Impact of Serum Glucose Levels on Outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics
3. Results
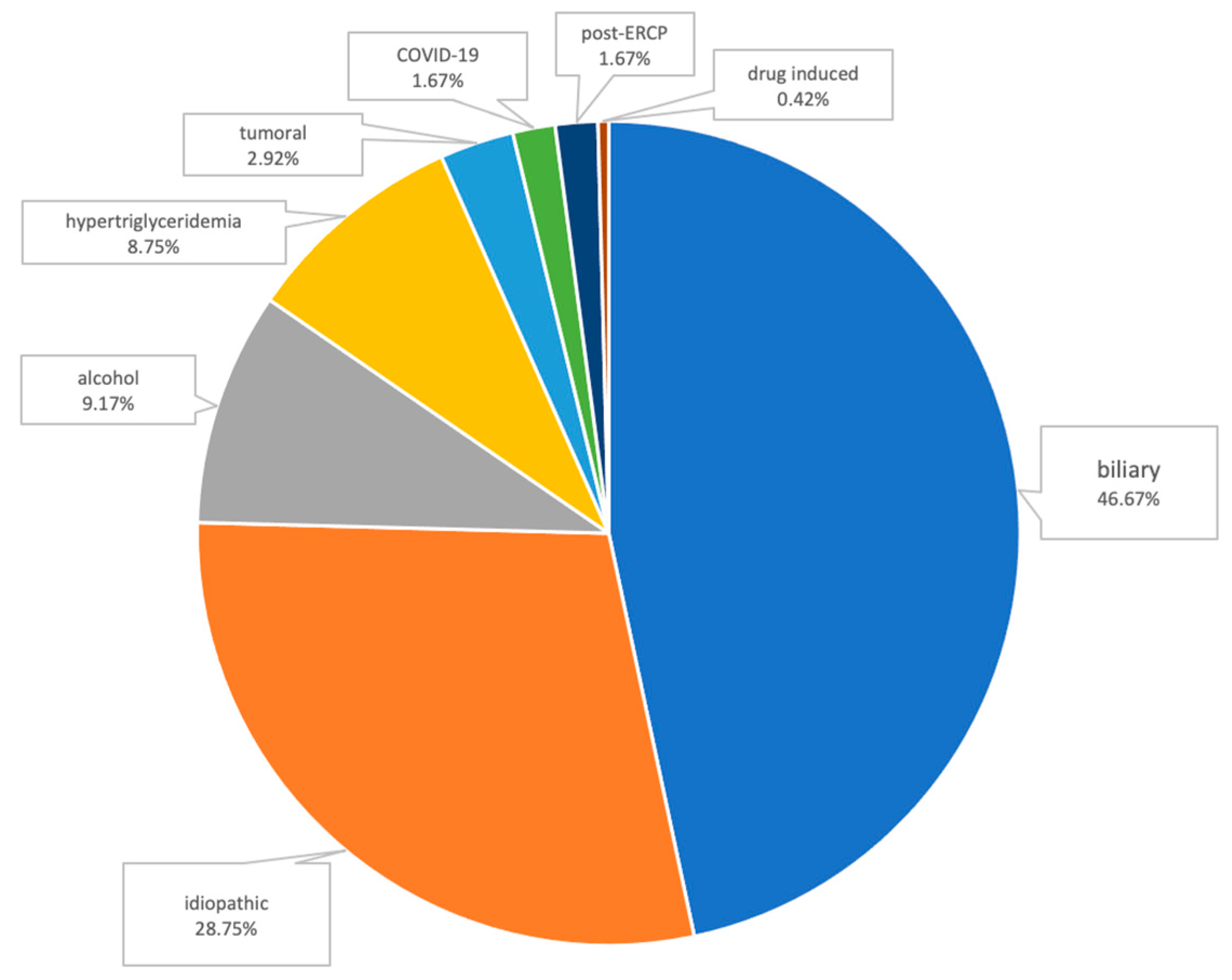
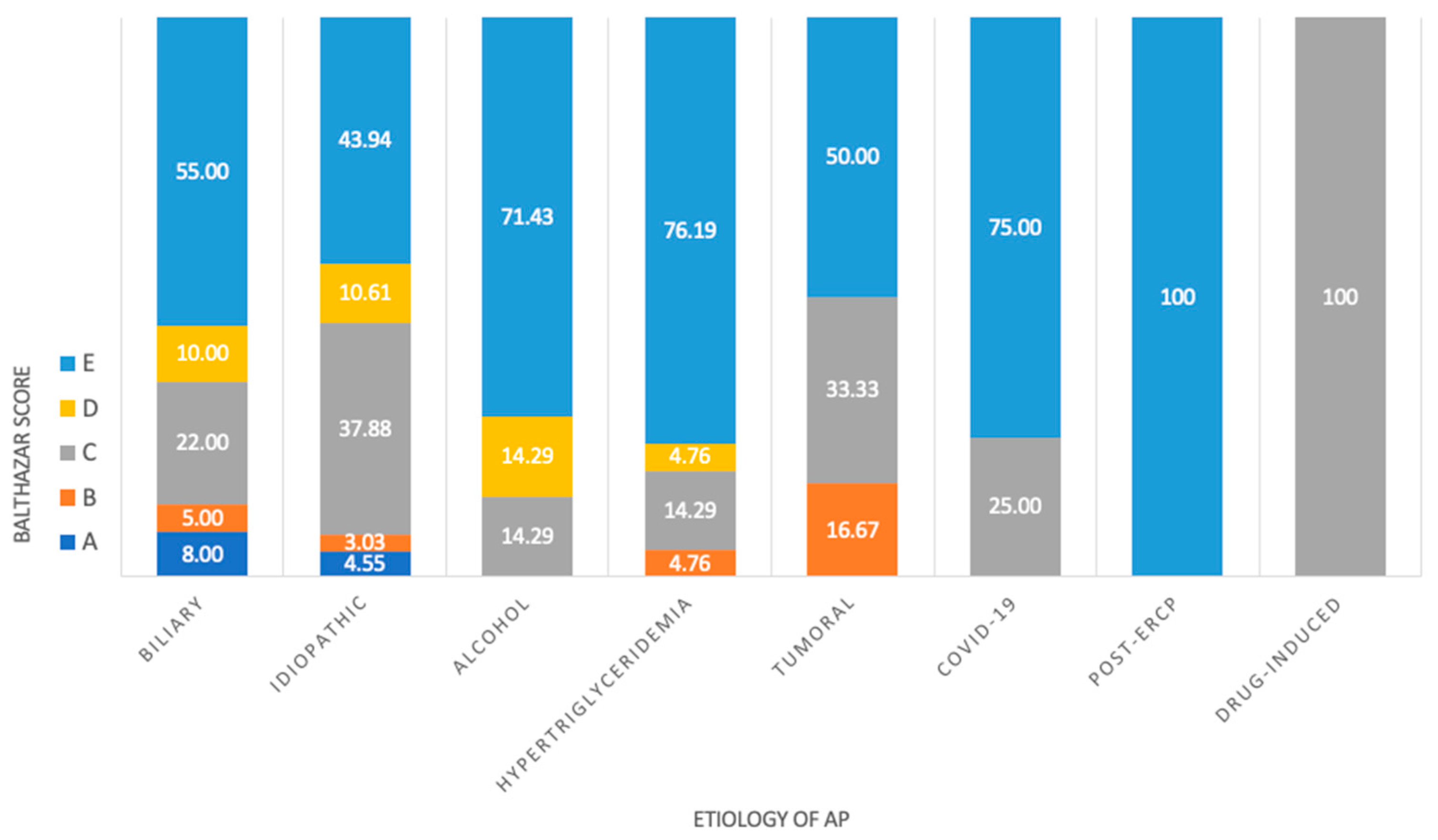
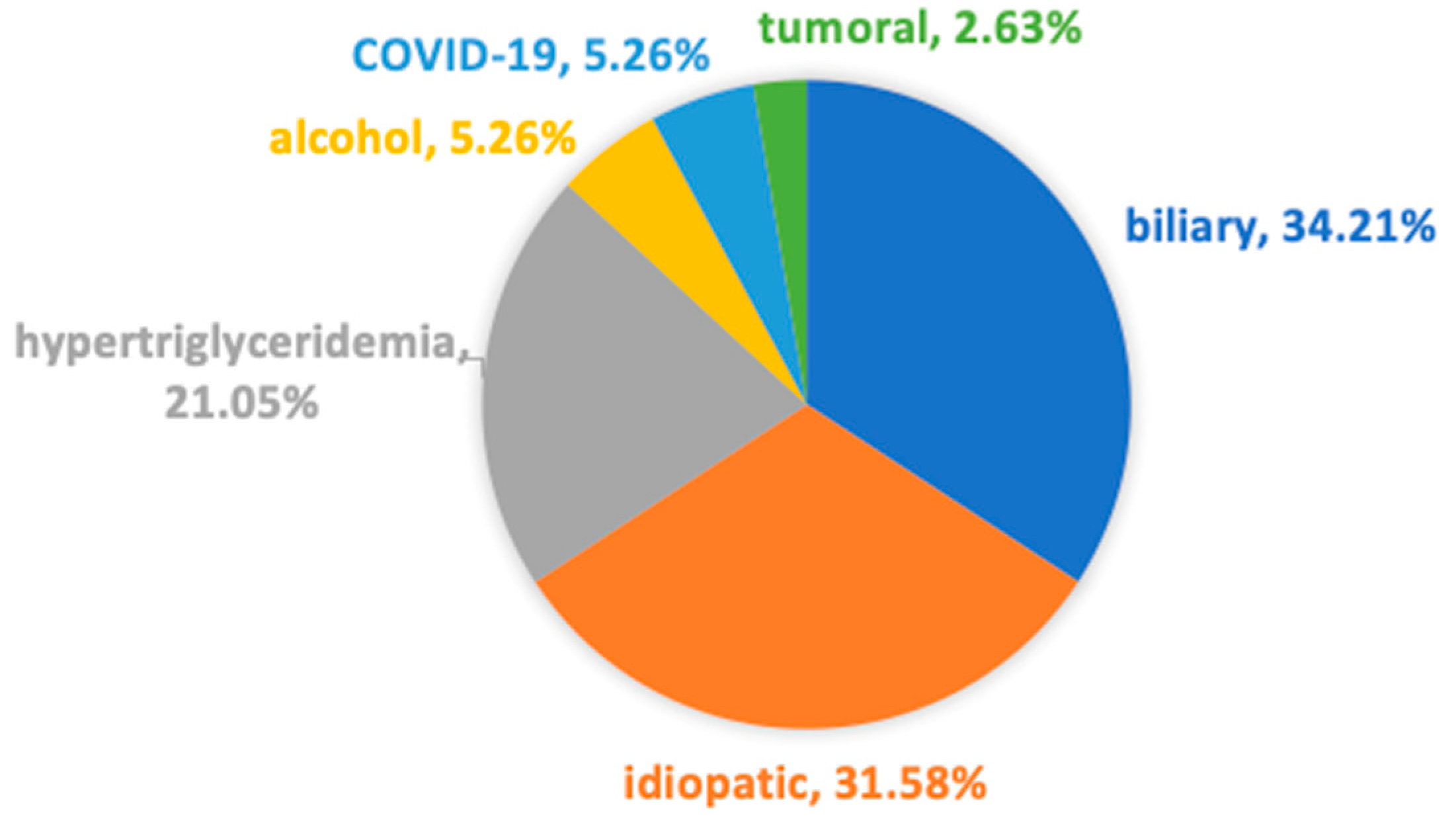
3.1. Etiology
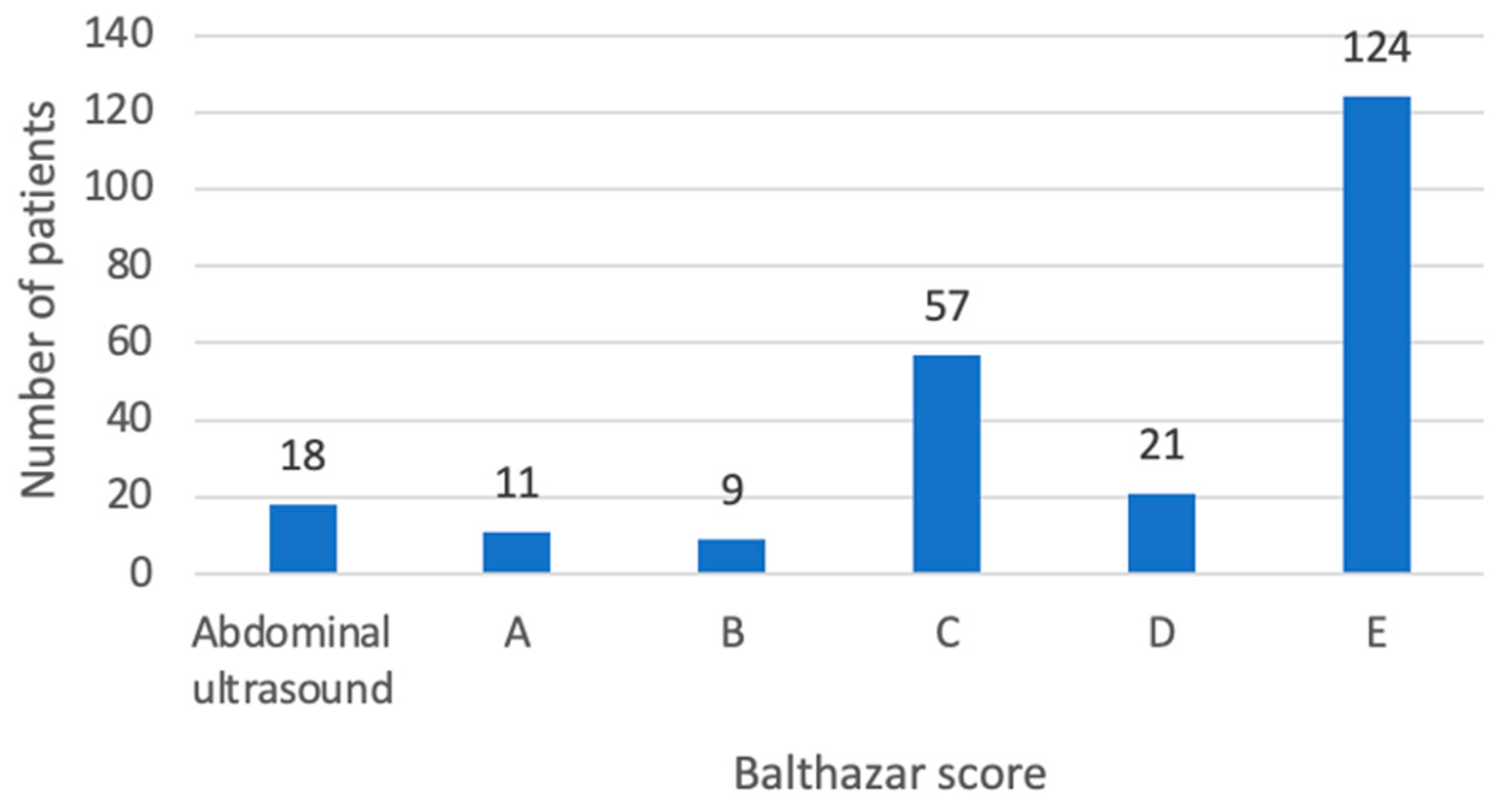
3.2. CT Imaging
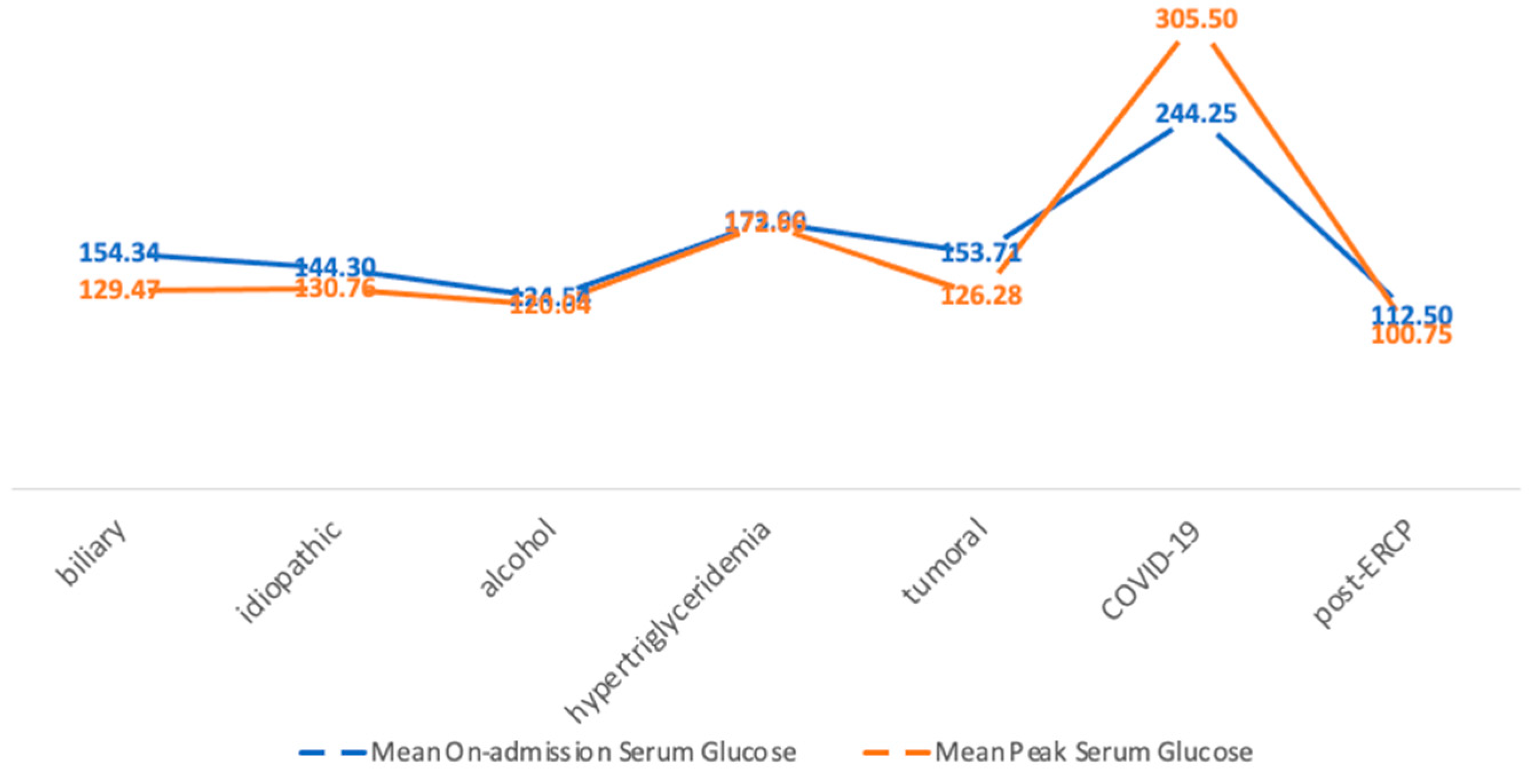
3.3. Serum Glucose Levels
3.4. Pre-Existing DM
3.5. The Length of Hospitalization
3.6. The CRP Levels
3.7. Antibiotic Therapy
3.8. Mortality
3.9. HbA1c
3.10. Follow-Up
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iannuzzi, J.P.; King, J.A.; Leong, J.H.; Quan, J.; Windsor, J.W.; Tanyingoh, D.; Coward, S.; Forbes, N.; Heitman, S.J.; Shaheen, A.A.; et al. Global Incidence of Acute Pancreatitis Is Increasing Over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, A.Y.; Tan, M.L.; Wu, L.M.; Asrani, V.M.; Windsor, J.A.; Yadav, D.; Petrov, M.S. Global incidence and mortality of pancreatic diseases: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of population-based cohort studies. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciochina, M.; Balaban, D.V.; Manucu, G.; Jinga, M.; Gheorghe, C. The Impact of Pancreatic Exocrine Diseases on the β-Cell and Glucose Metabolism—A Review with Currently Available Evidence. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czapári, D.; Váradi, A.; Farkas, N.; Nyári, G.; Márta, K.; Váncsa, S.; Nagy, R.; Teutsch, B.; Bunduc, S.; Erőss, B.; et al. Detailed Characteristics of Post-discharge Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauphine, C. Identification of Admission Values Predictive of Complicated Acute Alcoholic Pancreatitis. Arch. Surg. 2004, 139, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Jin, T.; Zhu, P.; Yao, L.; Li, L.; Cai, W.; Mukherjee, R.; Du, D.; Fu, X.; et al. Stress Hyperglycemia Is Independently Associated with Persistent Organ Failure in Acute Pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 1879–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.; Juhász, M.F.; Görbe, A.; Váradi, A.; Izbéki, F.; Vincze, Á.; Sarlós, P.; Czimmer, J.; Szepes, Z.; Takács, T.; et al. Glucose levels show independent and dose-dependent association with worsening acute pancreatitis outcomes: Post-hoc analysis of a prospective, international cohort of 2250 acute pancreatitis cases. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.F.; Song, Y.; Liu, C.S.; Geng, J.L. Correlation between the glucose level and the development of acute pancreatitis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. S1), S17–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCowen, K.C.; Malhotra, A.; Bistrian, B.R. Stress-Induced Hyperglycemia. Crit. Care Clin. 2001, 17, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egi, M.; Bellomo, R.; Stachowski, E.; French, C.J.; Hart, G.K.; Hegarty, C.; Bailey, M. Blood glucose concentration and outcome of critical illness: The impact of diabetes. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girman, C.J.; Kou, T.D.; Cai, B.; Alexander, C.M.; O’Neill, E.A.; Williams-Herman, D.E.; Katz, L. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus have higher risk for acute pancreatitis compared with those without diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 12, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindise, E.; Elkhatib, I.; Kuruvilla, A.; Silva, R. Temporal