Endothelial Glycocalyx Shedding and Hemodynamic Variables During Hepatic and Pancreatic Resection Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
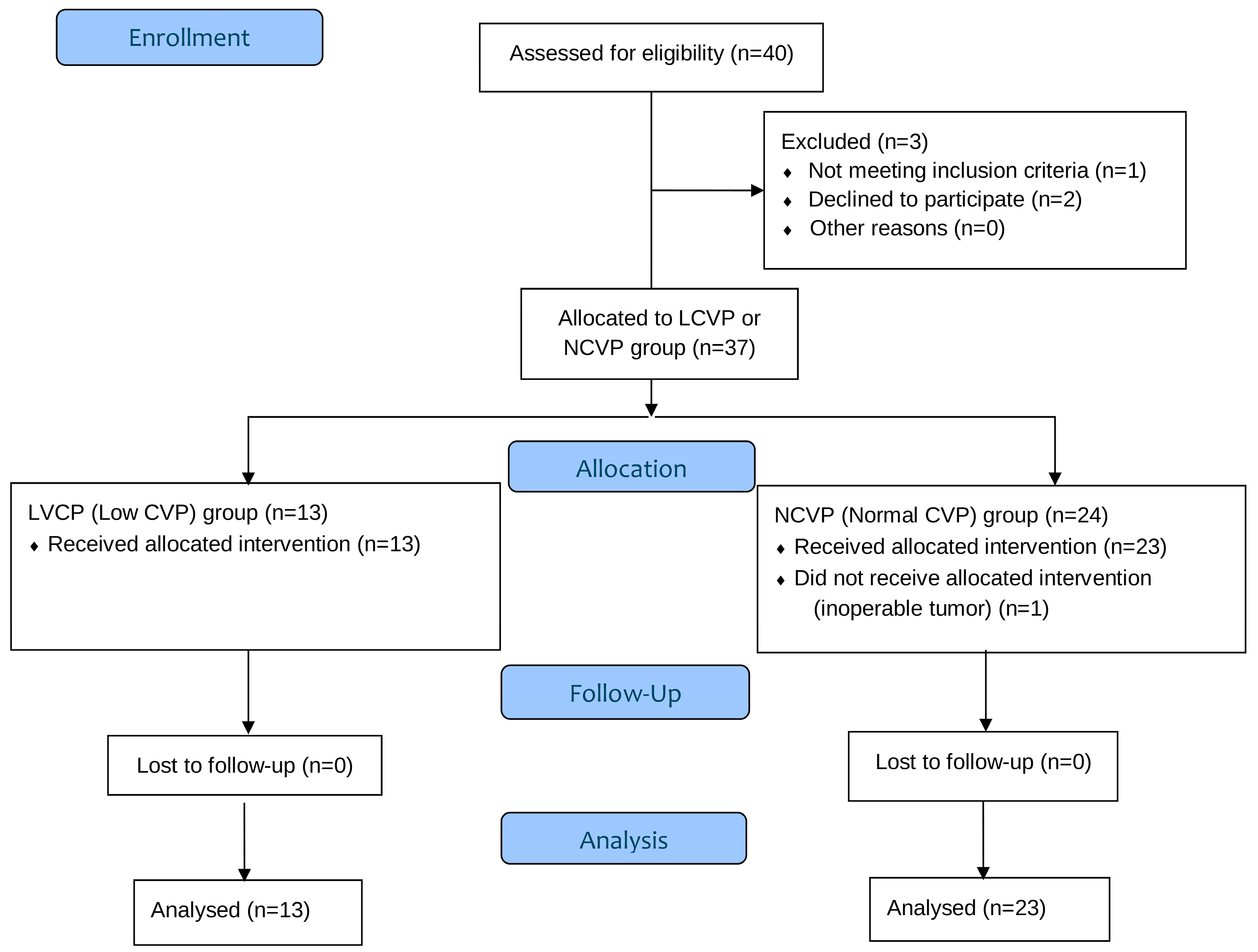
2.1. Participants and Eligibility Criteria
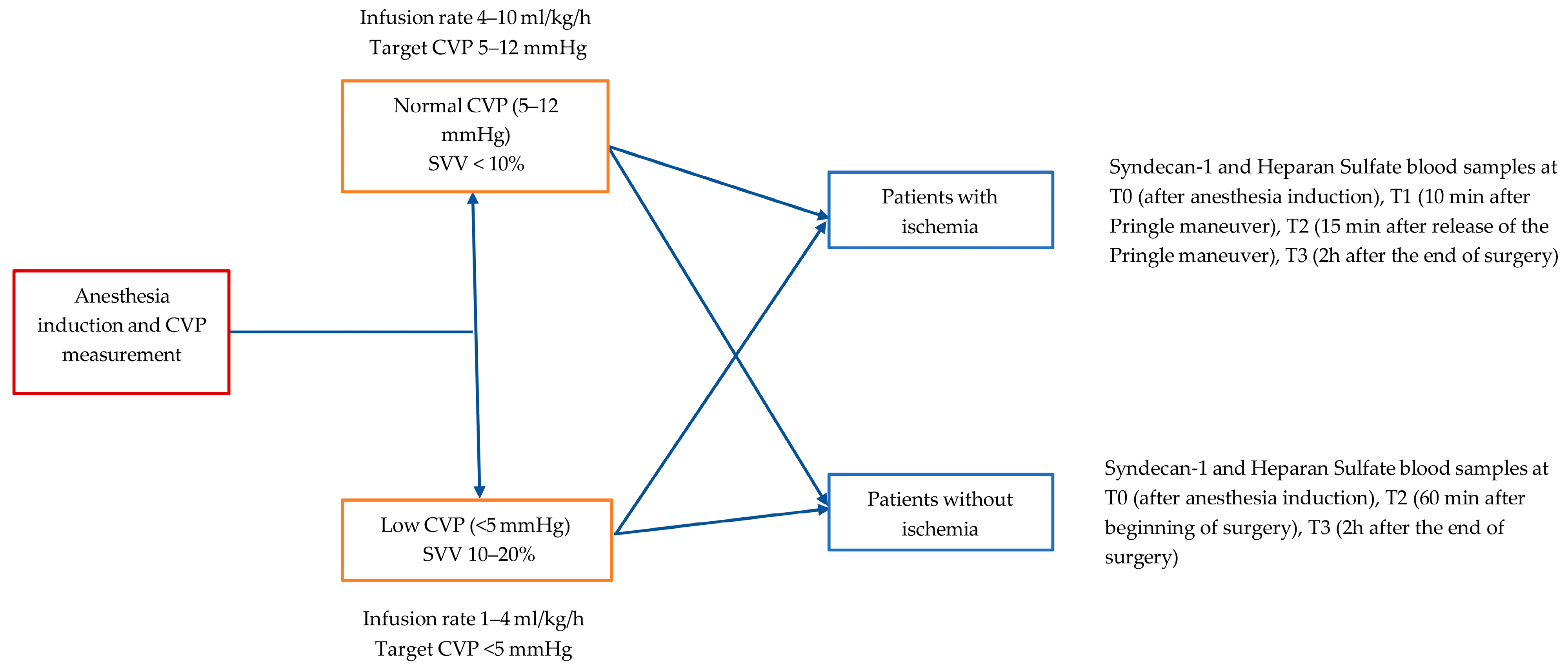
2.2. Perioperative Management
2.3. Perioperative Fluid Regimen Protocol
2.4. Assessment of Endothelial Glycocalyx Disruption
- Patients with ischemia: T0 (after anesthesia induction), T1 (10 min after Pringle maneuver), T2 (15 min after release of the Pringle maneuver), T3 (2 h after the end of surgery)
- Patients without ischemia: T0 (after anesthesia induction), T2 (60 min after the beginning of surgery), T3 (2 h after the end of surgery)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EG | Endothelial Glycocalyx |
| LSECs | Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| Wnt2 | Wingless-type MMTV integration site family member 2 |
| CVP | Central Venous Pressure |
| CO | Cardiac Output |
| CI | Cardiac Index |
| SV | Stroke Volume |
| SVV | Stroke Volume Variation |
| LCVP | Low Central Venous Pressure |
| NCVP | Normal Central Venous Pressure |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Physical Status Classification System |
| PBR | Perfused boundary region |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| IBL | Intraoperative blood loss |
References
- Alphonsus, C.S.; Rodseth, R.N. The endothelial glycocalyx: A review of the vascular barrier. Anaesthesia 2014, 69, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitsma, S.; Slaaf, D.W.; Vink, H.; van Zandvoort, M.A.; Oude Egbrink, M.G. The endothelial glycocalyx: Composition, functions, and visualization. Pflug. Arch. 2007, 454, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, M.; Buggy, D.J. Intraoperative fluids: How much is too much? Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashandy, G.M. Implications of recent accumulating knowledge about endothelial glycocalyx on anesthetic management. J. Anesth. 2015, 29, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Golen, R.F.; Reiniers, M.J.; Vrisekoop, N.; Zuurbier, C.J.; Olthof, P.B.; van Rheenen, J.; van Gulik, T.M.; Parsons, B.J.; Heger, M. The mechanisms and physiological relevance of glycocalyx degradation in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 1098–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B.F.; Chappell, D.; Bruegger, D.; Annecke, T.; Jacob, M. Therapeutic strategies targeting the endothelial glycocalyx: Acute deficits, but great potential. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B.F.; Jacob, M.; Leipert, S.; Salmon, A.H.; Chappell, D. Degradation of the endothelial glycocalyx in clinical settings: Searching for the sheddases. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, J.A.; Kosky, J.R.; Ainslie, K.; Pang, Z.; Dull, R.O.; Tarbell, J.M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycan is a mechanosensor on endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, e136–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehm, M.; Bruegger, D.; Christ, F.; Conzen, P.; Thiel, M.; Jacob, M.; Chappell, D.; Stoeckelhuber, M.; Welsch, U.; Reichart, B.; et al. Shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx in patients undergoing major vascular surgery with global and regional ischemia. Circulation 2007, 116, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppan, J.; Hofer, S.; Funke, B.; Brenner, T.; Henrich, M.; Martin, E.; Weitz, J.; Hofmann, U.; Weigand, M.A. Sepsis and major abdominal surgery lead to flaking of the endothelial glycocalyx. J. Surg. Res. 2011, 165, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, T.; Nakanuma, S.; Ahmed, A.; Makino, I.; Hayashi, H.; Oyama, K.; Nakagawara, H.; Tajima, H.; Takamura, H.; Ninomiya, I.; et al. Ischemia reperfusion-facilitated sinusoidal endothelial cell injury in liver transplantation and the resulting impact of extravasated platelet aggregation. Eur. Surg. 2016, 48, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Hosono, K.; Amano, H. Responses of hepatic sinusoidal cells to liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1171317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, B.-S.; Nolan, D.J.; Butler, J.M.; James, D.; Babazadeh, A.O.; Rosenwaks, Z.; Mittal, V.; Kobayashi, H.; Shido, K.; Lyden, D.; et al. Inductive angiocrine signals from sinusoidal endothelium are required for liver regeneration. Nature 2010, 468, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, J.; Lemoinne, S.; Boulanger, C.; Durand, F.; Moreau, R.; Valla, D.; Rautou, P.-E. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyrniotis, V.; Kostopanagiotou, G.; Theodoraki, K.; Tsantoulas, D.; Contis, J.C. The role of central venous pressure and type of vascular control in blood loss during major liver resections. Am. J. Surg. 2004, 187, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntington, J.T.; Royall, N.A.; Schmidt, C.R. Minimizing blood loss during hepatectomy: A literature review. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 109, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.K. Fluid management in living donor hepatectomy: Recent issues and perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12757–12766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongerius, I.M.; Mungroop, T.H.; Uz, Z.; Geerts, B.F.; Immink, R.V.; Rutten, M.V.H.; Hollmann, M.W.; van Gulik, T.M.; Besselink, M.G.; Veelo, D.P. Goal-directed fluid therapy vs. low central venous pressure during major open liver resections (GALILEO): A surgeon- and patient-blinded randomized controlled trial. HPB Off. J. Int. HepatoPancreato Biliary Assoc. 2021, 23, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-S.; Shen, Q.-H.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Shen, X.; Lai, L.; Hou, X.-M.; Liu, K. Application of controlled low central venous pressure during hepatectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Anesth. 2021, 75, 110467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Chen, T.; Chen, Z. Effect of controlled low central venous pressure technique on postoperative hepatic insufficiency in patients undergoing a major hepatic resection. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 8286–8293. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, L.; Yanase, F.; Tosif, S.; Riedel, B.; Bellomo, R.; Hahn, R.G. Trajectory of plasma syndecan-1 and heparan sulphate during major surgery: A retrospective observational study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2023, 67, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, J.S.; Bazancir, L.A.; Johansson, P.I.; Sørensen, H.; Achiam, M.P.; Olsen, A.A. Major open abdominal surgery is associated with increased levels of endothelial damage and interleukin-6. Microvasc. Res. 2023, 148, 104543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.Y.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Shin, H.J.; Cho, J.; Nam, D.J.; Kim, S.Y. Effect of volatile and total intravenous anesthesia on syndecan-1 shedding after minimally invasive gastrectomy: A randomized trial. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindermans, M.; Joachim, J.; Manquat, E.; Levé, C.; Hong, A.; Mateo, J.; Mebazaa, A.; Gayat, E.; De Backer, D.; Vallée, F. Micro- and macrocirculatory effects of norepinephrine on anaesthesia-induced hypotension: A prospective preliminary study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.N.; Yang, S.J.; Shih, P.Y.; Wang, M.J.; Fan, S.Z.; Tsai, J.C.; Sun, W.Z.; Liu, C.M.; Yeh, Y.C. Comparing effects of intraoperative fluid and vasopressor infusion on intestinal microcirculation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarta-Mantilla, M.; Fernández-Sarmiento, J.; Acevedo, L.; Mulett, H.; Nieto, A.; Lucena, N.; Lancheros, J.; Duque, C. Microcirculation, endothelium and glycocalyx changes associated with the use of milrinone in children with septic shock. Transl. Pediatr. 