Potential of Alkaloids from Zanthoxylum nitidum var. tomentosum in Treating Rat Rheumatoid Arthritis Model and Validation of Molecular Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.1.1. Drugs and Reagents
2.1.2. Animals
2.1.3. Cells
2.2. In Vivo Screening Study of Anti-RA Active Extracts of RSH
2.2.1. Preparation of Different Extracts from RSH
2.2.2. Construction of RA Rat Model and Drug Administration
2.2.3. Serum Collection and Measurement of Inflammatory Factors
2.3. Pharmacology of Anti-RA Network and Molecular Docking Prediction of Alkaloids from RSH (ARSHs)
2.3.1. Determination of Active Components in ARSHs
2.3.2. Collection and Screening of Targets and Construction of Network Diagrams
2.3.3. GO Analysis and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.3.4. Molecular Docking of Components and Targets
2.4. Validation Experiments on the Anti-RA Effects and Mechanisms of ARSHs
2.4.1. Proliferation Inhibition of Key ARSHs on MH7A Cells
2.4.2. Detection of Inflammatory Factors in MH7A Cells by ELISA
2.4.3. Determination of Apoptosis in MH7A Cells by Flow Cytometry
2.4.4. Western Blot Detection of Bax, Bcl-2, SRC, STAT3, MAPK3 Expression
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Activity of Different Extracts from RSH Against RA
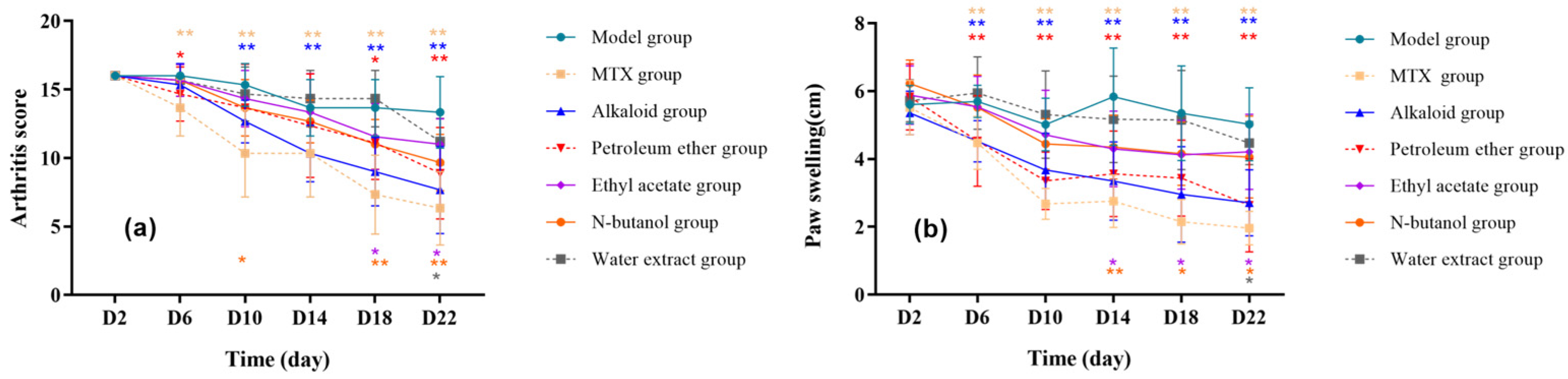
3.1.1. Effect of Different RSH Extracts on Arthritis Index and Toe Swelling in RA Rats
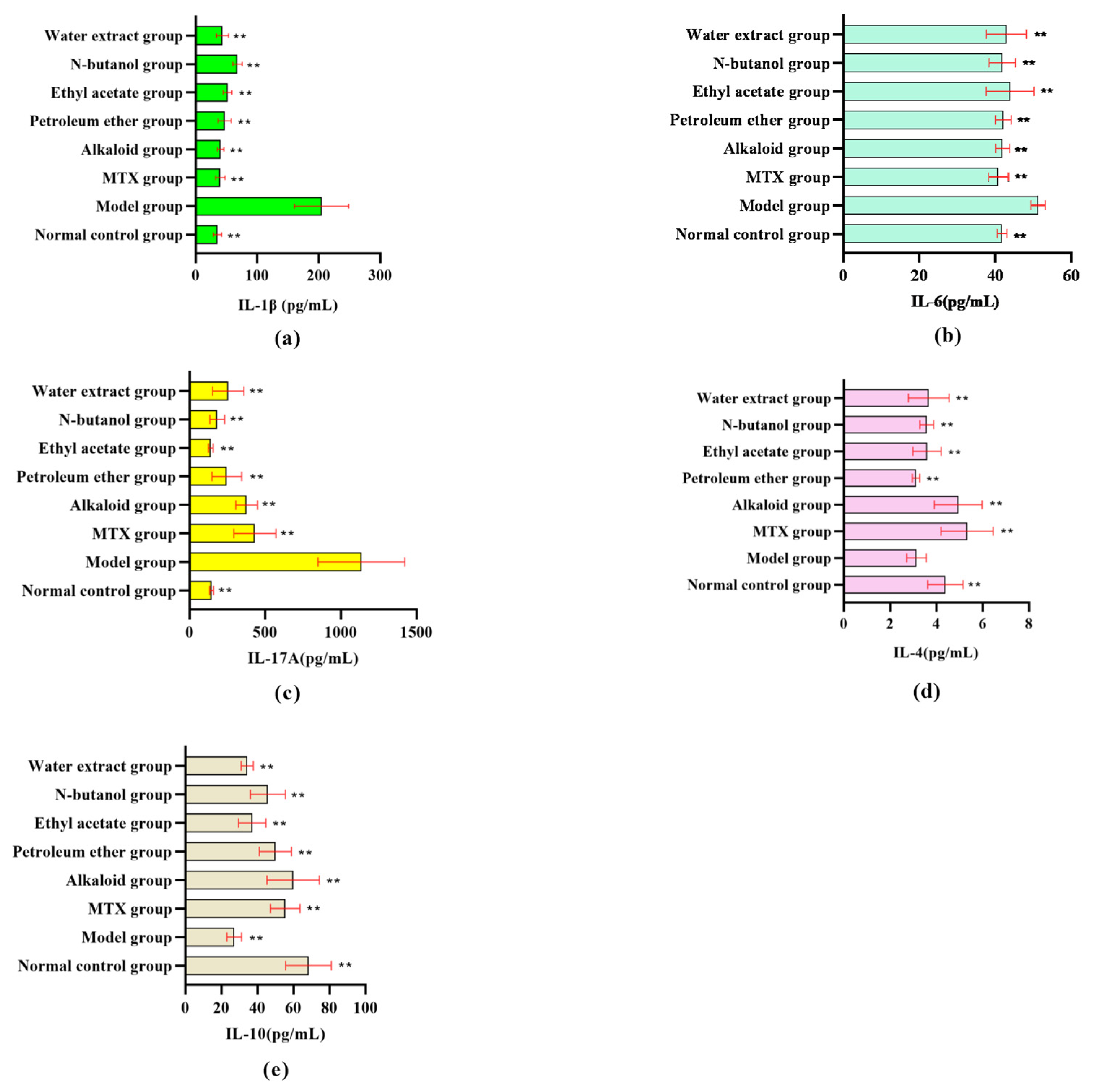
3.1.2. Effect of Different RSH Extracts on Inflammatory Factors in RA Rat Serum
3.2. Network Pharmacological Analysis of Alkaloids from RSH (ARSHs) Against RA
3.2.1. Confirmation of the Composition of ARSHs
3.2.2. Network Pharmacologic Analysis
3.3. Molecular Docking Analysis
3.4. Experimental Validation of the Predicted Targets of ARSHs Against RA
3.4.1. Effect of ARSH Components on the Viability of MH7A Cells
3.4.2. Effect of ARSH Components on Inflammatory Factors in MH7A Cells
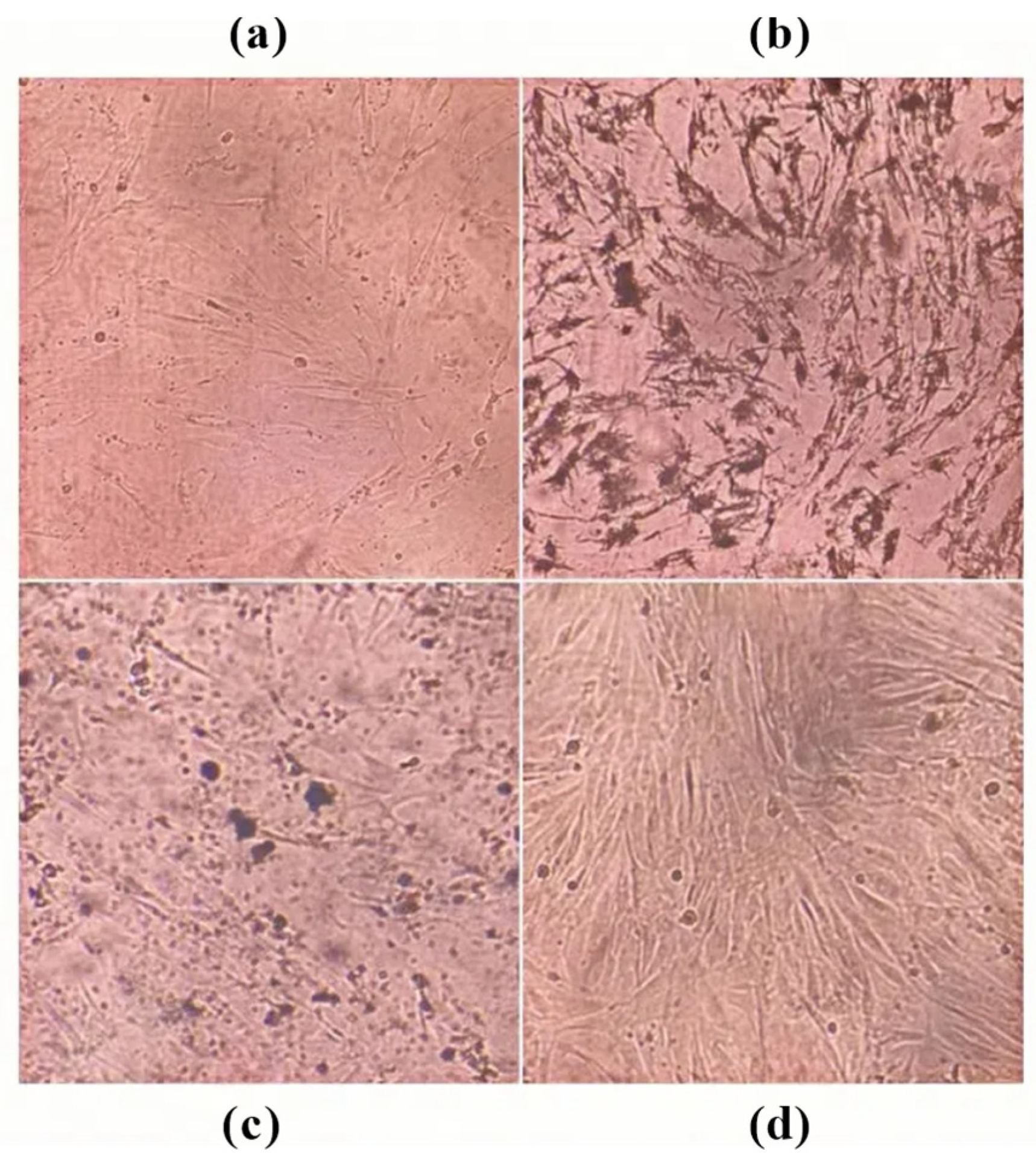
3.4.3. Effect of ARSH Components on Apoptosis in MH7A Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Outlooks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Bax | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma-2 |
| BP | biological process |
| CC | cellular component |
| CFA | complete Freund’s adjuvant |
| CMC-Na | carboxymethyl cellulose-Na |
| DMARDs | disease-modifying antirheumatic drug |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GCs | glucocorticosteroid |
| GO | gene ontology |
| IC50 | half maximal inhibitory concentration |
| IL | interleukin |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| MAPK1 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
| MAPK3 | mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 |
