Unlocking the Anti-Breast Cancer Potential of Aralia chinensis L.
Abstract
1. Introduction
Botanical Description of Chinensis
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of TSAC
2.3. Preparation of Samples for LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.4. Animals
2.5. Preparation of Medicated Serum Samples
2.6. UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap MS Condition
2.7. Data Processing and Chemical Identification
2.8. Network Analysis
2.8.1. Collection of Targets for Active Ingredients
2.8.2. Collection of Breast Cancer-Related Genes
2.8.3. Construction of Active Compound–Target and Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Networks
2.8.4. Analyses of the GO Functional Enrichment and KEGG Pathway
2.8.5. Molecular Docking
2.9. Experimental Validation In Vitro
2.9.1. Cell Culture
2.9.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.9.3. Colony Formation Assay
2.9.4. Migration Assay
2.10. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.11. Western Blot Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of Chemical Compounds
3.2. Triterpenoid Saponins
3.3. Triterpenoids
3.4. Other Compounds
3.5. Identification and Characterization of the Absorbed Prototype Chemicals in Rat Serum
3.6. Results of Network Pharmacology Analysis
3.6.1. Targets of the Prototype Active Compounds
3.6.2. Functional Analysis of Breast Cancer-Related Genes
3.6.3. Intersection Analysis of Targets of Absorbed Active Components and Breast Cancer-Related Genes
3.7. Molecular Docking
3.8. Results of Experimental Validation In Vitro
3.8.1. TSAC Inhibited the Proliferation and Colony of MCF-7 Cells
3.8.2. TSAC Inhibited Migration Rates of MCF-7 Cells
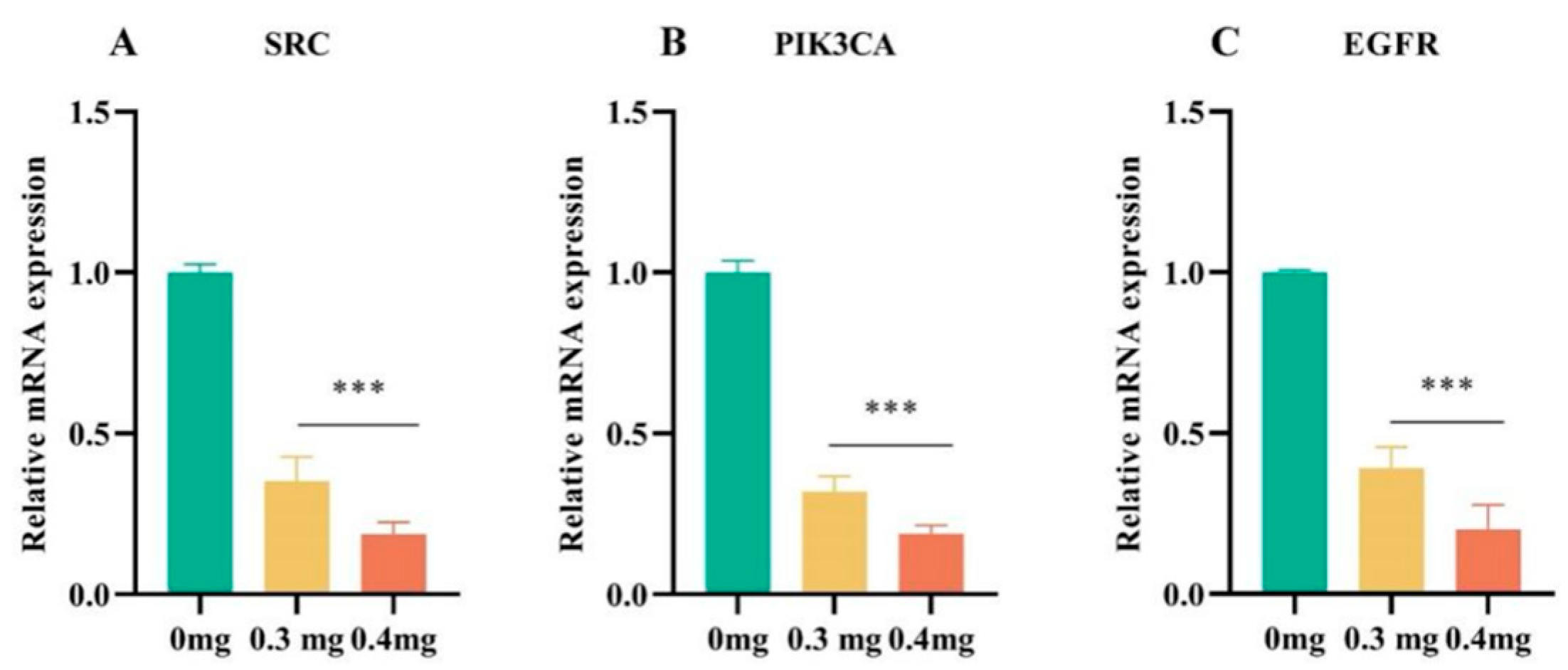
3.8.3. Effect of TSAC on the Expression of Genes
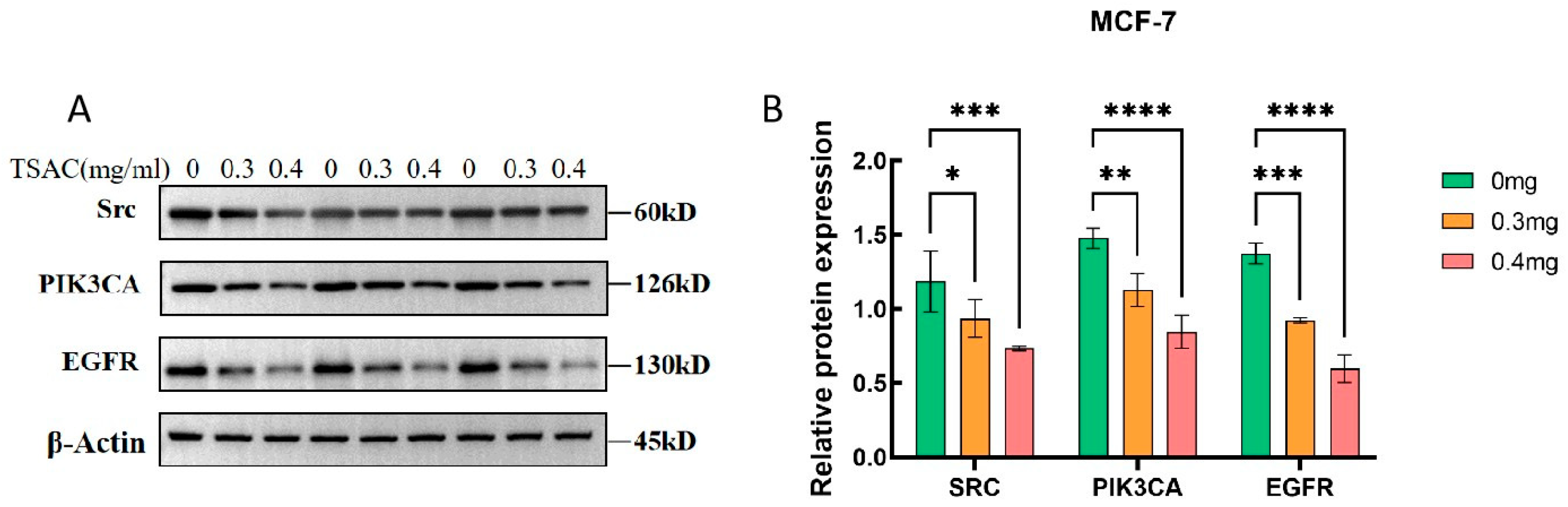
3.8.4. TSAC Suppressed SRC, PI3K, and EGFR Expression in MCF-7 Cells
4. Discussion
4.1. Introduction to TCM and Aralia in Cancer Therapy
4.2. Pharmacological Research Status and Challenges of Aralia
4.3. Clinical Applications and Resource Sustainability Concerns
4.4. Chemical Profiling of TSAC and Identification of Absorbed Components
4.5. Serum Pharmacochemistry: Rationale for Identifying Bioactive Compounds
4.6. Network Pharmacology and Mechanism Elucidation of TSAC in Breast Cancer
4.7. Proposed Mechanism of Action and Experimental Validation
4.8. Conclusion and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Miller, K.D.; Kramer, J.L.; Newman, L.A.; Minihan, A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 524–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Chen, R.; Wang, S.; Sun, K.; Zeng, H.; Wei, W.; He, J. Breast cancer incidence and mortality in women in China: Temporal trends and projections to 2030. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 18, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast cancer treatment: A review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, C.K. Tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, G.M.; Cullen, G.D.; O’Sullivan, C.C. Evolving standards of care and new challenges in the management of HER2-positive breast cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Merkher, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, N.; Leonov, S.; Chen, Y. Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for triple-negative breast cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.W. The Landscape of New Drugs in Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020, 89, 102065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perou, C.; Sorlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; Van De Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Lett. Nat. 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlinger, M.; Rowan, A.J.; Horswell, S.; Larkin, J.; Endesfelder, D.; Gronroos, E.; Martinez, P.; Matthews, N.; Stewart, A.; Tarpey, P.; et al. Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Onuma, E.; Yocum, R.C.; Ogata, E. Treatment of malignancy-associated hypercalcemia and cachexia with humanized anti-parathyroid hormone-related protein antibody. Semin. Oncol. 