Supramarginal Resection of Metastatic Brain Tumors: A Meta-Analysis Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
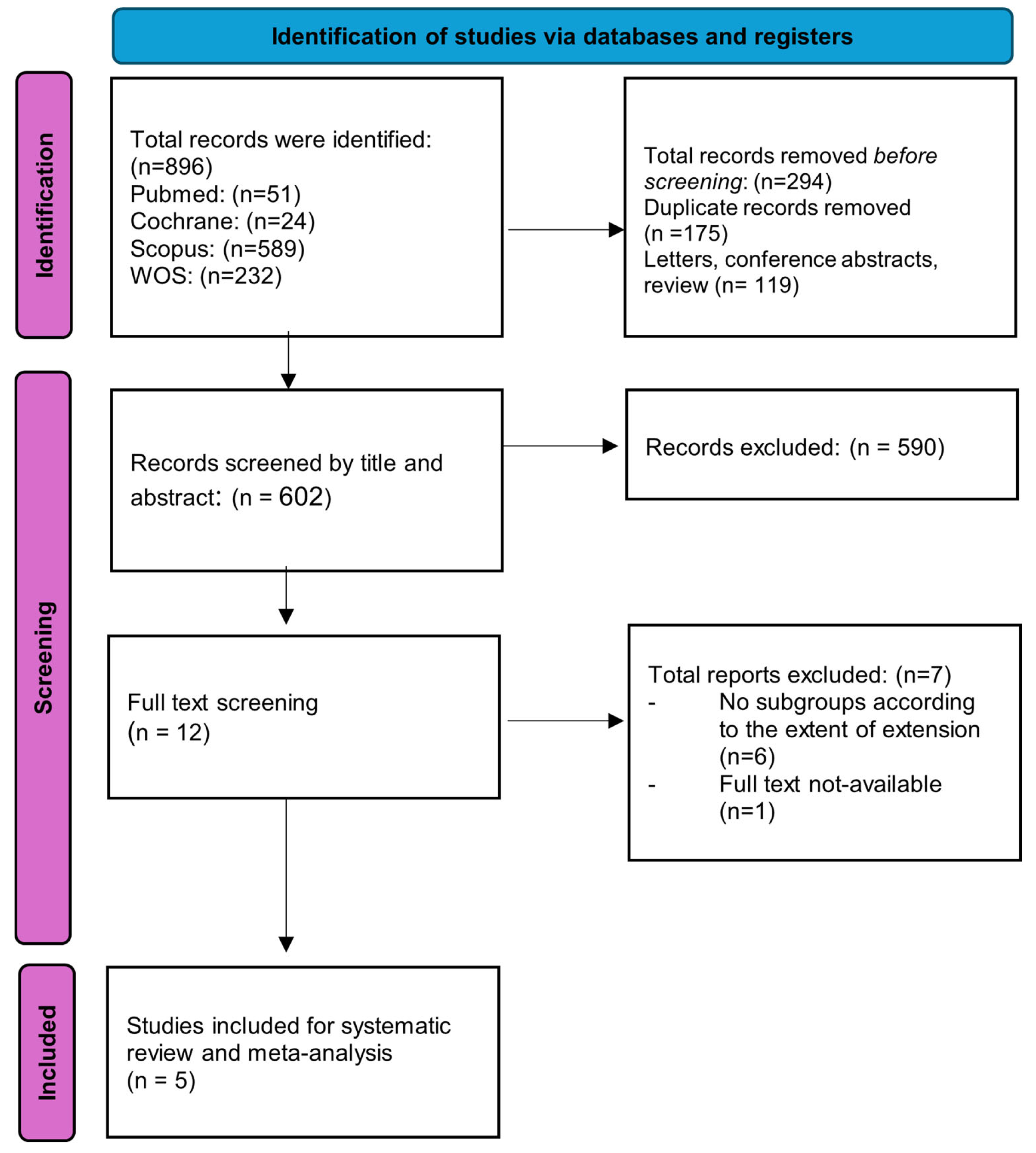
2. Materials and Methods
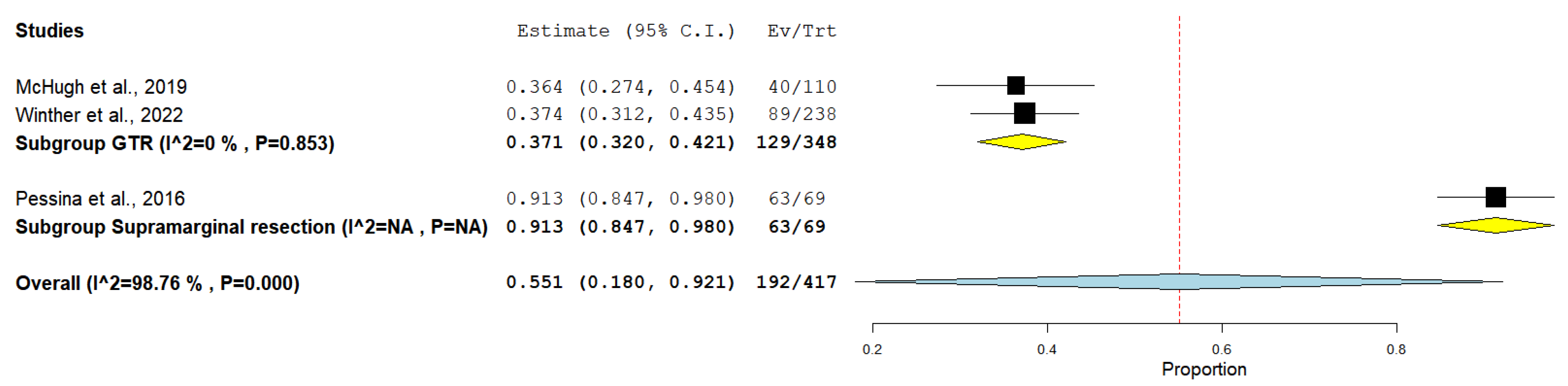
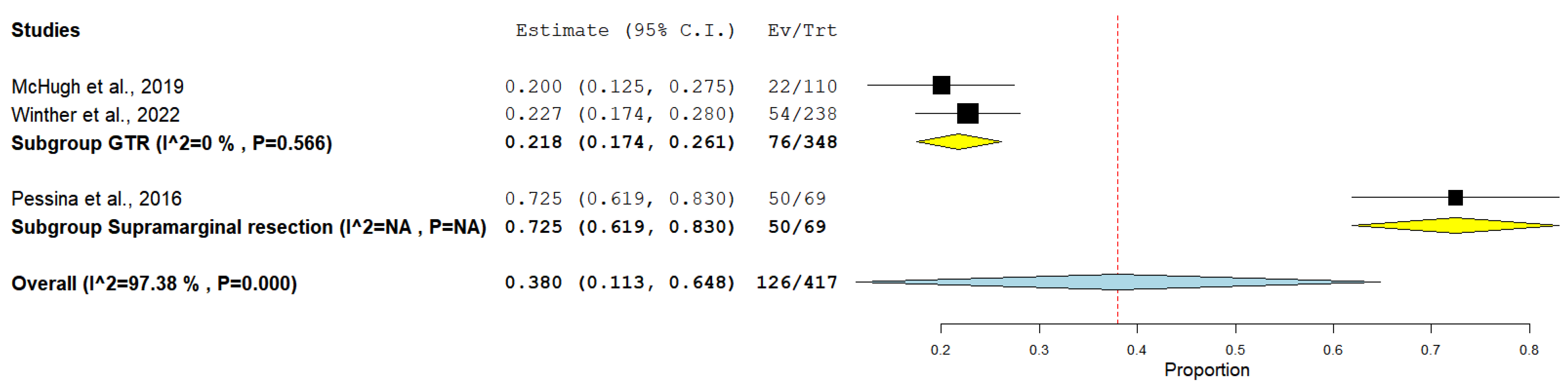
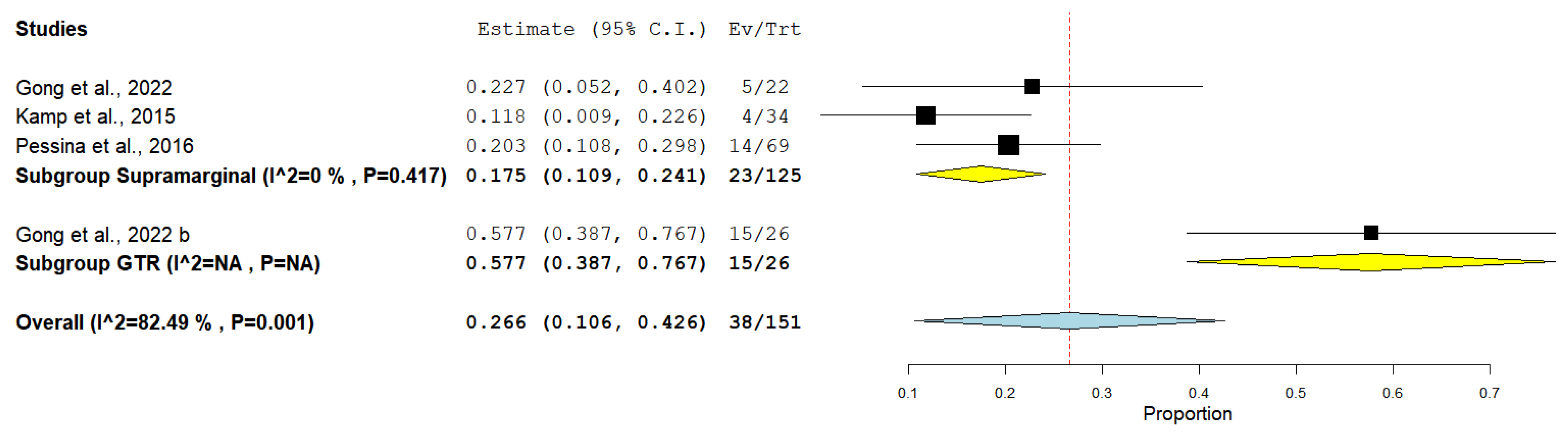
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lukas, R.V.; Gabikian, P.; Garza, M.; Chmura, S.J. Treatment of Brain Metastases. Oncology 2014, 87, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patchell, R.A. The Management of Brain Metastases. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2003, 29, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; DeAngelis, L.M. Treatment of Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3475–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.J.; Suki, D.; Hatiboglu, M.A.; Rao, V.Y.; Fox, B.D.; Sawaya, R. Impact of Surgical Methodology on the Complication Rate and Functional Outcome of Patients with a Single Brain Metastasis. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.; Kim, J.H. Revisiting the Role of Surgical Resection for Brain Metastasis. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2023, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, C.; Berberich, W.; Schnabel, K. Tumor-Related Prognostic Factors for Remission of Brain Metastases after Radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 39, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelbaum, M.A.; Angelov, L.; Lee, S.Y.; Li, L.; Barnett, G.H.; Suh, J.H. Local Control of Brain Metastases by Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Relation to Dose to the Tumor Margin. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 104, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.; Scott, C.; Souhami, L.; Dinapoli, R.; Kline, R.; Loeffler, J.; Farnan, N. Single Dose Radiosurgical Treatment of Recurrent Previously Irradiated Primary Brain Tumors and Brain Metastases: Final Report of RTOG Protocol 90-05. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 47, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchell, R.A.; Tibbs, P.A.; Regine, W.F.; Dempsey, R.J.; Mohiuddin, M.; Kryscio, R.J.; Markesbery, W.R.; Foon, K.A.; Young, B. Postoperative Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Single Metastases to the Brain: A Randomized Trial. JAMA 1998, 280, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, M.; Soffietti, R.; Abacioglu, U.; Villà, S.; Fauchon, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Fariselli, L.; Tzuk-Shina, T.; Kortmann, R.D.; Carrie, C.; et al. Adjuvant Whole-Brain Radiotherapy versus Observation after Radiosurgery or Surgical Resection of One to Three Cerebral Metastases: Results of the EORTC 22952–26001 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thon, N.; Kreth, F.W.; Tonn, J.C. The Role of Surgery for Brain Metastases from Solid Tumors. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 149, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plataniotis, G.A.; Theofanopoulou, M.; Sotiriadou, K.; Vlychou, M.; Fountoulis, G.; Fezoulidis, J. The Volume of Brain Metastases May Be of Prognostic Significance in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Classified as RTOG-RPA Classes 2 and 3. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.) 2006, 18, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaresan, N.; Galicich, J.H. Surgical Treatment of Single Brain Metastases from Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Investig. 1985, 3, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.J.; Suki, D.; Fox, B.D.; Pelloski, C.E.; Maldaun, M.V.C.; Sawaya, R.E.; Lang, F.F.; Rao, G. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Metastatic Brain Tumors: A Comprehensive Review of Complications. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bentzen, S.M.; Renschler, M.; Mehta, M.P. Regression after Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases Correlates with Survival and Improved Neurocognitive Function. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Kim, Y.Z.; Nam, B.H.; Shin, S.H.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Zo, J.I.; Lee, S.H. Reduced Local Recurrence of a Single Brain Metastasis through Microscopic Total Resection. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 110, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, C.; Franchi, T.; Mathew, G.; Kerwan, A.; Nicola, M.; Griffin, M.; Agha, M.; Agha, R. PRISMA 2020 Statement: What’s New and the Importance of Reporting Guidelines. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated Guidance for Trusted Systematic Reviews: A New Edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, ED000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; Robertson, J.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analysis. 2000. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in Meta-Analysis Detected by a Simple, Graphical Test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessina, F.; Navarria, P.; Cozzi, L.; Ascolese, A.M.; Maggi, G.; Rossi, M.; Riva, M.; Scorsetti, M.; Bello, L. Role of Surgical Resection in Patients with Single Large Brain Metastases: Feasibility, Morbidity, and Local Control Evaluation. World Neurosurg. 2016, 94, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther, R.R.; Hjermstad, M.J.; Skovlund, E.; Aass, N.; Helseth, E.; Kaasa, S.; Yri, O.E.; Vik-Mo, E.O. Surgery for Brain Metastases-Impact of the Extent of Resection. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 2773–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Jiang, T.; Zuo, D. Recurrence Benefit from Supramarginal Resection in Brain Metastases of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, M.A.; Rapp, M.; Slotty, P.J.; Turowski, B.; Sadat, H.; Smuga, M.; Dibué-Adjei, M.; Steiger, H.J.; Szelényi, A.; Sabel, M. Incidence of Local In-Brain Progression after Supramarginal Resection of Cerebral Metastases. Acta Neurochir. 2015, 157, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, F.A.; Kow, C.Y.; Falkov, A.; Heppner, P.; Law, A.; Bok, A.; Schweder, P. Metastatic Melanoma: Surgical Treatment of Brain Metastases—Analysis of 110 Patients. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 73, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siam, L.; Bleckmann, A.; Chaung, H.N.; Mohr, A.; Klemm, F.; Barrantes-Freer, A.; Blazquez, R.; Wolff, H.A.; Lüke, F.; Rohde, V.; et al. The Metastatic Infiltration at the Metastasis/Brain Parenchyma-Interface Is Very Heterogeneous and Has a Significant Impact on Survival in a Prospective Study. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29254–29267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, E.F.; Slater, J. Metastatic brain tumors. results of surgical and nonsurgical treatment. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 1964, 44, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stortebecker, T.P. Metastatic Tumors of the Brain from a Neurosurgical Point of View; a Follow-up Study of 158 Cases. J. Neurosurg. 1954, 11, 84–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groshev, A.; Padalia, D.; Patel, S.; Garcia-Getting, R.; Sahebjam, S.; Forsyth, P.A.; Vrionis, F.D.; Etame, A.B. Clinical Outcomes from Maximum-Safe Resection of Primary and Metastatic Brain Tumors Using Awake Craniotomy. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2017, 157, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinruecke, M.; Pronin, S.; Gherman, A.V.; Emelifeonwu, J.; Liaquat, I. Survival and Complications Following Supra- and Infratentorial Brain Metastasis Resection. Surgeon 2023, 21, e279–e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacho-Díaz, B.; Lorenzana-Mendoza, N.A.; Chávez-Hernandez, J.D.; González-Aguilar, A.; Reyes-Soto, G.; Herrera-Gómez, Á. Clinical Manifestations and Location of Brain Metastases as Prognostic Markers. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2019, 43, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermeyer, S.; Schmutzer-Sondergeld, M.; Weller, J.; Katzendobler, S.; Kirchleitner, S.; Forbrig, R.; Harter, P.N.; Baumgarten, L.V.; Schichor, C.; Stoecklein, V.; et al. Neurosurgical Resection of Multiple Brain Metastases: Outcomes, Complications, and Survival Rates in a Retrospective Analysis. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2024, 169, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jünger, S.T.; Pennig, L.; Schödel, P.; Goldbrunner, R.; Friker, L.; Kocher, M.; Proescholdt, M.; Grau, S. The Debatable Benefit of Gross-Total Resection of Brain Metastases in a Comprehensive Treatment Setting. Cancers 2021, 13, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author and Year | Country | Study Design | Sample Size | Primary Tumor | Number of Metastases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gong et al., 2022 [23] | China | Retrospective cohort | 48 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Single or multiple |
| Kamp et al., 2015 [24] | Germany | Retrospective cohort | 34 | Adenocarcinoma 25 (73.5%) Small cell cancer 2 (5.9%) Clear cell cancer 1 (2.9%) Squamous cell cancer 1 (2.9%) Malignant melanoma 5 (14.7%) | Single or multiple |
| McHugh et al., 2019 [25] | New Zealand | Retrospective cohort | 110 | Melanoma (100%) | Single or multiple |
| Pessina et al., 2016 [21] | Italy | Retrospective cohort | 69 | Breast cancer 24 (34.8%) Non-small cell lung cancer 21 (30.4%) Melanoma 15 (21.7%) Other (clear cell carcinoma, colon) 9 (13.1%) | Single |
| Winther et al., 2022 [22] | United States | Retrospective cohort | 238 | Lung 79 (33%) Melanoma 59 (25%) Colorectal 27 (11%) Breast 22 (9%) Kidney 13 (5%) Other 26 (12%) Unknown origin 12 (5%) | Single |
| Author and Year | Study Groups | Age | Sex (Males%) | Postoperative Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gong et al., 2022 [23] | Supramarginal | 60.5 ± 10.1 | 11 (50%) | NR |
