Ciguatoxins Evoke Potent CGRP Release by Activation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Subtypes NaV1.9, NaV1.7 and NaV1.1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals, Preparation of Skin Flaps and Solutions
2.2. Stimulation Procedure and Compounds
2.3. Enzyme Immunoassay
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
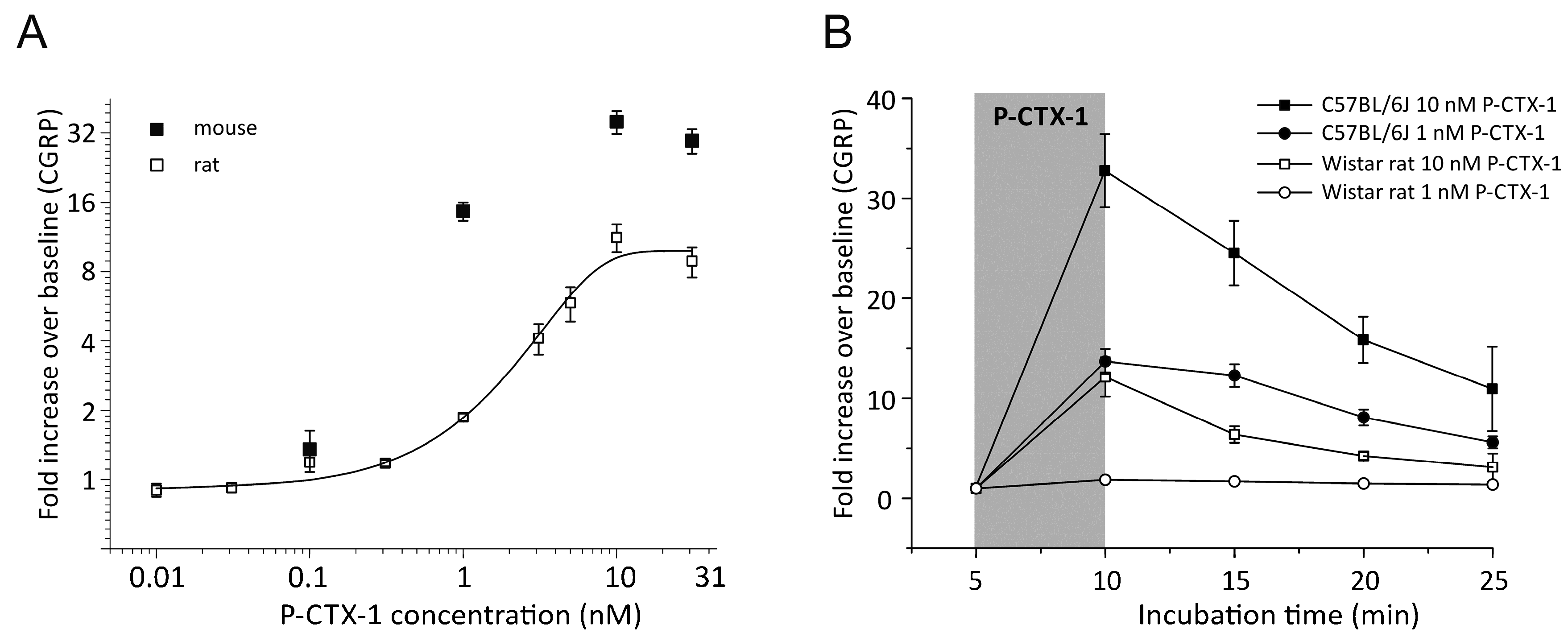
3.1. P-CTX-1-Induced CGRP-Release Is Greater in Mouse Than Rat Skin
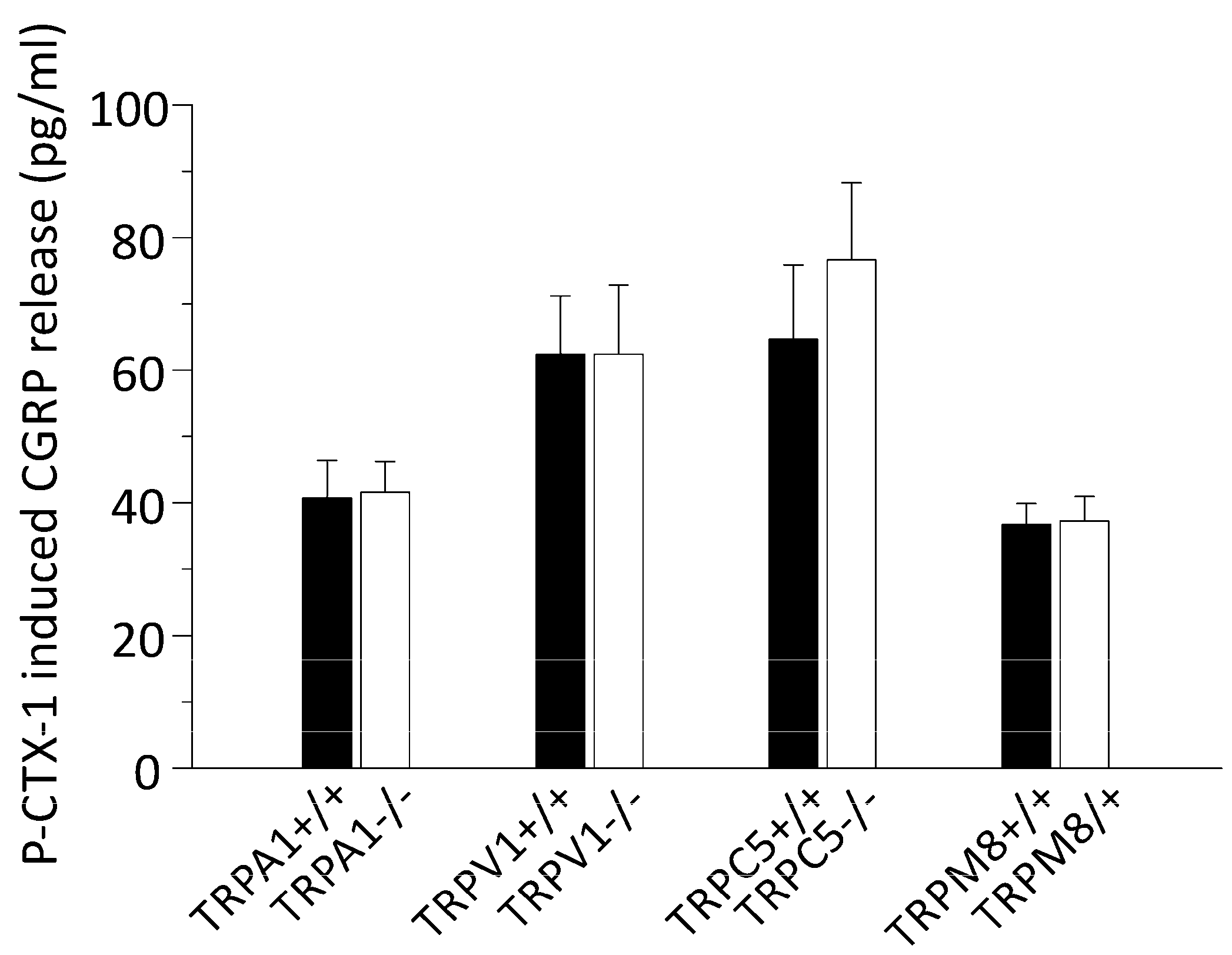
3.2. P-CTX-1-Induced CGRP Release Requires Extracellular Calcium but Is Not Reduced in Mice Deficient of TRPV1, TRPA1, TRPM8, or TRPC5
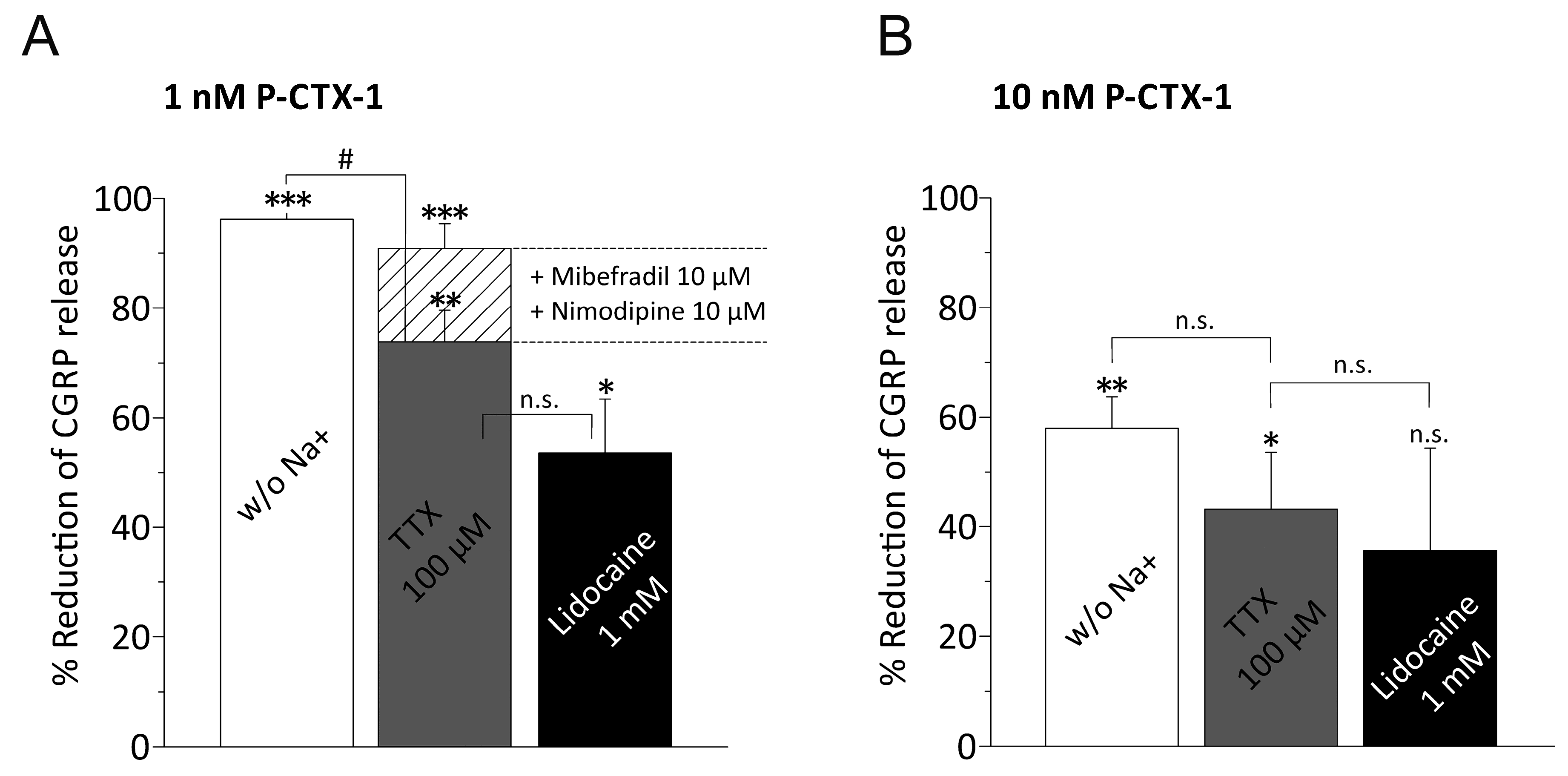
3.3. P-CTX-1-Induced CGRP Release Requires Extracellular Sodium and Activation of VGSCs
3.4. P-CTX-1-Induced VGSC Opening Triggers Activation of L- and T-Type VGCC
3.5. Distinct VGSC Subtypes Mediate the P-CTX-1-Induced CGRP Release
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera: Australian perspectives on a global problem. Toxicon 2006, 48, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnis, R.; Kuberski, T.; Laugier, S. Clinical Observations on 3009 Cases of Ciguatera (Fish Poisoning) in the South-Pacific. Am. J. Trop Med. Hyg. 1979, 28, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strachan, L.C.; Lewis, R.J.; Nicholson, G.M. Differential actions of Pacific ciguatoxin-1 on sodium channel subtypes in mammalian sensory neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 288, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, K.; Inoue, M.; Miyahara, H.; Miyazaki, K.; Hirama, M. A quantitative and comparative study of the effects of a synthetic ciguatoxin CTX3C on the kinetic properties of voltage-dependent sodium channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 142, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inserra, M.C.; Israel, M.R.; Caldwell, A.; Castro, J.; Deuis, J.R.; Harrington, A.M.; Keramidas, A.; Garcia-Caraballo, S.; Maddern, J.; Erickson, A.; et al. Multiple sodium channel isoforms mediate the pathological effects of Pacific ciguatoxin-1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, I.; Touska, F.; Hess, A.; Hinsbey, R.; Sattler, S.; Lampert, A.; Sergejeva, M.; Sharov, A.; Collins, L.S.; Eberhardt, M.; et al. Ciguatoxins activate specific cold pain pathways to elicit burning pain from cooling. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3795–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlereth, T.; Breimhorst, M.; Werner, N.; Pottschmidt, K.; Drummond, P.D.; Birklein, F. Inhibition of neuropeptide degradation suppresses sweating but increases the area of the axon reflex flare. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, K.; Deuis, J.R.; Inserra, M.C.; Collins, L.S.; Namer, B.; Cabot, P.J.; Reeh, P.W.; Lewis, R.J.; Vetter, I. Analgesic treatment of ciguatoxin-induced cold allodynia. Pain 2013, 154, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, M.; Dux, M.; Namer, B.; Miljkovic, J.; Cordasic, N.; Will, C.; Kichko, T.I.; de la Roche, J.; Fischer, M.; Suarez, S.A.; et al. H2S and NO cooperatively regulate vascular tone by activating a neuroendocrine HNO-TRPA1-CGRP signalling pathway. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassini, R.; Materazzi, S.; Benemei, S.; Geppetti, P. The TRPA1 channel in inflammatory and neuropathic pain and migraine. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 167, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCoy, E.S.; Taylor-Blake, B.; Street, S.E.; Pribisko, A.L.; Zheng, J.; Zylka, M.J. Peptidergic CGRPalpha primary sensory neurons encode heat and itch and tonically suppress sensitivity to cold. Neuron 2013, 78, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, M.A.; Leffler, A.; Niedermirtl, F.; Babes, A.; Zimmermann, K.; Filipovic, M.R.; Izydorczyk, I.; Eberhardt, M.; Kichko, T.I.; Mueller-Tribbensee, S.M.; et al. TRPA1 and substance P mediate colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, D.A.; Mapp, P.I.; Kelly, S. Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the joint: Contributions to pain and inflammation. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, R.C.; House, D.; Ryan, J.C. Defining the neurotoxin derived illness chronic ciguatera using markers of chronic systemic inflammatory disturbances: A case/control study. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Garrec, R.; L’Herondelle, K.; Le Gall-Ianotto, C.; Lebonvallet, N.; Leschiera, R.; Buhe, V.; Talagas, M.; Vetter, I.; Lewis, R.J.; Misery, L. Release of neuropeptides from a neuro-cutaneous co-culture model: A novel in vitro model for studying sensory effects of ciguatoxins. Toxicon 2016, 116, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, K.; Santos, S.; Chapman, M.L.; Krafte, D.S.; Marron, B.E.; West, C.W.; Krambis, M.J.; Antonio, B.M.; Zellmer, S.G.; Printzenhoff, D.; et al. Voltage sensor interaction site for selective small molecule inhibitors of voltage-gated