2003, 30, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Wolchok, J.D. Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1583–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.Z.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, S.; Xue, Y.F.; Tang, D.Y.; Yang, J.; Mei, Y.; Li, G.W.; Xie, Y. Ursolic acid augments the chemosensitivity of drug-resistant breast cancer cells to doxorubicin by AMPK-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 205, 115278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Tian, X.C.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, H.C.; Zhou, H.R.; Wang, Y.H.; Jiang, S.L. Exploring traditional Chinese medicine-based diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer based on molecular typing. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2023, 46, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Gutter-Kapon, L.; Ilan, N.; Batool, T.; Singh, K.; Digre, A.; Luo, Z.; Sandler, S.; Shaked, Y.; Sanderson, R.D.; et al. Significance of host heparanase in promoting tumor growth and metastasis. Matrix Biol. 2020, 93, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Zeng, R.; He, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ding, Y. Multifunctional Biomimetic Liposomes with Improved Tumor-Targeting for TNBC Treatment by Combination of Chemotherapy, Anti-Angiogenesis and Immunotherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2400046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ke, H.; Liu, P.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Ke, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y. Mechanisms of Yiai Fuzheng Formula in the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Based on UPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS, Network Pharmacology, and Experimental Validation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Li, L.; Hu, Y.; Lei, J.; Feng, L. Compound Chinese Medicine as an Adjunctive Therapy to Chemotherapy for Stage Ⅳ Triple-negative Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2022, 31, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Ran, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Comparative chloroplast genomic and phylogenetic analysis of Aralia and related species. Plant Sci. J. 2023, 41, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, N.; Hu, M.; Yu, S.; Sun, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, P.; Yang, J.; Ma, G.; Xu, X.; et al. Congmujingnosides B-G, Triterpene saponins from the stem of Aralia chinensis and their protective effects against H2O2-induced myocardial cell injury. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikov, A.N.; Pozharitskaya, O.N.; Makarov, V.G. Aralia elata var. Mandshurica (Rupr. & Maxim.) J. Wen: An Overview of Pharmacological Studies. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharmacol. 2016, 23, 1409–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, J.; Li, L.; Ma, Q.; Wang, M.; Ye, J.; Yu, L.; Sun, G. Progress in research on chemical constituents and pharmacological action of Aralia elata. Chin. Pharm. J. 2023, 58, 856–864. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Bi, M.; Wu, S.; Niu, W.; Ji, B.; You, Y.; Xiao, H. Total saponins from leaves of Aralia elata Seem. exhibit antitumor effects on human breast cancer in vitro and vivo. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2013, 29, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wang, W.; Xiao, H. The evaluation of anti-breast cancer activity and safety pharmacology of the ethanol extract of Aralia elata Seem. Leaves. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, Y.; Huang, D.; Fang, Q. Effect of aralosdie C on proliferation and migration of breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 35, 2094–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. The Attenuated Action of the Total Saponineof Aralia elata Seem Leaveson Tumor-Bearing Micetreaded with Fluorouracil. Master’s Thesis, Heilongjiang University, Harbin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, H. Synergistic Anticancer Effect of Thetotal Saponine of Aralia elata Seem leaves Combined with 5-Fluorouracil In Vitro. Master’s Thesis, Heilongjiang University, Harbin, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. The study on the Anti-Breast Cancer Effects and Mechanisms of Total Saponins from Leaves of Aralia elata Seem. Master’s Thesis, Heilongjiang University, Harbin, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Editorial Committee, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Vol. 54 (Araliaceae); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1978; pp. 160–161. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Iconographia Cormophytorum Sinicorum Tomus II; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1972; p. 1043. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.G.; Li, G.Y.; Liang, J.; Ortori, C.A.; Yang, B.-Y.; Kuang, H.-X.; Barrett, D.A. A strategy for characterization of triterpene saponins in Caulophyllum robustum Hairy Roots by liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.R.; Han, S.Y.; Li, P.P. Recent highlights of Chinese medicine for advanced lung cancer. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2017, 23, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Li, C.I.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, J.G.; Chiang, J.H.; Li, T.C. Traditional Chinese medicine as adjunctive therapy improves the long-term survival of lung cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fan, T.; Li, M.; Zhang, G.; Guo, W.; Yang, X.; Jiang, C.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Tang, A.; et al. Andrographolide potentiates PD-1 blockade immunotherapy by inhibiting COX2-mediated PGE2 release. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.; Sur, B.; Yeom, M.; Lee, B.; Kim, K.S.; Rodriguez, J.P.; Lee, S.; Kang, K.S.; Huh, C.-K.; Lee, S.C.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects of the ethanolic extract of Aralia continentalis Kitag. in IL-1β-stimulated human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and rodent models of polyarthritis and nociception. Phytomedicine 2018, 38, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lv, Z.; Meng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, L. Determination of total saponin content of Aralia elata (Miq.) Seem. and evaluation of its antiinflammation and analgesic effects. Biotic Resour. 2017, 39, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, D.; Yan, J. Study on the extraction of total saponin from the root bark of Aralia chinensis and its effect on the proliferation of Lymphoma Daudi cells. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 12, 93–95, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, H.X.; Wang, Z.B.; Wang, Q.H.; Yang, B.Y.; Xiao, H.B.; Okada, Y.; Okuyama, T. Triterpene glucosides from the leaves of Aralia elata and their cytotoxic activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2013, 10, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Dong, X.; Yu, Y.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Total aralosides of Aralia elata (Miq) Seem (TASAES) ameliorate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by modulating IRE1α-mediated JNK and NF-κB pathways in ApoE-/- mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 163, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lu, W.; Song, X.; Yu, M.; Wen, C. Mechanism of the aralosides against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injurybased on the NLRP3 inflammation pathway. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2020, 35, 1441–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Ai, Q.; Zhou, P.; Qin, M.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. SIRT1/AMPK and Akt/eNOS signaling pathways are involved in endothelial protection of total aralosides of aralia Elata (Miq) Seem against high-fat diet-induced atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, M.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Yoo, J.M.; Hong, E.K.; Ju, S.; Choi, W.