The Possibilities of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Reflect Functional and Structural Graft Changes 1 Year After Kidney Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Evaluation of Graft Function
- eGFR ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (n = 11) vs. <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (n = 16).
- ACR ≥ 3 mg/mmol (n = 13) vs. ACR <3 mg/mmol (n = 14);
- PCR ≥ 15 mg/mmol (n = 15) vs. PCR <15 mg/mmol (n = 12).
2.4. Evaluation of Renal Allograft Biopsies
- No or minimal IF/TA (n = 7).
- Mild-to-moderate or severe IF/TA (n = 8).
2.5. MRI Imaging, Protocol and Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and Clinical Findings in the Follow-Up Post-Transplant Period
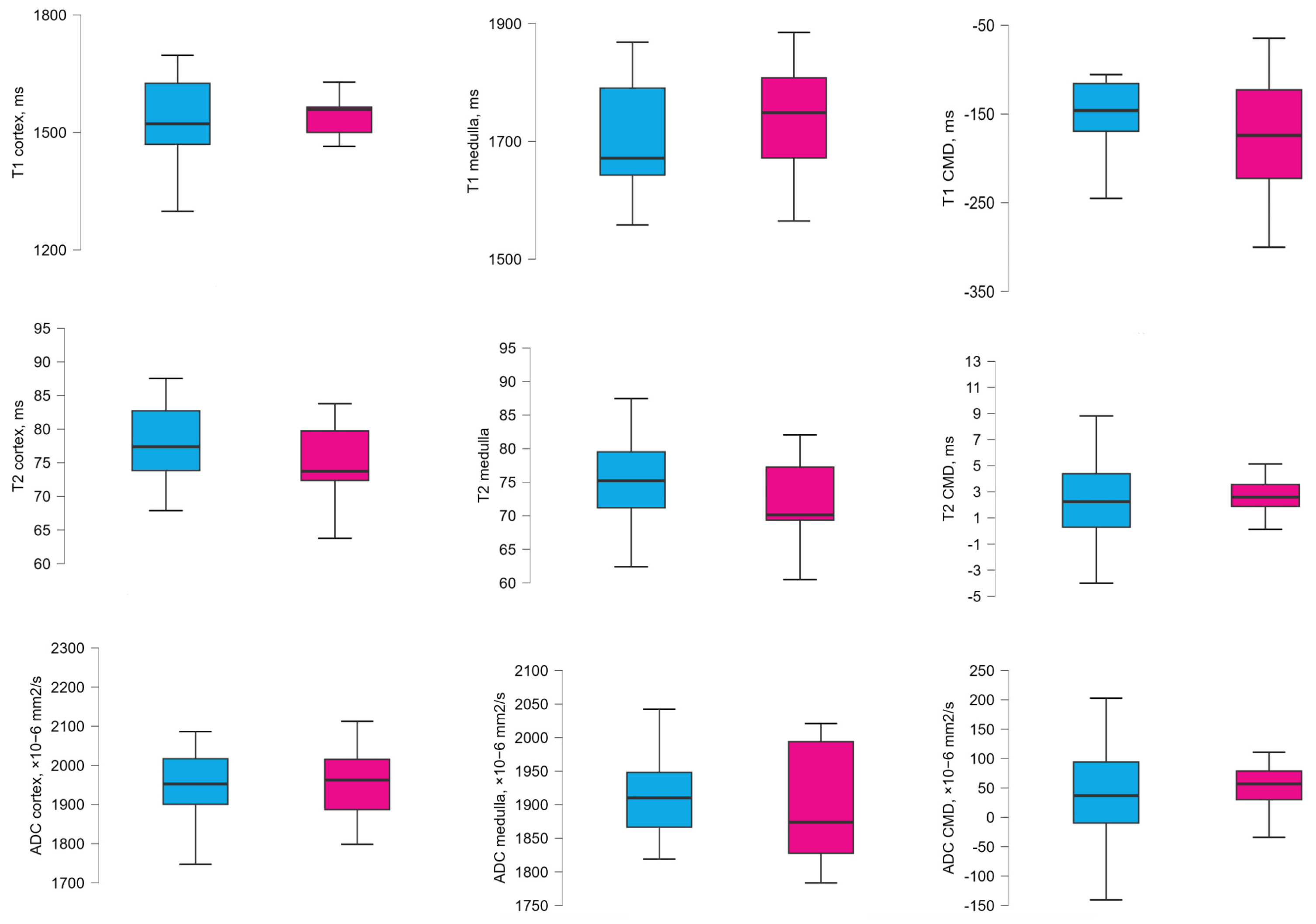
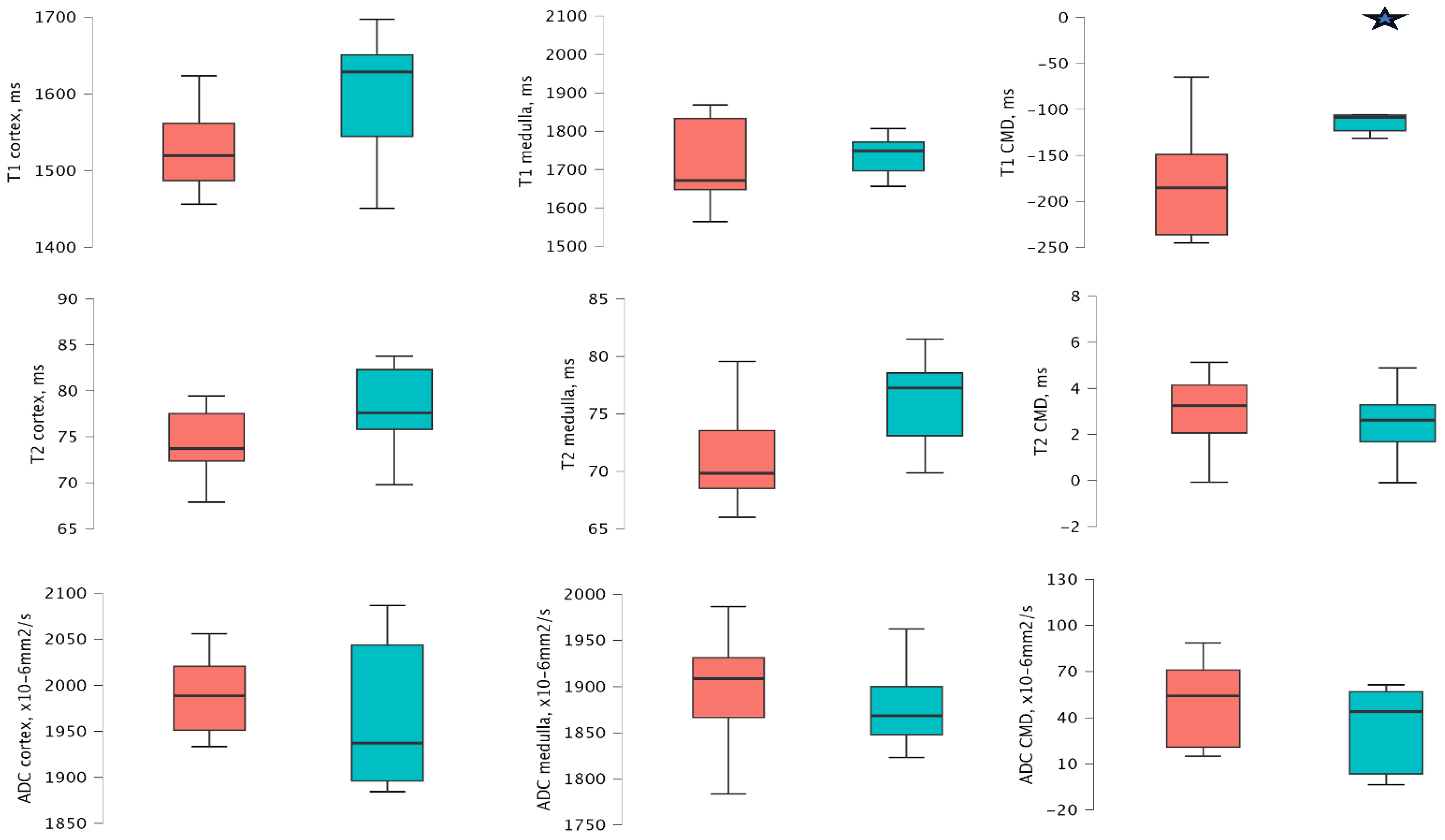
3.2. MRI Values According to the eGFR Groups 1 Year After Transplantation
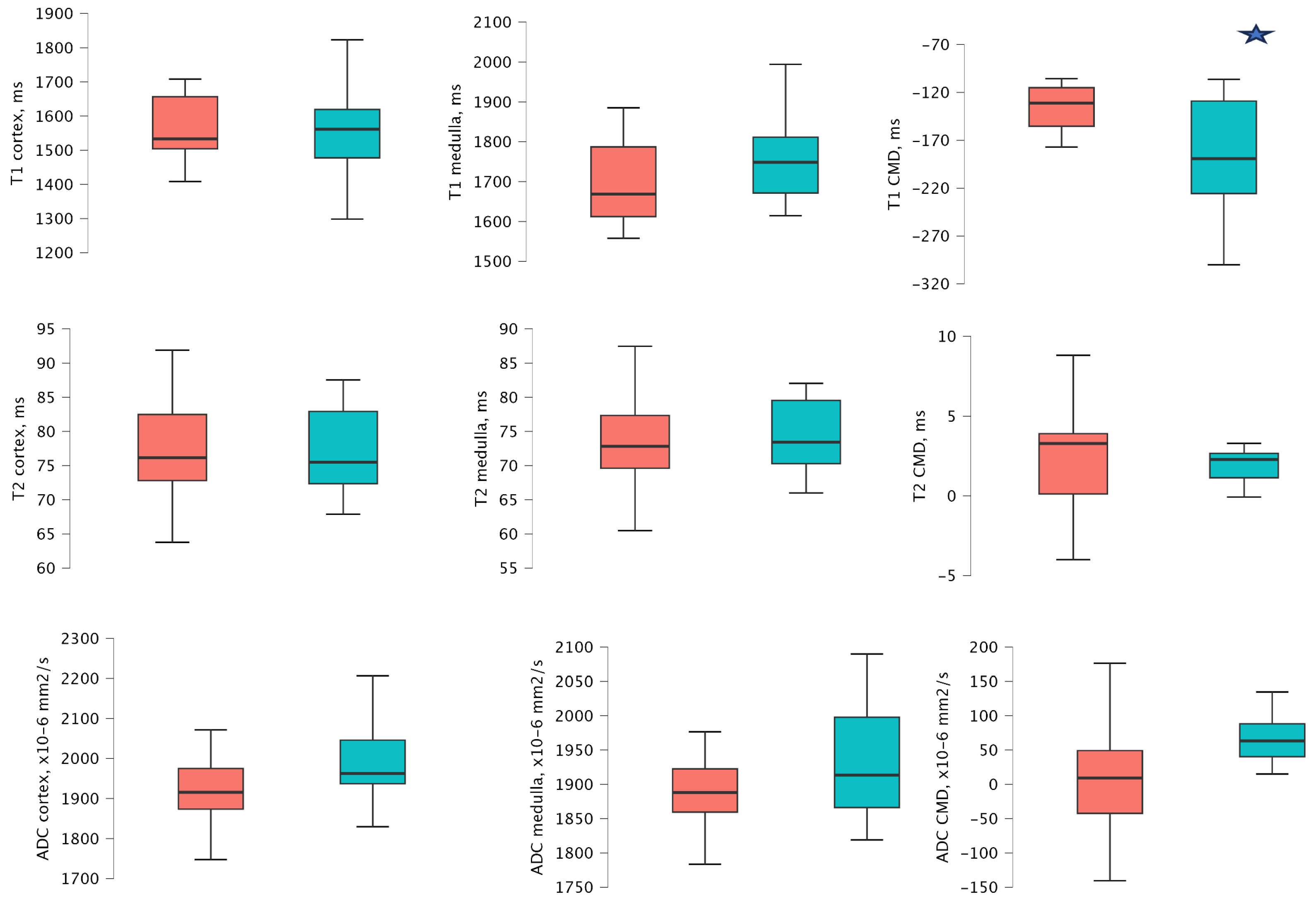
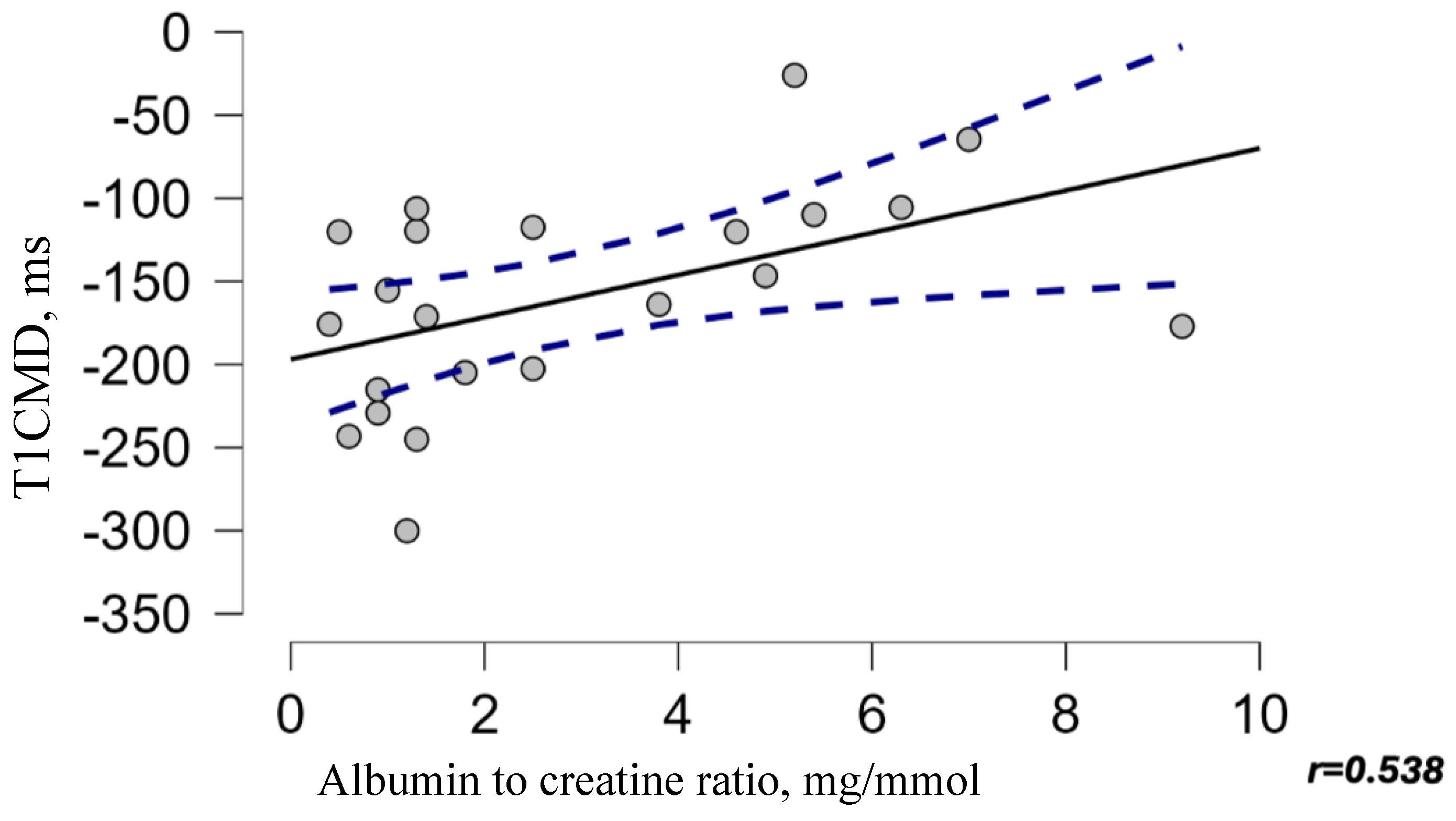
3.3. MRI Values According to the ACR Groups 1 Year After Transplantation
3.4. MRI Values According to the PCR Groups 1 Year After Transplantation
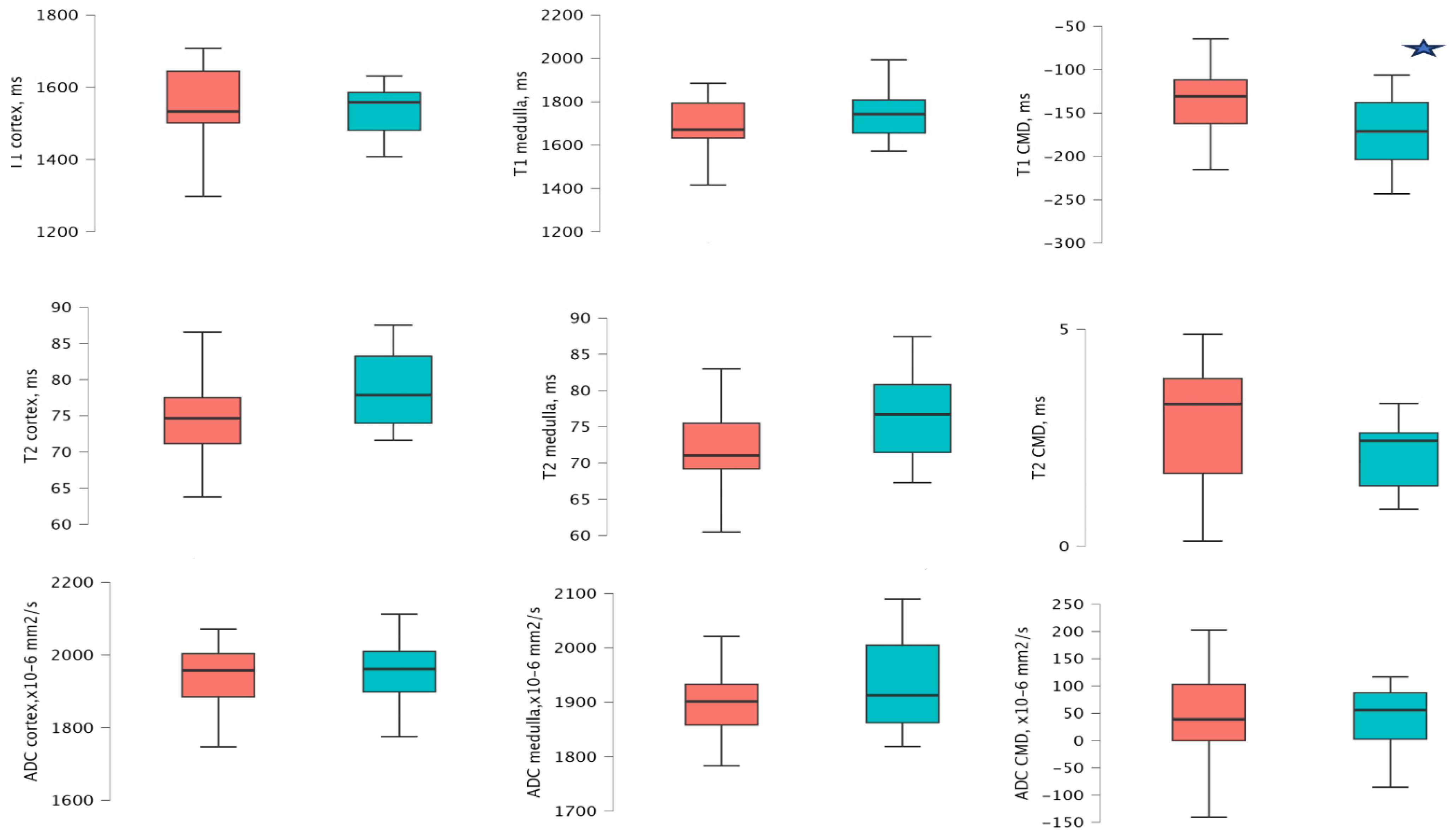
3.5. MRI Values According to the IF/TA Groups 1 Year After Transplantation
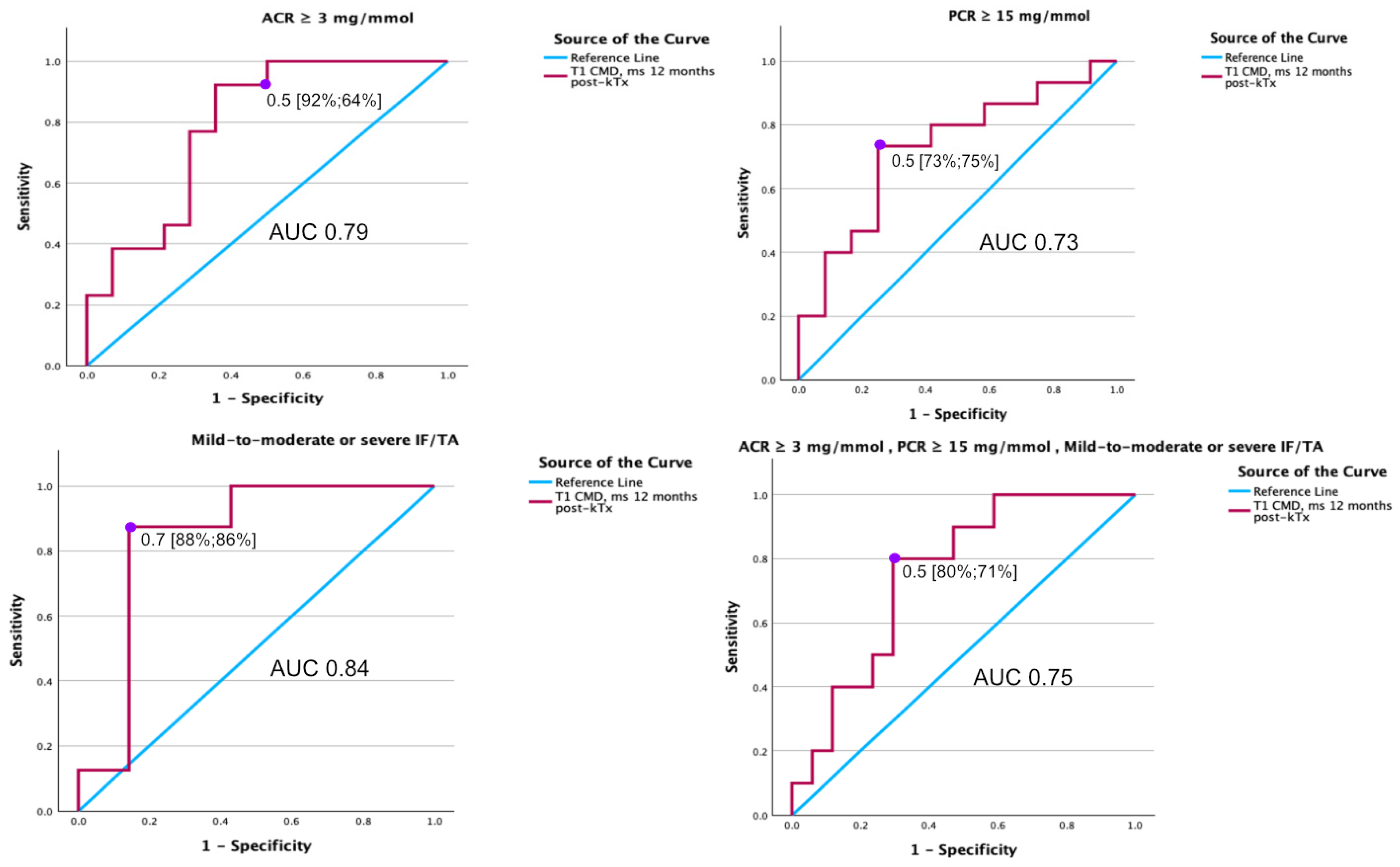
3.6. Diagnostic Value of MRI T1 Map Parameters for Detecting ACR, PCR, and IF/TA 1 Year After kTx
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| kTx | Kidney transplantation |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| IF/TA | Interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| ADC | The apparent diffusion coefficient |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| ARC | Albumin to creatinine ratio |
| PRC | Protein to creatinine ratio |
| PNF | Primary non-function |
| MRR | Magnetic resonance relaxometry |
| MOLLI | A modified Look–Locker inversion recovery |
| SSFP | A single-shot balanced steady-state free precession |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted imaging |
| CMD | Corticomedullary differentiation |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| CI | 95% confidence intervals |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) |
| ICC | The intraclass correlation coefficient |
Appendix A
| Characteristics | n (Pathology/Total) |
|---|---|
| History of acute and chronic recurrent pyelonephritis | 9/27 |
| Cytomegalovirus infection | 1/27 |
| Polyomavirus viremia | 3/27 |
| Hospital administration (another reasons) | 5/27 |
| Medication | |
| Renin–angiotensin system inhibitor | 3/27 |
| Angiotensin receptor blocker | 5/27 |
| Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor | 1/27 |
Appendix A.1. KTx Biopsy Evaluation
| 1 Year After kTx Biopsy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | N (Total/Pathology) | |
| Glomerular count | 30.40 (14.37) | 15/15 |
| Glomerular sclerosis, score | 1.00 (1.31) | 15/7 |
| Glomerulitis, score | 0.67 (0.82) | 15/7 |
| Inflammatory infiltrates | 0.00 (0.00) | 15/0 |
| Peritubulatcapillaritis, score | 0.20 (0.41) | 15/3 |
| Interstitial fibrosis, score | 0.80 (0.86) | 15/9 |
| Tubular atrophy, score | 0.87 (0.74) | 15/11 |
| Tubulitis, score | 0.13 (0.35) | 2/15 |
