The Regulatory Effects of Exercise and Metformin on Biomarkers in Obesity: A Focus on Uric Acid, Irisin, Adiponutrin, Adropin, and Copeptin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
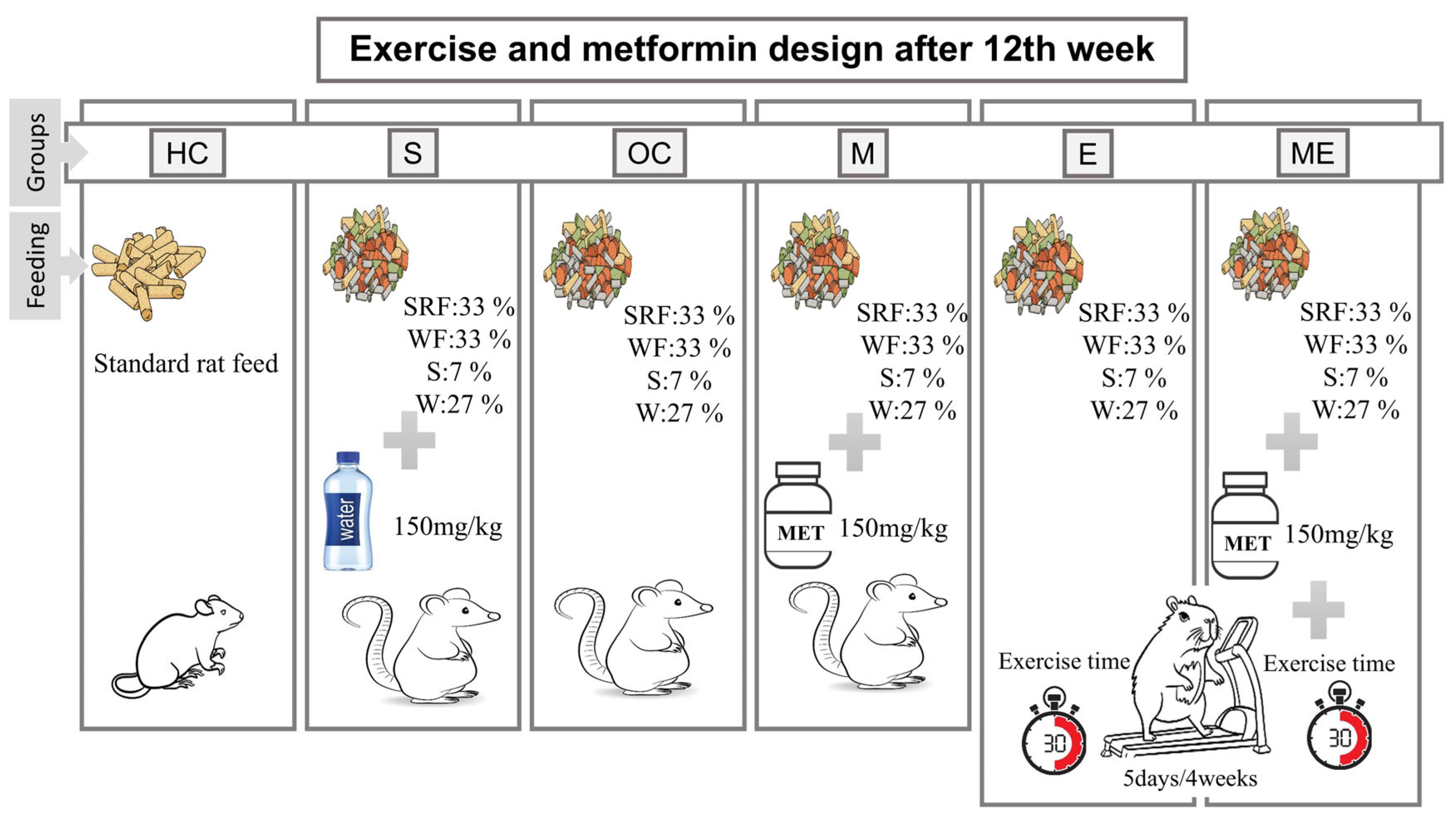
2.1. Research Groups and Termination
2.2. Exercise Protocol
2.3. Diet Protocol and Determining Obesity
2.4. Metformin Intervention
2.5. Biochemical Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Oppert, J.M.; Ciangura, C.; Bellicha, A. Physical activity and exercise for weight loss and maintenance in people living with obesity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, S.; Del Buono, M.G.; Ozemek, C.; Lavie, C.J. Obesity, risk of diabetes and role of physical activity, exercise training and cardiorespiratory fitness. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 62, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fock, K.M.; Khoo, J. Diet and exercise in management of obesity and overweight. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, T.; Pošćić, N.; Colitti, M. Factors involved in white-to-brown adipose tissue conversion and in thermogenesis: A review. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levri, K.M.; Slaymaker, E.; Last, A.; Yeh, J.; Ference, J.; D’Amico, F.; Wilson, S.A. Metformin as treatment for overweight and obese adults: A systematic review. Ann. Fam. Med. 2005, 3, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarwa, R.; Brunetti, V.C.; Aloe, S.; Henderson, M.; Platt, R.W.; Filion, K.B. Efficacy and safety of metformin for obesity: A systematic review. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e20201610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerevanian, A.; Soukas, A.A. Metformin: Mechanisms in human obesity and weight loss. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziqubu, K.