Checkpoint Inhibitor Pneumonitis: Key Insights for Pulmonologists
Abstract
1. Introduction
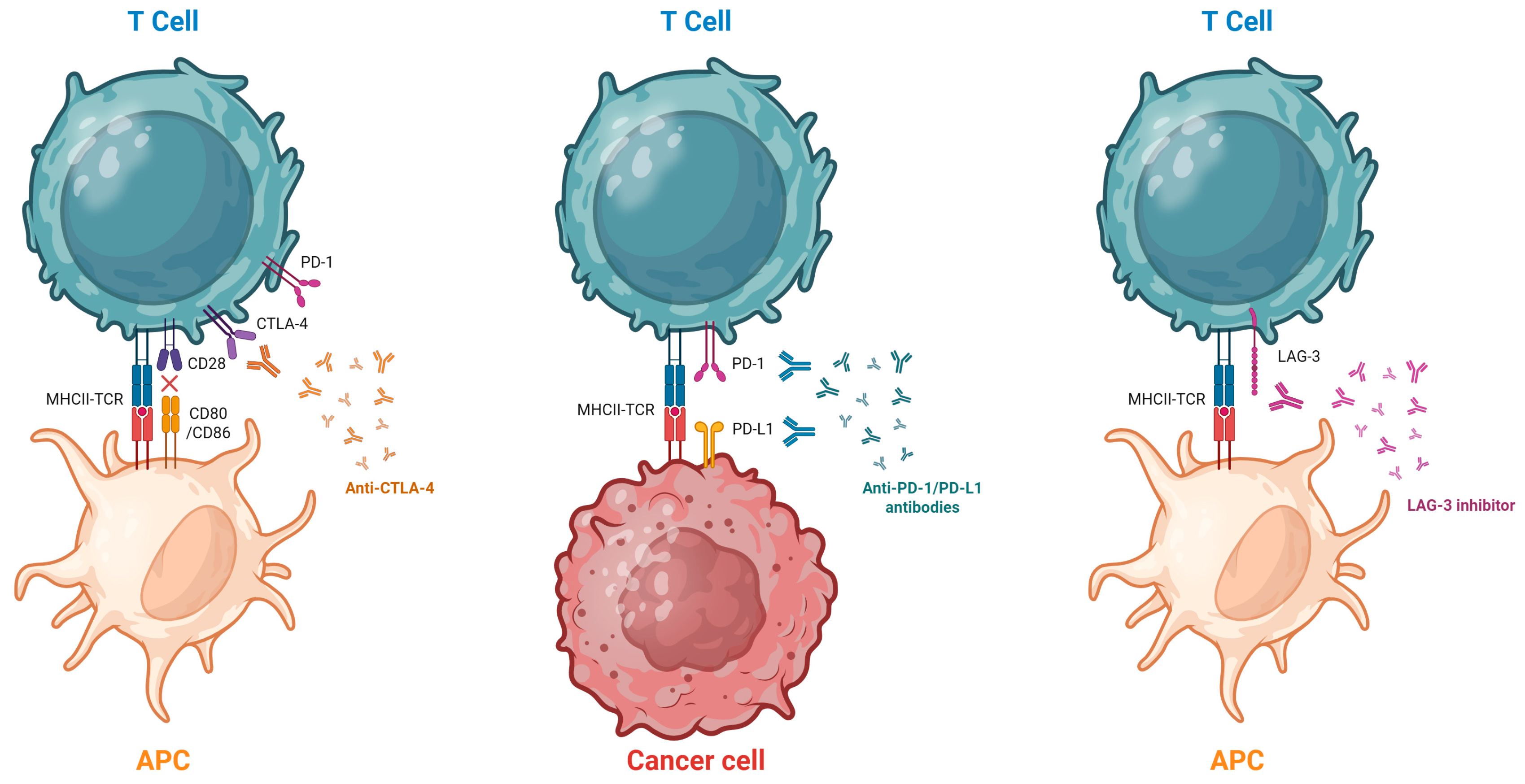
2. Mechanism of Action of ICIs and Pathophysiology
2.1. Molecular Basis of Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
2.2. Pathophysiology of Pneumonitis
3. Risk Factors for Pneumonitis
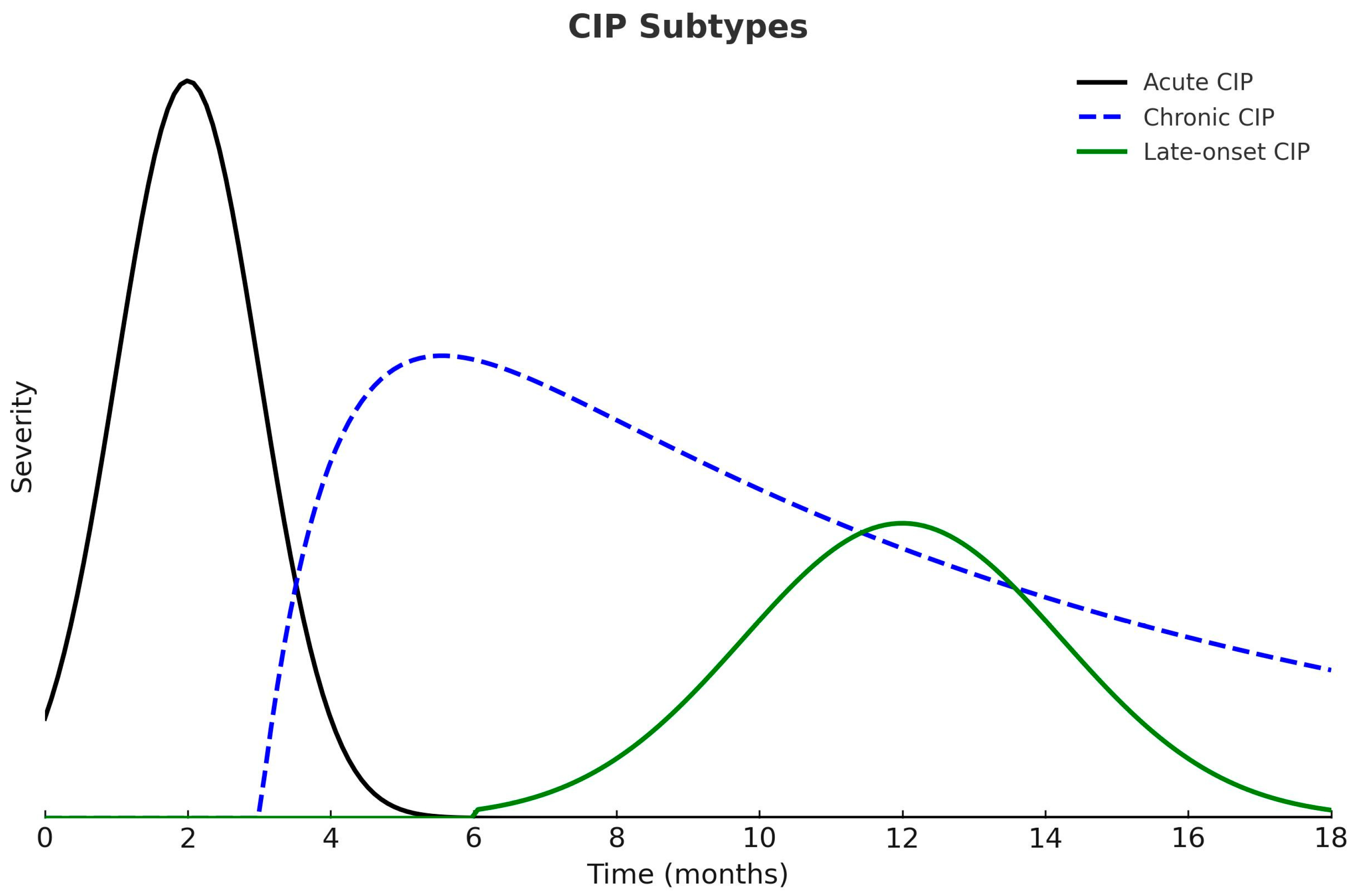
4. Clinical Presentation
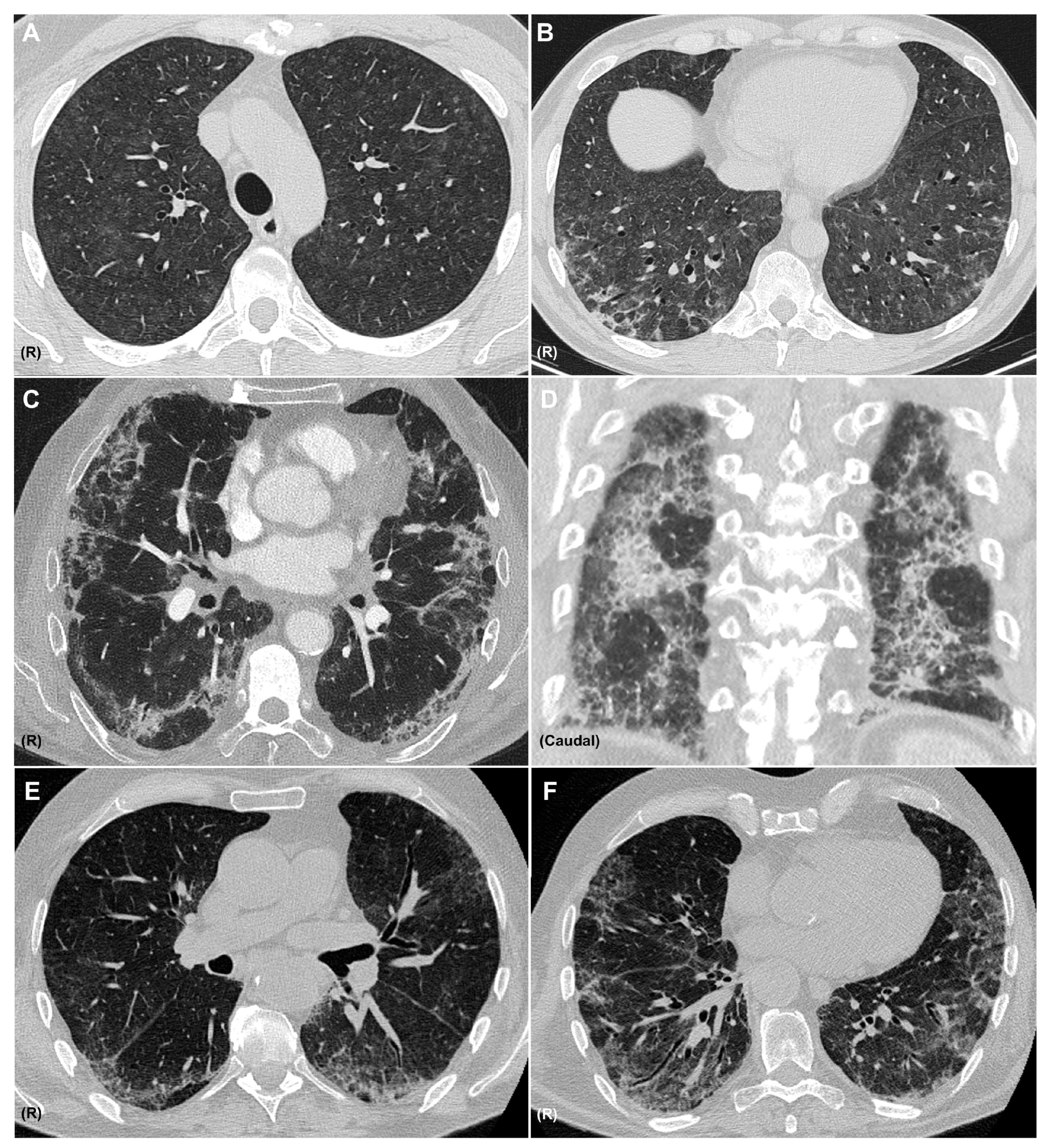
5. Radiology
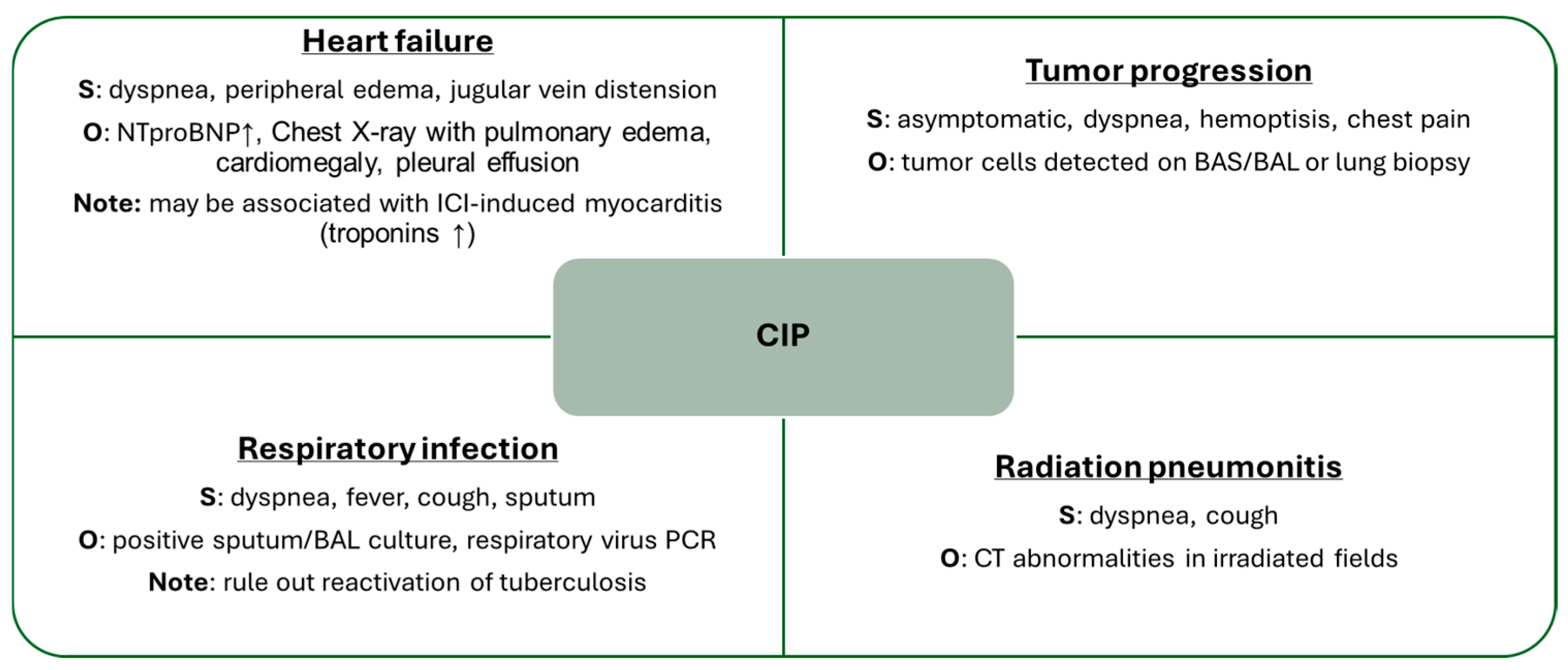
6. Diagnosis
7. Treatment
- Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG), which neutralize autoantibodies and modulate T and B cell functions, with lower infection risk [64].
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APC | Antigen-presenting cell |
| ASCO | American Society of Clinical Oncology |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage |
| CIP | Checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 |
| DLCO | Diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide |
| ECOG | Eastern cooperative oncology group |
| ESMO | European Society for Medical Oncology |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1 s |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| GGO | Ground-glass opacities |
| ICIs | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IGRA | Interferon-gamma release assay |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-17 | Interleukin 17 |
| ILAs | Pulmonary interstitial abnormalities |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| irAEs | Immune-related adverse events |
| IV | Intravenous |
| IVIG | Intravenous immunoglobulin |
| LAG-3 | Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer. |
| NSIP | Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide |
| O2 | oxygen |
| PD-1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 ligand |
| PFT | Pulmonary function testing |
| SBRT | Stereotactic body radiotherapy |
| SITC | Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| Th1 | Lymphocytes T helper 1 |
| Th17 | Lymphocytes T helper 17 |
| TNF-alpha | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
References
- Suresh, K.; Naidoo, J.; Lin, C.T.; Danoff, S. Immune checkpoint immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: Benefits and pulmonary toxicities. Chest 2018, 154, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Abu-Sbeih, H.; Ascierto, P.A.; Brufsky, J.; Cappelli, L.C.; Cortazar, F.B.; Gerber, D.E.; Hamad, L.; Hansen, E.; Johnson, D.B.; et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) clinical practice guideline on immune checkpoint inhibitor-related adverse events. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkor, K.N.; Jang, H.; Sail, R. A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines for managing pulmonary toxicities caused by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2023, 17, 11795549231203153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gan, L.; Xue, J. Checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis induced by anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: Occurrence and mechanism. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 830631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbar, M.I.; Suresh, K. Pulmonary toxicity of immune checkpoint immunotherapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e170503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. LAG-3 as the third checkpoint inhibitor. Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, L.M.; Salinas, V.H.; Brown, K.E.; Vanguri, V.K.; Freeman, G.J.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-L1 regulates the development, maintenance, and function of induced regulatory T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 3015–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spranger, S.; Spaapen, R.M.; Zha, Y.; Williams, J.; Meng, Y.; Ha, T.T.; Gajewski, T.F. Up-regulation of PD-L1, IDO, and Tregs in the melanoma tumor microenvironment is driven by CD8+ T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 200ra116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, D.R.; Krummel, M.F.; Allison, J.P. Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science 1996, 271, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisielow, M.; Kisielow, J.; Capoferri-Sollami, G.; Karjalainen, K. Expression of lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG-3) on B cells is induced by T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 2081–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, J.F.; Goldberg, M.V.; Getnet, D.; Bruno, T.C.; Yen, H.-R.; Pyle, K.J.; Hipkiss, E.; Vignali, D.A.A.; Pardoll, D.M.; Drake, C.G. Functionally distinct LAG-3 and PD-1 subsets on activated and chronically stimulated CD8 T cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 6659–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Naidoo, J.; Zhong, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Mammen, J.; De Flores, M.V.; Cappelli, L.; Balaji, A.; Palmer, T.; Forde, P.M.; et al. The alveolar immune cell landscape is dysregulated in checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4305–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Lou, D.F.; Li, D.Y.; Jiang, W.; Dong, J.Y.; Gao, W.; Chen, H.C. Elevated levels of IL-17A and IL-35 in plasma and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid are associated with checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Sheshadri, A.; Shannon, V.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Kantarjian, H.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Ravandi, F.; Im, J.S.; Boddu, P.; Bashoura, L.; et al. Distinct immunophenotypes of T cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from leukemia patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor–related pulmonary complications. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 590494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Gao, C.; Luo, J. Metabolism characteristics of Th17 and regulatory T cells in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 828191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.H.; Mirabolfathinejad, S.G.; Katta, H.; Cumpian, A.M.; Gong, L.; Caetano, M.S.; Moghaddam, S.J.; Dong, C. T helper 17 cells play a critical pathogenic role in lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5664–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.A.; Gao, J.; Miura, Y.; Blando, J.; Tidwell, R.S.S.; Zhao, H.; Subudhi, S.K.; Tawbi, H.; Keung, E.; Wargo, J.; et al. Autoimmune antibodies correlate with immune checkpoint therapy-induced toxicities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22246–22251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhassani, A.R.; Schuler, G.; Kirchberger, M.C.; Heinzerling, L. C-reactive protein as an early marker of immune-related adverse events. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Spencer, C.N.; Nezi, L.; Reuben, A.; Andrews, M.C.; Karpinets, T.V.; Prieto, P.A.; Vicente, D.; Hoffman, K.; Wei, S.C.; et al. Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, K.; He, Y.; Shang, Y.; Hu, X.; Deng, X.; Zhao, L.; Ma, X.; Mu, X.; Li, R.; et al. The potential role of lung microbiota and lauroylcarnitine in T-cell activation associated with checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis. EBioMedicine 2024, 106, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voong, K.R.; Hazell, S.Z.; Fu, W.; Hu, C.; Lin, C.T.; Ding, K.; Suresh, K.; Hayman, J.; Hales, R.K.; Alfaifi, S.; et al. Relationship between prior radiotherapy and checkpoint-inhibitor pneumonitis in patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e470–e479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiu, B.C.; Zubiri, L.; Iheke, J.; Pahalyants, V.; Theodosakis, N.; Ugwu-Dike, P.; Seo, J.; Tang, K.; Sise, M.E.; Sullivan, R.; et al. Real-world incidence and impact of pneumonitis in lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, P.; Faverio, P.; Ferrari, K.; Bonti, V.; Marsili, S.; Mazzei, M.A.; Mazzoni, F.; Bartolucci, M.; Scotti, V.; Bertolini, F.; et al. Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-related lung toxicity: A multicentre real-life retrospective portrait from six Italian centres. Life 2022, 12, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennamadhavuni, A.; Abushahin, L.; Jin, N.; Presley, C.J.; Manne, A. Risk factors and biomarkers for immune-related adverse events: A practical guide to identifying high-risk patients and rechallenging immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 779691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumimoto, H.; Noda, S.; Koide, H.; Douke, Y.; Sakai, K.; Nishikawa, A.; Tomioka, A.; Hori, M.; Nakato, H.; Kimura, Y.; et al. Pre-existing autoimmune disease as a risk factor for immune-related adverse events in cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0306995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altan, M.; Li, Q.Z.; Wang, Q.; Vokes, N.I.; Sheshadri, A.; Gao, J.; Zhu, C.; Tran, H.T.; Gandhi, S.; Antonoff, M.B.; et al. Distinct patterns of auto-reactive antibodies associated with organ-specific immune-related adverse events. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1322818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies, A.M.; Johnson, D.B.; Ramanujam, S.; Atkinson, V.G.; Wong, A.N.M.; Park, J.J.; McQuade, J.L.; Shoushtari, A.N.; Tsai, K.K.; Eroglu, Z.; et al. Anti-PD-1 therapy in patients with advanced melanoma and preexisting autoimmune disorders or major toxicity with ipilimumab. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillane, D.; Pepe, C.; Kasymjanova, G.; Cruiziat, D.; Cohen, S.; Naimer, J.; Agulnik, J. Does pre-existing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease increase the risk of checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis in advanced/metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer? Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, F.; Jin, S.; Gao, W.; Chen, S.; Guo, R. Checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis in Chinese lung cancer patients: Clinical characteristics and risk factors. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 3957–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, Y.; Nie, L.; Wang, G.; Sun, K.; Cheng, Y. Clinical outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and pre-existing interstitial lung diseases. Chest 2022, 16, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoji, K.; Masuda, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Horimasu, Y.; Nakashima, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Iwamoto, H.; Fujitaka, K.; Hamada, H.; et al. Association of preexisting interstitial lung abnormalities with immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced interstitial lung disease among patients with non-lung cancers. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2022906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Voong, K.R.; Shankar, B.; Forde, P.M.; Ettinger, D.S.; Marrone, K.A.; Kelly, R.J.; Hann, C.L.; Levy, B.; Feliciano, J.L.; et al. Pneumonitis in non–small-cell lung cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint immunotherapy: Incidence and risk factors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, M.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Hatabu, H.; Ramaiya, N.H.; Hodi, F.S. Incidence of programmed cell death 1 inhibitor-related pneumonitis in patients with advanced cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, J.; Wang, X.; Woo, K.M.; Iyriboz, T.; Halpenny, D.; Cunningham, J.; Chaft, J.E.; Segal, N.H.; Callahan, M.K.; Lesokhin, A.M.; et al. Pneumonitis in patients treated with anti-programmed death-1/programmed death ligand 1 therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud-Coffin, P.; Maillet, D.; Gan, H.K.; Stelmes, J.-J.; You, B.; Dalle, S.; Péron, J. A systematic review of adverse events in randomized trials assessing immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomatou, G.; Tzilas, V.; Kotteas, E.; Syrigos, K.; Bouros, D. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis. Respiration 2021, 99, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Cho, Y.-J.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, C.