2024, 13, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Golen, R.F.; van Gulik, T.M.; Heger, M. Mechanistic overview of reactive species-induced degradation of the endothelial glycocalyx during hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1382–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, D.; Jacob, M. Role of the glycocalyx in fluid management: Small things matter. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 28, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarczyk, J.M.; Fridfinnson, J.A.; Kumar, A.; Blanchard, L.; Rabbani, R.; Bell, D.; Funk, D.; Turgeon, A.F.; Abou-Setta, A.M.; Zarychanski, R. Incorporating dynamic assessment of fluid responsiveness into goal-directed therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benes, J.; Chytra, I.; Altmann, P.; Hluchy, M.; Kasal, E.; Svitak, R.; Pradl, R.; Stepan, M. Intraoperative fluid optimization using stroke volume variation in high risk surgical patients: Results of prospective randomized study. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liang, X.; Chai, F.; Shi, D.; Wang, Y. Goal-directed fluid therapy using stroke volume variation on length of stay and postoperative gastrointestinal function after major abdominal surgery-a randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angappan, S.; Parida, S.; Vasudevan, A.; Badhe, A.S. The comparison of stroke volume variation with central venous pressure in predicting fluid responsiveness in septic patients with acute circulatory failure. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. Peer-Rev. Off. Publ. Indian Soc. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 19, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, J.; Lebherz-Eichinger, D.; Erdoes, G.; Berlakovich, G.; Bacher, A.; Krenn, C.G.; Faybik, P. Alterations of endothelial glycocalyx during orthotopic liver transplantation in patients with end-stage liver disease. Transplantation 2015, 99, 2118–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passov, A.; Schramko, A.; Mäkisalo, H.; Nordin, A.; Andersson, S.; Pesonen, E.; Ilmakunnas, M. Graft glycocalyx degradation in human liver transplantation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauter, L.; Kollmann, D.; Schiefer, J.; Spasic, M.; Raeven, P.; Dingfelder, J.; Pereyra, D.; Baron, D.M.; Pompouridou, E.; Soliman, T.; et