The Influence of Mucinous Histology on the Prognosis of Stage II and III Colorectal Cancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Approval
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
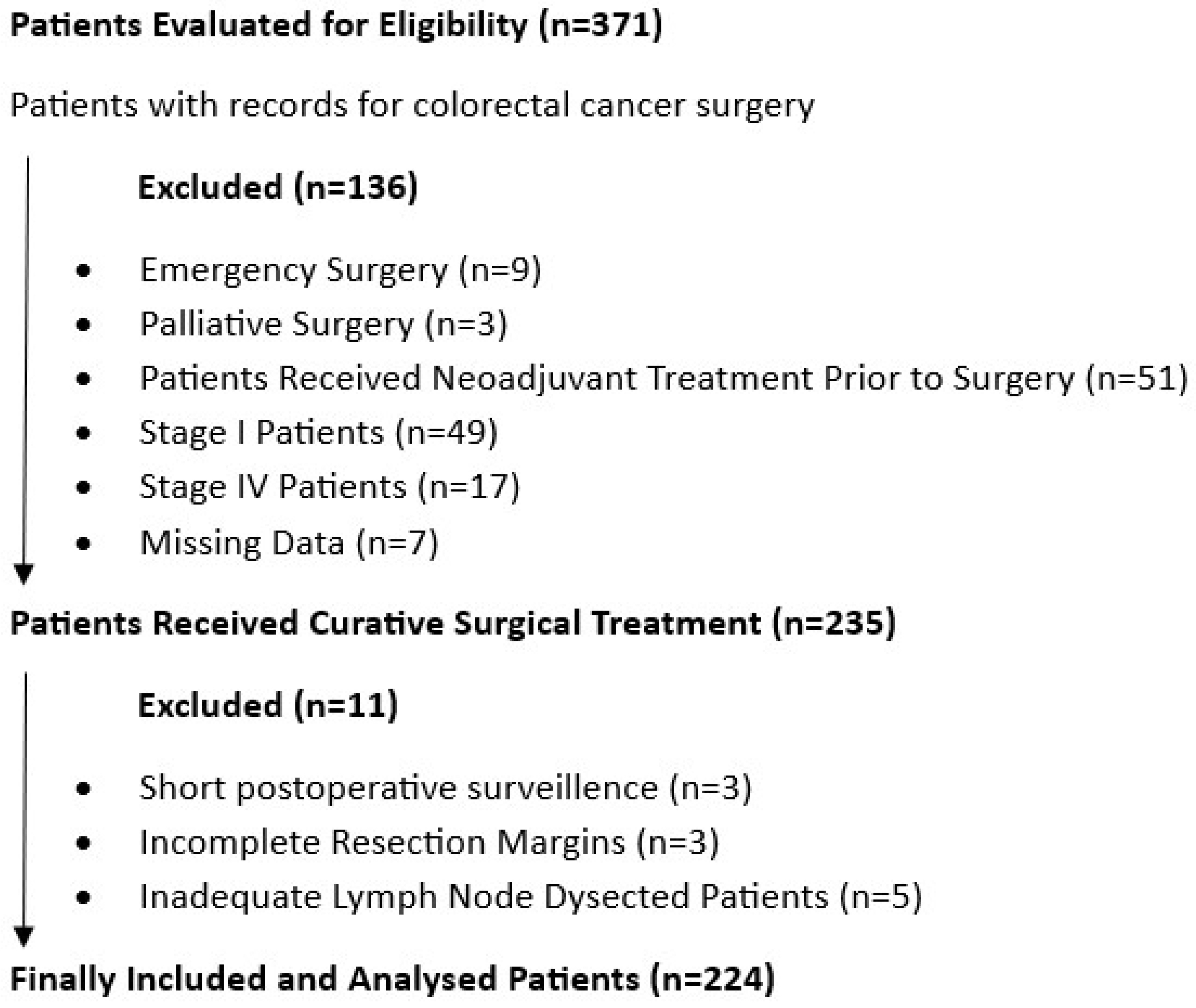
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Surgery and Followup
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Future Directions
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sicklick, J.K.; Kato, S.; Okamura, R.; Schwaederle, M.; Hahn, M.E.; Williams, C.B.; De, P.; Krie, A.; Piccioni, D.E.; Miller, V.A.; et al. Molecular profiling of cancer patients enables personalized combination therapy: The I-PREDICT study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, J.; Cohen, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Christie, M.; Simons, K.; Lee, M.; Wong, R.; Kosmider, S.; Ananda, S.; McKendrick, J.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analyses as Markers of Recurrence Risk and Benefit of Adjuvant Therapy for Stage III Colon Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, S.; Kong, J.C. Individualized chemotherapy and immunotherapy for rectal cancer: The next step forward. ANZ J. Surg. 2023, 93, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Cen, S.; Ding, G.; Wu, W. Mucinous colorectal adenocarcinoma: Clinical pathology and treatment options. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupinacci, R.M.; Mello, E.S.; Coelho, F.F.; Kruger, J.A.P.; Perini, M.V.; Pinheiro, R.S.; Fonseca, G.M.; Cecconello, I.; Herman, P. Prognostic implication of mucinous histology in resected colorectal cancer liver metastases. Surgery 2014, 155, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettington, M.; Walker, N.; Clouston, A.; Brown, I.; Leggett, B.; Whitehall, V. The serrated pathway to colorectal carcinoma: Current concepts and challenges. Histopathology 2013, 62, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2073–2087.e2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betge, J.; Schneider, N.I.; Harbaum, L.; Pollheimer, M.J.; Lindtner, R.A.; Kornprat, P.; Ebert, M.P.; Langner, C. MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6 in colorectal cancer: Expression profiles and clinical significance. Virchows Arch. 2016, 469, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kufe, D.W. Mucins in cancer: Function, prognosis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zwam, P.H.; Vink-Börger, E.M.; Bronkhorst, C.M.; de Bruine, A.P.; van der Wurff, A.A.; Rutten, H.J.T.; Lemmens, V.; Nagtegaal, I.D.; Hugen, N. Prognosis of mucinous colon cancer is determined by histological biomarkers rather than microsatellite instability. Histopathology 2023, 82, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yang, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, R.; Shang, W.; Yuan, W.; Yang, F.; Sun, Q.; Xia, L. Clinical significance of mucinous component in colorectal adenocarcinoma: A propensity score-matched study. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, M.G.; Malietzis, G.; Constantinides, V.; Pellino, G.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. Clinicopathological factors and survival outcomes of signet-ring cell and mucinous carcinoma versus adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Discov. Oncol. 2021, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Huh, J.W.; Lee, W.Y.; Yun, S.H.; Kim, H.C.; Cho, Y.B.; Park, Y.; Shin, J.K. Prognostic Impact of Mucinous Adenocarcinoma in Stage II and III Colon Cancer. Dis. Colon Rectum 2023, 66, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, X.; Wu, Z.; Hu, H.; Cai, Y.; Li, J.; Ling, J.; Ding, M.; Li, W.; Deng, Y. Mucinous Adenocarcinoma Predicts Poor Response and Prognosis in Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of Individual Participant Data From 3 Prospective Studies. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2021, 20, e240–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, J.M.; Garmon, E.H. American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status Classification System. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, K.; Wilmanski, T.; Diener, C.; Earls, J.C.; Zimmer, A.; Lincoln, B.; Hadlock, J.J.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T.; et al. Multiomic signatures of body mass index identify heterogeneous health phenotypes and responses to a lifestyle intervention. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 996–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahadi, M.; Sokolova, A.; Brown, I.; Chou, A.; Gill, A.J. The 2019 World Health Organization Classification of appendiceal, colorectal and anal canal tumours: An update and critical assessment. Pathology 2021, 53, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavien, P.A.; Barkun, J.; de Oliveira, M.L.; Vauthey, J.N.; Dindo, D.; Schulick, R.D.; de Santibañes, E.; Pekolj, J.; Slankamenac, K.; Bassi, C.; et al. The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: Five-year experience. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, I.S.; O’Connell, E.; Fichtner, M.; McNamara, D.A.; Kay, E.W.; Prehn, J.H.M.; Furney, S.J.; Burke, J.P. Mucinous adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum: A genomic analysis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 120, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglio, A.E.V.; Grillo, T.G.; De Oliveira, E.C.S.; Di Stasi, L.C.; Sassaki, L.Y. Gut microbiota, inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Yang, Y.; Shi, J.Y.; Li, Y.K.; Xu, J.X.; Cheng, Y.; Gu, J. Mucinous adenocarcinoma: A unique clinicopathological subtype in colorectal cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2021, 13, 1567–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, E.; Reynolds, I.S.; McNamara, D.A.; Burke, J.P.; Prehn, J.H.M. Resistance to Cell Death in Mucinous Colorectal Cancer—A Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantero-Recasens, G.; Alonso-Marañón, J.; Lobo-Jarne, T.; Garrido, M.; Iglesias, M.; Espinosa, L.; Malhotra, V. Reversing