Desquamative Gingivitis Revisited: A Narrative Review on Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Challenges, and Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.1.1. Clinical Features and Etiology
1.1.2. Epidemiological Features
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
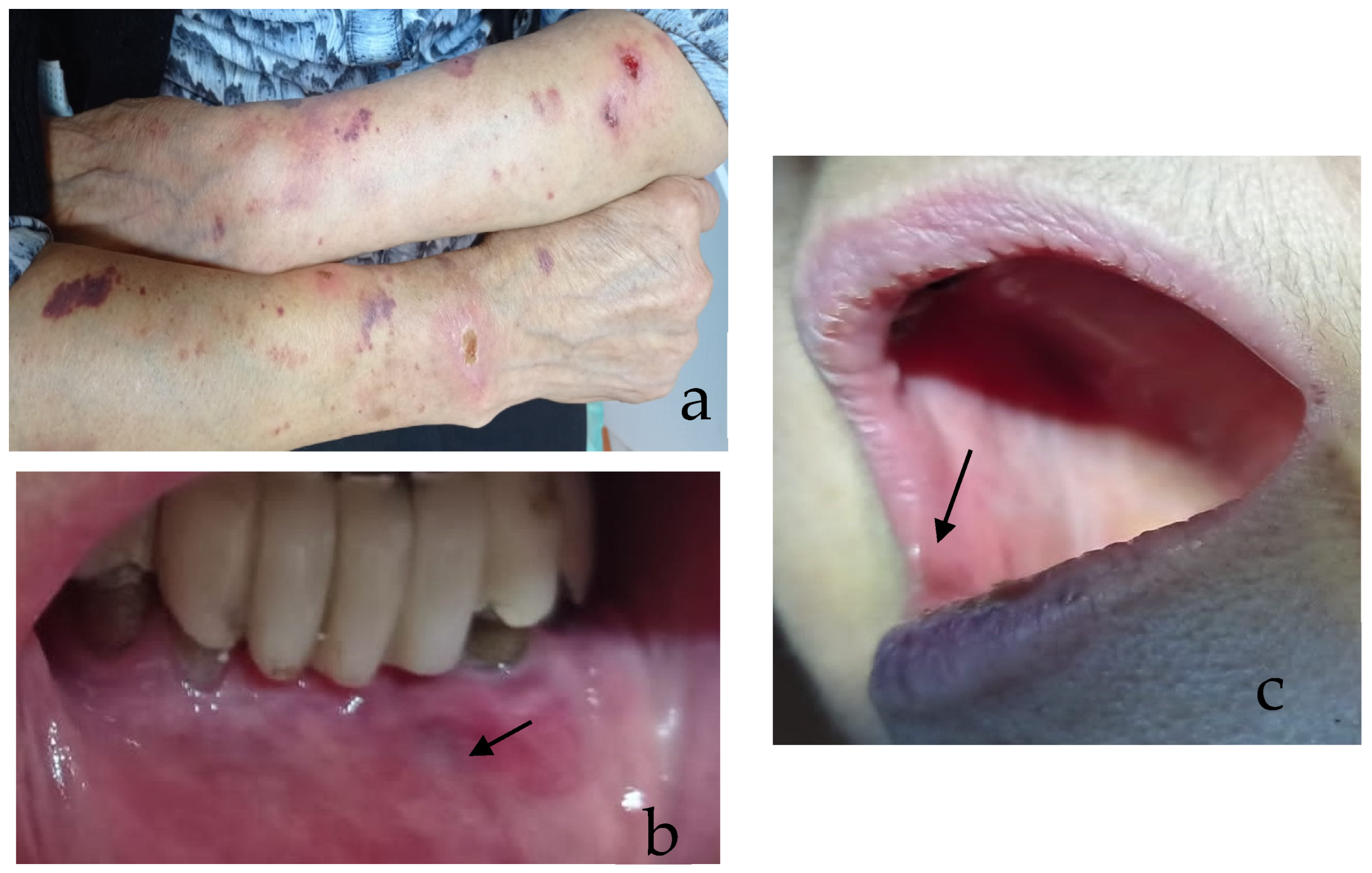
2.4. Case Report
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Clinical Features
- The mild form, in which erythema is present, but this is painless;
- The moderate form, characterized by bright red and grey areas with patchy distribution, involving marginal and attached gingiva, smooth and shiny, slight pitting under pressure; also, massaging of the gingiva with the finger results in peeling of the epithelium and exposure of the bleeding connective tissue;
- The severe form, in which wide areas of the oral cavity are involved, surface epithelium appears shredded, and air-blowing causes a bubble in the gingival epithelium; it is painful and associated with a burning sensation.
