µ-Conotoxins Modulating Sodium Currents in Pain Perception and Transmission: A Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
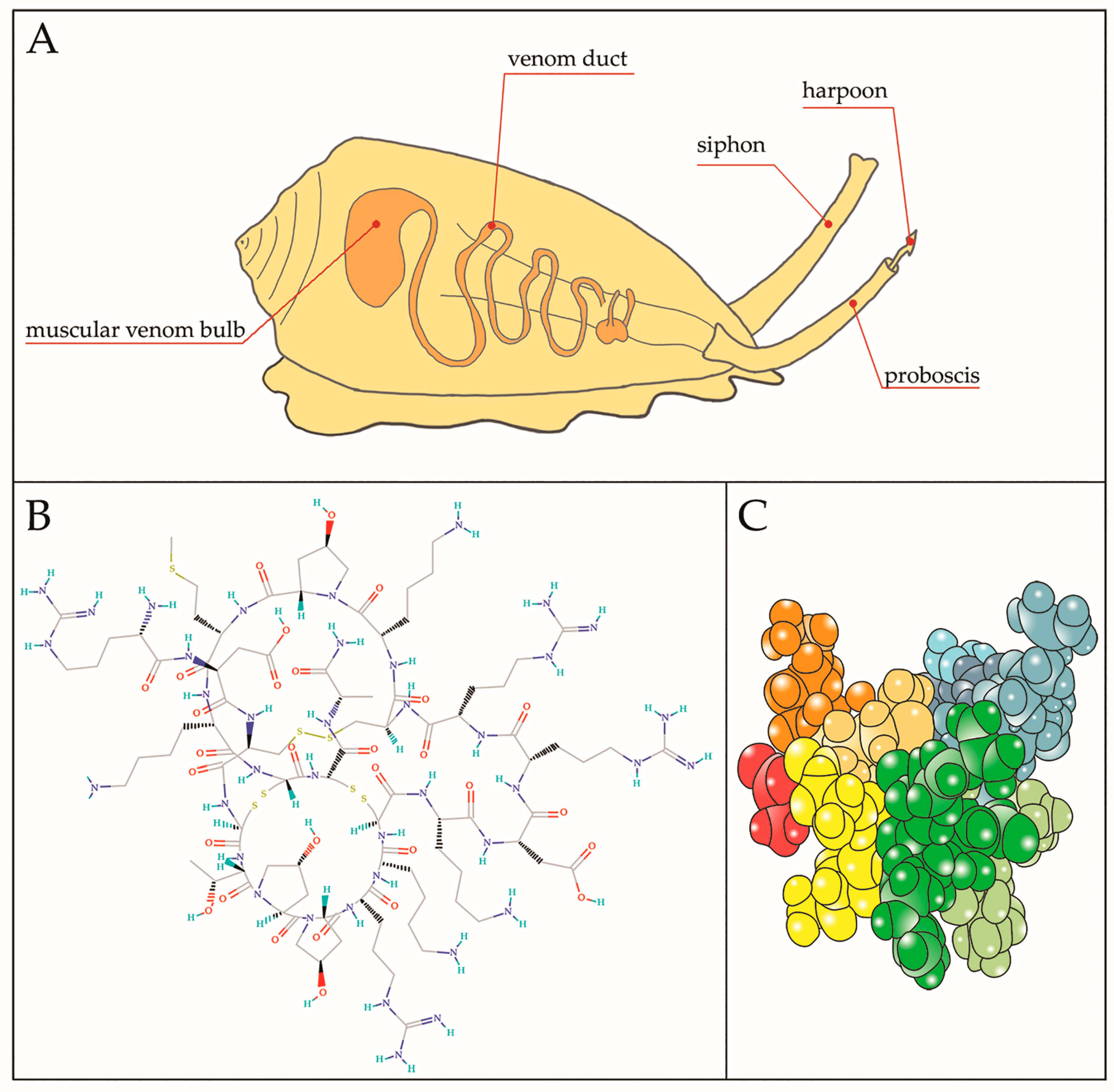
:1. Introduction
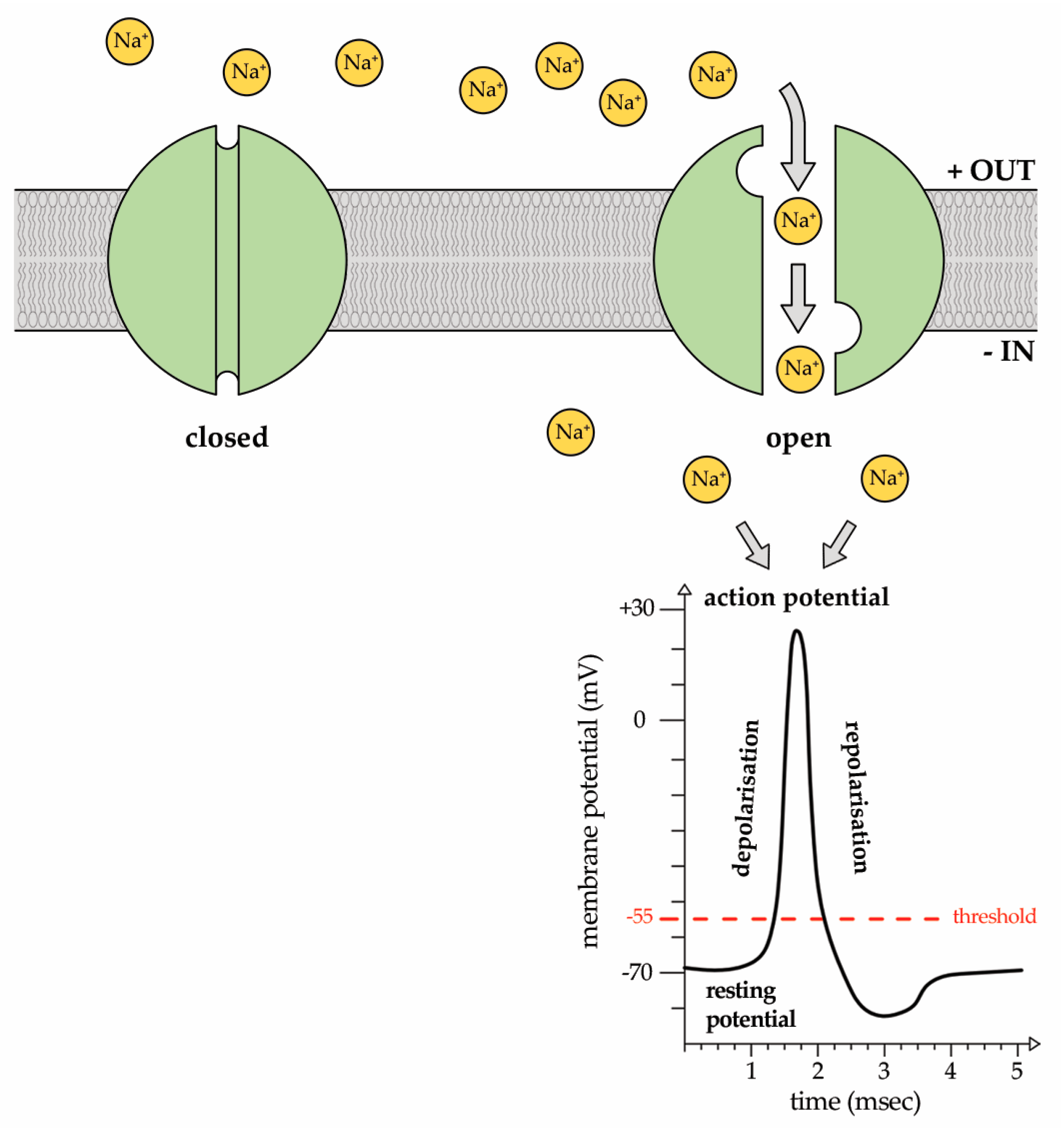
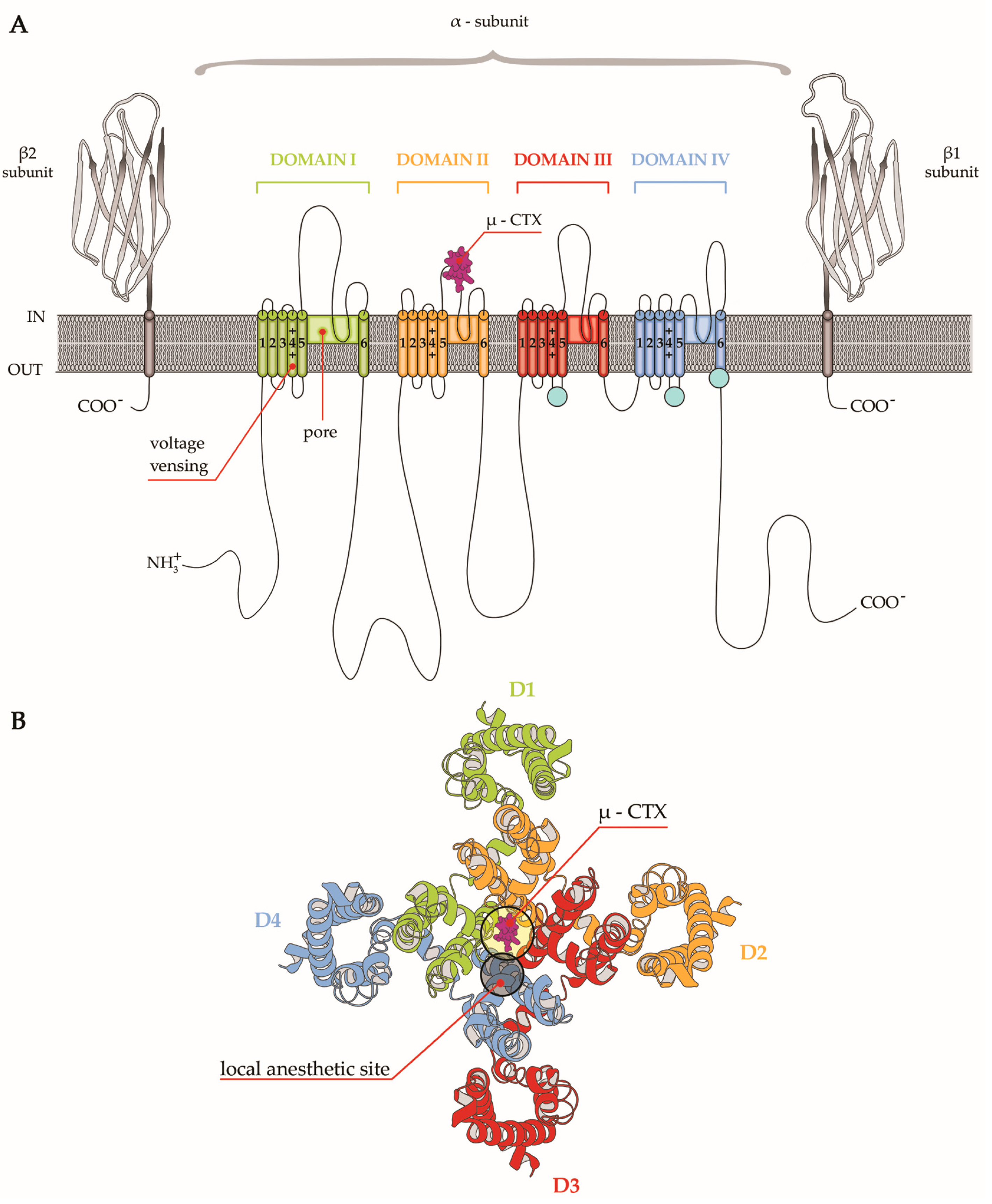
2. Sodium (Na+) Ion Currents
3. Na+ Currents—Linked Channelopathies
4. µ-CTX Modulating Nav Currents
5. µ-CTX Targeting Nav Channels in the Modulation of Pain States
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terlau, H.; Olivera, B.M. Conus venoms: A rich source of novel ion channel-targeted peptides. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stix, G. A toxin against pain. Sci. Am. 2005, 292, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layer, R.T.; McIntosh, J.M. Conotoxins: Therapeutic potential and application. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Terlau, H. Toxins from cone snails: Properties, applications and biotechnological production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halai, R.; Craik, D.J. Conotoxins: Natural product drug leads. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, R.; Karim, S.; Amjad Kamal, M.; Wilson, M.C.; Mirza, Z. Conotoxins: Structure, therapeutic potential and pharmacological applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosti, E.; Boni, R. Electrical events during gamete maturation and fertilization in animals and humans. Hum. Reprod. Update 2004, 10, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, B.; Olivera, B. Chapter three-venom peptides from cone snails: Pharmacological probes for voltage-gated sodium channels. Curr. Top. Membr. 2016, 78, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Huxley, A.F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 1952, 117, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnew, W.S.; Levinson, S.R.; Brabson, J.S.; Raftery, M.A. Purification of the tetrodotoxin-binding component associated with the voltage-sensitive sodium channel from Electrophorus electricus electroplax membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 2606–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A. Structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels at atomic resolution. Exp. Physiol. 2014, 99, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuis, J.R.; Mueller, A.; Israel, M.R.; Vetter, I. The pharmacology of voltage-gated sodium channel activators. Neuropharmacology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clairfeuille, T.; Xu, H.; Koth, C.M.; Payandeh, J. Voltage-gated sodium channels viewed through a structural biology lens. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 45, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagal, S.K.; Marron, B.E.; Owen, R.M.; Storer, R.I.; Swain, N.A. Voltage gated sodium channels as drug discovery targets. Channels 2015, 9, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, H.A.; Isom, L.L. Sodium channel β subunits: Emerging targets in channelopathies. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015, 77, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.N.; Boorman, J.P.; Okuse, K.; Baker, M.D. Voltage-gated sodium channels and pain pathways. J. Neurobiol. 2004, 61, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A.; Perez-Reyes, E.; Snutch, T.P.; Striessnig, J. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVIII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated calcium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, R.S. The channelopathies: Novel insights into molecular and genetic mechanisms of human disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1986–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-B. Channelopathies. Korean J. Pediatr. 2014, 57, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andavan, G.S.; Lemmens-Gruber, R. Voltage-gated sodium channels: Mutations, channelopathies and targets. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, T.R.; Sheets, P.L.; Waxman, S.G. The roles of sodium channels in nociception: Implications for mechanisms of pain. Pain 2007, 131, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Cummins, T.R.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. From genes to pain: Nav 1.7 and human pain disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahine, M.; O’Leary, M.E. Regulatory role of voltage-gated Na+ channel β subunits in sensory neurons. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fertleman, C.R.; Baker, M.D.; Parker, K.A.; Moffatt, S.; Elmslie, F.V.; Abrahamsen, B.; Ostman, J.; Klugbauer, N.; Wood, J.N.; Gardiner, R.M. SCN9A mutations in paroxysmal extreme pain disorder: Allelic variants underlie distinct channel defects and phenotypes. Neuron 2006, 52, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.J.; Reimann, F.; Nicholas, A.K.; Thornton, G.; Roberts, E.; Springell, K.; Karbani, G.; Jafri, H.; Mannan, J.; Raashid, Y. An SCN9A channelopathy causes congenital inability to experience pain. Nature 2006, 444, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Wickenden, A.D.; Chaplan, S.R. Sodium channel blockers for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Neurotherapeutics 2009, 6, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luiz, A.P.; Wood, J.N. Chapter six-sodium channels in pain and cancer: New therapeutic opportunities. Adv. Pharmacol. 2016, 75, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kao, C. Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and their significance in the study of excitation phenomena. Pharmacol. Rev. 1966, 18, 997–1049. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, L.E. Sodium channel inhibiting marine toxins. In Marine Toxins as Research Tools; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 67–97. [Google Scholar]