-S.; Elata, A. Aralia elata Inhibits neurodegeneration by downregulating O-GlcNAcylation of NF-κB in diabetic mice. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 10, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Xi, M.-M.; Li, Y.W.; Duan, J.L.; Wang, L.; Weng, Y.; Jia, N.; Cao, S.S.; Li, R.L.; Wang, C.; et al. Insulinotropic effect of Chikusetsu saponin IVa in diabetic rats and pancreatic β-cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, T.; Sun, H.L. Research of the lipid metabolic effects of the bud of Aralia chinensis in steatosis hepatocyte L-02. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2016, 18, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.; Yu, L.; Cui, J.; Zhu, Y.-R.; Guo, C.; Wei, G.; Duan, J.L.; Yin, Y.; Guan, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; et al. Antihyperglycemic, hypolipidemic and antioxidant activities of total saponins extracted from Aralia taibaiensis in experimental Type 2 diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.A.; Hwang, Y.J.; Kim, G.R.; Choe, J.-S. Extracts from Aralia elata (Miq) seem alleviate hepatosteatosis via improving hepatic insulin sensitivity. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeong, C.S. Suppressive effects on the biosynthesis of inflammatory mediators by aralia Elata extract fractions in macrophage cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 28, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Xu, H.; Wen, F.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Yao, F.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Effect of the total saponins of Aralia elata (Miq) Seem on cardiac contractile function and intracellular calcium cycling regulation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Cui, J.; Jia, N.; Wu, Y.; Xi, M.; Wen, A. Chikusetsu Saponin I. Chikusetsu saponin IVa Regulates glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation: Implications in antihyperglycemic and hypolipidemic effects. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Qiu, J.; Wang, C.; Dou, X.; Lu, D.; et al. Calenduloside E Ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via modulating a pyroptosis-dependent pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, L. Pro-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of araloside A on human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 306, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Cheng, S.; Liu, R.; Yu, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.-L.; Yan, G.; Zheng, M.; Zhe Min, J. Comprehensive characterization of the chemical composition of Lurong Dabu decoction and its absorbed prototypes and metabolites in rat plasma using UHPLC-Q exactive Orbitrap-HRMS. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Gao, Y.; Yang, K.; Wu, D.; Xu, X.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Araloside C attenuates atherosclerosis by modulating macrophage polarization via Sirt1-mediated autophagy. Aging 2020, 12, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.L.; Zhang, A.H.; Sun, H.; Han, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.J. An effective method for determining the ingredients of Shuanghuanglian formula in blood samples using high-resolution LC-MS coupled with background subtraction and a multiple data processing approach. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 3191–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Feng, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F. Target recognition and network pharmacology for revealing anti-diabetes mechanisms of natural product. J. Comput. Sci. 2020, 45, 101186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Ning, Z.-W.; Huang, T.; Wen, B.; Liao, C.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, H.-T.; Bian, Z.-X.; Leaves, C.P. Cyclocarya paliurus Leaves Tea improves dyslipidemia in diabetic mice: A lipidomics-based network pharmacology study. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-S.; Xia, T.; Luo, Z.-Y.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Hu, Y.-N.; Chen, F.-L.; Tang, Q.