| MF | molecular function |
| MH7A | fibroblast-like synovial cells of human rheumatoid arthritis |
| MTT | thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide |
| MTX | methotrexate |
| NASIDs | nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| OD | optical density |
| One-way ANOVA | one-way analysis of variance |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PMSF | phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| RIPA | radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SRC | proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TBST | Tris-HCl and Tween solution |
| TCMSP | Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform |
| TEMED | N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| Tris | Tris hydroxyl methyl aminomethan |
| WB | Western blot |
References
- Lei, T.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Wang, G.; Han, J. Exploring the Mechanism of Topical Application of Clematis Florida in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis through Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xue, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, G.; Wang, R. From Tea to Functional Foods: Exploring Caryopteris Mongolica Bunge for Anti-Rheumatoid Arthritis and Unraveling Its Potential Mechanisms. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhan, S.-W.; Wang, C.-J.; Wu, K.-T.; Siu, K.-K.; Ko, J.-Y.; Huang, W.-C.; Chou, W.-Y.; Cheng, J.-H. Comparison of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy with Non-Steroid Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Intra-Articular Hyaluronic Acid Injection for Early Osteoarthritis of the Knees. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Chan, F.K.L. Current Knowledge on Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug-Induced Small-Bowel Damage: A Comprehensive Review. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubille, C.; Richer, V.; Starnino, T.; McCourt, C.; McFarlane, A.; Fleming, P.; Siu, S.; Kraft, J.; Lynde, C.; Pope, J.; et al. The Effects of Tumour Necrosis Factor Inhibitors, Methotrexate, Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Corticosteroids on Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, B.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Azizi, G.; Hajighasemi, F.; Mirshafiey, A. The Role of Leukotrienes in Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2014, 24, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, V.; Alonso, V.; Domingo, J.L. Oxidative Stress as a Mechanism Underlying Sulfasalazine-Induced Toxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2011, 10, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, X.; Feng, H.; Ruan, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, K.; Wang, H.; et