Quantifying Tumor Heterogeneity from Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Prostate Using Texture Analysis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
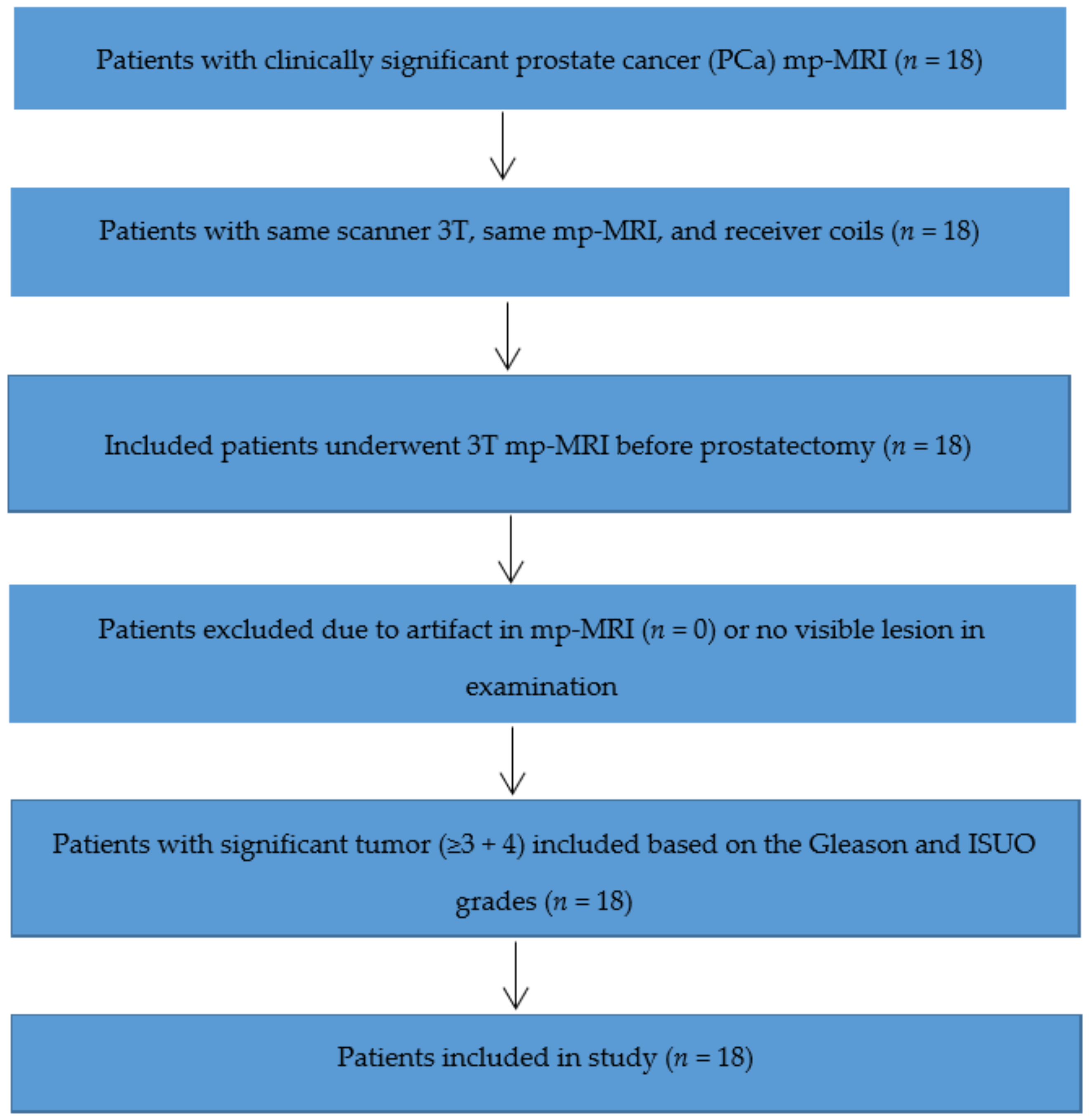
2.1. Patient Group
2.2. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.3. Prostatectomy Specimen Procedure
2.4. Histopathology Review
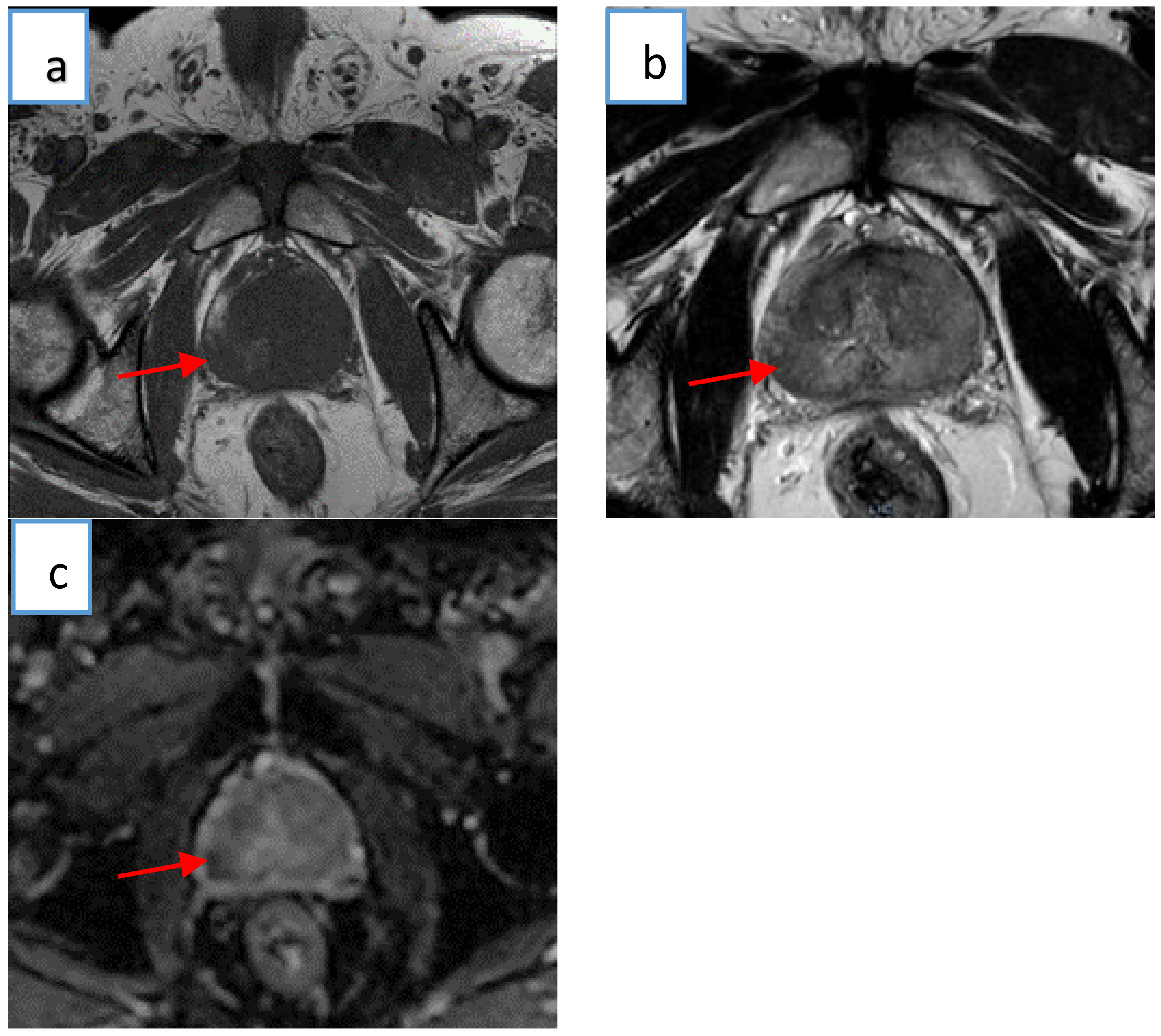
2.5. Histology–MRI Matching
2.6. Magnetic Resonance Textural Analysis
2.7. First-Order Statistical Method
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Group
3.2. Textural Parameters
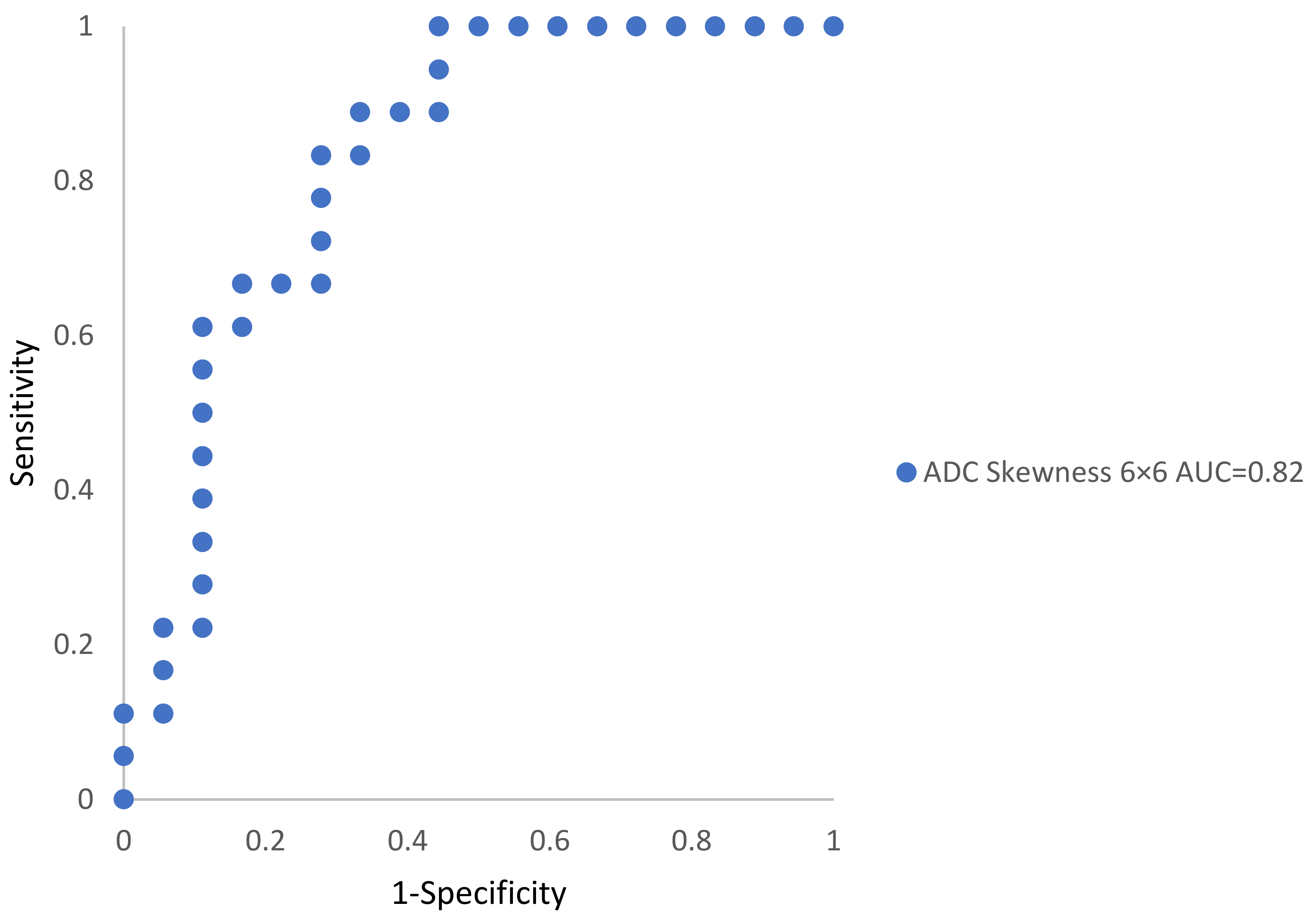
3.3. Disease Classification (Textural Metrics)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Ranking | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | Rejected |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.001 | 0.001852 | 1 |
| 2 | 0.08000 | 0.003704 | 0 |
| 3 | 0.20000 | 0.005556 | 0 |
| 4 | 0.22000 | 0.007407 | 0 |
| 5 | 0.29000 | 0.009259 | 0 |
| 6 | 0.37000 | 0.011111 | 0 |
| 7 | 0.46000 | 0.012963 | 0 |
| 8 | 0.48000 | 0.014815 | 0 |
| 9 | 0.50000 | 0.016667 | 0 |
| 10 | 0.54000 | 0.018519 | 0 |
| 11 | 0.54000 | 0.020370 | 0 |
| 12 | 0.56000 | 0.022222 | 0 |
| 13 | 0.56000 | 0.024074 | 0 |
| 14 | 0.60000 | 0.025926 | 0 |
| 15 | 0.64000 | 0.027778 | 0 |
| 16 | 0.65000 | 0.029630 | 0 |
| 17 | 0.68000 | 0.031481 | 0 |
| 18 | 0.71000 | 0.033333 | 0 |
| 19 | 0.72000 | 0.035185 | 0 |
| 20 | 0.75000 | 0.037037 | 0 |
| 21 | 0.80000 | 0.038889 | 0 |
| 22 | 0.81000 | 0.040741 | 0 |
| 23 | 0.82000 | 0.042593 | 0 |
| 24 | 0.84000 | 0.044444 | 0 |
| 25 | 0.87000 | 0.046296 | 0 |
| 26 | 0.89000 | 0.048148 | 0 |
| 27 | 0.94000 | 0.050000 | 0 |
References
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of prostate cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, S.; Das, S. A Review of Imaging Methods for Prostate Cancer Detection. Biomed. Eng. Comput. Biol. 2016, 7, BECB-S34255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delongchamps, N.B.; Rouanne, M.; Flam, T.; Beuvon, F.; Liberatore, M.; Zerbib, M.; Cornud, F. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for the detection and localization of prostate cancer: Combination of T2-weighted, dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted imaging. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barentsz, J.O.; Richenberg, J.; Clements, R.; Choyke, P.; Verma, S.; Villeirs, G.; Rouviere, O.; Logager, V.; Fütterer, J.J. ESUR prostate MR guidelines 2012. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hameed, M.; Ganeshan, B.; Shur, J.; Mukherjee, S.; Afaq, A.; Batura, D. The clinical utility of prostate cancer heterogeneity using texture analysis of multiparametric MRI. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 51, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganeshan, B.; Miles, K.; Young, R.; Chatwin, C. Hepatic entropy and uniformity: Additional parameters that can potentially increase the effectiveness of contrast enhancement during abdominal CT. Clin. Radiol. 2007, 62, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganeshan, B.; Abaleke, S.; Young, R.C.; Chatwin, C.R.; Miles, K.A. Texture analysis of non-small cell lung cancer on unenhanced computed tomography: Initial evidence for a relationship with tumour glucose metabolism and stage. Cancer Imaging 2010, 10, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davnall, F.; Yip, C.S.; Ljungqvist, G.; Selmi, M.; Ng, F.; Sanghera, B.; Ganeshan, B.; Miles, K.A.; Cook, G.J.; Goh, V. Assessment of tumor heterogeneity: An emerging imaging tool for clinical practice? Insights Imaging 2012, 3, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miles, K.A.; Ganeshan, B.; Griffiths, M.R.; Young, R.C.; Chatwin, C.R. Colorectal cancer: Texture analysis of portal phase hepatic CT images as a potential marker of survival. Radiology 2009, 250, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orczyk, C.; Villers, A.; Rusinek, H.; Lepennec, V.; Bazille, C.; Giganti, F.; Mikheev, A.; Bernaudin, M.; Emberton, M.; Fohlen, A. Prostate cancer heterogeneity: Texture analysis score based on multiple magnetic resonance imaging sequences for detection, stratification and selection of lesions at time of biopsy. BJU Int. 2019, 124, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andor, N.; Graham, T.A.; Jansen, M.; Xia, L.C.; Aktipis, C.A.; Petritsch, C.; Ji, H.P.; Maley, C.C. Pan-cancer analysis of the extent and consequences of intratumor heterogeneity. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganeshan, B.; Miles, K.A. Quantifying tumour heterogeneity with CT. Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miles, K.A.; Ganeshan, B.; Hayball, M.P. CT texture analysis using the filtration-histogram method: What do the measurements mean? Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arivazhagan, S.; Ganesan, L. Texture classification using wavelet transform. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2003, 24, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, H.S.; Benigno, S.; Ganeshan, B.; Dikaios, N.; Johnston, E.W.; Allen, C.; Kirkham, A.; Groves, A.M.; Ahmed, H.U.; Emberton, M. Textural analysis of multiparametric MRI detects transition zone prostate cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 2348–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bostwick, D.G. Gleason grading of prostatic needle biopsies. Correlation with grade in 316 matched prostatectomies. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1994, 18, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostwick, D.G.; Grignon, D.J.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Amin, M.B.; Cohen, M.; Crawford, D.; Gospadarowicz, M.; Kaplan, R.S.; Miller, D.S.; Montironi, R. Prognostic factors in prostate cancer: College of American Pathologists consensus statement 1999. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2000, 124, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montironi, R.; Mazzucchelli, R.; van der Kwast, T. Morphological assessment of radical prostatectomy specimens. A protocol with clinical relevance. Virchows Arch. 2003, 442, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaratunga, H.; Montironi, R.; True, L.; Epstein, J.I.; Griffiths, D.F.; Humphrey, P.A.; Van Der Kwast, T.; Wheeler, T.M.; Srigley, J.R.; Delahunt, B. International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on handling and staging of radical prostatectomy specimens. Working group 1: Specimen handling. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srigley, J.R. Key issues in handling and reporting radical prostatectomy specimens. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2006, 130, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostwick, D.G.; Montironi, R. Evaluating radical prostatectomy specimens: Therapeutic and prognostic importance. Virchows Arch. 1997, 430, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakr, W.A.; Grignon, D.J. Prostate: Practice parameters, pathologic staging, and handling radical prostatectomy specimens. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 26, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renshaw, A.; Chang, H.; D’Amico, A. An abbreviated protocol for processing radical prostatectomy specimens: Analysis of tumor grade, stage, margin status, and volume. J. Urol. Pathol. 1996, 5, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Littrup, P.J.; Williams, C.; Egglin, T.; Kane, R. Determination of prostate volume with transrectal US for cancer screening. Part II. Accuracy of in vitro and in vivo techniques. Radiology 1991, 179, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egevad, L. Handling of radical prostatectomy specimens. Histopathology 2012, 60, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierorazio, P.M.; Walsh, P.C.; Partin, A.W.; Epstein, J.I. Prognostic G leason grade grouping: Data based on the modified G leason scoring system. BJU Int. 2013, 111, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szczypiński, P.M.; Strzelecki, M.; Materka, A.; Klepaczko, A. MaZda—A software package for image texture analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2009, 94, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, R. ImageJ. In Fundamentals of Digital Imaging in Medicine; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Materka, A.; Strzelecki, M. Texture analysis methods—A review. Tech. Univ. Lodz Inst. Electron. COST B11 Rep. Bruss. 1998, 10, 4968. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, N.; Agrawal, R. First and second order statistics features for classification of magnetic resonance brain images. J. Signal Inf. Process. 2012, 3, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L., Jr. Python Tutorial; Centrum voor Wiskunde en Informatica Amsterdam: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 620. [Google Scholar]