chemorefraction in colorectal cancer cells by controlling mucin secretion. eLife 2022, 11, e73926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, R.S.; Cates, J.M.M.; Washington, K. Associations among histological characteristics and patient outcomes in colorectal carcinoma with a mucinous component. Histopathology 2019, 74, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tümay, V.; Guner, O.S. The association of mucinous histology with clinicopathological characteristics and long-term oncological outcome in patients with colorectal cancer. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2020, 91, 639–648. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Yi, C.; Wiredu Ocansey, D.K.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, F. Farnesoid-X receptor as a therapeutic target for inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1016836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Li, L.; Sun, D.; Liu, X.; Xia, Z.; Xue, S.; Chen, B.; Qin, H.; Ai, J.; Jiang, H. Farnesoid X Receptor Constructs an Immunosuppressive Microenvironment and Sensitizes FXRhighPD-L1low NSCLC to Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaginis, C.; Karandrea, D.; Alexandrou, P.T.; Giannopoulou, I.; Tsourouflis, G.; Troungos, C.; Danas, E.; Keramopoulos, A.; Patsouris, E.S.; Nakopoulou, L.; et al. High Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) expression is a strong and independent prognosticator in invasive breast carcinoma. Neoplasma 2017, 64, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Alive | Not Alive | p, † | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 168 (%75) | n = 56 (%25) | |||
| Gender | Male | 107 (63.7%) | 30 (53.6%) | 0.178 |
| Female | 61 (36.3%) | 26 (46.4%) | ||
| Tumor Site | Caecum | 25 (14.9%) | 8 (14.3%) | 0.709 |
| Right Colon | 40 (23.8%) | 15 (26.8%) | ||
| Transverse Colon | 8 (4.8%) | 3 (5.4%) | ||
| Left Colon | 13 (7.7%) | 8 (14.3%) | ||
| Sigmoid Colon | 55 (32.7%) | 15 (26.8%) | ||
| Rectum | 27 (16.1%) | 7 (12.5%) | ||