| Arteriolar hyalinosis, score | 0.66 (0.62) | 15/9 |
| IF/TA* score | 1.67 (1.54) | 15/11 |
Appendix B
Appendix B.1. Imagine Analyses
- Image analyses were independently conducted by a radiologist and a nephrologist. A comprehensive description of the methodology is provided in our previous publication [20]. The intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) assessing agreement between the two specialists for kidney transplants (kTx) at 1-year post-transplantation were as follows: T1 map, cortical: 0.971 (95% CI 0.920–0.988); medulla: 0.955 (95% CI 0.877–0.981) (p < 0.001).
- T2 map, cortical: 0.986 (95% CI 0.970–0.994); medulla: 0.979 (95% CI 0.943–0.991) (p < 0.001).
- ADC, cortical: 0.956 (95% CI 0.898–0.980); medulla: 0.866 (95% CI 0.709–0.938) (p < 0.001).
Appendix C
| eGFR ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recipients | n = 11 | n = 16 | |
| T1 map of cortex (ms) | 1558.53 (1497.45–1596.67) | 1522.00 (1469.68–1625.41) | 0.716 |
| T1 map of medulla (ms) | 1748.76 (1643.18–1833.32) | 1668.72 (1628.56–1787.13) | 0.451 |
| T1 map of CMD 1 (ms) | −171.19 (−215.87(–)−119.94) | −146.04 (−169.50(–)−115.59) | 0.544 |
| T2 map of cortex (ms) | 73.73 (72.37–79.72) | 77.39 (73.84–82.73) | 0.451 |
| T2 map of the medulla (ms) | 70.13 (69.36–77.24) | 75.22 (71.19–79.52) | 0.272 |
| T2 map of CMD 1 (ms) | 2.60 (1.88–3.56) | 2.24 (0.286–4.39) | 0.693 |
| ADC value of cortex (×10−6 mm2/s) | 1962.50 (1887.00–2015.50) | 1952.50 (1900.50–2016.88) | 0.824 |
| ADC value of medulla (×10−6 mm2/s) | 1874.00 (1827.75–1994.00) | 1910.25 (1866.63–1948.25) | 0.512 |
| ADC CMD 1 (×10−6 mm2/s) | 57.00 (30.00–79.00) | 37.00 (−9.63–94.38) | 0.521 |
Appendix D
| ACR < 3 mg/mmol | ACR ≥ 3 mg/mmol | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recipients | n = 14 | n = 13 | |
| T1 map of cortex (ms) | 1561.44 (1477.67–1619.28) | 1524.68 (1500.01–1651.92) | 0.905 |
| T1 map of medulla (ms) | 1743.02 (1665.90–1810.56) | 1666.02 (1572.19–1783.74) | 0.239 |
| T1 map of CMD 1 (ms) | −189.19 (−255.65(–)−129.01) | −130.55 (−146.69(–)−106.96) | 0.009 |
| T2 map of cortex (ms) | 75.50 (72.35–82.93) | 76.16 (72.81–82.48) | 0.981 |
| T2 map of the medulla (ms) | 73.43 (70.28–79.54) | 74.30 (69.83–77.59) | 0.943 |
| T2 map of CMD 1 (ms) | 2.43 (1.22–3.13) | 3.28 (0.12–3.90) | 0.961 |
| ADC value of cortex (×10−6 mm2/s) | 1962.50 (1937.70–2045.75) | 1915.50 (1873.50–1975.00) | 0.094 |
| ADC value of medulla (×10−6 mm2/s) | 1913.50 (1866.13–1997.75) | 1888.00 (1859.50–1922.50) | 0.239 |
| ADC CMD 1 (×10−6 mm2/s) | 63.25 (40.25–88.13) | 15.00 (−28.00–61.50) | 0.225 |
Appendix E
| PCR < 15 mg/mmol | PCR ≥ 15 mg/mmol | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recipients | n = 12 | n = 15 | |
| T1 map of cortex (ms) | 1561.44 (1484.73–1612.03) | 1524.68 (1478.14–1637.73) | 0.981 |
| T1 map of medulla (ms) | 1743.02 (1655.43–1808.87) | 1671.43 (1595.15–1790.52) | 0.373 |
| T1 map of CMD 1 (ms) | −173.49 (−210.95(–)−146.60) | −130.55 (−157.05(–)−108.44) | 0.047 |
| T2 map of cortex (ms) | 77.87 (73.97–83.25) | 75.56 (71.19–80.05) | 0.347 |
| T2 map of the medulla (ms) | 76.69 (71.46–80.82) | 71.34 (69.41–76.50) | 0.217 |