al. Quality Assessment of Corydalis Saxicola Bunting Using Quantitative Analysis of Multi-Components by Single Marker and Fingerprint Analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2024, 47, e70028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Shen, C.; Zhang, S.; Di, H.; Wang, Y.; Guan, F. A Comprehensive Review of the Phytochemistry and Therapeutic Efficacy of Viola Yedoensis Makino. Molecules 2025, 30, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.-W.; Duan, Y.-Y.; Pang, H.-Q.; Xu, S.-H.; Hu, S.-Q.; Cheng, K.-G.; Liang, D.; Shi, W. Spectrum-Effect Relationship Analysis of Bioactive Compounds in Zanthoxylum Nitidum (Roxb.) DC. by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Coupled with Comprehensive Filtering Approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 794277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, Z.-J.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Xie, T.-Z.; Xu, X.-J.; Xiang, M.-L.; Chen, Y.-C.; Luo, X.-D. Phytochemical and Anti-MRSA Constituents of Zanthoxylum nitidum. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; Shi, Y.; Hong, Y.; Xu, W.; Xu, H.; Feng, J.; Xie, M.; Li, Y.; et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Four Main Compounds of Zanthoxylum nitidum (Roxb.) DC: A Comprehensive Study on Biological Processes, Anti-Inflammatory Effects, and Myocardial Toxicity. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, A.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Lu, S.; Li, Q.; Guo, H.; Liu, X.; Lu, Z. Analgesic Effect of Zanthoxylum nitidum Extract in Inflammatory Pain Models through Targeting of ERK and NF-κB Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Pu, H.; Guan, H.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, W.; Cheng, X.; Ji, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C. Rapid Identification and Pharmacokinetic Studies of Multiple Active Alkaloids in Rat Plasma through UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and UPLC-MS/MS after the Oral Administration of Zanthoxylum nitidum Extract. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 186, 113232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Chen, D. Alkaloids from the Roots of Zanthoxylum nitidum and Their Antiviral and Antifungal Effects. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 1718–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Ma, R.; Yang, Y.; Mo, Z.; Pu, X.; Li, C. Zanthoxylum nitidum (Roxb.) DC: Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacological Activities and Toxicology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 260, 112946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-J.; Lin, Y.-H.; Day, S.