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E.; Mthembu, S.X.H.; Mabhida, S.E.; Jack, B.U.; Nyambuya, T.M.; Nkambule, B.B.; Basson, A.K.; Tiano, L.; Dludla, P.V. Anti-obesity effects of metformin: A scoping review evaluating the feasibility of brown adipose tissue as a therapeutic target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S. Three new players in energy regulation: Preptin, adropin and irisin. Peptides 2014, 56, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho-Jr, J.D.S.; Camacho, F.A.; Cavararo, C.D.S.; Baião, P.F.; Medeiros, R.F.; Barroso, S.G.; de Matos, A.C. Irisin and cardiometabolic disorders in obesity: A systematic review. Int. J. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 581015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baulande, S.; Lasnier, F.; Lucas, M.; Pairault, J. Adiponutrin, a transmembrane protein corresponding to a novel dietary-and obesity-linked mRNA specifically expressed in the adipose lineage. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 33336–33344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Lu, J.; Hu, J.; Gong, X. Unveiling the multifaceted role of adropin in various diseases. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2024, 54, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalleh, R.; Torpy, D.J. The emerging role of copeptin. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2021, 42, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Enhörning, S.; Malan, L. Copeptin relates to a fatty liver and measures of obesity in a South African population with mixed ethnicities. Endocrine 2019, 65, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsushima, Y.; Nishizawa, H.; Tochino, Y.; Nakatsuji, H.; Sekimoto, R.; Nagao, H.; Shirakura, T.; Kato, K.; Imaizumi, K.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Uric acid secretion from adipose tissue and its increase in obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 27138–27149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viollet, B.; Guigas, B.; Garcia, N.S.; Leclerc, J.; Foretz, M.; Andreelli, F. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of metformin: An overview. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S. A short history, principles, and types of ELISA, and our laboratory experience with peptide/protein analyses using ELISA. Peptides 2015, 72, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Emre, E.; Ugur, K.; Aydin, M.A.; Sahin, İ.; Cinar, V.; Akbulut, T. An overview of ELISA: A review and update on best laboratory practices for quantifying peptides and proteins in biological fluids. J. Int. Med. Res. 2025, 53, 03000605251315913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L. Distribution Theory for Glass’s Estimator of Effect Size and Related Estimators. J. Educ. Stat. 1981, 6, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, H.D. Designing Experiments and Analyzing Data: A Model Comparison Perspective; Routledge: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.B.; Forsythe, A.B. Robust tests for the equality of variances. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1974, 69, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnet, C.W. A multiple comparison procedure for comparing several treatments with a control. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1955, 50, 1096–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Meng, X.; Shan, R.; Zi, T.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, D.; Qu, R.; Guo, X.; et al. Temporal relationship between hyperuricemia and obesity, and its association with future risk of type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Lawrence, W.R.; Yang, J.; Tian, J.; Li, C.; Lian, W.; He, J.; Qu, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Association between serum uric acid and obesity in Chinese adults: A 9-year longitudinal data analysis. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e041919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Liang, W.