Effect of Remimazolam and Propofol on Blood Glucose and Serum Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Clinical Trial with Prospective Randomized Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
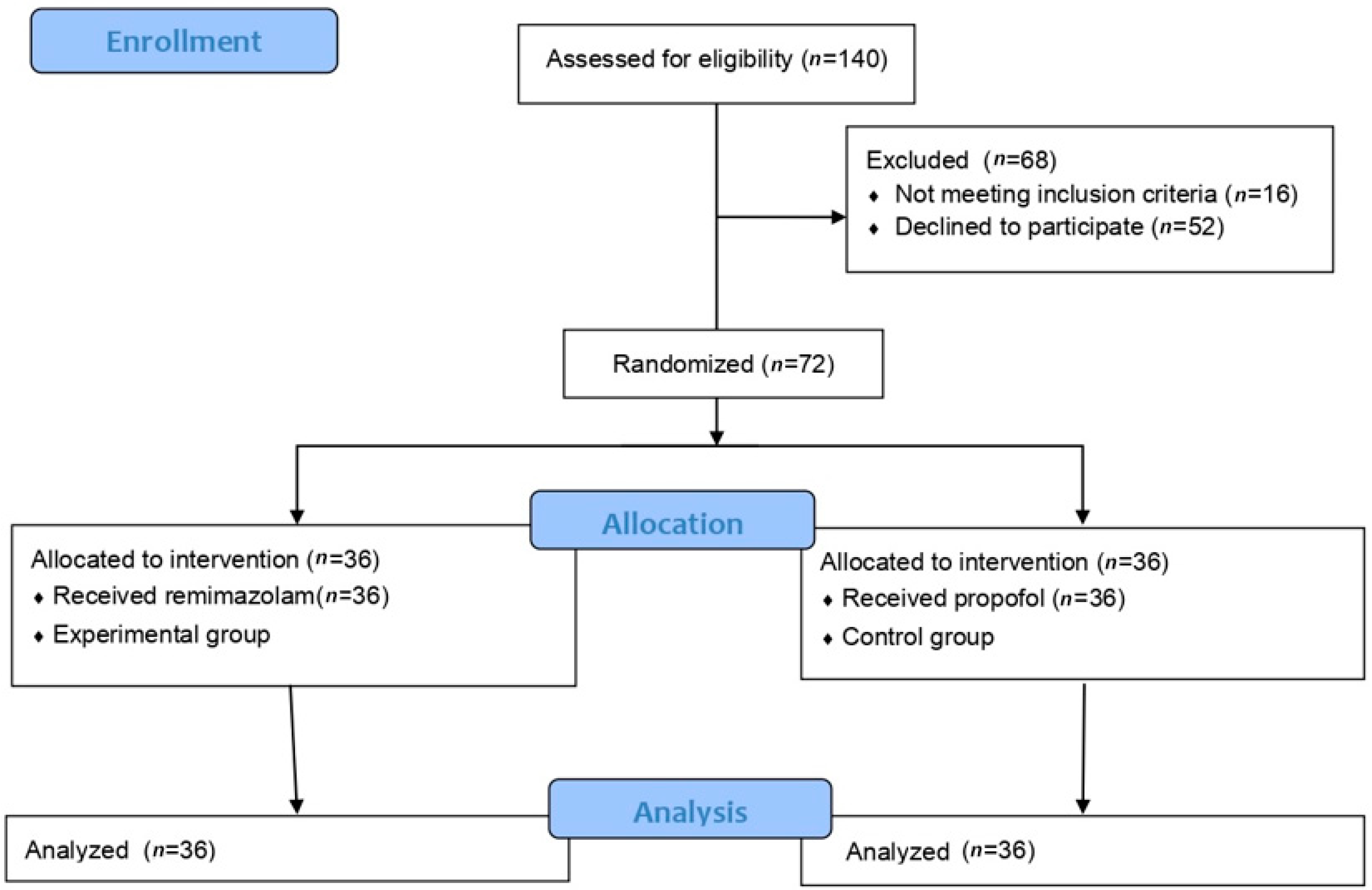
2. Materials and Methods
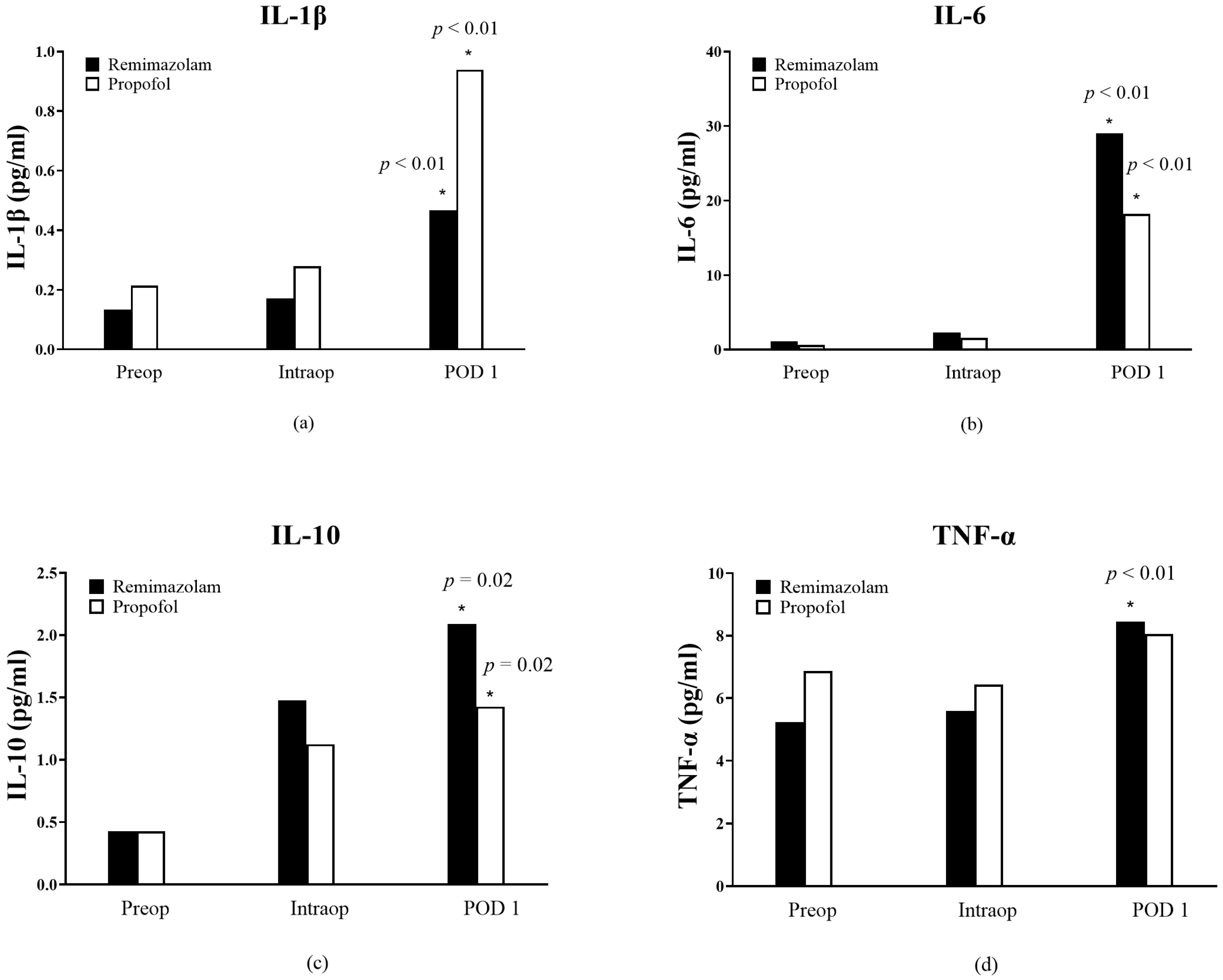
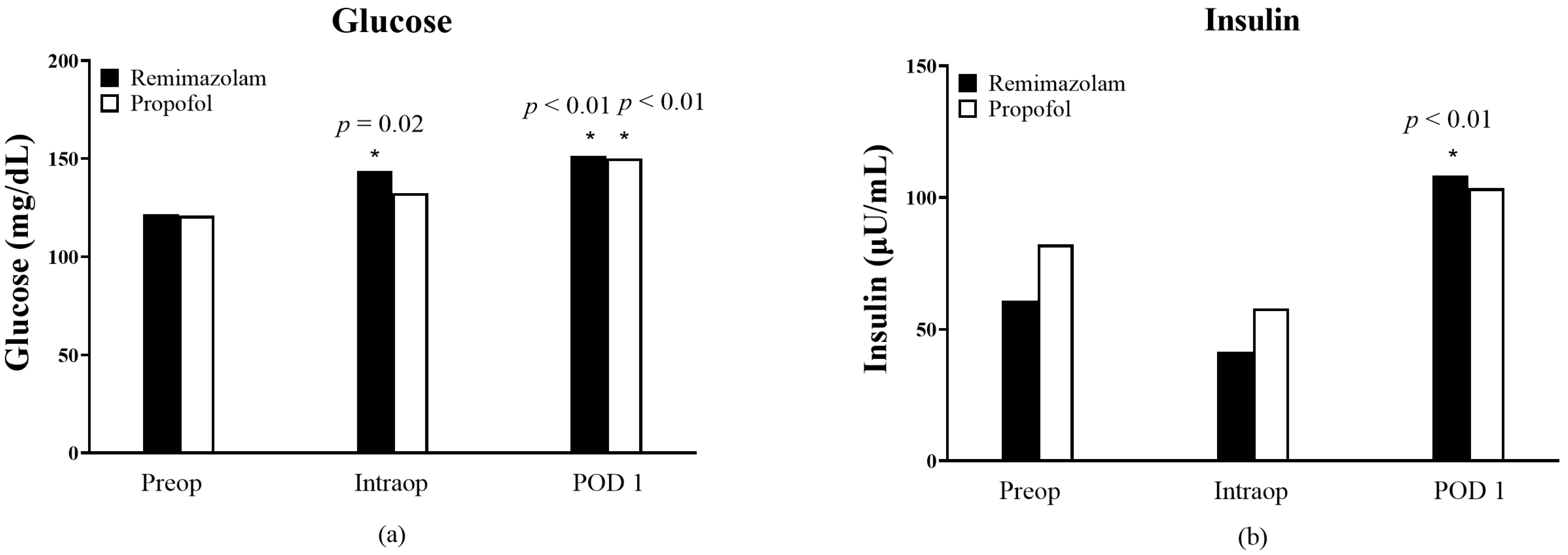
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheisson, G.; Jacqueminet, S.; Cosson, E.; Ichai, C.; Leguerrier, A.M.; Nicolescu-Catargi, B.; Ouattara, A.; Tauveron, I.; Valensi, P.; Benhamou, D. Perioperative management of adult diabetic patients. Review of hyperglycaemia: Definitions and pathophysiology. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2018, 37 (Suppl. 1), S5–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galway, U.; Chahar, P.; Schmidt, M.T.; Araujo-Duran, J.A.; Shivakumar, J.; Turan, A.; Ruetzler, K. Perioperative challenges in management of diabetic patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geerlings, S.E.; Hoepelman, A.I. Immune dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1999, 26, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakaran, S.; Surani, S.R. Guidelines for Perioperative Management of the Diabetic Patient. Surg. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 284063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneemilch, C.E.; Schilling, T.; Bank, U. Effects of general anaesthesia on inflammation. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2004, 18, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, W.T.; Armstrong, M.A.; McBride, S.J. Immunomodulation: An important concept in modern anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 1996, 51, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, S.J. Remimazolam: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Fechner, J. Remimazolam—Current knowledge on a new intravenous benzodiazepine anesthetic agent. Korean J. Anesthesiol. Anesthesiol. 