| T Stage | T2 | 5 (3.0%) | 2 (3.6%) | 0.003 ** |
| T3 | 146 (86.9%) | 38 (67.9%) | ||
| T4 | 17 (10.1%) | 16 (28.6%) | ||
| N Stage | N0 | 112 (66.7%) | 33 (58.9%) | 0.165 |
| N1 | 37 (22.0%) | 11 (19.6%) | ||
| N2 | 19 (11.3%) | 12 (21.4%) | ||
| LVI | Negative | 113 (67.3%) | 32 (57.1%) | 0.170 |
| Positive | 55 (32.7%) | 24 (42.9%) | ||
| PNI | Negative | 130 (77.4%) | 33 (58.9%) | 0.007 ** |
| Positive | 38 (22.6%) | 23 (41.1%) | ||
| Grade | Good | 24 (14.3%) | 6 (10.7%) | 0.089 |
| Moderate | 129 (76.8%) | 39 (69.6%) | ||
| Poor | 15 (8.9%) | 11 (19.6%) | ||
| TNM Stage | II | 114 (67.9%) | 33 (58.9%) | 0.223 |
| III | 54 (32.1%) | 23 (41.1%) | ||
| Complications | Minor | 99 (59.0%) | 33 (58.9%) | 1.000 |
| Major | 69 (41.0%) | 23 (41.1%) | ||
| BMI | Underweight | 3 (1.8%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.087 |
| Normal Weight | 56 (33.3%) | 16 (28.6%) | ||
| Overweight | 78 (46.4%) | 21 (37.5%) | ||
| Obesity | 31 (18.5%) | 19 (33.9%) | ||
| ASA Score | 1 | 2 (1.2%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.113 |
| 2 | 44 (26.2%) | 17 (30.4%) | ||
| 3 | 118 (70.2%) | 34 (60.7%) | ||
| 4 | 4 (2.4%) | 5 (8.9%) | ||
| Anastomosis Leakage | No | 153 (91.1%) | 49 (87.5%) | 0.437 |
| Yes | 15 (8.9%) | 7 (12.5%) | ||
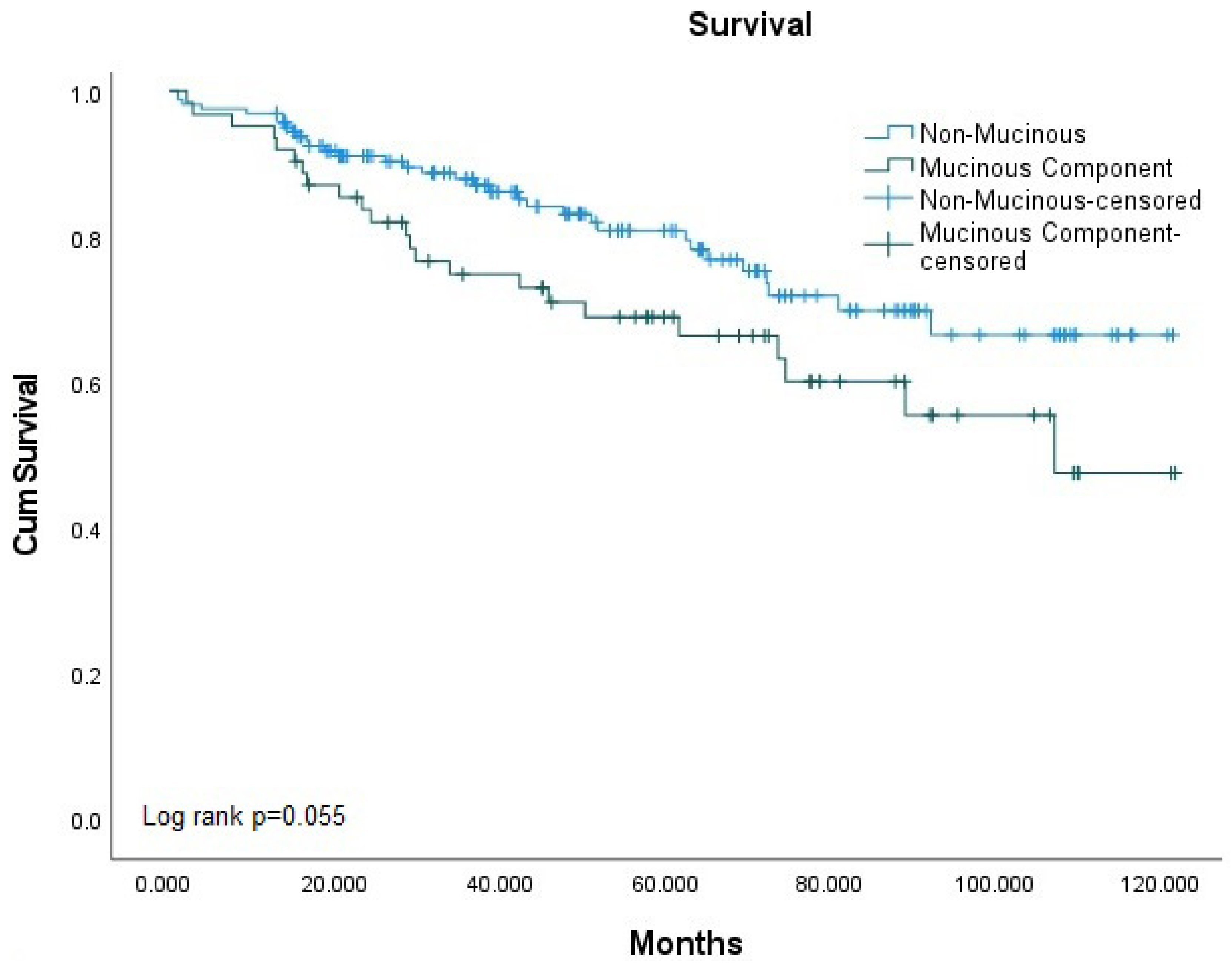
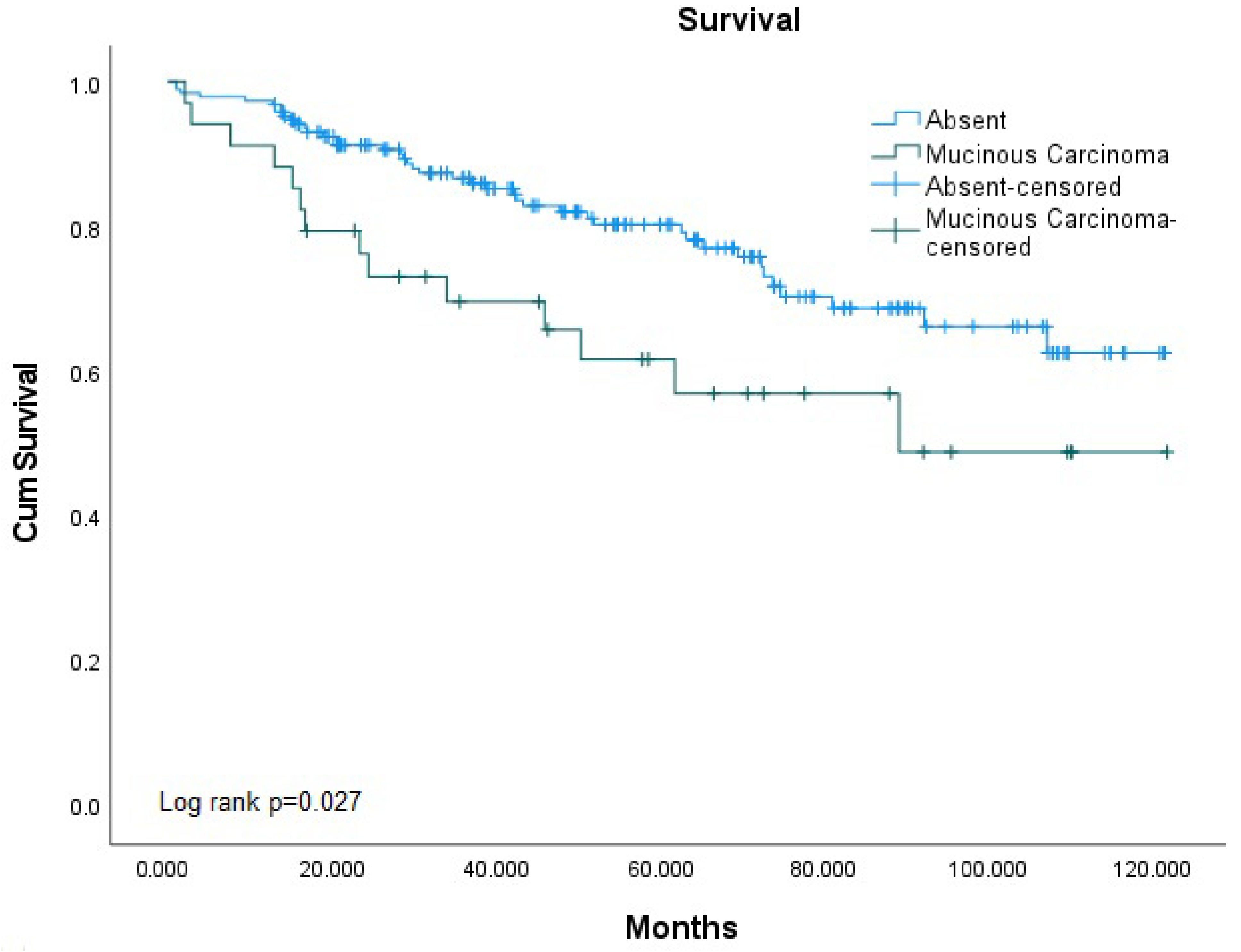
| Mucinous Histology | Non-Mucinous | 129 (76.8%) | 33 (58.9%) | 0.025 * |
| Mucinous Component | 19 (11.3%) | 9 (16.1%) | ||
| Mucinous Carcinoma | 20 (11.9%) | 14 (25.0%) | ||
| Mean ± SD | p ‡ | |||
| Alive | Not Alive | |||
| Age | 62.02 ± 11.88 | 64.46 ± 13.59 | 0.015 * | |
| LOS/Days | 10.44 ± 7.08 | 13.63 ± 12.77 | 0.020 * | |
| Variables | nMAC (n = 162) | MCP (n = 28) | MAC (n = 34) | p, † | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 103 (63.6%) | 17 (60.7%) | 17 (50.0%) | 0.335 | |
| Female | 59 (36.4%) | 11 (39.3%) | 17 (50.0%) | |||
| Tumor Site | Caecum | 21 (13.0%) | 3 (10.7%) | 9 (26.5%) | 0.054 | |
| Right Colon | 33 (20.4%) | 10 (35.7%) | 12 (35.3%) | |||