-F.; Tan, X.-M. Network pharmacology and pharmacokinetics integrated strategy to investigate the pharmacological mechanism of Xianglian pill on ulcerative colitis. Phytomedicine 2021, 82, 153458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, X.; Zhou, D.Y.; Zhou, D.; Liu, K.; Chen, L.J.; Liu, W.H. A bioinformatics and network pharmacology approach to the mechanisms of action of Shenxiao decoction for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Phytomedicine 2020, 69, 153192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tian, S.; Lu, D.; Yang, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, F.; Tu, D.; Ge, G.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, T.; et al. Systems pharmacological study illustrates the immune regulation, anti-infection, anti-inflammation, and multi-organ protection mechanism of Qing-Fei-Pai-Du decoction in the treatment of COVID-19. Phytomedicine 2021, 85, 153315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, T.D.; Bang-Christensen, S.R.; Jørgensen, A.M.; Løppke, C.; Spliid, C.B.; Sand, N.T.; Clausen, T.M.; Salanti, A.; Agerbæk, M.Ø. The role of proteoglycans in cancer metastasis and circulating tumor cell analysis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dituri, F.; Gigante, G.; Scialpi, R.; Mancarella, S.; Fabregat, I.; Giannelli, G. Proteoglycans in cancer: Friends or enemies? A special focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiguchi, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto-Ibusuki, M.; Goto-Yamaguchi, L.; Fujiki, Y.; Fujiwara, S.; Sueta, A.; Hayashi, M.; Takeshita, T.; Inao, T.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor Receptor-1 protein expression is associated with prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor Receptor-2-Negative primary breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.J.; Diez-Gonzalez, L.; Ace, O.; Vera-Badillo, F.; Seruga, B.; Jordán, J.; Amir, E.; Pandiella, A.; Ocaña, A. Prognostic relevance of receptor tyrosine kinase expression in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Moran, T.; Queralt, C.; Porta, R.; Cardenal, F.; Camps, C.; Majem, M.; Lopez-Vivanco, G.; Isla, D.; Provencio, M.; et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 79, 34–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, M.; Shinde, Y.; Pawara, R.; Noolvi, M.; Surana, S.; Ahmad, I.; Patel, H. Emerging approaches to overcome acquired drug resistance obstacles to osimertinib in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 1008–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sun, M.M.; Zhang, G.G.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.S.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Sequence (5’–3’) |
|---|---|
| β-actin | Forward: TGAGCTGCGTTTTACACCCT |
| Reverse: AAGTCAGTGTACAGGCCAGC | |
| SRC | Forward: TGGTTTCAGAGGAGCCCATTTAC |
| Reverse: CACTTTGCACACCAGGTTCTCTC | |
| PIK3CA | Forward: TATTGTCGTGCATGTGGGATGTA |
| Reverse: GCAGGGTTTAGAGGAGACAGAAA | |
| EGFR | Forward: CTGGGTGCGGAAGAGAAAGAATA |
| Reverse: CCAAAGGTCATCAACTCCCAAAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, J.; Li, L.; Shu, Y.; Xie, C.; Lu, T.; Chai, H. Unlocking the Anti-Breast Cancer Potential of Aralia chinensis L. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080662
Xue J, Li L, Shu Y, Xie C, Lu T, Chai H. Unlocking the Anti-Breast Cancer Potential of Aralia chinensis L. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(8):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080662
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Juan, Lei Li, Yongjia Shu, Chengshi Xie, Tian Lu, and Huifang Chai. 2025. "Unlocking the Anti-Breast Cancer Potential of Aralia chinensis L." Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 8: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080662
APA StyleXue, J., Li, L., Shu, Y., Xie, C., Lu, T., & Chai, H. (2025). Unlocking the Anti-Breast Cancer Potential of Aralia chinensis L. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(8), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080662







