The Role of Epstein-Barr Virus in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Epidemiology
4. Diagnostics of EBV Infection
4.1. Serological Tests
4.1.1. Heterophile Antibody Test
4.1.2. EBV-Specific Antibody Tests
4.1.3. Avidity Test
4.2. Molecular Methods
4.3. In Situ Hybridization
5. Immunology
5.1. The Structure of the EBV Virus
5.2. The Infection of Epithelial Cells and B Lymphocytes
5.3. Lytic Phase
5.4. The Body’s Response to EBV Infection
5.5. Reactivation
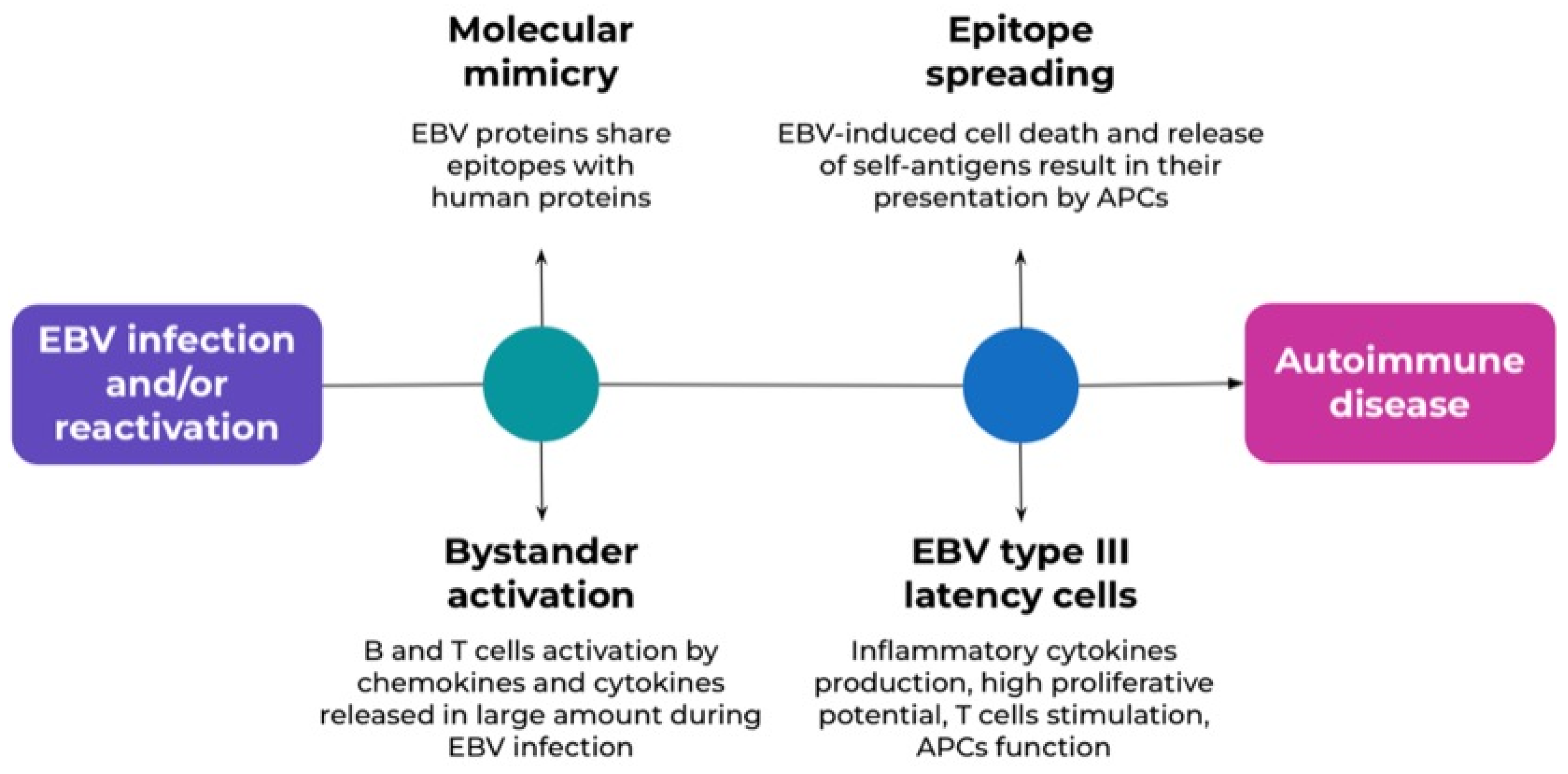
5.6. Autoimmunity
5.7. T-Bet+ B Cells
5.8. Coinfection with Other Viruses
5.9. Genetic Predispositions
6. EBV and Autoimmune Diseases
6.1. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
6.2. Diabetes Mellitus Type I
6.3. Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
6.4. Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases
| Study | AD | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Loosen et al. Infectious mononucleosis is associated with an increased incidence of Crohn’s disease: results from a cohort study of 31 862 outpatients in Germany | IBD |
|
| Zhang et al. Impact of Epstein-Barr virus infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease | IBD |
|
| Mohammed et al. The possible Association between Epstein-Barr Virus and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus | T1D |
|
| Chen et al. Fulminant Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Associated With Drug Hypersensitivity and Epstein-Barr Virus Infection: A Case Report | T1D |
|
| Laurynenka et al. A High Prevalence of Anti-EBNA1 Heteroantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Supports Anti-EBNA1 as an Origin for SLE Autoantibodies | SLE |
|
| Banko et al. Epstein-Barr virus infection as potential indicator of the occurrence and clinical presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus | SLE |
|
| Barcelos et al. Association between EBV serological patterns and lymphocytic profile of SjS patients support a virally triggered autoimmune epithelitis | SjS |
|
| Xuan et al. Serological Evidence for the Association Between Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and Sjögren’s Syndrome | SjS |
|
| Li et al. Evaluation of serum Epstein-Barr virus envelope glycoproteins antibodies and their association with systemic autoimmune diseases | RA |
|
| Munir et al. Frequency and association of Epstein-Barr Virus genotype in rheumatoid arthritis patients of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan | RA |
|
| Pyzik et al. Does the Epstein-Barr Virus Play a Role in the Pathogenesis of Graves’ Disease? | AITD |
|
| Nagata et al. Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in peripheral B lymphocytes induces IgM-type thyrotropin receptor autoantibody production in patients with Graves’ disease | AITD |
|
| Cavalcante et al. Epstein-Barr virus persistence and reactivation in myasthenia gravis thymus [62] | MG |
|
| Cavalcante et al. Toll-like receptors 7 and 9 in myasthenia gravis thymus: amplifiers of autoimmunity? [64] | MG |
|
| Zachova et al. Role of Epstein-Barr Virus in Pathogenesis and Racial Distribution of IgA Nephropathy [65] | IgAN |
|
| Sato et al. Acute kidney injury in an adult patient with IgA nephropathy and chronic replicative Epstein-Barr virus infection [67] | IgAN |
|
| Lanz et al. Clonally expanded B cells in multiple sclerosis bind EBV EBNA1 and GlialCAM [13] | MS |
|
| Al-Obaidi et al. The potential role of Epstein Barr virus in multiple sclerosis molecular and serological study [71]. | MS |
|
| Jacobs et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between Epstein–Barr virus, multiple sclerosis and other risk factors [68] | MS |
|
| Bjornevik et al. Longitudinal analysis reveals high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with multiple sclerosis [4] | MS |
|
6.5. Myasthenia Gravis
6.6. IgA Nephropathy
6.7. Multiple Sclerosis
6.8. Primary Immune Regulatory Disorders
7. Vaccination