| T2 map of CMD 1 (ms) | 2.43 (1.06–2.82) | 3.28 (0.94–4.06) | 0.435 |
| ADC value of cortex (×10−6 mm2/s) | 1961.75 (1901.88–2063.63) | 1957.50 (1884.25–2003.50) | 0.510 |
| ADC value of medulla (×10−6 mm2/s) | 1912.50 (1862.88–2005.25) | 1901.50 (1858.50–1933.00) | 0.323 |
| ADC CMD 1 (×10−6 mm2/s) | 55.75 (2.75–87.38) | 39.00 (0.00–103.00) | 0.961 |
Appendix F
| No or Minimal Fibrosis/Tubular Atrophy | Mild-to-Moderate or Severe Fibrosis/Tubular Atrophy | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recipients | n = 7 | n = 8 | |
| T1 map of cortex (ms) | 1519.33 (1487.08–1561.66) | 1596.44 (1506.25–1640.87) | 0.336 |
| T1 map of medulla (ms) | 1671.43 (647.78–1833.32) | 1743.02 (1631.40–1769.20) | 0.536 |
| T1 map of CMD 1 (ms) | −215.16 (−244.14(–)−151.04) | −108.44 (−122.96(–)−106.10) | 0.029 |
| T2 map of cortex (ms) | 73.73 (72.37–77.52) | 77.39 (73.32–82.25) | 0.613 |
| T2 map of the medulla (ms) | 69.83 (68.51–73.55) | 75.78 (71.40–78.07) | 0.232 |
| T2 map of CMD 1 (ms) | 3.90 (2.24–4.68) | 2.63 (1.69–3.929) | 0.336 |
| ADC value of cortex (×10−6 mm2/s) | 1962.50 (1940.50–2018.75) | 1902.50 (1870.75–987.13) | 0.463 |
| ADC value of medulla (×10−6 mm2/s) | 1908.50 (1866.75–1931.00) | 1878.25 (1855.75–1924.63) | 0.867 |
| ADC CMD 1 (×10−6 mm2/s) | 69.50 (27.00–80.00) | 23.75 (−11.13–58.13) | 0.183 |
References
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Kidney Int. 2024, 105, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, G.A. Proteinuria in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Prevalence, Prognosis, and Evidence-Based Management. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 54, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gansevoort, R.T.; Matsushita, K.; Van Der Velde, M.; Astor, B.C.; Woodward, M.; Levey, A.S.; De Jong, P.E.; Coresh, J. Lower Estimated GFR and Higher Albuminuria are Associated with Adverse Kidney Outcomes. A Collaborative Meta-Analysis of General and High-Risk Population Cohorts. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.P.; Krzesinski, J.-M. Is Very Low Always Useful? The Case of Very Low-Grade Albuminuria in Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 769–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, D.; Pérez, G.; Marrero, D.; Porrini, E.; Rufino, M.; Manuel González-Posada, J.; Delgado, P.; Torres, A. Early Association of Low-Grade Albuminuria and Allograft Dysfunction Predicts Renal Transplant Outcomes. Transplantation 2012, 93, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucşa, C.; Ştefan, G.; Tacu, D.; Sinescu, I.; Sinescu, R.D.; Hârza, M. Does the KDIGO CKD Risk Stratification Based on GFR and Proteinuria Predict Kidney Graft Failure? Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copur, S.; Tanriover, C.; Yavuz, F.; Soler, M.J.; Ortiz, A.; Covic, A.; Kanbay, M. Novel Strategies in Nephrology: What to Expect from the Future? Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serón, D.; Moreso, F. Protocol Biopsies in Renal Transplantation: Prognostic Value of Structural Monitoring. Kidney Int. 2007, 72, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesens, M.; Roufosse, C.; Haas, M.; Lefaucheur, C.; Mannon, R.B.; Adam, B.A.; Aubert, O.; Böhmig, G.A.; Callemeyn, J.