Factors Affecting the Survival of Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Treated with CDK 4/6 Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
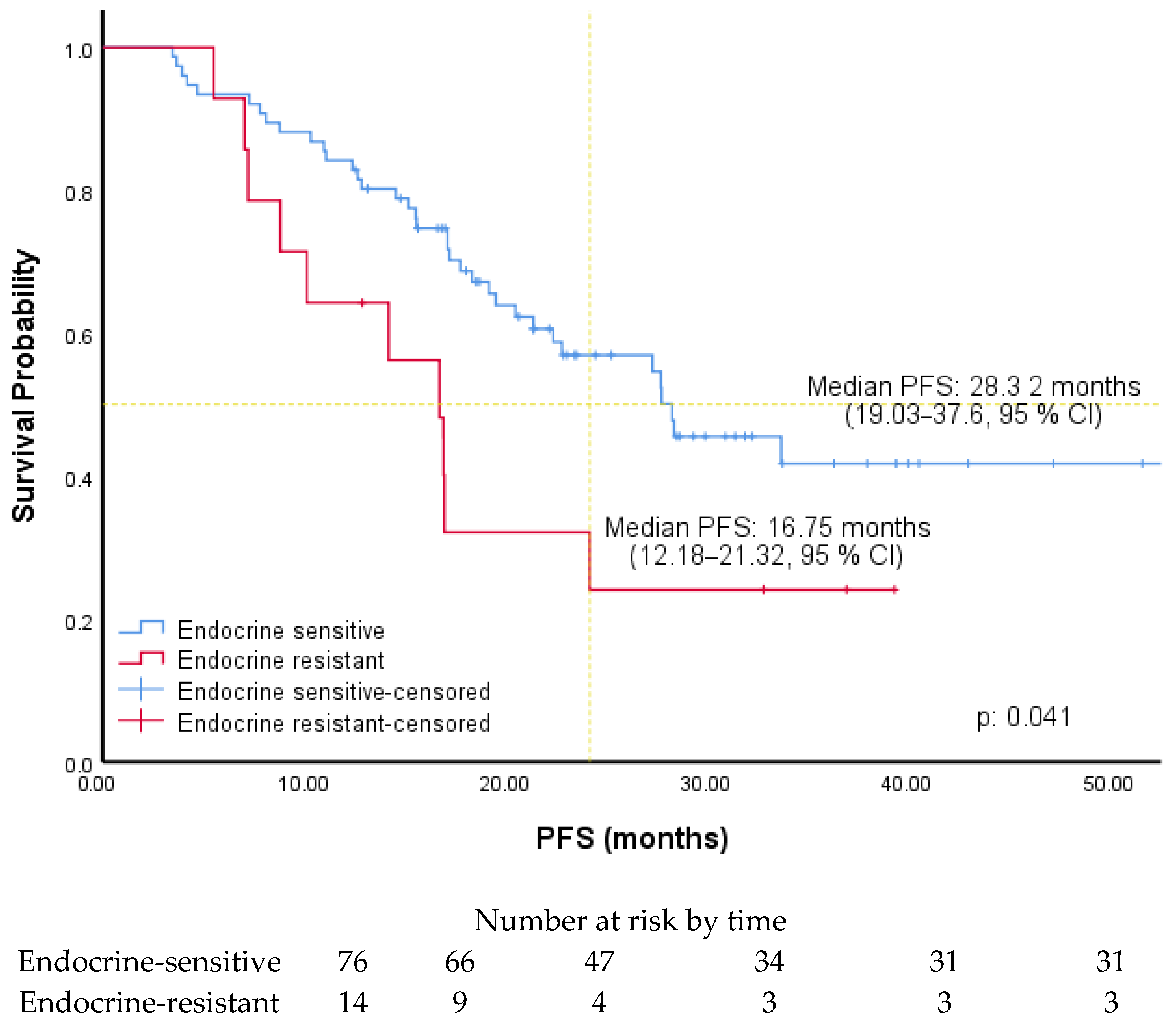
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parise, C.A.; Bauer, K.R.; Brown, M.M.; Caggiano, V. Breast cancer subtypes as defined by the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) among women with invasive breast cancer in California, 1999–2004. Breast J. 2009, 15, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caswell-Jin, J.L.; Plevritis, S.K.; Tian, L.; Cadham, C.J.; Xu, C.; Stout, N.K.; Sledge, G.W.; Mandelblatt, J.S.; Kurian, A.W. Change in Survival in Metastatic Breast Cancer with Treatment Advances: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018, 2, pky062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.; Zielinski, C.; Ruiz-Borrego, M.; Carrasco, E.; Turner, N.; Ciruelos, E.M.; Muñoz, M.; Bermejo, B.; Margeli, M.; Anton, A.; et al. Palbociclib in combination with endocrine therapy versus capecitabine in hormonal receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor 2-negative, aromatase inhibitor-resistant metastatic breast cancer: A phase III randomised controlled trial-PEARL. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, S.C.; Lee, S.S.; Abraham, J. Mechanisms of therapeutic CDK4/6 inhibition in breast cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2017, 44, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.J.; Cheng, J.; Bloomquist, E.; Sanchez, J.; Wedam, S.B.; Singh, H.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Ibrahim, A.; Sridhara, R.; Goldberg, K.B.; et al. CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment for patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced or metastatic breast cancer: A US Food and Drug Administration pooled analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.S.; Sonke, G.S.; Hart, L.; Campone, M.; Petrakova, K.; Winer, E.P.; Janni, W.; et al. Overall Survival with Ribociclib plus Letrozole