White Matter Microstructural Alterations in Type 2 Diabetes: A Combined UK Biobank Study of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. UK Biobank Cohort
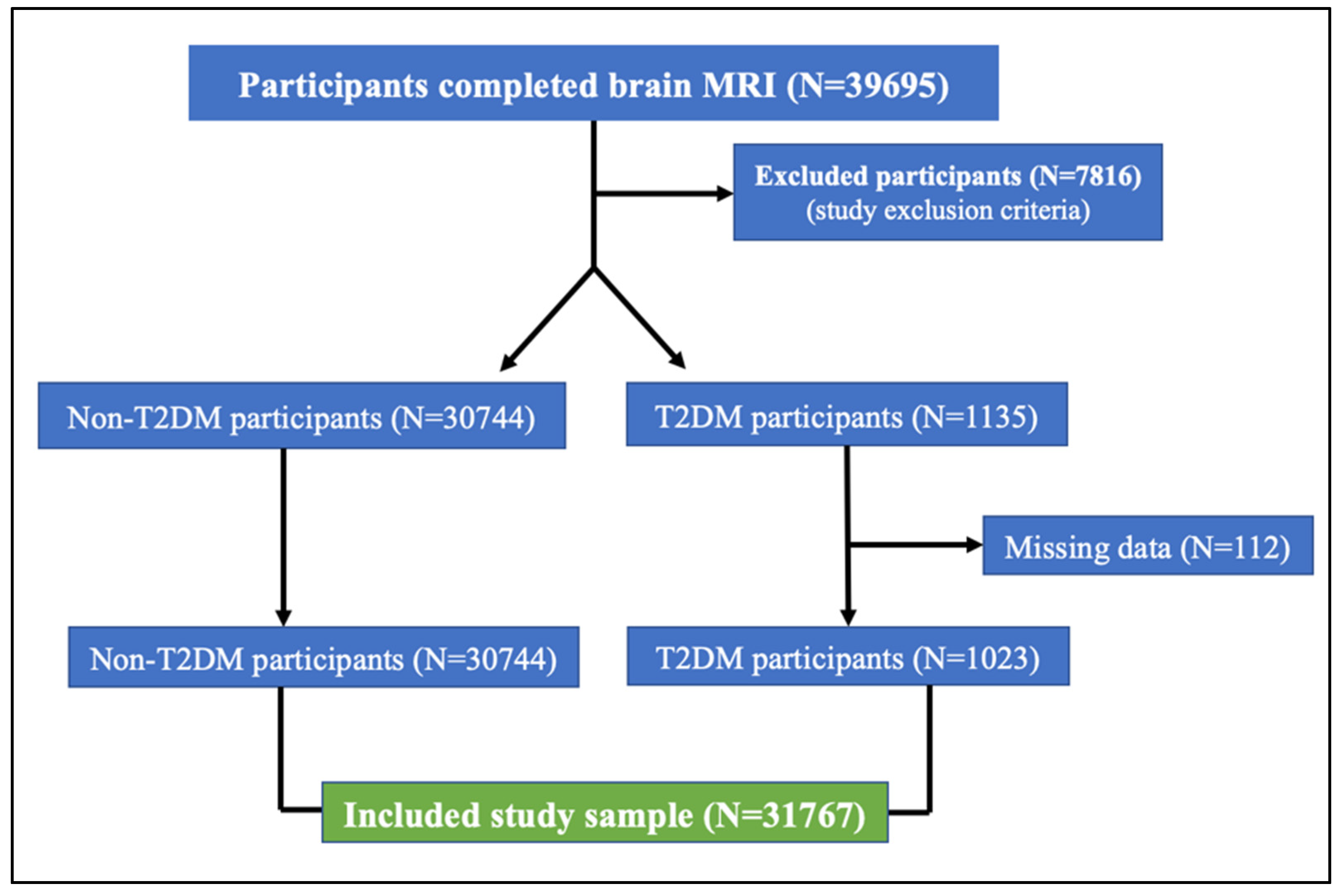
2.2. Clinical Characteristics and Sample Selection
2.3. Brain MRI Acquisition
2.4. Diffusion Image Processing
2.4.1. DTI and NODDI Fitting
2.4.2. White Matter Tract Skeleton Analysis
2.5. Modelling in UK Biobank Brain Imaging
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
3.2. White Matter Intergroup Differences and Association with Metabolic Profile: Overview
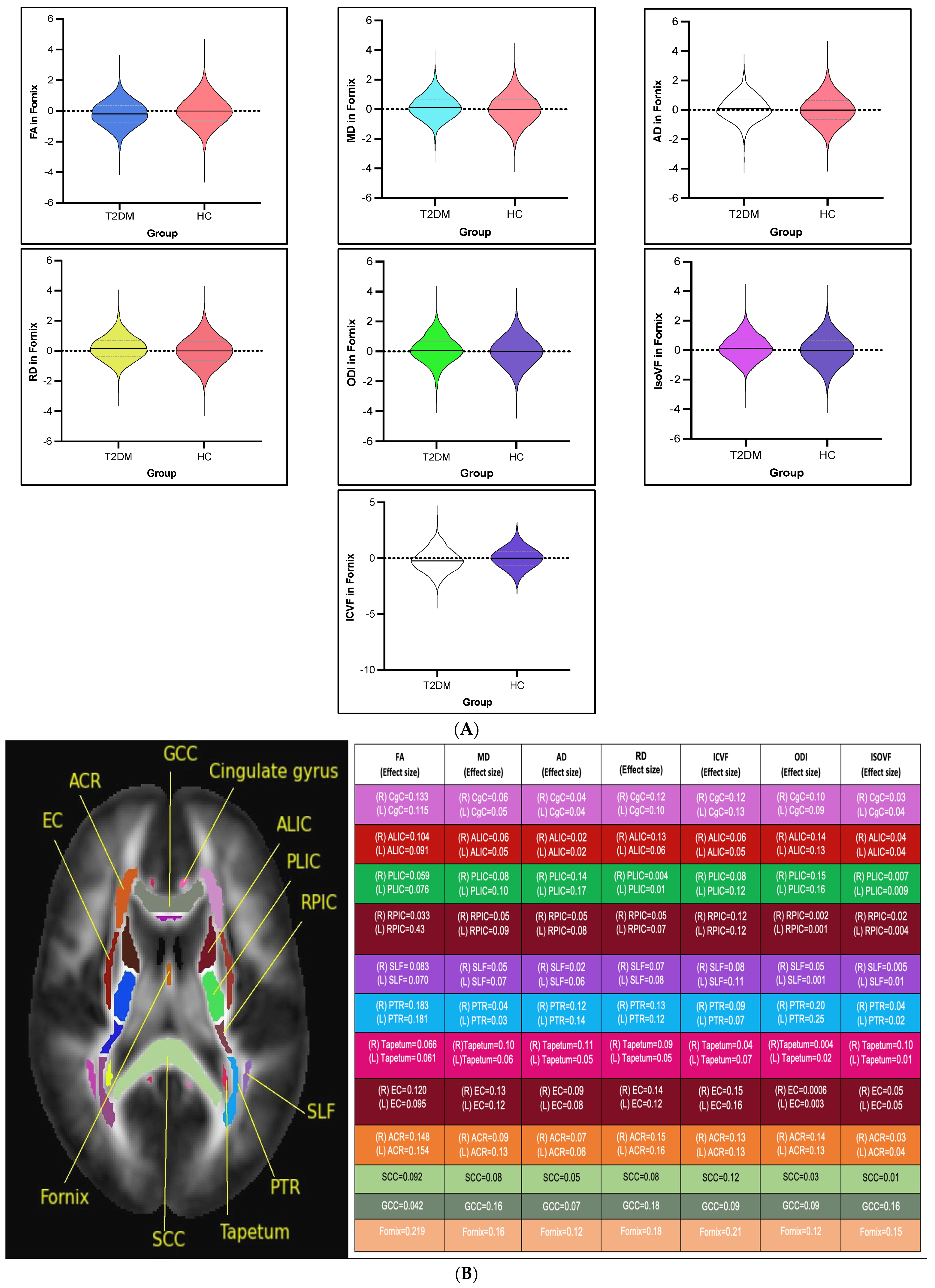
3.2.1. DTI Intergroup White Matter Differences
3.2.2. NODDI Intergroup White Matter Differences
3.3. Diffusion Measures and Correlation with Metabolic Profile
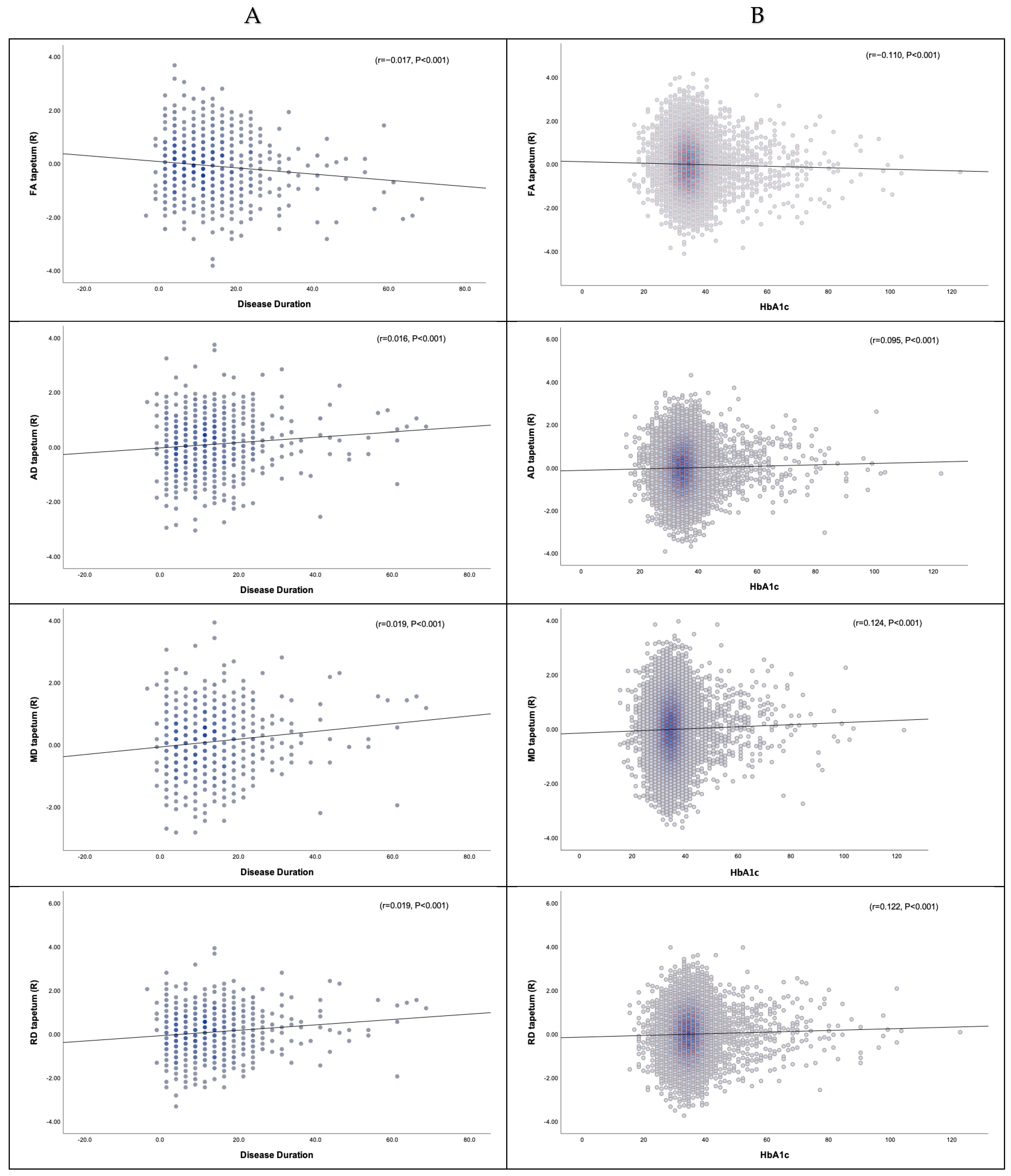
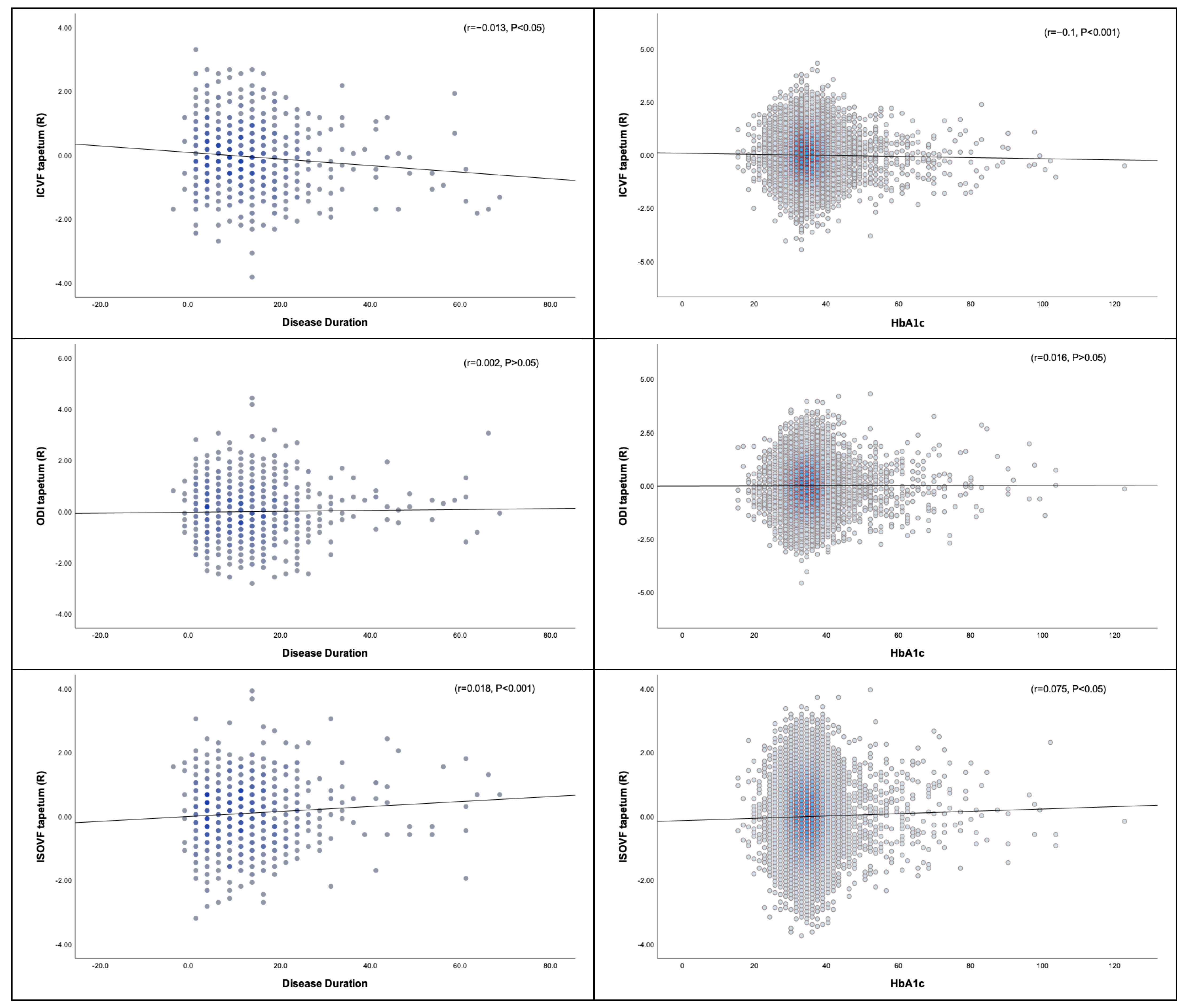
3.3.1. Disease Duration, HbA1c, and DTI
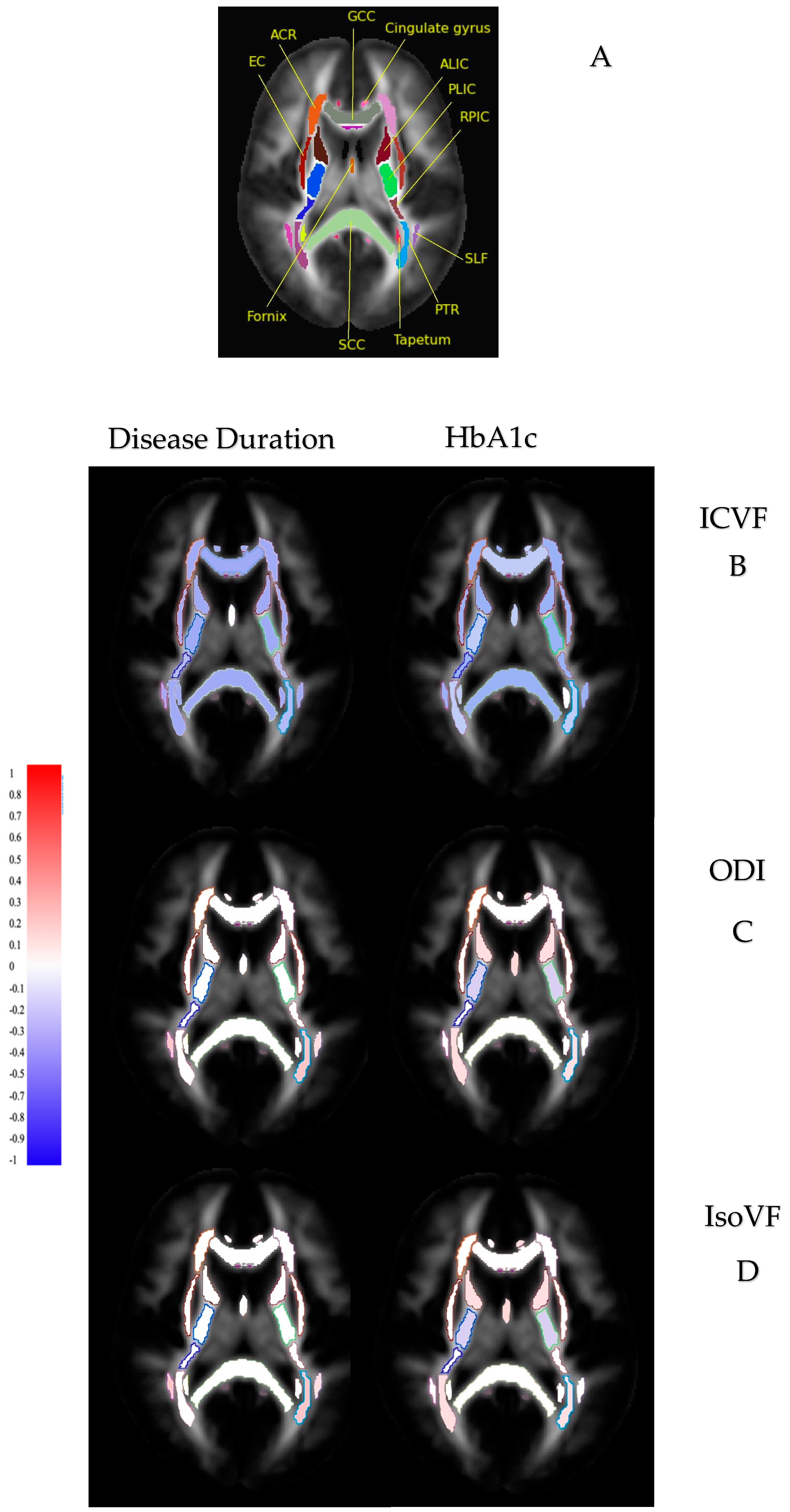
3.3.2. Disease Duration, HbA1c, and NODDI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ong, K.L.; Stafford, L.K.; McLaughlin, S.A.; Boyko, E.J.; Vollset, S.E.; Smith, A.E.; Dalton, B.E.; Duprey, J.; Cruz, J.A.; Hagins, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmet, P.; Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Shaw, J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 2001, 414, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 diabetes—Global burden of disease and forecasted trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2017, 389, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, A.; Tench, C.; Stevenson, R.; Felmban, G.; Altokhis, A.; Aldhebaib, A.; Dineen, R.A.; Constantinescu, C.S.; Quattrocchi, C. brain sciences Review Investigating Brain Microstructural Alterations in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruehl, H.; Sweat, V.; Tirsi, A.; Shah, B.; Convit, A.; Bruehl, H.; Sweat, V.; Tirsi, A.; Shah, B.; Convit, A. Obese Adolescents with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Have Hippocampal and Frontal Lobe Volume Reductions. Neurosci. Med. 2011, 2, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, P.L.; Javier, D.C.; Ryan, C.M.; Tsui, W.H.; Ardekani, B.A.; Ten, S.; Convit, A. Preliminary evidence for brain complications in obese adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, K.; Shu, N.; Zhang, Z. Disrupted White Matter Network and Cognitive Decline in Type 2 Diabetes Patients. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 53, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijmer, Y.D.; Leemans, A.; Brundel, M.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biessels, G.J.; Utrecht Vascular Cognitive Impairment Study, G. Disruption of the cerebral white matter network is related to slowing of information processing speed in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2112–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Yu, J.H.; Shin, M.S.; Shin, Y.W.; Kim, M.S. Hyperglycemia Reduces Efficiency of Brain Networks in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS ONE Electron. Resour. 