Clinical and Histological Long-Term Follow-Up of De Novo HBV-Infection after Liver Transplantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
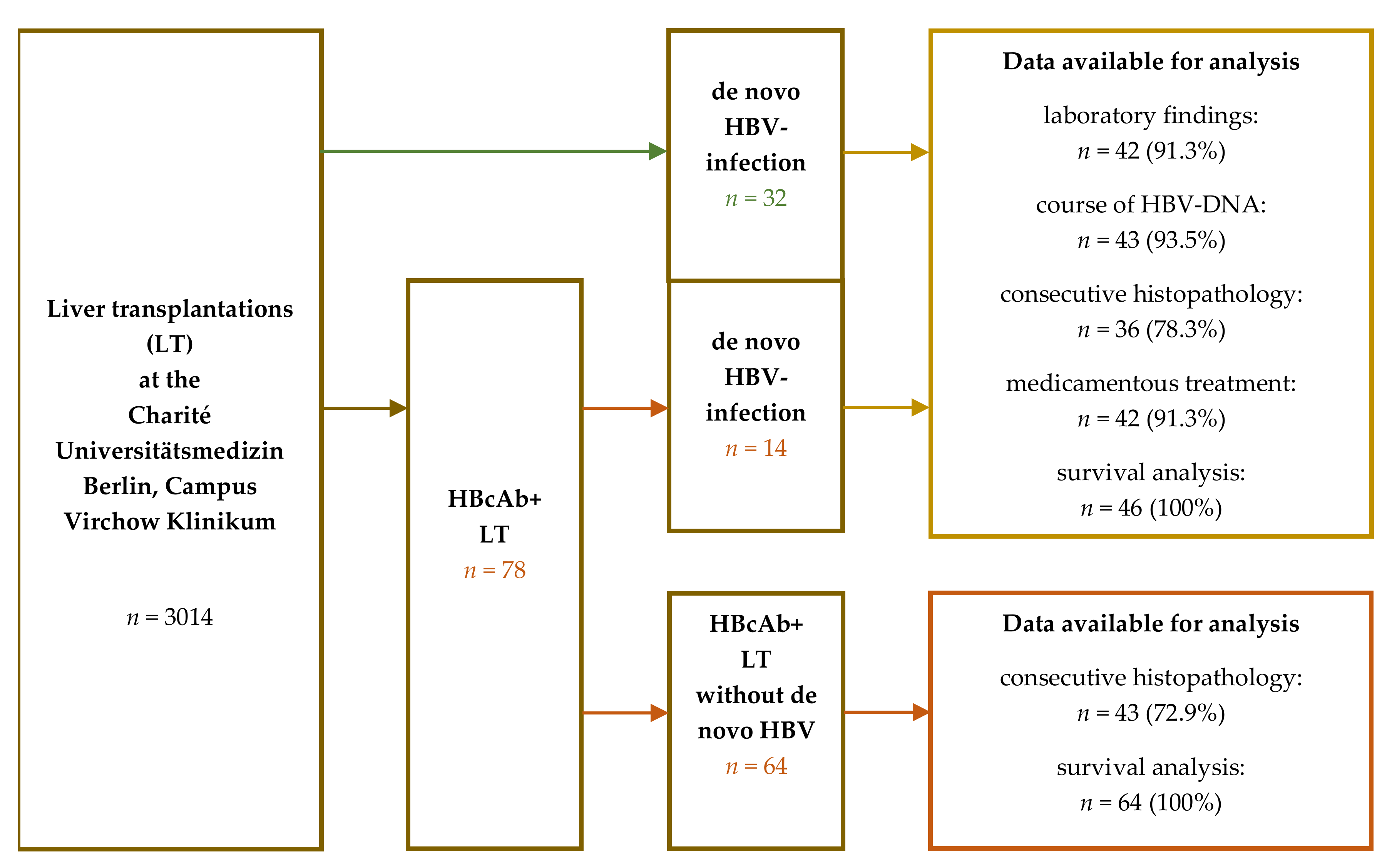
2. Materials and Methods
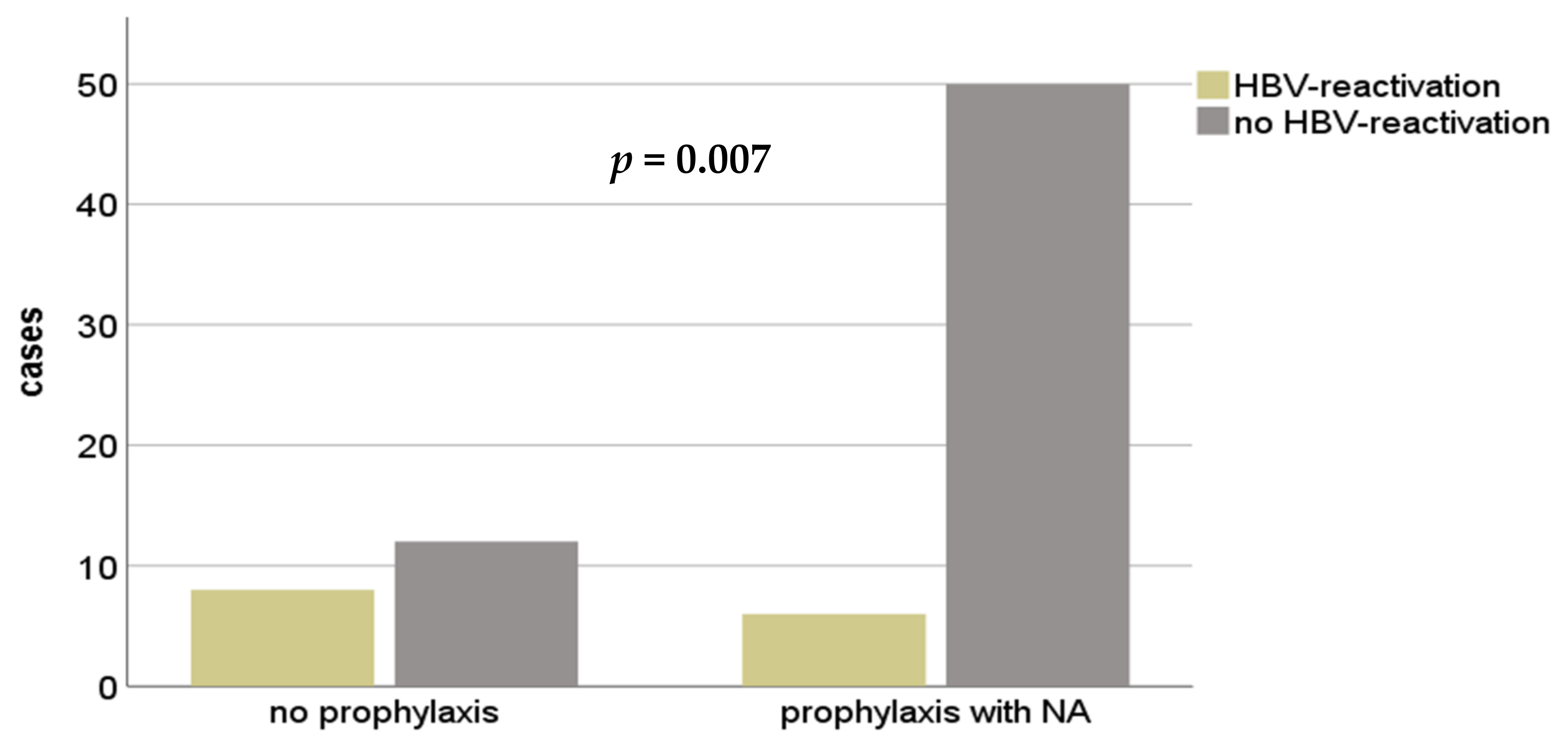
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADF | adenofovir |
| AIH | autoimmune hepatitis |
| ALD | alcoholic liver disease |
| ALF | acute liver failure |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| Anti-HBc | hepatitis B core antibody |
| Anti-HBe | hepatitis B e antibody |
| Anti-HBs | hepatitis B surface antibody |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ETV | entecavir |
| ESLD | end stage liver disease |
| HBV | hepatitis B virus |
| HBcAb | hepatitis B core antibody |
| HBeAg | hepatitis B e antigen |
| HBIG | hepatitis B immunoglobulin |
| HBsAg | hepatitis B surface antigen |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | hepatitis C virus |
| IFN | interferone |
| ITBL | ischemic type biliary lesions |
| LT | liver transplantation |
| LAM | lamivudine |
| NA | nucleos(t)ide analog |
| NASH | nonalcoholic steatohepatitis |
| PBC | primary biliary cholangitis |
| PSC | primary sclerosing cholangitis |
| TA | transaminase |
| TDF | tenofovir |
References
- Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B: The virus and disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M. The Role of cccDNA in HBV Maintenance. Viruses 2017, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chauhan, R.; Lingala, S.; Gadiparthi, C.; Lahiri, N.; Mohanty, S.R.; Wu, J.; Michalak, T.I.; Satapathy, S.K. Reactivation of hepatitis B after liver transplantation: Current knowledge, molecular mechanisms and implications in management. World J. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yan, L.N. Current therapeutic strategies for recurrent hepatitis B virus infection after liver transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 2468–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.K.; Akamatsu, N.; Togashi, J.; Ichida, A.; Kawahara, T.; Maki, H.; Nishioka, Y.; Kokudo, T.; Mihara, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; et al. Hepatitis B virus recurrence after living donor liver transplantation of anti-HBc-positive grafts: A 22-year