2022, 75, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevassus, H.; Mourand, I.; Molinier, N.; Lacarelle, B.; Brun, J.F.; Petit, P. Assessment of single-dose benzodiazepines on insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity and glucose effectiveness in healthy volunteers: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized cross-over trial [ISRCTN08745124]. BMC Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylutka, A.; Walas, Ł.; Zembron-Lacny, A. Level of IL-6, TNF, and IL-1β and age-related diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1330386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhenany, H.A.; Linardi, R.L.; Ortved, K.F. Differential modulation of inflammatory cytokines by recombinant IL-10 in IL-1β and TNF-α–stimulated equine chondrocytes and synoviocytes: Impact of washing and timing on cytokine responses. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.; Akash, M.S. Mechanisms of inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: How are they interlinked? J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukimoto, S.; Kitaura, A.; Kuroda, H.; Imaizumi, U.; Yoshino, F.; Yoshida, A.; Nakao, S.; Ohta, N.; Nakajima, Y.; Sanuki, T. Anti-inflammatory potential of remimazolam: A laboratory and clinical investigation. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, S.; Kushner, I.; Samols, D. C-reactive Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48487–48490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, A.L.; Cerra, F.B. Multiple organ failure syndrome in the 1990s. Systemic inflammatory response and organ dysfunction. Jama 1994, 271, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmore, D.W. From Cuthbertson to fast-track surgery: 70 years of progress in reducing stress in surgical patients. Ann. Surg. 2002, 236, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nseir, S.; Makris, D.; Mathieu, D.; Durocher, A.; Marquette, C.H. Intensive Care Unit-acquired infection as a side effect of sedation. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langouche, L.; Van den Berghe, G. Glucose metabolism and insulin therapy. Crit. Care Clin. 2006, 22, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drayton, D.J.; Birch, R.J.; D’Souza-Ferrer, C.; Ayres, M.; Howell, S.J.; Ajjan, R.A. Diabetes mellitus and perioperative outcomes: A scoping review of the literature. Br. J. Anaesth. 