The Influence of the Q-Angle and Muscle Strength on Idiopathic Anterior Knee Pain in Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
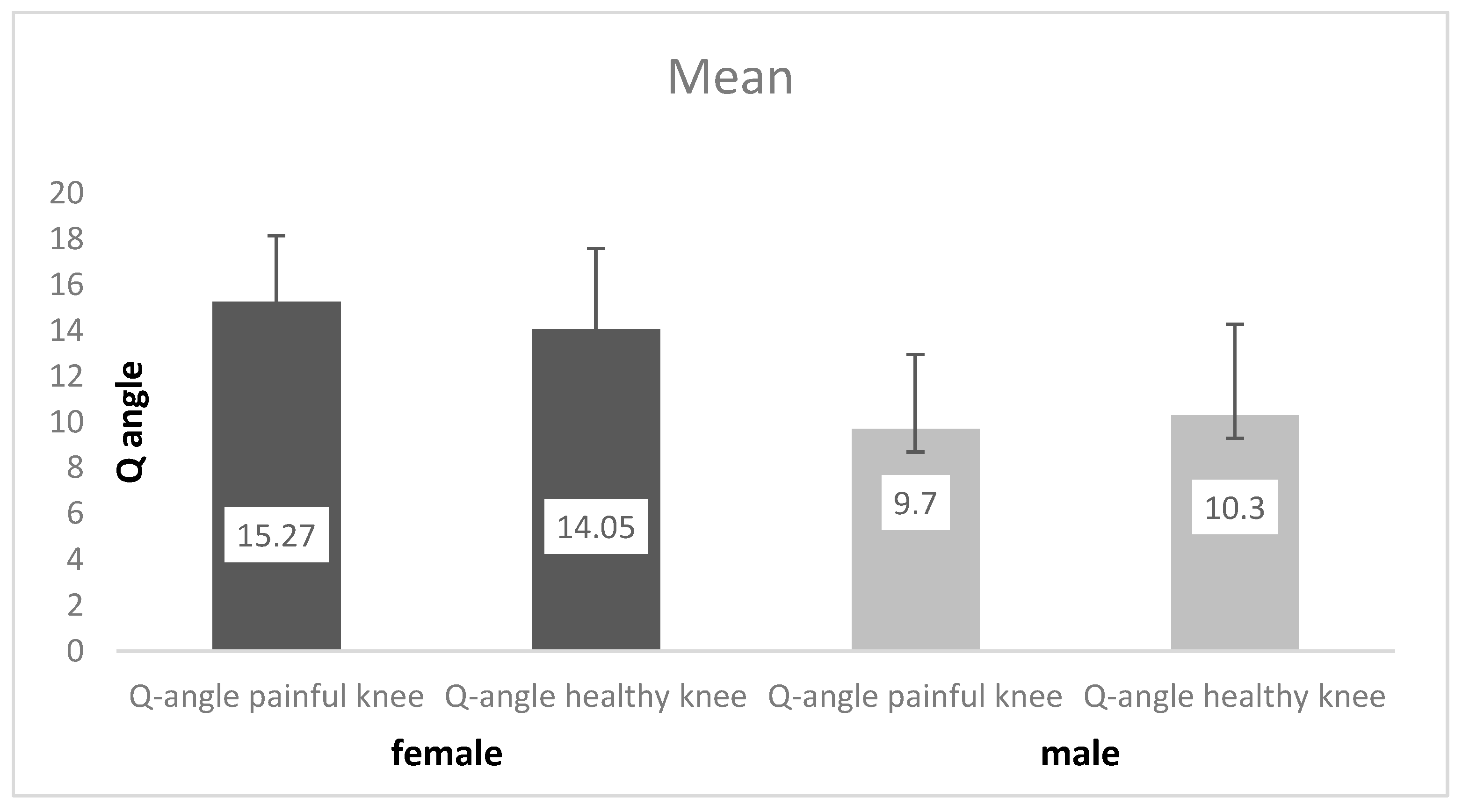
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shea, K.; Pfeiffer, R.; Curtin, M. Idiopathic anterior knee pain in adolescents. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 34, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomee, R.; Augustsson, J.; Karlsson, J. Patellofemoral pain syndrome: A review of current issues. Sports Med. 1999, 28, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutbill, J.; Ladly, K.; Bray, R.; Thorne, P.; Verhoef, M. Anterior knee pain: A Review. J. Sport. Med. 1997, 7, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, B.; Brindle, T.; Sheehan, F. Re-evaluating the functional implications of the Q-angle and its relationship to in-vivo patellofemoral kinematics. Clin. Biomech. 2014, 29, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.; Tumia, N.; Maffulli, N. Anterior knee pain. Trauma 2005, 7, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witvrouw, E.; Lysens, R.; Bellemans, J.; Cambier, D.; Vanderstraeten, G. Intrinsic risk factors for the development of anterior knee pain in an athletic population. Am. J. Sports Med. 2000, 28, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimon, G.; Murray, D.; Sandow, M.; Goodfellow, J. Natural history of anterior knee pain: A 14- to 20-year follow-up of nonoperative management. J. Ped. Orthop. 1998, 18, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Alfonso, V.; Rosello-Sastre, E.; Monteagudo-Castro, C.; Esquerdo, J. Quantitative analysis of nerve changes in the lateral retinaculum in patients with isolated symptomatic patellofemoral malalignment. A preliminary study. Am. J. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbank, J.; Pynsent, P.; Poortvliet, J.; Phillips, H. Mechanical Factors in the Incidence of the Knee Pain in Adolescents and Young Adults. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1984, 66, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, F.; Derasari, A.; Fine, K.; Brindle, T.; Alter, K. Q-angle and J-sign: Indicative of maltracking subgroups in patellofemoral pain. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brattstroem, H. Shape of the intercondylar grove normaly and recurrent dislocation of patella. A clinical and X-ray-anatomical investigatione. Acta Orthop. Scand. Suppl. 1964, 68, 1–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, B. Chronic anteriror knee pain in the adolescent. Ped. Ann. 1991, 20, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; White, L.; Jones, A.; Hui, A.C. Idiopathic anterior knee pain in the young. A prospective controlled trial. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2010, 76, 356–359. [Google Scholar]
