Abstract
An UPLC-qTOF-MS-based dereplication study led to the targeted isolation of seven bromoindole alkaloids from the sub-Arctic sponge Geodia barretti. This includes three new metabolites, namely geobarrettin A–C (1–3) and four known compounds, barettin (4), 8,9-dihydrobarettin (5), 6-bromoconicamin (6), and l-6-bromohypaphorine (7). The chemical structures of compounds 1–7 were elucidated by extensive analysis of the NMR and HRESIMS data. The absolute stereochemistry of geobarrettin A (1) was assigned by ECD analysis and Marfey’s method employing the new reagent l-Nα-(1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl)tryptophanamide (l-FDTA). The isolated compounds were screened for anti-inflammatory activity using human dendritic cells (DCs). Both 2 and 3 reduced DC secretion of IL-12p40, but 3 concomitantly increased IL-10 production. Maturing DCs treated with 2 or 3 before co-culturing with allogeneic CD4+ T cells decreased T cell secretion of IFN-γ, indicating a reduction in Th1 differentiation. Although barettin (4) reduced DC secretion of IL-12p40 and IL-10 (IC50 values 11.8 and 21.0 μM for IL-10 and IL-12p40, respectively), maturing DCs in the presence of 4 did not affect the ability of T cells to secrete IFN-γ or IL-17, but reduced their secretion of IL-10. These results indicate that 2 and 3 may be useful for the treatment of inflammation, mainly of the Th1 type.
1. Introduction
Many chronic illnesses, including cancer, neurological diseases, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases, exhibit dysregulation of pathways that have been linked to inflammation [1,2]. A vast number of unique marine natural products possessing in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity have been isolated [3,4], however, no marine-derived anti-inflammatory agent is currently on the market. Therefore, the search and development of new natural products to treat chronic inflammatory diseases is of great importance [5,6]. Marine sponges, due to their phenomenal biological and chemical diversity, are considered as a notable source of natural products with potential anti-inflammatory activity [5,7,8].
Geodia barretti Bowerbank (family Geodiidae, class Demospongiae, order Astrophorida) is an abundant cold-water sponge with a wide geographic distribution, including the Icelandic waters. G. barretti has been reported to contain 6-bromoindole alkaloids [9,10,11,12,13], including barettin (4) [10], 8,9-dihydrobarettin (5) [11], bromobenzisoxazolone barettin [12], 6-bromoconicamin (6) [14], and 2-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium [13], as well as nucleosides [15], peptides [16], sterols and fatty acids [17].
The chemical structure of barettins isolated from G. barretti feature a diketopiperazine (DKP)-type cyclic dipeptide, a condensation product of arginine (Arg) and 6-bromo-8-en-tryptophan residues in a “head-to-tail” fashion [11,18]. The DKP core, present in many bioactive compounds, is a relevant scaffold for drug discovery and development [19]. Barettins display interesting biological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antifouling, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory, and selective serotonin (5-HT) receptor ligand effects [11,12,13,20,21]. In particular, barettin (4), the major compound in G. barretti has shown potent antifouling, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities [11,12,20], making it a potential lead compound in prevention of chronic inflammatory diseases. Therefore, the search for new barettins is of great interest for investigation of their anti-inflammatory effects and structure–activity relationships.
The present study was undertaken to isolate 6-bromoindole derivatives from the Icelandic sponge G. barretti and to evaluate their anti-inflammatory activity on human monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DCs) and their ability to activate T cell responses. DCs play an important role in initiation of adaptive immune responses by activating naïve T cells and inducing their differentiation by cytokine secretion [22]. The naïve CD4+ T cells differentiate into different T helper (Th) effector cells, such as Th1, Th2, Th9, or Th17 phenotypes, which participate in various inflammatory diseases [23,24,25] or, if the DCs secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10, into T regulatory cells (Tregs) [26]. In this study, we describe (i) the isolation and structure elucidation of three new 6-bromoindole derivatives, geobarrettin A–C (1–3) and four known 6-bromoindole alkaloids (4–7), (ii) the absolute stereoassignment of geobarrettin A (1) using the Marfey’s method employing the new reagent l-Nα-(1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl)tryptophanamide (l-FDTA) followed by HPLC comparison with standards, and (iii) the re-evaluation of the stereochemical configuration of barettin (4).
2. Results
The sponge G. barretti was collected at the west of Iceland (−388 m) and kept frozen until work-up. The CH2Cl2:CH3OH (v/v, 1:1) soluble extract of the sponge was partitioned into five subextracts (hexane, chloroform, dichloromethane, n-butanol, and water) using a modified Kupchan solvent partitioning method [27,28]. The crude extracts and subextracts were chemically profiled by UPLC-qTOF-MS for selective and sensitive detection of bromoindoles and other trace components [29,30]. The bromoindole containing chloroform and dichloromethane subextracts were combined and purified by a combination of RP-VLC and HPLC to afford three new 6-bromoindole derivatives geobarrettin A–C (1–3) and four known alkaloids 4–7 (Figure 1).
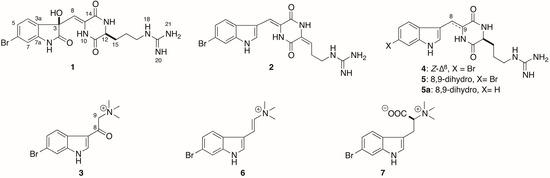
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of compounds 1–7 and 5a.
