Infection Risk in Dermatology Patients Receiving Next-Generation Medication: A Meta-Analysis of JAK Inhibitors and Biologics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
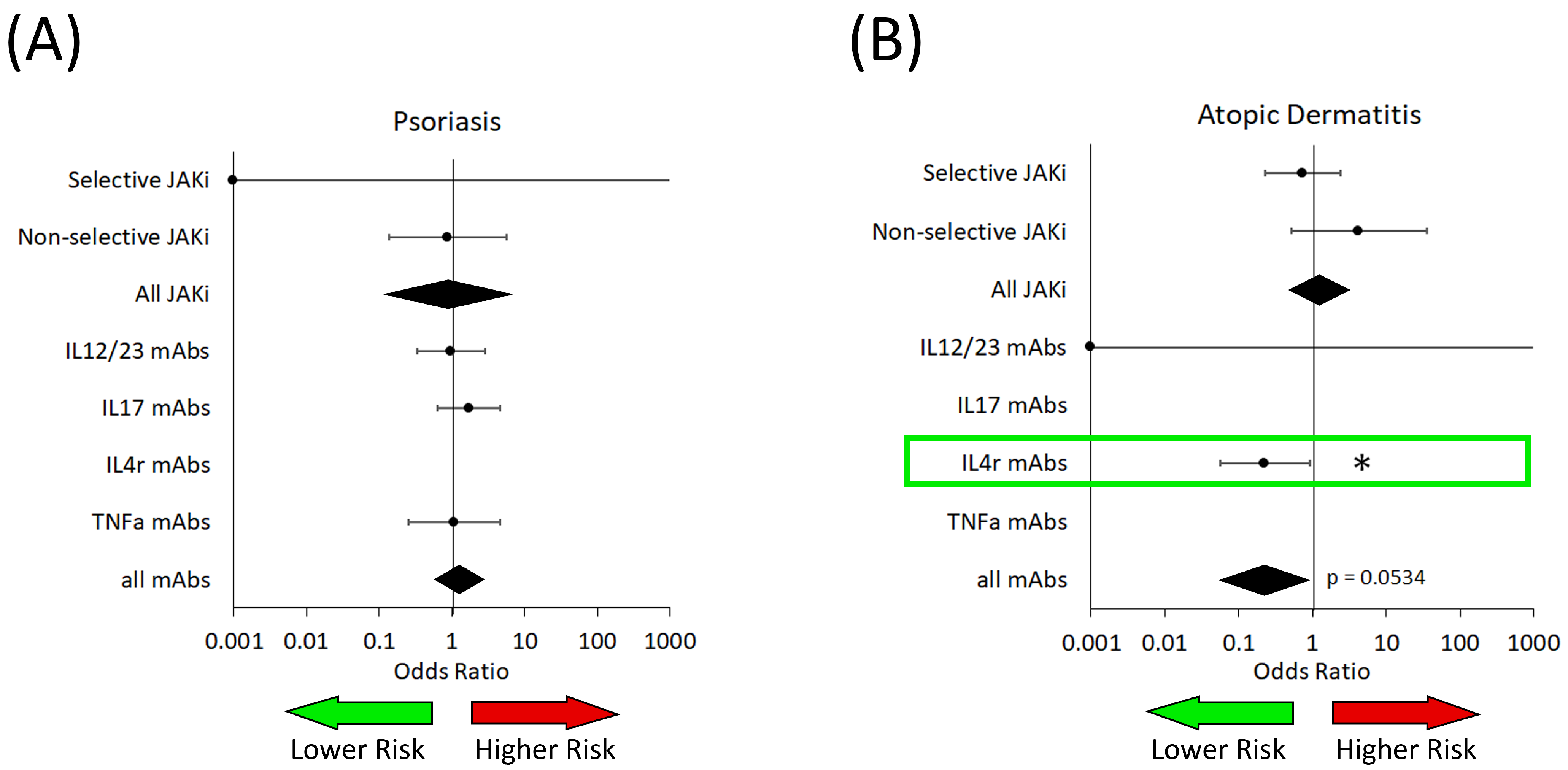
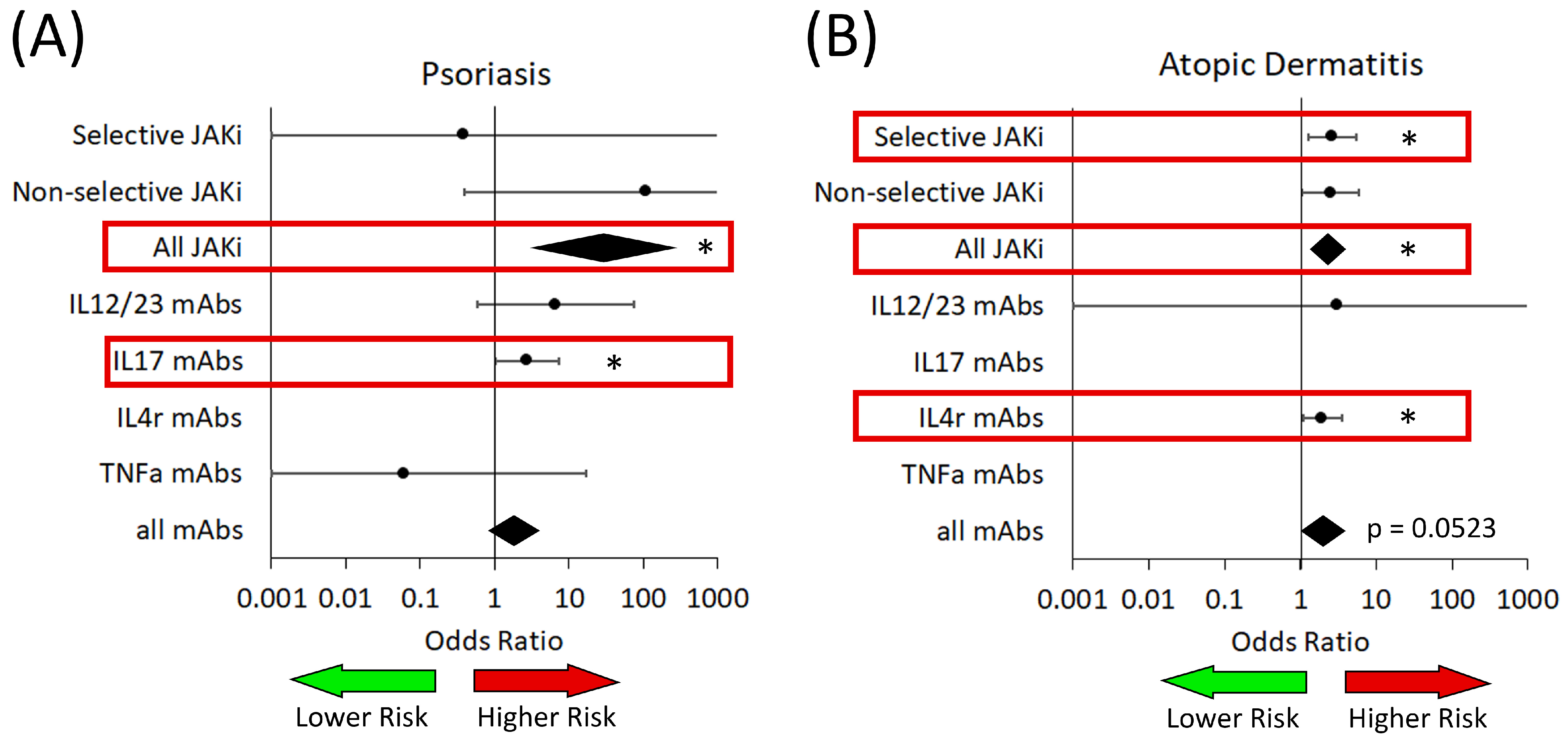
3.2. Fungal Infections
3.3. Bacterial Infections
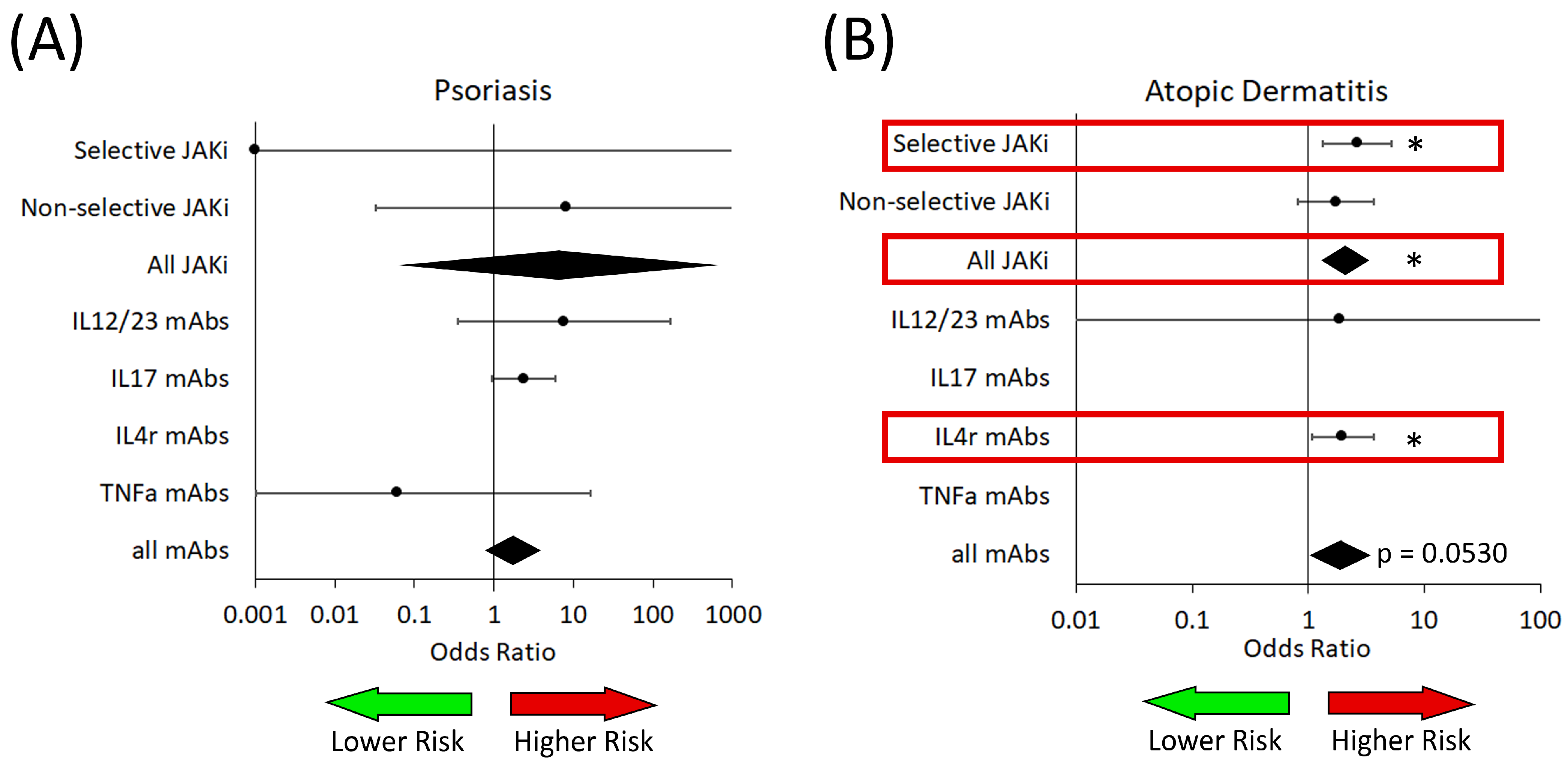
3.4. Viral Infections
3.5. Herpes Simplex and Herpes Zoster Infections
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | Alopecia areata |
| AD | Atopic dermatitis |
| HS | Hidradenitis suppurativa |
| PsO | Psoriasis |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| JAKi | Janus Kinase inhibitors |
| TYK2 | Tyrosine Kinase 2 |
| IL | Interleukin |
| DMARDs | Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs |
| STAT | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation |
| RORγt | retinoic acid orphan receptor γt |
| GATA-3 | G-A-T-A—3 binding protein |
References
- Curtis, K.L.; Stubblefield, O.; Lipner, S.R. Alopecia Areata Is Associated with Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Alcohol Use in a Case-Control Study of 4785 Patients. Skin. Appendage Disord. 2024, 10, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, S.R.; Gomez, B.; Meng, X.; Germino, R. Secukinumab rapidly improves EQ-5D health status in patients with psoriasis: Pooled analysis from four phase 3 trials. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2021, 32, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Hung, C.Y.; Tsai, T.F. Efficacy and Safety of Biologics and Small Molecules for Moderate-to-Severe Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmesen, M.E.R.; Gren, S.T.; Frøstrup, A.G.; Thomsen, S.F.; Egeberg, A.; Thein, D. Psychosocial and mental impact of alopecia areata: Analysis of the Danish Skin Cohort. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 39, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, B.; Blaiss, M.S. The burden of atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2018, 39, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, S.; Farah, R.; Hordinsky, M. Systemic Immunotherapies, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Garnock-Jones, K.P.; Keam, S.J. Adalimumab: A Review in Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2016, 17, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.; Ahmed, M.; Conway, R.; Carey, J.J. Risk of infection with methotrexate therapy in inflammatory diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.L.; Zhou, L.; Sudano, D.G.; Ashbeck, E.L.; Kwoh, C.K.; Krebs, L.; Sheer, A.; Smith, J.; Tudeen, M.; Lo-Ciganic, W.H. Risk of Coccidioidomycosis Infection Among Individuals Using Biologic Response Modifiers, Corticosteroids, and Oral Small Molecules. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2024, 6, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, P.A.; Verheyden, M.; Jansson, N.; Sebaratnam, D.; Sullivan, J. Infection risk with JAK inhibitors in dermatoses: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2025, 64, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka-Takaichi, M.; Ghanian, S.; Katzka, D.A.; Torgerson, R.R.; Alavi, A. Candida Infection Associated with Anti-IL-17 Medication: A Systematic Analysis and Review of the Literature. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, N.C.; Benedict, K.; Toda, M.; Gold, J.A.W.; Lipner, S.R. Low incidence of invasive fungal infections in a large observational cohort of patients initiating IL-17 or IL-23 inhibitor therapy, United States, 2016–2022. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 91, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, C.W.; Näslund-Koch, C.; Zachariae, C.; Seidelin, J.B.; Nielsen, S.D.; Ostrowski, S.R.; Astvad, K.M.T.; Brock, I.; Iversen, L.; Rasmussen, M.K.; et al. Adverse Events and Immune Response in Psoriasis Patients Receiving Interleukin-17 Inhibitors. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2025, 105, adv43685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Hiruma, J.; Harada, K.; Fujimori, K.; Suzuki, R.; Mori, M.; Okura, M.; Abe, N.; Harada, K.; Okubo, Y. Risk of fungal infection in patients with psoriasis receiving biologics: A retrospective single-center cohort study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2025, 92, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Liu, G.; Yang, R. Reciprocal modulation between TH17 and other helper T cell lineages. J. Cell Physiol. 2011, 226, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchti, F.; LeibundGut-Landmann, S. New insights into immunity to skin fungi shape our understanding of health and disease. Parasite Immunol. 2023, 45, e12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yao, Z. Roles of Infection in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.S.; Siegfried, E.C.; Cork, M.J.; Arkwright, P.D.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Ramien, M.; Khokhar, F.A.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, A.; Cyr, S.L. Infections in Children Aged 6 Months to 5 Years Treated with Dupilumab in a Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Pediatr. Drugs 2024, 26, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Castillo, J.M.; McGurk, A.; Strakosha, M.; Vega-Mendoza, D.; Smith, S.E.M.; Stafstrom, K.; Elkins, M.; Chou, J.; Wang, Y.H.; Geha, R.S. IL-4 receptor alpha blockade dampens allergic