in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.S.; Im, S.A.; Colleoni, M.; Franke, F.; Bardia, A.; Cardoso, F.; Harbeck, N.; Hurvitz, S.; Chow, L.; Sohn, J.; et al. Updated Overall Survival of Ribociclib plus Endocrine Therapy versus Endocrine Therapy Alone in Pre- and Perimenopausal Patients with HR+/HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer in MONALEESA-7: A Phase III Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Neven, P.; Chia, S.; Jerusalem, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Im, S.; Petrakova, K.; Valeria Bianchi, G.; Martín, M.; Nusch, A.; et al. Ribociclib plus fulvestrant for postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer in the phase III randomized MONALEESA-3 trial: Updated overall survival. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelmon, K.; Walshe, J.M.; Mahtani, R.; Joy, A.A.; Karuturi, M.; Neven, P.; Lu, D.R.; Kim, S.; Schnell, P.; Bananis, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of palbociclib in patients with estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer with preexisting conditions: A post hoc analysis of PALOMA-2. Breast 2021, 59, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, W.; Shen, X.; Li, G.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Huang, P.; Shi, L.; Ye, W.; et al. Ki67 and progesterone receptor status predicts sensitivity to palbociclib: A real-world study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleschi, M.; Maltoni, R.; Ravaioli, S.; Vagheggini, A.; Mannozzi, F.; Fanini, F.; Pirini, F.; Tumedei, M.M.; Barzotti, E.; Cecconetto, L.; et al. Ki67 and PR in Patients Treated with CDK4/6 Inhibitors: A Real-World Experience. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikanai, A.; Horimoto, Y.; Ishizuka, Y.; Uomori, T.; Nakai, K.; Arakawa, A.; Saito, M. Clinicopathological Features Related to the Efficacy of CDK4/6 Inhibitor-Based Treatments in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer 2022, 16, 