Abstract
Background and objectives: Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women worldwide. Early stage diagnosis is important for predicting increases in treatment success rates and decreases in patient mortality. Recently, circulating biomarkers such as circulating tumor cells, circulating tumor DNA, exosomes, and circulating microRNAs have been examined as blood-based markers for the diagnosis of breast cancer. Although miR-202 has been studied for its function or expression in breast cancer, its potential diagnostic value in a clinical setting remains elusive and miR-202 has not been investigated in South Korea. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the diagnostic utility of miR-202 in plasma samples of breast cancer patients in South Korea. Materials and Methods: We investigated miR-202 expression in the plasma of 30 breast cancer patients during diagnosis along with 30 healthy controls in South Korea by quantitative reverse transcription PCR. Results: The results showed that circulating miR-202 levels were significantly elevated in the breast cancer patients compared with those in healthy controls (p < 0.001). The sensitivity and specificity of circulating miR-202 were 90.0% and 93.0%, respectively. Additionally, circulating miR-202 showed high positivity at early stage. The positive rate of miR-202 was as follows: 100% (10/10) for stage I, 90% (9/10) for stage II, and 80% (8/10) for stage III. miR-202 was also a predictor of a 9.6-fold high risk for breast cancer (p < 0.001). Conclusions: Additional alternative molecular biomarkers for diagnosis and management of pre-cancer patients are needed. Circulating miR-202 might be potential diagnostic tool for detecting early stage breast cancer.
1. Introduction
Breast cancer is one of the common causes of cancer-mediated deaths among women worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 1.5 million newly diagnosed cases and 570,000 deaths related to breast cancer were recorded in 2012. Breast cancer represents approximately 25% of total cancer cases and 15% of total deaths among women [1]. In the Republic of Korea, a total of 19,142 incidences of breast cancer with 2338 mortalities were reported in 2015 [2].
Despite continuous advancements in diagnosis methods, early diagnosis and improvement in survival are still difficult. The early detection and application of improved treatment are extremely important to improve the survival and quality of life for breast cancer patients. Along with simplicity, rapidness, and non-invasiveness, blood-based tumor markers are playing an increasingly important role in the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer.
MicroRNAs (also known as miRNA or miR) are non-cording RNAs (19–25 nucleotides long) involved in the regulation of various cellular processes [3,4]. miRNAs bind to the 3′-untranslated regions (UTRs) of the target mRNAs, thereby either inhibiting their translation or inducing their sequence-specific degradation, leading to the silencing of respective gene expression. miRNAs regulating the expression of target mRNAs that promote tumor growth, invasion, angiogenesis, metastasis, and immune evasion have emerged as one of the major components in cancer biology [5,6,7,8,9]. miRNAs circulating in the blood have been identified, and their profiles reflect the variety of cancer types, suggesting that their circulating population is partly derived from cancer [10,11].
Recent studies have demonstrated that miR-202 is associated with several types of cancers such as ovarian cancer [12], lung cancer [13], and colorectal cancer [14]. miR-202 has been reported to have either a tumor-suppressive or oncogenic function (Table 1) [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28].

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of miR-202 in tissue and blood samples.
This discrepancy is presumed to be the result of differences in the sample processing methods, type of samples, detection methods, and characteristics of the recruited study groups. Some studies showed that miR-202 was significantly upregulated in breast cancer patients compared with that in healthy controls [24]. Additionally, it was highly expressed in the drug-resistant breast cancer tissues [25]. However, some studies reported that it was downregulated in breast cancer cells and inhibited the tumorigenesis of breast cancer [27,28]. Although miR-202 has been studied for its function or expression in breast cancer, little is known about its potential diagnostic value in a clinical setting. miR-202 has not been investigated in South Korea. Here, we evaluated the diagnostic utility of miR-202 in plasma samples of breast cancer patients in South Korea. Furthermore, miR-202-based risk prediction for diagnosing breast cancer was investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
Plasma samples of 30 breast cancer patients (stages I–III) from the Department of Surgery, Yonsei Severance Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea, between 2011 to 2015 were used for miR-202 expression analysis (Table 2). Data such as the age and Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) stage of total 30 breast cancer patients were obtained from patients’ electrical medical records. For healthy control, plasma samples were obtained from 30 healthy donors. This study was approved by the institutional ethics committee at Yonsei Severance Hospital (approval no.: 4-2011-0011, date: 7 March 2011).