Trends in Incidence and Outcomes of Acute Pancreatitis in Hospitalized Patients in the United States From 2002 to 2013. Pancreas 2019, 48, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institutul National de Sanatate Publica. Evidenta Evolutiei Diabetului Zaharat in Perioada 2012–2021; Institutul National de Sanatate Publica: Bucharest, Romania, 2022.
- Cui, Y.; Andersen, D.K. Pancreatogenic Diabetes: Special Considerations for Management. Pancreatology 2011, 11, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodmansey, C.; McGovern, A.P.; McCullough, K.A.; Whyte, M.B.; Munro, N.M.; Correa, A.C.; Gatenby, P.A.; Jones, S.A.; de Lusignan, S. Incidence, Demographics, and Clinical Characteristics of Diabetes of the Exocrine Pancreas (Type 3c): A Retrospective Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, A.; Park, W.G. Acute pancreatitis and diabetes mellitus: A review. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, M.P.; Finnis, M.E.; Phillips, L.K.; Kar, P.; Bihari, S.; Biradar, V.; Moodie, S.; Horowitz, M.; Shaw, J.E.; Deane, A.M. Stress Induced Hyperglycemia and the Subsequent Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Survivors of Critical Illness. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.L.M.; Singh, P.P.; Phillips, A.R.J.; Murphy, R.; Windsor, J.A.; Petrov, M.S. Newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus after acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2014, 63, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.A.; Bradley, D.; Conwell, D.L.; Dungan, K.; Krishna, S.G.; Wyne, K.; Bellin, M.D.; Yadav, D.; Andersen, D.K.; Serrano, J.; et al. Diabetes following acute