Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysates and Their Peptide Fractions Regulate Cytokine Production in Splenic Macrophages and Lymphocytes Involving the TLR4-NFκB/MAPK Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Hydrolysates and Their Peptide Fractions
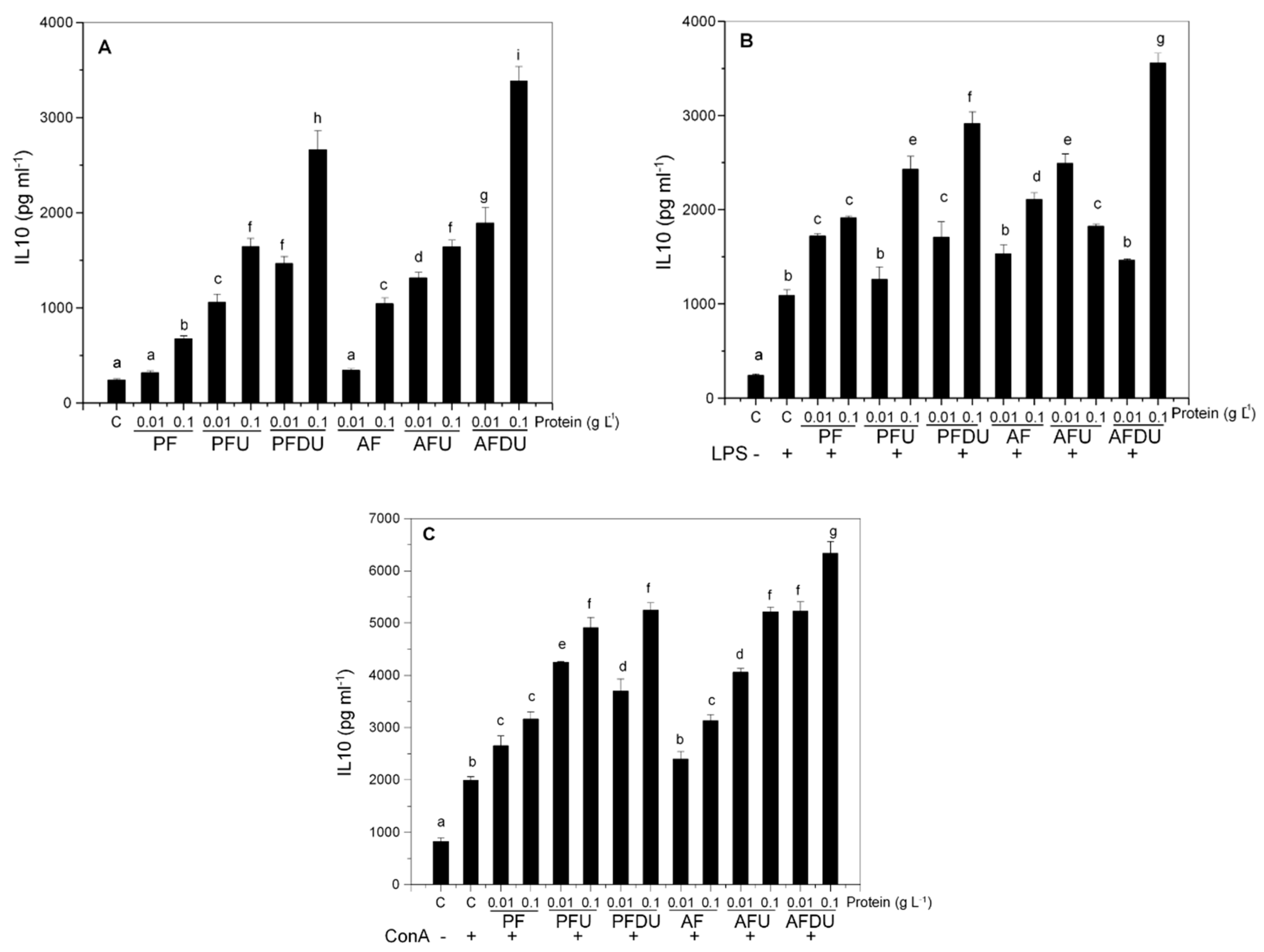
2.2. Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysate and Their Peptide Fractions Induce the Expression of the Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine IL-10 in Spleen Cells
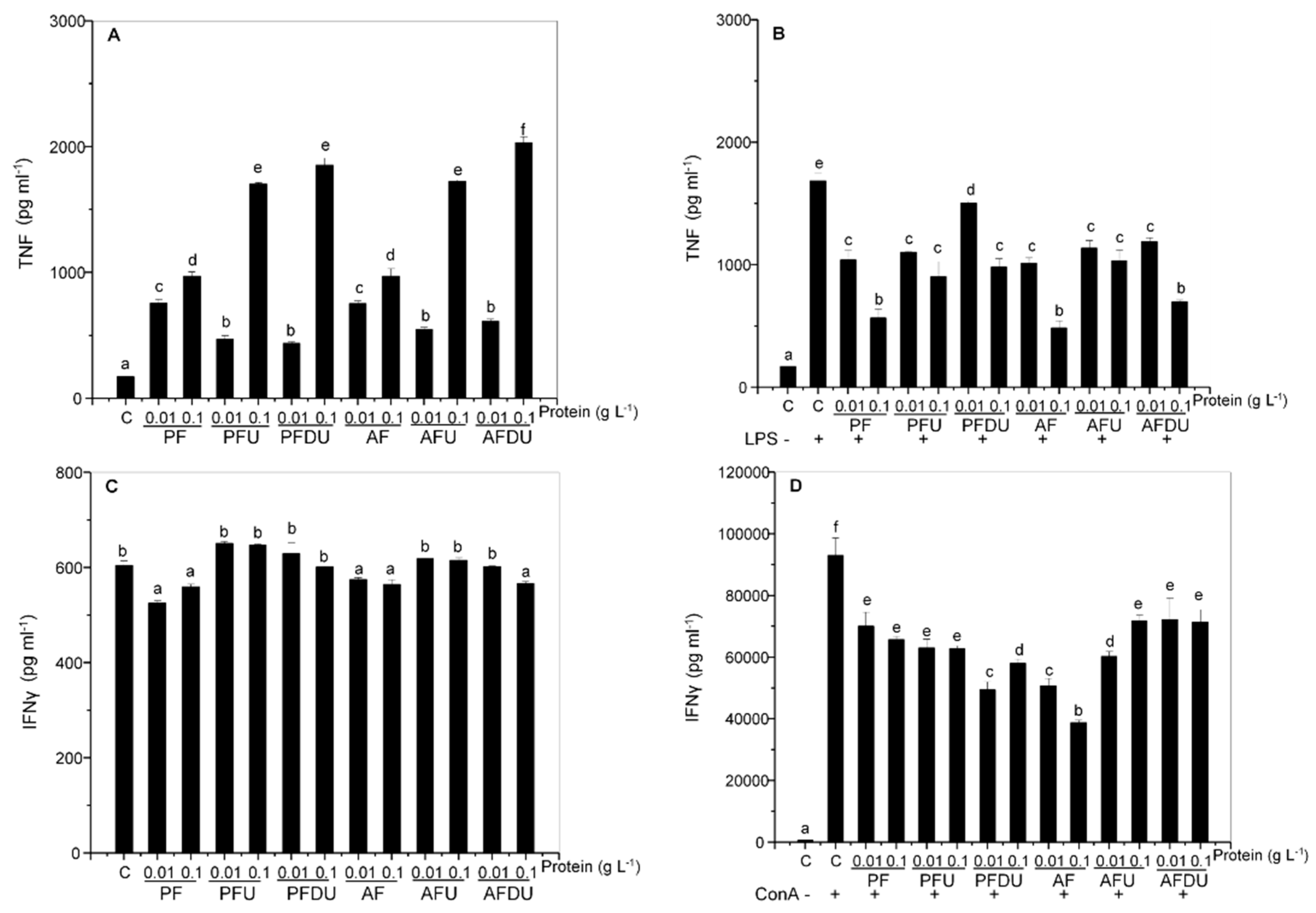
2.3. Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysates and Their Peptide Fractions Regulate the Expression of Proinflammatory Cytokines TNF and IFN-γ in Spleen Cells
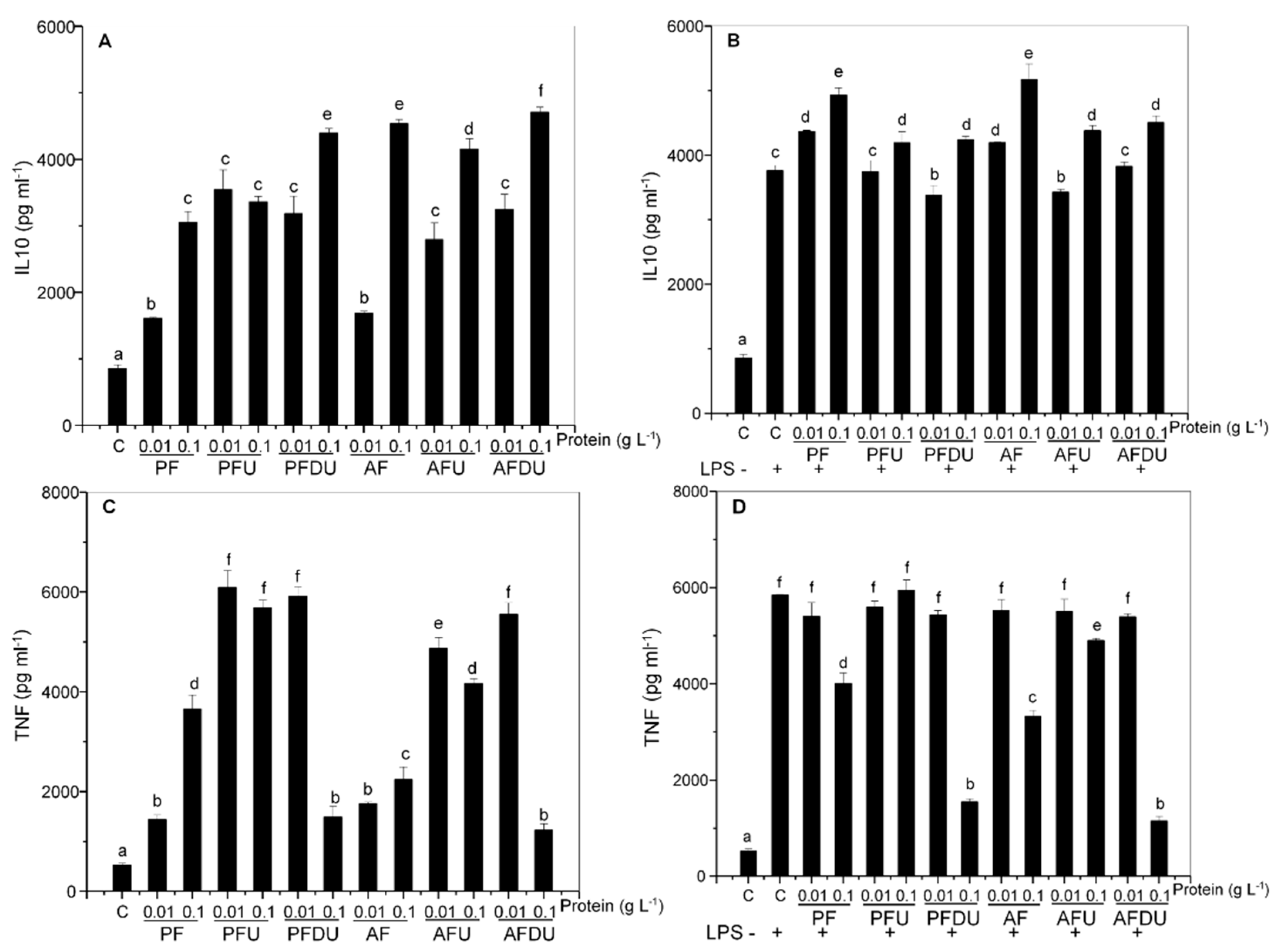
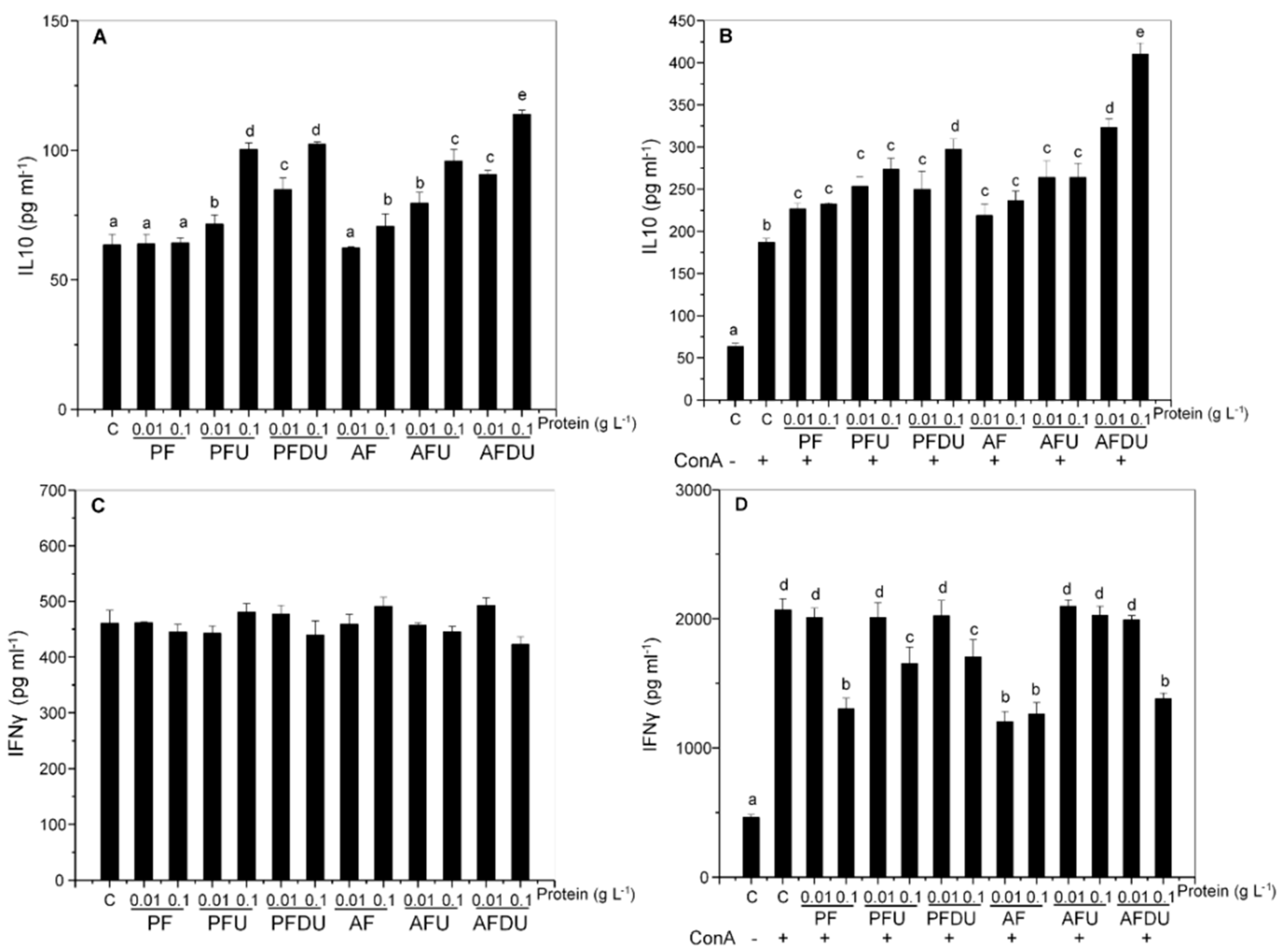
2.4. Macrophages and T Lymphocytes Contribute to the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysates and Their Peptide Fractions
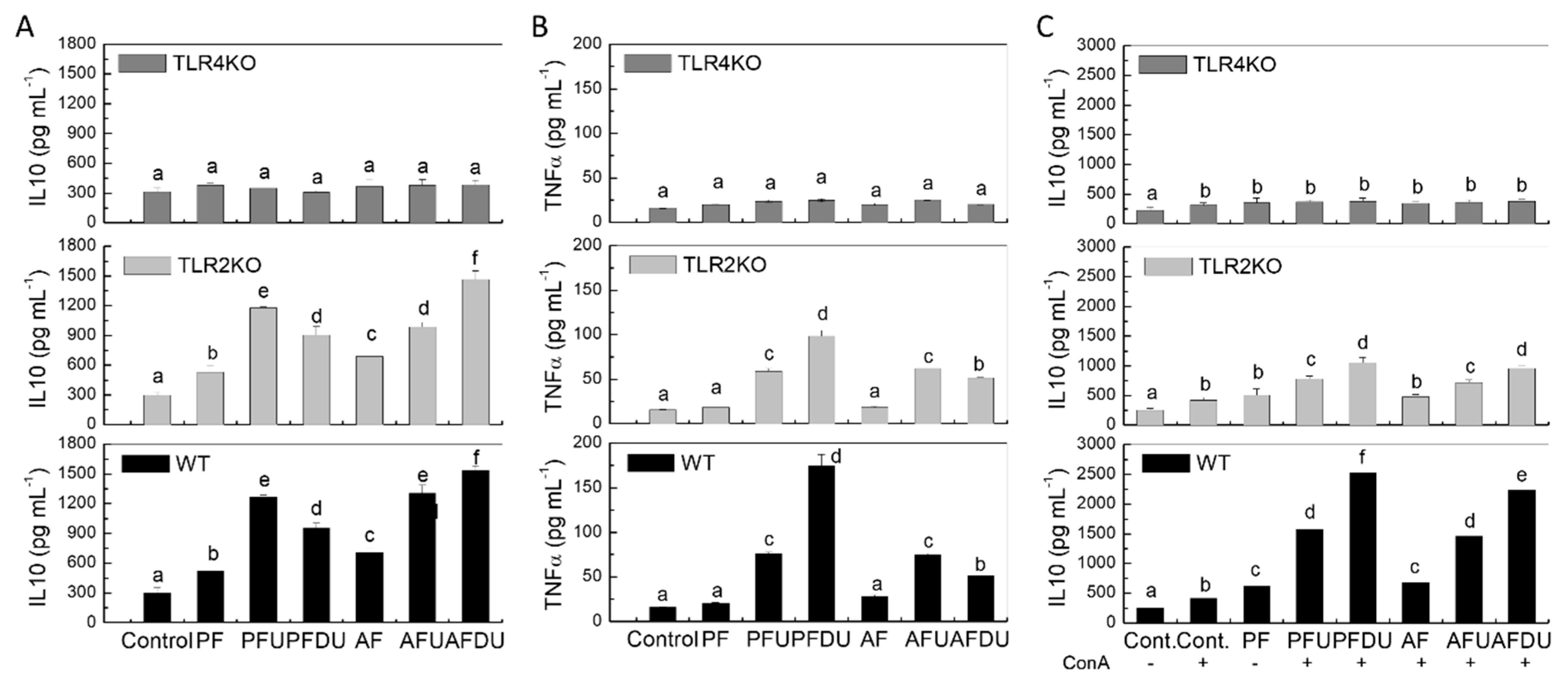
2.5. Effect of Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysate and Their Peptide Fractions by Splenocytes Are Mediated through TLR4 and TLR2
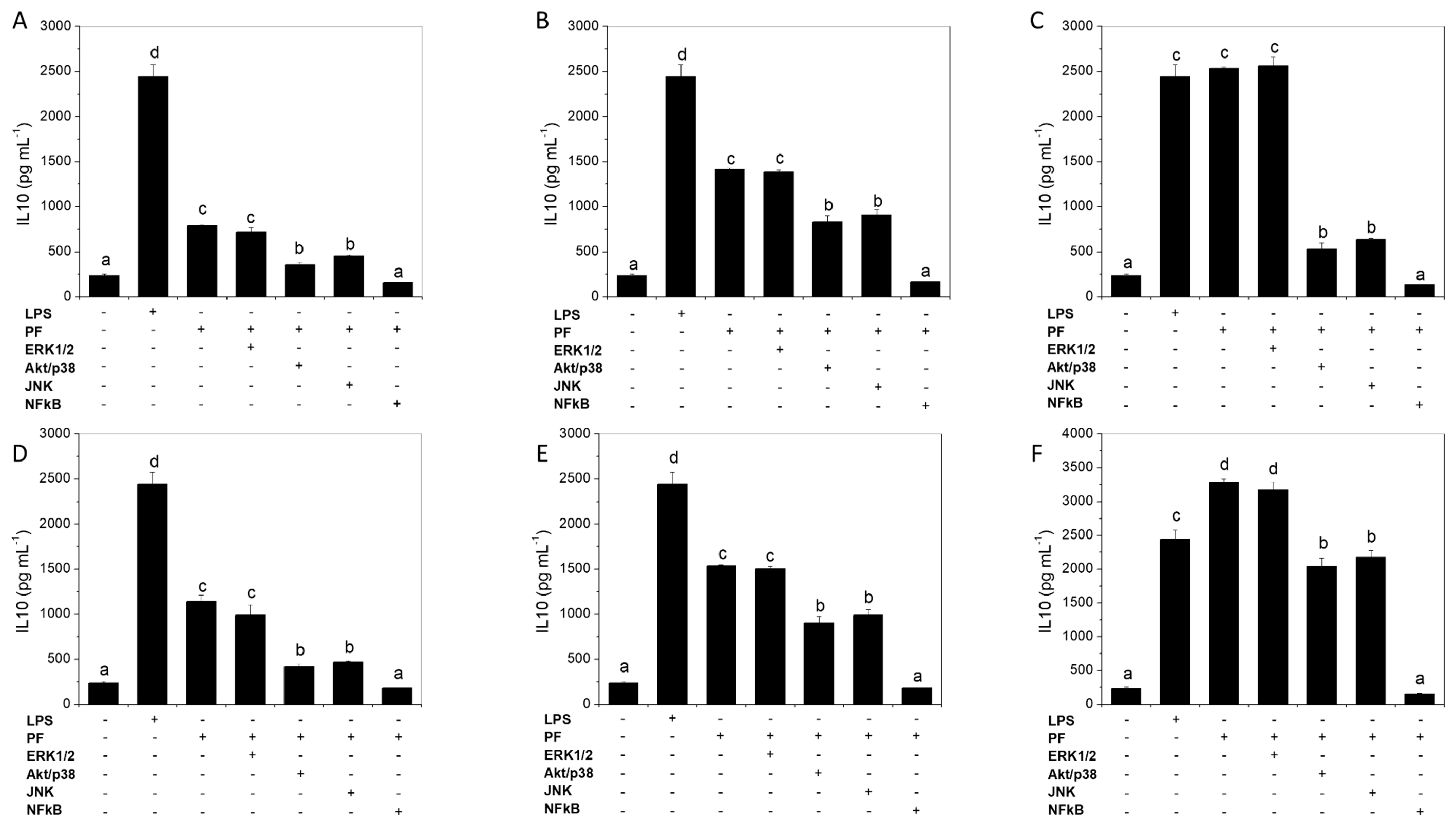
2.6. NFκB Activation Is Needed for IL-10 Induction by Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysate and Peptide Fractions, with Secondary Involvement of JNK and p38 MAPK
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Raw Materials
4.3. Preparation of Hydrolysates
- -
- Hydrolysate PF: hydrolysis with P enzyme 2 h + hydrolysis with F enzyme during 2 h; total reaction time, 4 h.
- -
- Hydrolysate AF: hydrolysis with A enzyme 2 h + hydrolysis with F enzyme during 2 h; total reaction time, 4 h.