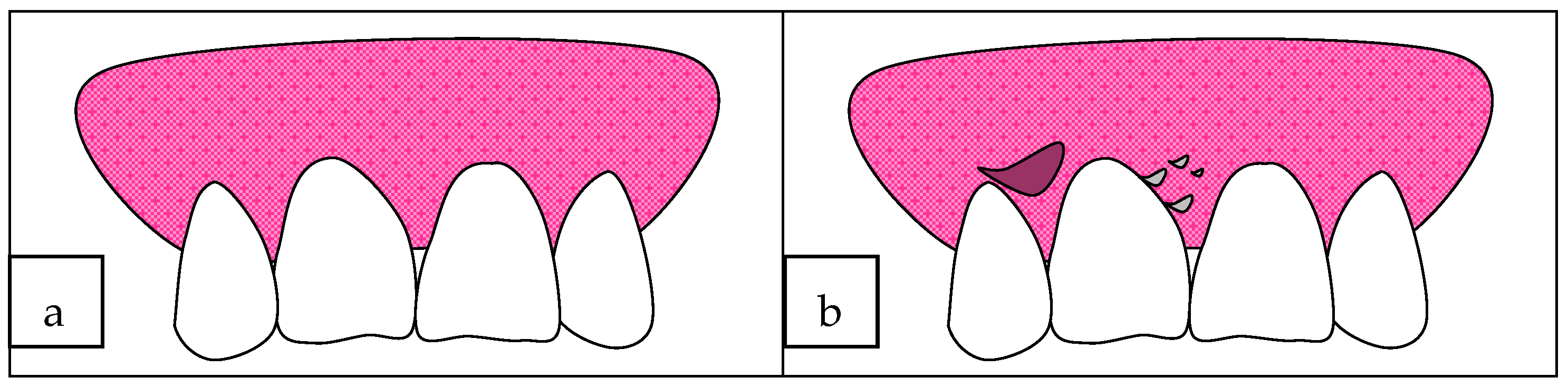

3.2. Histological Analysis
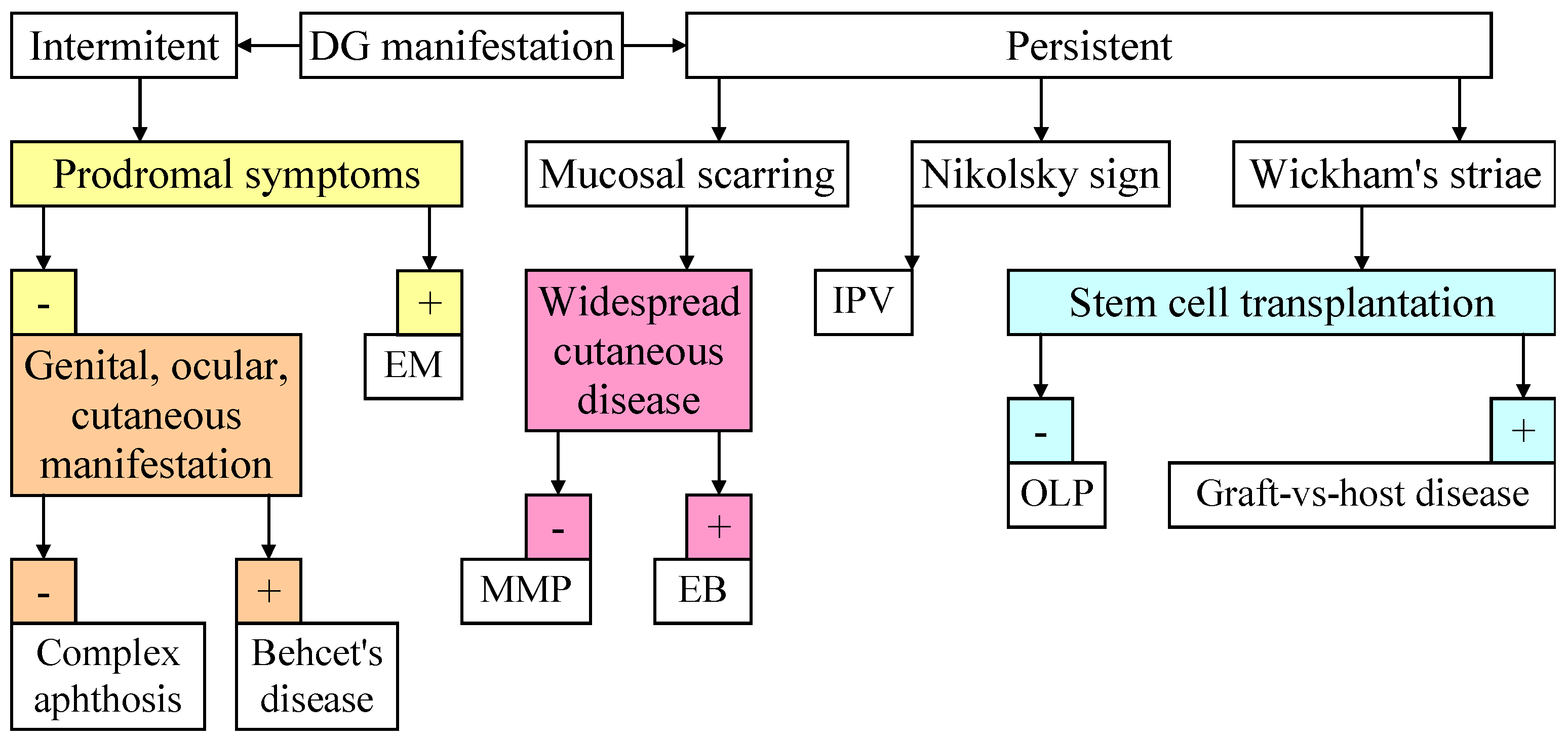
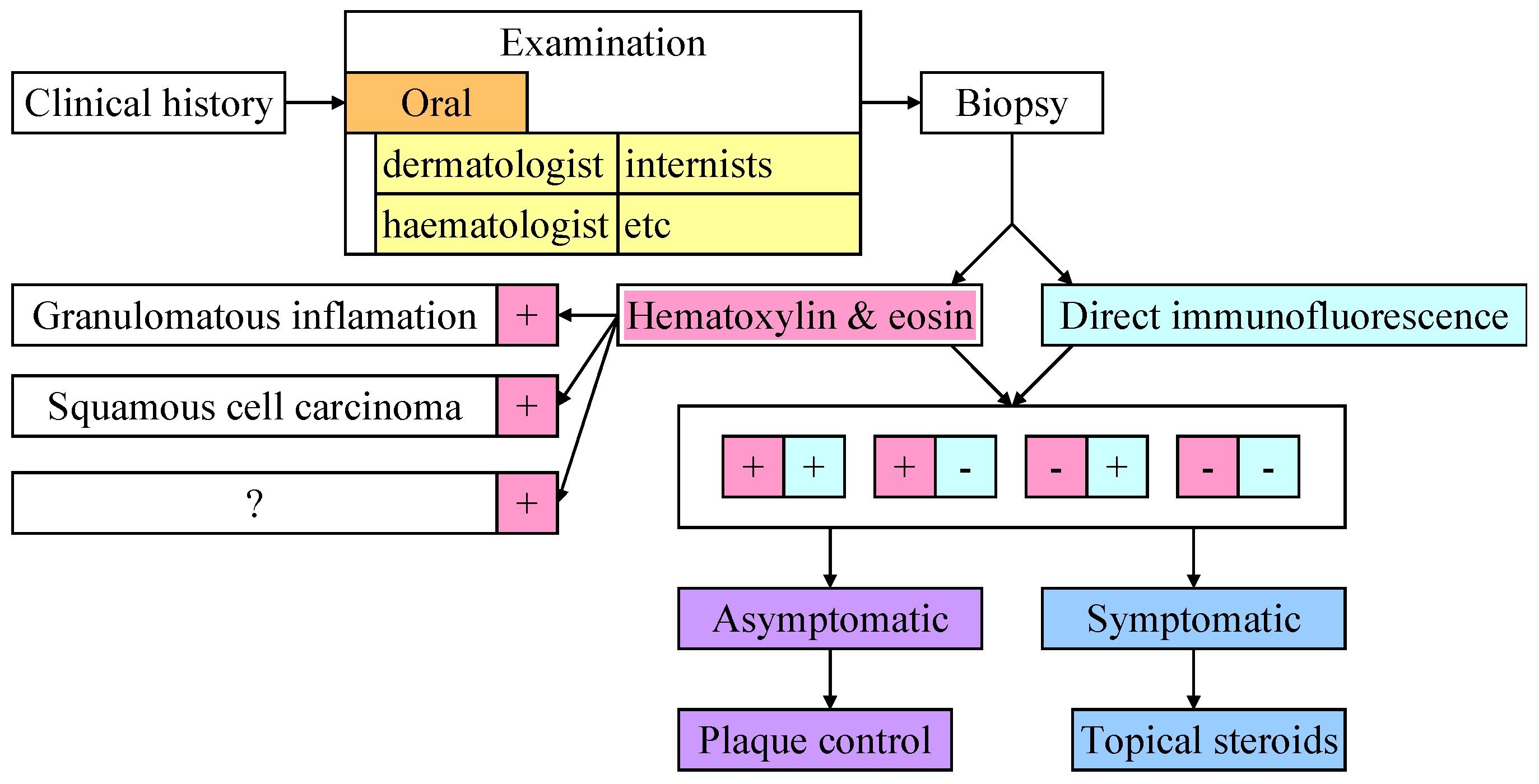
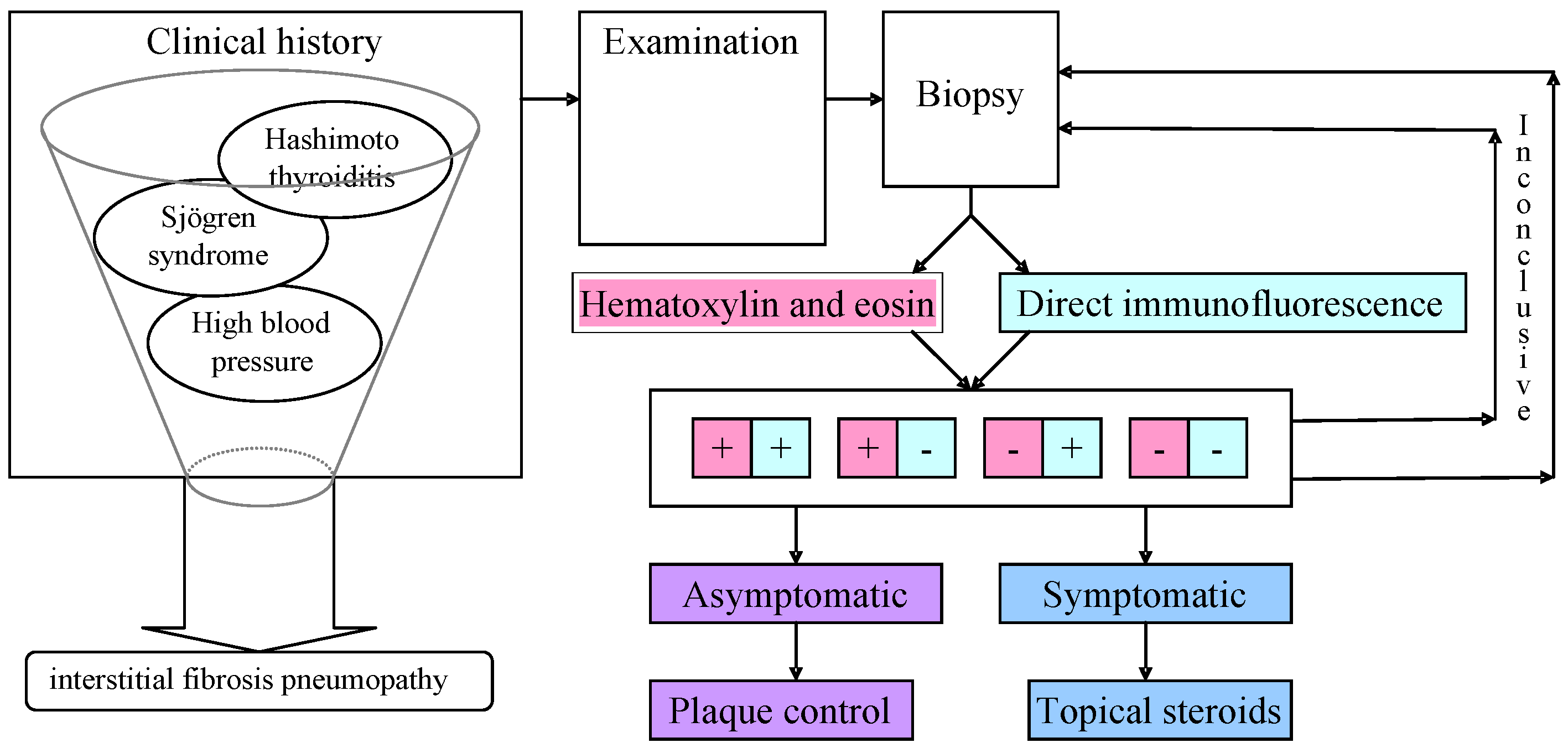
3.3. Diagnostic
3.4. Differential Diagnosis
3.5. Disease Management
- Identification and elimination of the underlying cause whenever it is possible (avoidance of known/suspected allergens and irritants);
- Improvement of oral hygiene with consequent reduction of generalized plaque-induced inflammation and associated symptoms;
- Treatment of the underlying disease where available;
- Local or systemic immunosuppressive treatment (corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory drugs);
- Other drugs: antimetabolites (cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and methotrexate), antibiotics (tetracyclines), dapsone, and immunoglobulins;
- Plasmapheresis;
- Surgery, gingival grafting, and/or laser therapy.
3.6. Treatment
3.7. Case Report Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Innocentini, L.M.A.R.; Fonseca, F.P.; Scarini, J.F. Klinische Entscheidungsfindung in der Zahnmedizin; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaneva, B.; Mutafchieva, M.; Shentov, P.; Tomov, G. Guided Biofilm Therapy for Management of “Desquamative Gingivitis”—Clinical Cases. Clin. Pract. 2024, 14, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kommalapati, V.; Latha, H.A.; Sekhar, B.R.; Kumar, S.D.; Ramya, D. Immunologically Mediated Diseases of the Oral Cavity—A Systematic Review. RGUHS J. Med. Sci. 2023, 13, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsushima, F.; Sakurai, J.; Uesugi, A.; Oikawa, Y.; Ohsako, T.; Mochizuki, Y.; Hirai, H.; Kayamori, K.; Harada, H. Malignant transformation of oral lichen planus: A retrospective study of 565 Japanese patients. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radochová, V.; Koberová Ivančaková, R.; Heneberk, O.; Slezák, R. The Characteristics of Patients with Oral Lichen Planus and Malignant Transformation—A Retrospective Study of 271 Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daume, L.; Kreis, C.; Bohner, L.; Jung, S.; Kleinheinz, J. Clinical characteristics of oral lichen planus and its causal context with dental restorative materials and oral health-related quality of life. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha-Hosseini, F.; Gholamrezayi, E.; Moosavi, M.S. Patch test of dental materials in Oral Lichen Planus with considering the role of saliva. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, H.; Meijer, J.M.; Diercks, G.F.H.; Sieben, N.E.; Bolling, M.C.; Pas, H.H.; Horvath, B. Assessment of Diagnostic Strategy for Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormond, M.; McParland, H.; Thakrar, P.; Donaldson, A.; Andiappan, M.; Cook, R.; Escudier, M.; Higham, J.; Hullah, E.; McMillan, R.; et al. Validation of an Oral Disease Severity Score (ODSS) tool for use in oral mucous membrane pemphigoid. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, F.D.; Galleggiante, S.; Laudadio, C.; Contaldo, M.; Stasio, D.D.; Tampoia, M.; Petruzzi, M. Serum and Salivary BP180 NC 16a Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay in Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid. Analysis of a Cohort of 25 Patients. Proceedings 2019, 35, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualgasim, A.O.B.; Yousif, Y.O. Oral mucosal disorders of inpatients with mucocutaneous diseases from Khartoum, Sudan. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegarelli, D.J.; Zegarelli, E.V. Intraoral pemphigus vulgaris. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 1989, 44, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassab, A.R.G.; Navabi, N.; Pour, M.M.; Charrosta, N.; Hashemipour, M.A. Quality of life in patients with chronic oral mucosal conditions: A qualitative research. Pesqui. Bras. Odontopediatria Clín. Integr. 2021, 21, e0092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegarelli, D.J.; Sabbagh, E. Relative incidence of intraoral pemphigus vulgaris, mucus membrane pemphigoid and lichen planus. Ann. Dent. 1989, 48, 5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Endo, H.; Rees, T.D.; Niwa, H.; Kuyama, K.; Oshima, M.; Serizawa, T.; Tanaka, S.; Iijima, M.; Komiya, M.; Ito, T. Desquamative Gingivitis: Early Sign of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris. In Periodontology and Dental Implantology; Manakil, J., Ed.; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoopler, E.T.; Sollecito, T.P.; DeRossi, S.S. Desquamative gingivitis: Early presenting symptom of mucocutaneous disease. Quintessence Int. 2003, 34, 582. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, W.P. Unusual Cutaneous Manifestations of Drug Hypersensitivity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1967, 51, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruch-Gerharz, D.; Hertl, M.; Ruzicka, T. Mucous membrane pemphigoid: Clinical aspects, immunopathological features and therapy. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2007, 17, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchia, D.; Caproni, M.; Volpi, W.; Fabbri, P. Naturally occurring regulatory T cells in mucous membrane pemphigoid lesions. Acta Dermatoven. APA 2009, 18, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kridin, K. Emerging treatment options for the management of pemphigus vulgaris. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Rees, T.D.; Wright, J.M.; Plemons, J.M. Childhood oral pemphigoid: A case report and review of the literature. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2001, 30, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharfi, M.; Khaled, A.; Anane, R.; Fazaa, B.; Kamoun, M.R. Early Onset Childhood Cicatricial Pemphigoid: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2010, 27, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.B.; Kumar, S.K.S.; Zain, R.B. Oral lichen planus and lichenoid reactions: Etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, management and malignant transformation. J. Oral Sci. 2007, 49, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramon-Fluixá, C.; Bagan-Sebastian, J.; Milian, M.M.; Scully, C. Periodontal status in patients with oral lichen planus: A study of 90 cases. Oral Dis. 1999, 5, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguire, A.; Neiders, M.F.; Nisengard, R.J. Desquamative Gingivitis. In Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology; Carranza, F.A., Newman, M.G., Takei, H.H., Eds.; W.B. Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 411–433. [Google Scholar]
- Popova, C. Desquamative gingivitis as a symptom of different mucocutaneous disorders. J. IMAB 2007, 13, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, S.; Gargano, M.; Matentzoglu, N.; Carmody, L.C.; Lewis-Smith, D.; Vasilevsky, N.A.; Danis, D.; Balagura, G.; Baynam, G.; Brower, A.M.; et al. The Human Phenotype Ontology in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, C.; Laskaris, G. Mucocutaneous disorders. Periodontology 2000 1998, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, J.; Kalimo, K.; Happonen, R.P. Contact allergy to dental restorative materials in patients with oral lichenoid lesions. Contact Dermat. 