pancreatitis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahariev, O.J.; Bunduc, S.; Kovács, A.; Demeter, D.; Havelda, L.; Budai, B.C.; Veres, D.S.; Hosszufalusi, N.; Erőss, B.M.; Teutsch, B.; et al. Risk factors for diabetes mellitus after acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2024, 10, 1257222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharmal, S.H.; Cho, J.; Alarcon Ramos, G.C.; Ko, J.; Stuart, C.E.; Modesto, A.E.; Singh, R.G.; Petrov, M.S. Trajectories of glycaemia following acute pancreatitis: A prospective longitudinal cohort study with 24 months follow-up. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, M.; Zhu, X.; Lugea, A.; Waldron, R.T.; Pandol, S.J.; Li, L. Incidence of New Onset Diabetes Mellitus Secondary to Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.N.; Yang, C.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Lu, C.L.; Li, C.Y. Risk of Diabetes Mellitus after First-Attack Acute Pancreatitis: A National Population-Based Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilstrap, L.G.; Chernew, M.E.; Nguyen, C.A.; Alam, S.; Bai, B.; McWilliams, J.M.; Landon, B.E.; Landrum, M.B. Association Between Clinical Practice Group Adherence to Quality Measures and Adverse Outcomes Among Adult Patients with Diabetes. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e199139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, B.; Gao, H.; Gao, L.; Hua, R.; Xu, J.D. ACE2 in the Gut: The Center of the 2019-nCoV Infected Pathology. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 708336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwinson, A.