sodium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2724–E2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.B.; Gray, J.; Gunthorpe, M.J.; Hatcher, J.P.; Davey, P.T.; Overend, P.; Harries, M.H.; Latcham, J.; Clapham, C.; Atkinson, K.; et al. Vanilloid receptor-1 is essential for inflammatory thermal hyperalgesia. Nature 2000, 405, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, K.Y.; Allchorne, A.J.; Vollrath, M.A.; Christensen, A.P.; Zhang, D.S.; Woolf, C.J.; Corey, D.P. TRPA1 contributes to cold, mechanical, and chemical Nociception but is not essential for hair-cell transduction. Neuron 2006, 50, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaka, A.; Murray, A.N.; Mathur, J.; Earley, T.J.; Petrus, M.J.; Patapoutian, A. TRPM8 is required for cold sensation in mice. Neuron 2007, 54, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, K.D.; Shwe, U.T.; Abramowitz, J.; Wu, H.; Rhee, S.W.; Howell, M.D.; Gottschall, P.E.; Freichel, M.; Flockerzi, V.; Birnbaumer, L.; et al. Canonical transient receptor channel 5 (TRPC5) and TRPC1/4 contribute to seizure and excitotoxicity by distinct cellular mechanisms. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akopian, A.N.; Souslova, V.; England, S.; Okuse, K.; Ogata, N.; Ure, J.; Smith, A.; Kerr, B.J.; McMahon, S.B.; Boyce, S.; et al. The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, M.D.; Chandra, S.Y.; Ding, Y.; Waxman, S.G.; Wood, J.N. GTP-induced tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ current regulates excitability in mouse and rat small diameter sensory neurones. J. Physiol. 2003, 548, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minett, M.S.; Nassar, M.A.; Clark, A.K.; Passmore, G.; Dickenson, A.H.; Wang, F.; Malcangio, M.; Wood, J.N. Distinct NaV1.7-dependent pain sensations require different sets of sensory and sympathetic neurons. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M.; Poli, M.A.; Norton, R.S.; MacLeod, J.K.; Sheil, M.M. Purification and characterization of ciguatoxins from moray eel (Lycodontis javanicus, Muraenidae). Toxicon 1991, 29, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, K.; Reeh, P.W.; Averbeck, B. S+ -flurbiprofen but not 5-HT1 agonists suppress basal and stimulated CGRP and PGE2 release from isolated rat dura mater. Pain 2003, 103, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbeck, B.; Reeh, P.W. Interactions of inflammatory mediators stimulating release of calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance P and prostaglandin E(2) from isolated rat skin. Neuropharmacology 