Table 2.
Clinical characteristics of breast cancer patients.
2.2. miRNA Extraction
For the extraction of miRNAs from plasma, the NuceloSpin® miRNA Plasma kit (Macherely-Nagel, Düren, Germany) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All the preparation and handling procedures were conducted under RNase-free conditions. Extracted miRNA was stored at −80 °C until used.
2.3. miRNA Expression Analysis
Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized using the TaqMan microRNA Reverse Transcriptase kit (Applied Biosystems by Life Technologies, Foster City, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Briefly, 5 µL of miRNA was used for cDNA synthesis. Reverse transcriptase (RT) mixture contained 0.15 µL of 100 mM dNTP mix (100 mM of each dATP, dGTP, dCTP, and dTTP), 1 µL of 50 U/µL reverse transcriptase, 1.5 µL of 10× reverse transcriptase buffer, 0.19 µL of 20 U/µL RNase inhibitor, and 3 µL of miRNA-specific primer. The volume of RT mixture was adjusted to 15 µL with nuclease-free water. The following primers of TaqMan small RNA assays (Applied Biosystems by Life Technologies) were used: hsa-miR-16 and hsa-miR-202. The temperature profile for cDNA synthesis reaction was: 16 °C for 30 min, 42 °C for 30 min, and 85 °C for 5 min.
The miRNA expression was quantified by determining the cycle threshold (CT), which is the number of PCR cycles required for the fluorescence to exceed a value significantly higher than the background fluorescence, using the TaqMan small RNA assays (Applied Biosystems by Life Technologies) with miRNA-specific primers according to the manufacturer’s instructions [29]. Briefly, 1.4 µL of cDNA was added to 10 µL of probe qPCR mix with 1 µL of miRNA-specific primer and 7.6 µL of nuclease-free water in the final volume of 20 µL. RT-qPCR reactions were performed on the CFX96 Real-Time PCR System Detector (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Samples were run in duplicate for each experiment. Data were analyzed using the comparative ΔΔCT method (2−ΔΔCT) with miR-16 as an endogenous control for plasma [30,31,32]. To monitor contamination of the reagents, a negative control was included for each primer pair. PCR cycling conditions were as follows: 95 °C for 10 min, 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, and 60 °C for 60 s.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
All the statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism version 6.0 (La Jolla, CA, USA) and SPSS Statistics version 21.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Student’s t-test was used for comparing miR-202 expression between normal and cancer plasma samples, as well as to investigate miR-202 expression in the patients according to TNM stage. To assess the diagnostic utility of miR-202, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) was calculated. The risk of breast cancer for miR-202 was analyzed by the chi-square test. Each stage of breast cancer was compared with healthy control. The effects were reported as odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). In all the analyses, p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
Blood samples were collected from 30 breast cancer patients who did not receive any anti-tumor treatment. The characteristics of the subjects involved in this study are shown in Table 2. The age of these 30 patients ranged from 31 to 76 years. There were 10 patients with stage I (33.3%), 10 with stage II (33.3%), and 10 with stage III (33.3%) breast cancer.
3.2. Diagnostic Value of Circulating miR-202
To investigate the diagnostic utility of miR-202 in plasma samples, its expression levels were investigated by RT-qPCR, which were significantly higher in the breast cancer patients than in the healthy controls (p < 0.001; Figure 1a). The diagnostic performance of miR-202 was determined by the analysis of ROC curve. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of miR-202 was 0.9500 (95% CI, 0.8842–1.016, p < 0.0001; Figure 1b). At the cut-off value of 2.1, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of miR-202 were 90.0% (95% CI, 73.5–97.9), 93.3% (95% CI, 77.9–99.2), 90.3% (95% CI, 76.1–96.5), and 93.1% (95% CI, 77.9–98.1), respectively (Figure 1c).