11782234211065148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odan, N.; Kikawa, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Minohata, J.; Suwa, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Okuno, T.; Miyashita, M.; Saito, M.; Yamagami, K.; et al. Real-World Outcomes of Treating Advanced Breast Cancer Patients With Palbociclib: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study in Japan-The KBCOG-14 Study. Breast Cancer 2020, 14, 1178223420983843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Leo, A.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Sledge, G.W.; Jr Martin, M.; Lin, Y.; Frenzel, M.; Hardebeck, M.C.; Smith, I.C.; Llombart-Cussac, A.; Goetz, M.P.; et al. Prognostic characteristics in hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer and characterization of abemaciclib efficacy. NPJ Breast Cancer 2018, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofanilli, M.; DeMichele, A.; Giorgetti, C.; Turner, N.C.; Slamon, D.J.; Im, S.A.; Masuda, N.; Verma, S.; Loi, S.; Colleoni, M.; et al. Predictors of prolonged benefit from palbociclib plus fulvestrant in women with endocrine-resistant hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative metastatic breast cancer in PALOMA-3. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 104, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, I.; Berner, K.; Mathis, M.; Hensgen, C.; Mayer, S.; Erbes, T.; Juhasz-Böss, I.; Asberger, J. Real-World Data Analysis of CDK4/6 Inhibitor Therapy-A Patient-Centric Single Center Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Peng, J.; Sun, N.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L. Effect of PR status on the prognosis of advanced ER-high HER2-negative breast cancer patients receiving CDK4/6 inhibitor combined with endocrine as first-line therapy. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonke, G.S.; Van Ommen-Nijhof, A.; Wortelboer, N.; van der Noort, V.; Swinkels, A.C.; Blommestein, H.M.; Beeker, A.; Beelen, K.; Hamming, L.C.; Heijns, J.B.; et al. Primary outcome analysis of the phase 3 SONIA trial (BOOG 2017-03) on selecting the optimal position of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors for patients with hormone receptor-positive (HR+), HER2-negative (HER2-) advanced breast cancer (ABC). Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, LBA1000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.F.; Tsai, Y.F.; Chao, T.C.; Lien, P.J.; Lin, Y.S.; Feng, C.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Cheng, H.F.; Liu, C.Y.; Lai, J.I.; et al. Real-world experience with CDK4/6 inhibitors in hormone receptor-positive metastatic and recurrent breast cancer: Findings from an Asian population. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, K.; Wang, X.; Shao, X. Prognostic Parameters of Palbociclib in HR+/HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer: A Narrative Review. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231173504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Doval, D.C.; Batra, U.; Goyal, P.; Bothra, S.J.; Agarwal, C.; Choudhary, D.K.; Yadav, A.; Koyalla, V.P.B.; Sharma, M.; et al. Ki-67 labeling index as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 49, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, S.R.D.; Toi, M.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Rastogi, P.; Campone, M.; Neven, P.; Huang, C.-S.; Huober, J.; Jaliffe, G.G.; Cicin, I.; et al. Abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer (monarchE): Results from a preplanned interim analysis of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yerushalmi, R.; Woods, R.; Ravdin, P.M.; Hayes, M.M.; Gelmon, K.A. Ki67 in breast cancer: Prognostic and predictive potential. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Azambuja, E.; Cardoso, F.; de Castro, G.; Colozza, M., Jr.; Mano, M.S.; Durbecq, V.; Sotiriou, C.; Larsimont, D.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.J.; Paesmans, M. Ki-67 as prognostic marker in early breast cancer: A meta-analysis of published studies involving 12,155 patients. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lei, W.; Fang, Z.; Jiang, R.; Wang, X. Efficacy, safety, and predictive model of Palbociclib in the treatment of HR-positive and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.B.; Kim, J.; Sohn, G.; Kim, J.; Chung, I.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Ko, B.S.; Son, B.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; et al. A Nomogram for Predicting the Oncotype DX Recurrence Score in Women with T1-3N0-1miM0 Hormone Receptor–Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor 2 (HER2)–Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliskan Yildirim, E.; Atag, E.; Coban, E.; Umit Unal, O.; Celebi, A.; Keser, M.; Uzun, M.; Keskinkilic, M.; Tanrikulu Simsek, E.; Sari, M.; et al. The effect of low HER2 expression on treatment outcomes in metastatic hormone receptor positive breast cancer patients treated with a combination of a CDK4/6 inhibitor and endocrine therapy: A multicentric retrospective study. Breast 2023, 70, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaf, B.; Abu-Fares, H.; Tamimi, F.; Al-Sawajneh, S.; Salama, O.; Daoud, R.; Alhajahjeh, A.; Al-Lababidi, S.; Abdel-Razeq, H. Differences in Treatment Outcomes Between Patients with HER2-Low versus HER2-Zero, Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced-Stage Breast Cancer Treated with Ribociclib. Breast Cancer 2023, 15, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Martin, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Jones, S.; Im, S.A.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Moulder, S.; et al. Palbociclib and Letrozole in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Campone, M.; Blackwell, K.L.; André, F.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Ribociclib as First-Line Therapy for HR-Positive, Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Neven, P.; Chia, S.; Fasching, P.A.; De Laurentiis, M.; Im, S.A.; Petrakova, K.; Bianchi, G.V.; Esteva, F.J.; Martín, M.; et al. Phase III Randomized Study of Ribociclib and Fulvestrant in Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer: MONALEESA-3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | All Patients, n (%) | Luminal A, n (%) | Luminal B, n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| <65 years | 63 (70%) | 31 (70.5%) | 32 (69.6%) | |