| Transverse Colon | 8 (4.9%) | 3 (10.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | |||
| Left Colon | 14 (8.6%) | 4 (14.3%) | 3 (8.8%) | |||
| Sigmoid Colon | 58 (35.8%) | 5 (17.9%) | 7 (20.6%) | |||
| Rectum | 28 (17.3%) | 3 (10.7%) | 3 (8.8%) | |||
| T Stage | T2 | 4 (2.5%) | 1 (3.6%) | 2 (5.9%) | 0.666 | |
| T3 | 136 (84.0%) | 23 (82.1%) | 25 (73.5%) | |||
| T4 | 22 (13.6%) | 4 (14.3%) | 7 (20.6%) | |||
| N Stage | N0 | 108 (66.7%) | 17 (60.7%) | 20 (58.8%) | 0.667 | |
| N1 | 34 (21.0%) | 5 (17.9%) | 9 (26.5%) | |||
| N2 | 34 (21.0%) | 6 (21.4%) | 5 (14.7%) | |||
| LVI | Negative | 105 (64.8%) | 16 (57.1%) | 24 (70.6%) | 0.544 | |
| Positive | 57 (35.2%) | 12 (42.9%) | 10 (29.4%) | |||
| PNI | Negative | 115 (71.0%) | 22 (78.6%) | 26 (76.5%) | 0.616 | |
| Positive | 47 (29.0%) | 6 (21.4%) | 8 (23.5%) | |||
| Grade | Good | 22 (13.6%) | 3 (10.7%) | 5 (14.7%) | 0.151 | |
| Moderate | 126 (77.8%) | 21 (75.0%) | 21 (61.8%) | |||
| Poor | 14 (8.6%) | 4 (14.3%) | 8 (23.5%) | |||
| TNM Stage | II | 108 (66.7%) | 17 (60.7%) | 20 (58.8%) | 0.612 | |
| III | 54 (33.3%) | 11 (39.3%) | 14 (41.2%) | |||
| Complications | Minor | 93 (57.4%) | 18 (64.3%) | 21 (61.8%) | 0.741 | |
| Major | 69 (42.6%) | 10 (35.7%) | 13 (38.2%) | |||
| BMI | Underweight | 3 (1.9%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.555 | |
| Normal Weight | 55 (34.0%) | 10 (35.7%) | 7 (20.6%) | |||
| Overweight | 71 (43.8%) | 10 (35.7%) | 18 (52.9%) | |||
| Obesity | 33 (20.4%) | 8 (28.6%) | 9 (26.5%) | |||
| ASA Score | 1 | 2 (1.2%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.208 | |
| 2 | 39 (24.1%) | 13 (46.4%) | 9 (26.5%) | |||
| 3 | 113 (69.8%) | 14 (50.0%) | 25 (73.5%) | |||
| 4 | 8 (4.9%) | 1 (3.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | |||
| Anastomosis Leak | Negative | 145 (89.5%) | 27 (96.4%) | 30 (88.2%) | 0.481 | |
| Positive | 17 (10.5%) | 1 (3.6%) | 4 (11.8%) | |||
| Overall Survival | Alive | 129 (79.6%) | 19 (67.9%) | 20 (58.8%) | 0.025 * | |