2.1. Structural Elucidation
Compound 1 was obtained as a yellow solid. Its UV spectrum was characteristic for an oxindole skeleton with absorption λmax at 217 and 263 nm [31,32], while the IR spectrum showed the presence of OH (νmax 3352 cm−1), NH2 (νmax 3285, 3214, and 1614 cm−1), and lactam (νmax 1679 cm−1) functionalities. The characteristic isotope pseudo-molecular ion peaks at m/z 451.0728:453.0732 ([M + H]+) in a 1:1 ratio in the HRESIMS spectrum of 1 suggested the presence of a bromine atom in the molecule. The HRESIMS data indicated the molecular formula of C17H2079BrN6O4, corresponding to eleven degrees of unsaturation. This formula was supported by the 1H, 13C NMR, and HSQC data, indicating the presence of three methylenes (δC 42.0, 32.6 and 24.8), three aromatic methines (δC 127.1, 126.9 and 115.0), one aliphatic methine (δC 56.0), an isolated olefinic methine (δC 112.8), four quaternary aromatic carbons (δC 143.9, 132.4, 132.2, and 124.7), one tertiary alcohol (δC 78.3), and four quaternary heteroatom-bounded sp2 carbons (δC 179.3, 167.2, 160.5 and 158.7). The 1H NMR spectrum in CD3OD contained three aromatic resonances, including a broad singlet at δH 7.11 (1H) and an overlapped 2H broad singlet at δH 7.25 (Table 1). When acquired in DMSO-d6, these aromatic signals were resolved into a well-separated ABX system at δH 7.26 (1H, d, J = 7.9 Hz, H-4), 7.23 (1H, dd, J = 7.9, 1.5 Hz, H-5), and 7.03 (1H, d, J = 1.5 Hz, H-7), suggesting the presence of a trisubstituted benzene ring. The chemical shift of the quaternary aromatic carbon C-7a (δC 143.9) indicated that C-7a was substituted by an NH group. The characteristic resonances of the amide carbonyl C-2 at δC 179.3 and the oxygenated carbon (C-3, δC 78.3), as well as the HMBC correlations observed from H-4 to C-3, C-6, and C-7a, and from H-7 to C-3a, assisted the construction of a 3-hydroxy-2-oxindole skeleton. The chemical shifts for carbon atoms were in good agreement with those of previously published 3-hydroxy-2-oxindole scaffolds [33,34]. The position of the bromine atom at C-6 was determined based on the HMBC correlations H-4/C-3, H-4/C-6, and H-4/C-7a; H-5/C-3a and H-5/C-7; as well as H-7/C-3a, H-7/C-5, and H-7/C-6. This was supported by the NOE correlations between H-4/H-8 observed in spectrum run in CD3OD and a weak cross peak between H-7/NH-1 in spectrum run in DMSO-d6, in combination with characteristic coupling constant values, namely J4,5 (7.9 Hz) and J5,7 (1.5 Hz). A similar weak cross peak between H-7/NH-1 has previously been observed for 6-bromoindole cyclic guanidine alkaloids [35]. The presence of two amide carbonyl signals C-11 (δC 167.2) and C-14 (δC 160.5) suggested the presence of a DKP moiety attached to the oxindole skeleton and the chemical shift of C-14 indicated that this carbon was conjugated to a double bond (Δ8). Cross correlations observed in the HMBC spectrum between H-12/C-11, H-12/C-14, H-8/C-14, H-8/C-3, and H-8/C-9 supported this assumption. 1H-1H COSY spectrum indicated the presence of an additional linear spin system starting from H-12 (δH 4.28, 1H, t, J = 6.0 Hz) and including three aliphatic methylene signals H2-15 (δH 1.89, 1H, m; δH 2.01, 1H, m), H2-16 (δH 1.67, 1H, m; 1.74, 1H, m), and H2-17 (δH 3.24, 2H, t, J = 6.0 Hz). The molecular fragments described above account for all atoms except three nitrogen atoms and one quaternary carbon atom (δC 158.7, C-19) and for 10 of 11 degrees of unsaturation. The position of the remaining three nitrogen atoms and the carbon atom was assigned to a guanidine group connected to the linear spin system at C-17 based on the HMBC correlation between H2-17/C-19 (Figure 2). This suggested that the aliphatic side chain linked to the DKP moiety was an Arg residue. Further examination of the NMR data revealed that spectroscopic data of compound 1 were very similar to those of compound 4 [10], with the main differences being the upfield shift of the H-7 resonance (δH 7.03 (1H d, J = 1.5 Hz) in compound 1; δH 7.67 (1H d, J = 1.6 Hz) in compound 4) and the replacement of the indole Δ2 double bond by a hydroxyl group at C-3 and a carbonyl group at C-2. The latter was confirmed by the HMBC correlation observed between H-8 and C-2 (Figure 2). The structure proposed for compound 1 is consistent with its molecular formula (m/z 451.0728 [M + H]+, C17H2079BrN6O4) in comparison to that of compound 4 (m/z 419.0830 [M + H]+, C17H2079BrN6O2). The geometry of the exocyclic double bond Δ8 was defined as Z based on NOESY correlations observed in H-8/H-4 and NH-10/NH-1.

Table 1.
NMR spectroscopic data for compounds 1–3 (δ in ppm, 600 MHz for 1H NMR and 150 MHz for 13C NMR).
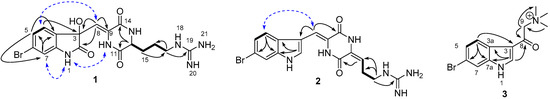
Figure 2.
Key HMBC (H→C), 1H-1H COSY (−) and NOESY (H↔H, in dashed blue) correlations of compounds 1–3.
The configurations of two chiral centers at C-3 and C-12 in compound 1 were determined using a combination of techniques. The absolute configuration of C-3 was determined by comparison of the ECD spectra (Figure 3) of the hydrogenolysis product of compound 1 with the compound (R)-3-propyldioxindole (8), which share the dioxindole core structure. (R)-8 was obtained by hydrogenolysis of R-dioxindole (8a, a gift from Dr. Annaliese K. Franz (University of California, Davis)) (Scheme 1) [37]. The CD spectra of (R)-8 (EtOH, 23 °C) revealed Cotton effects (λ 208 nm (Δε +13.1), 232 (−10.7), 259 (+3.5)) similar to dioxindoles recently investigated [38]. Hydrogenolysis of geobarretin A (1) (Scheme 1) gave debromodihydrogeobarrettin A (1a) with a CD spectrum identical to that of (R)-8 (Figure 3). Given the identical CD spectra of 1a and (R)-8, whose absolute configuration was established by X-ray crystallography, and the similarity of their Cotton effects with those of (R)-5-methyldioxindole [39] and the natural product (+)-trikentramide I [38], the C-3 configuration of compound 1 was assigned as R, unambiguously.
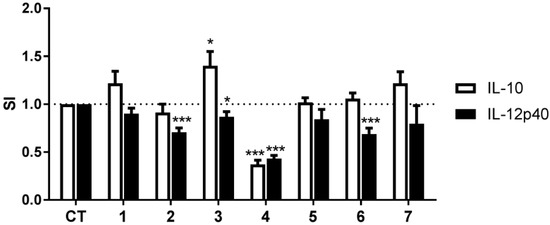
Figure 3.
Comparison of CD of model compound (R)-3-propyldioxindole (8) and debromodihydrogeobarrettin A (1a). Red line: (R)-8; Blue line: 1a.
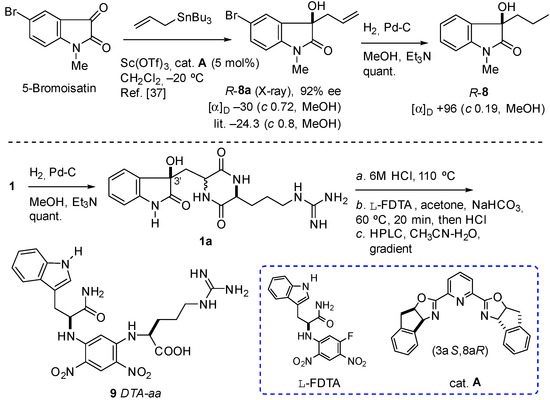
Scheme 1.
Hydrogenolysis of (R)-(8a) to (R)-(8) and hydrogenation, hydrolysis, and l-FDTA-derivatization of geobarrettin A (1) to 9.