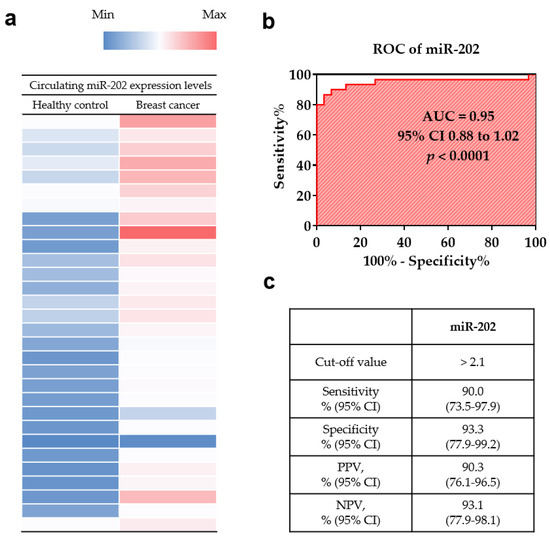
Figure 1.
Diagnostic utility of circulating miR-202 in plasma for breast cancer. (a) Heatmap of circulating miR-202 in breast cancer patients and healthy controls. The color scheme is based on the gene expression level with upregulation in the red color and down regulation in the blue color. (b) The receiver operator characteristic curve (ROC) analysis of circulating miR-202. (c) Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of circulating miR-202.
3.3. Circulating miR-202 Expression According to TNM Stages
Subsequently, the expression levels of circulating miR-202 were analyzed according to TNM stages, revealing a statistically significant difference between the expression level of each stage and healthy control (p < 0.001 for stage I, p < 0.001 for stage II, and p = 0.001 for stage III; Figure 2a). Importantly, the positivity rate was 95% (19/20) for early stage (stages I and II; Figure 2a).
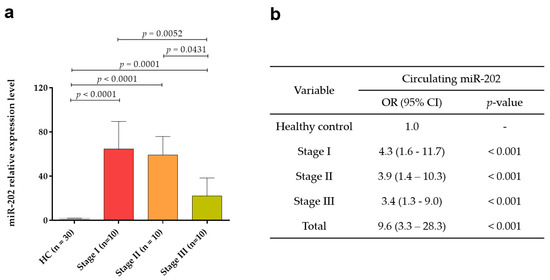
Figure 2.
Expression levels of circulating miR-202 according to Tumor-Node-Metastasis (TNM) stage. (a) The relative expression of circulating miR-202 in plasma of breast cancer patients and healthy controls at different breast cancer stages (stages I, II, and III). (b) Odds ratios (ORs) of circulating miR-202 according to TNM stage.
To investigate the prediction power for diagnosis of breast cancer, the risk of breast cancer for miR-202 was determined. We found that miR-202 conferred a 4.3-fold (95% CI, 1.6–11.7, p < 0.001) at stage I, 3.9-fold (95% CI, 1.4–10.3, p < 0.001) at stage II, 3.4-fold (95% CI, 1.3–9.0, p < 0.001) at stage III, and 9.6 fold (95% CI, 3.3–28.3, p < 0.001) in total breast cancer patients (Figure 2b).
4. Discussion
The detection of circulating biomarkers can provide the understanding of their clinical implications and their potential use in a liquid biopsy for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer [33,34]. Among circulating biomarkers, circulating miRNAs are abundant in the circulatory system of blood and are resistant to RNase-mediated degradation. Circulating miRNAs are also stable in harsh conditions, including bipolar pH, extended storage, freeze–thaw cycles, and in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections [35,36]. In this study, to evaluate circulating miR-202 as a diagnostic tool for breast cancer, the performance characteristics of its sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV were determined using plasma samples of the breast cancer patients.