| Not Alive | 33 (20.4%) | 9 (32.1%) | 14 (41.2%) | |||
| Mean ± SD | F | p, § | ||||
| Age | 62.94 ± 12.00 | 58.68 ± 13.04 | 64.44 ± 13.07 | 1.865 | 0.157 | |
| LOS | 11.17 ± 7.65 | 9.79 ± 4.79 | 12.74 ± 15.15 | 0.853 | 0.428 | |
| Univariate | Multivariate | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prognostic Factors | OR | 95% CI | p | OR | 95% CI | p | |
| T2 | 0.005 ** | 0.031 * | |||||
| T Stage | T3 | 0.651 | 0.121–3.485 | 0.616 | 0.612 | 0.108–3.474 | 0.580 |
| T4 | 2.353 | 0.398–13.900 | 0.345 | 1.808 | 0.282–11.586 | 0.532 | |
| PNI | 2.384 | 1.253–4.538 | 0.008 ** | 2.283 | 1.140–4.572 | 0.020 * | |
| nMAC | 0.029 * | 0.030 * | |||||
| MH | MCP | 1.852 | 0.768–4.466 | 0.170 | 2.037 | 0.805–5.152 | 0.133 |
| MAC | 2.736 | 1.251–5.986 | 0.012 * | 2.814 | 1.233–6.418 | 0.014 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aydin, İ.C.; Torun, M.; Sönmez, M.R.; Ademoğlu, S.; Sunar, A.O.; Uzun, O.; Gülmez, S.; Polat, E.; Duman, M. The Influence of Mucinous Histology on the Prognosis of Stage II and III Colorectal Cancers. Medicina 2025, 61, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030456
Aydin İC, Torun M, Sönmez MR, Ademoğlu S, Sunar AO, Uzun O, Gülmez S, Polat E, Duman M. The Influence of Mucinous Histology on the Prognosis of Stage II and III Colorectal Cancers. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030456
Chicago/Turabian StyleAydin, İsa Caner, Mehmet Torun, Mehmet Reşit Sönmez, Serkan Ademoğlu, Ahmet Orhan Sunar, Orhan Uzun, Selçuk Gülmez, Erdal Polat, and Mustafa Duman. 2025. "The Influence of Mucinous Histology on the Prognosis of Stage II and III Colorectal Cancers" Medicina 61, no. 3: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030456
APA StyleAydin, İ. C., Torun, M., Sönmez, M. R., Ademoğlu, S., Sunar, A. O., Uzun, O., Gülmez, S., Polat, E., & Duman, M. (2025). The Influence of Mucinous Histology on the Prognosis of Stage II and III Colorectal Cancers. Medicina, 61(3), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030456