2001, 40, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, K.; Reeh, P.W.; Sauer, S.K. TRPV1, TRPA1, and CB1 in the isolated vagus nerve--axonal chemosensitivity and control of neuropeptide release. Neuropeptides 2011, 45, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kichko, T.I.; Kobal, G.; Reeh, P.W. Cigarette smoke has sensory effects through nicotinic and TRPA1 but not TRPV1 receptors on the isolated mouse trachea and larynx. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, L812–L820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuypers, E.; Yanagihara, A.; Rainier, J.D.; Tytgat, J. TRPV1 as a key determinant in ciguatera and neurotoxic shellfish poisoning. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 361, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, N.C.; Lewis, R.J.; Pearn, J.H.; Bourke, A.T.; Holmes, M.J.; Bourke, J.B.; Shields, W.J. Ciguatera in Australia. Occurrence, clinical features, pathophysiology and management. Med. J. Aust. 1986, 145, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coyle, D.E.; Sperelakis, N. Bupivacaine and lidocaine blockade of calcium-mediated slow action potentials in guinea pig ventricular muscle. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1987, 242, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spitzer, M.J.; Reeh, P.W.; Sauer, S.K. Mechanisms of potassium- and capsaicin-induced axonal calcitonin gene-related peptide release: Involvement of L- and T-type calcium channels and TRPV1 but not sodium channels. Neuroscience 2008, 151, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usoskin, D.; Furlan, A.; Islam, S.; Abdo, H.; Lonnerberg, P.; Lou, D.; Hjerling-Leffler, J.; Haeggstrom, J.; Kharchenko, O.; Kharchenko, P.V.; et al. Unbiased classification of sensory neuron types by large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osteen, J.D.; Herzig, V.; Gilchrist, J.; Emrick, J.J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Castro, J.; Garcia-Caraballo, S.; Grundy, L.; Rychkov, G.Y.; et al. Selective spider toxins reveal a role for the NaV1.1 channel in mechanical pain. Nature 2016, 534, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackel, D.; Krug, S.M.; Sauer, R.S.; Mousa, S.A.; Bocker, A.; Pflucke, D.; Wrede, E.J.; Kistner, K.; Hoffmann, T.; Niedermirtl, B.; et al. Transient opening of the perineurial barrier for analgesic drug delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2018–E2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, K.; Hein, A.; Hager, U.; Kaczmarek, J.S.; Turnquist, B.P.; Clapham, D.E.; Reeh, P.W. Phenotyping sensory nerve endings in vitro in the mouse. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 174–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, K.; Leffler, A.; Babes, A.; Cendan, C.M.; Carr, R.W.; Kobayashi, J.; Nau, C.; Wood, J.N.; Reeh, P.W. Sensory neuron sodium channel NaV1.8 is essential for pain at low temperatures. Nature 2007, 447, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller-Brem, S.; Muff, R.; Fischer, J.A. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and calcitonin secretion from a human medullary thyroid carcinoma cell line: Effects of ionomycin, phorbol ester and forskolin. J. Endocrinol. 1988, 119, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.Y.; Neher, E. Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis in the somata of dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neuron 1996, 17, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, C.; Wen, P.J.; Nguyen-Huu, T.D.; Alvarez, M.; Benoit, E.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Baden, D.G.; Molgo, J.; Meunier, F.A. Brevenal inhibits pacific ciguatoxin-1B-induced neurosecretion from bovine chromaffin cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molgo, J.B.E. Involvement of Na+ in the actions of ciguatoxins and brevetoxins that stimulate neurotransmitter release and affect synaptic transmission. In Perspectives in Molecular Toxinology; Menez, A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: London, UK, 2002; pp. 67–94. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey, I.S.; Delling, M.; Clapham, D.E. An introduction to TRP channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2006, 68, 619–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaka, A.; Earley, T.J.; Watson, J.; Patapoutian, A. Visualizing cold spots: TRPM8-expressing sensory neurons and their projections. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, K.; Lennerz, J.K.; Hein, A.; Link, A.S.; Kaczmarek, J.S.; Delling, M.; Uysal, S.; Pfeifer, J.D.; Riccio, A.; Clapham, D.E. Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 5 (TRPC5) is a cold-transducer in the peripheral nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18114–18119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscheweyh, R.; Forsthuber, L.; Schoffnegger, D.; Sandkuhler, J. Modification of classical neurochemical markers in identified primary afferent neurons with Abeta-, Adelta-, and C-fibers after chronic constriction injury in mice. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 502, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, P.W.; Lawson, S.N. Cell type and conduction velocity of rat primary sensory neurons with calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity. Neuroscience 1990, 34, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renganathan, M.; Cummins, T.R.; Waxman, S.G. Contribution of Nav1.8 sodium channels to action potential electrogenesis in DRG neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blair, N.T.; Bean, B.P. Roles of tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive Na+ current, TTX-resistant Na+ current, and Ca2+ current in the action potentials of nociceptive sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 10277–10290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abrahamsen, B.; Zhao, J.; Asante, C.O.; Cendan, C.M.; Marsh, S.; Martinez-Barbera, J.P.; Nassar, M.A.; Dickenson, A.H.; Wood, J.N. The cell and molecular basis of mechanical, cold, and inflammatory pain. Science 2008, 321, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Cummins, T.R.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. Sodium channels in normal and pathological pain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 33, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockley, J.R.; Boundouki, G.; Cibert-Goton, V.; McGuire, C.; Yip, P.K.; Chan, C.; Tranter, M.; Wood, J.N.; Nassar, M.A.; Blackshaw, L.A.; et al. Multiple roles for NaV1.9 in the activation of visceral afferents by noxious inflammatory, mechanical, and human disease-derived stimuli. Pain 2014, 155, 1962–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. NaV1.9: A sodium channel linked to human pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maingret, F.; Coste, B.; Padilla, F.; Clerc, N.; Crest, M.; Korogod, S.M.; Delmas, P. Inflammatory mediators increase NaV1.9 current and excitability in nociceptors through a coincident detection mechanism. J. Gen. Physiol. 2008, 131, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, R.C.; Lewis, R.J.; Adams, D.J. Ciguatoxin-induced oscillations in membrane potential and action potential firing in rat parasympathetic neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, E.; Vale, C.; Sasaki, M.; Fuwa, H.; Konno, Y.; Perez, S.