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Grover, M. Colonic expression of Ace2, the SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor, is suppressed by commensal human microbiota. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1984105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepis, T.; Larghi, A.; Papa, A.; Miele, L.; Panzuto, F.; De Biase, L.; Annibale, B.; Cattani, P.; Rapaccini, G.L. SARS-CoV2 RNA detection in a pancreatic pseudocyst sample. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1011–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunti, K.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Kahn, S.E.; Gabbay, R.A.; Buse, J.B. COVID-19, Hyperglycemia, and New-Onset Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 2645–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tian, S.; Chen, T.; Cui, Z.; Shi, N.; Zhong, X.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, T.; Chen, L.; et al. Newly diagnosed diabetes is associated with a higher risk of mortality than known diabetes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppelli, A.; Giannarelli, R.; Aragona, M.; Penno, G.; Falcone, M.; Tiseo, G.; Ghiadoni, L.; Barbieri, G.; Monzani, F.; Virdis, A.; et al. Hyperglycemia at Hospital Admission Is Associated with Severity of the Prognosis in Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: The Pisa COVID-19 Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 2345–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyadi, O.; Tehami, N.; de-Madaria, E.; Siau, K. Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: Prevention, Diagnosis and Management. Medicina 2022, 58, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusczek, E.R.; Colling, K.; Muratore, S.; Conwell, D.; Freeman, M.; Beilman, G. Stereotypical Metabolic Response to Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Show Alterations in Pancreatic Function Regardless of Post-Procedure Pancreatitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Miguel-Yanes, J.; Méndez-Bailón, M.; Jiménez-García, R.; González-Asanza, C.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Muñoz-Rivas, N.; López-de-Andrés, A. Tendencies and Outcomes in Endoscopic Biliary Sphincterotomies among People with or without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Spain, 2003–2013. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2016, 108, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Hu, L.H.; Ren, H.B.; Zhao, A.J.; Qian, Y.Y.; Sun, X.T.; Su, S.; Zhu, S.-G.; Yu, J.; Zou, W.-B.; et al. Incidence and risk factors for post-ERCP pancreatitis in chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 86, 519–524.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuta, K. Impaired glucose tolerance in acute pancreatitis. WJG 2015, 21, 7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umapathy, C.; Raina, A.; Saligram, S.; Tang, G.; Papachristou, G.I.; Rabinovitz, M.; Chennat, J.; Zeh, H.; Zureikat, A.H.; Hogg, M.E.; et al. Natural History After Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis: A Large US Tertiary Care Experience. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2016, 20, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garip, G. Effects of disease severity and necrosis on pancreatic dysfunction after acute pancreatitis. WJG 2013, 19, 8065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| On-Admission Glycemia | Peak Serum Glycemia | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <100 mg/dL | ≥100 mg/dL | p-value | <100 mg/dL | ≥100 mg/dL | p-value | |