- Akin, O.; Sala, E.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Kuroiwa, K.; Ishill, N.M.; Pucar, D.; Scardino, P.T.; Hricak, H. Transition zone prostate cancers: Features, detection, localization, and staging at endorectal MR imaging. Radiology 2006, 239, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oto, A.; Kayhan, A.; Jiang, Y.; Tretiakova, M.; Yang, C.; Antic, T.; Dahi, F.; Shalhav, A.L.; Karczmar, G.; Stadler, W.M. Prostate cancer: Differentiation of central gland cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia by using diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2010, 257, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donati, O.F.; Mazaheri, Y.; Afaq, A.; Vargas, H.A.; Zheng, J.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Hricak, H.; Akin, O. Prostate cancer aggressiveness: Assessment with whole-lesion histogram analysis of the apparent diffusion coefficient. Radiology 2013, 271, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ing, N.; Huang, F.; Conley, A.; You, S.; Ma, Z.; Klimov, S.; Ohe, C.; Yuan, X.; Amin, M.B.; Figlin, R. A novel machine learning approach reveals latent vascular phenotypes predictive of renal cancer outcome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, A.; Miles, K. Prostate-specific membrane antigen PET/MRI validation of MR textural analysis for detection of transition zone prostate cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 5290–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, J.C.; Barentsz, J.O.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Haider, M.A.; Macura, K.J.; Margolis, D.; Schnall, M.D.; Shtern, F.; Tempany, C.M. PI-RADS prostate imaging—Reporting and data system: 2015, version 2. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Tumor Significance | Subject Number | Mean Years | Mean PSA (ng/mL) | Mean Area (cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Significant (≥3 + 4) | 18 | 63 | 7.5 | 1.58 |