| ≥65 years | 27 (30%) | 13 (29.5%) | 14 (30.4%) | 0.927 |
| Sex | ||||
| Women | 87 (96.7%) | 43 (97.7%) | 44 (95.7%) | |
| Men | 3 (3.3%) | 1 (2.3%) | 2 (4.3%) | 0.584 |
| Smoking | ||||
| Yes | 15 (16.7%) | 8 (18.2%) | 7 (15.2%) | |
| No | 75 (83.3%) | 36 (81.8%) | 39 (84.8%) | 0.706 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| DM | 19 (21.1%) | 10 (22.7%) | 9 (19.6%) | 0.713 |
| HT | 29 (32.2%) | 12 (27.3%) | 17 (37%) | 0.326 |
| CAD | 9 (10%) | 4 (9.1%) | 5 (10.9%) | 0.779 |
| ECOG-PS | ||||
| 0–1 | 79 (87.8%) | 39 (88.6%) | 40 (87%) | |
| 2 | 11 (12.2%) | 5 (11.4%) | 6 (13%) | 0.808 |
| Polypharmacy | ||||
| Yes | 19 (21.1%) | 11 (25%) | 8 (17.4%) | |
| No | 71 (78.9%) | 33 (75%) | 38 (82.6%) | 0.337 |
| Histology | ||||
| Ductal carcinoma | 74 (82.2%) | 35 (79.5%) | 39 (84.8%) | |
| Lobular carcinoma | 12 (13.3%) | 7 (15.9%) | 5 (10.9%) | |
| Others | 4 (4.4%) | 2 (4.5%) | 2 (4.3%) | 0.777 |
| Grade | ||||
| 1–2 | 63 (70%) | 41 (93.2%) | 22 (47.8%) | |
| 3 | 27 (30%) | 3 (6.8%) | 24 (52.2%) | <0.001 |
| Menopausal Status | ||||
| Premenopause | 41 (45.6%) | 22 (50%) | 19 (41.3%) | |
| Postmenopause | 49 (54.4%) | 22 (50%) | 27 (58.7%) | 0.408 |
| Breast cancer | ||||
| De novo | 44 (48.9%) | 24 (54.5%) | 20 (43.5%) | |
| Recurrent | 46 (51.1%) | 20 (45.5%) | 26 (56.5%) | 0.294 |
| Metastatic sites | ||||
| Visceral | 51 (56.7%) | 22 (50%) | 29 (63%) | |
| Non-visceral | 39 (43.3%) | 22 (50%) | 17 (37%) | 0.212 |
| Metastatic sites | ||||
| Bone | 79 (87.8%) | 41 (93.2%) | 38 (82.6%) | 0.126 |
| Liver | 16 (17.8%) | 7 (15.9%) | 9 (19.6%) | 0.650 |
| Lung | 29 (32.2%) | 14 (31.8%) | 15 (32.6%) | 0.936 |
| Cranial | 3 (3.3%) | 0 | 3 (6.5%) | 0.085 |
| Lymph nodes, distant | 23 (25.6%) | 9 (20.5%) | 14 (30.4%) | 0.278 |
| Number of metastatic sites | ||||
| 1 | 47 (52.2%) | 24 (54.5%) | 23 (50%) | |
| 2 | 22 (24.4%) | 10 (22.7%) | 12 (26.1%) | |