- Pratheepa, V.; Vasconcelos, V. Binding and pharmacokinetics of the sodium channel blocking toxins (Saxitoxin and the Tetrodotoxins). Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, F.R.; Cobos, E.J.; Tejada, M.Á.; Sánchez-Fernández, C.; González-Cano, R.; Cendán, C.M. Tetrodotoxin (TTX) as a therapeutic agent for pain. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, R.S.; Olivera, B.M. Conotoxins down under. Toxicon 2006, 48, 780–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safavi-Hemami, H.; Siero, W.A.; Gorasia, D.G.; Young, N.D.; MacMillan, D.; Williamson, N.A.; Purcell, A.W. Specialisation of the venom gland proteome in predatory cone snails reveals functional diversification of the conotoxin biosynthetic pathway. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3904–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.A.; Tomaselli, G.F. Using the deadly μ-conotoxins as probes of voltage-gated sodium channels. Toxicon 2004, 44, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivera, B.M.; Cruz, L.J. Conotoxins, in retrospect. Toxicon 2001, 39, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.R.; Bulaj, G.; Norton, R.S. Structure and function of μ-conotoxins, peptide-based sodium channel blockers with analgesic activity. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1677–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, K.-J.; Olivera, B.M.; Watkins, M.; Jacobsen, R.B.; Gray, W.R.; Floresca, C.Z.; Cruz, L.J.; Hillyard, D.R.; Brink, A.; Terlau, H. μ-Conotoxin PIIIA, a new peptide for discriminating among tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na channel subtypes. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 4473–4481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walewska, A.; Skalicky, J.J.; Davis, D.R.; Zhang, M.-M.; Lopez-Vera, E.; Watkins, M.; Han, T.S.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G. NMR-based mapping of disulfide bridges in cysteine-rich peptides: Application to the μ-conotoxin SxIIIA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14280–14286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leipold, E.; DeBie, H.; Zorn, S.; Adolfo, B.; Olivera, B.M.; Terlau, H.; Heinemann, S.H. µO-conotoxins inhibit Nav channels by interfering with their voltage sensors in domain-2. Channels 2007, 1, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, L.; Gray, W.; Olivera, B.M.; Zeikus, R.; Kerr, L.; Yoshikami, D.; Moczydlowski, E. Conus geographus toxins that discriminate between neuronal and muscle sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 9280–9288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, R.A.; Ennis, I.L.; Xue, T.; Nguyen, H.M.; Tomaselli, G.F.; Goldin, A.L.; Marbán, E. Molecular basis of isoform-specific μ-conotoxin block of cardiac, skeletal muscle, and brain Na+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8717–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safo, P.; Rosenbaum, T.; Shcherbatko, A.; Choi, D.-Y.; Han, E.; Toledo-Aral, J.J.; Olivera, B.M.; Brehm, P.; Mandel, G. Distinction among neuronal subtypes of voltage-activated sodium channels by μ-conotoxin PIIIA. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Robinson, A.; Chung, S.-H. Mechanism of μ-conotoxin PIIIA binding to the voltage-gated Na+ channel NaV 1.4. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93267. [Google Scholar]