| GTR | 55.2 ± 11 | 11 (42.3%) | ||
| Kamp et al., 2015 [24] | Supramarginal | 60 ± 12.5 | 10 (29.4%) | NR |
| McHugh et al., 2019 [25] | GTR | 59.9 ± 10.95 | 69 (63%) | NR |
| Pessina et al., 2016 [21] | Supramarginal | 51 ± 6 | 27 (39%) | NR |
| Winther et al., 2022 [22] | GTR | 64 ± 11.8 | 115 (48%) | Intracranial hemorrhage 7 (3%) Pneumonia or pulmonary embolism 1 (0.4%) Bone flap infection 1 (0.4%) CSF leakage 2 (2%) Intracerebral abscess 2 (2%) Other complications in need of neurosurgical intervention 3 (1%) |
| Study | Cohort Studies | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection | Comparability | Outcome | Score | Quality | ||||||
| Representativeness of the Exposed Cohort | Selection of the Non-Exposed Cohort | Ascertainment of Exposure | Demonstration that Outcome of Interest Was Not Present at Start of the Study | Comparability of Cohorts on the Basis of the Design or Analysis: (Age and Sex) | Assessment of Outcome | Was Follow-Up Long Enough for Outcomes to Occur? | Adequacy of Follow-Up of Cohorts | |||
| Gong et al., 2022 [23] | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 9 | good |
| Kamp et al., 2015 [24] | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 8 | good | |
| McHugh et al., 2019 [25] | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 9 | good |
| Pessina et al., 2016 [21] | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 8 | good | |
| Winther et al., 2022 [22] | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 9 | good |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tofan, F.A.; Massoud, A.T.; Faur, C.I.; Florian, S.I. Supramarginal Resection of Metastatic Brain Tumors: A Meta-Analysis Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081446
Tofan FA, Massoud AT, Faur CI, Florian SI. Supramarginal Resection of Metastatic Brain Tumors: A Meta-Analysis Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081446
Chicago/Turabian StyleTofan, Florin Adrian, Ahmed T. Massoud, Cosmin Ioan Faur, and Stefan Ioan Florian. 2025. "Supramarginal Resection of Metastatic Brain Tumors: A Meta-Analysis Study" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081446
APA StyleTofan, F. A., Massoud, A. T., Faur, C. I., & Florian, S. I. (2025). Supramarginal Resection of Metastatic Brain Tumors: A Meta-Analysis Study. Medicina, 61(8), 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081446