Determination of amino acid configuration using Marfey’s method and chiral derivatizing agents (CDAs) such as l-fluoro-2-4-dinitrophenyl-5-l-alanine amide (FDAA, Marfey’s reagent) or the homolog, l-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl-5-l-leucineamide (FDLA), are popular and effective [40]. Compound 1a was hydrolyzed (6 M HCl, 110 °C) and the product was derivatized with the new CDA, l-FDTA [41], to produce 9. Comparison with standards d- and l-Arg-DTA derivatives was then achieved using HPLC (Figure S32) and UPLC-MS analyses. d- and l-Arg-DTA derivatives were observed with integral values of 19:81 suggesting either natural 1 is partially racemic at C-12, or that Arg underwent partial racemization under the conditions of hydrolysis. The latter possibility is ruled out by precedence; Arg essentially is stable to the conditions of hydrolysis. In a careful systematic study Kaiser and Benner (2005) demonstrated that the amount of d-Arg produced during acid hydrolysis of l-Arg (110 °C, 6 M HCl, 20 h) is not more than 1.0 ± 0% of the total for free amino acid, or 2.8 ± 0.4% when bonded in lysozyme [42]. We conclude that compound 1 is a cryptic mixture of diastereomers with stereofidelity at C-3, but partial epimerization at C-12. Therefore, the configuration of geobarrettin A (1) is 3R, 8Z, 12S.
Geobarrettin B (2) was isolated as a yellow solid. The UV spectrum showed the characteristic indole chromophore with absorptions at λmax 230, 270, and 289 nm [43]. Its molecular formula C17H1879BrN6O2 was deduced by HRESIMS (m/z 417.0675/419.0685 1:1, [M + H]+), indicating the presence of a bromine atom and 12 degrees of unsaturation. Detailed analysis of the 1H, 13C NMR (Table 1) and HSQC data suggested the planar structure of compound 2 to be very similar to that of the known compound barettin (4). Comparison of the 1D NMR spectra of compounds 2 and 4 suggested that the only difference was the presence of a double bond in the Arg side chain of 2, namely between C-12 (δC 130.5) and C-15 (δC 114.9). The HMBC correlations from H-15 (δH 5.98, t, J = 7.8 Hz) to C-11 and C-17, and from H-16 (δH 2.57, q, J = 7.8 Hz) to C-12, as well as COSY correlations between H-15/H2-16 and H2-16/H2-17 supported the position of the unsaturation at Δ12. Finally the two mass units difference between the molecular formulae of 2 and 4, as determined by HRESIMS data, clearly supported 2 being the ∆12 unsaturated analog of 4. The geometry of Δ12 in α,β-dehydroamino-acids was determined by analyzing the reported trends in chemical shift differences of vinyl protons in E- and Z-isomers. Comparison of the chemical shift of H-15 (δH 5.98) in compound 2 with that of alkylidene-2,5-piperazinedione derivatives reported in the literature [44,45] therefore supports an E-Δ12 configuration. Hence compound 2 is the Δ12 dehydro-derivative of barettin (4), which we named as geobarrettin B.
Geobarrettin C (3) was obtained as a yellow oil. The molecular formula C13H16BrN2O+ was assigned to compound 3 by its HRESIMS data. Analysis of the 1H and 13C NMR spectra pointed out the presence of a substituted 6-bromoindole scaffold. The substituent was identified as N,N,N-trimethyl-2-oxoethanaminium salt, based on the 1D NMR spectra that possessed resonances of a methylene group at δC 67.8 and δH 4.92 (2H, s, H-9), a conjugated keto group at δC 186.0 (C-8), and three methyl signals at δC 54.9; δH 3.42 (9H, s, -N(CH3)3). The HMBC correlations observed between CH3-N/C-9, H2-9/C-8, and H-2/C-8 indicated the N,N,N-trimethyl-2-oxoethanaminium moiety to be attached to 6-bromoindole at C-3 position (δC 116.1). A literature search showed that 3 is an oxidation product of a previously isolated secondary alcohol 2-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium (C13H18BrN2O+) [13]. Thus, compound 3 was identified as the quaternary ammonium salt 2-(6-bromo-1H-indol-3-yl)-N,N,N-trimethyl-2-oxoethanaminium and named as geobarrettin C (3).
The gross structures of the remaining known compounds, barettin (4) [10], 8,9-dihydrobarettin (5) [11], 6-bromoconicamin (6) [14], and l-6-bromohypaphorine (7) [46] were identified by comparison of their NMR, HRMS, and specific rotation data with those reported in the literature.
The sole chiral amino acid residue in barettin (4), first reported in 1986 from a deep-water specimen of G. barretti collected in Sweden, presumably from Koster fjord [12], was assigned as Pro, but the configuration was not determined at that time. A second report of 4 in 2004 from a Norwegian deep-water sample of G. barretti [11] corrected the structure to an Arg-containing DKP, but also omitted the specific rotation. Finally, the configuration of 4 was established as l-Arg by comparison of optical rotations of natural and synthetic 4 [42]. Although they had similar signs, the specific rotations of synthetic and natural 4 were different ( −32.5 (c 2, MeOH) [18]; natural 4 [α]D −25 (c 3, MeOH)) [9]. In the present study, the rotation of 4 was found to be even higher ( −84 (c 0.5, MeOH)). In order to resolve this paradox, the l-FDTA method was applied to the hydrolysate as described above for 1. HPLC analysis detected the presence of d-Arg-DTA and l-Arg-DTA in a ratio of 19:81 suggesting l-Arg was predominant, but—as with 3—our sample of 4 was also partially racemic. Assuming no racemization occurred during the synthesis of 4 [42], our finding would be consistent with partially racemic natural 4 in the Swedish sample. The hydrolysis was repeated on debromo-8,9-dihydrobarettin (5a) (Figure 1), obtained by hydrogenolysis of 4, and the product was again converted to l-DTA derivatives and analyzed by HPLC as before to give d-Arg-DTA and l-Arg-DTA (19:81).
The structure of compound 7 was assigned as 6-bromohypaphorine by comparing the recorded and published NMR data [46]. The sign of optical rotation of compound 7 ( +36, c 0.2, EtOH) was similar to that of l-6-bromohypaphorine ([α]D +58, c 0.25, EtOH) [46] and opposite to that of the d-6-bromohypaphorine ( −27, c 0.80, MeOH-CF3COOH, 8:1) [47]. Hence, compound 7 was assigned as l-6-bromohypaphorine.
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
To evaluate the potential anti-inflammatory activity of compounds 1–7, their effects on DC secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-12p40 and the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was determined. The tested compounds did not show cytotoxic effects on the DCs, with the cell viability being more than 90% in the presence of the compounds at 10 μg/mL (data not shown). Compound 4 inhibited by more than 50% secretion of both IL-12p40 and IL-10. Compounds 2 and 6 decreased DC secretion of IL-12p40 by 29 and 32%, respectively, without affecting secretion of IL-10, which suggests an overall anti-inflammatory activity of these compounds. Compound 3 slightly decreased DC secretion of IL-12p40 (13%) but increased secretion of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 by 40%, which also suggests an anti-inflammatory activity. Compounds 1, 5, and 7 did not affect DC secretion of IL-12p40 or IL-10 (Figure 4).
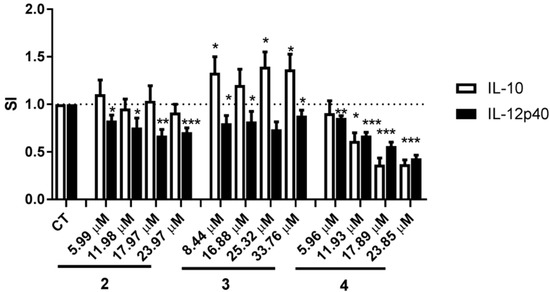
Figure 4.
