Prognostic Value of Blood Urea Nitrogen to Albumin Ratio in Elderly Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
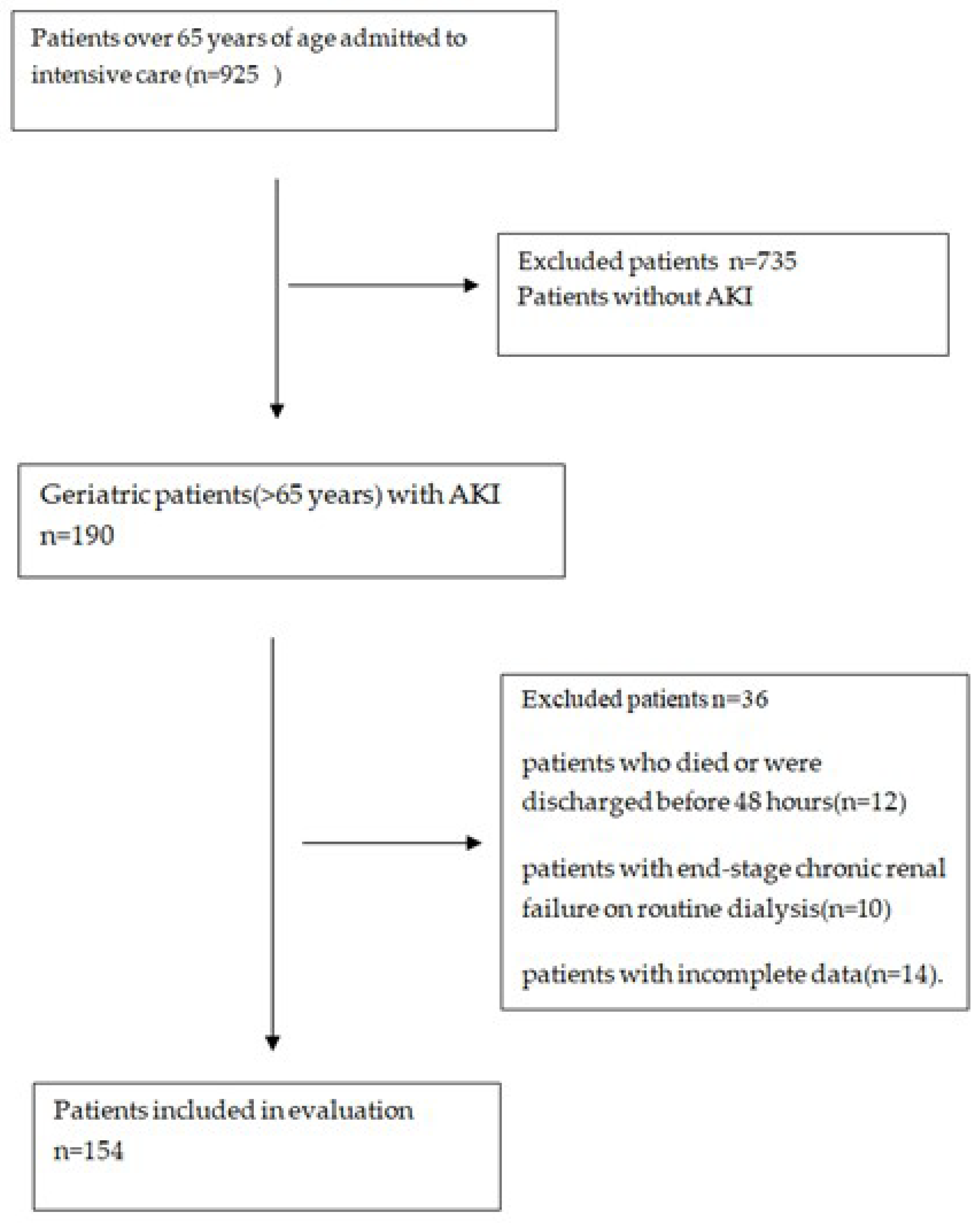
2.1. Study Design and Patient Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| GCS | Glasgow Coma Scale |
| APACHE II | Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation |
| RRT | Renal replacement therapy |
| MV | Mechanical ventilation |
| LOS | Length of stay |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| LDH | Lactic dehydrogenase |
| Crp | C-reactive protein |
| APTT | Activated partial thromboplastin time |
| INR | International normalized ratio |
| BAR | BUN/albumin |
References
- Kellum, J.A.; Romagnani, P.; Ashuntantang, G.; Ronco, C.; Zarbock, A.; Anders, H.J. Acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, S.A.; Long, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chertow, G.M. Cost of acute kidneyinjury in hospitalized patients. J. Hosp. Med. 2017, 12, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Muller, J.; de Heer, G.; Braune, S.; Fuhrmann, V.; Kluge, S. Clinical characteristics and outcome of very elderly patients ≥90 years in intensive care: A retrospective observational study. Ann. Intensive Care 2015, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane-Gill, S.L.; Sileanu, F.E.; Murugan, R.; Trietley, G.S.; Handler, S.M.; Kellum, J.A. Risk factors for acute kidney injury in older adults with critical illness: A retrospective cohort study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Lv, D. Prognostic value of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio for mortality in acute kidney injury. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Lai, Q.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Kang, H.; Wang, H.; Liao, D. Prognostic implication of lactic dehydrogenase-to-albumin ratio in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2023, 27, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, R.W.; Zolfaghari, P.; Wan, Y.; Pearse, R.M.; Puthucheary, Z.; Prowle, J.R. Elevated urea-to-creatinine ratio provides a biochemical signature of muscle catabolism and persistent critical illness after major trauma. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 1718–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, D.H.; Sullivan, S.C.; Bopp, M.M.; Roberson, P.K.; Lensing, S.Y. BUN as an Independent Predictor of Post-Hospital-Discharge Mortality among Older Veterans. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belinskaia, D.A.; Voronina, P.A.; Shmurak, V.I.; Jenkins, R.O.; Goncharov, N.V. Serum Albumin in Health and Disease: Esterase, Antioxidant, Transporting and Signaling Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Robinson, R. Low serum albumin and total lymphocyte count as predictors of 30 day hospital readmission in patients 65 years of age or older. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, F.; Wang, R.; Lu, W.; Hu, H.; Li, Z.; Shui, H. Prognostic value of blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio for acute kidney injury and in-hospital mortality in intensive care unit patients with intracerebral haemorrhage: A retrospective cohort study using the MIMIC-IV database. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e069503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi, Y.; Duan, H.; Liu, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y. Blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio is associated with all-cause mortality in patients with AKI: A cohort study. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1353956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bae, S.J.; Kim, K.; Yun, S.J.; Lee, S.H. Predictive performance of blood urea nitrogen to serum albumin ratio in elderly patients with gastrointestinal bleeding. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 41, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acehan, S. Acute kidney injury and COVID-19: The predictive power of BUN/albumin ratio for renal replacement therapy requirement. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 193, 3015–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, I.; Gameiro, J.; Resina, C.; Outerelo, C. In-hospital mortality in elderly patients with acute kidney injury requiring dialysis: A cohort analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akposso, K.; Hertig, A.; Couprie, R.; Flahaut, A.; Alberti, C.; Karras, G.A.; Haymann, J.P.; Costa De Beauregard, M.A.; Lahlou, A.; Rondeau, E.; et al. Acute renal failure in patients over 80 years old: 25-years’ experience. Intensive Care Med. 2000, 26, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, H.S.; Bhat, A.; Aravindan, A.N.; Sud, K.; Jha, V.; Gupta, K.L.; Sakhuja, V. Predictors of mortality in elderly patients with acute renal failure in a developing country. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2007, 39, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhong, L.; Lu, J.; Hu, B.; Shen, Q.; Gao, P. Clinical significance of the lactate-to-albumin ratio on prognosis in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2350238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ding, F.; Gu, Y. Elderly patients with acute kidney injury (AKI): Clinical features and risk factors for mortality. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 54, e47–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Min, J.; Lu, J.; Zhong, L.; Luo, H. Association between lactate/albumin ratio and prognosis in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2374451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kazory, A. Emergence of blood urea nitrogen as a biomarker of neurohormonal activation in heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 106, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Lin, Y.R.; Zhao, L.L.; Yang, W.C.; Chang, Y.J.; Wu, H.P. Clinical factors in predicting acute renal failure caused by rhabdomyolysis in the ED. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 31, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, M.; Rondeau, P.; Singh, N.R.; Tarnus, E.; Bourdon, E. The antioxidant properties of serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Don, B.R.; Kaysen, G. Serum albumin: Relationship to inflammation and nutrition. Semin. Dial. 2004, 17, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artero, A.; Zaragoza, R.; Camarena, J.J.; Sancho, S.; González, R.; Nogueira, J.M. Prognostic factors of mortality in patients with community-acquired bloodstream infection with severe sepsis and septic shock. J. Crit. Care 2010, 25, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; Dubois, M.J.; Navickis, R.J.; Wilkes, M.M. Hypoalbuminemia in acute illness: Is there a rationale for intervention? A meta-analysis of cohort studies and controlled trials. Ann. Surg. 2003, 237, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Contreras, A.M.; Ramírez, M.; Cueva, L.; Alvarez, S.; de Loza, R.; Gamba, G. Low serum albumin and the increased risk of amikacin nephrotoxicity. Rev. Invest. Clin. 1994, 46, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murashima, M.; Nishimoto, M.; Kokubu, M.; Hamano, T.; Matsui, M.; Eriguchi, M.; Samejima, K.I.; Akai, Y.; Tsuruya, K. Inflammation as a predictor of acute kidney injury and mediator of higher mortality after acute kidney injury in non-cardiac surgery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wiedermann, C.J.; Wiedermann, W.; Joannidis, M. Hypoalbuminemia and acute kidney injury: A meta-analysis of observational clinical studies. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Han, T.; Cheng, T.; Liao, Y.; Tang, S.; Liu, B.; He, Y.; Gu, Z.; Lei, C.; Cao, Y.; Cao, Y. Analysis of the Value of the Blood Urea Nitrogen to Albumin Ratio as a Predictor of Mortality in Patients with Sepsis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dundar, Z.D.; Kucukceran, K.; Ayranci, M.K. Blood urea nitrogen to albumin ratio is a predictor of in-hospital mortality in older emergency department patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 46, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Peng, Y.; Ni, H.; Lin, L.; Luo, B.; Huang, X.; Chen, L.; Lin, Y. Blood-urea-nitrogen-to-serum-albumin ratio in predicting the value of patients with contrast-induced nephropathy for coronary heart disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2024, 56, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Duan, Q.; Ge, P.; Shao, Y. Elevated Blood Urea Nitrogen to Serum Albumin Ratio Is an Adverse Prognostic Predictor for Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 888736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, W.; Dong, S.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yao, L.; Li, Q.; Qin, Z.; Wang, T. Blood urea nitrogen-to-albumin ratio independently predicts 30-day mortality in acute respiratory failure patients: A retrospective cohort study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 4892–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, J.; Peng, J.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, L. Association Between Blood Urea Nitrogen to Serum Albumin Ratio and Mortality in Critically Ill Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Retrospective Study. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2025, 20, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- He, T.; Li, G.; Xu, S.; Guo, L.; Tang, B. Blood Urea Nitrogen to Serum Albumin Ratio in the Prediction of Acute Kidney Injury of Patients with Rib Fracture in Intensive Care Unit. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 154) | Survivors (n = 86) | Non-Survivors (n = 68) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical parameter, (mean ± SD), n (%) | ||||
| Age (years) | 76.76 ± 7.28 | 76.66 ± 6.92 | 76.88 ± 7.77 | 0.853 |
| Gender (male) | 77 (50%) | 41 (47.67%) | 36 (52.94%) | 0.516 |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 57 (37.01%) | 36 (41.86%) | 21 (30.88%) | 0.161 |
| Hypertension | 76 (49.35%) | 44 (51.16%) | 32 (47.06%) | 0.613 |
| Heart disease | 65 (42.21%) | 39 (45.35%) | 26 (38.24%) | 0.375 |
| Lung disease | 33 (21.43%) | 24 (27.91%) | 9 (13.24%) | 0.028 |
| Liver disease | 3 (1.95%) | 1 (1.16%) | 2 (2.94%) | 0.428 |
| Neurological diseases | 34 (22.08%) | 16 (18.6%) | 18 (26.47%) | 0.243 |
| Malignancy | 14 (9.09%) | 7 (8.14%) | 7 (10.29%) | 0.644 |
