Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Genus Phyllospongia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Natural Products from Phyllospongia spp.
2.1. Phyllospongia dendyi
2.2. Phyllospongia (syn. Carteriospongia) foliascens
2.3. Phyllospongia lamellosa
2.4. Phyllospongia madagascarensis
2.5. Phyllospongia papyracea
2.6. Carteriospongia (syn. Phyllospongia) flabellifera
2.7. Other Phyllospongia spp.
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keyzers, R.A.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Anti-inflammatory metabolites from marine sponges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.H.; Ding, Y.; Jacob, M.R.; Agarwal, A.K.; Clark, A.M.; Ferreira, D.; Liang, Z.; Li, X. Puupehanol, a sesquiterpene-dihydroquinone derivative from the marine sponge Hyrtios sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6140–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonlarppradab, C.; Faulkner, D.J. Eurysterols A and B, cytotoxic and antifungal steroidal sulfates from a marine sponge of the genus Euryspongia. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Sharma, U.; Schulz, T.C.; McLean, A.B.; Robins, A.J.; West, L.M. Bicyclic C21 terpenoids from the marine sponge Clathria compressa. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camille, C.; Bugni, T.S.; Feng, X.; Kay, H.M.; Orendt, A.M.; Irel, C.M. Tedanolide C: A potent new 18-membered-ring cytotoxic macrolide isolated from the Papua New Guinea marine sponge Ircinia sp. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 2510–2513. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Cheng, C.; Reimer, A.; Kozjak-Pavlovic, V.; Ibrahim, A.K.; Rudel, T.; Hentschel, U.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ahmed, S.A. Antichlamydial sterol from the Red Sea sponge Callyspongia aff. implexa. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.Q.; Su, J.Y.; Zeng, L.M.; Liu, Q. The secondary metabolites of marine sponge Phallospongia foliascens. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1998, 37, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.H.A.; Rateb, M.E.; Hetta, M.; Abdelaziz, T.A.; Sleim, M.A.; Jaspars, M.; Mohammed, R. Scalarane sesterterpenes from the Egyptian Red Sea sponge Phyllospongia lamellosa. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.T.; Wells, R.J. Furodendin, a C22 degraded terpene from the sponge Phyllospongia dendyi. Experientia 1980, 36, 814–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.B.; Kalidindi, R.S.; Trimurtulu, G.; Rao, D.V. Metabolites of Porifera, Part III. New 24-Methylscalaranes from Phyllospongia dendyi of the Indian Ocean. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Konno, A.; Adachi, K.; Shizuri, Y. Four new bioactive bromophenols from the Palauan sponge Phyllospongia dendyi. Fish. Sci. 2001, 67, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Namikoshi, M.; Meguro, S.; Nagai, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Yao, X. Isolation and characterization of polybrominated diphenyl ethers as inhibitors of microtubule assembly from the marine sponge Phyllospongia dendyi collected at Palau. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, H.; Tsukitani, Y.; Shimizu, I.; Kobayashi, M.; Kitagawa, I. Foliaspongin, an antiinflammatory bishomosesterterpene from the marine sponge Phyllospongia foliascens (Pallas). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 1492–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, I.; Kobayashi, M.; Lee, N.K.; Oyama, Y.; Kyogoku, Y. Marine Natural Products XX. Bioactive scalarane-type bishomosesterterpenes from the Okinawan marine sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 2078–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, L.M.; Su, J.Y.; Francis, J.S. A new sesterterpene from the sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Chin. Chem. Lett. 1991, 2, 543–544. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.M.; Fu, X.; Su, J.Y. Phyllofenone A, a new scalarane sesterterpene from the sponge Phyllospongia foliascens (Pallas). Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 1991, 7, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.M.; Fu, X.; Su, J.Y. Novel bishomoscalarane sesterterpenes from the sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 1991, 54, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, L.M.; Su, J.Y.; Chen, S.; Snyder, J.K. Bishomoscalarane sesterterpenes from the sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 1991, 12, 1486–1487. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, L.M.; Su, J.Y. Acetoxy phyllofolactone A—A novel bishomoscalarane sesterterpene from the South China Sea sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 1992, 13, 628–629. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, L.M.; Su, J.Y.; Païs, M.; Potier, P. Scalarane-type bishomosesterterpenes from the sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, L.M.; Su, J.Y.; Païs, M.; Potier, P. Two new sesterterpenes from a South China Sea Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 1985–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, L.M.; Su, J.Y.; Païs, M.; Potier, P. Phyllofolactones C and D, two new minor homoscalarane sesterterpenes from the Chinese sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Tang, H.F.; Yi, Y.H.; Lin, H.W. Scalarane sesterterpenes from the Chinese sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Wu, Z.H.; Shao, C.L.; Pang, S.; Liang, X.Y.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wang, C.Y. Cytotoxic scalarane sesterterpenoids from the South China Sea sponge Carteriospongia foliascens. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 4016–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Yi, Y.H.; Yang, F.; Chen, W.S.; Lin, H.W. Sesterterpenes and a new sterol from the marine sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Molecules 2010, 15, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Kaisin, M.; Moussiaux, B. Ichthyotoxic sesterterpenoids from the new guinean sponge Carteriospongia foliascens. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 4603–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, J.P.; Meerssche, M.V.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D. A new 20,24-dimethylscalarane derivative isolated from the sponge Carteriospongia foliascens, C30H42O6. Acta Cryst. 1985, 41, 1222–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Hollander, I.; Feldberg, L.; Frommer, E.; Mallon, R.; Tahir, A.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Scalarane-based sesterterpenoid RCE-protease inhibitors isolated from the Indonesian marine sponge Carteriospongia foliascens. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.V.R.; Venkateswarlu, Y.; Rao, J.V. A new bishomoscalarane sesterterpene 12-epi-phyllofolactone-B from Phyllospongia foliascens. Indian J. Chem. B 1993, 32, 1196–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, P.F.; Quinn, R.J.; Tucker, D.J. Structural elucidation of a novel scalarane derivative by using high-field (14.1T) NMR. Spectroscopy. Aust. J. Chem. 1991, 44, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.J.; Tucker, D.J. Two novel bisalkylated norscalaranes from the sponge Carteriospongia foliascens. Aust. J. Chem. 1989, 42, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaru, K.; Ramadas, M.; Osamu, M.; Nittala, S. Marine terpenes and terpenoids XVI: Revised structure of the marine furanoterpene (+)-furospongin-1. J. Chem. Res.-Synop. 1992, 11, 366–367. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://apps.webofknowledge.com/Search.do?product=WOS&SID=V2B6tzoudOkWop SGj2w&search_mode=GeneralSearch&prID=b0222ef8-1c6f-4f79-b3bf-ed19663b27c6 (accessed on 3 January 2017).