2022, 128, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werzowa, J.; Pacini, G.; Hecking, M.; Fidler, C.; Haidinger, M.; Brath, H.; Thomas, A.; Säemann, M.D.; Tura, A. Comparison of glycemic control and variability in patients with type 2 and posttransplantation diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berghe, G.; Wouters, P.; Weekers, F.; Verwaest, C.; Bruyninckx, F.; Schetz, M.; Vlasselaers, D.; Ferdinande, P.; Lauwers, P.; Bouillon, R. Intensive insulin therapy in critically ill patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGirt, M.J.; Woodworth, G.F.; Brooke, B.S.; Coon, A.L.; Jain, S.; Buck, D.; Huang, J.; Clatterbuck, R.E.; Tamargo, R.J.; Perler, B.A. Hyperglycemia independently increases the risk of perioperative stroke, myocardial infarction, and death after carotid endarterectomy. Neurosurgery 2006, 58, 1066–1073; discussion 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouattara, A.; Lecomte, P.; Le Manach, Y.; Landi, M.; Jacqueminet, S.; Platonov, I.; Bonnet, N.; Riou, B.; Coriat, P. Poor intraoperative blood glucose control is associated with a worsened hospital outcome after cardiac surgery in diabetic patients. Anesthesiology 2005, 103, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwoun, M.O.; Ling, P.R.; Lydon, E.; Imrich, A.; Qu, Z.; Palombo, J.; Bistrian, B.R. Immunologic effects of acute hyperglycemia in nondiabetic rats. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1997, 21, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weekers, F.; Giulietti, A.P.; Michalaki, M.; Coopmans, W.; Van Herck, E.; Mathieu, C.; Van den Berghe, G. Metabolic, endocrine, and immune effects of stress hyperglycemia in a rabbit model of prolonged critical illness. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 5329–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, H.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. Effect of Propofol on breast Cancer cell, the immune system, and patient outcome. BMC Anesth. Anesthesiol. 2018, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.M.; Chen, T.G.; Chen, T.L.; Lin, L.L.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, H.C.; Wu, C.H. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects of propofol on lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1042, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, G.U.; Song, Y.; Park, J.; Ki, Y.M.; Han, D.W. Effects of propofol on the inflammatory response during robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: A prospective randomized controlled study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; An, S.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Zeng, Z. Remimazolam reduces sepsis-associated acute liver injury by activation of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors and p38 inhibition of macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; He, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, C.; Liang, P. Impact of total intravenous anesthesia and total inhalation anesthesia as the anesthesia maintenance approaches on blood glucose level and postoperative complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yin, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L. Stress Response to Propofol versus Isoflurane Anesthesia in Patients Undergoing Gastric Surgery. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2019, 29, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Lai, T.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; He, F.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Y. Effect of remimazolam induction on hemodynamics in patients undergoing valve replacement surgery: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2021, 9, e00851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagry, H.S.; Raghavendran, S.; Carli, F. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance: Perioperative considerations. Anesthesiology 2008, 108, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganong, W.F. Review of Medical Physiology, 22nd ed.; Lange Medical/McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Avramoglu, R.K.; Basciano, H.; Adeli, K. Lipid and lipoprotein dysregulation in insulin resistant states. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 368, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorell, A.; Loftenius, A.; Andersson, B.; Ljungqvist, O. Postoperative insulin resistance and circulating concentrations of stress hormones and cytokines. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 15, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Propofol (n = 36) | Remimazolam (n = 36) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.3 ± 11.6 | 65.7 ± 12.1 | 0.45 |
| Sex (F/M) | 20 (55.5)/16 (44.5) | 17 (47.2)/19 (52.8) | 0.64 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.7 ± 3.8 | 25.4 ± 4.9 | 0.65 |
| HTN | 26 (72.2) | 24 (66.6) | 0.80 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 7 (19.4) | 15 (41.6) | 0.07 |
| Pulmonary disease | 8 (22.2) | 12 (33.3) | 0.43 |
| Endocrine disease | 10 (27.7) | 3 (8.3) | 0.06 |
| Neurologic disorder | 7 (19.4) | 5 (13.8) | 0.75 |
| Nephropathy | 6 (16.6) | 8 (22.2) | 0.77 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.0 ± 1.3 | 6.8 ± 0.76 | 0.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.H.; Yoon, S.M.; Ahn, J.H.; Choi, Y.J. Effect of Remimazolam and Propofol on Blood Glucose and Serum Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Clinical Trial with Prospective Randomized Control. Medicina 2025, 61, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030523
Kim SH, Yoon SM, Ahn JH, Choi YJ. Effect of Remimazolam and Propofol on Blood Glucose and Serum Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Clinical Trial with Prospective Randomized Control. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030523
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sang Hun, Sang Min Yoon, Ji Hye Ahn, and Yoon Ji Choi. 2025. "Effect of Remimazolam and Propofol on Blood Glucose and Serum Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Clinical Trial with Prospective Randomized Control" Medicina 61, no. 3: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030523
APA StyleKim, S. H., Yoon, S. M., Ahn, J. H., & Choi, Y. J. (2025). Effect of Remimazolam and Propofol on Blood Glucose and Serum Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Clinical Trial with Prospective Randomized Control. Medicina, 61(3), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030523