2016, 11, e0157268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjari Moghaddam, H.; Ghazi Sherbaf, F.; Aarabi, M.H. Brain microstructural abnormalities in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 55, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, T.; Yang, M.; Chen, C.; Tao, J.; Liang, S. Abnormalities of Brain White Matter in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 693890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.C. Multiple-Fiber Reconstruction Algorithms for Diffusion MRI. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1064, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Sui, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X.J.; Yang, S.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, W. Brain microstructural alterations in type 2 diabetes: Diffusion kurtosis imaging provides added value to diffusion tensor imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.Q.; Qin, X.W.; Lu, X.S.; Ni, X.C.; Zhang, X.Y.Q. White Matter Microstructural Abnormalities in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Analysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.L.; Hasan, K.M.; Lazar, M.; Tsuruda, J.S.; Parker, D.L. Analysis of partial volume effects in diffusion-tensor MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001, 45, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, S.; Gabrielli, A.; Palombo, M.; Maraviglia, B.; Capuani, S. Non-Gaussian diffusion imaging: A brief practical review. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 29, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Schneider, T.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Alexander, D.C. NODDI: Practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. Neuroimage 2012, 61, 1000–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, K.; Hori, M.; Aoki, S. NODDI in clinical research. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 346, 108908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, W. Application of neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging to characterize brain microstructural abnormalities in type-2 diabetics with mild cognitive impairment. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.L.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Bangerter, N.K.; Thomas, D.L.; Yacoub, E.; Xu, J.; Bartsch, A.J.; Jbabdi, S.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Andersson, J.L.R.; et al. Multimodal population brain imaging in the UK Biobank prospective epidemiological study. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK Biobank: An Open Access Resource for Identifying the Causes of a Wide Range of Complex Diseases of Middle and Old Age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Biobank. UK Biobank: A Major Resource for Health Research. Available online: https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/ (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- UK Biobank. 