al. Endothelial glycocalyx damage marker syndecan-1 during hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion of donor grafts facilitates prediction of early allograft dysfunction after liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2025, 14, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT04058236. Glycocalyx Levels in Patients Undergoing Pancreatectomy. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04058236 (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Trocheris-Fumery, O.; Flet, T.; Scetbon, C.; Tarpin, P.; Meynier, J.; Badaoui, R.; De Broca, B.; Sabbagh, C.; Régimbeau, J.M.; De Sousa, P.; et al. Early Use of Norepinephrine in High-risk Patients Undergoing Major Abdominal Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesthesiology 2025, 143, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovas, A.; Seidel, L.M.; Vink, H.; Pohlkötter, T.; Pavenstädt, H.; Ertmer, C.; Hessler, M.; Kümpers, P. Association of sublingual microcirculation parameters and endothelial glycocalyx dimensions in resuscitated sepsis. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Gallego, C.; Tan, K.S.; Arslan-Carlon, V.; Gonen, M.; Denis, S.C.; Langdon-Embry, L.; Grant, F.; Kingham, T.P.; DeMatteo, R.P.; Allen, P.J.; et al. Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Using Stroke Volume Variation for Resuscitation after Low Central Venous Pressure-Assisted Liver Resection: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2015, 221, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Jun, I.G.; Cho, S.S.; Kim, S.K.; Hwang, G.S.; Kim, Y.K. Effect of stroke volume variation-directed fluid management on blood loss during living-donor right hepatectomy: A randomised controlled study. Anaesthesia 2015, 70, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunki-Jacobs, E.M.; Philips, P.; Scoggins, C.R.; McMasters, K.M.; Martin, R.C., 2nd. Stroke volume variation in hepatic resection: A replacement for standard central venous pressure monitoring. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, K.W.; Chen, W.Y.; Chia, Y.Y. Low versus high stroke volume variation-guided fluid management and reduction of postoperative complications after liver resection: A randomized clinical trial. Asian J. Anesthesiol. 2023, 61, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, R.; Amemiya, H.; Hosomura, N.; Kawaida, H.; Higuchi, Y.; Nakayama, T.; Shoda, K.; Furuya, S.; Akaike, H.; Kawaguchi, Y.; et al. Stroke volume variation monitoring to minimize blood loss in hepatocellular carcinoma resection. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Normal CVP Group Without Ischemia (n = 16) | Low CVP Group Without Ischemia (n = 8) | p | Normal CVP Group with Ischemia (n = 7) | Low CVP Group with Ischemia (n = 5) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61.8 ± 13.0 | 63.1 ± 11.9 | 0.814 | 58.7 ± 13.1 | 58.2 ± 9.8 | 0.943 |