inflammation and upregulates IL-17A expression to promote S aureus clearance in antigen sensitized mouse skin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenova, E.; Skabytska, Y.; Hoetzenecker, W.; Weindl, G.; Sauer, K.; Tham, M.; Kim, K.W.; Park, J.H.; Seo, J.H.; Ignatova, D.; et al. IL-4 abrogates TH17 cell-mediated inflammation by selective silencing of IL-23 in antigen-presenting cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2163–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzina, I.G.; Keegan, A.D.; Heller, N.M.; Rook, G.A.W.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Atamas, S.P. Regulation of inflammation by interleukin-4: A review of “alternatives”. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, K.; Reinhardt, R.L. The differential expression of IL-4 and IL-13 and its impact on type-2 immunity. Cytokine 2015, 75, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundahl, M.L.E.; Mitermite, M.; Ryan, D.G.; Case, S.; Williams, N.C.; Yang, M.; Lynch, R.I.; Lagan, E.; Lebre, F.M.; Gorman, A.L.; et al. Macrophage innate training induced by IL-4 and IL-13 activation enhances OXPHOS driven anti-mycobacterial responses. eLife 2022, 11, e74690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, C.; Trivedi, S.; Wijesundara, D.K.; Jackson, R.J. IL-4 and IL-13 receptors: Roles in immunity and powerful vaccine adjuvants. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2014, 25, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgewood, C.; Newton, D.; Bragazzi, N.; Wittmann, M.; McGonagle, D. Unexpected connections of the IL-23/IL-17 and IL-4/IL-13 cytokine axes in inflammatory arthritis and enthesitis. Semin. Immunol. 2021, 58, 101520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, Z.Z.N.; Exton, L.S.; Jabbar-Lopez, Z.; Mohd Mustapa, M.F.; Samarasekera, E.J.; Burden, A.D.; Murphy, R.; Owen, C.M.; Parslew, R.; Venning, V.; et al. Risk of Serious Infections in Patients with Psoriasis on Biologic Therapies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Bian, Q.; Rong, D.; Wang, L.; Song, J.; Huang, H.S.; Zeng, J.; Mei, J.; Wang, P.Y. JAK/STAT pathway: Extracellular signals, diseases, immunity, and therapeutic regimens. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1110765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, F.H.N.; Kwan, A.; Winder, N.; Mughal, A.; Collado-Rojas, C.; Muthana, M. Understanding Immune Responses to Viruses—Do Underlying Th1/Th2 Cell Biases Predict Outcome? Viruses 2022, 14, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, W.H.; Renaudineau, Y. Not just another klass (JAK) of inhibitors for allergies. J. Allergy Hypersensit. Dis. 2024, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Yao, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Yuan, X.; Chu, Q.