| n | 42 | 198 | 83 | 157 | ||
| Age (years), mean | 49.36 | 57.36 | 0.0012 | 53.35 | 57.97 | 0.029 |
| Male, n (%) | 21 (50) | 128 (64.6) | 0.1092 | 39 (47) | 110 (70) | 0.00077 |
| Pre-existing DM, n (%) | 1 (2.4) | 37 (18.7) | 0.0165 | 3 (3.6) | 35 (22.3) | 0.00034 |
| Balthazar score, n | ||||||
| A | 5 | 6 | 0.036 | 5 | 6 | 0.652 |
| B | 0 | 9 | 0.336 | 2 | 7 | 0.662 |
| C | 13 | 44 | 0.313 | 24 | 33 | 0.227 |
| D | 1 | 20 | 0.191 | 12 | 9 | 0.042 |
| E | 20 | 104 | 0.683 | 36 | 88 | 0.083 |
| Etiology, n | ||||||
| Biliary | 17 | 95 | 0.475 | 41 | 71 | 0.631 |
| Idiopathic | 14 | 55 | 0.593 | 26 | 43 | 0.623 |
| Alcohol | 2 | 20 | 0.427 | 3 | 19 | 0.053 |
| Hypertriglyceridemia | 6 | 15 | 0.273 | 6 | 15 | 0.714 |
| Tumoral | 0 | 7 | 0.464 | 3 | 4 | 0.949 |
| COVID-19 | 1 | 3 | 0.730 | 0 | 4 | 0.349 |
| Post-ERCP * | 1 | 3 | 1.0 | 3 | 1 | 0.237 |
| Drug-induced | 1 | 0 | 0.391 | 1 | 0 | 0.745 |
| Length of hospitalization (days), mean | 8.62 | 8.44 | 0.8755 | 6.53 | 9.49 | 0.00105 |
| CRP, mean (mg/dL) | 124.64 | 195.25 | 0.0017 | 150.92 | 199.80 | 0.0041 |
| Antibiotherapy, n (%) | 18 (42.9) | 93 (47) | 0.7526 | 31 (37.3) | 80 (51) | 0.0608 |
| Mortality, n (%) | 4 (9.5) | 8 (4) | 0.2752 | 3 (3.6) | 9 (5.7) | 0.6857 |
| Balthazar Score | Mean On-Admission Serum Glucose (mg/dL) | Mean Peak Serum Glucose (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 107.54 ± 28.79 | 101 ± 27.14 |
| B | 182.66 ± 107.72 | 174.66 ± 87.90 |
| C | 146.68 ± 82.14 | 120.82 ± 52.49 |
| D | 138.19 ± 62.18 | 114 ± 46.93 |