- Keizer, D.W.; West, P.J.; Lee, E.F.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G.; Norton, R.S. Structural basis for tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel binding by μ-conotoxin SmIIIA. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 46805–46813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.J.; Watson, M.; Adams, D.J.; Hammarström, A.K.; Gage, P.W.; Hill, J.M.; Craik, D.J.; Thomas, L.; Adams, D.; Alewood, P.F. Solution structure of μ-conotoxin PIIIA, a preferential inhibitor of persistent tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 27247–27255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leipold, E.; Ullrich, F.; Thiele, M.; Tietze, A.A.; Terlau, H.; Imhof, D.; Heinemann, S.H. Subtype-specific block of voltage-gated K+ channels by μ-conopeptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Chung, S.-H. Binding modes of μ-conotoxin to the bacterial sodium channel (Na V Ab). Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulaj, G.; West, P.J.; Garrett, J.E.; Watkins, M.; Zhang, M.-M.; Norton, R.S.; Smith, B.J.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M. Novel conotoxins from Conus striatus and Conus kinoshitai selectively block TTX-resistant sodium channels. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 7259–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-M.; Green, B.R.; Catlin, P.; Fiedler, B.; Azam, L.; Chadwick, A.; Terlau, H.; McArthur, J.R.; French, R.J.; Gulyas, J. Structure/function characterization of μ-conotoxin KIIIA, an analgesic, nearly irreversible blocker of mammalian neuronal sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 30699–30706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Zhang, M.-M.; Yoshikami, D.; Azam, L.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G.; Norton, R.S. Structure, dynamics, and selectivity of the sodium channel blocker μ-conotoxin SIIIA. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 10940–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, H.; Lu, W.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Chi, C.-W. A novel conotoxin from Conus striatus, μ-SIIIA, selectively blocking rat tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels. Toxicon 2006, 47, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, P.J.; Bulaj, G.; Garrett, J.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Yoshikami, D. μ-Conotoxin SmIIIA, a potent inhibitor of tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels in amphibian sympathetic and sensory neurons. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 15388–15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Schroeder, C.I.; Ekberg, J.; Nielsen, K.J.; Loughnan, M.; Thomas, L.; Adams, D.A.; Drinkwater, R.