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nowalk, A.; Green, M. Epstein-Barr Virus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houen, G.; Trier, N.H. Epstein-Barr Virus and Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 587380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Michaels, M.G. Epstein–Barr Virus Infection and Posttransplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornevik, K.; Münz, C.; Cohen, J.I.; Ascherio, A. Epstein–Barr virus as a leading cause of multiple sclerosis: Mechanisms and implications. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Cao, Z. Impact of Epstein–Barr virus infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1001055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smatti, M.K.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Ali, N.H.; Pintus, G.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Nasrallah, G.K. Epstein–Barr Virus Epidemiology, Serology, and Genetic Variability of LMP-1 Oncogene Among Healthy Population: An Update. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentzer, A.J.; Brenner, N.; Allen, N.; Littlejohns, T.J.; Chong, A.Y.; Cortes, A.; Almond, R.; Hill, M.; Sheard, S.; McVean, G.; et al. Identification of host–pathogen-disease relationships using a scalable multiplex serology platform in UK Biobank. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuri, A.; Jacobs, B.M.; Vickaryous, N.; Pakpoor, J.; Middeldorp, J.; Giovannoni, G.; Dobson, R. Epidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus infection and infectious mononucleosis in the United Kingdom. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.R.; Jackson, C.; Lewis, J.E.; Taylor, G.S.; Thomas, O.G.; Stagg, H.R. Predictors of Epstein-Barr virus serostatus and implications for vaccine policy: A systematic review of the literature. J. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 010404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjalgrim, H.; Friborg, J.; Melbye, M. The epidemiology of EBV and its association with malignant disease. In Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis; Arvin, A., Campadelli-Fiume, G., Mocarski, E., Moore, P.S., Roizman, B., Whitley, R., Yamanishi, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 929–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-R. Epstein–Barr Virus, the Immune System, and Associated Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunmire, S.K.; Hogquist, K.A.; Balfour, H.H. Infectious Mononucleosis. In Epstein Barr Virus Volume 1; Münz, C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 211–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balfour, H.H.; Odumade, O.A.; Schmeling, D.O.; Mullan, B.D.; Ed, J.A.; Knight, J.A.; Vezinba, H.E.; Thomas, W.; Hogquist, K.A. Behavioral, Virologic, and Immunologic Factors Associated with Acquisition and Severity of Primary Epstein–Barr Virus Infection in University Students. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.-H. EBV and human cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, T.V.; Brewer, R.C.; Ho, P.P.; Moon, J.-S.; Jude, K.M.; Fernandez, D.; Fernandes, R.A.; Gomez, A.M.; Nadj, G.S.; Bartley, C.-M.; et al. Clonally expanded B cells in multiple sclerosis bind EBV EBNA1 and GlialCAM. Nature 2022, 603, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-Q.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, X.-Y.; Zhang, M.-L.; Jing, X.-T.; Wang, Y.-F.; Gan, H.-T. Clinical features of Epstein–Barr virus in the intestinal mucosa and blood of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhu, W.; Akihisa, T.; Li, W.; Kikuchi, T.; Liu, W.; Feng, F.; Zhang, J. Prophylactic and Therapeutic EBV Vaccines: Major Scientific Obstacles, Historical Progress, and Future Direction. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusalah, M.A.H.; Gan, S.H.; Al-Hatamleh, M.A.I.; Irekeola, A.A.; Shueb, R.H.; Yean Yean, C. Recent Advances in Diagnostic Approaches for Epstein–Barr Virus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternbæk, L.; Draborg, A.H.; Østerlund, M.T.; Iversen, L.V.; Troelsen, L.; Theander, E.; Nielsen, C.T.; Jacobsen, S.; Houen, G. Increased antibody levels to stage-specific Epstein–Barr virus antigens in systemic autoimmune diseases reveal a common pathology. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2019, 79, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jog, N.R.; James, J.A. Epstein Barr Virus and Autoimmune Responses in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 623944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Warner, B.E.; Wang, R.; Adams-Haduch, J.; Reznik, A.S.; Dou, J.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Y.-T.; Koh, W.-P.; Bäckerholm, A.; et al. Serologic Profiling Using an Epstein-Barr Virus Mammalian Expression Library Identifies EBNA1 IgA as a Prediagnostic Marker for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 5221–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhong, L.; Kang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhai, A.-X.; Wu, C.; Zeng, M.-S.; Zhu, Q.-Y. Evaluation of serum Epstein–Barr virus envelope glycoproteins antibodies and their association with systemic autoimmune diseases. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, 29595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, M.; Kitamura, N.; Nagasawa, Y.; Tsuzuki, H.; Iwata, M.; Nagatsuka, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Imai, K.; Fujiwara, S. Are Viral Infections Key Inducers of Autoimmune Diseases? Focus on Epstein–Barr Virus. Viruses 2022, 14, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, S.A.d.S.; Viana, J.B.G.d.O.; Góes, H.C.A.; Fonseca, R.R.d.S.; Laurentino, R.V.; Costa, I.B.; Oliviera-Fihlo, A.B.; Machado, L.F.A. Epidemiology of the Epstein–Barr Virus in Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases in Northern Brazil. Viruses 2022, 14, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.d.M.; Alves, C.E.d.C.; Pontes, G.S. Epstein-Barr virus: The mastermind of immune chaos. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1297994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzymski, P.; Szuster-Ciesielska, A. Epstein-Barr virus and autoimmunity: Effective preventive and therapeutic strategies are urgently needed. Rheumatology 2023, 61, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SoRelle, E.D.; Reinoso-Vizcaino, N.M.; Horn, G.Q.; Luftig, M.A. Epstein-Barr virus perpetuates B cell germinal center dynamics and generation of autoimmune-associated phenotypes in vitro. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1001145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. A common mechanism links Epstein-Barr virus infections and autoimmune diseases. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobollik, S.; Meyer, L.; Buettner, M.; Klemmer, S.; Kempkes, B.; Kremmer, E.; Niedobitek, G.; Jungnickel, B. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 inhibits AID expression during EBV-driven B-cell growth. Blood 2006, 108, 3859–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, A.; Khan, S.; Saleem, A.; Nusrat, H.; Khan, S.A.; Sayyed, H.; Khalid, A.; Javed, B.; Fatima, H. The Role of Epstein–Barr Virus Molecular Mimicry in Various Autoimmune Diseases. Scand. J. Immunol. 2025, 101, 70016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogers, L.; Kuiper, K.L.; Smolders, J.; Rip, J.; van Luijn, M.M. Epstein–Barr virus and genetic risk variants as determinants of T-bet+ B cell-driven autoimmune diseases. Immunol. Lett. 2023, 261, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugliesi, F.; Pasquero, S.; Griffante, G.; Scutera, S.; Albano, C.; Pacheco, S.F.C.; Riva, G.; Dell’Oste, V.; Biolatti, M. Human Cytomegalovirus and Autoimmune Diseases: Where Are We? Viruses 2021, 13, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, C.; Wang, C.; Ramasamy, A.; Fonken, C.; Morse, B.; Lopez, N.; Wylie, D.; Melamed, E. Molecular mimicry as a mechanism of viral immune evasion and autoimmunity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, F.; Rasizadeh, R.; Sharaflou, S.; Aghbash, P.S.; Shamekh, A.; Jafari-Sales, A.; Baghi, H.B. Coinfection of EBV with other pathogens: A narrative review. Front. Virol. 