Coral Carbonic Anhydrases: Regulation by Ocean Acidification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. pH Dependency of Coral Carbonic Anhydrases
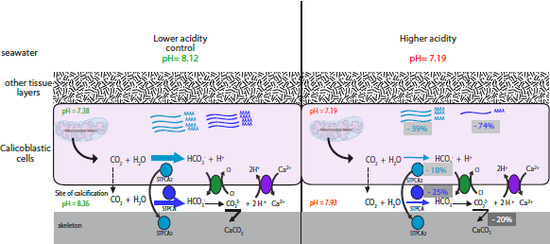
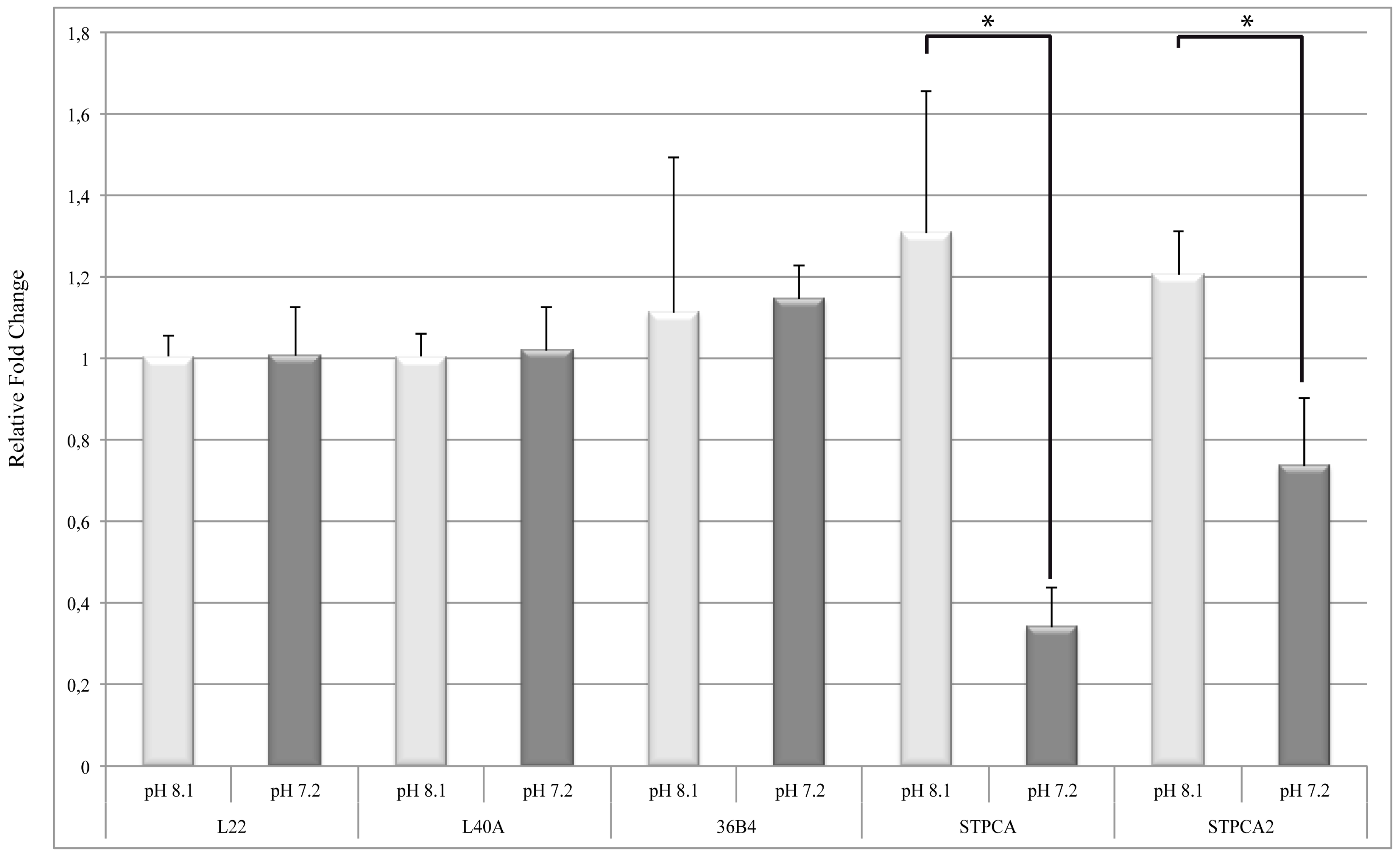
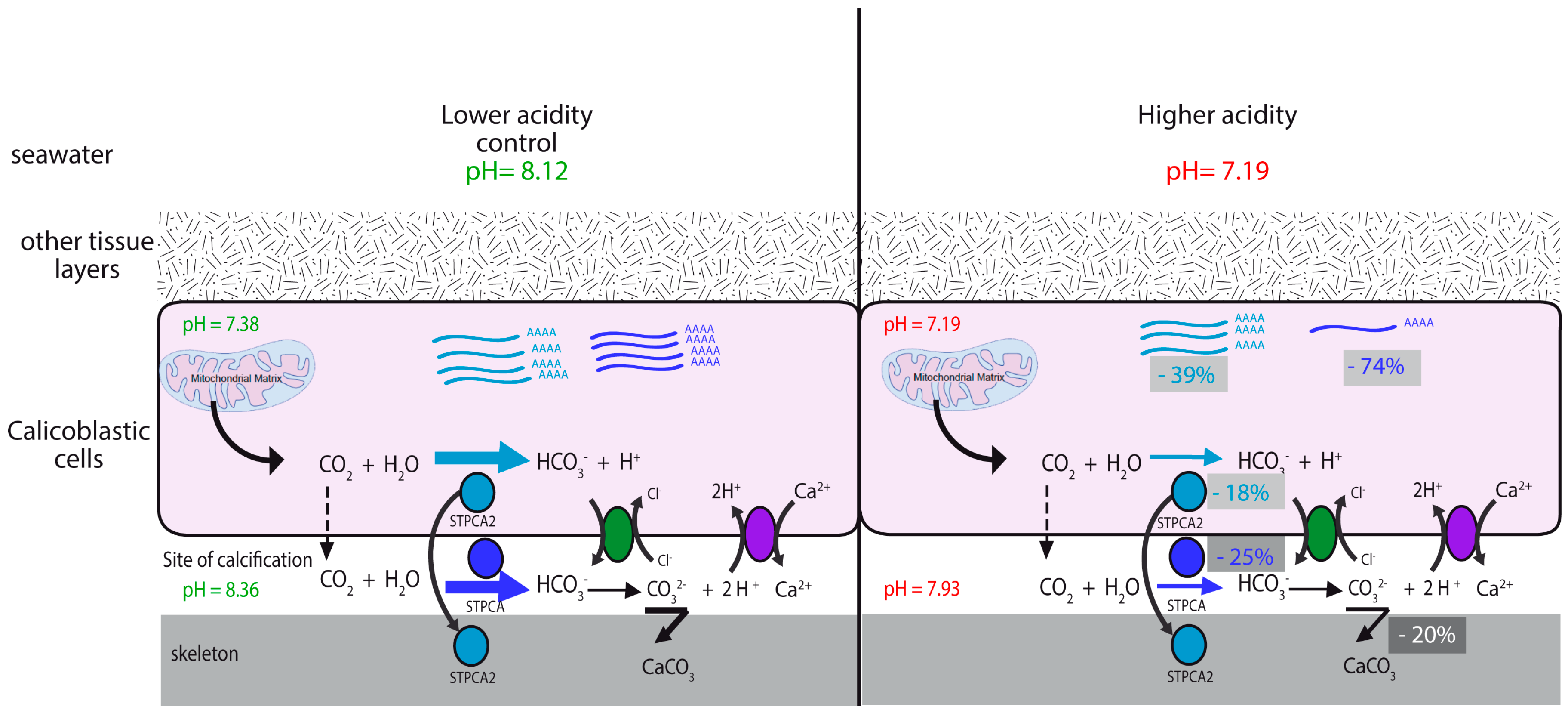
2.2. pH Dependency of Coral Carbonic Anhydrases: Effect of Ocean Acidification
2.3. pH and Temperature Dependency of Coral Carbonic Anhydrases
3. Material and Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA | Carbonic Anhydrase |
| STPCA | Stylophora pistillata carbonic anhydrase (ACA53457) |
| STPCA2 | Stylophora pistillata carbonic anhydrase (ACE95141) |
| OA | Ocean Acidification |
References
- IPCC, 2014: Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups i, ii and iii to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151.
