Investigation of the Systemic Immune Inflammation (SII) Index as an Indicator of Morbidity and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy Patients in a 4-Year Follow-Up Period
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Diabetes Consensus Group. Diabetes Mellitus Tanı, Sınıflama ve İzlem İlkeleri. In Diyabet Tanı ve Tedavi Rehberi 2019, 9th ed.; Balcı, M.K., Ed.; Turkish Diabetes Foundation: İstanbul, Turkey, 2020; pp. 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Jain, N.; Verma, H.; Sharma, K. A Cross-sectional Study to Assess Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Microvascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2021, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaeli, A.A.; Gül, Ö.Ö. Diabetes Mellitusun Epidemiyolojisi. In Diabetes Mellitusun Tanı, Tedavi ve İzlemi, 1st ed.; İmamoğlu, Ş., Ersoy, C.Ö., Eds.; Bursa Uludağ University: Bursa, Turkey, 2022; pp. 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- De Ferranti, S.D.; Boer, I.H.; Vivian, F.; Fox, C.S.; Golden, S.H.; Lavie, C.J.; Magge, S.N.; Marx, N.; McGuire, D.K.; Orchard, T.J.; et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. Circulation 2014, 130, 1110–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, J.; Fauci, A.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Hauser, S.L.; Longo, D.L.; Loscalzo, J. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, 20th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 2850–2889. [Google Scholar]
- Lonardo, A. Liver Fibrosis: More than meets the eye. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.; He, J.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, S.; Dou, K. The Combined Effect of Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Prognosis of Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Large-Scale Cohort Study. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 6415–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Song, Y.; Sun, Y.; Du, H.; Cai, Y.; You, Q.; Fu, H.; Shao, L. Systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with diabetic kidney disease in Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: Evidence from NHANES 2011–2018. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1071465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Geng, J.; Yang, Q.; Su, B.; Liao, R. Systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with increased urinary albumin excretion: A population-based study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 863640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, S.; Sun, Y.; Hua, Y. Monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio and systemic inflammation response index are associated with the risk of metabolic disorders and cardiovascular diseases in general rural population. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 944991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Garcia-Arumi, J.; Gerendas, B.S.; Midena, E.; Sivaprasad, S.; Tadayoni, R.; Wolf, S.; Loewensteing, A. Guidelines for the management of retinal vein occlusion by the European Society of Retina Specialists (EURETINA). Ophthalmologica 2019, 242, 123–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buse, J.B.; Wexler, D.J.; Tsapas, A.; Rossing, P.; Mingrone, G.; Mathieu, C.