2024, 4, 1482329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lledó-Delgado, A.; Preston-Hurlburt, P.; Higdon, L.; Hu, A.; James, E.; Lim, N.; Long, S.A.; McNamara, J.; Nguyen, H.; Serti, E.; et al. Latent EBV enhances the efficacy of anti-CD3 mAb in Type 1 diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, L. Genetic susceptibility determines Epstein–Barr-virus-associated risk of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2025, 21, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, T.V.; Robinson, W.H. Connecting the dots: Presentation of EBV antigens on HLA class II risk alleles connects the two main risk factors of multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2420070121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costenbader, K.; Karlson, E. Epstein–Barr virus and rheumatoid arthritis: Is there a link? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Kohyama, M.; Yasumizu, Y.; Tada, A.; Tanzawa, K.; Shishido, T.; Kishida, K.; Jin, H.; Nishide, M.; Kawada, S.; et al. Neoself-antigens are the primary target for autoreactive T cells in human lupus. Cell 2024, 187, 6071–6087.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, C.; Farooq, U.; Haseeb, M. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Nandy, A.; Petralia, F.; Porter, C.K.; Elledge, S.; Anand, R.; Croitoru, K.; Dunn, G.; Dennis-Heyward, E.; Eran, A.; Field, M.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus Exposure Precedes Crohn’s Disease Development. Gastroenterology 2025, 169, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaugerie, L.; Rahier, J.-F.; Kirchgesner, J. Predicting, Preventing, and Managing Treatment-Related Complications in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1324–1335.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyams, J.S.; Dubinsky, M.C.; Baldassano, R.N.; Colletti, R.B.; Cucchiara, S.; Escher, J.; Faubion, W.; Fell, J.; Gold, B.D.; Griffiths, A.; et al. Infliximab Is Not Associated with Increased Risk of Malignancy or Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1901–1914.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaugerie, L.; Brousse, N.; Bouvier, A.M.; Colombel, J.F.; Lémann, M.; Cosnes, J.; Hébuterne, X.; Cortot, A.; Bouhnik, Y.; Gendre, J.P.; et al. Lymphoproliferative disorders in patients receiving thiopurines for inflammatory bowel disease: A prospective observational cohort study. Lancet 2009, 374, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loosen, S.H.; Kostev, K.; Schöler, D.; Orth, H.-M.; Freise, N.F.; Jensen, B.-E.O.; May, P.; Bode, J.G.; Roderburg, C.; Luedde, T. Infectious mononucleosis is associated with an increased incidence of Crohn’s disease: Results from a cohort study of 31 862 outpatients in Germany. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 35, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkkonen, P.; Hyöty, H.; Ilonen, J.; Reijonen, H.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Leinikki, P. Antibody reactivity to an Epstein–Barr virus BERF4-encoded epitope occurring also in Asp-57 region of HLA-DQ8 β chain. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 95, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettler, T.; von Herrath, M. Protection against or triggering of Type 1 diabetes? Different roles for viral infections. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-C.; Liao, J.-Y. Epidemiologic Implication of the Association between Herpes Simplex Virus Infection and the Risk of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Case-Control Study in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.H.; Albatool Sabr, A.I. The possible Association between Epstein-Barr Virus and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Iraqi J. Med. Sci. 2019, 17, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Tian, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Fulminant Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Associated with Drug Hypersensitivity and Epstein–Barr Virus Infection: A Case Report. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 884878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, Y.; Hanafusa, T.; Imagawa, A. Pathogenesis of fulminant type 1 diabetes: Genes, viruses and the immune mechanism, and usefulness of patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells for future research. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrasiabi, A.; Keane, J.T.; Ong, L.T.C.; Alinejad-Rokny, H.; Fewings, N.L.; Booth, D.R.; Parnell, G.P.; Swaminathan, S. Genetic and transcriptomic analyses support a switch to lytic phase in Epstein Barr virus infection as an important driver in developing Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 127, 102781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurynenka, V.; Ding, L.; Kaufman, K.M.; James, J.A.; Harley, J.B. A High Prevalence of Anti-EBNA1 Heteroantibodies in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Supports Anti-EBNA1 as an Origin for SLE Autoantibodies. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 830993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guta, S.; Abrahamovych, O.; Abrahamovych, U.; Tsyhanyk, L.; Farmaha, M. INFECTIOUSNESS OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS PATIENTS WITH CYTOMEGALOVIRUS AND EPSTEIN-BARR VIRUS. Georgian Med. News 2023, 338, 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Banko, A.; Cirkovic, A.; Miskovic, R.; Jeremic, I.; Grk, M.; Basaric, M.; Lazarevic, I.; Raskovic, S.; Despotovic, A.; Miljanovic, D. Epstein-Barr virus infection as potential indicator of the occurrence and clinical presentation of systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1307589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jog, N.R.; Young, K.A.; Munroe, M.E.; Harmon, M.T.; Guthridge, J.M.; Kelly, J.A.; Kamen, D.L.; Gilkeson, G.S. Weisman, M.H.; Karp, D.R.; et al. Association of Epstein-Barr virus serological reactivation with transitioning to systemic lupus erythematosus in at-risk individuals. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygun, D.; Kuskucu, M.A.; Sahin, S.; Adrovic, A.; Barut, K.; Yıldız, M.; Sharifova, S.; Mililli, K.; Cokugras, H.; Camcıoglu, Y.; et al. Epstein–Barr virus, cytomegalovirus and BK polyomavirus burden in juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus: Correlation with clinical and laboratory indices of disease activity. Lupus 2020, 29, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadi, S.; Najafizadeh, S.R.; Nejati, A.; Teymoori-Rad, M.; Shahmahmoodi, S.; Shirazi, F.G.; Shokri, F.; Marashi, S.M. Overall Status of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection, IFN-a, and TLR-7/9 in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematous. Iran. J. Immunol. 2021, 18, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tu, J.; Huang, M.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, L. A retrospective cohort study of Epstein-Barr virus infection status and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 43, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, B.; Bai, M.; Cai, S.; Wang, B.; Zhong, J.; Dong, L. Clinical characteristics of SLE patients infected with Epstein-Barr virus and potential associated risk factors. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truszewska, A.; Wirkowska, A.; Gala, K.; Truszewski, P.; Krzemień-Ojak, Ł.; Mucha, K.; Pączek, L.; Foroncewicz, B. EBV load is associated with cfDNA fragmentation and renal damage in SLE patients. Lupus 2021, 30, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Pu, J.; Cai, F.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, R.; Zhuang, S.; Liang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Song, J.; et al. Chronic Epstein-Barr virus infection: A potential junction between primary Sjögren’s syndrome and lymphoma. Cytokine 2023, 168, 156227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, F.; Martins, C.; Monteiro, R.; Cardigos, J.; Prussiani, T.; Sítima, M.; Alves, N.; Vaz-Patto, J.; Cunha-Branco, J.; Borrego, L.