experience at a single center. Biosci. Trends 2019, 13, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, S.Y.; Lu, L.; Wang, H.L. Fibrosing cholestatic hepatitis: Clinicopathologic spectrum, diagnosis and pathogenesis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2008, 1, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Desmet, V.J.; Gerber, M.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Manns, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Classification of chronic hepatitis: Diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology 1994, 19, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokuhara, A.; Tanaka, E.; Yagi, S.; Mizokami, M.; Hashikura, Y.; Kawasaki, S.; Kiyosawa, K. De novo infection of hepatitis B virus in patients with orthotopic liver transplantation: Analysis by determining complete sequence of the genome. J. Med. Virol. 2000, 62, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, A.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, H.; Yi, N.-J.; Suh, K.-S. De Novo Hepatitis B Virus Infection after Liver Transplantation in Hepatitis B Core-positive Recipients Using Hepatitis B Core-negative Grafts. Transplant. Proc. 2019, 51, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallari, A.; De Raffele, E.; Bellusci, R.; Miniero, R.; Vivarelli, M.; Galli, S.; Luchetti, R.; Fruet, F.; Giordano, E.; Mazziotti, A.; et al. De Novo Hepatitis B and C Viral Infection after Liver Transplantation. World J. Surg. 1997, 21, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholongitas, E.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Burroughs, A.K. Liver grafts from anti-hepatitis B core positive donors: A systematic review. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nair, A.P.; Sasi, S.; Al-Maslamani, M.S.; Chandra, P.; Hashim, S.A.; Abu Jarir, S.; Derbala, M. Epidemiological characteristics of de novo hepatitis B infection in liver transplant recipients-An experience from a tertiary care centre in Qatar. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2020, 22, e13444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, J.; Lo, R.; Chan, S.C.; Chok, K.; Wong, T.; Sharr, W.; Cheung, T.T.; Chan, A.C.; Dai, W.C.; Sin, S.L.; et al. Outcomes including liver histology after liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B using oral antiviral therapy alone. Liver Transpl. 