- Chan, N.C.S.; Connolly, S.R. Sensitivity of coral calcification to ocean acidification: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, A.; Moya, A.; Tambutté, S.; Allemand, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Zoccola, D. Carbonic anhydrases in anthozoan corals—A review. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya, A.; Tambutté, S.; Bertucci, A.; Tambutté, E.; Lotto, S.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Allemand, D.; Zoccola, D. Carbonic anhydrase in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata: Characterization, localization, and role in biomineralization. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25475–25484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccola, D.; Ganot, P.; Bertucci, A.; Caminiti-Segonds, N.; Techer, N.; Voolstra, C.R.; Aranda, M.; Tambutté, E.; Allemand, D.; Casey, J.R.; et al. Bicarbonate transporters in corals point towards a key step in the evolution of cnidarian calcification. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccola, D.; Tambutté, É.; Kulhanek, E.; Puverel, S.; Scimeca, J.-C.; Allemand, D.; Tambutté, S. Molecular cloning and localization of a PMCA P-type calcium ATPase from the coral Stylophora pistillata. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1663, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccola, D.; Tambutté, É.; Sénegas-Balas, F.; Michiels, J.-F.; Failla, J.-P.; Jaubert, J.; Allemand, D. Cloning of a calcium channel A1 subunit from the reef-building coral, Stylophora pistillata. Gene 1999, 227, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venn, A.A.; Tambutté, E.; Holcomb, M.; Laurent, J.; Allemand, D.; Tambutté, S. Impact of seawater acidification on pH at the tissue-skeleton interface and calcification in reef corals. PNAS 2013, 110, 1634–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allemand, D.; Tambutté, É.; Zoccola, D.; Tambutté, S. Coral calcification, cells to reefs. In Coral Reefs: An Ecosystem in Transition; Dubinsky, Z., Stambler, N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 119–150. [Google Scholar]