2014. Available online: http://biobank.ctsu.ox.ac.uk/crystal/refer.cgi?id=2367 (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Jenkinson, M.; Bangerter, N.K.; Andersson, J.L.R.; Griffanti, L.; Douaud, G.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Jbabdi, S.; Hernandez-Fernandez, M.; Vallee, E.; et al. Image processing and Quality Control for the first 10,000 brain imaging datasets from UK Biobank. Neuroimage 2018, 166, 400–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.L.R.; Sotiropoulos, S.N. An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. Neuroimage 2016, 125, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, J.L.R.; Graham, M.S.; Zsoldos, E.; Sotiropoulos, S.N. Incorporating outlier detection and replacement into a non-parametric framework for movement and distortion correction of diffusion MR images. Neuroimage 2016, 141, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasser, M.F.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Wilson, J.A.; Coalson, T.S.; Fischl, B.; Andersson, J.L.; Xu, J.; Jbabdi, S.; Webster, M.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage 2013, 80, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Miller, K.L. UK Biobank Brain Imaging Documentation UK Biobank Brain Imaging Documentation Contributors to UK Biobank Brain Imaging. 2020. Available online: http://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk (accessed on 22 October 2021).
- FDT/UserGuide—FslWiki. Available online: https://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl/fslwiki/FDT/UserGuide#DTIFIT (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Daducci, A.; Canales-Rodríguez, E.J.; Zhang, H.; Dyrby, T.B.; Alexander, D.C.; Thiran, J.P. Accelerated Microstructure Imaging via Convex Optimization (AMICO) from diffusion MRI data. Neuroimage 2015, 105, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Rueckert, D.; Nichols, T.E.; Mackay, C.E.; Watkins, K.E.; Ciccarelli, O.; Cader, M.Z.; Matthews, P.M.; et al. Tract-based spatial statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1487–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, M.; Vernooij, M.W.; Klein, S.; Ikram, M.A.; Vos, F.M.; Smith, S.M.; Niessen, W.J.; Andersson, J.L.R. Improving alignment in Tract-based spatial statistics: Evaluation and optimization of image registration. Neuroimage 2013, 76, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, K.; Faria, A.V.; Van Zijl, P.C.; Mori, S.; Nagae-Poetscher. MRI Atlas of Human White Matter; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Available online: https://books.google.co.uk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=ltwRYlvFNLIC&oi=fnd&pg=PR5&ots=geIMk92Kgn&sig=SYvCENlh1MXHtwUjO22hXUC-GbU&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 27 October 2021).