2015, 21, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teegen, E.M.; Maurer, M.M.; Globke, B.; Pratschke, J.; Eurich, D. Liver transplantation for Hepatitis-B-associated liver disease—Three decades of experience. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2019, 21, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, H.; Kim, D.; Na, G.; Kim, E.; Lee, S.; Hong, T.; You, Y.; Choi, J.; Yoon, S.K. De novo hepatitis B virus infection developing after liver transplantation using a graft positive for hepatitis B core antibody. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2015, 89, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabia, R.; Levy, M.F.; Crippin, J.; Tillery, W.; Netto, G.J.; Aguanno, J.; Dysert, P.; Goldstein, R.M.; Husberg, B.S.; Gonwa, T.A.; et al. De novo hepatitis B infection after liver transplantation: Source of disease, incidence, and impact. Liver Transplant. Surg. 1998, 4, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poethko-Muller, C.; Zimmermann, R.; Hamouda, O.; Faber, M.; Stark, K.; Ross, R.S.; Thamm, M. Epidemiology of hepatitis A, B, and C among adults in Germany: Results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS1). Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundh. Gesundh. 2013, 56, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcellin, P.; Gane, E.; Buti, M.; Afdhal, N.; Sievert, W.; Jacobson, I.M.; Washington, M.K.; Germanidis, G.; Flaherty, J.F.; Aguilar Schall, R.; et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: A 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet 2013, 381, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, G.S.; Park, J.B.; Kwon, C.H.; Choe, Y.H.; Joh, J.W.; Lee, S.K. De novo hepatitis b prophylaxis with hepatitis B virus vaccine and hepatitis B immunoglobulin in pediatric recipients of core antibody-positive livers. Liver Transpl. 