- Tambutté, S.; Holcomb, M.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Reynaud, S.; Tambutté, E.; Zoccola, D.; Allemand, D. Coral biomineralization: From the gene to the environment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 408, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.L.; Mass, T.; Haramaty, L.; Zelzion, E.; Bhattacharya, D.; Falkowski, P.G. Proteomic analysis of skeletal organic matrix from the stony coral Stylophora pistillata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3788–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mass, T.; Drake, J.L.; Peters, E.C.; Jiang, W.; Falkowski, P.G. Immunolocalization of skeletal matrix proteins in tissue and mineral of the coral Stylophora pistillata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12728–12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Silva, P.; Kaandorp, J.; Herbst, F.; Plasseraud, L.; Alcaraz, G.; Stern, C.; Corneillat, M.; Guichard, N.; Durlet, C.; Luquet, G.; et al. The skeleton of the staghorn coral Acropora millepora: Molecular and structural characterization. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97454. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifah, R.G.; Edsall, J.T. Carbon dioxide hydration activity of carbonic anhydrase: Kinetics of alkylated anhydrases B and C from humans (metalloenzymes-isoenzymes-active sites-mechanism). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindskog, S.; Coleman, J.E. The catalytic mechanism of carbonic anhydrase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 2505–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allemand, D.; Ferrier-Pages, C.; Furla, P.; Houlbreque, F.; Puverel, S.; Reynaud, S.; Tambutté, E.; Tambutté, S.; Zoccola, D. Biomineralisation in reef-building corals: From molecular mechanisms to environmental control. C. R. Palevol 2004, 3, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambutté, E.; Venn, A.A.; Holcomb, M.; Segonds, N.; Techer, N.; Zoccola, D.; Allemand, D.; Tambutté, S. Morphological plasticity of the coral skeleton under CO2-driven seawater acidification. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venn, A.A.; Tambutté, E.; Holcomb, M.; Allemand, D.; Tambutté, S. Live tissue imaging shows reef corals elevate pH under their calcifying tissue relative to seawater. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaniewska, P.; Campbell, P.R.; Kline, D.I.; Rodriguez-Lanetty, M.; Miller, D.J.; Dove, S.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Major cellular and physiological impacts of ocean acidification on a reef building coral. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaniewska, P.; Chan, C.K.; Kline, D.; Ling, E.Y.; Rosic, N.; Edwards, D.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Dove, S. Transcriptomic changes in coral holobionts provide insights into physiological challenges of future climate and ocean change. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya, A.; Huisman, L.; Ball, E.E.; Hayward, D.C.; Grasso, L.C.; Chua, C.M.; Woo, H.N.; Gattuso, J.P.; ForêT, S.; Miller, D.J. Whole transcriptome analysis of the coral Acropora millepora reveals complex responses to CO2-driven acidification during the initiation of calcification. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2440–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, D.; Bobeszko, T.; Ainsworth, T.; Leggat, W. The combined effects of temperature and CO2 lead to altered gene expression in Acropora aspera. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocker, M.M.; Noonan, S.; Humphrey, C.; Moya, A.; Willis, B.L.; Bay, L.K. Expression of calcification and metabolism-related genes in response to elevated pCO2 and temperature in the reef-building coral Acropora millepora. Mar. Genom. 2015, 24, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Dupiol, J.; Zoccola, D.; Tambutté, E.; Grunau, C.; Cosseau, C.; Smith, K.M.; Freitag, M.; Dheilly, N.M.; Allemand, D.; Tambutté, S. Genes related to ion-transport and energy production are upregulated in response to CO2-driven pH decrease in corals: New insights from transcriptome analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58652. [Google Scholar]