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Chen, I.-S. New benzenoids and anti-inflammatory constituents from Zanthoxylum nitidum. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Chen, G.; Qin, W.-Y.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, J.; Rong, X.-F. Xitong Wan Attenuates Inflammation Development through Inhibiting the Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB in Rats with Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, T.; Cheng, T.-F.; Jia, Y.-R.; Li, P.; Li, F. Anti-Rheumatoid Arthritis Effects of Traditional Chinese Herb Couple in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 205, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, G.; Bernards, N.; Dollé, F.; Boisgard, R. [18F]DPA-714 as a Biomarker for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis in an Animal Model. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; He, L.; Hu, N.; Zhao, X.; Gong, L.; Wang, C.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata Lipid-Soluble Alkaloids Alleviates IL-1β-Induced Inflammation of Human Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs Signaling Pathways and Inducing Apoptosis. Cytokine 2022, 151, 155809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadisaputri, Y.E.; Nurhaniefah, A.A.; Sukmara, S.; Zuhrotun, A.; Hendriani, R.; Sopyan, I. Callyspongia spp.: Secondary Metabolites, Pharmacological Activities, and Mechanisms. Metabolites 2023, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.-M.; Ketharnathan, S.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Rajakumar, G. Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Stride from Research to Clinical Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, E.M.; Mullan, R.; McCormick, J.; Connolly, M.; Sullivan, O.; Fitzgerald, O.; Bresnihan, B.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. Human Rheumatoid Arthritis Tissue Production of IL-17A Drives Matrix and Cartilage Degradation: Synergy with Tumour Necrosis Factor-Alpha, Oncostatin M and Response to Biologic Therapies. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Li, C.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, F.; Liu, R. Total Saponins from Nigella Glandulifera Seeds Ameliorate Adjuvant-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis in Rats by Inhibition of an Inflammatory Response and Bone Erosion. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6613527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porro, C.; Cianciulli, A.; Panaro, M.A. The Regulatory Role of IL-10 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, P.