- Kannus, P.; Natri, A.; Paakkala, T.; Jarvinen, M. An outcome study of chronic patellofemoral pain syndrome. Seven-year follow-up of patients in a randomized, controlled trial. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1999, 81, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, J.; Thomee, R.; Sward, L. Eleven year follow-up of patello-femoral pain syndrome. Clin. J. Sport. Med. 1996, 6, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natari, A.; Kannus, P.; Jarvinen, M. Which factors predict the long-term outcome in chronic patellofemoral pain syndrome? A 7-yr prospective follow-up study. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 30, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, C.J.; Spalding, T.J. Association between anatomical features and anterior knee pain in a “fit” service population. J. R. Nav. Med. Serv. 2004, 90, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandow, M.J.; Goodfellow, J.W. The natural history of anterior knee pain in adolescents. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1985, 67, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulkerson, J.; Arendt, E. Anterior knee pain in females. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2000, 372, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulkerson, J.; Hungerford, D.S. Disorders of the Patellofemoral Joint, 2nd ed.; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Caylor, D.; Fites, R.; Worrell, T.W. The relationship between quadriceps angle and anterior knee pain syndrome. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1993, 17, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, D.; Doral, M.N. Is there any relationship between Q-angle and lower extremity malalignment? Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2012, 46, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haim, A.; Yaniv, M.; Dekel, S.; Amir, H. Patellofemoral pain syndrome: Validity of clinical and radiological features. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006, 451, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, C.; Thapa, S.S.; Lamichhane, A.P. The relationship of quadriceps angle and anterior knee pain. J. Clin. Diagnostic Res. 2018, 12, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Dde, O.; Briani, R.V.; Pazzinatto, M.F.; Gonçalves, A.V.; Ferrari, D.; Aragão, F.A.; de Azevedo, F.M. Q-angle static or dynamic mesurements, which is the best choice for patellofemoral pain? Clin. Biomech. 2015, 30, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phatama, K.Y.; Isma, S.P.P.; Devi, L.K.; Siahaan, L.D.; Pribadi, A.; Pradana, A.S.; Mustasir, E.; Hidayat, M. Relationship of anterior knee pain with quadriceps angle and anthropometric mesurements in an Asia female population. Malays. Orthop. J. 2022, 16, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Erkocak, O.F.; Altan, E.; Altintas, M.; Turkmen, F.; Aydin, B.K.; Bayar, A. Lower extremity rotational deformities and patellofemoral alignment parameters in patients with anterior knee pain. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 3011–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Stefanyshyn, D. Greater Q angle may not be a risk factor of Patellofemoral Pain Syndrom. Clin. Biomech. 2011, 26, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Arvidsson, H.; Arvidsson, I.; Eriksson, E. Electrical stimulation of vastusmedialis and stretching of lateral thigh muscles in patients with patello-femoral symptoms. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 1993, 1, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, D.; Citaker, S.; Kerimoglu, U.; Atay, O.A.; Nyland, J.; Callaghan, M.; Yakut, Y.; Yüksel, I.; Doral, M.N. Women with patellofemoral pain syndrome have quadriceps femoris volume and strength deficiency. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2011, 19, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boling, M.C.; Padua, D.A.; Marschall, S.W.; Guskiewicz, K.; Pyne, S.; Beutler, A. A prospective investigation of biomechanical risk factors for patellofemoral pain syndrome: The Joint Undertaking to Monitor and Prevent ACL Injury (JUMP-ACL) cohort. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 2108–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, M.J.; Oldham, J.A. Quadriceps atrophy: To what extent does it exist in patellofemoral pain syndrome? Brit. J. Sport Med. 2004, 23, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, L.S.; Webster, K.E.; McClelland, J.A.; Cook, J. Does quadriceps atrophy exist in individuals with patellofemoral pain? A systematic literature review with meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2013, 43, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sac, A.; Tasmektepligil, M.Y. Correlation between the Q angle and the isokinetic strenght and muscle activity. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehab. 2018, 64, 308–313. [Google Scholar]
| Muscle Strength | Mean | Number | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male subgroup | Idiopathic AKP | 18.983 | 30 | 3.4876 |
| Non-affected knee | 22.517 | 30 | 2.2456 | |
| Female subgroup | Idiopathic AKP | 16.634 | 41 | 4.9548 |
| Non-affected knee | 19.902 | 41 | 3.6318 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milovanović, D.; Begović, N.; Bukva, B.; Dučić, S.; Vlahović, A.; Paunović, Z.; Kadija, M.; Topalović, N.; Stijak, L. The Influence of the Q-Angle and Muscle Strength on Idiopathic Anterior Knee Pain in Adolescents. Medicina 2023, 59, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59061016
Milovanović D, Begović N, Bukva B, Dučić S, Vlahović A, Paunović Z, Kadija M, Topalović N, Stijak L. The Influence of the Q-Angle and Muscle Strength on Idiopathic Anterior Knee Pain in Adolescents. Medicina. 2023; 59(6):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59061016
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilovanović, Darko, Ninoslav Begović, Bojan Bukva, Siniša Dučić, Aleksandar Vlahović, Zoran Paunović, Marko Kadija, Nikola Topalović, and Lazar Stijak. 2023. "The Influence of the Q-Angle and Muscle Strength on Idiopathic Anterior Knee Pain in Adolescents" Medicina 59, no. 6: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59061016
APA StyleMilovanović, D., Begović, N., Bukva, B., Dučić, S., Vlahović, A., Paunović, Z., Kadija, M., Topalović, N., & Stijak, L. (2023). The Influence of the Q-Angle and Muscle Strength on Idiopathic Anterior Knee Pain in Adolescents. Medicina, 59(6), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59061016