- Chang, L.C.; Otero-Quintero, S.; Nicholas, G.M.; Bewley, C.A. Phyllolactones A–E: New bishomoscalarane sesterterpenes from the marine sponge Phyllospongia lamellosa. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 5731–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, L.P.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Stonik, V.A. New scalarane-based sesterterpenes from the sponge Phyllospongia madagascarensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1507–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.J.; Li, H.J. New sesterterpenoids from the marine sponge Phyllospongia papyracea. Helv. Chim. Acta 2007, 90, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Amagata, T.; Tenney, K.; Crews, P. Additional scalarane sesterterpenes from the sponge Phyllospongia papyracea. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.W.; Crews, P.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A. Cytotoxic phyllactone analogs from the marine sponge Phyllospongia papyrecea. Med. Chem. 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyabalanage, T.; Ratnayake, R.; Bokesch, H.R.; Ransom, T.T.; Henrich, C.J.; Beutler, J.A.; McMahon, J.B.; Gustafson, K.R. Flabelliferins A and B, sesterterpenoids from the South Pacific sponge Carteriospongia flabellifera. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, J.S.; James, C.C. Sesterterpenes from a Pacific sponge, Carteriospongia flabellifera. J. Nat. Prod. 1988, 51, 745–748. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, C.R.; Junichi, T.; de Voogd, N.; Higa, T. New scalarane class sesterterpenes from an Indonesian sponge, Phyllospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 62, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Harinantenaina, L.; Brodie, P.J.; Maharavo, J.; Bakary, G.; TenDyke, K.; Shen, Y.; Kingston, D.G.I. Antiproliferative homoscalarane sesterterpenes from two Madagascan sponges. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2912–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.Q.; Zeng, L.M.; Su, J.Y. Studies on the sponge Phyllospongia sp. (II). Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1997, 36, 116–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.Q.; Su, J.Y.; Zeng, L.M. Ceramide from the marine sponge Phyllospongia sp. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1997, 36, 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mcculloch, M.W.B.; Bugni, T.S.; Concepcion, G.P.; Coombs, G.S.; Harper, M.K.; Kaur, S.; Mangalindan, G.C.; Mutizwa, M.M.; Veltri, V.A.; Virshup, D.M.; et al. Carteriosulfonic acids A–C, GSK-3β inhibitors from a Carteriospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, K.D.; Ghisalberti, E.L.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Structural study of a new dialkylated scalarane from a Carteriospongia sp. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1983, 41, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
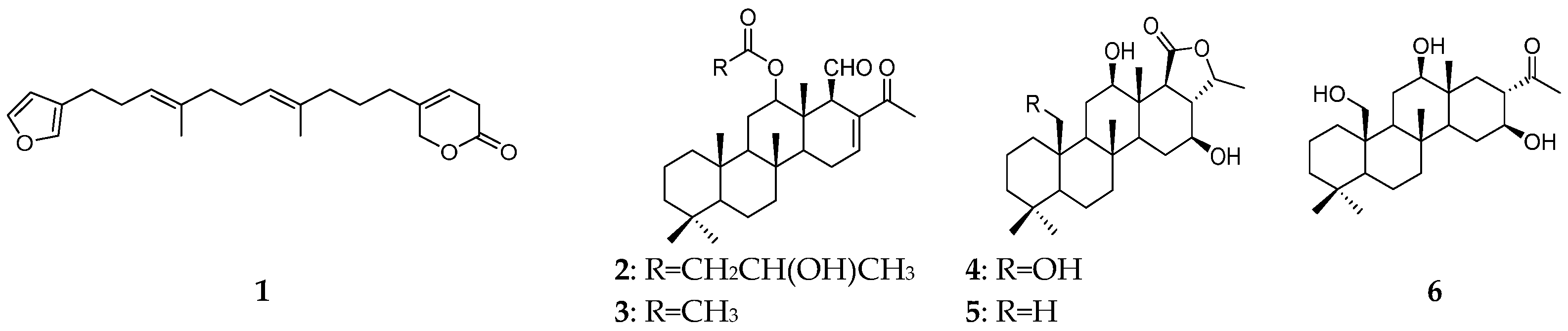
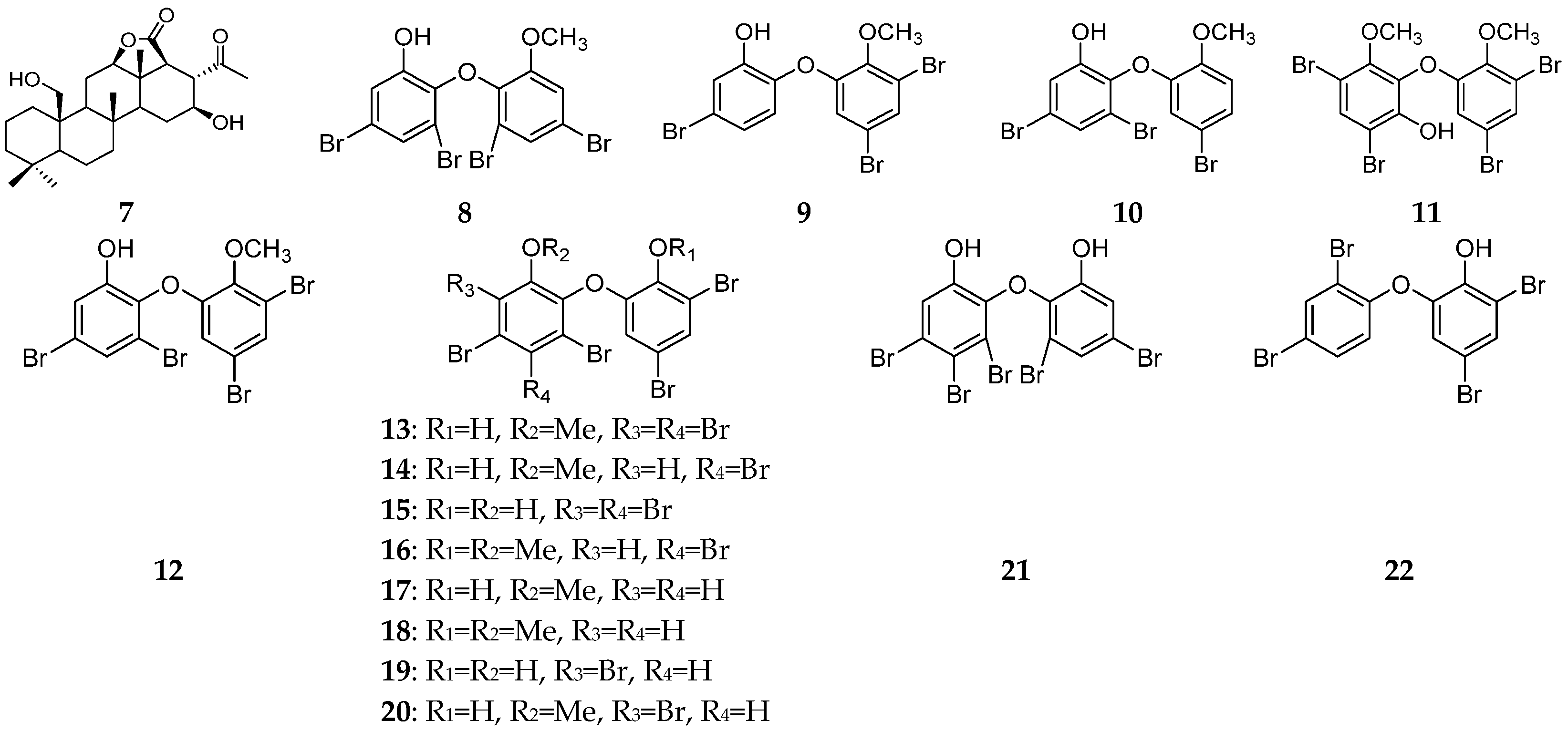
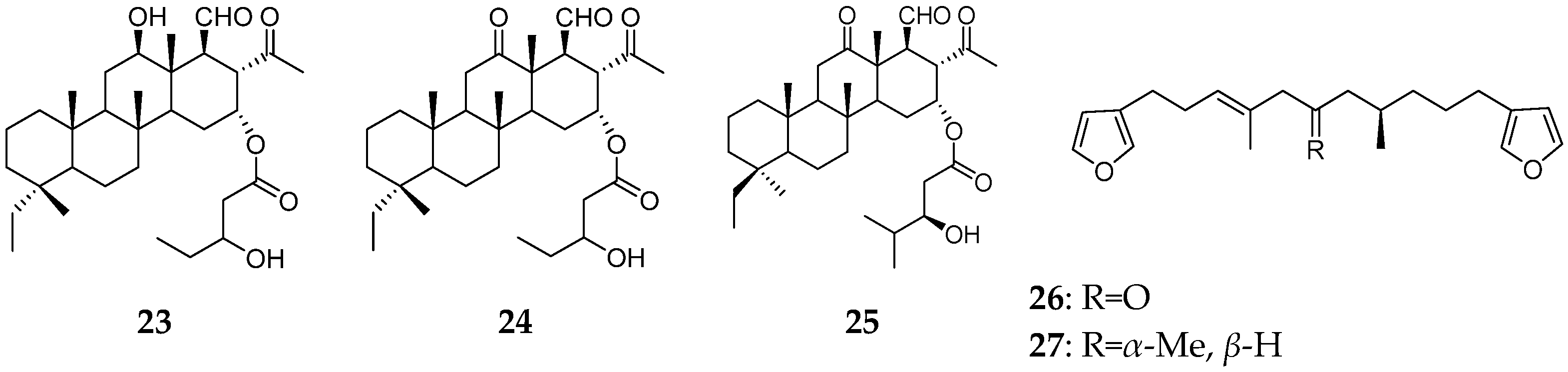
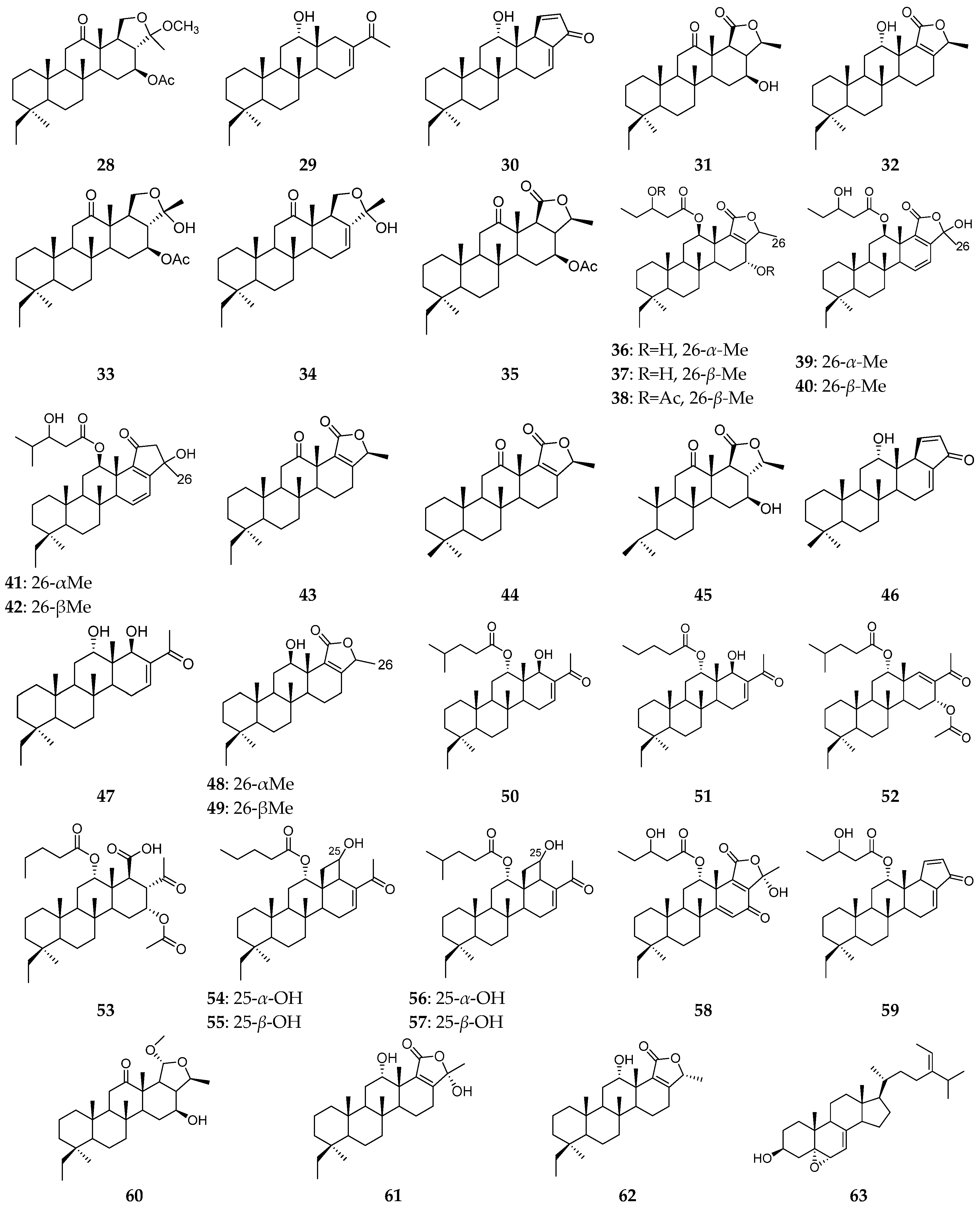
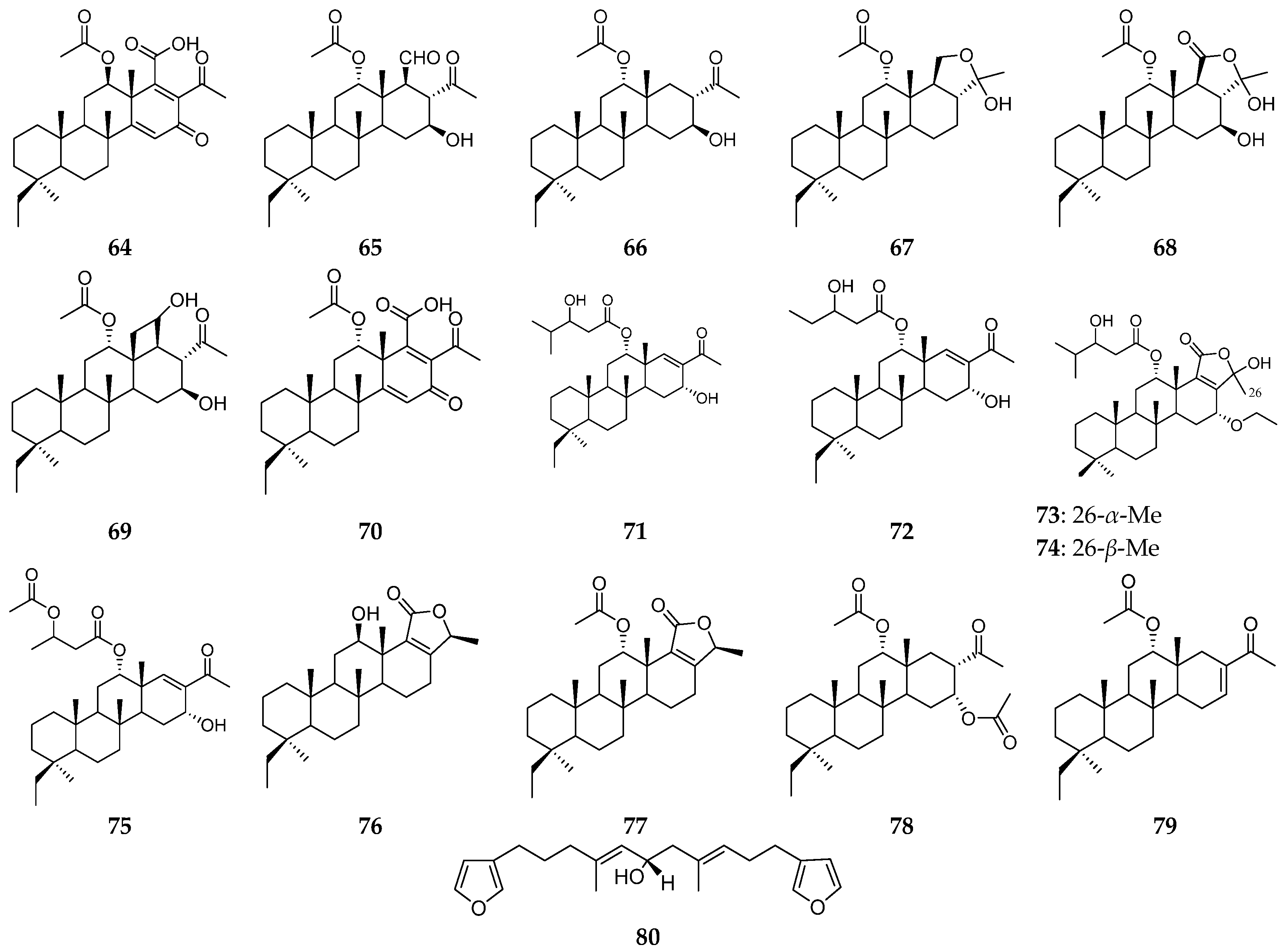
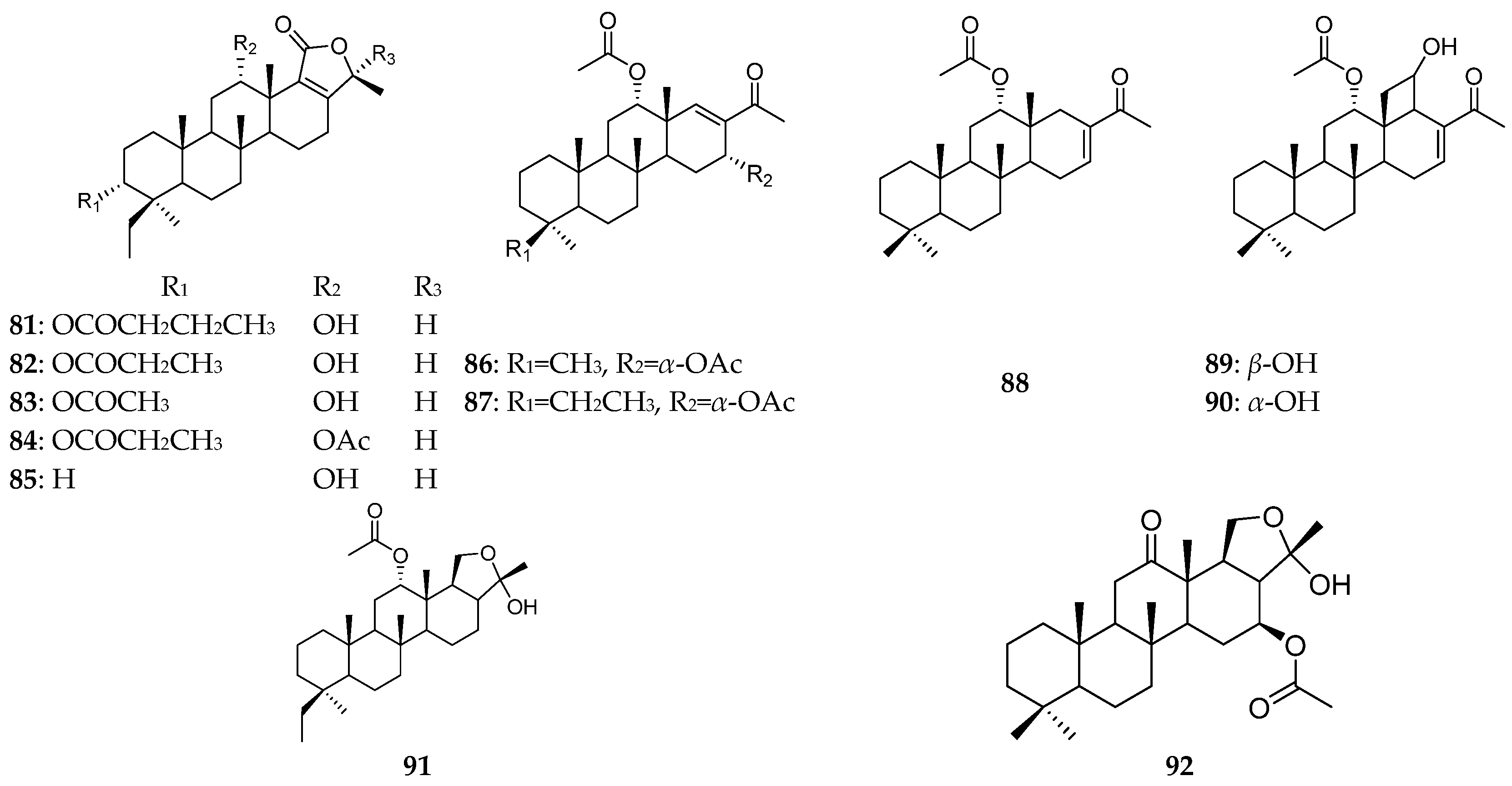
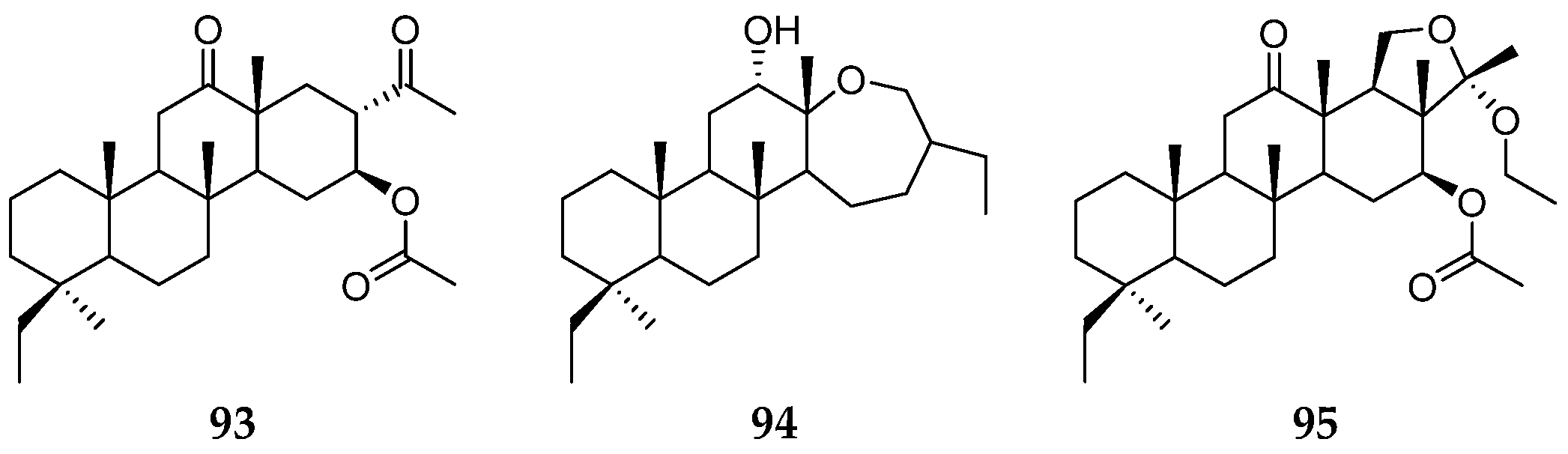
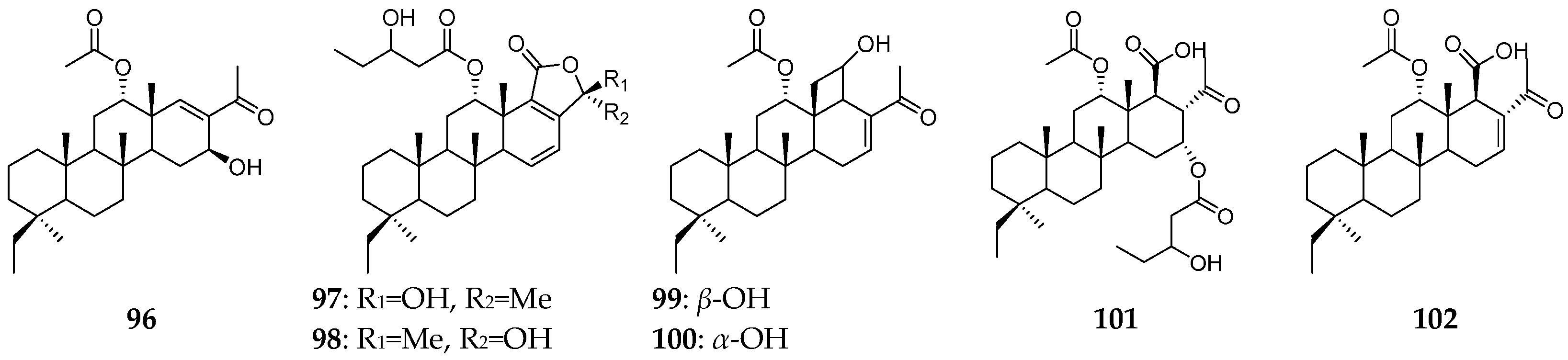
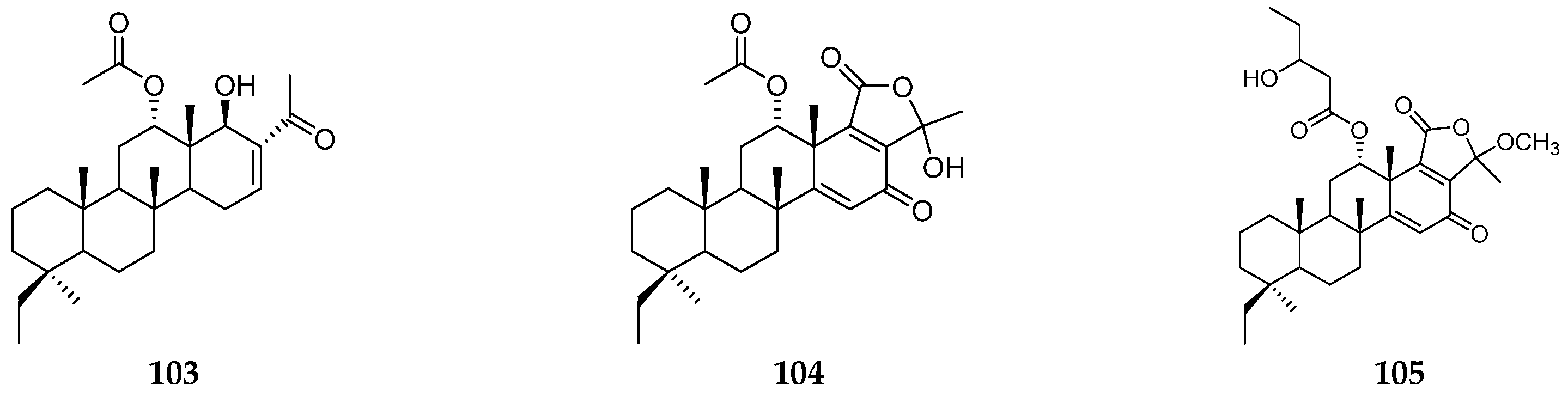
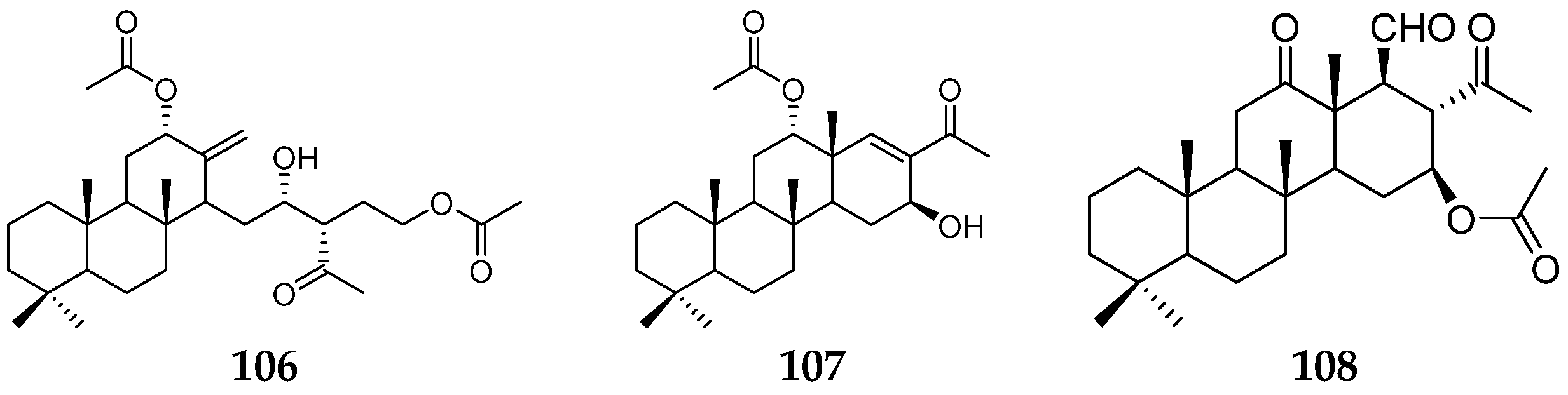
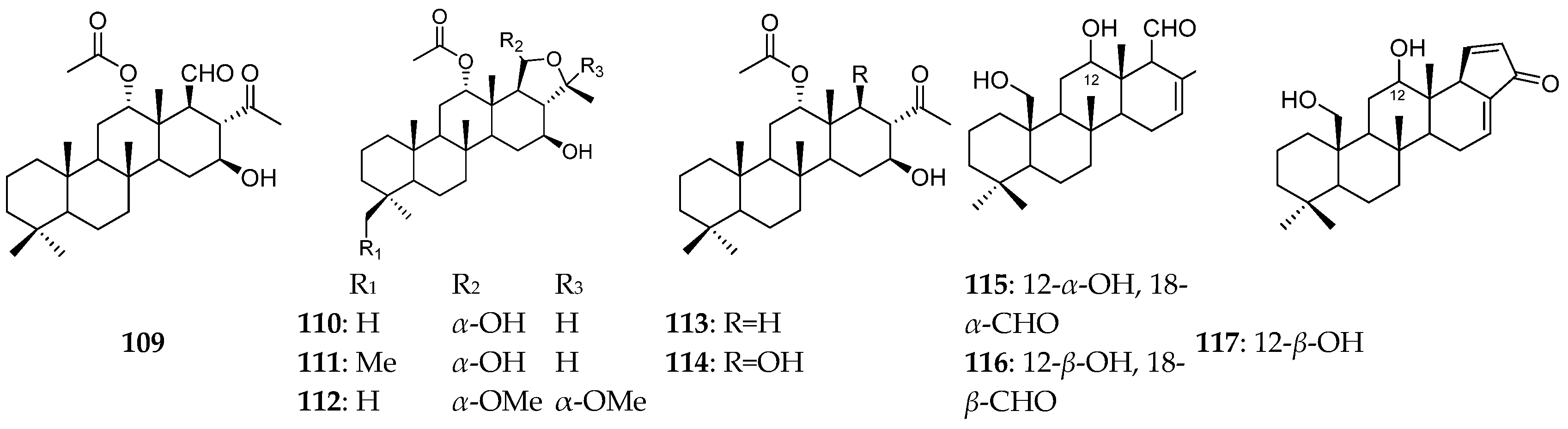
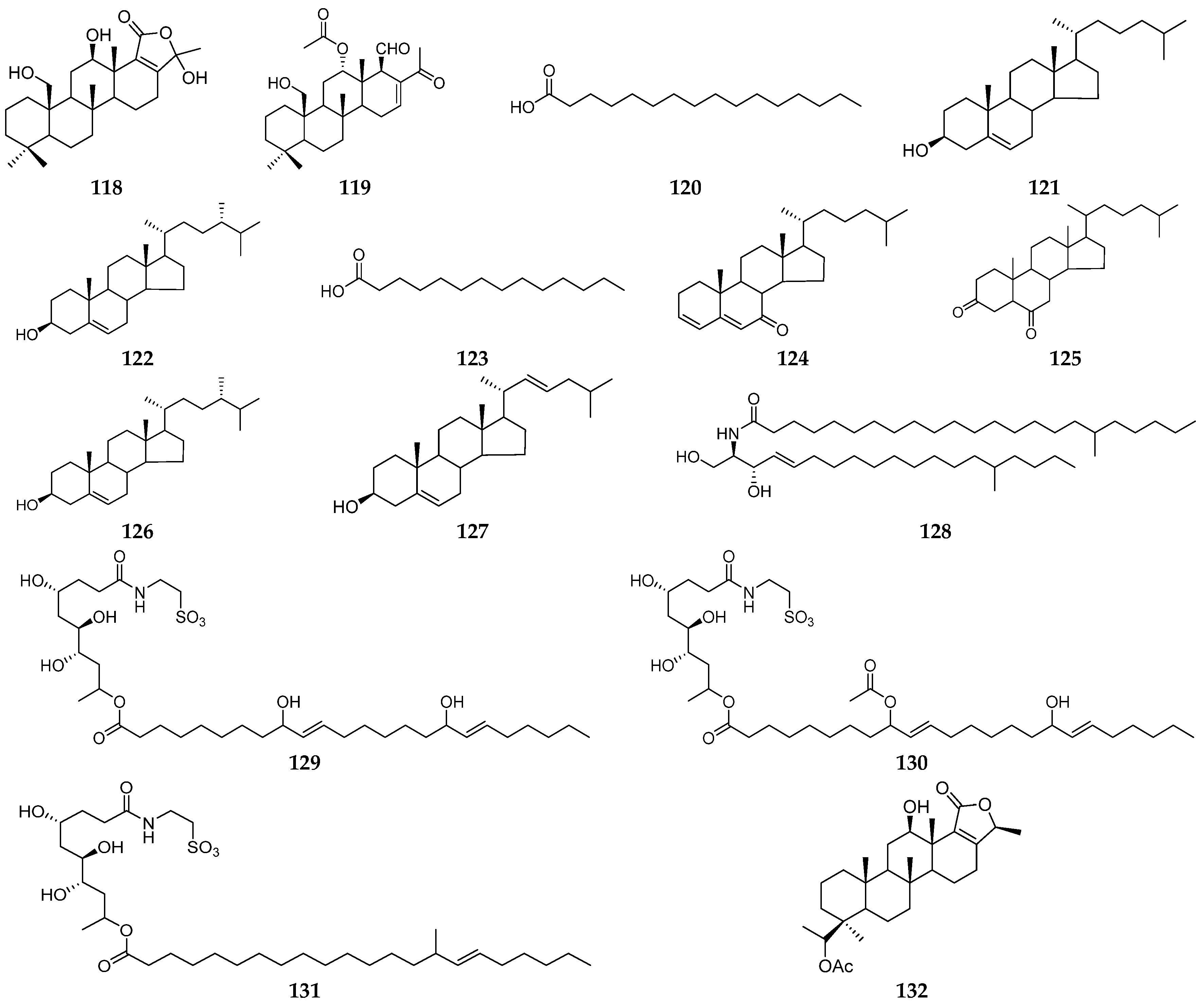
| Organism | Locality | Compound | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phyllospongia dendyi | the Great Barrier Reef | furodendin (1), sesterterpenes (2, 3) | [9] |
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | scalaranes (4–6), sesterterpene (7) | [10] | |