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Isolation and structure-activity of μ-conotoxin TIIIA, a potent inhibitor of tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-gated sodium channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holford, M.; Zhang, M.-M.; Gowd, K.H.; Azam, L.; Green, B.R.; Watkins, M.; Ownby, J.-P.; Yoshikami, D.; Bulaj, G.; Olivera, B.M. Pruning nature: Biodiversity-derived discovery of novel sodium channel blocking conotoxins from Conus bullatus. Toxicon 2009, 53, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Z.; Zhang, M.-M.; Gupta, K.; Gajewiak, J.; Gulyas, J.; Balaram, P.; Rivier, J.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Yoshikami, D.; Bulaj, G. Mammalian neuronal sodium channel blocker μ-conotoxin BuIIIB has a structured N-terminus that influences potency. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favreau, P.; Benoit, E.; Hocking, H.G.; Carlier, L.; D’hoedt, D.; Leipold, E.; Markgraf, R.; Schlumberger, S.; Córdova, M.A.; Gaertner, H. A novel µ-conopeptide, CnIIIC, exerts potent and preferential inhibition of NaV1. 2/1.4 channels and blocks neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 166, 1654–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, B.R.; Gajewiak, J.; Chhabra, S.; Skalicky, J.J.; Zhang, M.-M.; Rivier, J.E.; Bulaj, G.; Olivera, B.M.; Yoshikami, D.; Norton, R.S. Structural basis for the inhibition of voltage-gated sodium channels by conotoxin μO § -GVIIJ. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 7205–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-M.; Fiedler, B.; Green, B.R.; Catlin, P.; Watkins, M.; Garrett, J.E.; Smith, B.J.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G. Structural and functional diversities among μ-conotoxins targeting TTX-resistant sodium channels. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 3723–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, S.; Min, X.; Shao, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, M. A novel μ-conotoxin from worm-hunting Conus tessulatus that selectively inhibit rat TTX-resistant sodium currents. Toxicon 2017, 130, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, N.L.; Ekberg, J.A.; Thomas, L.; Adams, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Craik, D.J. Structures of μO-conotoxins from Conus marmoreus inhibitors of tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive and TTX-resistant sodium channels in mammalian sensory neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25774–25782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorn, S.; Leipold, E.; Hansel, A.; Bulaj, G.; Olivera, B.M.; Terlau, H.; Heinemann, S.H. The μO-conotoxin MrVIA inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels by associating with domain-3. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 1360–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekberg, J.; Jayamanne, A.; Vaughan, C.W.; Aslan, S.; Thomas, L.; Mould, J.; Drinkwater, R.; Baker, M.; Abrahamsen, B.; Wood, J. μO-conotoxin MrVIB selectively blocks Nav1. 