| ≥3 | 21 (23.3%) | 10 (22.7%) | 11 (23.9%) | 0.902 |
| Prior therapy for EBC | ||||
| Surgery | 54 (60%) | 24 (54.5%) | 30 (65.2%) | 0.302 |
| Chemotherapy | 46 (51.1%) | 20 (45.5%) | 26 (56.5%) | 0.294 |
| Endocrine therapy | 46 (51.1%) | 20 (45.5%) | 26 (56.5%) | 0.294 |
| Endocrine therapy during CDK4/6i | ||||
| Aromatase inhibitors | 76 (84.4%) | 38 (86.4%) | 38 (82.6%) | |
| Fulvestrant | 14 (15.6%) | 6 (13.6%) | 8 (17.4%) | 0.623 |
| Dose Reduction | ||||
| Yes | 45 (50%) | 21 (47.7%) | 24 (52.2%) | |
| No | 45 (50%) | 23 (52.3%) | 22 (47.8%) | 0.673 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age | ||||||
| <65 years (R) | 0.60 | 0.29–1.25 | 0.174 | |||
| ≥65 years | ||||||
| Menopausal Status | ||||||
| Premenopause | 1.08 | 0.60–1.94 | 0.787 | |||
| Postmenopause | ||||||
| Smoking | ||||||
| Yes | 0.65 | 0.28–1.56 | 0.342 | |||
| No (R) | ||||||
| Polypharmacy | ||||||
| Yes | 1.14 | 0.56–2.30 | 0.714 | |||
| No (R) | ||||||
| Grade | ||||||
| 1–2 | 1.75 | 0.96–3.19 | 0.069 | |||
| 3 | ||||||
| Luminal type | ||||||
| Luminal A | 2.28 | 1.24–4.21 | 0.008 | 1.39 | 0.52–3.67 | 0.511 |
| Luminal B | ||||||
| Breast cancer | ||||||
| De novo | 1.57 | 0.87–2.83 | 0.130 | |||
| Recurrent | ||||||
| Metastatic sites | ||||||
| Non-visceral (R) | 0.93 | 0.52–1.67 | 0.820 | |||
| Visceral | ||||||
| Bone metastasis | 1.50 | |||||
| Yes | 0.59–3.80 | 0.392 | ||||
| No (R) | ||||||
| Liver metastasis | ||||||
| Yes | 2.23 | 1.17–4.24 | 0.014 | 1.55 | 0.76–3.16 | 0.227 |
| No (R) | ||||||
| Lung metastasis | ||||||
| Yes | 0.62 | 0.31–1.22 | 0.163 | |||
| No (R) | ||||||
| Cranial metastasis | ||||||
| Yes | 1.87 | 0.45–7.75 | 0.387 | |||
| No (R) | ||||||
| Lymph nodes, distant | ||||||
| Yes | 0.95 | 0.48–1.87 | 0.878 | |||
| No (R) | ||||||
| Endocrine therapy during CDK 4/6i | ||||||
| Aromatase inhibitors (R) | 2.05 | 1.01–4.15 | 0.045 | 1.98 | 0.96–4.08 | 0.064 |
| Fulvestrant | ||||||
| CDK 4/6i adverse events | ||||||
| Yes | 1.71 | 0.41–7.06 | 0.458 | |||
| No (R) | ||||||
| Dose Reduction | ||||||
| Yes | 0.92 | 0.51–1.64 | 0.780 | |||