- Alfaro-Almagro, F.; McCarthy, P.; Afyouni, S.; Andersson, J.L.R.; Bastiani, M.; Miller, K.L.; Nichols, T.E.; Smith, S.M. Confound modelling in UK Biobank brain imaging. Neuroimage 2021, 224, 117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.K.; Sun, S.W.; Ju, W.K.; Lin, S.J.; Cross, A.H.; Neufeld, A.H. Diffusion tensor imaging detects and differentiates axon and myelin degeneration in mouse optic nerve after retinal ischemia. Neuroimage 2003, 20, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, D.; Go, C.; Rutka, J.T.; Rydenhag, B.; Mabbott, D.J.; Snead, O.C.; Raybaud, C.R.; Widjaja, E. Bilateral diffusion tensor abnormalities of temporal lobe and cingulate gyrus white matter in children with temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 81, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Sui, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Karaman, M.M.; Cai, K.; Anderson, T.M.; Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.J. A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study on White Matter Abnormalities in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Using Tract-Based Spatial Statistics. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Du, W.; Gao, B.; Gao, J.; Hu, S.; Song, Q.; Wang, W.; Miao, Y. White matter microstructure alterations in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its correlation with cerebral small vessel disease and cognitive performance. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pan, P.; Li, J.; Tang, M.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Ai, K.; Lei, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Analysis of white matter tract integrity using diffusion kurtosis imaging reveals the correlation of white matter microstructural abnormalities with cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1327339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slattery, C.F.; Zhang, J.; Paterson, R.W.; Foulkes, A.J.M.; Carton, A.; Macpherson, K.; Mancini, L.; Thomas, D.L.; Modat, M.; Toussaint, N.; et al. ApoE influences regional white-matter axonal density loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 57, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriach, M.; Flores-Bellver, M.; Romero, F.J.; Barcia, J.M. Diabetes and the brain: Oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.; Archer, D.B.; Chu, W.T.; Coombes, S.A.; Lai, S.; Wilkes, B.J.; McFarland, N.R.; Okun, M.S.; Black, M.L.; Herschel, E.; et al. Neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI) and free-water imaging in Parkinsonism. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 5094–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grussu, F.; Schneider, T.; Tur, C.; Yates, R.L.; Tachrount, M.; Ianuş, A.; Yiannakas, M.C.; Newcombe, J.; Zhang, H.; Alexander, D.C.; et al. Neurite dispersion: A new marker of multiple sclerosis spinal cord pathology? Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2017, 4, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gregory, S.; Scahill, R.I.; Durr, A.; Thomas, D.L.; Lehericy, S.; Rees, G.; Tabrizi, S.J.; Zhang, H. In vivo characterization of white matter pathology in premanifest huntington’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, N.W.; Caverzasi, E.; Graham, S.J.; Hutchison, M.G.; Schweizer, T.A. White matter microstructure in athletes with a history of concussion: Comparing diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI). Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 4201–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caverzasi, E.; Papinutto, N.; Castellano, A.; Zhu, A.H.; Scifo, P.; Riva, M.; Bello, L.; Falini, A.; Bharatha, A.; Henry, R.G. Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging Color Maps to Characterize Brain Diffusion in Neurologic Disorders. J. Neuroimaging 2016, 26, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, S.; Hori, M.; Ueda, R.; Hayashi, S.; Inaji, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Maehara, T.; Ishii, K.; Aoki, S.; Nariai, T. Unraveling Specific Brain Microstructural Damage in Moyamoya Disease Using Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Positron Emission Tomography. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierpaoli, C.; Basser, P.J. Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn. Reson. Med. 1996, 36, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelescu, I.O.; Veraart, J.; Fieremans, E.; Novikov, D.S. Degeneracy in model parameter estimation for multi-compartmental diffusion in neuronal tissue. NMR Biomed. 2016, 29, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Kelley, D.A.C.; Banerjee, S.; Lupo, J.M.; Chang, S.M.; Xu, D.; Hess, C.P.; Nelson, S.J. Clinically feasible NODDI characterization of glioma using multiband EPI at 7 T. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 9, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampinen, B.; Szczepankiewicz, F.; Mårtensson, J.; van Westen, D.; Sundgren, P.C.; Nilsson, M. Neurite density imaging versus imaging of microscopic anisotropy in diffusion MRI: A model comparison using spherical tensor encoding. Neuroimage 2017, 147, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cohort Characteristics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 1023) T2DM (Mean ± SD)% | (N = 30744) Non-T2DM (mean ± SD)% | χ2/T | Mean Difference | 95% CI | ||