-M. Association between EBV serological patterns and lymphocytic profile of SjS patients support a virally triggered autoimmune epithelitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, J.; Ji, Z.; Wang, B.; Zeng, X.; Chen, R.; He, Y.; Rao, P.; Wu, P.; Shi, G. Serological Evidence for the Association Between Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorgato, C.C.; Lins-e-Silva, M.; Leão, J.C.; Vasconcelos, L.R.; Romão, T.P.; Duarte, A.L.; Gueiros, L.A. EBV and CMV viral load in rheumatoid arthritis and their role in associated Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, S.; Attaullah, S.; Munir, M.; Saleem, A.; Ali, I. Frequency and association of Epstein-Barr Virus genotype in rheumatoid arthritis patients of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, J.F.M.; Ward, L.S. Thyroid autoimmune diseases and thyroid tumors: Would EBV infection be the link? J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 19141–19142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, M.N.; Mohamed, F.I.; Osman, M.M.; Jadid, A.A.; Abdalrhman, I.K.; Yousif, A.M.; Alabid, T.; Edris, A.M.M.; Mohamed, N.S.; Siddig, E.E.; et al. Molecular detection of Epstein-Barr virus among Sudanese patients diagnosed with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. BMC Res. Notes 2023, 16, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyzik, A.; Grywalska, E.; Matyjaszek-Matuszek, B.; Ludian, J.; Kiszczak-Bochyńska, E.; Smoleń, A.; Roliński, J.; Pyzik, D. Does the Epstein–Barr Virus Play a Role in the Pathogenesis of Graves’ Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirino, S.; Nakatani, H.; Honma, A.; Shinbo, A.; Onda, K.; Okada, M.; Imai, M.; Suzuki, N.; Oshiba, A.; Nagasawa, M. An eight-year-old girl with autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type3A that developed during the course of primary Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infection: Clinical implication of EBV in autoimmune thyroid disease. Immunol. Med. 2020, 43, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamoto, N.; Nagata, K.; Hara, S.; Nakayama, Y.; Kuwamoto, S.; Matsushita, M.; Kato, M.; Hayashi, K. Subclinical Epstein-Barr Virus Primary Infection and Lytic Reactivation Induce Thyrotropin Receptor Autoantibodies. Viral Immunol. 2019, 32, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Hayashi, K.; Kumata, K.; Satoh, Y.; Osaki, M.; Nakayama, Y.; Kuwamoto, S.; Ichihara, Y.; Okura, T.; Matsuzawa, K.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in peripheral B lymphocytes induces IgM-type thyrotropin receptor autoantibody production in patients with Graves’ disease. Endocr. J. 2023, 70, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, P.; Barberis, M.; Baggi, F.; Passerini, L.; Cannone, M.; Arnoldi, E.; Novellino, L.; Cornelio, F.; Mantegazza, R. Increased Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression in Thymus of Myasthenic Patients with Thymitis and Thymic Involution. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, P.; Galbardi, B.; Franzi, S.; Marcuzzo, S.; Barzago, C.; Bonanno, S.; Camera, G.; Maggi, L.; Kapetis, D.; Andreetta, F.; et al. Increased expression of Toll-like receptors 7 and 9 in myasthenia gravis thymus characterized by active Epstein–Barr virus infection. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcguire, L.J.; Huang, D.P.; Teoh, R.; Arnold, M.; Wong, K.; Lee, A.C.K. Epstein-Barr Virus Genome in Thymoma and Thymic Lymphoid Hyperplasia. Am. J. Pathol. 1988, 131, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, P.; Barzago, C.; Baggi, F.; Antozzi, C.; Maggi, L.; Kapetis, D.; Andreetta, F.; Biasiucci, A.; Motta, T.; Giardina, C.; et al. Toll-like receptors 7 and 9 in myasthenia gravis thymus: Amplifiers of autoimmunity? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1413, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachova, K.; Kosztyu, P.; Zadrazil, J.; Matousovic, K.; Vondrak, K.; Hubacek, P.; Julian, B.A.