-J.; Robertson, L.; Welzel, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhihua, Y.; Kaixin, G.; Runyue, H.; Zehuai, W.; Korotkova, M.; Göransson, U. Where Traditional Chinese Medicine Meets Western Medicine in the Prevention of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.; Bradley, L.; Smith, A.; Foxwell, B. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Is the Dominant Mediator of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of IL-10 in Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Luo, L.; Tian, L.; Yin, S.; Ma, X.; Cheng, S.; Tang, W.; Yu, J.; Ma, W.; Zhou, X.; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Promotes IL-10 Expression in Inflammatory Macrophages through Src-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgrignani, J.; Garofalo, M.; Matkovic, M.; Merulla, J.; Catapano, C.V.; Cavalli, A. Structural Biology of STAT3 and Its Implications for Anticancer Therapies Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, U.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Robinson, P.; Tweardy, D.J. Targeting Janus Kinases and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 to Treat Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Cancer: Rationale, Progress, and Caution. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 486–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-Y.; Cho, I.-S.; Bashyal, N.; Naya, F.J.; Tsai, M.-J.; Yoon, J.S.; Choi, J.-M.; Park, C.-H.; Kim, S.-S.; Suh-Kim, H. ERK Regulates NeuroD1-Mediated Neurite Outgrowth via Proteasomal Degradation. Exp. Neurobiol. 2020, 29, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Song, S.-W.; Ge, Y.; Jin, J.-Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Tan, X.-D. The Ras-ERK Signaling Pathway Regulates Acetylated Activating Transcription Factor 2 via P300 in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Chen, Q. Adipokines: New Therapeutic Target for Osteoarthritis? Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boffa, A.; Merli, G.; Andriolo, L.; Lattermann, C.; Salzmann, G.M.; Filardo, G. Synovial Fluid Biomarkers in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Quantitative Evaluation Using BIPEDs Criteria. Cartilage 2021, 13, 82S–103S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.C.; Choi, Y. Biology of the TRANCE Axis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003, 14, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.Y.; Boyle, W.J.; Penninger, J.M. Osteoprotegerin Ligand: A Common Link between Osteoclastogenesis, Lymph Node Formation and Lymphocyte Development. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1999, 77, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, L.; Li, R.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S. The IL-17 Family in Diseases: From Bench to Bedside. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Hong, G.-L.; Jung, D.