| Palau Islands | bromophenols (8–12) and diphenyl ethers (13–22) | [11,12] | |
| P. (syn. Carteriospongia) foliascens | the Okinawa | foliaspongin (23), dehydrofoliaspongin (24), phyllofoliaspongin (25), dihydrofurospongin-2 (26), furospongin-1 (27) | [13,14] |
| the South China Sea | phylloketal (28), phyllofenone A (29), phyllofenone B (30), phyllofolactones A–B (31–32), phyllohemiketals A (33) and B (34), acetoxy phyllofolactone A (35), phyllactones A–G (36–42), phyllofolactones C–D (43–44), phyllofolactone L (45), phyllofenone D–E (46–47), phyllofolactone F–G (48–49), carteriofenones A-K (50–60), analogue (61), phyllofolactone M (62), sterol (63) | [7,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25] | |
| Papua New Guinea | 20,24-dimethylscalaranes (64–70) | [26,27] | |
| the Indonesia Sea | scalaranes (71–75) | [28] | |
| the South Pacific | 12-epi-phyllofolactone B (76) | [29] | |
| the Great Barrier Reef | scalaranes (77–79) | [30,31] | |
| unknown | furanoterpene (80) | [32] | |
| P. lamellosa | the Indo-West Pacific Ocean | phyllolactones A–E (81–85) | [33] |
| the Egyptian Red Sea | phyllospongins A–E (86–90), sesterterpenes (76, 91, 92) | [8] | |
| P. madagascarensis | Northern Madagascar | sesterterpenes (93–95) | [34] |
| P. papyracea | Hainan Island | scalaranes (96–98) | [35] |
| Papua New Guinea | bishomoscalarane sesterterpenes (99–104) | [36] | |
| Sangihe Island | phyllactone H (105) | [37] | |
| C. (syn. P.) flabellifera | the South Pacific Ocean | flabelliferins A (106) and B (107) | [38] |
| the Great Barrier Reef | sesterterpenoid (108) | [39] | |
| Unclassified P. spp. | the Indonesia Sea | scalaranes (109–114) | [40] |
| Northern Madagascar | homoscalarane sesterterpenes (115–119) | [41] | |
| the South China Sea | fatty acids (120, 123), steroids (121, 122, 124–127), phylloamide A (128) | [42,43] | |
| Philippines | carteriosulfonic acids A–C (129–131) | [44] | |
| Fiji | sesterterpene (132) | [45] |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Dong, M.; Wang, H.; Crews, P. Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Genus Phyllospongia. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010012
Zhang H, Dong M, Wang H, Crews P. Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Genus Phyllospongia. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huawei, Menglian Dong, Hong Wang, and Phillip Crews. 2017. "Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Genus Phyllospongia" Marine Drugs 15, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010012
APA StyleZhang, H., Dong, M., Wang, H., & Crews, P. (2017). Secondary Metabolites from the Marine Sponge Genus Phyllospongia. Marine Drugs, 15(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010012