4.4. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of Hydrolysates
4.5. Fractionation of Hydrolysates and Digested Hydrolysates
4.6. Fast Protein Liquid Chromatography (FPLC) of Hydrolysates and Ultrafiltered Fractions (<1 kDa)
4.7. Animals
4.8. Spleen Mononuclear Cells Ex Vivo Culture
4.9. Protein Determination
4.10. Cytokine Determination
4.11. Cell Toxicity Assay
4.12. NFκB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Inhibitors Assay
4.13. Data and Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | hydrolysate obtained with Alcalase + Flavourzyme |
| AFU | AF fractions with molecular weight <1 kDa |
| AFDU | fractions with molecular weight <1 kDa from in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of AF |
| PF | hydrolysate obtained with Purazyme + Flavourzyme |
| PFDU | fractions with molecular weight <1 kDa from in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of PF |
| PFU | PF fractions with molecular weight <1 kDa |
| TLR | Toll-like receptors |
References
- Peña-Rodríguez, A.; Mawhinney, T.P.; Ricque-Marie, D.; Cruz-Suárez, L.E. Chemical composition of cultivated seaweed Ulva clathrata (Roth) C. Agardh. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Vieira, L.; Almeida, A.P.; Kijjoa, A. The Marine Macroalgae of the Genus Ulva: Chemistry, Biological Activitiesand Potential Applications. Oceanography 2013, 1, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive proteins, peptides, and amino acids from macroalgae (1). J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-K.; Wijesekara, I. Development and biological activities of marine-derived bioactive peptides: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Bai, L.