| Other | 5 (3.25%) | 3 (3.49%) | 2 (2.94%) | 0.849 |
| Clinical scores, (mean ± SD) | ||||
| GCS | 11.87 ± 3.78 | 13.83 ± 1.88 | 9.4 ± 4.13 | <0.001 |
| APACHE II | 20.79 ± 8.73 | 17.12 ± 6.51 | 25.43 ± 9.02 | <0.001 |
| Treatments/examination, n (%) | ||||
| Oliguria (first day) | 69 (44.81%) | 26 (30.23%) | 43 (63.24%) | <0.001 |
| Diuretic use | 71 (46.1%) | 33 (38.37%) | 38 (55.88%) | 0.030 |
| RRT used [n (%)] | 24 (15.58%) | 5 (5.81%) | 19 (27.94%) | <0.001 |
| Vasopressor requirement | 60 (38.96%) | 3 (3.49%) | 57 (83.82%) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis | 56 (36.36%) | 17 (19.77%) | 39 (57.35%) | <0.001 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 74 (48.05%) | 7 (8.14%) | 67 (98.53%) | <0.001 |
| Treatments/examination, (mean ± SD) | ||||
| ICU LOS (day) | 12.71 ± 14.79 | 9.44 ± 10.62 | 16.85 ± 18.04 | 0.092 |
| Hospital LOS (day) | 16.9 ± 16.14 | 15.34 ± 13.5 | 18.88 ± 18.88 | 0.940 |
| Laboratory parameters, (mean ± SD) | ||||
| WBC | 15.8 ± 8.86 | 15.72 ± 9.67 | 15.9 ± 7.79 | 0.898 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 11.92 ± 10.61 | 10.95 ± 2.48 | 13.13 ± 15.7 | 0.497 |
| Platelet | 257.51 ± 124.58 | 261.37 ± 123.25 | 252.63 ± 127 | 0.667 |
| RDW-SD | 51.73 ± 8.95 | 51.07 ± 9.11 | 52.57 ± 8.73 | 0.233 |
| RDW-CV | 16.81 ± 3.01 | 16.68 ± 2.98 | 16.97 ± 3.05 | 0.637 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 57.38 ± 43.5 | 53.08 ± 48.17 | 62.82 ± 36.37 | 0.013 |
| Creatinine (umol/L) | 2.25 ± 1.35 | 2.08 ± 0.93 | 2.46 ± 1.73 | 0.154 |
| Glucose (md/dL) | 177.86 ± 86.65 | 174.23 ± 84.92 | 182.46 ± 89.2 | 0.560 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 138.69 ± 7.29 | 137.86 ± 5.98 | 139.75 ± 8.6 | 0.126 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.67 ± 0.91 | 4.75 ± 0.93 | 4.58 ± 0.9 | 0.267 |
| Magnesium (mmol/L) | 1.94 ± 0.41 | 1.89 ± 0.39 | 2.02 ± 0.42 | 0.072 |
| Phosphate (mmol/L) | 4.09 ± 1.88 | 3.65 ± 1.2 | 4.71 ± 2.45 | 0.010 |
| LDH | 452.46 ± 574.04 | 419.29 ± 670.24 | 494.41 ± 423.52 | 0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 31.54 ± 6.11 | 32.93 ± 5.81 | 29.77 ± 6.07 | 0.001 |
| C-Reactive protein (mg/dL) | 97.13 ± 81.12 | 83.75 ± 75.61 | 114.05 ± 85.17 | 0.004 |
| APTT | 30.39 ± 12.31 | 29.35 ± 12.56 | 31.69 ± 11.95 | 0.025 |
| INR | 1.45 ± 0.65 | 1.39 ± 0.55 | 1.54 ± 0.76 | 0.007 |
| Lactate (mg/dL) | 2.8 ± 2.24 | 2.43 ± 1.8 | 3.26 ± 2.63 | 0.060 |
| Bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 21.36 ± 12.23 | 21.01 ± 4.34 | 21.81 ± 17.81 | 0.720 |
| Bun/albumin | 1.93 ± 1.45 | 1.68 ± 1.44 | 2.25 ± 1.42 | 0.015 |