-Y.; Karunasagara, S.; Jeong, W.-I.; Jung, J.-Y. IL-17 Deficiency Aggravates the Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy through the Reduction of Autophagosome Formation in Mice. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, M.N.D.; Zoccheddu, M.; Yang, S.; Nygaard, G.; Secchi, C.; Doody, K.M.; Slowikowski, K.; Mizoguchi, F.; Humby, F.; Hands, R.; et al. Synoviocyte-Targeted Therapy Synergizes with TNF Inhibition in Arthritis Reversal. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- As, L. Regulation of Apoptosis by the Bcl-2 Family of Proteins: Field on a Brink. Cells 2020, 9, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walensky, L.D. Targeting BAX to Drug Death Directly. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Characteristics | Score |
|---|---|
| Normal, no symptoms | 0 |
| Slight swelling or little erythema in ankle or wrist joints | 1 |
| Mild swelling and little erythema at ankle and wrist joints | 2 |
| Moderate swelling and more erythema at ankle to metatarsal or metacarpal joints | 3 |
| Severe swelling and a lot of redness from the ankle to the metatarsals | 4 |
| Groups | IC50 (μg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Magnoflorine | 789.6492 ± 22.6635 |
| Nitidine chloride | 481.2247 ± 7.0282 |
| Dihydrochelerythrine | 360.3517 ± 0.9453 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Zou, L.; Zeng, Y.; Xia, T.; Liu, Z.; Hu, K.; Wang, L.; Feng, J. Potential of Alkaloids from Zanthoxylum nitidum var. tomentosum in Treating Rat Rheumatoid Arthritis Model and Validation of Molecular Mechanisms. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080661
Shen Y, Zou L, Zeng Y, Xia T, Liu Z, Hu K, Wang L, Feng J. Potential of Alkaloids from Zanthoxylum nitidum var. tomentosum in Treating Rat Rheumatoid Arthritis Model and Validation of Molecular Mechanisms. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(8):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080661
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yuanle, Linghui Zou, Yinggang Zeng, Ting Xia, Zhenjie Liu, Kaili Hu, Liuping Wang, and Jianfang Feng. 2025. "Potential of Alkaloids from Zanthoxylum nitidum var. tomentosum in Treating Rat Rheumatoid Arthritis Model and Validation of Molecular Mechanisms" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 8: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080661
APA StyleShen, Y., Zou, L., Zeng, Y., Xia, T., Liu, Z., Hu, K., Wang, L., & Feng, J. (2025). Potential of Alkaloids from Zanthoxylum nitidum var. tomentosum in Treating Rat Rheumatoid Arthritis Model and Validation of Molecular Mechanisms. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(8), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080661