The effects of compounds 1–7 on dendritic cell (DC) secretion of IL-12p40 and IL-10. DCs were matured and activated by TNF-α, IL-1β and LPS in the absence (solvent control (CT)) or presence of compounds 1–7 at 10 μg/mL for 24 h. The supernatants were collected and the concentrations of IL-12p40 and IL-10 were determined by ELISA. The data are presented as SI, i.e., the concentration of each cytokine in the supernatant of cells matured and activated in the presence of compounds divided by the concentration of the cytokine in the supernatant of cells matured and activated in the presence of solvent control. The results are shown as mean + standard error of the mean (SEM), n = 7–11, except for compound 7, n = 3. Different from CT: * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001.
We next examined whether compounds 2, 3, and 4 affected cytokine secretion by the DCs in a dose-dependent manner. The effects of compounds 2 and 3 on IL-12p40 and IL-10 secretion by DCs were not dose-dependent although for compound 2 there was a tendency towards an increasing effect on IL-12p40 secretion at higher concentrations. Compound 4 inhibited secretion of IL-12p40 and IL-10 in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 being 21.04 μM for IL-12p40 and 11.80 μM for IL-10 (Figure 5), with IL-12p40 and IL-10 secretion decreasing at the lowest concentrations tested, i.e., 5.96 μM (2.5 μg/mL) and 11.93 μM (5 μg/mL), respectively.
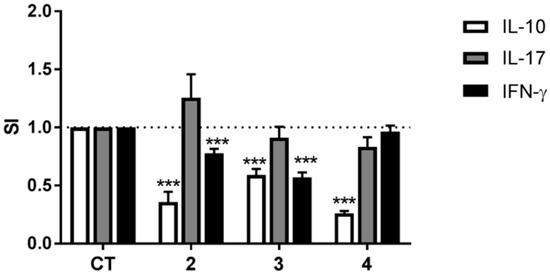
Figure 5.
Dose-dependent inhibition of cytokines IL-12p40 and IL-10 by compounds 2–4. DCs were matured and activated by TNF-α, IL-1β, and LPS in the absence (solvent control (CT)) or presence of indicated concentration of compound 2 (5.99, 11.98, 17.97, and 23.97 μM), compound 3 (8.44, 16.88, 25.32, and 33.76 μM), and compound 4 (5.96, 11.93, 17.89, and 23.85 μM). The levels of IL-12p40 and IL-10 in the supernatants were determined by ELISA. The data are presented as SI. The results are shown as mean + SEM, n = 5–11. Different from CT: * p ˂ 0.05, ** p ˂ 0.01, *** p ˂ 0.001.
To further elucidate the anti-inflammatory activity of compounds 2–4, DCs matured in their presence were co-cultured with allogeneic CD4+ T cells and the differentiation of the T cells investigated by determining secretion of the cytokines IL-10, IL-17, and IFN-γ. T cells co-cultured with DCs matured in the presence of compounds 2 or 3 secreted less IL-10 and IFN-γ than T cells co-cultured with DCs matured in the absence of the compounds, but maturing DCs in the presence of compounds 2 or 3 did not affect T cell secretion of IL-17 (Figure 6). Co-culturing T cells with DCs matured in the presence of compound 4 resulted in a substantial decrease in secretion of IL-10 with no effect on secretion of either IL-17 or IFN-γ.
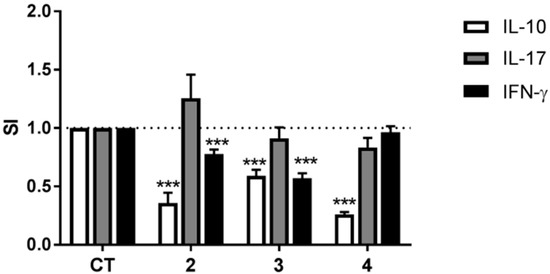
Figure 6.
The effects of compounds 2–4 on the ability of DCs to induce cytokine secretion by allogeneic CD4+ T cells. DCs matured and activated in the absence (solvent control (CT)) or presence of compounds 2–4 at a concentration of 10 μg/mL for 24 h were co-cultured with isolated allogeneic CD4+ T cells for six days and the concentrations of IFN-γ, IL-17, and IL-10 in the supernatants were determined by ELISA. The data are presented as SI, i.e., the concentration of each cytokine in the supernatant of co-cultures containing DCs treated with compounds divided by the concentration of each cytokine in the supernatant of co-cultures containing DCs treated with solvent control. The results are shown as mean + SEM, n = 9–12. Different from CT: *** p < 0.001.
3. Discussion
Three new 6-bromoindole derivatives were isolated from G. barretti, including a dioxindole featuring a DKP-type cyclic dipeptide, geobarrettin A (1); a 6-bromoindole possessing DKP system, geobarrettin B (2); and a new 6-bromoindole alkaloid, geobarrettin C (3).
Compounds 2 and 3 inhibited IL-12p40 production by DCs and DCs treated with compounds 2 and 3 reduced IFN-γ secretion by co-cultured T cells, hence reduced Th1 responses, which are linked to inflammatory disorders and many chronic inflammatory diseases [48,49]. As IL-12 is the main inducer of Th1 polarization of T cells with subsequent IFN-γ secretion [50], the down-regulation of IFN-γ observed in the co-culture of T cells with DCs is most likely resulting from a reduced ability of the DCs matured in the presence of compounds 2 and 3 to secrete IL-12p40 (one of the two chains that form the IL-12 molecule). Compound 2 did not affect IL-10 secretion by DCs but compound 3 increased IL-10 secretion by DCs. Therefore, the decreased concentration of IL-10 in co-cultures of T cells and DCs matured in the presence of compounds 2 and 3 was unexpected. The reduced IL-10 levels observed in the co-cultures were most likely the result of reduced secretion by the T cells but not the DCs, but whether it is so needs to be confirmed, e.g., by intracellular staining for IL-10 on T cells and DCs in the co-culture experiments. Although the decreased secretion of IL-10 in the co-cultures may hamper the anti-inflammatory effect of compounds 2 and 3, the downregulation of IFN-γ secretion is strongly suggestive of inhibition of inflammatory Th1 response and subsequently that compounds 2 and 3 may have the potential of being a starting point for development of new anti-inflammatory drugs.
The anti-inflammatory effect of compound 4, shown previously in a monocytic cell line [6], was confirmed in the present study as it downregulated secretion of IL-12p40 by the DCs. However, compound 4 also downregulated IL-10 production, which could interfere with the anti-inflammatory effect observed by reduced IL-12p40 secretion. This seemed to be the case as, when DCs treated with compound 4 were co-cultured with T cells, the effect of compound 4 was not anti-inflammatory as neither Th1 nor Th17 cytokines were affected. These results were unexpected and suggest that the effect of compound 4 to decrease IL-10 secretion by the DCs seems to be the determining factor, overriding the effect of downregulation of IL-12p40 and subsequently leading to a reduction in IL-10 in the co-culture of the two cell types.