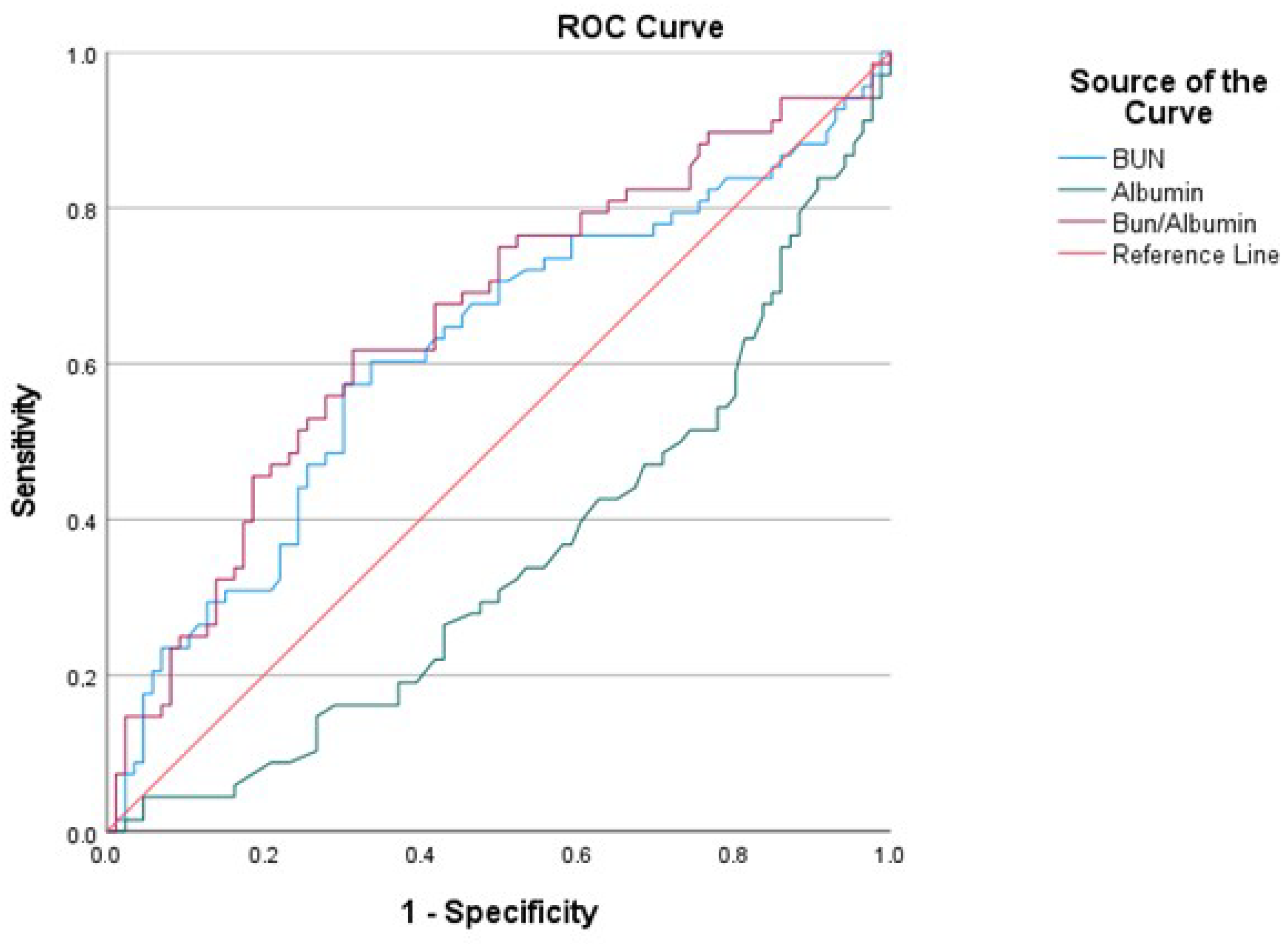
| AUC | SE | %95 CI (Lower–Upper) | Cut-Off | Sensitivity | Specificity | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BUN | 0.617 | 0.047 | 0.525–0.708 | 48.4 | 0.6029 | 0.5930 | 0.013 |
| Albumin | 0.651 | 0.044 | 0.564–0.738 | 31.5 | 0.6047 | 0.6029 | 0.001 |
| Bun/albumin | 0.655 | 0.045 | 0.567–0.743 | 1.507 | 0.6176 | 0.6163 | 0.001 |
| Characteristics | BAR < 1.507 (n = 79) | BAR ≥ 1.507 (n = 75) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical parameters, (mean ± SD), n (%) | |||
| Age (years) | 76.32 ± 6.57 | 77.21 ± 7.97 | 0.566 |
| Gender (male) | 41 (52.56%) | 36 (47.37%) | 0.872 |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 30 (38.46%) | 27 (35.53%) | 0.357 |
| Hypertension | 45 (57.69%) | 31 (40.79%) | 0.004 |
| Heart disease | 29 (37.18%) | 36 (47.37%) | 0.444 |
| Lung disease | 18 (23.08%) | 15 (19.74%) | 0.978 |
| Liver disease | 1 (1.28%) | 2 (2.63%) | 0.530 |
| Neurological diseases | 14 (17.95%) | 20 (26.32%) | 0.181 |
| Malignancy | 6 (7.69%) | 8 (10.53%) | 0.221 |
| Other | 3 (3.85%) | 2 (2.63%) | 0.692 |
| Clinical scores, (mean ± SD) | |||
| GCS | 12.05 ± 3.96 | 11.68 ± 3.6 | 0.157 |
| APACHE 2 | 18.49 ± 7.9 | 23.14 ± 8.97 | <0.001 |
| Treatments/examination, n (%) | |||
| Oliguria (first day) | 29 (37.18%) | 40 (52.63%) | 0.006 |
| Diuretic use | 35 (44.87%) | 36 (47.37%) | 0.646 |
| RRT used | 8 (10.26%) | 16 (21.05%) | 0.005 |
| Vasopressor requirement | 24 (30.77%) | 36 (47.37%) | 0.010 |
| Sepsis | 26 (33.33%) | 30 (39.47%) | 0.024 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 31 (39.74%) | 43 (56.58%) | 0.025 |
| Treatments/examination, (mean ± SD) | |||
| ICU LOS (day) | 12.67 ± 14.94 | 12.76 ± 14.74 | 0.533 |
| Hospital LOS (day) | 17.38 ± 16.29 | 16.41 ± 16.07 | 0.775 |
| Laboratory parameters, (mean ± SD) | |||
| WBC | 15.47 ± 8.96 | 16.14 ± 8.81 | 0.765 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 11.33 ± 2.37 | 12.52 ± 14.94 | 0.684 |
| Platelet | 259.92 ± 122.68 | 255.04 ± 127.27 | 0.714 |
| RDW-SD | 50.03 ± 7.37 | 53.47 ± 10.08 | 0.005 |
| RDW-CV | 16.19 ± 2.37 | 17.44 ± 3.44 | 0.002 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 35.17 ± 8.33 | 80.19 ± 52.42 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (umol/L) | 1.72 ± 0.57 | 2.8 ± 1.67 | <0.001 |
| Glucose (md/dL) | 180.42 ± 86.78 | 175.24 ± 87.01 | 0.161 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 138.69 ± 6.67 | 138.7 ± 7.92 | 0.471 |
| Potassium (mmol/l) | 4.46 ± 0.87 | 4.9 ± 0.91 | 0.024 |
| Magnesium (mmol/L) | 1.86 ± 0.33 | 2.03 ± 0.46 | 0.004 |