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Davies, M.J. 2019 update to: Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-H.; Wen, W.X.; Jiang, Z.-P.; Du, Z.-P.; Ma, Z.-H.; Lu, A.-L.; Li, H.-P.; Yuan, F.; Wu, S.B.; Guo, J.W.; et al. The clinical value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) for predicting the occurrence and severity of pneumonia in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, U.; Gurdogan, M. TyG index as a predictor of spontaneous coronary artery dissection in young women. Postgrad. Med. 2023, 135, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birinci, Ş.A. Digital Opportunity for Patients to Manage Their Health: Turkey National Personal Health Record System (The e-Nabız). Balkan Med. J. 2023, 40, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archundia Herrera, M.C.; Subhan, F.B.; Chan, C.B. Dietary patterns and cardiovascular disease risk in people with type 2 diabetes. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caussy, C.; Aubin, A.; Loomba, R. The relationship between type 2 diabetes, NAFLD, and cardiovascular risk. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2021, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraj, S.; Dasu, M.R.; Jialal, I. Diabetes is a proinflammatory state: A translational perspective. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 5, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.V.; Shaw, L.C.; Grant, M.B. Inflammation in the pathogenesis of microvascular complications in diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitouni, K.; Steyn, M.; Earle, K.A. Residual renal and cardiovascular disease risk in conventionally-treated patients with type 2 diabetes: The potential of non-traditional biomarkers. Minerva Med. 2018, 109, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo, J.-A.C.; Yu, J.-S.; Vos, S.; Bapputty, R.; Corcino, Y.L.; Hubal, A.; Daw, J.; Arora, S.; Sun, W.; Lu, Z.-L.; et al. Disruption of retinal inflammation and the development of diabetic retinopathy in mice by a CD40-derived peptide or mutation of CD40 in Müller cells. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 2157–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngblood, H.; Robinson, R.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, S. Proteomic biomarkers of retinal inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambo, G.M.; Asmelash, D.; Alemayehu, E.; Gedefie, A.; Duguma, T.; Kebede, S.S. Changes in selected hematological parameters in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1294290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Correlation between insulin resistance and the rate of neutrophils-lymphocytes, monocytes-lymphocytes, platelets-lymphocytes in type 2 diabetic patients. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovenzana, A.; Carnovale, D.; Phillips, B.; Petrelli, A.; Giannoukakis, N. Neutrophils and their role in the aetiopathogenesis of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2022, 38, e3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njeim, R.; Azar, W.S.; Fares, A.H.; Azar, S.T.; Kassouf, H.K.; Eid, A.A. NETosis contributes to the pathogenesis of diabetes and its complications. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2020, 65, R65–R76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirenjen, S.; Narayanan, J.; Tamilanban, T.; Subramaniyan, V.; Chitra, V.; Fuloria, N.K.; Wong, L.S.; Ramachawolran, G.; Sekar, M.; Gupta, G.; et al. Exploring the contribution of pro-inflammatory cytokines to impaired wound healing in diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1216321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klisic, A.; Scepanovic, A.; Kotur-Stevuljevic, J.; Ninic, A. Novel leukocyte and thrombocyte indexes in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 2775–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziedzic, E.A.; Gasior, J.S.; Tuzimek, A.; Paleczny, J.; Junka, A.; Dabrowski, M.; Jankowski, P. Investigation of the associations of novel inflammatory biomarkers-Systemic Inflammatory Index (SII) and Systemic Inflammatory Response Index (SIRI)-With the severity of coronary artery disease and acute coronary syndrome occurrence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Pan, X.; Jia, B.; Chen, S. Exploring the Correlation Between the Systemic Immune Inflammation Index (SII), Systemic Inflammatory Response Index (SIRI), and Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 3827–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvarna, R.; Biswas, M.; Shenoy, R.P.; Prabhu, M.M. Association of clinical variables as a predictor marker in type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic complications. J. Biomed. 2023, 43, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dan, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Wan, Q.; et al. Increased Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Was Associated with Type 2 Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Cross-Sectional Study in the Chinese Population. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 6039–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, T.T.; Ozkul, F.N.; Balci, B. Could Systemic Inflammatory Index Predict Diabetic Kidney Injury in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus? Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-André, V.; Charbit, B.; Biton, A.; Rouilly, V.; Possémé, C.; Bertrand, A.; Rotival, M.; Bergstedt, J.; Patin, E.; Albert, M.L.; et al. The Milieu Intérieur Consortium. Smoking changes adaptive immunity with persistent effects. Nature 2024, 626, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Duan, H.; Kong, J.; Li, Z. Relationship between C-reactive protein level and diabetic retinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrijević, D.; Andrijević, L.; Antić, J.; Rakić, G.; Pastor, K. Hemogram-based decision tree models for discriminating COVID-19 from RSV in infants. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2023, 37, e24862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| N = 523 | |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 63.5 ± 9.3 |
| Gender, female | 211 (40.3) |
| Duration of DM, years | |
| <5 years | 18 (3.4) |
| 5–10 years | 103 (19.7) |
| >10 years | 402 (76.9) |
| Insulin use status in DM, yes | 362 (69.2) |
| Hypertension, yes | 489 (93.5) |