1997, 36, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, A. Contact Allergy to (Ingredients of) Toothpastes. Dermatitis 2017, 28, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsailidi, E.A.; Kalogirou, E.M.; Michelogiannakis, D.; Vlachodimitropoulos, D.; Tosios, K.I. Hypersensitivity reaction of the gingiva to chlorhexidine: Case report and literature review. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020, 130, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Rees, T.D. Cinnamon products as a possible etiologic factor in orofacial granulomatosis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2007, 12, E440. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, S.M.; Shamsudeen, S.M.; Assiri, K.I.; Muburak, H.; Kaleem, S.M.; Khan, A.A.; Shariff, M. Drug induced oral erythema multiforme: Case report. Medicine 2021, 100, e22387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Dulcey, V.; López-Labady, J.; Villarroel-Dorrego, M.; Frías, J.; Tirado, W.; González, N.; Pérez Alfonzo, R. Oral manifestations associated with antimalarial therapy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2020, 29, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayangco, L.; Rogers, R.S. Oral manifestations of erythema multiforme. Dermatol. Clin. 2003, 21, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.T.; Valerin, M.A.; Napeñas, J.J.; Lockhart, P.B. Oral manifestations of patients with lupus erythematosus. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 49, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinbu, Y.; Demitsu, T. Oral ulcerations due to drug medications. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2014, 50, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intong, L.R.; Murrell, D.F. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: New diagnostic criteria and classification. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolic-Jakoba, N.; Spin-Neto, R.; Wenzel, A.; Villa-Correa, Y.A.; Isaza-Guzmán, D.M.; Tobón-Arroyave, S.I. American Academy of Periodontology Task Force Report on the Update to the 1999 Classification of Periodontal Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodont. 2015, 86, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribante, A.; Pellegrini, M.; Li Vigni, G.; Pulicari, F.; Spadari, F. Desquamative Gingivitis, Oral Hygiene, and Autoimmune Oral Diseases: A Scoping Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, X.; Zheng, X.; Ge, S.; Wen, H.; Lin, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, L. Global Prevalence and Incidence Estimates of Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K. Subepidermal autoimmune bullous diseases: Overview, epidemiology, and associations. Immunol. Res. 2018, 66, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.B.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Yu, D.S.; Han, K.D.; Park, Y.G. Incidence and death rate of pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus in Korea: A nationwide, population-based study (2006–2015). J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, M.L.; Wittwer, J.W.; Miller, R.L. Desquamative gingivitis in a 13-year-old male. Case report. J. Periodontol. 1981, 52, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillant, L.; Chauchaix-Barthès, S.; Hüttenberger, B.; Arbeille, B.; Machet, M.; Jan, V.; Goga, D.; Lorette, G. Le syndrome “gingivite érosive chronique”: Étude rétrospective de 33 cas. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2000, 127, 381. [Google Scholar]