| Sequence Parameter | T1 | T2 | ADC Map Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Repetition time (ms) | 4755.32 | 724.99 | 4137.73 |
| Echo time (ms) | 100 | 6.48 | 84.94 |
| Flip angle (degrees) | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| Bandwidth (Hz/px) | 210 | 620 | 2068 |
| Field of view (mm) | 180 | 180 | 180 |
| Phase FoV % | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Slice gap (mm) | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Average | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| Phase encoding direction | COL | ROW | COL |
| Base matrix | 256 | 560 | 144 |
| Number of acquisitions | 5 | 7 | 15 |
| Acquisition duration(s) | 217.49 | 304.34 | 297.91 |
| Sequence | Non-Tumor Regions (Mean ± SEM) | Significant Tumor (Mean ± SEM) | p-Value | ROC-AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC 3 × 3 | 0.06 ± 0.12 | 0.43 ± 0.15 | 0.94 | 0.66 |
| T2 3 × 3 | 0.28 ± 0.94 | 0.01 ± 0.10 | 0.54 | 0.31 |
| T1 3 × 3 | −0.16 ± 0.78 | 0.12 ± 0.10 | 0.29 | 0.39 |
| ADC 6 × 6 | −0.14 ± 0.13 | 0.49 ± 0.11 | 0.001 | 0.82 |
| T26 × 6 | 0.14 ± 0.15 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.8 | 0.47 |
| T1 6 × 6 | 0.05 ± 0.13 | 0.06 ± 0.17 | 0.2 | 0.37 |
| ADC 9 × 9 | −0.13 ± 0.12 | 0.17 ± 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.66 |
| T2 9 × 9 | −0.03 ± 0.16 | 0.12 ± 0.10 | 0.48 | 0.43 |
| T1 9 × 9 | −0.20 ± 0.17 | 0.16 ± 0.18 | 0.5 | 0.56 |
| Sequence | Non-Tumor Regions (Mean ± SEM) | Significant Tumor (Mean ± SEM) | p-Value | ROC-AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC 3 × 3 | −0.72 ± 0.10 | −0.41 ± 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.58 |
| T2 3 × 3 | 0.13 ± 0.11 | 0.19 ± 0.15 | 0.6 | 0.55 |
| T1 3 × 3 | −0.57 ± 0.14 | 0.37 ± 0.40 | 0.46 | 0.57 |
| ADC 6 × 6 | −0.64 ± 0.16 | −0.47 ± 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.61 |
| T2 6 × 6 | −0.01 ± 0.24 | −0.34 ± 0.16 | 0.72 | 0.53 |
| T1 6 × 6 | 0.01 ± 0.19 | 0.22 ± 0.43 | 0.65 | 0.54 |