| Phosphate (mmol/L) | 3.72 ± 1.77 | 4.45 ± 1.94 | 0.020 |
| LDH | 454.62 ± 655.02 | 450.25 ± 481.37 | 0.939 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 33.29 ± 5.32 | 29.73 ± 6.38 | <0.001 |
| C-Reactive protein (mg/dL) | 81.98 ± 63.83 | 112.67 ± 93.58 | 0.001 |
| APTT | 28.44 ± 6.78 | 32.38 ± 15.94 | 0.039 |
| INR | 1.36 ± 0.46 | 1.56 ± 0.79 | 0.036 |
| Lactate (mg/dL) | 2.83 ± 2.27 | 2.76 ± 2.22 | 0.505 |
| Bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 21.37 ± 5.23 | 21.36 ± 16.64 | 0.723 |
| MORTALITY | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survival | Ex | p | ||
| n (%) | n (%) | |||
| BUN | ≥48.4 | 35 (40.7%) | 41 (60.29%) | 0.016 |
| Albumin | ≥31.5 | 52 (60.47%) | 27 (39.71%) | 0.010 |
| Bun/albumin | ≥1.507 | 33 (38.37%) | 42 (61.76%) | 0.004 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (95%CI) | p | RR (95%CI) | p | R2 | |
| BUN < 48.4 vs. BUN ≥ 48.4 | 2.213 (1.156–4.234) | 0.016 | - | - | 0.898 |
| Albumin ≥ 31.5 vs. albumin < 31.5 | 2.322 (1.212–4.450) | 0.011 | - | - | |
| Bun/albumin < 1.507 vs. Bun/albumin ≥ 1.507 | 2.594 (1.349–4.991) | 0.004 | 3.944 (1.483–23.790) | 0.023 | |
| Lung disease, yes vs. none | 2.538 (1.091–5.917) | 0.031 | - | - | |
| Oliguria (first day), none vs. yes | 3.969 (2.002–7.791) | <0.001 | - | - | |
| Diuretic use, none vs. yes | 2.034 (1.066–3.883) | 0.031 | - | - | |
| RRT used [n (%)], none vs. yes | 6.282 (2.205–17.898) | 0.001 | - | - | |
| Vasopressor requirement none, vs. yes | 143.364 (38.283–536.871) | <0.001 | 21.067 (3.287–135.009) | 0.001 | |
| Sepsis, none vs. yes | 5.458 (2.668–11.169) | <0.001 | - | - | |
| Mechanical ventilation, none vs. yes | 75.614 (9.072–630.221) | <0.001 | 37.672 (25.595–399.298) | <0.001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayrakçı, S.; Eygi, E. Prognostic Value of Blood Urea Nitrogen to Albumin Ratio in Elderly Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071233
Bayrakçı S, Eygi E. Prognostic Value of Blood Urea Nitrogen to Albumin Ratio in Elderly Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071233
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayrakçı, Sinem, and Elif Eygi. 2025. "Prognostic Value of Blood Urea Nitrogen to Albumin Ratio in Elderly Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Study" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071233
APA StyleBayrakçı, S., & Eygi, E. (2025). Prognostic Value of Blood Urea Nitrogen to Albumin Ratio in Elderly Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Study. Medicina, 61(7), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071233