| M/F | 7/9 | 6/2 | 0.211 | 4/3 | 3/2 | 1.000 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.8 ± 2.2 | 24.8 ± 5.1 | 0.196 | 27.0 ± 4.1 | 26.9 ± 1.4 | 0.956 |
| ASA (II/III) | 5/10/1 | 4/4/0 | 0.565 | 1/5/ 1 | 2/3/0 | 0.462 |
| Smoking (n/y) | 12/4 | 6/2 | 0.565 | 5/2 | 4/1 | 1.000 |
| Presence of Concomitant disease (n/y) | ||||||
| Peripheral vascular disease | 15/1 | 8/0 | 1.000 | 6/1 | 5/0 | 1.000 |
| Arrhythmias | 14/2 | 7/1 | 1.000 | 7/0 | 5/0 | 1.000 |
| Dyslipidemia | 14/2 | 7/1 | 1.000 | 5/2 | 4/1 | 1.000 |
| Hypertension | 11/5 | 5/3 | 1.000 | 6/1 | 3/2 | 1.000 |
| Diabetes | 14/2 | 6/2 | 1.000 | 6/1 | 5/0 | 1.000 |
| Hypothyroidism | 14/2 | 7/1 | 1.000 | 5/2 | 4/1 | 1.000 |
| Renal failure | 15/1 | 8/0 | 1.000 | 6/1 | 5/0 | 1.000 |
| Metastatic cancer | 14/2 | 6/2 | 0.578 | 5/2 | 1/4 | 0.242 |
| Solid tumor no metastasis | 4/12 | 2/6 | 1.000 | 2/5 | 4/1 | 0.242 |
| Normal CVP Group Without Ischemia (n = 16) | Low CVP Group Without Ischemia (n = 8) | p | Normal CVP Group with Ischemia (n = 7) | Normal CVP Group with Ischemia (n = 5) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Procedure (hepatectomy/pancreatectomy) | 8/8 | 4/4 | 1.000 | 6/1 | 4/1 | 1.000 |
| Anesthesia duration (min) | 452 (130–660) | 480 (220–640) | 0.624 | 235 (180–660) | 360 (175–515) | 0.755 |
| Procedure duration (min) | 392 (105–590) | 350 (180–600) | 0.671 | 180 (120–600) | 290 (120–420) | 0.530 |
| Ischemia time (min) (pringle maneuver) | - | - | - | 20 (13–28) | 35 (13–50) | 0.149 |
| Crystalloids (mL) | 3350 (900–6500) | 3500 (1200–4600) | 0.671 | 2000 (1700–4700) | 3700 (1300–5700) | 0.755 |
| Phenylephrine (mg) | 0.6 (0–3) | 0.4 (0–1.5) | 0.720 | 0.6 (0–2.7) | 0.8 (0.3–1.5) | 0.639 |
| Ephedrine (mg) | 2.5 ± 6.5 | 3.7 ± 4.8 | 0.413 | 0.7 ± 1.8 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.755 |
| Τ0 | Τ1 | Τ3 | p-Value Within Groups | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
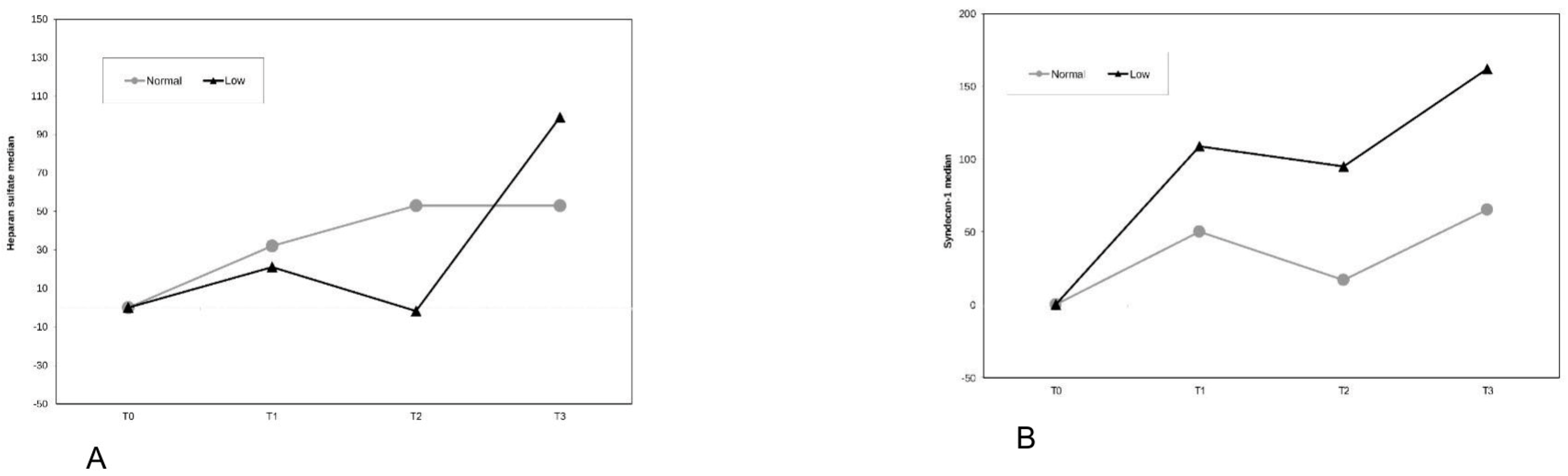
| Heparan Sulfate (ng/mL) | ||||
| NCVP (n = 16) | 258.7 [137.5] | 427.8 [361.1] | 538.6 [340.1] | 0.007 |
| LCVP (n = 8) | 305.4 [100.3] | 654.5 [643.4] | 644.3 [873.8] | 0.005 |
| p-value (between groups) | 0.667 | 0.193 | 0.667 | |