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Nie, Z.; Chen, Y.; He, L.; Jin, Y.; Yao, Y. Association between serum uric acid levels and obesity among university students (China). Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 2407–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, H.; Gao, H.; Ren, Q.; He, J. The abundance of bifidobacterium in relation to visceral obesity and serum uric acid. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, T. Responses of uric acid, glucose, thyroid hormones and liver enzymes to aerobic and combined exercises in university students. High. Educ. Stud. 2020, 10, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krzystek-Korpacka, M.; Patryn, E.; Kustrzeba-Wojcicka, I.; Chrzanowska, J.; Gamian, A.; Noczynska, A. The effect of a one-year weight reduction program on serum uric acid in overweight/obese children and adolescents. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011, 49, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Lian, F.; Chen, D.; Qiu, Q.; Xu, H.; Liang, L.; Yang, X. Physical exercises and weight loss in obese patients help to improve uric acid. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 94893–94899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.I.; D’Souza, C.; Singh, J.; Adeghate, E. Adropin’s role in energy homeostasis and metabolic disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasaszwili, M.; Billert, M.; Strowski, M.Z.; Nowak, K.W.; Skrzypski, M. Adropin as a fat-burning hormone with multiple functions-Review of a decade of research. Molecules 2020, 25, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Y.-J.; Ge, R.-K.; Zhou, M.; Hu, H.; Liu, H.; Cui, J.; Li, L.-L.; Dong, Y.-F.; et al. Aerobic exercise improves endothelial function and serum adropin levels in obese adolescents independent of body weight loss. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S.; Kilinc, F.; Ugur, K.; Aydin, M.A.; Yalcin, M.H.; Kuloglu, T.; Tektemur, N.K.; Albayrak, S.; Emre, E.; Yardim, M.; et al. Effects of irisin and exercise on adropin and betatrophin in a new metabolic syndrome model. Biotech. Histochem. 2024, 99, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tičinović Kurir, T.; Miličević, T.; Novak, A.; Vilović, M.; Božić, J. Adropin–potential link in cardiovascular protection for obese male type 2 diabetes mellitus patients treated with liraglutide. Acta Clin. Croat. 2020, 59, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkudelski, T.; Konieczna, K.; Szkudelska, K. Regulatory effects of metformin, an antidiabetic biguanide drug, on the metabolism of primary rat adipocytes. Molecules 2022, 27, 5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karise, I.; Bargut, T.C.; Del Sol, M.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A. Metformin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and thermogenesis in brown adipocytes of mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.E.; Hoffstedt, J.; Parikh, H.; Carlsson, E.; Wabitsch, M.; Bondeson, A.-G.; Hedenbro, J.; Tornqvist, H.; Groop, L.; Ridderstråle, M. Variation in the adiponutrin gene influences its expression and associates with obesity. Diabetes 2006, 55, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscella, A.; Stefàno, E.; Lunetti, P.; Capobianco, L.; Marsigliante, S. The regulation of fat metabolism during aerobic exercise. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Enhörning, S.; Cimini, F.A.; Capoccia, D.; Chiappetta, C.; Di Cristofano, C.; Silecchia, G.; Leonetti, F.; Melander, O.; Cavallo, M.G. Elevated plasma copeptin levels identify the presence and severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obesity. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enhörning, S.; Bankir, L.; Bouby, N.; Struck, J.; Hedblad, B.; Persson, M.; Melander, O. Copeptin, a marker of vasopressin, in abdominal obesity, diabetes and microalbuminuria: The prospective Malmö Diet and Cancer Study cardiovascular cohort. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Humpire, R.; Soriano-Moreno, D.R.; Galindo-Yllu, B.; Zafra-Tanaka, J.H. Association between copeptin and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review. J. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 2022, 5237903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enhörning, S.; Struck, J.; Wirfält, E.; Hedblad, B.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Melander, O. Plasma copeptin, a unifying factor behind the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1065–E1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malin, S.K.; Stewart, N.R. Metformin may contribute to inter-individual variability for glycemic responses to exercise. Front. Endocrin. 2020, 11, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopka, A.R.; Laurin, J.L.; Schoenberg, H.M.; Reid, J.J.; Castor, W.M.; Wolff, C.A.; Musci, R.V.; Safairad, O.D.; Linden, M.A.; Biela, L.M.; et al. Metformin inhibits mitochondrial adaptations to aerobic exercise training in older adults. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, T. How does an ıntensive exercise training changes ırisin and heat shock protein 70 levels in trained males? Int. J. Appl. Exerc. Physiol. 2020, 9, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Akbulut, T.; Cinar, V.; Aydin, S.; Yardim, M. The role of different exercises in irisin, heat shock protein 70 and some biochemical parameters. J. Med. Biochem. 2022, 41, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.; Rioux, B.V.; Goulet, E.D.; Johanssen, N.M.; Swift, D.L.; Bouchard, D.R.; Loewen, H.; Sénéchal, M. Effect of an acute exercise bout on immediate post-exercise irisin concentration in adults: A meta-analysis. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; So, B.; Son, J.S.; Yoon, D.; Song, W. Effect of aerobic training and resistance training on circulating irisin level and their association with change of body composition in overweight/obese adults: A pilot study. Physiol. Res. 2016, 65, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeki, P.S.; Pranoto, A.; Prasetya, R.E.; Sugiharto, S. Irisin serum increasing pattern is higher at moderate-intensity continuous exercise than at moderate-intensity interval exercise in obese females. Comp. Exer. Physiol. 2021, 17, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öner, S.; Yasul, Y. Exercise, Irisin ve Obesity. Gaziantep Univ. J. Sports Sci. 2022, 7, 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- Taherzadeh, S.; Rasoulian, B.; Khaleghi, M.; Rashidipour, M.; Mogharnasi, M.; Kaeidi, A. Anti-obesity effects of aerobic exercise along with Rosa canina seed extract supplementation in rats: The role of irisin and adipolin. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 17, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, S.-W.; Shen, Z.-H.; Xu, M.; Yang, C.-J.; Li, F.; Feng, Y.-B.; Yun, J.-T.; Wang, L.; et al. Swimming exercise increases serum irisin level and reduces body fat mass in high-fat-diet fed Wistar rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Boström, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Meng, Y.; Li, S.; Donelan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Cui, T.; et al. Irisin stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling. Diabetes 2014, 63, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
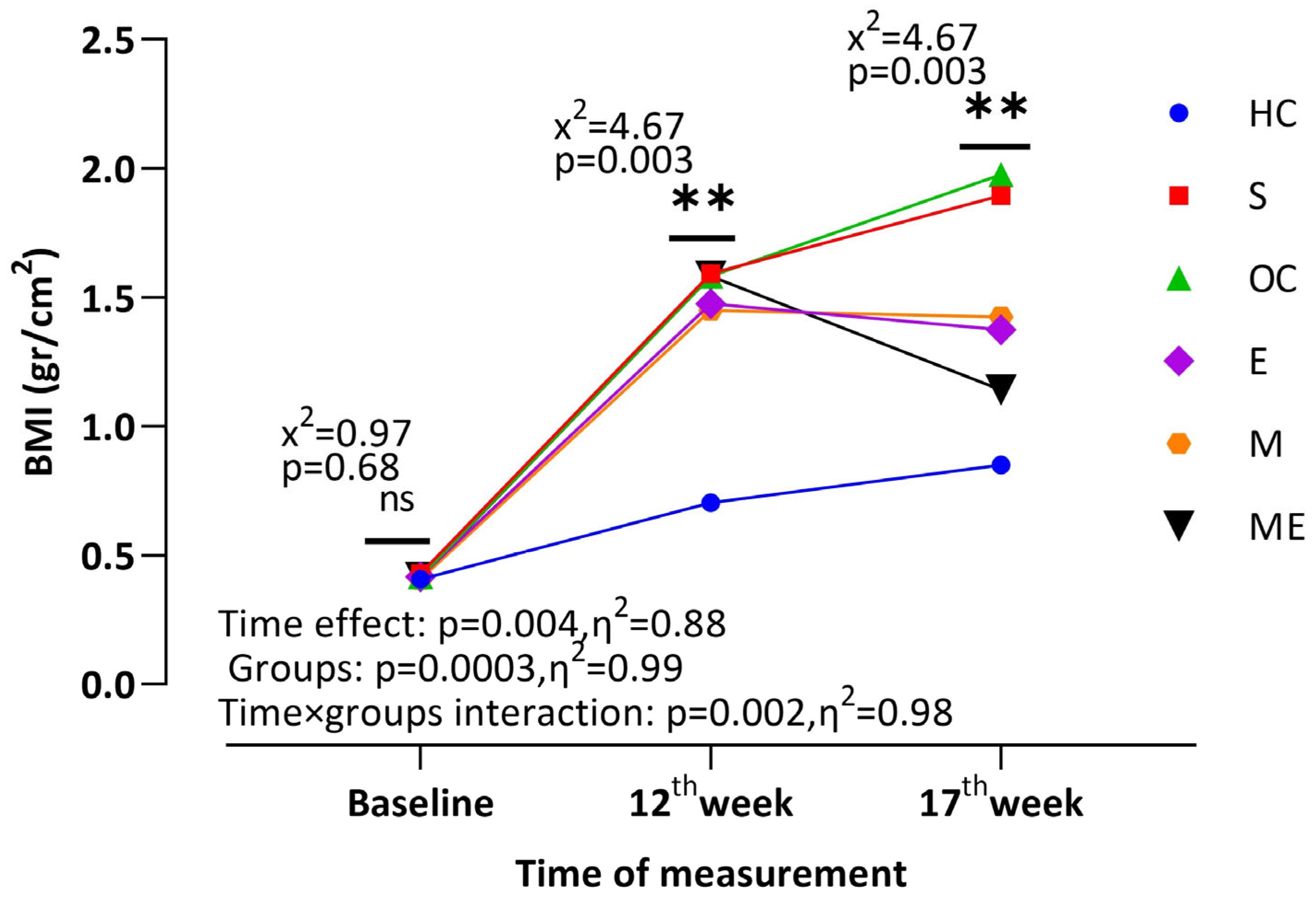
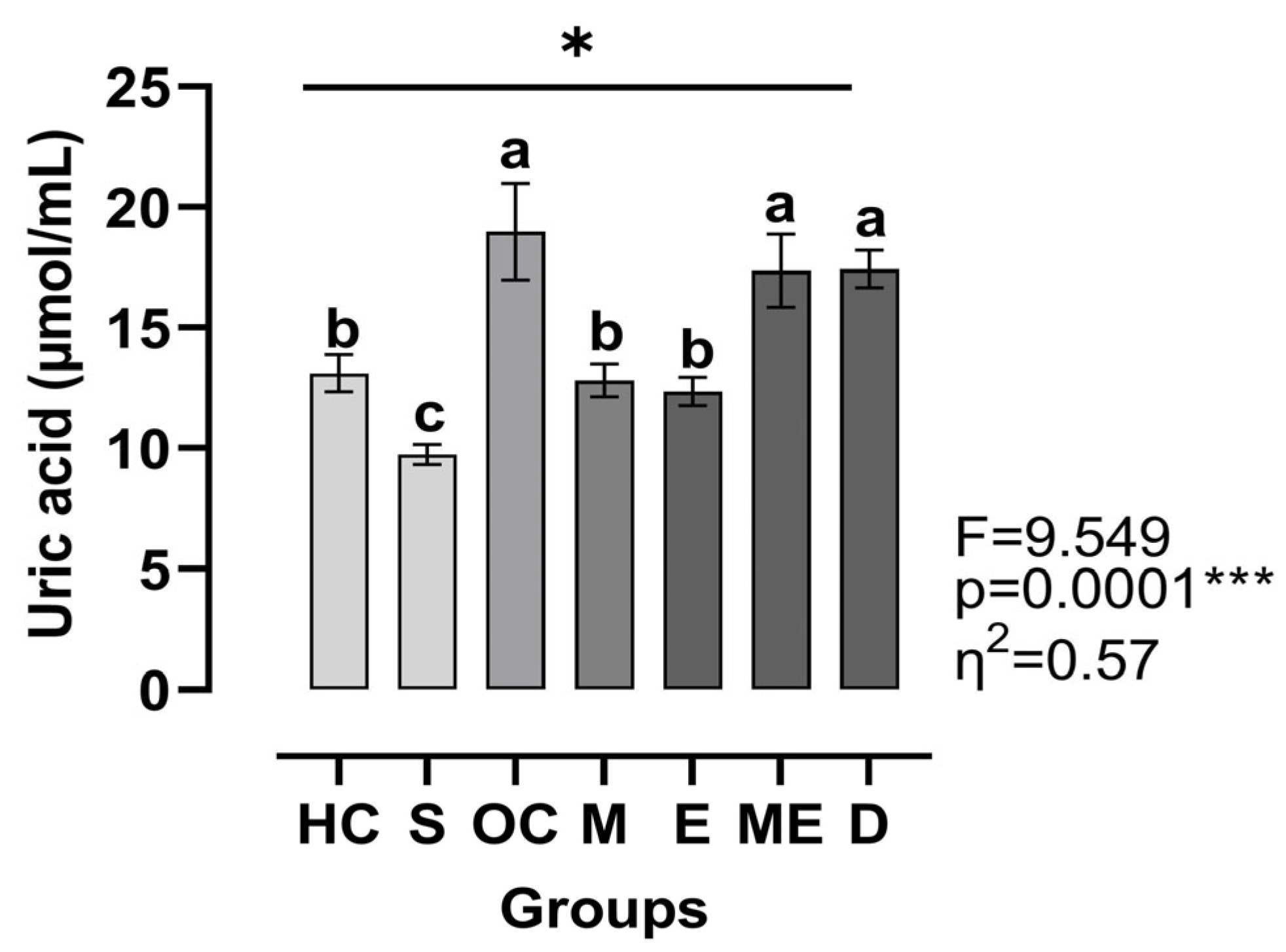
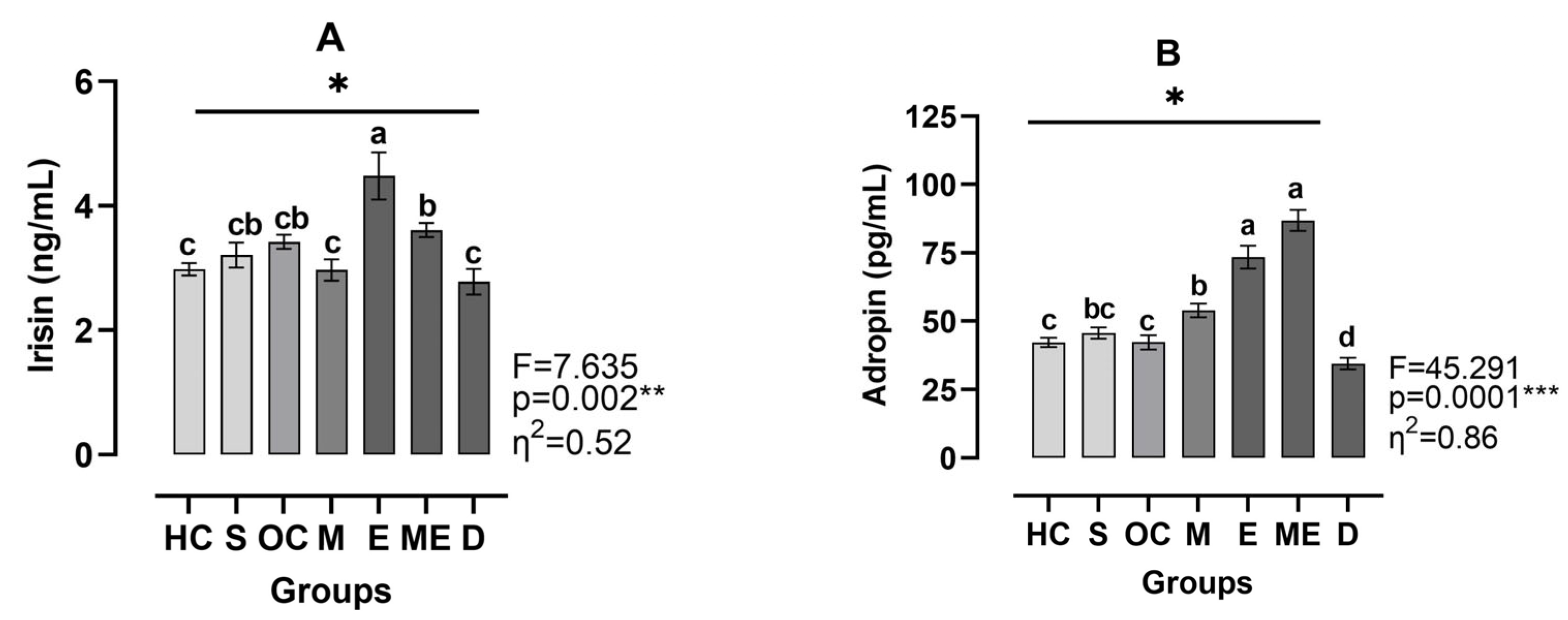
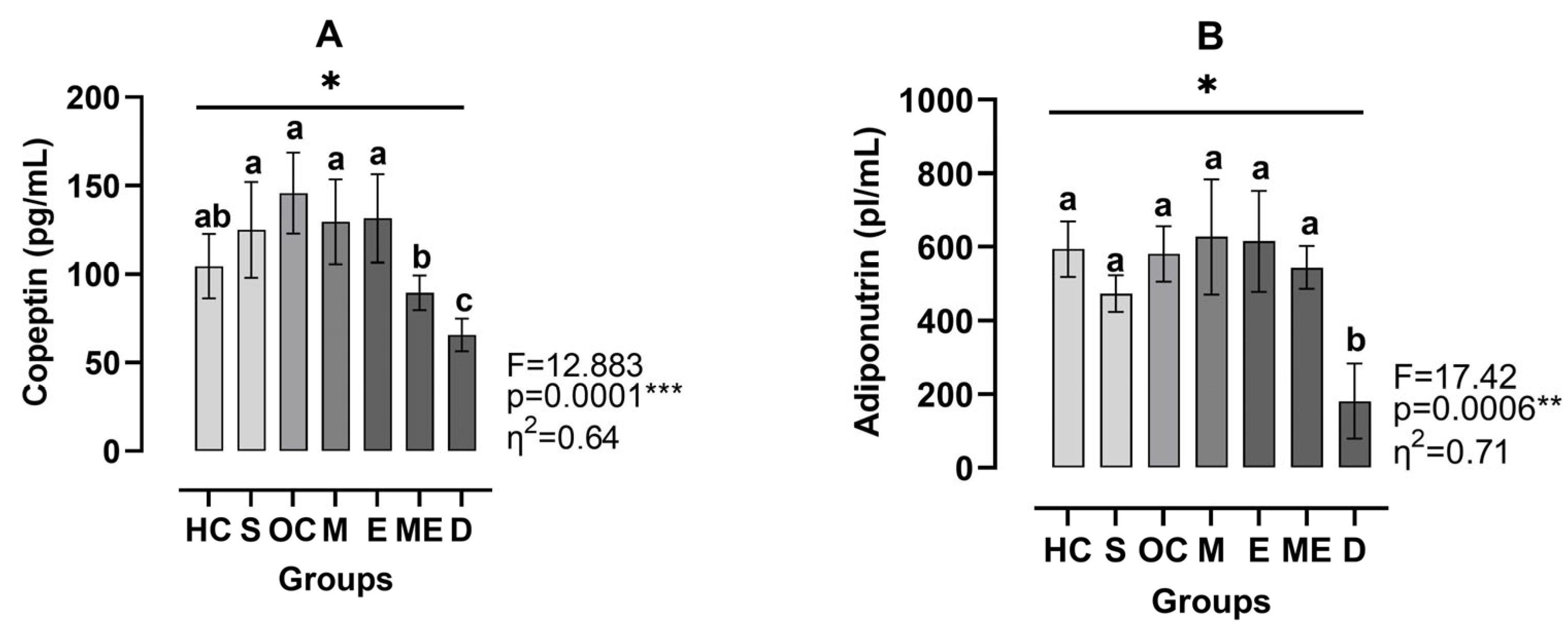
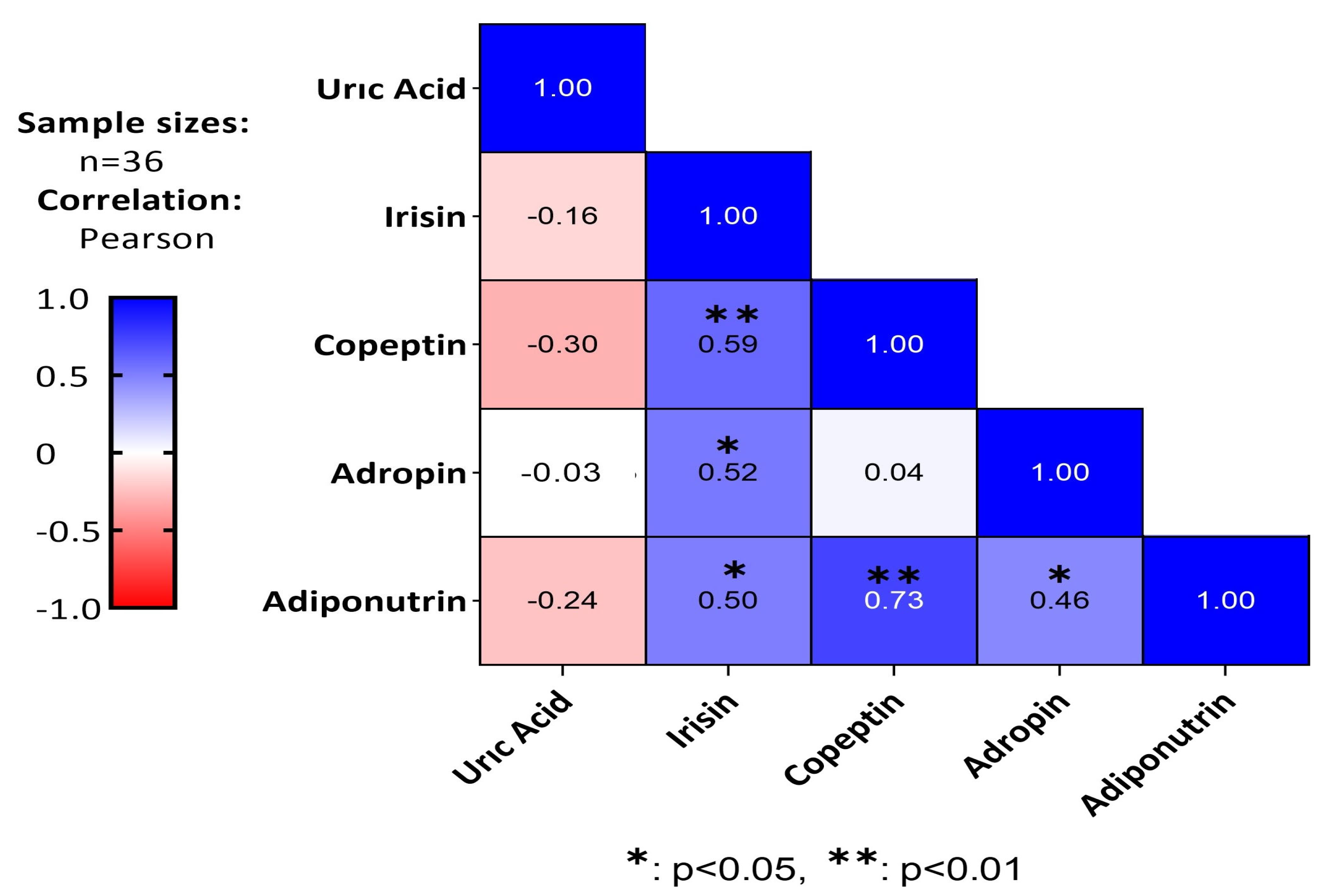
| Groups | Baseline (g) | 12th wk (g) | 17th wk (g) | Inter-wk | Intra-wk | wk × G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | ||||