8 sensory neuron specific sodium channels and chronic pain behavior without motor deficits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17030–17035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, I.; Dekan, Z.; Knapp, O.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Isolation, characterization and total regioselective synthesis of the novel μO-conotoxin MfVIA from Conus magnificus that targets voltage-gated sodium channels. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajewiak, J.; Azam, L.; Imperial, J.; Walewska, A.; Green, B.R.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Raghuraman, S.; Ueberheide, B.; Bern, M.; Zhou, H.M. A disulfide tether stabilizes the block of sodium channels by the conotoxin μO § -GVIIJ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2758–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMario, F.J. Inherited Pain Syndromes and Ion Channels; Seminars in Pediatric Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Dubin, A.E.; Patapoutian, A. Nociceptors: The sensors of the pain pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3760–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskin, D.J.; Richard, P. The economic costs of pain in the United States. J. Pain 2012, 13, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R. Neuropathic pain: A clinical perspective. In Sensory Nerves; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. Voltage-gated sodium channels: Therapeutic targets for pain. Pain Med. 2009, 10, 1260–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hains, B.C.; Saab, C.Y.; Klein, J.P.; Craner, M.J.; Waxman, S.G. Altered sodium channel expression in second-order spinal sensory neurons contributes to pain after peripheral nerve injury. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4832–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampert, A.; O’Reilly, A.O.; Reeh, P.; Leffler, A. Sodium channelopathies and pain. Pflugers Arch. 2010, 460, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clare, J.J. Targeting voltage-gated sodium channels for pain therapy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2010, 19, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, Y.; MacFarlane, J.; MacDonald, M.; Thompson, J.; Dube, M.P.; Mattice, M.; Fraser, R.; Young, C.; Hossain, S.; Pape, T. Loss-of-function mutations in the Nav1. 7 gene underlie congenital indifference to pain in multiple human populations. Clin. Genet. 2007, 71, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akopian, A.N.; Sivilotti, L.; Wood, J.N. A tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel expressed by sensory neurons. Nature 1996, 379, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djouhri, L.; Fang, X.; Okuse, K.; Wood, J.N.; Berry, C.M.; Lawson, S.N. The TTX-resistant sodium channel Nav1. 8 (SNS/PN3): Expression and correlation with membrane properties in rat nociceptive primary afferent neurons. J. Physiol. 