-T.; et al. Characteristics, incidence, and risk factors of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 125, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, M.; Mikami, T.; Niimura, T.; Zamami, Y.; Uesawa, Y.; Chuma, M.; Ishizawa, K. The risk factors associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis. Oncology 2021, 99, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksienski, D.; Wai, E.S.; Croteau, N.S.; Freeman, A.T.; Chan, A.; Fiorino, L.; Poonja, Z.; Fenton, D.; Patterson, T.; Irons, S.; et al. Association of age with differences in immune-related adverse events and survival of patients with advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer receiving pembrolizumab or nivolumab. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2020, 11, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, K.; Ikemura, S.; Sato, T.; Shimozaki, K.; Okamori, S.; Yamada, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Jinzaki, M.; Hirai, I.; et al. Pre-existing interstitial lung abnormalities and immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis in solid tumors. Oncologist 2024, 29, e108–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin, F.; Desir, C.; Ben Mustapha, S.; Mievis, C.; Coucke, P.; Hustinx, R. Incidence, risk factors, and CT characteristics of radiation recall pneumonitis induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor in lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 157, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, S.; Liang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Qiao, L.; Chen, F.; Hu, P.; Zhang, J. Effect of sequence of radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy on the incidence of pneumonitis in patients with lung cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2024, 25, 18–28.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadranel, J.; Canellas, A.; Matton, L.; Darrason, M.; Parrot, A.; Naccache, J.M.; Lavolé, A.; Ruppert, A.-M.; Fallet, V. Pulmonary complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 180058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Duan, L.; Si, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Shi, J. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated pneumonitis. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzanov, I.; Diab, A.; Abdallah, K.; Bingham, C.O.; Brogdon, C.; Dadu, R.; Hamad, L.; Kim, S.; Lacouture, M.E.; LeBoeuf, N.R.; et al. Managing toxicities associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: Consensus recommendations from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) toxicity management working group. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunger, M.; Rakshit, S.; Pasupuleti, V.; Hernandez, A.V.; Mazzone, P.; Stevenson, J.; Pennell, N.A.; Velcheti, V. Incidence of pneumonitis with use of programmed death 1 and programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Chest 2017, 152, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, J.; Murphy, C.; Atkins, M.B.; Brahmer, J.R.; Champiat, S.; Feltquate, D.; Krug, L.M.; Moslehi, J.; Pietanza, M.C.; Riemer, J.; et al. Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) consensus definitions for immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated immune-related adverse events terminology. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johkoh, T.; Lee, K.S.; Nishino, M.; Travis, W.D.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Ryerson, C.J.; Franquet, T.; Bankier, A.A.; Brown, K.K.; et al. Chest CT diagnosis and clinical management of drug-related pneumonitis in patients receiving molecular targeting agents and immune checkpoint inhibitors: A position paper from the Fleischner Society. Chest 2021, 159, 1107–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, B.; Zhang, J.; Naqash, A.R.; Forde, P.M.; Feliciano, J.L.; Marrone, K.A.; Ettinger, D.S.; Hann, C.L.; Brahmer, J.R.; Ricciuti, B.; et al. Multisystem immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, V.E.; Fernandes, L.L.; Weinstock, C.; Tang, S.; Agarwal, S.; Brave, M.; Ning, Y.-M.; Singh, H.; Suzman, D.; Xu, J.; et al. Analysis of the association between adverse events and outcome in patients receiving a programmed death protein 1 or programmed death ligand 1 antibody. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ma, W.; Wu, D.; Lyu, M.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C. Prognostic relevance of immune-related adverse events in lung cancer patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 1559–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryerson, C.J.; Adegunsoye, A.; Piciucchi, S.; Hariri, L.P.; Khor, Y.H.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Wells, A.U.; Sharma, A.; Cooper, W.A.; Antoniou, K.; et al. Update of the International Multidisciplinary Classification of the Interstitial Pneumonias: An ERS/ATS Statement. Eur. Respir. J. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Kanne, J.P.; Henry, T.S.; Revels, J.W.; Gotway, M.B.; Ketai, L.H. Medication-induced pulmonary injury: A scenario- and pattern-based approach to a perplexing problem. Radiographics 2022, 42, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykaza, I.; Murciano-Goroff, Y.R.; Desilets, A.; Harada, G.; Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Lee, C.-H.; Rudin, C.M.; Kelsen, D.P.; Stadler, Z.K.; et al. Sarcoid-like reactions in patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors for advanced solid tumors. Oncologist 2025, 30, oyaf017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, C.A.; Busto, U.; Sellers, E.M.; Sandor, P.; Ruiz, I.; Roberts, E.A.; Janecek, E.; Domecq, C.; Greenblatt, D.J. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1981, 30, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanen, J.; Obeid, M.; Spain, L.; Carbonnel, F.; Wang, Y.; Robert, C.; Lyon, A.; Wick, W.; Kostine, M.; Peters, S.; et al. Management of toxicities from immunotherapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 1217–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, B.J.; Naidoo, J.; Santomasso, B.D.; Lacchetti, C.; Adkins, S.; Anadkat, M.; Atkins, M.B.; Brassil, K.J.; Caterino, J.M.; Chau, I.; et al. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 4073–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.M.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhang, S.; Xing, Q.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Lin, Q.H.; Shen, L.