- Bagan, J.; Muzio, L.; Scully, C. Number III Mucous membrane pemphigoid. Oral Dis. 2005, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markopoulos, A.K.; Antoniades, D.; Papanayotou, P.; Trigonidis, G. Desquamative gingivitis: A clinical, histopathologic, and immunologic study. Quintessence Int. 1996, 27, 763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rogers, R.S.; Sheridan, P.J.; Nightingale, S.H. Desquamative gingivitis: Clinical, histopathologic, immunopathologic, and therapeutic observations. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1982, 7, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, C.; Carrozzo, M.; Gandolfo, S.; Puiatti, P.; Monteil, R. Update on mucous membrane pemphigoid: A heterogeneous immune-mediated subepithelial blistering entity. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1999, 88, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisengard, R.J.; Neiders, M. Desquamative lesions of the gingiva. J. Periodontol. 1981, 52, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Russo, L.; Fedele, S.; Guiglia, R.; Ciavarella, D.; Lo Muzio, L.; Gallo, P.; Di Liberto, C.; Campisi, G. Diagnostic pathways and clinical significance of desquamative gingivitis. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignogna, M.D.; Fortuna, G.; Leuci, S.; Ruoppo, E.; Marasca, F.; Matarasso, S. Nikolsky’s sign on the gingival mucosa: A clinical tool for oral health practitioners. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yih, W.T.; Maier, T.; Kratochivil, F.; Zieper, M.B. Analysis of desquamative gingivitis using direct immunofluorescence in conjunction with histology. J. Periodontal. 1998, 69, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, J.; Varela-Centelles, P.I.; Limeres-Posse, J.; Seoane-Romero, J.M. A punch technique for gingival incisional biopsy. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, T.D. Vesiculo-ulcerative diseases and periodontal practice. J. Periodontol. 1995, 66, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TD, R. Academy report: Position paper: Oral features of mucocutaneous disorders. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaguchi, M.; Iwata, H. The Diagnosis and Blistering Mechanisms of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, D.F.; Peña, S.; Joly, P.; Marinovic, B.; Hashimoto, T.; Diaz, L.A.; Sinha, A.A.; Payne, A.S.; Daneshpazhooh, M.; Eming, R.; et al. Diagnosis and management of pemphigus: Recommendations of an international panel of experts. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, S.; Desai, R.S.; Bansal, S.P.; Shirsat, P.M.; Prasad, P. Efficacy of anti-desmoglein 1 and anti-desmoglein 3 levels by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay compared to biopsy of chronic oral ulcerative diseases with positive Nikolsky’s sign to diagnose oral pemphigus vulgaris with or without skin involvement: A retrospective institutional observational pilot study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2023, 136, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnie, R.; Dobson, M.; Chrystal, A.; Hijazi, K. Oral lichen planus and lichenoid lesions—Challenges and pitfalls for the general dental practitioner. Br. Dent. J. 2024, 236, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maderal, A.D.; Lee Salisbury, P.; Jorizzo, J.L. Desquamative gingivitis: Diagnosis and treatment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Gould, A.; Kurago, Z.; Fantasia, J.; Muller, S. Diagnosis of oral lichen planus: A position paper of the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2016, 122, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonavoglia, A.; Leone, P.; Dammacco, R.; Di Lernia, G.; Petruzzi, M.; Bonamonte, D.; Vacca, A.; Racanelli, V.; Dammacco, F. Pemphigus and mucous membrane pemphigoid: An update from diagnosis to therapy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marker, P.; Krogdahl, A. Plasma cell gingivitis apparently related to the use of khat: Report of a case. Br. Dent. J. 2002, 192, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gordon, S.C.; Daley, T.D. Foreign body gingivitis: Clinical and microscopic features of 61 cases. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radio. Endod. 1997, 83, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highfield, J. Diagnosis and classification of periodontal disease. Austral. Dent. J. 2009, 54, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, S. Desquamative gingivitis—A clinical sign in mucous membrane pemphigoid: Report of a case and review of literature. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2014, 6, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagari, E.; Damoulis, P.D. Desquamative gingivitis as a manifestation of chronic mucocutaneous disease. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2011, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduino, P.G.; Farci, V.; D’Aiuto, F.; Carcieri, P.; Carbone, M.; Tanteri, C.; Gardino, N.; Gandolfo, S.; Carrozzo, M.; Broccoletti, R. Periodontal status in oral mucous membrane pemphigoid: Initial results of a case-control study. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, A.R.; Manojkumar, S.T.; Arjun, R. Pemphigus vulgaris with significant periodontal findings: A case report. J. Calif. Dent. Assoc. 2010, 38, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.D. A Novel Approach for the Treatment of Desquamative Gingivitis. Available online: http://perioimplantadvisory.com/clinical-tips/hygiene-techniques/article/16411597/a-novel-approach-for-the-treatment-of-desquamative-gingivitis (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Corrocher, G.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Mansueto, P.; Martinelli, N.; Esposito-Pellitteri, M.; Gelio, S.; Lombardo, G.; Pacor, M.L. Comparison of topical tacrolimus 0.1% in pectin ointment with clobetasol 0.5% ointment in adults with moderate to severe desquamative gingivitis: A 4-week, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Clin. Ther. 2006, 28, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragelund, C.; Kieffer-Kristensen, L.; Reibel, J.; Bennett, E.P. Oral candidosis in lichen planus: The diagnostic approach is of major therapeutic importance. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2013, 17, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, C.S.; Thomsen, K. Fusidic acid cream in the treatment of plasma cell balanitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1992, 27, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Halgatti, V.; Maheshwari, S.; Santosh, B.S. Comparative study of the efficacy of herbal antioxdants oxitard and aloe vera in the treatment of oral submucous fibrosis. J. Clin. Exper. Dent. 2014, 6, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S. The impact of estrogen on periodontal tissue integrity and inflammation—A mini review. Front. Dent. Med. 2025, 6, 1455755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravitis, K.; Daley, T.D.; Lochhead, M.A. Management of patients with foreign body gingivitis: Report of 2 cases with histologic findings. J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2005, 71, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Joly, P.; Horvath, B.; Patsatsi, A.; Uzun, S.; Bech, R.; Beissert, S.; Bergman, R.; Bernard, P.; Borradori, L.; Caproni, M.; et al. Updated S2K guidelines on the management of pemphigus vulgaris and foliaceus initiated by the european academy of dermatology and venereology (EADV). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1900–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.A.; Rogers, R.S.; Bruce, A.J. Oral lichen planus. Clin. Dermatol. 2016, 34, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtsche, M.M.; Zillikens, D.; Schmidt, E. Schleimhautpemphigoid. Hautarzt 2018, 69, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokumbi, O.; Wetter, D.A. Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of erythema multiforme: A review for the practicing dermatologist. Int. J. Dermatol. 2012, 51, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, G.; Brennan, M.T. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, manifestations, and management. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 57, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, A.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Fine, J.D.; Harper, N.; Has, C.; Magin, T.M.; Marinkovich, M.P.; Marshall, J.F.; McGrath, J.A.; et al. Epidermolysis bullosa. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.N.; Cohen, D.M.; Ojha, J.; Stewart, C.M.; Katz, J.; Bhattacharyya, I. Chronic ulcerative stomatitis: Diagnostic and management challenges--four new cases and review of literature. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2007, 104, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortuna, G.; Marinkovich, M.P. Linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmi, T.T. Dermatitis herpetiformis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 44, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dignan, F.L.; Scarisbrick, J.J.; Cornish, J.; Clark, A.; Amrolia, P.; Jackson, G.; Mahendra, P.; Taylor, P.C.; Shah, P.; Lightman, S.; et al. Haemato-oncology Task Force of British Committee for Standards in Haematology; British Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Organ-specific management and supportive care in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leao, J.C.; Ingafou, M.; Khan, A.; Scully, C.; Porter, S. Desquamative gingivitis: Retrospective analysis of disease associations of a large cohort. Oral Dis. 2008, 14, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mucocutaneous Disorders ([28]): | Allergic Reactions: |
| └OLP └MMP └IPV | └Dental materials [29] └Toothpastes [30] └Other additives (e.g., [31,32]) |
| Possibly drug induced ([33,34]): | Induced lesions: |
| └EM [35] └LE [36] | └Drug-induced erosive lesions [37] └Sensitive skin and mucosa (e.g., EB [38]) |
| DG | Estimated Incidence |
|---|---|
| OLP | 0.89% in the general population; 0.98% from clinical patients [41] |
| MMP | From 0.0001% to 0.0003% [42] |
| IPV | <0.0002% [43] |
| OLP:MMP:IPV | 15:2:1 [12]; 15:15:1 [44]; 15:15:6 [45]; x:3:1 [46] |
| Category | Number of Articles/Studies |
|---|---|
| Records identified | 137 |
| Duplicates removed | 12 |
| Records screened | 125 |
| Records excluded | 16 |
| Full-text articles assessed for eligibility | 109 |
| Full-text articles excluded | 13 |
| Studies included in the present review | 96 |
| Studies included in qualitative synthesis | 26 |
| Underlying Disease | Tissue: Pattern of Immune Deposits | Sera: Types of Antibodies |
|---|---|---|
| Cicatricial pemphigoid | Basement membrane zone (97%) | Basement membrane (23%) |
| Bullous pemphigoid | Basement membrane zone (100%) | Basement membrane (97%) |
| Pemphigus, all forms | Epithelial intercellular deposits (100%) | Intercellular antibodies of epithelium (over 95%) |