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Novak, Z.; Kostovicikova, K.; et al. Role of Epstein-Barr Virus in Pathogenesis and Racial Distribution of IgA Nephropathy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestecky, J.; Julian, B.A.; Raska, M. IgA Nephropathy: Pleiotropic impact of Epstein-Barr virus infection on immunopathogenesis and racial incidence of the disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1085922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Furuyama, K.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sato, A.; Iguchi, A.; Yoshita, K.; Ito, Y.; Imai, N.; Yamazaki, H.; et al. Acute kidney injury in an adult patient with IgA nephropathy and chronic replicative Epstein–Barr virus infection. CEN Case Rep. 2019, 8, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, B.M.; Giovannoni, G.; Cuzick, J.; Dobson, R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between Epstein–Barr virus, multiple sclerosis and other risk factors. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 1281–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Larsson, S.C. An atlas on risk factors for multiple sclerosis: A Mendelian randomization study. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroufi, H.; Mortazavi, S.H.; Sahraian, M.A.; Eskandarieh, S. Environmental risk factors of multiple sclerosis in the Middle East and North Africa region: A systematic review. Curr. J. Neurol. 2021, 20, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, A.B.; Ali, Z.A.; Rasool Almashta, S.A.; Faisel Ghazi, H. THE POTENTIAL ROLE OF EPSTEIN BARR VIRUS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS MOLECULAR AND SEROLOGICAL STUDY. Wiad. Lek. 2022, 75, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornevik, K.; Cortese, M.; Healy, B.C.; Kuhle, J.; Mina, M.J.; Leng, Y.; Elledge, S.J.; Niebuhr, D.W.; Scher, A.I.; Munger, K.L.; et al. Longitudinal analysis reveals high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with multiple sclerosis. Science 2022, 375, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, C.S.; Baloh, C.H. Immunodeficiency: Overview of primary immune regulatory disorders (PIRDs). Allergy Asthma Proc. 2024, 45, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov n.d. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Cui, X.; Snapper, C.M. Epstein Barr Virus: Development of Vaccines and Immune Cell Therapy for EBV-Associated Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 734471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Antibodies | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heterophile | VCA IgM | VCA IgG | EA-D | EBNA-1 | |
| Acute primary infection | + | + | + | + | − |
| Past infection | − | − | + | − | + |
| Past active infection | − | − | +++ | + | + |
| EBV reactivation, Burkitt’s lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma | − | +/− | + | +/− | + |
| Seronegative | − | − | − | − | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morawiec, N.; Adamczyk, B.; Spyra, A.; Herba, M.; Boczek, S.; Korbel, N.; Polechoński, P.; Adamczyk-Sowa, M. The Role of Epstein-Barr Virus in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Medicina 2025, 61, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071148
Morawiec N, Adamczyk B, Spyra A, Herba M, Boczek S, Korbel N, Polechoński P, Adamczyk-Sowa M. The Role of Epstein-Barr Virus in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071148
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorawiec, Natalia, Bożena Adamczyk, Aleksandra Spyra, Mikołaj Herba, Sylwia Boczek, Natalia Korbel, Piotr Polechoński, and Monika Adamczyk-Sowa. 2025. "The Role of Epstein-Barr Virus in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071148
APA StyleMorawiec, N., Adamczyk, B., Spyra, A., Herba, M., Boczek, S., Korbel, N., Polechoński, P., & Adamczyk-Sowa, M. (2025). The Role of Epstein-Barr Virus in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Medicina, 61(7), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071148