- Hoadley, K.D.; Pettay, D.T.; Grottoli, A.G.; Cai, W.J.; Melman, T.F.; Schoepf, V.; Hu, X.; Li, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Physiological response to elevated temperature and pCO2 varies across four pacific coral species: Understanding the unique host + symbiont response. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Mumby, P.-J.; Hooten, A.J.; Steneck, R.S.; Greenfield, P.; Gomez, E.; Harvell, C.D.; Sale, P.F.; Edwards, A.J.; Caldeira, K.; et al. Coral reefs under rapid climate change and ocean acidification. Science 2007, 318, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barshis, D.J.; Ladner, J.T.; Oliver, T.A.; Seneca, F.O.; Traylor-Knowles, N.; Palumbi, S.R. Genomic basis for coral resilience to climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, S.E.; Morgan, M.B.; Gleason, D.F.; Snell, T.W. Development of a coral cDNA array to examine gene expression profiles in Montastraea faveolata exposed to environmental stress. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenkel, C.D.; Meyer, E.; Matz, M.V. Gene expression under chronic heat stress in populations of the mustard hill coral (Porites astreoides) from different thermal environments. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 4322–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maor-Landaw, K.; Karako-Lampert, S.; Waldman Ben-Asher, H.; Goffredo, S.; Falini, G.; Dubinsky, Z.; Levy, O. Gene expression profiles during short-term heat stress in the red sea coral Stylophora pistillata. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3026–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, A.; Innocenti, A.; Scozzafava, A.; Tambutté, S.; Zoccola, D.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition studies with anions and sulfonamides of a new cytosolic enzyme from the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, A.; Innocenti, A.; Zoccola, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Allemand, D.; Tambutté, S.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Inhibition studies of a coral secretory isoform with inorganic anions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, A.; Innocenti, A.; Zoccola, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Tambutté, S.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition studies of a coral secretory isoform by sulfonamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5054–5058. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moya, A.; Tambutté, S.; Beranger, G.; Gaume, B.; Scimeca, J.C.; Allemand, D.; Zoccola, D. Cloning and use of a coral 36B4 gene to study the differential expression of coral genes between light and dark conditions. Mar. Biotechnol. (N.Y.) 2008, 10, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, A.; Tambutté, S.; Supuran, C.T.; Allemand, D.; Zoccola, D. A new coral carbonic anhydrase in Stylophora pistillata. Mar. Biotechnol. (N.Y.) 2011, 13, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
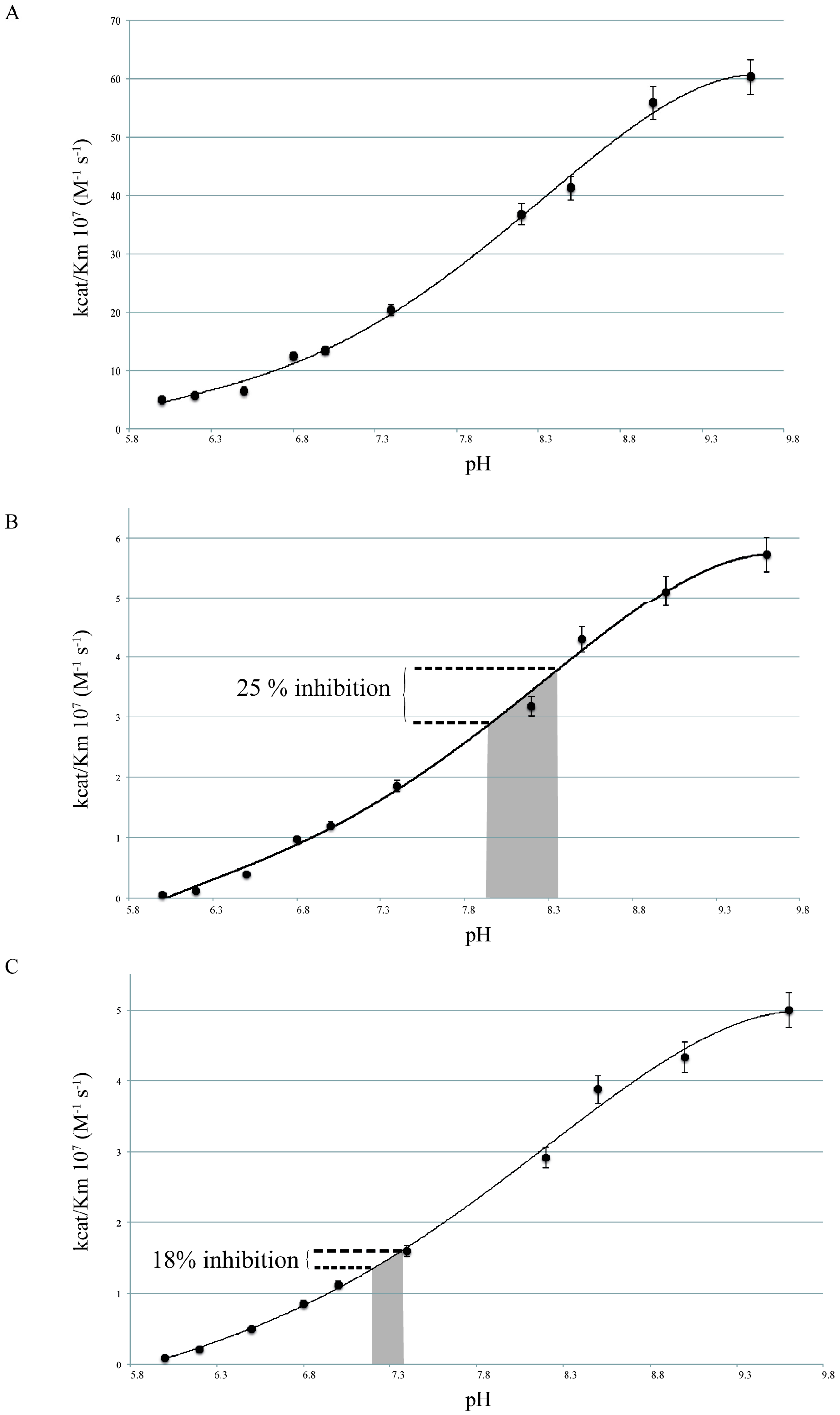
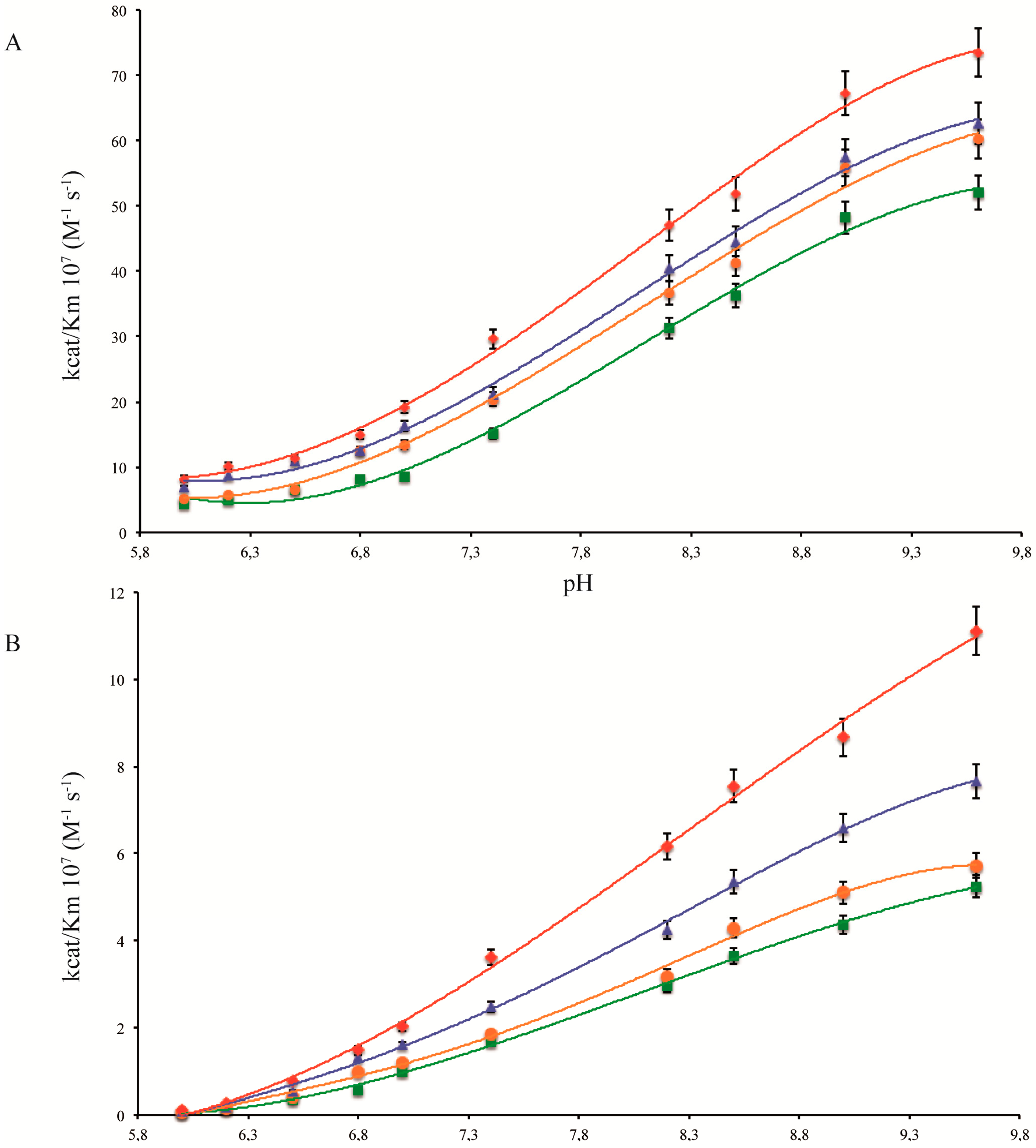
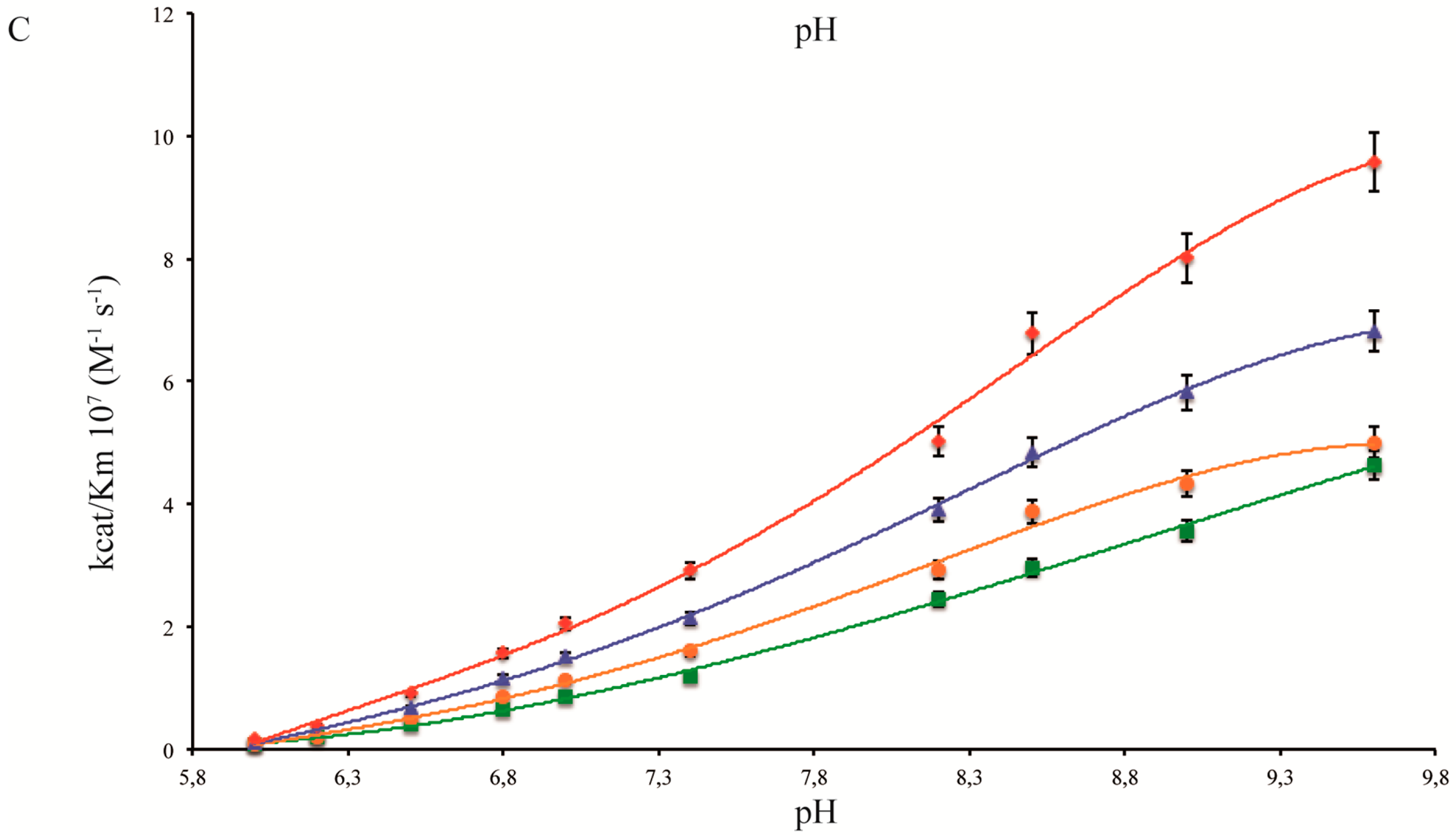
| STPCA | STPCA2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 25 °C | 28 °C | 25 °C | 28 °C |
| 8.36 | 3.943 × 106 s−1 | 4.929 × 106 s−1 | 3.200 × 106 s−1 | 4.309 × 106 s−1 |
| 7.93 | 2.965 × 106 s−1 | 3.766 × 106 s−1 | 2.410 × 106 s−11 | 3.286 × 106 s−1 |
| 7.38 | 1.856 × 106 s−1 | 2.401 × 106 s−1 | 1.494 × 106 s−1 | 2.098 × 106 s−1 |
| 7.19 | 1.530 × 106 s−1 | 1.981 × 106 s−1 | 1.221 × 106 s−1 | 1.737 × 106 s−1 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zoccola, D.; Innocenti, A.; Bertucci, A.; Tambutté, E.; Supuran, C.T.; Tambutté, S. Coral Carbonic Anhydrases: Regulation by Ocean Acidification. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060109
Zoccola D, Innocenti A, Bertucci A, Tambutté E, Supuran CT, Tambutté S. Coral Carbonic Anhydrases: Regulation by Ocean Acidification. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(6):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060109
Chicago/Turabian StyleZoccola, Didier, Alessio Innocenti, Anthony Bertucci, Eric Tambutté, Claudiu T. Supuran, and Sylvie Tambutté. 2016. "Coral Carbonic Anhydrases: Regulation by Ocean Acidification" Marine Drugs 14, no. 6: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060109
APA StyleZoccola, D., Innocenti, A., Bertucci, A., Tambutté, E., Supuran, C. T., & Tambutté, S. (2016). Coral Carbonic Anhydrases: Regulation by Ocean Acidification. Marine Drugs, 14(6), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060109