| Duration of hypertension, years | |
| ≤5 years | 37 (7.6) |
| >5 years | 452 (92.4) |
| Stroke, yes | 76 (14.5) |
| Heart failure, yes | 145 (27.7) |
| Lung pathology, yes | 25 (4.8) |
| Smoking status, ≥20 packets/year | 265 (50.7) |
| Continued smoking in the last 10 Years, yes | 133 (25.4) |
| Antihyperlipidemic/antitriglyceridemic drug use, yes | 364 (70.3) |
| SII | 821.4 ± 1010.8 |
| C-Reactive Protein, mg/dL | 1.9 ± 6.4 |
| The First-Year | The Following Three Years | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyneuropathy, yes | 206 (39.4) | 179 (43.3) | <0.001 |
| Retinopathy progression, yes | 106 (20.3) | 119 (28.8) | <0.001 |
| Coronary artery disease, yes | 154 (29.4) | 88 (21.3) | 0.555 |
| Acute-chronic renal failure, yes | 252 (48.2) | 207 (50.1) | <0.001 |
| Peripheral artery disease, yes | 138 (26.4) | 96 (23.2) | 0.362 |
| Hospitalization for any reason, yes | 363 (69.4) | 310 (75.1) | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization for DM, yes | 39 (7.5) | 34 (8.2) | 0.291 |
| Surgery for Retinopathy, yes | 522 (99.8) | 386 (93.5) | <0.001 |
| Death, yes | 108 (20.7) | 29 (7.0) | <0.001 |
| Microvascular Complications, yes | 390 (74.6) | 323 (61.8) | <0.001 |
| Macrovascular Complications, yes | 240 (45.9) | 159 (30.4) | <0.001 |
| Micro + Macrovascular complications, yes | 201 (38.4) | 142 (27.2) | <0.001 |
| Microvascular Complications + Death, yes | 91 (17.4) | 27 (5.2) | <0.001 |
| Macrovascular Complications + Death, yes | 73 (14.0) | 23 (4.4) | <0.001 |
| Micro + Macrovascular complications + Death, yes | 61 (11.7) | 22 (4.2) | <0.001 |
| Polyneuropathy | Coronary Artery Disease | Retinopathy Progression | Acute-Chronic Renal Failure | Peripheral Artery Disease | Hospitalization for Any Reason | Hospitalization for DM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The first-year | No | 803 ± 1151 | 772.4 ± 692 | 824.7 ± 1050.9 | 706.5 ± 566.9 | 756.4 ± 668.5 | 670.4 ± 490.3 | 833.1 ± 1041.8 |
| Yes | 849.6 ± 747 | 938.6 ± 1521.2 | 808.2 ± 838.8 | 944.9 ± 1322.7 | 1002.6 ± 1610.9 | 887.9 ± 1163.2 | 675.4 ± 463.8 | |
| p | 0.076 | 0.124 | 0.997 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.018 | 0.474 | |
| The following three years | No | 700.4 ± 562 | 712.4 ± 584.1 | 739.8 ± 609.7 | 680.7 ± 553.5 | 711.9 ± 609.5 | 609.7 ± 361.8 | 744.7 ± 610.6 |
| Yes | 770.5 ± 633.2 | 798.7 ± 629 | 708.6 ± 555.8 | 780.6 ± 629.5 | 793.1 ± 539 | 771 ± 648.9 | 576.2 ± 331.7 | |
| p | 0.119 | 0.085 | 0.831 | 0.016 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.139 |
| Microvascular Complications | Macrovascular Complications | Death | Micro + Macrovascular Complications | Microvascular Complications + Death | Macrovascular Complications + Death | Micro + Macrovascular complications + Death | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The first-year | No | 640.5 ± 471.1 | 736.5 ± 639.8 | 729.9 ± 593.1 | 725.7 ± 1122.6 | 735.6 ± 596.4 | 747.4 ± 606.5 | 746.7 ± 602.6 |
| Yes | 883.0 ± 1131.6 | 921.4 ± 1315.2 | 1172.9 ± 1861.7 | 820.1 ± 1422.2 | 1228.1 ± 2004.8 | 1277.4 ± 2206.4 | 1386.8 ± 2393.7 | |
| p | <0.001 | 0.006 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.001 | |