-H.; Xia, Z.-L.; Li, F.-F.; Zhu, B. Characterization of immunomodulatory factors and cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 8019–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.R.; Manser, R. The knowns and unknowns of pulmonary toxicity following immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies: A narrative review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2752–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Bonniaud, P.; Rossi, G.; Sverzellati, N.; Cottin, V. Drug-induced interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. Immune-related pulmonary toxicities of checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis, mechanism, and treatment strategies. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1138483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Huang, Y.-H. Treatment of steroid-refractory immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced intestinal pseudo-obstruction with infliximab. Rev. Española De Enfermedades Dig. 2024, 116, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadokawa, Y.; Takagi, M.; Yoshida, T.; Tatsumi, A.; Fujita, K.; Inoue, T.; Ohe, S.; Nakai, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Otsuka, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of infliximab for steroid-resistant immune-related adverse events: A retrospective study. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daetwyler, E.; Wallrabenstein, T.; König, D.; Cappelli, L.C.; Naidoo, J.; Zippelius, A.; Läubli, H. Corticosteroid-resistant immune-related adverse events: A systematic review. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e007409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shioiri, N.; Kikuchi, R.; Matsumoto, I.; Furukawa, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Abe, S. Effective treatment of steroid-resistant immune checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis with mycophenolate mofetil. Respirol. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e01356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, J.; Rizvi, H.; Fuentes, P.; Luo, J.; Schoenfeld, A.; Lin, I.-H.; Postow, M.; Callahan, M.; Voss, M.H.; Shah, N.J.; et al. Success and failure of additional immune modulators in steroid-refractory/resistant pneumonitis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.; Shireen, G.R.; Rachel, F.; Kirsner, R.S.; Maderal, A.D. Malignancy risk of non-biologic immunosuppressive therapies: A review of the literature with evidence-based treatment recommendations. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Risk of cancer recurrence in patients with immune-mediated diseases with use of immunosuppressive therapies: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 499–512.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Risk Factor | Study Comments |
|---|---|
| Male sex | Reported as a risk factor in some series; female predominance noted with CTLA-4 treatment [22,23,24] |
| Smoking | Reported as a CIP risk factor; also risk factor for lung and renal cancer [22,23] |
| Autoimmune disease | Associated with higher CIP risk; auto-reactive antibodies may contribute [25,26,27] |