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.; et al. The Banff 2022 Kidney Meeting Report: Reappraisal of Microvascular Inflammation and the Role of Biopsy-Based Transcript Diagnostics. Am. J. Transplant. 2024, 24, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Nephrology Renal Research Report. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1886–1903. [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, M.L.; McCulloch, T.A.; Harper, S.J.; Wheatley, T.J.; Edwards, C.M.; Feehally, J.; Furness, P.N. Early Measurement of Interstitial Fibrosis Predicts Long-Term Renal Function and Graft Survival in Renal Transplantation. J. Br. Surg. 1996, 83, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosio, F.G.; Grande, J.P.; Wadei, H.; Larson, T.S.; Griffin, M.D.; Stegall, M.D. Predicting Subsequent Decline in Kidney Allograft Function from Early Surveillance Biopsies. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 2464–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Q.Y.; Lim, C.C.; Tan, H.Z.; Sultana, R.; Kee, T.; Htay, H. Complications of Percutaneous Kidney Allograft Biopsy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Transplantation 2022, 106, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, N.M.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Boor, P.; Combe, C.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Eikefjord, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, N.; Golay, X.; Gordon, I.; Grenier, N.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease: A Position Paper from the European Cooperation in Science and Technology Action PARENCHIMA. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, ii4–ii14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekkers, I.A.; De Boer, A.; Sharma, K.; Cox, E.F.; Lamb, H.J.; Buckley, D.L.; Bane, O.; Morris, D.M.; Prasad, P.V.; Semple, S.I.K.; et al. Consensus-Based Technical Recommendations for Clinical Translation of Renal T1 and T2 Mapping MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phy. 2020, 33, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljimani, A.; Caroli, A.; Laustsen, C.; Francis, S.; Mendichovszky, I.A.; Bane, O.; Nery, F.; Sharma, K.; Pohlmann, A.; Dekkers, I.A.; et al. Consensus-Based Technical Recommendations for Clinical Translation of Renal Diffusion-Weighted MRI. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phy. 2020, 33, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisinger, M.; Risius, B.; Jordan, M.; Zelch, M.; Novick, A.; George, C. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Renal Transplants. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1984, 143, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hricak, H.; Terrier, F.; Demas, B.E. Renal Allografts: Evaluation by MR Imaging. Radiology 1986, 159, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, B.; Nelson, R.; Ball, T.; Wyly, J.; Bourke, E.; Delaney, V.; Bernardino, M. MR Imaging of Renal Transplants. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1986, 147, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bura, A.; Stonciute-Balniene, G.; Banisauskaite, A.; Velickiene, L.; Bumblyte, I.A.; Jankauskas, A.; Vaiciuniene, R. Potential MRI Biomarkers for Predicting Kidney Function and Histological Damage in Transplanted Deceased Donor Kidney Recipients. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, I.; Crowe, L.A.; Berchtold, L.; Moll, S.; Hadaya, K.; De Perrot, T.; Vesin, C.; Martin, P.-Y.; De Seigneux, S.; Vallée, J.-P. New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Index for Renal Fibrosis Assessment: A Comparison between Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and T1 Mapping with Histological Validation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.C.; Bressem, K.K.; Scheibl, S.; Nunninger, M.; Gentsch, A.; Fahlenkamp, U.L.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Hamm, B.; Makowski, M.R. Multiparametric Assessment of Changes in Renal Tissue after Kidney Transplantation with Quantitative MR Relaxometry and Diffusion-Tensor Imaging at 3 T. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Li, J.; Wan, J.; Tian, Y.; Wu, P.; Xu, R.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, L.; Zhu, M. Arterial Spin Labeling Combined with T1 Mapping for Assessment of Kidney Function and Histopathology in Patients with Long-Term Renal Transplant Survival after Kidney Transplantation. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2024, 14, 2415–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ksas, M.; EL-Metwally, D.; Fahmy, D.; Shebel, H. Early and Late Assessment of Renal Allograft Dysfunction Using Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) and Diffusion-Weighted Imaging (DWI): A Prospective Study. Abdom. Radiol. 2024, 49, 3902–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Chung, M.-C.; Pan, K.-J.; Ho, H.-C.; Chen, H.-M.; Ouyang, Y.-C.; Shu, K.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Chai, J.-W. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion-Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Investigation of Delayed Graft Function Immediately after Kidney Transplantation. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 2832996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathys, C.; Blondin, D.; Wittsack, H.-J.; Miese, F.; Rybacki, K.; Walther, C.; Holstein, A.; Lanzman, R. T2’ Imaging of Native Kidneys and Renal Allografts—A Feasibility Study. Fortschr. Röntgenstr. 2011, 183, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.T.; Selby, N.M.; Taal, M.W. Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Evaluate Kidney Structure, Function, and Pathology: Moving Toward Clinical Application. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 82, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberger, U.; Thoeny, H.C.; Binser, T.; Gugger, M.; Frey, F.J.; Boesch, C.; Vermathen, P. Evaluation of Renal Allograft Function Early after Transplantation with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Ren, T.; Li, Q.; Zuo, P.; Long, M.; Mo, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Shen, W. Assessment of Renal Allograft Function Early after Transplantation with Isotropic