| The following three years | No | 912.2 ± 1423.9 | 831.4 ± 1145.8 | 723.2 ± 582.6 | 821.8 ± 1122.6 | 818.4 ± 1023.3 | 815.4 ± 1020.1 | 814.3 ± 1019.4 |
| Yes | 765.1 ± 628.4 | 798.2 ± 598.3 | 844.4 ± 737.7 | 820.1 ± 620.9 | 874.2 ± 755.4 | 951.7 ± 786.9 | 982.1 ± 791.4 | |
| p | 0.772 | 0.195 | 0.661 | 0.081 | 0.718 | 0.306 | 0.175 |
| AUC | p | Cut-Off | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
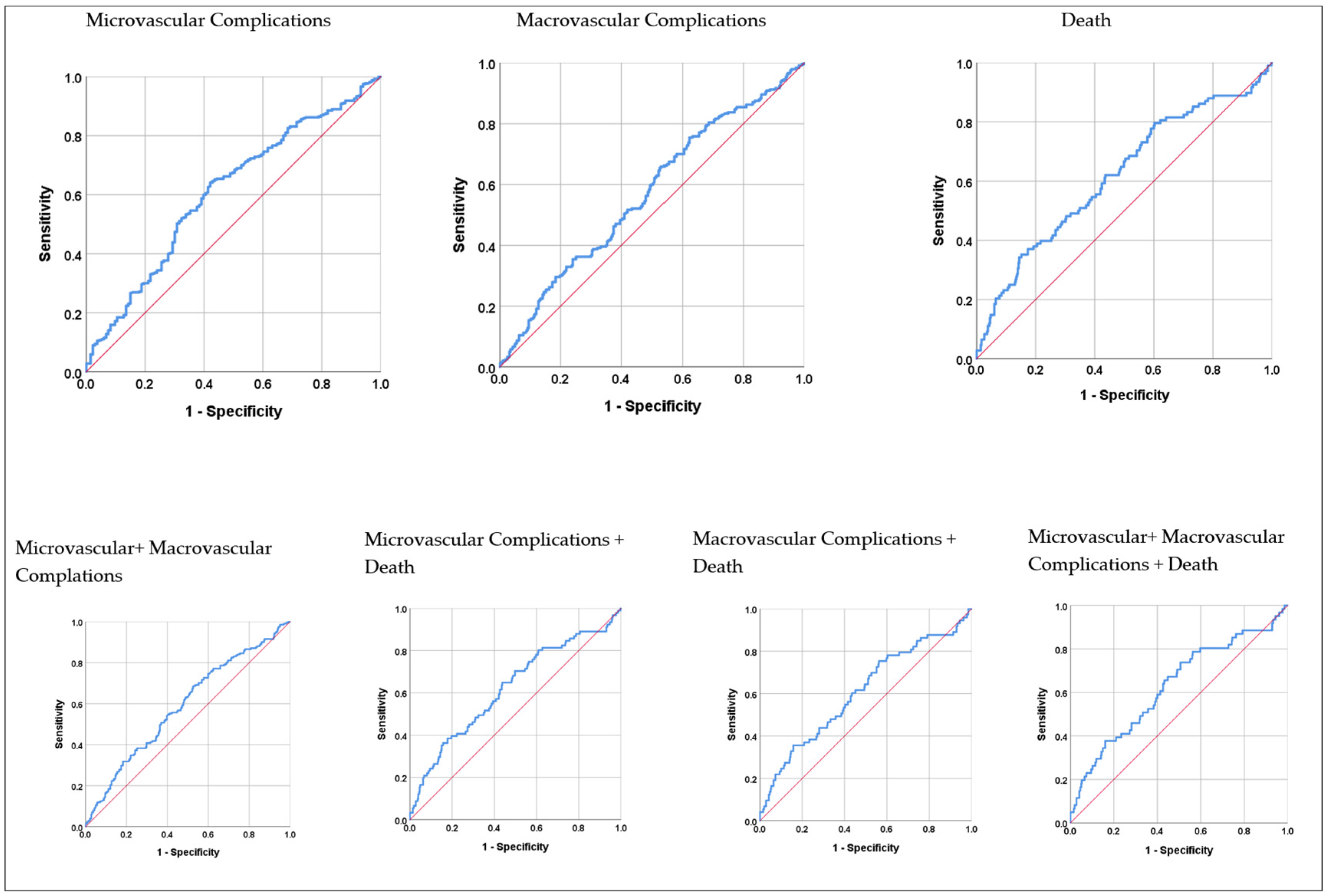
| The first-year | Microvascular Complications | 0.608 | <0.001 | >540.5 | 64.1 | 57.9 |
| Macrovascular Complications | 0.570 | 0.005 | >467.6 | 75.4 | 37.8 | |
| Death | 0.618 | <0.001 | >994.0 | 35.2 | 84.8 | |
| Micro + Macrovascular complications | 0.589 | <0.001 | >531.1 | 68.7 | 47.2 | |
| Microvascular Complications + Death | 0.622 | <0.001 | >634.2 | 64.8 | 56.3 | |
| Macrovascular Complications + Death | 0.607 | 0.004 | >1019.2 | 35.6 | 84.2 | |
| Micro + Macrovascular complications + Death | 0.629 | 0.001 | >594.0 | 73.8 | 49.4 | |
| The following three years | Microvascular Complications | 0.508 | 0.776 | >1019 | 84.5 | 23.5 |
| Macrovascular Complications | 0.536 | 0.192 | >467.6 | 74.2 | 34.3 | |
| Death | 0.524 | 0.711 | >838.5 | 37.9 | 77.8 | |
| Micro + Macrovascular complications | 0.550 | 0.080 | >657.7 | 52.8 | 58.3 | |
| Microvascular Complications + Death | 0.521 | 0.757 | >838.5 | 40.7 | 74.2 | |
| Macrovascular Complications + Death | 0.563 | 0.371 | >852.2 | 43.5 | 75.0 | |
| Micro + Macrovascular complications + Death | 0.585 | 0.223 | >852.2 | 45.5 | 75.1 |
| Variable | B | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | −132.996 | 0.292 |
| At least 20 pack-years of smoking | 180.053 | 0.034 |
| Antihyperlipidemic and antitriglyceridemic drug use | 2.806 | 0.967 |
| DM insulin usage | 11.876 | 0.861 |
| Gender | −22.822 | 0.758 |
| SII | CRP | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SII | r | 1.000 | 0.266 |
| p | <0.001 | ||
| CRP | r | 0.266 | 1.000 |
| p | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabakoglu, N.T.; Celik, M. Investigation of the Systemic Immune Inflammation (SII) Index as an Indicator of Morbidity and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy Patients in a 4-Year Follow-Up Period. Medicina 2024, 60, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060855
Tabakoglu NT, Celik M. Investigation of the Systemic Immune Inflammation (SII) Index as an Indicator of Morbidity and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy Patients in a 4-Year Follow-Up Period. Medicina. 2024; 60(6):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060855
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabakoglu, Nilgun Tan, and Mehmet Celik. 2024. "Investigation of the Systemic Immune Inflammation (SII) Index as an Indicator of Morbidity and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy Patients in a 4-Year Follow-Up Period" Medicina 60, no. 6: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060855
APA StyleTabakoglu, N. T., & Celik, M. (2024). Investigation of the Systemic Immune Inflammation (SII) Index as an Indicator of Morbidity and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy Patients in a 4-Year Follow-Up Period. Medicina, 60(6), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060855