| No (R) | ||||||
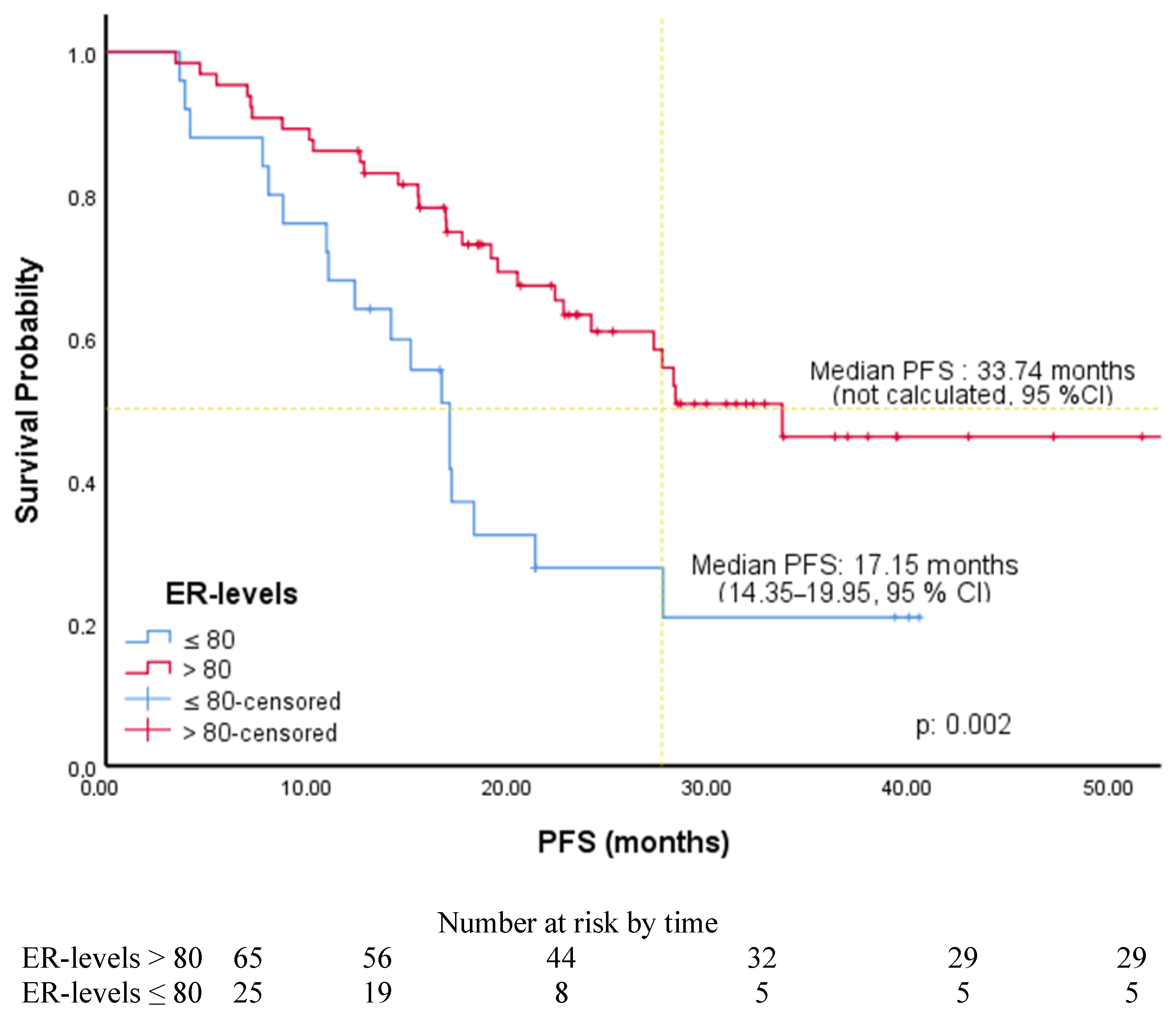
| ER (ROC) | ||||||
| ≤80 | 2.48 | 1.36–4.52 | 0.003 | 2.50 | 1.36–4.61 | 0.003 |
| >80 (R) | ||||||
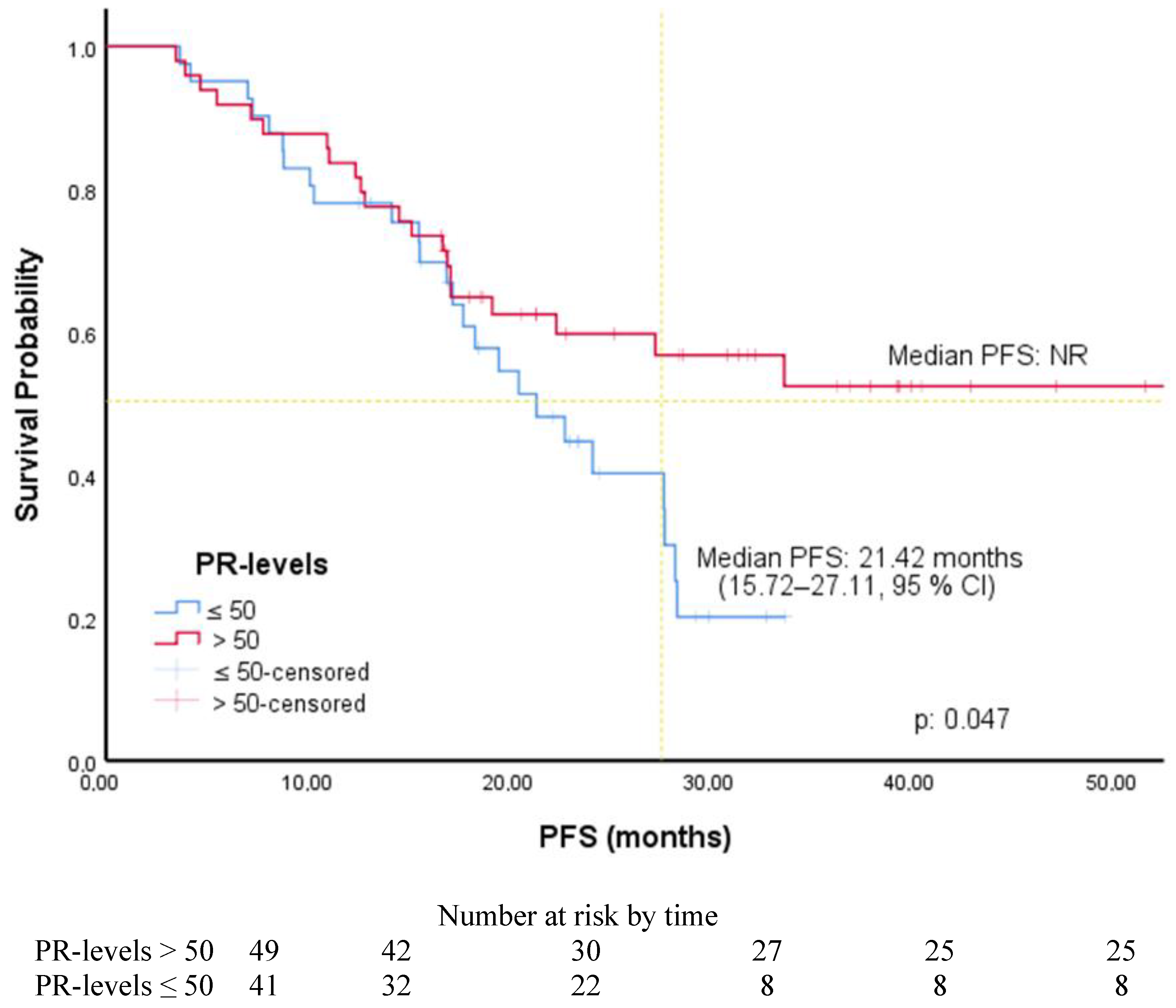
| PR (ROC) | ||||||
| ≤50 | 1.80 | 1.0–3.25 | 0.05 | 1.69 | 0.92–3.11 | 0.088 |
| >50 (R) | ||||||
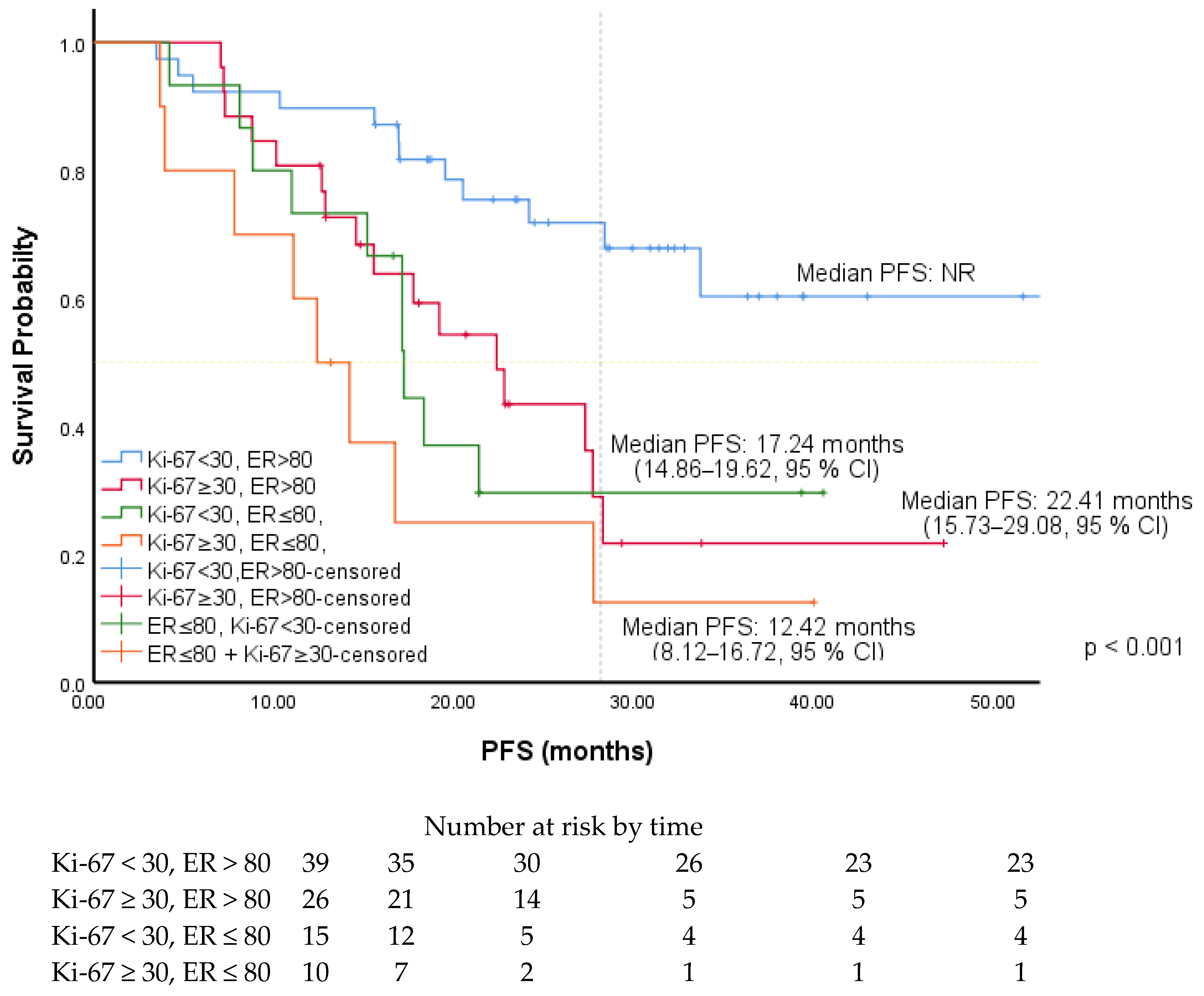
| Ki-67 (ROC) | ||||||
| <30 (R) | 2.31 | 1.28–4.14 | 0.005 | 2.22 | 1.22–4.05 | 0.009 |
| ≥30 | ||||||
| Her-2 positivity | 1.05 | 0.69–1.60 | 0.810 | |||
| ECOG | ||||||
| 1–2 (R) | 1.20 | 0.47–3.06 | 0.696 | |||
| 3 | ||||||
| Number of metastatic sites | ||||||
| 1 (R) | ||||||
| 2 | 1.16 | 0.59–2.43 | 0.695 | |||
| ≥3 | 1.27 | 0.63–2.53 | 0.503 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sucuoğlu İşleyen, Z.; Muğlu, H.; Alaca Topçu, Z.; Beşiroğlu, M.; Yasin, A.İ.; Topçu, A.; Şimşek, M.; Şeker, M.; Türk, H.M. Factors Affecting the Survival of Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Treated with CDK 4/6 Inhibitors. Medicina 2025, 61, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071279
Sucuoğlu İşleyen Z, Muğlu H, Alaca Topçu Z, Beşiroğlu M, Yasin Aİ, Topçu A, Şimşek M, Şeker M, Türk HM. Factors Affecting the Survival of Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Treated with CDK 4/6 Inhibitors. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071279
Chicago/Turabian StyleSucuoğlu İşleyen, Zehra, Harun Muğlu, Zeynep Alaca Topçu, Mehmet Beşiroğlu, Ayşe İrem Yasin, Atakan Topçu, Melih Şimşek, Mesut Şeker, and Hacı Mehmet Türk. 2025. "Factors Affecting the Survival of Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Treated with CDK 4/6 Inhibitors" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071279
APA StyleSucuoğlu İşleyen, Z., Muğlu, H., Alaca Topçu, Z., Beşiroğlu, M., Yasin, A. İ., Topçu, A., Şimşek, M., Şeker, M., & Türk, H. M. (2025). Factors Affecting the Survival of Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients Treated with CDK 4/6 Inhibitors. Medicina, 61(7), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071279