Despite structural similarities of compounds 1, 2, 4, and 5, which all possess the structure of a DKP-type cyclic dipeptide, there were remarkable differences in their anti-inflammatory effects. Oxidation of the indole ring in compound 1 as compared with compound 4 caused the disappearance of the anti-inflammatory activity, indicating that the indole skeleton is important in inhibition of cytokine secretion by the DCs. Both the number and the position of double bonds on the DKP-type cyclic dipeptide may affect the anti-inflammatory activity (2 vs. 4 vs. 5). The disappearance of the double bond at C-8 could decrease the anti-inflammatory activity, as compound 5 did not affect cytokine secretion by the DCs whilst compounds 4 and 2 did, suggesting that the double bond at C-8 is required for the activity. However, the double bond at C-12 may be responsible for the reduction of anti-inflammatory activity when comparing compound 2 with compound 4. Considering these observations, the bromotryptophan containing the double bond at C-8 may be important for the activity. The double bond at the N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium group increased the suppression of IL-12p40 production and increased the IL-10 secretion (6 vs. 7). Collectively, 6-bromoindole derivatives may have anti-inflammatory activity that depends on the bromotryptophan nucleus (1, 2, 4, and 5) or the side chain at C-3 position of the 6-bromoindole (3, 6, and 7), suggesting that there may be more than one potential target site or mode of action.
The observations described above indicate that G. barretti is a prolific source of 6-bromoindoles with potential anti-inflammatory activities, which may be a starting point for the development of new drug s with a potential for being used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases in the future.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Produres
Optical rotations were measured on a P-2000 polarimeter (Jasco, OK, USA) equipped with a 10 mm pathlength cell. UV spectra were recorded on a NanoVueTM spectrophotometer (GE Healthcare Life Science, Little Chalfont, UK). ECD spectra were measured on a JASCO J-810 spectropolarimeter in quartz cells (1 or 5 mm pathlength) at 23 °C. IR spectra were measured on a Spectrum TwoTM FTIR spectrometer (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AM-400 spectrometer (proton frequency 400.13 MHz and carbon frequency 100.62 MHz, respectively) for compounds 4–7 (in CD3OD and/or DMSO-d6) using TMS as an internal standard or a Bruker Avance 600 spectrometer (proton frequency 600.13 MHz and carbon frequency 150.76 MHz, respectively) for compounds 1 (in CD3OD and DMSO-d6), 2–3 (in CD3OD), and 7 (in DMSO-d6). The 1H NMR spectrum of compound 8 (in CDCl3) was recorded on a Varian Mercury 400 spectrometer and the 13C NMR spectrum was measured on a Varian Xsens 500 spectrometer equipped with a 13C{1H} cryoprobe at 125 MHz. High-resolution mass spectra were obtained on a Waters G1 Synapt qTOF mass spectrometer. An UHPLC system (ACQUITY UPLC Waters) was coupled in line with a qTOF mass spectrometer (Synapt G1, Waters) operating in the positive mode. HPLC was performed on a Dionex 3000 HPLC system equipped with a G1310A isopump, a G1322A degasser, a G1314A VWD detector (210 nm), a 250 × 21.2 mm Phenomenex Luna C18(2) column (5 μm), and a 250 × 4.6 mm Phenomenex Gemini-NX C18 column (5 μm). Alkaloids were detected by TLC on Merck silica gel F254 plates by immersing the plates in Dragendorff’s reagent. VLC chromatography was performed on C18 adsorbent (LiChroprep RP-18, 40–63 μm, Merck Inc., Darmstadt, Germany). All organic solvents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and were HPLC grade or the highest degree of purity.
4.2. Animal Materials
The sponge material Geodia barretti was collected in the west of Iceland (65°27.6′ N–30°46.6′ W) at 388 m depth in September 2010. The sponge was identified by Dr. Hans Tore Rapp, University of Bergen (Norway). A voucher specimen was deposited at the Department of Natural Products Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Iceland. The collected specimens (six in total) (wet weight, 1.8 kg) were immediately frozen and stored at −20 °C.
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
The frozen sponge material was cut into small pieces and lyophilized prior to extraction with CH2Cl2:CH3OH (v/v, 1:1) mixture (3 × 20 L, each for 24 h) at room temperature. The combined extracts were concentrated under vacuum to yield a dark gum and stored at −20 °C. The crude extract (1.8 g) was submitted to a modified Kupchan partition to yield five subextracts, namely hexane (fraction A), chloroform (fraction B), dichloromethane (fraction C), n-butanol (fraction D), and water (fraction E). Each fraction was analyzed by UPLC-qTOF-MS before preparative-scale isolation work commenced and the data were processed and analyzed by MassLynx programme and compared to available references in ChemSpider database [51] and SciFinder Scholar (Chemical Abstracts Service, Columbus, OH, USA). The fractions B and C showed similar patterns on TLC and the analysis of qTOF-MS data revealed similar chemical compositions. Thus, they were combined and fractionated by VLC on a C18 reversed-phase column using gradient elution of MeOH-H2O (10:90→ 100:0) mixtures to obtain nine fractions (F2.1−F2.9). F2.2 (750 mg) was purified by preparative HPLC (28:72:0.1 CH3CN-H2O-TFA, 8.0 mL/min) to afford compounds 3 (3.5 mg), 4 (7.3 mg), and 6 (1.5 mg) and two impure fractions (F2.2.1 and F2.2.2). F2.2.1 (78.9 mg) was purified by semi-preparative HPLC using CH3CN-H2O-TFA (27:73:0.1) to yield compounds 1 (1.8 mg) and 5 (1.2 mg). F2.2.2 (10.1 mg) was also re-chromatographed by semi-preparative HPLC (ACN-H2O-TFA, 31:69:1) to give compound 7 (5.3 mg). F2.4 (12.1 mg) was purified by semi-preparative HPLC (30:70:0.1 MeOH-H2O-TFA, 2.2 mL/min) to yield compound 2 (3.0 mg).
Geobarrettin A (1): yellow solid (1.8 mg); +7 (c 0.2, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) nm: 217 (3.17), 263 (2.64); IR νmax cm−1: 3352, 3214, 1679, 1441, 1205, 1138, 1057, 841, 802, 724; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 451.0728 [M + H]+ (calcd for C17H2079BrN6O4, 451.0729).
Geobarrettin B (2): yellow solid (3.0 mg); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) nm: 231 (3.62), 270 (3.39), 289 (3.41), 372 (3.51); IR νmax cm−1: 3297, 1677, 1438, 1206, 1139, 843, 803, 725; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 417.0675 [M + H]+ (calcd for C17H1879BrN6O2, 417.0675).
Geobarrettin C (3): yellow solid (3.5 mg); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) nm: 211 (3.42), 247 (3.17), 269 (3.12), 283 (2.95); IR νmax cm−1: 3207, 1676, 1523, 1445, 1203, 1134, 892, 802, 722; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 295.0440 [M]+ (calcd for C13H1679BrN2O+, 295.0446).
Barettin (4): dark yellow solid (7.3 mg); −84 (c 0.5, MeOH), lit. −32.5 (c 2, MeOH) [18], lit. [α] −25 (c 3, MeOH); HRESIMS m/z 419.0830 [M + H]+ (calcd for C17H2079BrN6O2, 419.0831); all remaining spectroscopic data are in good agreement with those previously published [9].
8,9-Dihydrobarettin (5): yellowish solid (1.2 mg); −12.5 (c 0.096, MeOH), lit. −24 (c 0.096, MeOH); HRESIMS m/z 421.0987 [M + H]+ (calcd for C17H2279BrN6O2, 421.0988); all remaining spectroscopic data are in good agreement with those previously published [11].