| D | 231.4 ± 9.8 | --- | --- | x2 = 54.000 p = 0.006 ** | Baseline × 12th wk Z = 5.232, p = 0.0001 *** Baseline × 16th wk Z = 4.132, p = 0.0002 *** 12th wk × 16th wk Z = 2.245, p = 0.01 * | Baseline × G x2 = 0.930, p = 0.90 12th wk × G x2 = 17.003, p = 0.002 ** 16th wk × G x2 = 26.626, p = 0.0001 *** |
| HC | 235.8 ± 11.0 | 370 ± 7.0 b | 430 ± 2.5 e | |||
| S | 232.6 ± 9.1 | 649.6 ± 6.3 a | 685.7 ± 7.0 a | |||
| OC | 233.0 ± 9.2 | 648.6 ± 5.4 a | 684.3 ± 3.3 a | |||
| E | 237.8 ± 11.0 | 657.7 ± 5.7 a | 557.5 ± 5.8 b | |||
| M | 233.3 ± 5.7 | 652.2 ± 7.7 a | 546.9 ± 5.0 c | |||
| ME | 236.8 ± 8.6 | 656.0 ± 7.1 a | 507.7 ± 7.8 d | |||
| Wk Mean | 234.7 C | 605.3 A | 568.1 B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akbulut, T.; Cinar, V.; Avcu, E.C.; Yasul, Y.; Aydemir, İ.; Kuloglu, T.; Artas, G.; Aydin, S. The Regulatory Effects of Exercise and Metformin on Biomarkers in Obesity: A Focus on Uric Acid, Irisin, Adiponutrin, Adropin, and Copeptin. Medicina 2025, 61, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030399
Akbulut T, Cinar V, Avcu EC, Yasul Y, Aydemir İ, Kuloglu T, Artas G, Aydin S. The Regulatory Effects of Exercise and Metformin on Biomarkers in Obesity: A Focus on Uric Acid, Irisin, Adiponutrin, Adropin, and Copeptin. Medicina. 2025; 61(3):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030399
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkbulut, Taner, Vedat Cinar, Emsal Cagla Avcu, Yavuz Yasul, İsa Aydemir, Tuncay Kuloglu, Gokhan Artas, and Suleyman Aydin. 2025. "The Regulatory Effects of Exercise and Metformin on Biomarkers in Obesity: A Focus on Uric Acid, Irisin, Adiponutrin, Adropin, and Copeptin" Medicina 61, no. 3: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030399
APA StyleAkbulut, T., Cinar, V., Avcu, E. C., Yasul, Y., Aydemir, İ., Kuloglu, T., Artas, G., & Aydin, S. (2025). The Regulatory Effects of Exercise and Metformin on Biomarkers in Obesity: A Focus on Uric Acid, Irisin, Adiponutrin, Adropin, and Copeptin. Medicina, 61(3), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61030399








