Metformin Increases Serum Isthmin-1 Levels and Lowers Low-Density Lipoprotein: Potential Implications for Lipid Metabolism in T2DM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
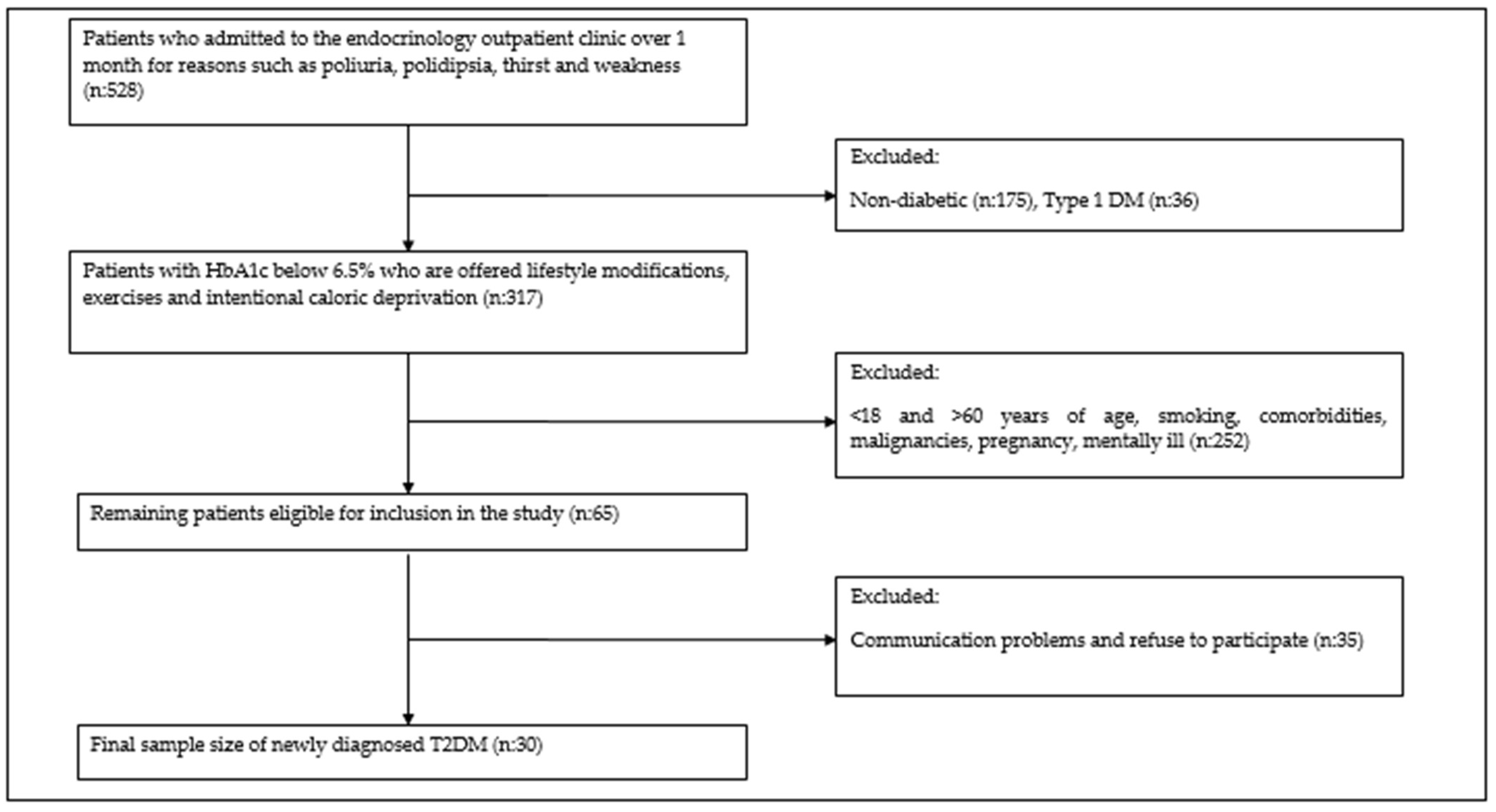
2.1. Study Participants and Study Plan
2.2. Biochemical Measurement of Isthmin-1 and Other Parameters
2.3. Immunostaining
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Immunreaktivity of Isthmin-1
3.2. Changes in Biochemical Parameters During Metformin Treatment
3.3. Changes in Isthmin 1 Levels During Metformin Treatment
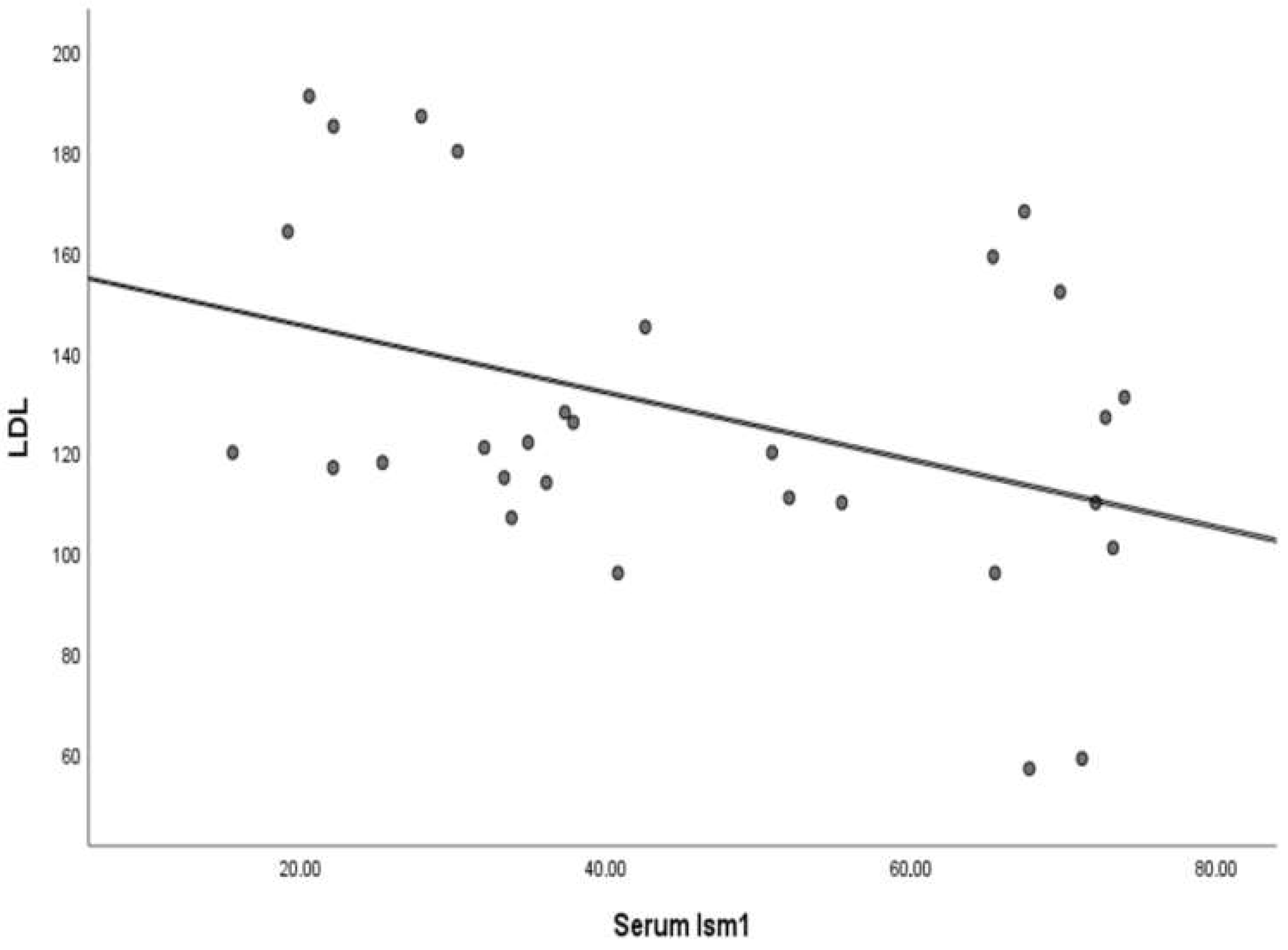
3.4. Analysis of Correlation Between Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drzewoski, J.; Hanefeld, M. The Current and Potential Therapeutic Use of Metformin—The Good Old Drug. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Rangel, E.; Inzucchi, S.E. Metformin: Clinical use in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higurashi, T.; Nakajima, A. Metformin and Colorectal Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triggle, C.R.; Mohammed, I.; Bshesh, K.; Marei, I.; Ye, K.; Ding, H.; MacDonald, R.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Hill, M.A. Metformin: Is it a drug for all reasons and diseases? Metabolism 2022, 133, 155223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, R.; Erez, O.; Hüttemann, M.; Maymon, E.; Panaitescu, B.; Conde-Agudelo, A.; Pacora, P.; Yoon, B.H.; Grossman, L.I. Metformin, the aspirin of the 21st century: Its role in gestational diabetes mellitus, prevention of preeclampsia and cancer, and the promotion of longevity. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 217, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rena, G.; Hardie, D.G.; Pearson, E.R. The mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pera, E.M.; Kim, J.I.; Martinez, S.L.; Brechner, M.; Li, S.Y.; Wessely, O.; De Robertis, E.M. Isthmin is a novel secreted protein expressed as part of the Fgf-8 synexpression group in the Xenopus midbrain-hindbrain organizer. Mech. Dev. 2002, 116, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, X.; Hu, C.; Teng, T.; Tang, Q.Z. A brief overview about the adipokine: Isthmin-1. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 939757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeren, J.; Scheja, L. Isthmin 1—A novel insulin-like adipokine. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 709–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Voilquin, L.; Jung, Y.; Aikio, M.A.; Sahai, T.; Dou, F.Y.; Roche, A.M.; Carcamo-Orive, I.; Knowles, J.W.; et al. Isthmin-1 is an adipokine that promotes glucose uptake and improves glucose tolerance and hepatic steatosis. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1836–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhawat, H.M.; Hazrat, Z.; Zhou, Z. Isthmin-A Multifaceted Protein Family. Cells 2022, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghuan, L.; Yang, Y.; Qianhe, M.; Na, Z.; Shicheng, C.; Bo, C.; XueJie, Y.I. Advances in research of biological functions of Isthmin-1. J. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 17, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Du, J.; Ge, X.; Peng, W.; Guo, X.; Li, W.; Huang, S. Circulating Ism1 Reduces the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes but not Diabetes-Associated NAFLD. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 890332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Laborde-Cárdenas, C.C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. The Role of Adipokines in Health and Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozel, N.; Kilinc, F. Investigation of plasma asprosin and saliva levels in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus patients treated with metformin. Endokrynol. Pol. 2021, 72, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Yus, M.; Casamayor, C.; Soriano-Godes, J.J.; Borlan, S.; Gonzalez-Irazabal, Y.; Garcia-Sobreviela, M.P.; Garcia-Rodriguez, B.; Del Moral-Bergos, R.; Calmarza, P.; Artigas, J.M.; et al. Isthmin-1 (ISM1), a novel adipokine that reflects abdominal adipose tissue distribution in individuals with obesity. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, J.H.; Vijayakumar, U.; Shanmugasundaram, M.; Lam, T.Y.W.; Liao, W.; Yang, Y.; Wong, W.S.F.; Ge, R. Isthmin-1 attenuates allergic Asthma by stimulating adiponectin expression and alveolar macrophage efferocytosis in mice. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Y.; Wei, H.J.; Tang, Y.Y. Isthmin: A multifunctional secretion protein. Cytokine 2024, 173, 156423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, M.; Feng, R.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.; Feng, R.; Liang, K.; Liu, J. Serum isthmin-1 levels are positively and independently correlated with albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2022, 10, e002972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.K.; Bae, K.H.; Lee, S.C.; Oh, K.J. The Latest Insights into Adipokines in Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadel, P.; Shrestha, S.; Sapkota, B.; Li, J.Y.; Tao, H. Asprosin and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A novel potential therapeutic implication. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2022, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, R.; Amin, S.; Hayat Bhat, M.; Malik, R.; Wani, H.A.; Majid, S. Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome-adipokine levels and effect of drugs. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2017, 33, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Patro-Małysza, J.; Trojnar, M.; Skórzyńska-Dziduszko, K.E.; Bartosiewicz, J.; Oleszczuk, J.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4-An “Inauspicious” Adipokine-In Serum and Urine of Post-Partum Women with Excessive Gestational Weight Gain and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Anguita-Ruiz, A.; Rico, M.C.; Leis, R.; Bueno, G.; Moreno, L.A.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, Á.; Aguilera, C.M. Serum levels of the novel adipokine isthmin-1 are associated with obesity in pubertal boys. World J. Pediatr. 2023, 19, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; He, J.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Ju, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Xia, M.; et al. Sex-specific association of circulating Isthmin-1 with isolated post-challenge hyperglycemia. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1394190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Du, H. Serum isthmin-1 is a potential biomarker for metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease in patients with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2024, 12, e004514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Brandmaier, S.; Messias, A.C.; Herder, C.; Draisma, H.H.; Demirkan, A.; Yu, Z.; Ried, J.S.; Haller, T.; Heier, M.; et al. Effects of metformin on metabolite profiles and LDL cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Fujita, H.; Waki, H. Pick the best of both glucose and lipid metabolism. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 1132–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillani, S.W.; Ghayedi, N.; Roosta, P.; Seddigh, P.; Nasiri, O. Effect of Metformin on Lipid Profiles of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2021, 13, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.Q.; Xu, M.Y.; Feng, R.Y.; Zhang, L.; Yin, X.F.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.B. Serum Isthmin-1 is negatively correlated with HDL-C in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2023, 37, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Cheng, P.C.; Tu, S.T.; Hsu, S.R.; Cheng, Y.C.; Liu, Y.H. Effect of metformin monotherapy on serum lipid profile in statin-naïve individuals with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cohort study. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Viollet, B. Metformin: Update on mechanisms of action and repurposing potential. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Banhos Danneskiold-Samsøe, N.; Ulicna, L.; Nguyen, Q.; Voilquin, L.; Lee, D.E.; White, J.P.; Jiang, Z.; Cuthbert, N.; Paramasivam, S.; et al. Phosphoproteomic mapping reveals distinct signaling actions and activation of muscle protein synthesis by Isthmin-1. eLife 2022, 11, e80014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashi, Z.; Mahrooz, A.; Kianmehr, A.; Alizadeh, A. The Role of Metformin Response in Lipid Metabolism in Patients with Recent-Onset Type 2 Diabetes: HbA1c Level as a Criterion for Designating Patients as Responders or Nonresponders to Metformin. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojić Damjanov, S.; Đerić, M.; Eremić Kojić, N. Glycated hemoglobin A1c as a modern biochemical marker of glucose regulation. Med. Pregl. 2014, 67, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrag, M.; Kassab, A.; Omezzine, A.; Belkacem, C.R.; Ben, F.I.F.; Douki, N.; Laouani, K.C.; Bouslema, A.; Ben, A.F. Saliva diagnostic utility in patients with type 2 diabetes: Future standard method. J. Med. Biochem. 2020, 39, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapher, M.; Wendler, O.; Gröschl, M.; Schäfer, R.; Iro, H.; Zenk, J. Salivary leptin as a candidate diagnostic marker in salivary gland tumors. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiougiannis, S.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Manoussakis, M.N.; Skopouli, F.N. Salivary gland epithelial cells: A new source of the immunoregulatory hormone adiponectin. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2295–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamali, I.; Roupas, N.D.; Armeni, A.K.; Theodoropoulou, A.; Markou, K.B.; Georgopoulos, N.A. Measurement of salivary resistin, visfatin and adiponectin levels. Peptides 2012, 33, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Meadows, M.L.; Maxwell, L. Assessment of Salivary Adipokines Resistin, Visfatin, and Ghrelin as Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Biomarkers. Biochem. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7463796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Control n (%) | New-Onset DM n (%) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| age # | 42.10 ± 8.94 | 52.64 ± 9.47 | 0.004 | |
| sex | M | 24 (80.0) | 17 (56.7) | 0.095 |
| F | 6 (20.0) | 13 (43.3) | ||
| Control | New-Onset DM | DM-Met | p Value * | p Value # | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (Min–Max) | Median (Min–Max) | Median (Min–Max) | |||
| FPG (mg/dL) | 90.50 (64–109) | 171.50 (108–303) | 125.0 (88–285) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.0 (4–10.6) | 7.3 (5.3–12.4) | 6.44 (5.1–11.6) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.3 (26.8–29.2) | 28.2 (27.3–34.1) | 28.4 (27.0–33.4) | 0.134 | 0.566 |