6-Bromoconicamin (6): colorless amorphous solid (1.5 mg); HRESIMS m/z 279.0495 [M]+ (C13H1679BrN2+, 279.0497); all remaining spectroscopic data are in good agreement with those previously published [14].
l-6-Bromohypaphorine (7): yellow solid (5.3 mg); [ +36 (c 0.2, EtOH); HRESIMS m/z 325.0550 [M + H]+ (calcd for C14H1879BrN2O2, 325.0546); all remaining spectroscopic data are in good agreement with those previously published [46].
4.4. Hydrogenolysis of R-Dioxindole (8a) to (R)-3-Propyldioxindole (8)
To a solution of (R)-dioxindole (8a) (16.7 mg, 59 μmol) (92% ee, [α]D −30 (c 0.72, MeOH); lit. (88% ee) −24.3 (c 0.8, MeOH) [37]) in MeOH (5.0 mL) containing Et3N (3 drops) was added 10% Pd-C (10 mg). The mixture was evacuated-purged with H2 and allowed to hydrogenate (1 atm, H2) for 7 h. Filtration of the mixture (Celite), followed by concentration of the eluate and passage through a short plug of silica (1:1 EtOAc-hexanes) to remove Et3N•HBr gave (R)-3-propyldioxindole (8) as a colorless solid. UV (CF3CH2OH) λmax (log ε) nm: 208 (3.10), 257 (3.32), 268 (sh), 286 (2.74). CD (CF3CH2OH) λmax (Δε) nm: 208 (+13.1), 219 (0), 232 (−10.7), 249 (0), 259 (+3.5). [α]D + 96 (c 0.19, MeOH); + 50 (c 0.21, CF3CH2OH). IR (ZnSe) νmax 3404, 2962, 1703, 1609, 1495, 1470, 1377, 1119, 1082, 754 cm–1; 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ 7.37 (1H, d, J = 7.2 Hz, H-4), 7.33 (1H, t, J = 7.6 Hz, H-6), 7.10 (1H, t, J = 7.6 Hz, H-5), 6.83 (1H, d, J = 7.6 Hz, H-7), 3.19 (3H, s, N-Me), 1.93 (2H, m, CH2-1′), 1.12 (2H, m, CH2-2′); 0.84 (3H, t, J = 7.2 Hz, C-CH3-3′); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz) δ 178.4 (C, C-2), 143.6 (C, C-7a), 130.1 (C, C-3a), 129.7 (CH, C-6), 124.0 (CH, C-5), 123.2 (CH, C-4), 108.5 (CH, C-7), 76.8 (C, C-3), 40.9 (CH2, C-1′), 26.3 (CH3, N-Me), 16.8 (CH2, C-2′), 14.2 (CH3, C-3′); HRESIMS m/z 228.0992 [M + Na]+ (calcd for C12H15NO2Na+, 228.0995) (Figures S26–S30).
4.5. Hydrogenolysis of Geobarrettin A (1) to Debromodihydrogeobarrettin A (1a)
A sample of compound 1 was hydrogenated (1 atm H2, MeOH, 20 equiv. Et3N) for 15 h. The mixture was filtered and concentrated to give a colorless solid (~0.4 mg) consisting of an equimolar mixture of debromodihydrogeobarrettin A (1a) and Et3N•HBr that was used, directly, for CD measurements and subsequent hydrolysis-DTA derivatization. UV-vis (CF3CH2OH) λmax (log ε) nm: 207 (4.15), 269 (3.65), 281 (sh) (Figure S31); CD (CF3CH2OH) λmax (Δε) nm: 208 (+13.1), 232 (−10.7), 259 (+3.5). Identical with that of (R)-(8) (Figure 3).
4.6. Acid Hydrolysis of Debromodihydrogeobarrettin B (1a)
Approximately 0.31 mg of compound 1a was separately hydrolyzed with 6 M HCl (0.8 mL) for 15 h at 110 °C, dried under a stream of N2 followed by high vacuum to remove volatiles, and the resulting material subjected to further derivatization (see below).
4.7. Absolute Configuration of the Amino Acid of Geobarrettin A (1)
The determination of absolute configuration of the amino acids was performed as previously described [41]. After hydrolysis of 1a, the residue was dissolved in acetone (50 μL) and treated with l-FDTA (25 mM in acetone, 50 μL) and 1 M NaHCO3 (50 μL) and heated to 80 °C for 20 min. After cooling to 23 °C, the sample was quenched with 1 M HCl (50 µL), centrifuged, and the supernatant analyzed by RP HPLC (10 μL injection, Phenomenex Luna C18, 4.6 × 250 mm, gradient elution profile (15/85–65/35 CH3CN-H2O-0.1 M NH4OAc-0.1% TFA, over 40 min, 0.7 mL/min). The l-FDTA derivatives were detected by UV-vis (λmax 335 nm). Two peaks were eluted with retention times (ratio 19:81), coinciding with authentic l-DTA derivatives of d-Arg (25.33 min), l-Arg (26.78 min), respectively.
4.8. Absolute Configuration of the Amino Acid of Barettin (4)
A sample of barettin (4, 1.7 mg) was hydrogenated (1 atm H2, 10% Pd-C, MeOH) for 19 h. The mixture was filtered and concentrated to give debromo-8,9-dihydrobarettin (5a) as a colorless solid (1.4 mg) consisting of an equimolar mixture of C-3 epimers. HRESIMS m/z 343.1874 [M + H]+ (calcd for C17H23N6O2, 343.1877). The residue was hydrolyzed under standard conditions (6 M HCl, 15 h, see above) and the hydrolysate converted to the l-DTA derivatives and analyzed by RP HPLC as before. Two peaks, A and B, were eluted with retention times of tR = 25.33 and 26.78 min (ratio A:B = 19:81), respectively, coinciding with authentic l-DTA derivatives of d- and l-Arg (25.33 and 26.78 min, respectively). When the same procedures were conducted on 4 without prior hydrogenation, d- and l-Arg-l-DTA derivatives were obtained in a ratio of 19:81 indicating partially racemic 4 (62% ee).
4.9. Maturation and Activation of DCs
DCs were developed and matured from human monocytes as previously described [52,53]. CD14+ monocytes were isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained from healthy human donors using CD14 Microbeads (Miltenyi Biotech, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany). Immature DCs were obtained by culturing CD14+ monocytes at 5 × 105 cells/mL for 7 days in the presence of IL-4 at 12.5 ng/mL and GM-CSF at 25 ng/mL (both from R&D Systems, Abingdon, England), with fresh medium and cytokines added at day 3. The immature DCs were matured and activated by culturing them at 2.5 × 105 cells/mL for 24 h with IL-1β at 10 ng/mL, TNF-α at 50 ng/mL (both from R&D Systems), and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) at 500 ng/mL (Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany). Pure compounds were dissolved in DMSO at the concentration of 10 μg/mL and added to the DCs at the same time as the cytokines and LPS. The final concentration of DMSO in the medium of DCs cultured with the pure compounds was 0.002% and the same concentration of DMSO was used as solvent control. In order to determine whether the effects of compounds 2–4 were dose-dependent, the concentrations of 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 μg/mL were used. After 24 h the mature and activated DCs were harvested and the effects of the pure compounds on DC maturation and activation determined by measuring cytokine concentration in the culture medium by ELISA. Cell viability was determined by counting cells following staining with trypan blue and calculating the percentage of live cells.