| ADC 9 × 9 | −0.78 ± 0.08 | −0.65 ± 0.10 | 0.81 | 0.52 |
| T2 9 × 9 | −0.09 ± 0.19 | −0.51 ± 0.14 | 0.82 | 0.47 |
| T1 9 × 9 | −0.08 ± −0.29 | −0.05 ± 0.45 | 0.56 | 0.55 |
| Sequence | Non-Tumor Regions (Mean ± SEM) | Significant Tumor (Mean ± SEM) | p-Value | ROC-AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC 3 × 3 | 4.09 ± 0.09 | 4.07 ± 0.15 | 0.84 | 0.48 |
| T2 3 × 3 | 6.25 ± 0.11 | 6.10 ± 0.22 | 0.75 | 0.46 |
| T1 3 × 3 | 5.61 ± 0.30 | 5.48 ± 0.31 | 0.71 | 0.53 |
| ADC 6 × 6 | 4.08 ± 0.09 | 4.15 ± 0.11 | 0.64 | 0.54 |
| T2 6 × 6 | 5.92 ± 0.12 | 5.86 ± 0.12 | 0.87 | 0.51 |
| T1 6 × 6 | 4.98 ± 0.31 | 4.85 ± 0.27 | 0.68 | 0.54 |
| ADC 9 × 9 | 4.02 ± 0.10 | 4.12 ± 0.11 | 0.54 | 0.55 |
| T2 9 × 9 | 5.72 ± 0.13 | 5.59 ± 0.16 | 0.56 | 0.55 |
| T1 9 × 9 | 4.58 ± 0.27 | 4.60 ± 0.24 | 0.89 | 0.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alanezi, S.T.; Sullivan, F.; Kleefeld, C.; Greally, J.F.; Kraśny, M.J.; Woulfe, P.; Sheppard, D.; Colgan, N. Quantifying Tumor Heterogeneity from Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Prostate Using Texture Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071631
Alanezi ST, Sullivan F, Kleefeld C, Greally JF, Kraśny MJ, Woulfe P, Sheppard D, Colgan N. Quantifying Tumor Heterogeneity from Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Prostate Using Texture Analysis. Cancers. 2022; 14(7):1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071631
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlanezi, Saleh T., Frank Sullivan, Christoph Kleefeld, John F. Greally, Marcin J. Kraśny, Peter Woulfe, Declan Sheppard, and Niall Colgan. 2022. "Quantifying Tumor Heterogeneity from Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Prostate Using Texture Analysis" Cancers 14, no. 7: 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071631
APA StyleAlanezi, S. T., Sullivan, F., Kleefeld, C., Greally, J. F., Kraśny, M. J., Woulfe, P., Sheppard, D., & Colgan, N. (2022). Quantifying Tumor Heterogeneity from Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Prostate Using Texture Analysis. Cancers, 14(7), 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071631