2016, 22, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onoe, T.; Tahara, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Ohdan, H. Prophylactic managements of hepatitis B viral infection in liver transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienzle, U.; Gunther, M.; Neuhaus, R.; Vandepapeliere, P.; Vollmar, J.; Lun, A.; Neuhaus, P. Immunization with an adjuvant hepatitis B vaccine after liver transplantation for hepatitis B-related disease. Hepatology 2003, 38, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkel, P.; Stoffel, M.; Lerut, J.; Horsmans, Y. Response to an experimental HBV vaccine permits withdrawal of HBIg prophylaxis in fulminant and selected chronic HBV-infected liver graft recipients. Liver Transpl. 2005, 11, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| De Novo HBV-Infection after LT | HbcAb+ LT without De Novo HBV-Infection | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 46 | n = 64 | ||
| Sex | 0.401 | ||
| female | n = 17 (37.0%) | n = 21 (33.8%) | |
| male | n = 29 (63.0%) | n = 43 (66.2%) | |
| Mean age at LT (std) | 49.26 years (11.5) | 54.43 years (12.8) | 0.031 |
| LT Indication | 0.005 | ||
| cirrhosis | n = 24 (52.2%) | n = 29 (45.3%) | |
| HCC | n = 3 (6.5%) | n = 15 (23.4%) | |
| HCV | n = 3 (6.5%)0 | n = 5 (7.8%) | |
| autoimmune | n = 11 (23.9%) | n = 4 (6.3%) | |
| other | n = 4 (8.7%) | n = 11 (17.2%) | |
| Backbone immune suppression | |||
| CNI | n = 40 (87.0%) | n = 63 (98.4%) | |
| MMF | n = 3 (6.5%) | n = 1 (0.6%) | 0.042 |
| Cortison | n = 3 (6.5%) | n = 0 (0%) | 0.06 |
| Combination therapy | 30 (65.2%) | 31 (48.4%) | |
| Reasons for Diagnosis of HBV | n.a | ||
| elevetaed TAs | n = 25 (54.3%) | ||
| elevated bilirubine/icterus | n = 2 (4.3%) | ||
| clinical signs of infection | n = 9 (19.6%) | ||
| routine check | n = 2 (4.3%) | ||
| Median Observation Period min-max) | 4344 days (123–9490) | 2133 days (150–6270) | <0.001 |
| Interquartile range Q1/Q3 | 2708.5/6191.5 days | 1140/3499.25 days | |
| Median histological observation (min-max) | 2362 days (106–8045) | 1825 (184–3654) | <0.001 |
| Status in last follow-up | 0.69 | ||
| alive | n = 27 (58.7%) | n = 41 (64.1%) | |
| deceased | n = 19 (41.3%) | n = 23 (35.9%) | |
| HBcAb-Status of liver transplant | n.a. | ||
| HBcAb+ | n = 14 (30.4%) | n = 64 (100%) | |
| HBcAb− | n = 32 (69.6%) | n = 0 (0%) | |
| HbsAG/HBV-DNA in last follow-up | n.a. | ||
| HbsAG/HBV-DNA+ | n = 32 (69.6%) | n = 0 (0%) | |
| HbsAG/HBV-DNA− | n = 11 (23.9.6%) | n = 64 (100%) | |
| no information | n = 3 (6.5%) |