| E | 157.68 ± 84.35 | 145.55 ± 77.92 |
| HbA1c | <5.7% | 5.7–6.4% | ≥6.5% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients (%) | 28 (51.9) | 22 (40.7) | 4 (7.4) |
| On-admission glycemia (mean ± SD) | 119.21 ± 23.25 | 148 ± 46.13 | 273.5 ± 87.37 |
| Peak serum glycemia (mean ± SD) | 109.62 ± 29.62 | 122.77 ± 25.09 | 259 ± 105.66 |
| CRP (mean) | 170.29 | 249.99 | 294.53 |
| Length of hospitalization (mean) | 8.03 | 12.95 | 26.25 |
| Need for AB (%) | 60.71 | 68.18 | 75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balaban, M.; Balaban, D.V.; Enache, I.; Nedelcu, I.C.; Jinga, M.; Gheorghe, C. Impact of Serum Glucose Levels on Outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Analysis. Medicina 2024, 60, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060856
Balaban M, Balaban DV, Enache I, Nedelcu IC, Jinga M, Gheorghe C. Impact of Serum Glucose Levels on Outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Analysis. Medicina. 2024; 60(6):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060856
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalaban, Marina, Daniel Vasile Balaban, Iulia Enache, Ioan Cristian Nedelcu, Mariana Jinga, and Cristian Gheorghe. 2024. "Impact of Serum Glucose Levels on Outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Analysis" Medicina 60, no. 6: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060856
APA StyleBalaban, M., Balaban, D. V., Enache, I., Nedelcu, I. C., Jinga, M., & Gheorghe, C. (2024). Impact of Serum Glucose Levels on Outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Analysis. Medicina, 60(6), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060856