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Calcium Oscillations Induced by Gambierol in Cerebellar Granule Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 110, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuypers, E.; Abdel-Mottaleb, Y.; Kopljar, I.; Rainier, J.D.; Raes, A.L.; Snyders, D.J.; Tytgat, J. Gambierol, a toxin produced by the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus, is a potent blocker of voltage-gated potassium channels. Toxicon 2008, 51, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birinyi-Strachan, L.C.; Gunning, S.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Nicholson, G.M. Block of voltage-gated potassium channels by Pacific ciguatoxin-1 contributes to increased neuronal excitability in rat sensory neurons. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2005, 204, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayliss, W.M. On the origin from the spinal cord of the vaso-dilator fibres of the hind-limb, and on the nature of these fibres. J. Physiol. 1901, 26, 173–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, M.; Guthmann, C.; Averbeck, B.; Reeh, P.W. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and prostaglandin E2 but not substance P release induced by antidromic nerve stimulation from rat skin in vitro. Neuroscience 1999, 89, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Touska, F.; Sattler, S.; Malsch, P.; Lewis, R.J.; Reeh, P.W.; Zimmermann, K. Ciguatoxins Evoke Potent CGRP Release by Activation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Subtypes NaV1.9, NaV1.7 and NaV1.1. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090269
Touska F, Sattler S, Malsch P, Lewis RJ, Reeh PW, Zimmermann K. Ciguatoxins Evoke Potent CGRP Release by Activation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Subtypes NaV1.9, NaV1.7 and NaV1.1. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(9):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090269
Chicago/Turabian StyleTouska, Filip, Simon Sattler, Philipp Malsch, Richard J. Lewis, Peter W. Reeh, and Katharina Zimmermann. 2017. "Ciguatoxins Evoke Potent CGRP Release by Activation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Subtypes NaV1.9, NaV1.7 and NaV1.1" Marine Drugs 15, no. 9: 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090269
APA StyleTouska, F., Sattler, S., Malsch, P., Lewis, R. J., Reeh, P. W., & Zimmermann, K. (2017). Ciguatoxins Evoke Potent CGRP Release by Activation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Subtypes NaV1.9, NaV1.7 and NaV1.1. Marine Drugs, 15(9), 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090269