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, L. Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: Autoimmune disorders and cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; Wollenberg, A.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Zhang, H.; Sierka, D.; Khokhar, F.A.; Vakil, J.; Shabbir, A.; Marco, A.R.; Cyr, S.L. No Increased Risk of Overall Infection in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis Treated for up to 4 Years with Dupilumab. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kridin, K.; Abdelghaffar, M.; Bieber, K.; Thaci, D.; Ludwig, R.J. The real-world, long-term risk of infections associated with dupilumab in atopic dermatitis: A global cohort study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.B.; Lebwohl, M.; Thaçi, D.; Gooderham, M.; Pinter, A.; Paul, C.; Gisondi, P.; Szilagyi, B.; White, K.; Deherder, D.; et al. Bimekizumab efficacy and safety through 3 years in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: Long-term results from the BE RADIANT phase IIIb trial open-label extension period. Br. J. Dermatol. 2025, 193, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanofi-Aventis US LLC. DUPIXENT® (Dupilumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Use. 2025. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2025/761055s070lbl.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- AbbVie. SKYRIZI® (Risankizumab-Rzaa) Injection, for Subcutaneous or Intravenous Use. 2024. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2025/761105s039,761262s011lbl.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Ergun, T.; Hosgoren Tekin, S.; Apti Sengun, O.; Akin Cakici, O.; Seckin, D.; Adiay, C.; Enul, H.; Yilmaz, S.; Ay, P.; Haklar, G.; et al. Immunogenicity, efficacy, and safety of CoronaVac and Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccines in patients with psoriasis receiving systemic therapies: A prospective cohort study. Vaccine 2023, 41, 4287–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miot, H.A.; Criado, P.R.; de Castro, C.C.S.; Ianhez, M.; Talhari, C.; Ramos, P.M. JAK-STAT pathway inhibitors in dermatology. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2023, 98, 656–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc. XELJANZ (Tofacitinib) Tablets, for Oral Use; XELJANZ XR (Tofacitinib) Extended-Release Tablets, for Oral Use; XELJANZ (Tofacitinib) Oral Solution. 2025. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/203214s026lbl.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Pfizer Labs. LITFULOTM (Ritlecitinib) Capsules, for Oral Use. 2023. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/215830s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- FDA, CDER. TREMFYA® (Guselkumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous or Intravenous Use. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2025/761061s026lbl.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Kridin, K.; Zirpel, H.; Mruwat, N.; Ludwig, R.J.; Thaci, D. Evaluating the risk of infections under interleukin 23 and interleukin 17 inhibitors relative to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors—A population-based study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Psoriasis | Atopic Dermatitis | Alopecia Areata | Hidradenitis Suppurativa | Vitiligo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungal infection | |||||
| N | 4147 | 3829 | 154 | 1957 | n/a |
| I2 | 22.5 | 34.2 | 0 | 29.4 | n/a |
| Viral infection | |||||
| N | 19746 | 8715 | 1348 | 1957 | 49 |
| I2 | 38.6 | 26.3 | 2.4 | 62.2 | 0 |
| Bacterial infection | |||||
| N | 18343 | 6630 | 60 | 1957 | n/a |
| I2 | 21.1 | 10.8 | 0 | 0.22 | n/a |
| Simplex infection | |||||
| N | 5359 | 8549 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| I2 | 92.6 | 24.7 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Zoster infection | |||||
| N | 18402 | 4768 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| I2 | 50.5 | 10.1 | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Psoriasis | Atopic Dermatitis | Alopecia Areata | Hidradenitis Suppurativa | Vitiligo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungal infections | |||||
| JAK inhibitors | OR: 4.88 (0.45–52.93) p = 0.2063 | OR: 1.41 (0.28–7.19) p = 0.7217 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9998 | No trials | No trials |
| Biologics | OR: 4.53 (2.34–8.78) p < 0.0001 | OR: 0.36 (0.03–6.30) p = 0.5158 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9998 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9967 | No trials |
| Viral infections | |||||
| JAK inhibitors | OR: 29.08 (3.06–276.36) p = 0.0043 | OR: 2.32 (1.46–3.69) p = 0.0013 | OR: 0.63 (0.27–1.43) p = 0.2036 | No trials | Not enough data |
| Biologics | OR: 1.79 (0.84–3.79) p = 0.1129 | OR: 1.98 (1.12–3.49) p = 0.0395 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9851 | OR: 2.35 (0.18–30.38) p = 0.4710 | No trials |
| Bacterial infections | |||||
| JAK inhibitors | OR: 0.86 (0.11–7.03) p = 0.8899 | OR: 1.21 (0.47–3.11) p = 0.8894 | Not enough data | No trials | No trials |
| Biologics | OR: 1.29 (0.59–2.79) p = 0.5197 | OR: 0.22 (0.06–0.88) p = 0.0534 * | Not enough data | OR: not estimable p = 0.9977 | No trials |