2003, 550, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renganathan, M.; Cummins, T.R.; Waxman, S.G. Contribution of Nav1. 8 sodium channels to action potential electrogenesis in DRG neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2001, 86, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knapp, O.; McArthur, J.R.; Adams, D.J. Conotoxins targeting neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel subtypes: Potential analgesics? Toxins 2012, 4, 1236–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, D.L.; Woods, C.G. Painful and painless channelopathies. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livett, B.G.; Gayler, K.R.; Khalil, Z. Drugs from the sea: Conopeptides as potential therapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahern, C.A.; Payandeh, J.; Bosmans, F.; Chanda, B. The hitchhiker’s guide to the voltage-gated sodium channel galaxy. J. Gen. Physiol. 2016, 147, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essack, M.; Bajic, V.B.; Archer, J.A. Conotoxins that confer therapeutic possibilities. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1244–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munasinghe, N.R.; Christie, M.J. Conotoxins that could provide analgesia through voltage gated sodium channel inhibition. Toxins 2015, 7, 5386–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, B.R.; Catlin, P.; Zhang, M.-M.; Fiedler, B.; Bayudan, W.; Morrison, A.; Norton, R.S.; Smith, B.J.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M. Conotoxins containing nonnatural backbone spacers: Cladistic-based design, chemical synthesis, and improved analgesic activity. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.J.; Yoshikami, D.; Azam, L.; Gajewiak, J.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G.; Zhang, M.-M. μ-Conotoxins that differentially block sodium channels NaV1. 1 through 1.8 identify those responsible for action potentials in sciatic nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10302–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.J.; Zhang, M.-M.; Gajewiak, J.; Azam, L.; Rivier, J.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Yoshikami, D. α- and β-subunit composition of voltage-gated sodium channels investigated with μ-conotoxins and the recently discovered μO § -conotoxin GVIIJ. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 113, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markgraf, R.; Leipold, E.; Schirmeyer, J.; Paolini-Bertrand, M.; Hartley, O.; Heinemann, S.H. Mechanism and molecular basis for the sodium channel subtype specificity of µ-conopeptide CnIIIC. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, S.; Kuyucak, S. Molecular dynamics study of binding of µ-conotoxin GIIIA to the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1. 4. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Mahdavi, S.; Kuyucak, S. Computational study of binding of μ-conotoxin GIIIA to bacterial sodium channels NaVAb and NaVRh. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 1929–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lera Ruiz, M.; Kraus, R.L. Voltage-gated sodium channels: Structure, function, pharmacology, and clinical indications. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7093–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, R.S. µ-Conotoxins as leads in the development of new analgesics. Molecules 2010, 15, 2825–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’brien, T.; Christrup, L.; Drewes, A.; Fallon, M.; Kress, H.; McQuay, H.; Mikus, G.; Morlion, B.; Perez-Cajaraville, J.; Pogatzki-Zahn, E. European Pain Federation position paper on appropriate opioid use in chronic pain management. Eur. J. Pain 2017, 21, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagal, S.K.; Brown, A.D.; Cox, P.J.; Omoto, K.; Owen, R.M.; Pryde, D.C.; Sidders, B.; Skerratt, S.E.; Stevens, E.B.; Storer, R.I. Ion channels as therapeutic targets: A drug discovery perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 56, 593–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagal, S.K.; Chapman, M.L.; Marron, B.E.; Prime, R.; Storer, R.I.; Swain, N.A. Recent progress in sodium channel modulators for pain. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 3690–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favreau, P.; Benoit, E.; Molgo, J.; Stocklin, R. Mu-Conotoxin Peptides and Use Thereof as a Local Anesthetic. U.S. Patent 20170226166 A1, 10 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock, B.G. The Facies dolorosa and the Conidae. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 54, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, M.; Yan, S.F.; Yan, N. Structure-based assessment of disease-related mutations in human voltage-gated sodium channels. Protein Cell 2017, 8, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, H.; O’Leary, B.C.; Hawkins, J.P.; Carpenter, K.E.; Roberts, C.M. Conus: First comprehensive conservation Red List assessment of a marine gastropod mollusc genus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tosti, E.; Boni, R.; Gallo, A. µ-Conotoxins Modulating Sodium Currents in Pain Perception and Transmission: A Therapeutic Potential. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15100295
Tosti E, Boni R, Gallo A. µ-Conotoxins Modulating Sodium Currents in Pain Perception and Transmission: A Therapeutic Potential. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(10):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15100295
Chicago/Turabian StyleTosti, Elisabetta, Raffaele Boni, and Alessandra Gallo. 2017. "µ-Conotoxins Modulating Sodium Currents in Pain Perception and Transmission: A Therapeutic Potential" Marine Drugs 15, no. 10: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15100295
APA StyleTosti, E., Boni, R., & Gallo, A. (2017). µ-Conotoxins Modulating Sodium Currents in Pain Perception and Transmission: A Therapeutic Potential. Marine Drugs, 15(10), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15100295