| Lichen planus | Globular deposits (cytoid bodies) in epidermis and dermis (97%) Fibrin deposits along basement membrane | None |
| Psoriasis | Stratum corneum deposits | None are specific for psoriasis |
| Other (hormonal, etc.) | Negative or few cytoid bodies | Negative |
| IgA | IgG | IgM | C3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epidermal basal layer | X | X | ||
| Intraepithelial layer | X | X | X | X |
| Basement membrane | X | X | X | |
| Epidermal–dermal border | X | |||
| Papillary dermis | X | X | X | |
| Blood vessel walls | X | X |
| Disease | Immunofluorescence Findings |
|---|---|
| Pemphigus vulgaris | IgG, IgA, and IgM in intraepithelial layer |
| Bullous pemphigoid | IgG and C3 in epidermal basal layer |
| Mucous membrane pemphigoid | IgG and C3 in epidermal basal layer |
| Paraneoplastic pemphigus | IgG and complement in intraepithelial layer and basement membrane |
| Linear IgA disease | Linear IgA along the epidermal–dermal border |
| Dermatitis herpetiformis | Granular IgA and complement in the tips of the papillary dermis |
| Chronic ulcerative stomatitis with stratified epithelial-specific antinuclear antibody | Speckled antinuclear antibody in lower third of epidermis |
| Lupus erythematosus | IgG and IgM in basement membrane |
| Erosive lichen planus | IgM in colloid bodies in papillary dermis |
| Erythema multiforme | IgM and C3 in blood vessel walls |
| DG | Treatment |
|---|---|
| FBG | Periodontal: quadrant root planning under local anesthesia, followed by appropriate instruction about oral hygiene. Surgical: gingival grafts for the areas judged to be most receded and unstable, the lower canine and premolar buccal regions [77]. |
| IPV | General principles of management and summary of treatment options for PV [78]. |
| OLP | Topical and systemic medications used in the OLP treatment in [79]. |
| MMP | Treatment algorithm (Behandlungsalgorithmus) in [80]. |
| EM | Approaches to treatment, as in [81]. |
| LE | Therapeutic options, as in [82]. |
| EB | Ongoing interventional clinical trials, as in [83]. |
| CUS | Doses of 200 mg hydroxychloroquine per day [84]. |
| LIA | Therapeutic options, as in [85]. |
| DH | Strict life-long gluten-free diet; wheat, rye, and barley are excluded from the diet, but the majority of patients with DH tolerate oats [86]. |
| GvH | Topical therapies, including steroid mouthwashes, are recommended as first-line treatment. Extracorporeal photopheresis is recommended as a second-line systemic therapy for steroid-refractory GvH [87]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rotaru, D.I.; Porumb, I.C.; Jäntschi, L.; Chisnoiu, R.M. Desquamative Gingivitis Revisited: A Narrative Review on Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Challenges, and Treatment. Medicina 2025, 61, 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081483
Rotaru DI, Porumb IC, Jäntschi L, Chisnoiu RM. Desquamative Gingivitis Revisited: A Narrative Review on Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Challenges, and Treatment. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081483
Chicago/Turabian StyleRotaru, Doina Iulia, Ioana Chifor Porumb, Lorentz Jäntschi, and Radu Marcel Chisnoiu. 2025. "Desquamative Gingivitis Revisited: A Narrative Review on Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Challenges, and Treatment" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081483
APA StyleRotaru, D. I., Porumb, I. C., Jäntschi, L., & Chisnoiu, R. M. (2025). Desquamative Gingivitis Revisited: A Narrative Review on Pathophysiology, Diagnostic Challenges, and Treatment. Medicina, 61(8), 1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081483








