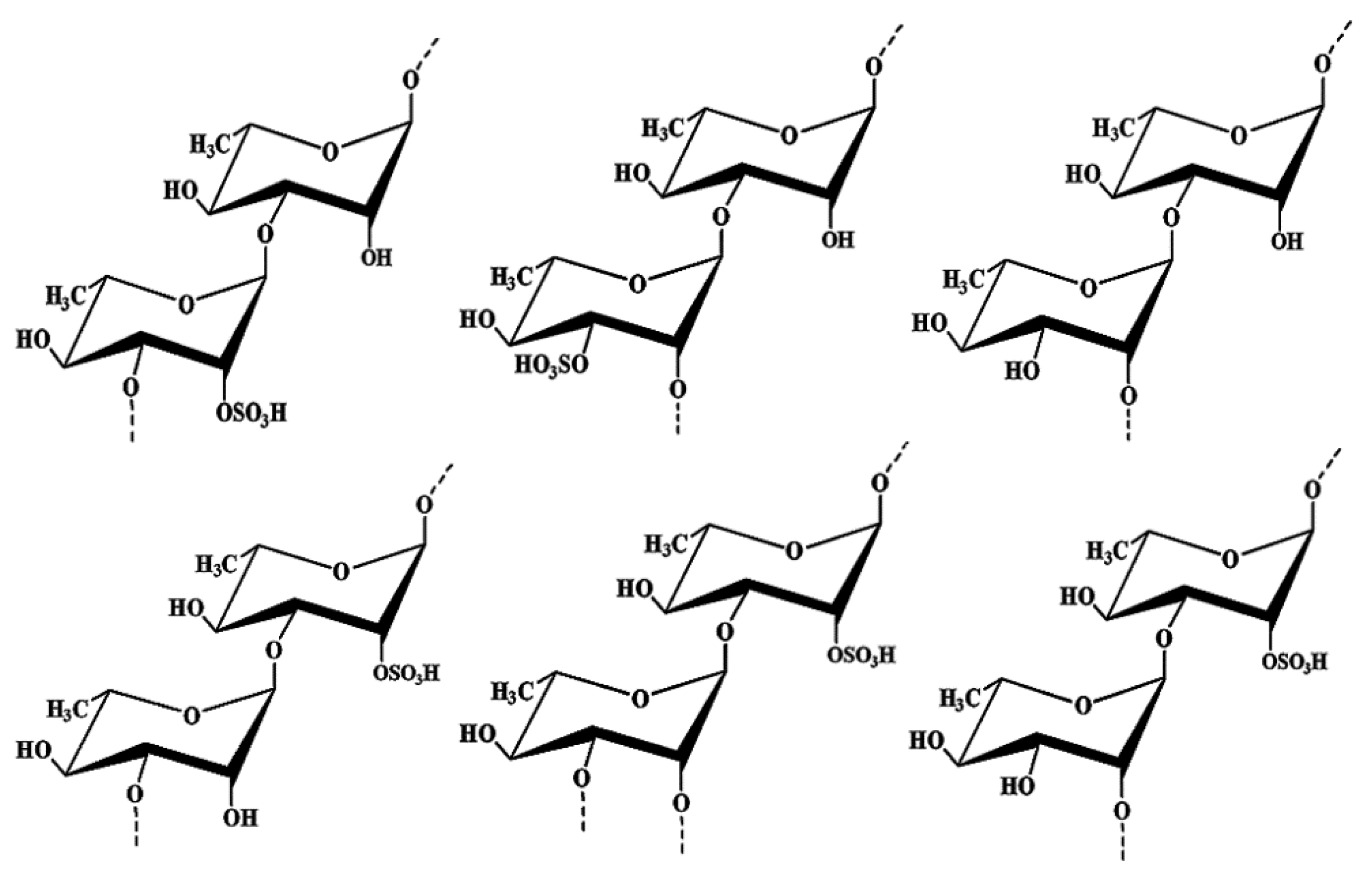
2.1. Structure Elucidation of the Seaweed Polysaccharide
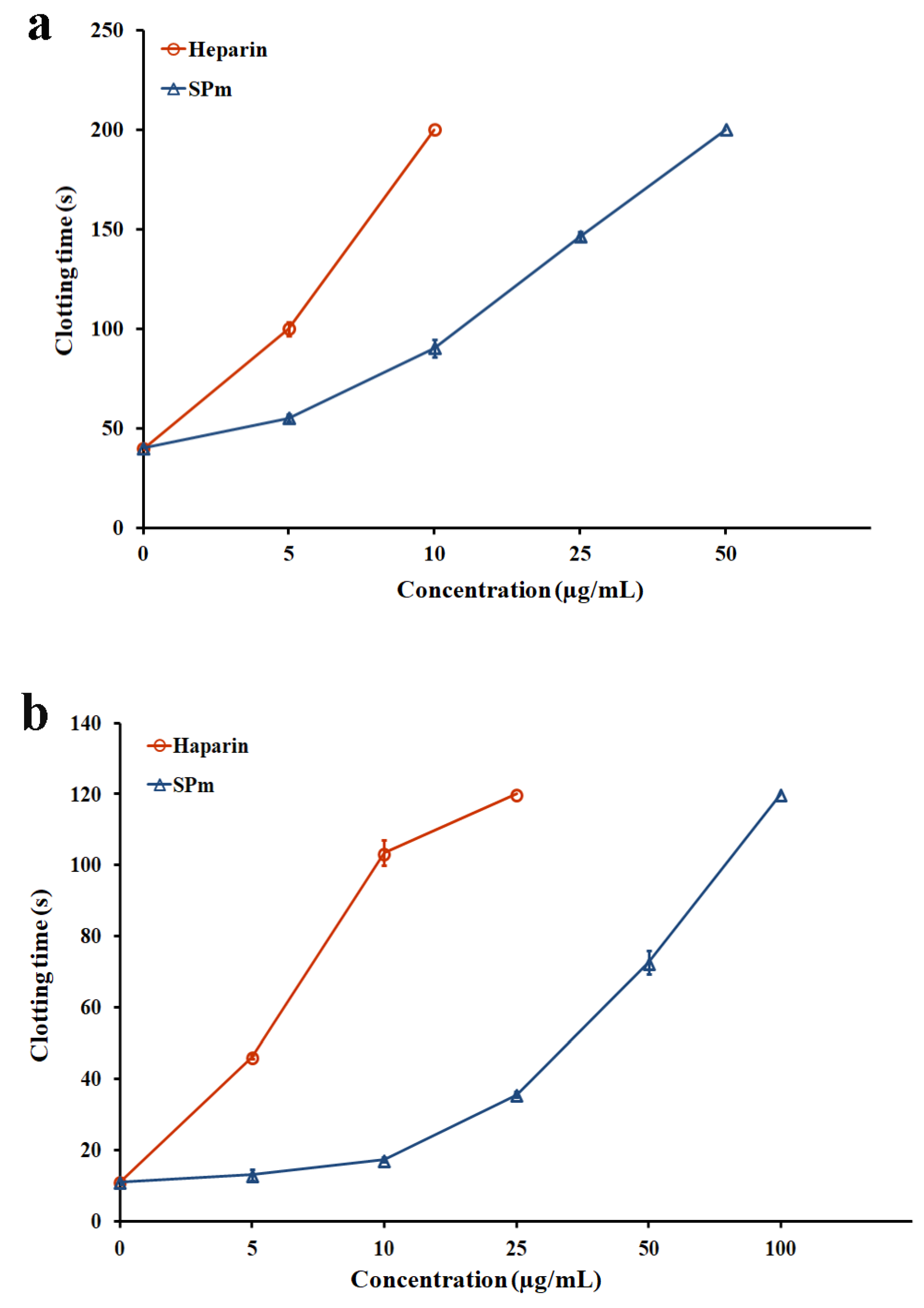
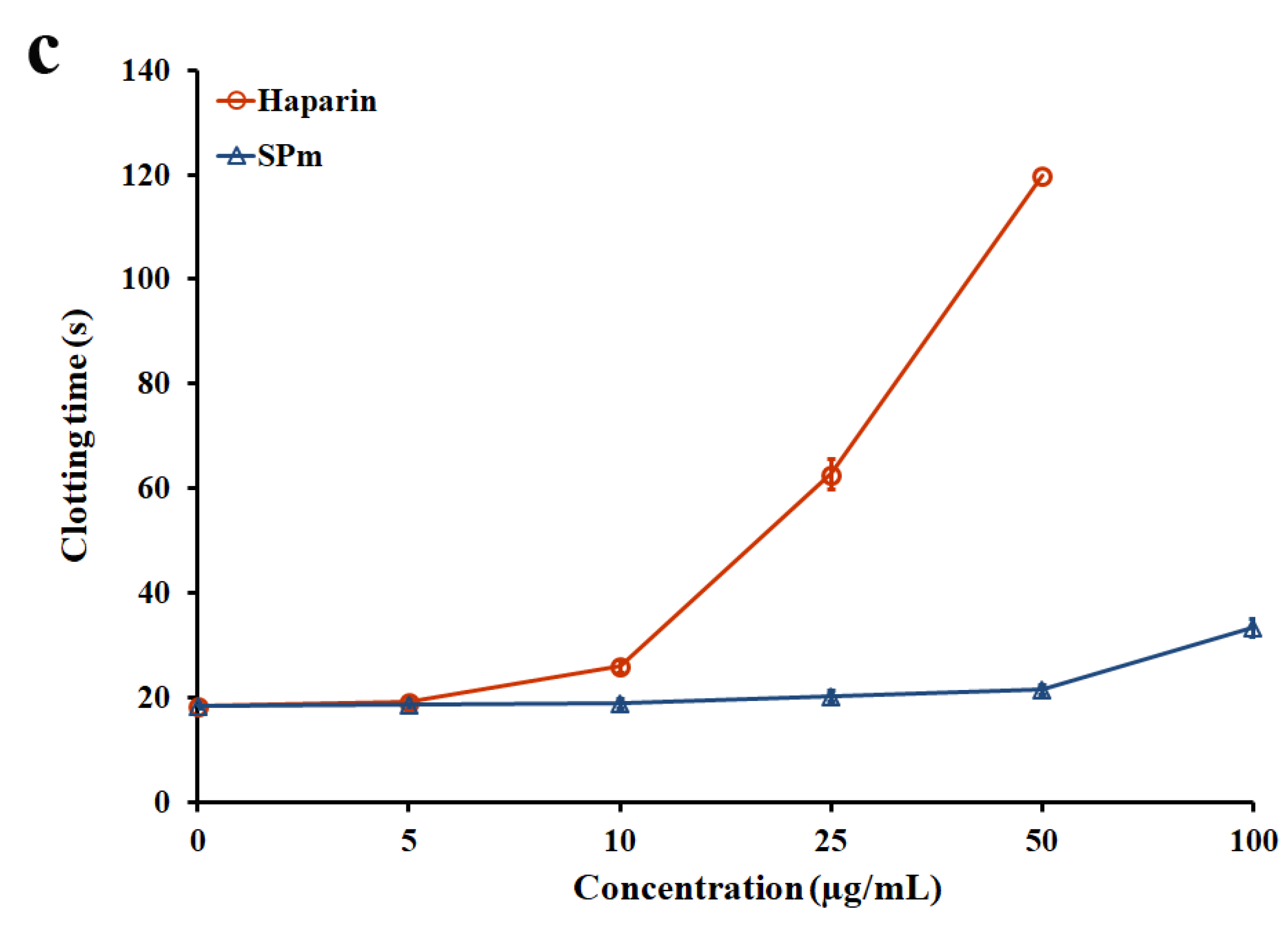
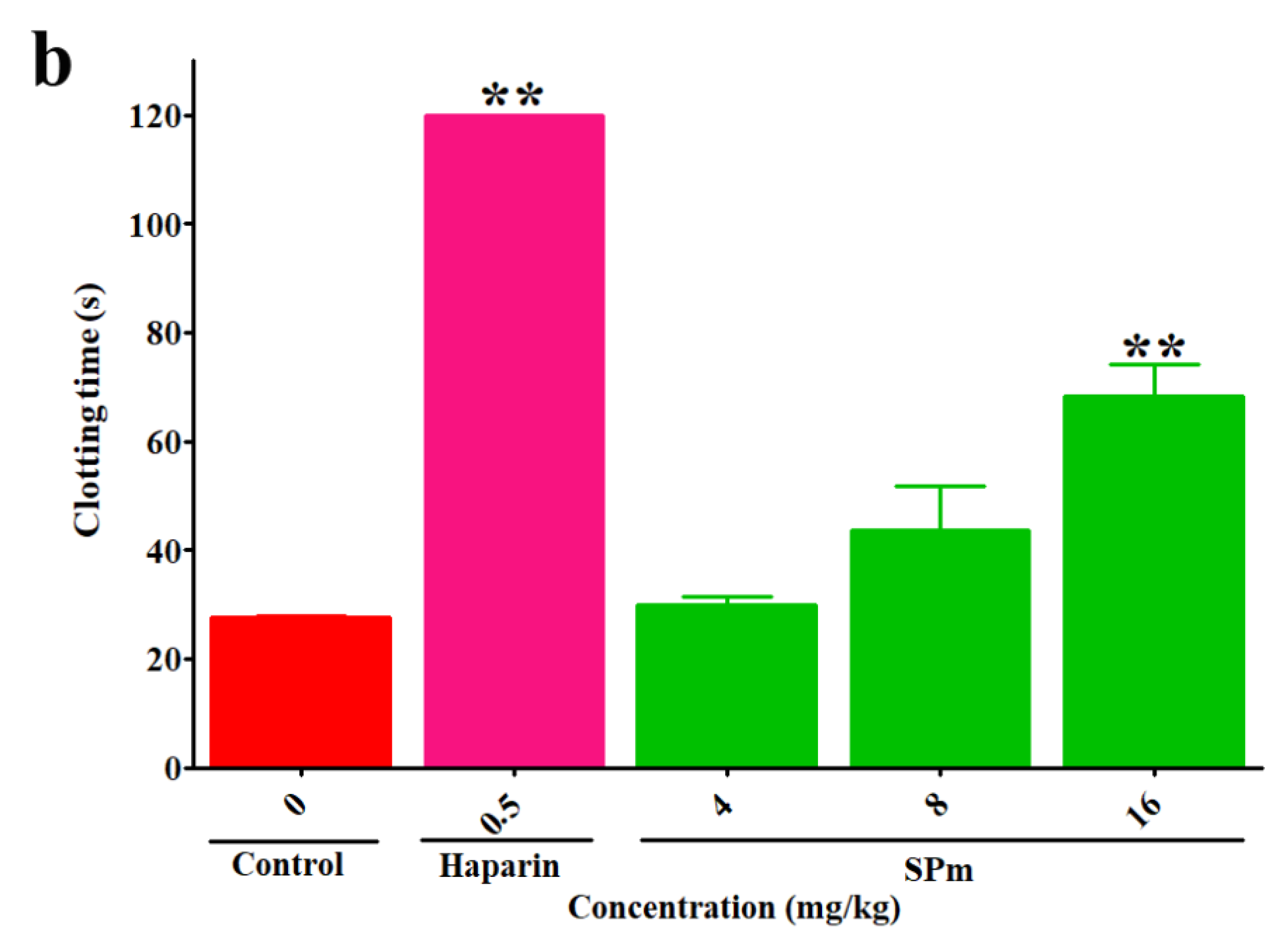
2.2. Anticoagulant Activity In Vitro and In Vivo of SPm
2.3. Fibrin(ogen)olytic Activity of SPm
2.4. Thrombolytic Activity of SPm
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Animals
3.3. Extraction and Purification of the Sulfated Polysaccharide
3.4. Composition Analysis
3.5. Structure Analysis
3.6. Evaluation of Anticoagulant Activity In Vitro
3.7. Assessment of Anticoagulant In Vivo and Fibrin(ogen)olytic Properties
3.8. Assay of Thrombolytic Activity In Vitro
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mackman, N. Triggers, targets and treatments for thrombosis. Nature 2008, 7181, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mega, J.L.; Siman, T. Pharmacology of antithrombotic drugs: An assessment of oral antiplatelet and anticoagulant treatments. Lancet 2015, 9990, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, P.C.Y.; Becker, D.L.; Stafford, A.R.; Fredenburgh, J.C.; Weitz, J.I. Molecular basis for the susceptibility of fibrin-bound thrombin to inactivation by heparin cofactor II in the presence of dermatan sulfate but not heparin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20959–20965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkentin, T.E. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: A clinicopathologic syndrome. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 82, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Qian, Y.; Zhou, X.D.; Pazandak, A.; Frazier, S.B.; Weiser, P.; Lu, H.; Zhang, L.J. Oversulfated chondroitin sulfate is not the sole contaminant in heparin. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linhardt, R.J.; Gunay, N.S. Production and chemical processing of low molecular weight heparins. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1999, 25, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schonberger, L.B. New variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1998, 12, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.R.; Pereira, M.S.; Fogue, D.; Mourão, P.A.S. Antithrombin-mediated anticoagulant activity of sulfated polysaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 20824–20835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darcy-Vrillon, B. Nutritional aspects of the developing use of marine macroalgae for the human food industry. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 1993, 44, S23–S35. [Google Scholar]
- Lahaye, M.; Robic, A. Structure and functional properties of Ulvan, a polysaccharide from green seaweeds. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, P.V.; Arata, P.X.; Ciancia, M. Polysaccharides from Codium species: Chemical structure and biological activity. Their role as components of the cell wall. Adv. Bot. Res. 2014, 71, 253–278. [Google Scholar]
- Usov, A.I. Polysaccharides of the red algae. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 2011, 65, 115–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.S.; Zheng, Y.; Fang, J.N. Recent advances in the study on poly- and oligo-saccharides with hypoglycemic activity. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 39, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Jeon, Y.J. Biological activities and potential industrial applications of fucose rich sulfated polysaccharides and fucoidans isolated from brown seaweeds: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, P.A.S.; Pereira, M.S.; Pavao, M.S.G.; Mulloy, B.; Tollefsen, D.M.; Mowinckel, M.C.; Abildgaard, U. Structure and anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from echinoderm. Sulfated fucose branches on the polysaccharide account for its high anticoagulant action. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23973–23984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.G.; Benevides, N.M.; Melo, M.R.; Valente, A.P.; Melo, F.R.; Mourão, P.A. Structure and anticoagulant activity of a sulfated galactan fromthe red alga, Gelidium crinale. Is there a specific structural requirement for theanticoagulant action? Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.S.; Melo, F.R.; Mourão, P.A.S. Is there a correlation between structure and anticoagulant action of sulfated galactans and sulfated fucans? Glycobiology 2002, 12, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H.; Pereira, M.S.; Valente, A.P.; Tollefsen, D.M.; Pavão, M.S.; Mourão, P.A. Selective cleavage and anticoagulant activity of a sulfated fucan: Stereospecific removal of a 2-sulfate ester from the polysaccharide by mild acid hydrolysis, preparation of oligosaccharides, and heparin cofactor II-dependent anticoagulant activity. Glycobiology 2005, 15, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.J.; Pyun, Y.R.; Hwang, J.K.; Mourão, P.A.S. A sulfated fucan from the brown alga Laminaria cichorioides has mainly heparin cofactor II-dependent anticoagulant activity. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2326–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Ovod, V.V.; Zdorovenko, G.M.; Gvozdyak, R.I.; Krohn, K.J. Structure of the O-polysaccharide and immunochemical relationships between the lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas syringae pathovar tomato and pathovar maculicola. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 258, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovod, V.V.; Zdorovenko, E.L.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kocharova, N.A.; Knirel, Y.A. Structural diversity of O-polysaccharides and serological classificationof Pseudomonas syringae pv. garcae and other strains of genomospecies 4. Microbiology 2004, 73, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Koizumi, S.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T. Structure of rhamnan sulfate from the green alga Monostroma nitidum and its anti-herpetic effect. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Lee, J.B.; Srisomporn, P.; Maeda, M.; Ozawa, T.; Sakuragawa, N. Inhibition of thrombin by sulfated polysaccharides isolated from green algae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1543, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T.; Sankawa, U.; Maeda, M. Antiviral activities against HSV-1, HCMV, and HIV-1 of rhamnan sulfate from Monostroma latissimum. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Liu, X.; He, X.X.; Wang, S.Y.; Cao, S.J.; Xia, Z.; Xian, H.L.; Qin, L.; Mao, W.J. Structure and anticoagulant property of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from the green seaweed Monostroma angicava. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 159, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hao, J.J.; He, X.X.; Wang, S.Y.; Cao, S.J.; Qin, L.; Mao, W.J. A rhamnan-type sulfated polysaccharide with novel structure from Monostroma angicava Kjellm (Chlorophyta) and its bioactivity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, M.; Uehara, T.; Harada, N.; Sekiguchi, M.; Hiraoka, A. Heparinoid-active sulphated polysaccharides from Monostroma nitidum and their distribution in the Chlorophyta. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3611–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassolato, J.E.F.; Noseda, M.D.; Pujol, C.A.; Pellizzari, F.M.; Damonte, E.B.; Duarte, M.E.R. Chemical structure and antiviral activity of the sulfated heterorhamnan isolated from the green seaweed Gayralia oxysperma. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Yamagaki, T.; Maeda, M.; Nakanishi, H. Rhamnan sulfate from cell walls of Monostroma latissimum. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Mao, W.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Qi, X.H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Xu, J.; Zhao, C.Q.; Hou, Y.J.; Yang, Y.P. Structural characterization of an anticoagulant-active sulfated polysaccharide isolated from green alga Monostroma latissimum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.J.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Qi, X.H.; Sun, H.H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, S.D. Chemical characteristic and anticoagulant activity of the sulfated polysaccharide isolated from Monostroma latissimum (Chlorophyta). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Mao, W.J.; Fang, F.; Li, H.Y.; Sun, H.H.; Chen, Y.; Qi, X.H. Chemical characteristics and anticoagulant activities of a sulfated polysaccharide and its fragments from Monostroma latissimum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.J.; Fang, F.; Li, H.Y.; Qi, X.H.; Sun, H.H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, S.D. Heparinoid-active two sulfated polysaccharides isolated from marine green algae Monostroma nitidum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, N.; Maeda, M. Chemical structure of antithrombin-active rhamnan sulfate from Monostroma nitidum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, S.S.; Key, N.S.; Greenberg, C.S. D-dimer antigen: Current concepts and future prospects. Blood 2009, 113, 2878–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, H.P.; Grant, P.J. Plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayakrishnan, V.; Kannappan, P.; Abdullah, N.; Ahmed, A.B.A. Cardioprotective activity of polysaccharides derived from marine algae: An overview. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 30, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K. Recent advances in marine algal anticoagulants. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 2, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekaraa, I.; Pangestutia, R.; Kim, S.K. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therho, T.T.; Hartiala, K. Method for determination of the sulfate content of glycosaminoglycans. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 41, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitter, T.; Muir, H.M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1962, 4, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.E.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nakashima, T.; Ueda, T.; Tomii, K.; Kouno, I. Facilediscrimination of aldose enantiomers by reversed-phase HPLC. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.L.; Conrad, H.E. Stoichiometric depolymerization of polyuronides and glycosaminoglycuronans to monosaccharides following reduction of their carbodiimide-activated carboxyl groups. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falshaw, R.; Furneaux, R.H. Structural analysis of carrageenans from thetetrasporic stages of the red algae, Gigartina lanceata and Gigartina chapmanii (Gigartinaceae, Rhodophyta). Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 307, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakomori, S. A rapid permethylation of glycolipid, and polysaccharide catalyzed by methylsulfinyl carbanion in dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Biochem. 1964, 55, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.J.; Henry, R.J.; Blakeney, A.B.; Stone, B.A. An improved procedure for the methylation analysis of oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 127, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Wada, H.; Abe, Y.; Tomatsu, H.; Nishioka, J.; Nobori, T. Clinical evaluation of a test for plasma fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products (FDP) based on monoclonal anti-FDP antibody technology: An application for the scoring system of the disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) diagnostic criteria. Rinsho Byori Jpn. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 51, 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Pulivarthi, S.; Gurram, M.K. Effectiveness of D-dimer as a screening test for venous thromboembolism: An update. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 6, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zucker, M.; Seligsohn, U.; Salomon, O.; Wolberg, A.S. Abnormal plasma clot structure and stability distinguish bleeding risk in patients with severe factor XI deficiency. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omura, K.; Hitosugi, M.; Zhu, X.; Ikeda, M.; Maeda, H.; Tokudome, S. A newly derived protein from Bacillus subtilis natto with both antithrombotic and fibrinolytic effects. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 99, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Concentration | D-dimer (mg/L) | PAI-1 (U/mL) | FDP (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0 mg/kg | <0.10 a | 1.17 ± 0.10 | 0.50 ± 0.01 |
| SPm b | 4 mg/kg | <0.10 | 0.56 ± 0.11 ** | 2.34 ± 0.42 ** |
| 8 mg/kg | 0.28 ± 0.05 **## | 0 **## | 4.67 ± 0.38 **## | |
| 16 mg/kg | 0.25 ± 0.03 **## | 0 **## | 3.94 ± 0.26 **## | |
| Urokinase | 20,000 U/kg | <0.10 | 0.62 ± 0.13 ** | 2.26 ± 0.52 ** |
| Sample | Concentration | Clot Lytic Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 0 mg/mL | 6.60 ± 0.14 |
| SPm a | 4 mg/mL | 12.87 ± 0.28 ** |
| 8 mg/mL | 23.47 ± 0.26 **# | |
| 16 mg/mL | 38.26 ± 0.54 **## | |
| Urokinase | 100 U/mL | 19.92 ± 0.66 ** |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Cao, S.; He, X.; Qin, L.; He, M.; Yang, Y.; Hao, J.; Mao, W. Structural Characteristics and Anticoagulant Property In Vitro and In Vivo of a Seaweed Sulfated Rhamnan. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16070243
Liu X, Wang S, Cao S, He X, Qin L, He M, Yang Y, Hao J, Mao W. Structural Characteristics and Anticoagulant Property In Vitro and In Vivo of a Seaweed Sulfated Rhamnan. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(7):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16070243
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xue, Shuyao Wang, Sujian Cao, Xiaoxi He, Ling Qin, Meijia He, Yajing Yang, Jiejie Hao, and Wenjun Mao. 2018. "Structural Characteristics and Anticoagulant Property In Vitro and In Vivo of a Seaweed Sulfated Rhamnan" Marine Drugs 16, no. 7: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16070243
APA StyleLiu, X., Wang, S., Cao, S., He, X., Qin, L., He, M., Yang, Y., Hao, J., & Mao, W. (2018). Structural Characteristics and Anticoagulant Property In Vitro and In Vivo of a Seaweed Sulfated Rhamnan. Marine Drugs, 16(7), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16070243