| Psoriasis | Atopic Dermatitis | Alopecia Areata | Hidradenitis Suppurativa | Vitiligo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungal infections | |||||
| Selective for JAK1 or TYK2 | OR: not estimable p = 0.1793 | OR: not estimable p = 0.7304 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9998 | No trials | No trials |
| Not selective for specific JAK | OR: 3.544 (0.02–689.21) p = 0.9980 | OR: 4.32 (0.27–70.36) p = 0.1236 | No trials | No trials | No trials |
| Viral infections | |||||
| Selective for JAK1 or TYK2 | OR: not estimable p = 0.3000 | OR: 2.6 (1.26–5.36) p = 0.0139 | OR: not estimable p = 0.8984 | No trials | Not enough data |
| Not selective for specific JAK | OR: not estimable p = 0.0891 | OR: 2.49 (1.04–5.98) p = 0.0523 * | OR: 0.59 (0.21–1.70) p = 0.2114 | No trials | Not enough data |
| Bacterial infections | |||||
| Selective for JAK1 or TYK2 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9971 | OR: 0.74 (0.21–2.37) p = 0.5598 | Not enough data | No trials | No trials |
| Not selective for specific JAK | OR: 0.88 (0.14–5.70) p = 0.8735 | OR: 4.27 (0.52–35.33) p = 0.1291 | Not enough data | No trials | No trials |
| Psoriasis | Atopic Dermatitis | Alopecia Areata | Hidradenitis Suppurativa | Vitiligo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungal infections | |||||
| IL12/23 Targeted | OR: not estimable p = 0.9946 | OR: not estimable p = 0.4689 | No trials | No trials | No trials |
| IL17 Targeted | OR: 6.07 (2.96–12.44) p < 0.0001 | No trials | No trials | OR: not estimable p = 0.9960 | No trials |
| IL4R Targeted | No trials | OR: not estimable p = 0.9976 | Not enough data | No trials | No trials |
| TNFa Targeted | OR: 0.52 (0.02–11.71) p = 0.6333 | No trials | No trials | OR: not estimable p = 0.9617 | No trials |
| Viral infections | |||||
| IL12/23 Targeted | OR: 6.70 (0.60–75.00) p = 0.1225 | OR: not estimable p = 0.4963 | No trials | No trials | No trials |
| IL17 Targeted | OR: 2.72 (1.02–7.23) p = 0.0454 | No trials | No trials | OR: not estimable p = 0.9977 | No trials |
| IL4R Targeted | No trials | OR: 1.97 (1.07–3.61) p = 0.0312 | Not enough data | No trials | Not enough data |
| TNFa Targeted | OR: 0.06 (<0.001–17.15) p = 0.2786 | No trials | No trials | OR: 4.35 (0.13–145.10) p = 0.3088 | No trials |
| Bacterial infections | |||||
| IL12/23 Targeted | OR: 0.96 (0.33–2.80) p = 0.9294 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9986 | No trials | No trials | No trials |
| IL17 Targeted | OR 1.74 (0.65–4.67) p = 0.2668 | No trials | No trials | Not enough data | No trials |
| IL4R Targeted | No trials | OR: 0.23 (0.06–0.92) p = 0.0394 | Not enough data | No trials | No trials |