4.10. Co-Culture of DCs and Allogeneic CD4+ T Cells
DCs matured in the presence/absence of a pure compound at 10 µg/mL or solvent control only were co-cultured with allogeneic CD4+ T cells at DC:T cell ratio of 1:10 (2 × 105 DCs/mL:2 × 106 T cells/mL) for 6 days. CD4+ T cells were obtained from PBMCs using CD4 Microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec). The effects of the pure compounds on the ability of the DCs to differentiate the CD4+ T cells were determined by measuring cytokine concentrations in the co-culture supernatants by ELISA.
4.11. Determination of Cytokine Concentration by ELISA
The concentrations of IL-12p40 and IL-10 in culture supernatants from DCs and of IFN-γ, IL-17 and IL-10 in supernatants from co-cultures of DCs and allogeneic CD4+ T cells were measured by sandwich ELISA using DuoSets from R&D Systems according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The results were expressed as secretion index (SI), which was calculated by dividing the cytokine concentration in supernatants from DCs cultured with pure compound or co-cultures of these DCs with allogeneic CD4+ T cells by the cytokine concentration in supernatants of DCs cultured with solvent only or co-cultures of these DCs with allogeneic CD4+ T cells.
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as the mean values ± standard error of the mean (SEM). As the data were not normally distributed, Mann-Whitney U test or Kruskal Wallis one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test were used to determine statistical differences between treatments (SigmaStat 3.1, Systat Software, San Jose, CA, USA) and p < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, three new 6-bromoindole derivatives, geobarrettin A–C (1–3), and four known ones (4–7) were obtained from the marine sponge G. barretti collected from west of Iceland. Compounds 2, 3 and 4 showed anti-inflammatory properties by inhibiting DC secretion of IL-12p40 with varying effects on IL-10, and the anti-inflammatory effect of compounds 2 and 3 was confirmed by inhibition of IFN-γ secretion in co-cultures of T cells and DCs matured in the presence of the compounds. It is increasingly being recognized that low-grade, subclinical inflammation is a significant pathogenic factor in many chronic diseases that have not, until now, been considered inflammatory in nature. Importantly, this includes most diseases that today are the main cause of morbidity and mortality in Western countries, such as atherosclerotic diseases, cancers, chronic pain disorders, and Alzheimer’s disease [54]. Therefore, the discovery of the two new 6-bromoindole derivatives with anti-inflammatory effects is important as they could be used in the development of treatments for diseases with inflammatory components.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/16/11/437/s1, The 1D and 2D NMR, HRESIMS, and IR spectra of the new compounds 1–3. The 1D NMR, UV, IR and HRESIMS spectra of 8. The UV spectrum and HPLC chromatogram of L-DPT derivative of the hydrolysate 1a.
Author Contributions
Methodology and formal analysis, X.D., C.R., I.H., J.F., T.F.M., D.T., and S.O.; Writing—original draft preparation, X.D.; Writing—review and editing, C.R., I.H., J.F., T.F.M., D.T., and S.O.; Supervision, I.H., J.F., D.T., and S.O.; Funding Acquisition, I.H., J.F., and S.O.
Funding
This research was funded by University of Iceland Research Fund (Doctoral Grant and Project Grant), AVS R&D Fund of Ministry of Fisheries and Agriculture in Iceland, the Landspitali University Hospital Research Fund, and the Memory Fund of Helga Jonsdottir and Sigurlidi Kristjansson. Funding from the National Institutes of Health (to T.F.M, R21 AT009783-01) is acknowledged.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Hans Tore Rapp at the University of Bergen for the identification of animal material, Nathalie Kringlstein for technical assistance, Annaliese Franz at University of California, Davis, for the generous gift of 8a, Sigridur Jonsdottir at University of Iceland for running NMR spectra on a Bruker AM-400 spectrometer, Finnur Freyr Eiriksson and Margret Thorsteinsdottir for running UPLC-qTOF-MS and Kare Telnes for giving the permission to use the sponge picture in the Graphical abstract.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Dubois, R.N. The Jeremiah Metzger Lecture: Inflammation, immune modulators, and chronic disease. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2015, 126, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fusetani, N. Marine pharmacology in 2012–2013: Marine compounds with antibacterial, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; Affecting the immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malve, H. Exploring the ocean for new drug developments: Marine pharmacology. J. Pharm. Bioallied. Sci. 2016, 8, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, K.; Kim, S.K. Marine invertebrate natural products for anti-inflammatory and chronic diseases. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 572859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; He, G.; Yang, M.; Li, D. Natural products and anti-inflammatory activity. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 15, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, Y.; Torres-Mendoza, D.; Jones, G.E.; Fernandez, P.L. Marine diterpenoids as potential anti-inflammatory agents. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 263543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyzers, R.A.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Anti-inflammatory metabolites from marine sponges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidgren, G.; Bohlin, L. Studies of Swedish marine organisms. 7. A novel biologically-active indole alkaloid from the sponge Geodia baretti. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27, 3283–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solter, S.; Dieckmann, R.; Blumenberg, M.; Francke, W. Barettin, revisited? Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 3385–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjogren, M.; Goransson, U.; Johnson, A.L.; Dahlstrom, M.; Andersson, R.; Bergman, J.; Jonsson, P.R.; Bohlin, L. Antifouling activity of brominated cyclopeptides from the marine sponge Geodia barretti. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedner, E.; Sjogren, M.; Hodzic, S.; Andersson, R.; Goransson, U.; Jonsson, P.R.; Bohlin, L. Antifouling activity of a dibrominated cyclopeptide from the marine sponge Geodia barretti. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, E.K.; Hansen, E.; Moodie, W.; Isaksson, J.; Sepcic, K.; Cergolj, M.; Svenson, J.; Andersen, J.H. Marine AChE inhibitors isolated from Geodia barretti: Natural compounds and their synthetic analogs. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Kubota, T.; Ishiyama, H.; Shibazaki, A.; Gonoi, T.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Heteroaromatic alkaloids, nakijinamines, from a sponge Suberites sp. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 8545–8550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidgren, G.; Bohlin, L.; Christophersen, C. Studies of Swedish marine organisms .10. Biologically-active compounds from the marine sponge Geodia barretti. J. Nat. Prod. 1988, 51, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, B.B.; Rosengren, K.J.; Gunasekera, S.; Schempp, S.; Bohlin, L.; Dahlstrom, M.; Clark, R.J.; Goransson, U. Goransson, U. Isolation, characterization, and synthesis of the barrettides: Disulfide-containing peptides from the marine sponge Geodia barretti. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hougaard, L.; Christophersen, C.; Nielsen, P.H.; Klitgaard, A.; Tendal, O. The chemical-composition of species of Geodia, Isops and Stryphnus (Choristida, Demospongia, Porifera)–a comparative-study with some taxonomical implications. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1991, 19, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.L.; Bergman, J.; Sjogren, M.; Bohlin, L. Synthesis of barettin. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthwick, A.D. 2,5-Diketopiperazines: Synthesis, reactions, medicinal chemistry, and bioactive natural products. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3641–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, K.F.; Hansen, E.; Osterud, B.; Eilertsen, K.E.; Bayer, A.; Engqvist, M.; Leszczak, K.; Jorgensen, T.O.; Andersen, J.H. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of barettin. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedner, E.; Sjogren, M.; Frandberg, P.A.; Johansson, T.; Goransson, U.; Dahlstrom, M.; Jonsson, P.; Nyberg, F.; Bohlin, L. Brominated cyclodipeptides from the marine sponge Geodia barretti as selective 5-HT ligands. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pooley, J.L.; Heath, W.R.; Shortman, K. Cutting edge: Intravenous soluble antigen is presented to CD4 T cells by CD8- dendritic cells, but cross-presented to CD8 T cells by CD8+ dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 5327–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manetti, R.; Gerosa, F.; Giudizi, M.G.; Biagiotti, R.; Parronchi, P.; Piccinni, M.P.; Sampognaro, S.; Maggi, E.; Romagnani, S.; Trinchieri, G.; et al. Interleukin 12 induces stable priming for interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) production during differentiation of human T helper (Th) cells and transient IFN-gamma production in established Th2 cell clones. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, N.; Ueno, H. Regulation of human helper T cell subset differentiation by cytokines. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 34, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, C.J.; Szymczak-Workman, A.L.; Collison, L.W.; Pillai, M.R.; Vignali, D.A. The development and function of regulatory T cells. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2603–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupchan, S.M.; Tsou, G.; Sigel, C.W. Datiscacin, a novel cytotoxic cucurbitacin 20-acetate from Datisca glomerata. J. Org. Chem. 1973, 38, 1420–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanwagenen, B.C.; Larsen, R.; Cardellina, J.H.; Randazzo, D.; Lidert, Z.C.; Swithenbank, C. Ulosantoin, a potent insecticide from the sponge Ulosa ruetzleri. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, F.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, H.J. Dereplication-guided isolation of novel hepatoprotective triterpenoid saponins from Celosiae semen by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 132, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.G.; Li, A.; Yan, B.C.; Niu, S.B.; Tang, J.W.; Li, X.N.; Du, X.; Challis, G.L.; Che, Y.; Sun, H.D.; et al. LC-MS-guided isolation of penicilfuranone A: A new antifibrotic furancarboxylic acid from the plant endophytic fungus Penicillium sp. sh18. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Di, Y.T.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, S.Z.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, C.J.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, X.H.; et al. Gelegamines A-E: Five new oxindole alkaloids from Gelsemium elegans. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 4551–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamano, Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Ichihara, Y.; Kizu, H.; Komiyama, K.; Pettit, G.R. Convolutamydine A, a novel bioactive hydroxyoxindole alkaloid from marine bryozoan Amathia Convoluta. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 2783–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xue, F.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y. Total synthesis of (+)-perophoramidine and determination of the absolute configuration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14052–14054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Saravanan, S.; Gupta, N.; Abdi, S.H.R.; Khan, N.U.; Kureshy, R.I.; Bajaj, H.C. Phosphotungstic acid as an efficient catalyst for allylation of isatins and N-tert-butyloxycarbonylamido sulfones under solvent-free conditions. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2014, 3, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Henriksen, N.M.; Skalicky, J.J.; Harper, M.K.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd; Ireland, C.M.; Van Wagoner, R.M. Araiosamines A-D: Tris-bromoindole cyclic guanidine alkaloids from the marine sponge Clathria (Thalysias) araiosa. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 5515–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.Q.; Sattler, I.; Thiericke, R.; Grabley, S.; Feng, X.Z. Maremycins C and D, new diketopiperazines, and maremycins E and F, novel polycyclic spiro-indole metabolites isolated from Streptomyces sp. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanhan, N.V.; Sahin, A.H.; Chang, T.W.; Fettinger, J.C.; Franz, A.K. Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of substituted 3-hydroxy-2-oxindoles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salib, M.N.; Molinski, T.F. Six trikentrin-like cyclopentanoindoles from trikentrion flabelliforme. Absolute structural assignment by NMR and ECD. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonderegger, O.J.; Burgi, T.; Limbach, L.K.; Baiker, A. Enantio selective reduction of isatin derivatives over cinchonidine modified Pt/alumina. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2004, 217, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phyo, Y.Z.; Ribeiro, J.; Fernandes, C.; Kijjoa, A.; Pinto, M.M.M. Marine natural peptides: Determination of absolute configuration using liquid chromatography methods and evaluation of bioactivities. Molecules 2018, 23, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salib, M.N.; Molinski, T.F. Cyclic hexapeptide dimers, antatollamides A and B, from the ascidian Didemnum molle. A tryptophan-derived auxiliary for l- and d-amino acid assignments. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 10181–10187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, K.; Benner, R. Hydrolysis-induced racemization of amino acids. Limnol. Oceanogr.-Meth. 2005, 3, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albinsson, B.; Norden, B. Excited-state properties of the indole chromophore: Electronic-transition moment directions from linear dichroism measurements: Effect of methyl and methoxy substituents. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 6204–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.G.; Hayakawa, M.; Mikami, K.; Yoshimura, J. Syntheses and configurational assignments of albonoursin and its three geometric isomers. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Hayakawa, M.; Suzuki, T.; Ohtsuka, A.; Yoshimura, J. α,β-Unsaturated carboxylic-acid derivatives. 13. Synthesis andconfiguration of alkyl 2-acylamino-2-alkenoates and their cyclized 2,5-piperazinedione derivatives. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1978, 51, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Makarieva, T.N.; Spirova, E.N.; Guzii, A.G.; Stonik, V.A.; Tsetlin, V.I. 6-Bromohypaphorine from marine nudibranch mollusk Hermissenda crassicornis is an agonist of human α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Nishi, J.; Ishibashi, M.; Kobayashi, J. Two new tryptophan-derived alkaloids from the Okinawan marine sponge Aplysina sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corthay, A. How do regulatory T cells work? Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 70, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnani, S. Th1 and Th2 in human diseases. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 80, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, K.; Guzzo, C.; Che Mat, N.F.; Ma, W.; Kumar, A. The IL-12 family of cytokines in infection, inflammation and autoimmune disorders. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2009, 8, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pence, H.E.; Williams, A. ChemSpider: An online chemical information resource. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freysdottir, J.; Sigurpalsson, M.B.; Omarsdottir, S.; Olafsdottir, E.S.; Vikingsson, A.; Hardardottir, I. Ethanol extract from birch bark (Betula pubescens) suppresses human dendritic cell mediated Th1 responses and directs it towards a Th17 regulatory response in vitro. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 136, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, X.; Oskarsson, J.T.; Omarsdottir, S.; Freysdottir, J.; Hardardottir, I. Lipophilic fractions from the marine sponge Halichondria sitiens decrease secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by dendritic cells and decrease their ability to induce a Th1 type response by allogeneic CD4+ T cells. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iso, H.; Cui, R.; Date, C.; Kikuchi, S.; Tamakoshi, A.; Group, J.S. C-reactive protein levels and risk of mortality from cardiovascular disease in Japanese: The JACC Study. Atherosclerosis 2009, 207, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).