In a previous study, the diagnostic potential of miR-202 was determined in whole blood samples of 24 breast cancer patients and 24 healthy control using RT-qPCR [37]. miR-202 was found to be highly expressed in breast cancer and the AUC for miR-202 was 0.68. In addition, Joosse et al. [24] reported that the miR-202 levels were elevated in a cohort of breast cancer patients (n = 102) compared with those in healthy controls (n = 37), which is identical to the results of this study. Our result showed that the sensitivity and specificity of circulating miR-202 were 90.0% and 93.0%, respectively. The AUC value was 0.95 (95% CI = 0.88–1.02, p < 0.0001).
Numerous studies focus on improving or developing a treatment for improved prognosis; however, one of the most promising approaches is to detect the cancer at the early stage. The mammography and ultrasound are currently the standard diagnostic tools, proven to be useful for the detection of early stage breast cancer. However, the need for a new minimally invasive diagnostic approach is necessary to complement the mammography and improve the detection rates and breast cancer screening regulations. The specificity of mammography is more than 95%, but the sensitivity is between 67% and 95%, and is highly dependent on diverse factors such as age, breast density, and the professional experience of the investigator [38,39]. We found that miR-202 was significantly upregulated in the plasma samples of early stage breast cancer (p < 0.001). Positivity rate was 100% (10/10) for stages I, 90% (9/10) for stage II, and 80% (8/10) for stage III. In addition, risk of breast cancer for miR-202 was 9.6-fold in the plasma of breast cancer patients compared with that in the plasma of healthy controls.
Several studies have investigated the circulating miRNAs for breast cancer. Chen et al. showed that the expression levels of miR-127-3p, miR-148b, miR-409-3p, miR-376a, miR-376c, miR-652, and miR-801 in the plasma of breast cancer patients were higher than the plasma of healthy controls. The diagnostic potential of these seven circulating miRs combined in 120 breast cancer patients showed an AUC value of 0.81 (95% CI 0.72–0.91) [40]. Additionally, Schrauder et al. reported that serum concentrations of miR-106a-5p and miR454-3p were higher in cancer patients than in healthy controls, whereas those of miR-195-5p, miR-495, and miR-34a-5p were downregulated in breast cancer patients. miR-195-5p and miR-495 can help differentiate between breast cancer and healthy controls with AUC values (sensitivity, specificity) of 0.901 (77.8%, 100%) and 0.901 (100%, 66.7%), respectively [37]. The sensitivity and specificity of miR-202 were comparable to those of other miRs for the breast cancer diagnostic method.
5. Conclusions
Our results show that miR-202-specific RT-qPCR may emerge as a useful tool in the diagnosis of breast cancer, and especially at its early stage. The limitation of this study was the small sample size from a single institution. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct additional studies using a large number of samples from the patients with various stages of breast cancer from multiple centers. Metastasis is one of the major causes of cancer-related deaths where early prediction can increase the survival rate. Investigation of the relationship between prognosis and the level of circulating miR-202 is also necessary.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.L and S.I.K.; methodology, D.H.; Data curation, J.K. and S.P.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K. and S.P.; writing—review and editing, H.L. and S.I.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.W.; Won, Y.J.; Kong, H.J.; Lee, E.S. Cancer statistics in Korea: Incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2015. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition, and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Faggioni, A.; Trivedi, P.; Slack, F.J. The nefarious nexus of noncoding RNAs in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Salck, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahlhut, C.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNAs and the cancer phenotype: Profiling, signatures and clinical implications. Genome Med. 2013, 5, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasinski, A.L.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNAs en route to the clinic: Progress in validating and targeting microRNAs for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Kaur, H. Cell-free miRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers in breast cancer: Significance in early diagnosis and metastasis prediction. Life Sci. 2020, 246, 117417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schetter, A.J.; Harris, C.C. Plasma microRNAs: A potential biomarker for colorectal cancer? Gut 2009, 58, 1318–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.Y.; Pan, S.S. MiR-202-5p suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion in ovarian cancer via regulating HOXB2. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2256–2263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Lv, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, N.; Lv, Y. miR-202 functions as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting STAT3. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lin, S.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, S. MiR-202 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer by targeting UHRF1. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Xing, T.; Wang, Q.; Liu, A.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, D. MicroRNA-202 inhibits cell migration and invasion through targeting FGF2 and inactivating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in endometrial carcinoma. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Y.; Wu, J.L.; Ni, Z.L. Overexpression of microRNA-202-3p protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through activation of TGF-beta1/Smads signaling pathway by targeting TRPM6. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 621–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Dong, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W. Long non-coding RNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1/microRNA-202-3p/periostin axis modulates invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human cervical cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 14170–14180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.B.; Qiu, H.; Chen, J.M.; Shi, W.; Chen, Y.S. MicroRNA-202-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal carcinoma by directly targeting SMARCC1. Gene 2018, 676, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Fan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, J. MicroRNA-202 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma by directly targeting metadherin. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.R.; Quan, Y.H. MicroRNA-202 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in lung cancer cells through targeting cyclin D1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 2278–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Chen, X.; Lu, P.; Ma, W.; Yue, D.; Song, L.; Fan, Q. MicroRNA-202 inhibits tumor progression by targeting LAMA1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Guo, W.; Ni, S.; Xiao, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, D.; Tan, C.; Xu, Q.; Zha, R.; et al. microRNA-202-3p inhibits cell proliferation by targeting ADP-ribosylation factor-like 5A in human colorectal carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Zhang, F.; Dong, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, Y. Low expression of microRNA-202 is associated with the metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Joosse, S.A.; Müller, V.; Steinbach, B.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Circulating cell-free cancer-testis MAGE-A RNA, BORIS RNA, let-7b and miR-202 in the blood of patients with breast cancer and benign breast diseases. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X. MiR-202-5p/PTEN mediates doxorubicin-resistance of breast cancer cells via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, L.; Khadka, V.S.; Ai, J.; Zou, H.; Ju, D.; Jiang, B.; Deng, Y.; Hu, X. Plasma microRNA pair panels as novel biomarkers for detection of early stage breast cancer. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Cao, C.; Dai, Q.; Chen, J.; Tu, J. miR-202 acts as a potential tumor suppressor in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Li, H.; Hu, C. MiR-202 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration in breast cancer by targeting ROCK1 gene. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 16008–16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applied Biosystems by Life Technologies. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/order/genome-database/details/mirna/002363?pluginName=&CID=&ICID= (accessed on 5 July 2020).
- Heneghan, H.M.; Miller, N.; Lowery, A.J.; Sweeney, K.J.; Newell, J.; Kerin, M.J. Circulating micrornas as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Ann. Surg. 2010, 251, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, C.; Rack, B.; Müller, V.; Janni, W.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Circulating microRNAs as blood-based markers for patients with primary and metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Shen, J.; Medico, L.; Wang, D.; Ambrosone, C.B.; Liu, S. A pilot study of circulating miRNAs as potential biomarkers of early stage breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chu, K.M. Circulating cell-free DNAs and miRNAs as promising non-invasive biomarkers for early detection of gastric cancer. Neoplasma 2016, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantel, K.; Speicher, M.R. The biology of circulating tumor cells. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.C.; Li, Q.G.; Ding, X.W.; Ding, Y.T. Circulating microRNAs: Potential biomarkers for cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauder, M.G.; Strick, R.; Schulz-Wendtland, R.; Strissel, P.L.; Kahmann, L.; Loehberg, C.R.; Lux, M.P.; Jud, S.M.; Hartmann, A.; Hein, A.; et al. Circulating micro-RNAs as potential blood-based markers for early stage breast cancer detection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglioretti, D.L.; Walker, R.; Weaver, D.L.; Buist, D.S.M.; Taplin, S.H.; Carney, P.A.; Rosenberg, R.D.; Dignan, M.B.; Zhang, Z.; White, E. Accuracy of screening mammography varies by week of menstrual cycle. Radiology 2011, 258, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, N.; Littenberg, B.; Geller, B.; Muss, H. Accuracy of screening mammography in older women. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ridzon, D.A.; Broomer, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Lee, D.H.; Nguyen, J.T.; Barbisin, M.; Xu, N.L.; Mahuvakar, V.R.; Andersen, M.R.; et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).