| AST (IU/L) | 18 (10–71) | 20.50 (8–77) | 20 (12–53) | 0.325 | 0.380 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 19.50 (11–68) | 25.50 (10–91) | 22.50 (8–78) | 0.027 | 0.106 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 25.00 (12–56) | 28.00 (15–57) | 29.50 (17–73) | 0.011 | 0.257 |
| Cr (mg/dL) | 0.70 (0.48–1.70) | 0.66 (0.46–1.70) | 0.70 (0.38–1.5) | 0.173 | 0.951 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 118.0 (57–191) | 136.0 (64–325) | 120.50 (60–185) | 0.004 | 0.015 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 199.0 (53–376) | 205.0 (83–747) | 200.0 (55–369) | 0.438 | 0.054 |
| Control | New-Onset DM | DM-Met | p Value * | p Value # | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (Min–Max) | Median (Min–Max) | Median (Min–Max) | |||
| Serum Ism1 (ng/mL) | 25.70 (9.25–68.67) | 25.95 (8.38–71.76) | 39.30 (15.54–73.92) | 0.923 | 0.028 |
| Saliva Ism1 (ng/mL) | 15.89 (2.67–37.81) | 14.56 (3.09–44.98) | 16.15 (7.59–26.63) | 0.813 | 0.510 |
| Ism1 | FPG | HbA1c | LDL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At diagnosis | rho | 0.161 | 0.216 | −0.204 |
| p value | 0.396 | 0.252 | 0.279 | |
| 3 months after metformin treatment | rho | −0.147 | 0.105 | −0.362 * |
| p value | 0.437 | 0.580 | 0.050 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bozoglan, M.Y.; Kuloglu, T.; Gozel, N.; Kılınc, F.; Cakmak, E.; Akkoç, R.F.; Dağoğlu Hark, B. Metformin Increases Serum Isthmin-1 Levels and Lowers Low-Density Lipoprotein: Potential Implications for Lipid Metabolism in T2DM. Medicina 2025, 61, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030522
Bozoglan MY, Kuloglu T, Gozel N, Kılınc F, Cakmak E, Akkoç RF, Dağoğlu Hark B. Metformin Increases Serum Isthmin-1 Levels and Lowers Low-Density Lipoprotein: Potential Implications for Lipid Metabolism in T2DM. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030522
Chicago/Turabian StyleBozoglan, Merve Yilmaz, Tuncay Kuloglu, Nevzat Gozel, Faruk Kılınc, Erkan Cakmak, Ramazan Fazıl Akkoç, and Betül Dağoğlu Hark. 2025. "Metformin Increases Serum Isthmin-1 Levels and Lowers Low-Density Lipoprotein: Potential Implications for Lipid Metabolism in T2DM" Medicina 61, no. 3: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030522
APA StyleBozoglan, M. Y., Kuloglu, T., Gozel, N., Kılınc, F., Cakmak, E., Akkoç, R. F., & Dağoğlu Hark, B. (2025). Metformin Increases Serum Isthmin-1 Levels and Lowers Low-Density Lipoprotein: Potential Implications for Lipid Metabolism in T2DM. Medicina, 61(3), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030522