Resolution Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzman, R.S.; Ljimani, A.; Pentang, G.; Zgoura, P.; Zenginli, H.; Kröpil, P.; Heusch, P.; Schek, J.; Miese, F.R.; Blondin, D.; et al. Kidney Transplant: Functional Assessment with Diffusion-Tensor MR Imaging at 3T. Radiology 2013, 266, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sułkowska, K.; Palczewski, P.; Furmańczyk-Zawiska, A.; Perkowska-Ptasińska, A.; Wójcik, D.; Szeszkowski, W.; Durlik, M.; Gołębiowski, M.; Małkowski, P. Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Assessment of Renal Function and Parenchymal Changes in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Preliminary Study. Ann. Transpl. Transplant. 2020, 25, e920232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, I.; Crowe, L.A.; De Perrot, T.; Berchtold, L.; Martin, P.; De Seigneux, S.; Vallée, J. Comparison of Readout-segmented and Conventional Single-shot for Echo-planar Diffusion-weighted Imaging in the Assessment of Kidney Interstitial Fibrosis. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Shang, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Gu, H.; Dou, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Native T1 Mapping in Assessing Kidney Fibrosis for Patients With Chronic Glomerulonephritis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 772326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.J.; Kamel, I.R.; Macura, K.J.; Bluemke, D.A. 3.0-T MR Imaging of the Abdomen: Comparison with 1.5 T. RadioGraphics 2008, 28, 1983–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Kozawa, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Fukaya, D.; Amano, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Tomori, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Niitsu, M.; Okada, H. Comparison of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Sequences with Laboratory Parameters for Prognosticating Renal Function in Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.; Aslam, I.; Crowe, L.; Pruijm, M.; De Perrot, T.; De Seigneux, S.; Vallée, J.-P.; Berchtold, L. T1 Mapping Magnetic Resonance Imaging Predicts Decline of Kidney Function. Clin. Kidney J. 2025, 18, sfaf032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.; Mahmoud, H.; Cox, E.; Noble, R.; Prestwich, B.; Kasmi, I.; Taal, M.W.; Francis, S.; Selby, N.M. Multiparametric MRI Assessment of Renal Structure and Function in Acute Kidney Injury and Renal Recovery. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Ding, Y.; Ding, X.; Fu, C.; Cao, B.; Nickel, D.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, M. Value of T1 Mapping in the Non-Invasive Assessment of Renal Pathologic Injury for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2025, 24, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, I.; Baid-Agrawal, S.; Unwin, R.; Morell, A.; Johansson, L.; Hockings, P.D. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Clinical Trials of Diabetic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverria-Chasco, R.; Martin-Moreno, P.L.; Aramendía-Vidaurreta, V.; Garcia-Ruiz, L.; Mora-Gutiérrez, J.M.; Vidorreta, M.; Villanueva, A.; Cano, D.; Bastarrika, G.; Garcia-Fernandez, N.; et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of Multiparametric Renal MRI in Kidney Transplant Patients. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 60, 1650–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.E.; Mahmoud, H.; Cox, E.F.; McCulloch, T.; Prestwich, B.L.; Taal, M.W.; Selby, N.M.; Francis, S.T. Quantitative Assessment of Renal Structural and Functional Changes in Chronic Kidney Disease Using Multi-Parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, M.; Ding, Y.; Qu, L.; Chen, C.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, C.; Gu, F. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for the Assessment of Renal Fibrosis of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Preliminary Study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck-Tölly, A.; Eder, M.; Beitzke, D.; Eskandary, F.; Agibetov, A.; Lampichler, K.; Hamböck, M.; Regele, H.; Kläger, J.; Nackenhorst, M.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Evaluation of Interstitial Fibrosis in Kidney Allografts. Transplant. Direct 2020, 6, e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhove, T.; Goldschmeding, R.; Kuypers, D. Kidney Fibrosis: Origins and Interventions. Transplantation 2017, 101, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffield, J.S. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms in Kidney Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.-G.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Tu, J.; Pan, P.; Ma, Q.; Wei, L.-Y.; Zhao, W.-L.; Shen, J.-K. Native T1 Mapping for Non-Invasive Quantitative Evaluation of Renal Function and Renal Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 5058–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhou, F.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pylypenko, D.; Yuan, L. Native T1-Mapping as a Predictor of Progressive Renal Function Decline in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchtold, L.; Friedli, I.; Crowe, L.A.; Martinez, C.; Moll, S.; Hadaya, K.; De Perrot, T.; Combescure, C.; Martin, P.-Y.; Vallée, J.-P.; et al. Validation of the Corticomedullary Difference in Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Derived Apparent Diffusion Coefficient for Kidney Fibrosis Detection: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, I.; Aamir, F.; Kassai, M.; Crowe, L.A.; Poletti, P.-A.; Seigneux, S.D.; Moll, S.; Berchtold, L.; Vallée, J.-P. Validation of Automatically Measured T1 Map Cortico-Medullary Difference (ΔT1) for eGFR and Fibrosis Assessment in Allograft Kidneys. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0277277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Recipients | One Year After Transplant |
|---|---|
| n = 27 | |
| Gender male (%) | 18 (66.70) |
| Age (years) | 43.00 (34.00–55.00) |
| Duration of kidney replacement therapy (months) | 16.00 (6.00–43.00) |
| HLA mismatch | 3 (3–4) |
| Kidney disease (%) | Chronic glomerulonephritis: 4 case (14.8%) Diabetic nephropathy: 1 case (3.7%) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: 4 cases (14.8%) Hypertensive nephropathy: 2 cases (7.4%) Other: 16 cases (59.3%) |