| Syndecan-1 (ng/mL) | ||||
| NCVP (n = 16) | 1.1 [7.9] | 1.5 [16.3] | 1.4 [14.4] | 0.185 |
| LCVP (n = 8) | 7.3 [17.8] | 7.3 [14.2] | 9.0 [11.5] | 1.000 |
| p-value (between groups) | 0.193 | 0.193 | 0.027 |
| Τ0 | Τ1 | Τ2 | Τ3 | p-Value Within Groups | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heparan Sulfate (ng/mL) | |||||
| NCVP (n = 7) | 254.3 [131.7] | 381.2 [242.9] | 388.8 [290] | 309.8 [383.4] | 0.419 |
| LCVP (n = 5) | 272.7 [289.8] | 281.9 [371.4] | 250.1 [396.4] | 273.8 [670.7] | 0.668 |
| p-value (between groups) | NS | NS | 0.242 | 0.567 | |
| Syndecan-1 (ng/mL) | |||||
| NCVP (n = 7) | 1.2 [1.9] | 2.4 [2.2] | 1.7 [1.8] | 3.2 [4.6] | 0.086 |
| LCVP (n = 5) | 1.1 [34.7] | 5.6 [42.3] | 6.1 [37.3] | 7.2 [38.6] | 0.062 |
| p-value (between groups) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.242 | 0.567 |
| CVP1 | CVP2 | CVP3 | CVP4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVV1 | r = −0.363 | |||
| SVV2 | r = −0.307 | |||
| SVV3 | r = 0.014 | |||
| SVV4 | r = −0.043 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kavezou, F.; Soulioti, E.; Kapetanakis, E.I.; Felekouras, E.; Arkadopoulos, N.; Nomikos, T.; Galanos, A.; Matsota, P.; Kostopanagiotou, G.; Sidiropoulou, T. Endothelial Glycocalyx Shedding and Hemodynamic Variables During Hepatic and Pancreatic Resection Surgery. Medicina 2025, 61, 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111938
Kavezou F, Soulioti E, Kapetanakis EI, Felekouras E, Arkadopoulos N, Nomikos T, Galanos A, Matsota P, Kostopanagiotou G, Sidiropoulou T. Endothelial Glycocalyx Shedding and Hemodynamic Variables During Hepatic and Pancreatic Resection Surgery. Medicina. 2025; 61(11):1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111938
Chicago/Turabian StyleKavezou, Foteini, Eleftheria Soulioti, Emmanouil I. Kapetanakis, Evangelos Felekouras, Nikolaos Arkadopoulos, Tzortzis Nomikos, Antonis Galanos, Paraskevi Matsota, Georgia Kostopanagiotou, and Tatiana Sidiropoulou. 2025. "Endothelial Glycocalyx Shedding and Hemodynamic Variables During Hepatic and Pancreatic Resection Surgery" Medicina 61, no. 11: 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111938
APA StyleKavezou, F., Soulioti, E., Kapetanakis, E. I., Felekouras, E., Arkadopoulos, N., Nomikos, T., Galanos, A., Matsota, P., Kostopanagiotou, G., & Sidiropoulou, T. (2025). Endothelial Glycocalyx Shedding and Hemodynamic Variables During Hepatic and Pancreatic Resection Surgery. Medicina, 61(11), 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61111938