| ECOG | Poor ECOG quality of life scale score, ≥1 or ≥2 [28,29] |
| Lung disease | COPD and asthma described as risk factors, particularly with low FEV1 [28,29,30] ILD and ILAs reported as risk factors [23,24,28,29,30,31] |
| Type of malignancy | Higher frequency in NSCLC (especially squamous cell carcinoma) and renal cell carcinoma [22,32,33] |
| Combination of ICIs | CTLA-4 plus other ICI doubles CIP incidence; linked to more severe cases [34,35] |
| Radiotherapy | Prior curative-intent thoracic radiotherapy associated with CIP; differentiation from radiation pneumonitis required [21,24] |
| Pattern | CT Findings |
|---|---|
| Ground glass opacities (GGO) | Areas of increased attenuation with preserved bronchovascular marking |
| Organizing Pneumonia | Multifocal patchy alveolar opacities, typically with peribronchovascular and/or peripheral distribution; may show the reversed halo sign |
| Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis | Poorly defined centrilobular nodules, bilateral ground-glass opacities, areas of decreased attenuation and vascularity (mosaic attenuation) |
| Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) | Patchy ground-glass opacities progressing to irregular reticular opacities, architectural distortion, and traction bronchiectasis, with or without consolidation; typically bilateral, symmetric, and lower-lobe predominant |
| Diffuse alveolar damage | Extensive bilateral ground-glass opacities and dependent airspace consolidation in the exudative phase; traction bronchiectasis and volume loss in organizing/fibrotic phases |
| Sarcoid-like | Peribronchial and mediastinal lymphadenopathy either associated with perilymphatic nodules or as an isolated finding. |
| Grade | Description | Management |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Asymptomatic; isolated CT findings | |
| 2 | Symptomatic; limits activities of daily living | |
| 3 | Severe symptoms; requires oxygen |
|
| 4 | Life-threatening; may require intubation |
|
| ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serra, C.; Benegas, M.; Alsina-Restoy, X.; Roger-Casals, N.; Hernández-González, F. Checkpoint Inhibitor Pneumonitis: Key Insights for Pulmonologists. Medicina 2025, 61, 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112064
Serra C, Benegas M, Alsina-Restoy X, Roger-Casals N, Hernández-González F. Checkpoint Inhibitor Pneumonitis: Key Insights for Pulmonologists. Medicina. 2025; 61(11):2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112064
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerra, Candela, Mariana Benegas, Xavier Alsina-Restoy, Nuria Roger-Casals, and Fernanda Hernández-González. 2025. "Checkpoint Inhibitor Pneumonitis: Key Insights for Pulmonologists" Medicina 61, no. 11: 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112064
APA StyleSerra, C., Benegas, M., Alsina-Restoy, X., Roger-Casals, N., & Hernández-González, F. (2025). Checkpoint Inhibitor Pneumonitis: Key Insights for Pulmonologists. Medicina, 61(11), 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112064