| Immunosuppression regimen | Methylprednisolone: 100% Mycophenolate mofetil: 100% Tacrolimus: 100% Induction therapy: Anti-thymocyte globulin: 3 cases (11.1%) INN-basiliximab: 24 cases (88.9%) |
| Creatinine before kTx (μmol/L) | 738.00 (507.00–952.00) |
| eGFR at discharge day (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 61.00 (46.00–79.00) |
| eGFR at 3 months post kTx (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 49.10 (45.40–68.10) |
| eGFR at 12 months post kTx (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 57.90 (49.70–68.40) |
| Albumin to creatinine ratio at 12 months post kTx (mg/mmol) | 2.50 (1.20–6.30) |
| Protein to creatinine ratio at 12 months post kTx (mg/mmol) | 15.70 (9.20–29.20) |
| Donors | |
| Age (years) | 54.00 (46.00–61.00) |
| Expanded criteria donor 1 (%) | 10 (37.00) |
| Cold ischemia time of transplanted kidney (min) | 720 (656.00–900.00) |
| MRI Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACR ≥ 3 mg/mmol | |||||
| AUC | Cl I95%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | p-value | |
| T1 cortex | 0.52 | 0.287–0.746 | 0.888 | ||
| T1 medulla | 0.36 | 0.148–0.577 | 0.209 | ||
| T1 CMD | 0.79 | 0.618–0.965 | 92 | 64 | 0.001 |
| PCR ≥ 15 mg/mmol | |||||
| T1 cortex | 0.50 | 0.269–0.719 | 0.961 | ||
| T1 medulla | 0.40 | 0.178–0.611 | 0.339 | ||
| T1 CMD | 0.73 | 0.533–0.923 | 73 | 75 | 0.022 |
| Mild-to-moderate or severe IF/TA | |||||
| T1 cortex | 0.66 | 0.360–0.961 | 0.295 | ||
| T1 medulla | 0.39 | 0.080–0.705 | 0.502 | ||
| T1 CMD | 0.84 | 0.601–1.077 | 88 | 86 | 0.005 |
| ACR ≥ 3 mg/mmol PCR ≥ 15 mg/mmol mild-to-moderate or severe IF/TA | |||||
| T1 cortex | 0.62 | 0.379–9.856 | 0.333 | ||
| T1 medulla | 0.48 | 0.247–0.718 | 0.883 | ||
| T1 CMD | 0.75 | 0.570–0.936 | 80 | 71 | 0.007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bura, A.; Stonciute-Balniene, G.; Velickiene, L.; Bumblyte, I.A.; Vaiciuniene, R.; Jankauskas, A. The Possibilities of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Reflect Functional and Structural Graft Changes 1 Year After Kidney Transplantation. Medicina 2025, 61, 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071268
Bura A, Stonciute-Balniene G, Velickiene L, Bumblyte IA, Vaiciuniene R, Jankauskas A. The Possibilities of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Reflect Functional and Structural Graft Changes 1 Year After Kidney Transplantation. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071268
Chicago/Turabian StyleBura, Andrejus, Gintare Stonciute-Balniene, Laura Velickiene, Inga Arune Bumblyte, Ruta Vaiciuniene, and Antanas Jankauskas. 2025. "The Possibilities of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Reflect Functional and Structural Graft Changes 1 Year After Kidney Transplantation" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071268
APA StyleBura, A., Stonciute-Balniene, G., Velickiene, L., Bumblyte, I. A., Vaiciuniene, R., & Jankauskas, A. (2025). The Possibilities of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Reflect Functional and Structural Graft Changes 1 Year After Kidney Transplantation. Medicina, 61(7), 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071268