| TNFa Targeted | OR: 1.06 (0.25–4.52) p = 0.8190 | No trials | No trials | OR: not estimable p = 1.0 | No trials |
| Herpes Simplex | Herpes Zoster | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psoriasis | AD | Psoriasis | AD | |
| JAK inhibitors | ||||
| Selective for JAK1 or TYK2 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9982 | OR: 2.66 (1.35–5.24) p = 0.0084 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9978 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9910 |
| Not selective for specific JAK | OR: not estimable p = 0.3989 | OR: 1.73 (0.81–3.69) p = 0.1321 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9954 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9979 |
| All JAK inhibitors | OR: 6.60 (0.07–666.38) p = 0.3834 | OR: 2.08 (1.30–3.33) p = 0.0061 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9978 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9978 |
| Biologics | ||||
| IL12/23 targeted | OR: 7.68 (0.36–165.23) p = 0.1762 | OR: not estimable p = 0.6804 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9581 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9987 |
| IL17 targeted | OR: 2.38 (0.94–6.01) p = 0.0663 | No trials | Not enough data † | No trials |
| IL4r targeted | No trials | OR: 1.98 (1.07–3.65) p = 0.0312 | No trials | OR: not estimable p = 0.9674 |
| TNFa targeted | OR: not estimable p = 0.2760 | No trials | OR: not estimable p = 0.9996 | No trials |
| All biologics | OR: 1.74 (0.78–3.87) p = 0.1710 | OR: 1.90 (1.08–3.34) p = 0.0530 * | OR: not estimable p = 0.9479 | OR: not estimable p = 0.9981 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, A.K.; Susmita; Economopoulos, V. Infection Risk in Dermatology Patients Receiving Next-Generation Medication: A Meta-Analysis of JAK Inhibitors and Biologics. Medicina 2025, 61, 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112053
Gupta AK, Susmita, Economopoulos V. Infection Risk in Dermatology Patients Receiving Next-Generation Medication: A Meta-Analysis of JAK Inhibitors and Biologics. Medicina. 2025; 61(11):2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112053
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Aditya K., Susmita, and Vasiliki Economopoulos. 2025. "Infection Risk in Dermatology Patients Receiving Next-Generation Medication: A Meta-Analysis of JAK Inhibitors and Biologics" Medicina 61, no. 11: 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112053
APA StyleGupta, A. K., Susmita, & Economopoulos, V. (2025). Infection Risk in Dermatology Patients Receiving Next-Generation Medication: A Meta-Analysis of JAK Inhibitors and Biologics. Medicina, 61(11), 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112053