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Gender F (%) | 339/39% | 16,588/53% | 172.4 | -- | -- | -- |
| Age (years) | 66 ± 7.04 | 64 ± 7.5 | 11.2 | 2.5 | 2.09 | 2.9 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 142.6 ± 18.05 | 136.03 ± 18.6 | 11.3 | 6.7 | 5.6 | 7.9 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 83.7 ± 10.4 | 81.2 ± 10.4 | 7.6 | 2.6 | 1.9 | 3.4 |
| Hb1AC (mmol/mol) | 47.08 ± 12.06 | 34.3 ± 3.5 | 32.6 | 12.9 | 12.1 | 13.6 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.8 ± 5.1 | 26.3 ± 4.3 | 21.3 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 3.8 |
| Disease duration (years) | 12.3 ± 9.3 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Education level | Missing 128 | Missing 2062 | ||||
| (A) | 183 (17.8%) | 4429 (14.4%) | 82.03 | |||
| (B) | 200 (19.5%) | 5394 (17.5%) | ||||
| (C) | 117 (11.4%) | 3735 (12.1%) | ||||
| (D) | 395 (38.6%) | 15124 (49.1%) | ||||
| Diffusion Indices | Disease Duration | HbA1c |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced FA | Number of tracts: 31/48 WM tracts | 35/48 WM tracts |
| Direction: negative correlation | Negative correlation | |
| Strength: weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | Weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | |
| Increased MD | Number of tracts: 30/48 WM tracts | 35/48 WM tracts |
| Direction: positive correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Strength: weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | Weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | |
| Increased AD | Number of tracts: 13/48 WM tracts | 18/48 WM tracts |
| Direction: positive correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Strength: weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | Weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | |
| Increased RD | Number of tracts: 39/48 WM tracts | 40/48 WM tracts |
| Direction: positive correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Strength: weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | Weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | |
| Reduced ICVF | Number of tracts: 43/48 WM tracts | 40/48 WM tracts |
| Direction: negative correlation | Negative correlation | |
| Strength: weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | Weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | |
| Increased ODI | Number of tracts: 3/48 WM tracts | 23/48 WM tracts |
| Direction: positive correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Strength: weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | Weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | |
| Increased IsoVF | Number of tracts: 8/48 WM tracts | 13/48 WM tracts |
| Direction: positive correlation | Positive correlation | |
| Strength: weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) | Weak (0 < r ≤ 0.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alotaibi, A.; Alqarras, M.; Podlasek, A.; Almanaa, A.; AlTokhis, A.; Aldhebaib, A.; Aldebasi, B.; Almutairi, M.; Tench, C.R.; Almanaa, M.; et al. White Matter Microstructural Alterations in Type 2 Diabetes: A Combined UK Biobank Study of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging. Medicina 2025, 61, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030455
Alotaibi A, Alqarras M, Podlasek A, Almanaa A, AlTokhis A, Aldhebaib A, Aldebasi B, Almutairi M, Tench CR, Almanaa M, et al. White Matter Microstructural Alterations in Type 2 Diabetes: A Combined UK Biobank Study of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030455
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlotaibi, Abdulmajeed, Mostafa Alqarras, Anna Podlasek, Abdullah Almanaa, Amjad AlTokhis, Ali Aldhebaib, Bader Aldebasi, Malak Almutairi, Chris R. Tench, Mansour Almanaa, and et al. 2025. "White Matter Microstructural Alterations in Type 2 Diabetes: A Combined UK Biobank Study of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging" Medicina 61, no. 3: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030455
APA StyleAlotaibi, A., Alqarras, M., Podlasek, A., Almanaa, A., AlTokhis, A., Aldhebaib, A., Aldebasi, B., Almutairi, M., Tench, C. R., Almanaa, M., Mohammadi-Nejad, A.-R., Constantinescu, C. S., Dineen, R. A., & Lee, S. (2025). White Matter Microstructural Alterations in Type 2 Diabetes: A Combined UK Biobank Study of Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging. Medicina, 61(3), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030455