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X. Marine Algae-Derived Bioactive Peptides for Human Nutrition and Health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9211–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, H.J.; Carrillo, O.; Almarales, A.; Bermúdez, R.C.; Lebeque, Y.; Fontaine, R.; Llauradó, G.; Beltrán, Y.; Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Immunostimulant activity of an enzymatic protein hydrolysate from green microalga Chlorella vulgaris on undernourished mice. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennamany, R.; Saboureau, D.; Mekideche, N.; Creppy, E.E. SECMA 1, a mitogenic hexapeptide from Ulva algeae modulates the production of proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans in human foreskin fibroblast. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1998, 17, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cian, R.E.; Lopez-Posadas, R.; Drago, S.R.; Medina, F.S.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Immunomodulatory Properties of the Protein Fraction from Phorphyra columbina. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8146–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cian, R.E.; Lopez-Posadas, R.; Drago, S.R.; Sanchez de Medina, F.; Martinez-Augustin, O. A Porphyra columbina hydrolysate upregulates IL-10 production in rat macrophages and lymphocytes through an NF-kappaB, and p38 and JNK dependent mechanism. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cian, R.E.; Martínez-Augustin, O.; Drago, S.R. Bioactive properties of peptides obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis from protein byproducts of Porphyra columbina. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Nakashima, F.; Honda, K.; Lu, Y.-J.; Kondo, T.; Ushida, Y.; Aizawa, K.; Suganuma, H.; Oe, S.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Toll-like Receptors as a Target of Food-derived Anti-inflammatory Compounds. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32757–32772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrchen, J.M.; Sunderkotter, C.; Foell, D.; Vogl, T.; Roth, J. The endogenous Toll-like receptor 4 agonist S100A8/S100A9 (calprotectin) as innate amplifier of infection, autoimmunity, and cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subirade, M. Report on Functional Foods. Food Quality and Standards Service (AGNS); Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shirwaikar, A.; Parmar, V.; Khan, S. The changing face of nutraceuticals—An overview. Int. J. Pharm. Life Sci. 2011, 2, 926–932. [Google Scholar]
- Adel-Patient, K.; Nutten, S.; Bernard, H.; Fritsche, R.; Ah-Leung, S.; Meziti, N.; Prioult, G.; Mercenier, A.; Wal, J.M. Immunomodulatory potential of partially hydrolyzed beta-lactoglobulin and large synthetic peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10858–10866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiewiet, M.B.G.; Dekkers, R.; Gros, M.; van Neerven, R.J.J.; Groeneveld, A.; de Vos, P.; Faas, M.M. Toll-like receptor mediated activation is possibly involved in immunoregulating properties of cow’s milk hydrolysates. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politis, I.; Theodorou, G.; Lampidonis, A.D.; Chronopoulou, R.; Baldi, A. Soya protein hydrolysates modify the expression of various pro-inflammatory genes induced by fatty acids in ovine phagocytes. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, V.K.; Venkatesh, Y.P. Characterization of onion lectin (Allium cepa agglutinin) as an immunomodulatory protein inducing Th1-type immune response in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 26, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Yang, C.; Nau, F.; Pasco, M.; Juneja, L.R.; Okubo, T.; Mine, Y. Immunomodulatory effects of egg white enzymatic hydrolysates containing immunodominant epitopes in a BALB/c mouse model of egg allergy. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2009, 57, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura-Campos, M.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Betancur-Ancona, D.; Hernandez-Escalante, V.M. Bioavailability of Bioactive Peptides. Food Rev. Int. 2011, 27, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Matsui, T. Current knowledge of intestinal absorption of bioactive peptides. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4306–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Gonzalez, M.; Capitan-Canadas, F.; Requena, P.; Ocon, B.; Romero-Calvo, I.; Aranda, C.; Suarez, M.D.; Zarzuelo, A.; Sanchez de Medina, F.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Validation of bovine glycomacropeptide as an intestinal anti-inflammatory nutraceutical in the lymphocyte-transfer model of colitis. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena, P.; Daddaoua, A.; Guadix, E.; Zarzuelo, A.; Suarez, M.D.; Sanchez de Medina, F.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Bovine glycomacropeptide induces cytokine production in human monocytes through the stimulation of the MAPK and the NF-kappaB signal transduction pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena, P.; Daddaoua, A.; Martínez-Plata, E.; González, M.; Zarzuelo, A.; Suárez, M.D.; Sánchez de Medina, F.; Martínez-Augustin, O. Bovine glycomacropeptide ameliorates experimental rat ileitis by mechanisms involving downregulation of interleukin 17. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Gonzalez, M.; Ocon, B.; Romero-Calvo, I.; Anzola, A.; Guadix, E.; Zarzuelo, A.; Suarez, M.D.; Sanchez de Medina, F.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Nondigestible oligosaccharides exert nonprebiotic effects on intestinal epithelial cells enhancing the immune response via activation of TLR4-NFkappaB. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitan-Canadas, F.; Ortega-Gonzalez, M.; Guadix, E.; Zarzuelo, A.; Suarez, M.D.; de Medina, F.S.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Prebiotic oligosaccharides directly modulate proinflammatory cytokine production in monocytes via activation of TLR4. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez de Medina, F.; Romero-Calvo, I.; Mascaraque, C.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Intestinal inflammation and mucosal barrier function. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 2394–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cian, R.E.; Drago, S.R.; Sánchez de Medina, F.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Proteins and Carbohydrates from Red Seaweeds: Evidence for Beneficial Effects on Gut Function and Microbiota. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5358–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.S.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, I.H.; Nam, T.J. A glycoprotein from Porphyra yezoensis produces anti-inflammatory effects in liposaccharide-stimulated macrophages via the TLR4 signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 28, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, S. Endogenous toll-like receptor ligands and their biological significance. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2592–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cian, R.E.; Salgado, P.R.; Drago, S.R.; Gonzalez, R.J.; Mauri, A.N. Development of naturally activated edible films with antioxidant properties prepared from red seaweed Porphyra columbina biopolymers. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dere, S.; Gunes, T.; Sivaci, R. Spectrophotometric Determination of Chlorophyll-A, B and Total Carotenoid Contents of Some Algae Species Using Different Solvents. Botany 1998, 22, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, P.M.; Petersen, D.; Dambmann, C. Improved Method for Determining Food Protein Degree of Hydrolysis. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Chirlaque, C.; Gamez-Belmonte, R.; Ocon, B.; Martinez-Moya, P.; Wirtz, S.; Sanchez de Medina, F.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Tissue Non-specific Alkaline Phosphatase Expression is Needed for the Full Stimulation of T Cells and T Cell-Dependent Colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.T.; Mallia, A.K.; Gartner, F.H.; Provenzano, M.D.; Fujimoto, E.K.; Goeke, N.M.; Olson, B.J.; Klenk, D.C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cian, R.E.; Hernández-Chirlaque, C.; Gámez-Belmonte, R.; Drago, S.R.; Sánchez de Medina, F.; Martínez-Augustin, O. Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysates and Their Peptide Fractions Regulate Cytokine Production in Splenic Macrophages and Lymphocytes Involving the TLR4-NFκB/MAPK Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16070235
Cian RE, Hernández-Chirlaque C, Gámez-Belmonte R, Drago SR, Sánchez de Medina F, Martínez-Augustin O. Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysates and Their Peptide Fractions Regulate Cytokine Production in Splenic Macrophages and Lymphocytes Involving the TLR4-NFκB/MAPK Pathways. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(7):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16070235
Chicago/Turabian StyleCian, Raúl E., Cristina Hernández-Chirlaque, Reyes Gámez-Belmonte, Silvina R. Drago, Fermín Sánchez de Medina, and Olga Martínez-Augustin. 2018. "Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysates and Their Peptide Fractions Regulate Cytokine Production in Splenic Macrophages and Lymphocytes Involving the TLR4-NFκB/MAPK Pathways" Marine Drugs 16, no. 7: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16070235
APA StyleCian, R. E., Hernández-Chirlaque, C., Gámez-Belmonte, R., Drago, S. R., Sánchez de Medina, F., & Martínez-Augustin, O. (2018). Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysates and Their Peptide Fractions Regulate Cytokine Production in Splenic Macrophages and Lymphocytes Involving the TLR4-NFκB/MAPK Pathways. Marine Drugs, 16(7), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16070235