| De Novo HBV-Infection after LT n = 46 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis of HBV-infection | ||
| HBsAg-positive | n = 46 (100%) | |
| HBV-DNA available | n = 29 (63.0%) | |
| Median laboratory parameters at diagnosis of de novo HBV-infection (min-max) | ||
| norm/threshold | ||
| HBV-DNA | <100 cop/mL | 7,056,000 (13,460–477,000,000) |
| ALT | <41 U/l | 32 (8–256) |
| AST | <50 U/l | 34 (11–402) |
| bilirubine | <1.2 mg/dl | 0.7 (0.2–9.5) |
| platelets | 150–370/nl | 162.5 (96–1127) |
| INR | 0.9–1.25 s | 1.1 (0.88–1.6) |
| pharmacological treatment | ||
| NA-monotherapy | n = 27 (58.7%) | |
| TDF/ETV | n = 14 (30.4%) | |
| ADV/LAM | n = 13 (28.3%) | |
| NA-combination therapy | n = 14 (30.4%) | |
| NA + NA | n = 13 (28.3%) | |
| NA + HBIg | n = 1 (2.2%) | |
| Re-LT | n = 2 (4.3%) | |
| Treatment success | ||
| HbsAg/HBV-DNA+ | n = 32 (69.6%) | |
| HbsAg/HBV-DNA− | n = 11 (23.9.6%) | |
| HBsAg seroconversion | n = 13 (28.3%) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ossami Saidy, R.R.; Eurich, F.; Postel, M.P.; Dobrindt, E.M.; Feldkamp, J.; Schaper, S.J.; Pratschke, J.; Globke, B.; Eurich, D. Clinical and Histological Long-Term Follow-Up of De Novo HBV-Infection after Liver Transplantation. Medicina 2021, 57, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080767
Ossami Saidy RR, Eurich F, Postel MP, Dobrindt EM, Feldkamp J, Schaper SJ, Pratschke J, Globke B, Eurich D. Clinical and Histological Long-Term Follow-Up of De Novo HBV-Infection after Liver Transplantation. Medicina. 2021; 57(8):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080767
Chicago/Turabian StyleOssami Saidy, Ramin Raul, Franziska Eurich, Maximilian Paul Postel, Eva Maria Dobrindt, Jasper Feldkamp, Selina Johanna Schaper, Johann Pratschke, Brigitta Globke, and Dennis Eurich. 2021. "Clinical and Histological Long-Term Follow-Up of De Novo HBV-Infection after Liver Transplantation" Medicina 57, no. 8: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080767
APA StyleOssami Saidy, R. R., Eurich, F., Postel, M. P., Dobrindt, E. M., Feldkamp, J., Schaper, S. J., Pratschke, J., Globke, B., & Eurich, D. (2021). Clinical and Histological Long-Term Follow-Up of De Novo HBV-Infection after Liver Transplantation. Medicina, 57(8), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57080767







