Targeting Intracellular Pathways in Atopic Dermatitis with Small Molecule Therapeutics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biologic Therapies
3. Janus Kinases Inhibitors
3.1. Background
3.2. Representatives
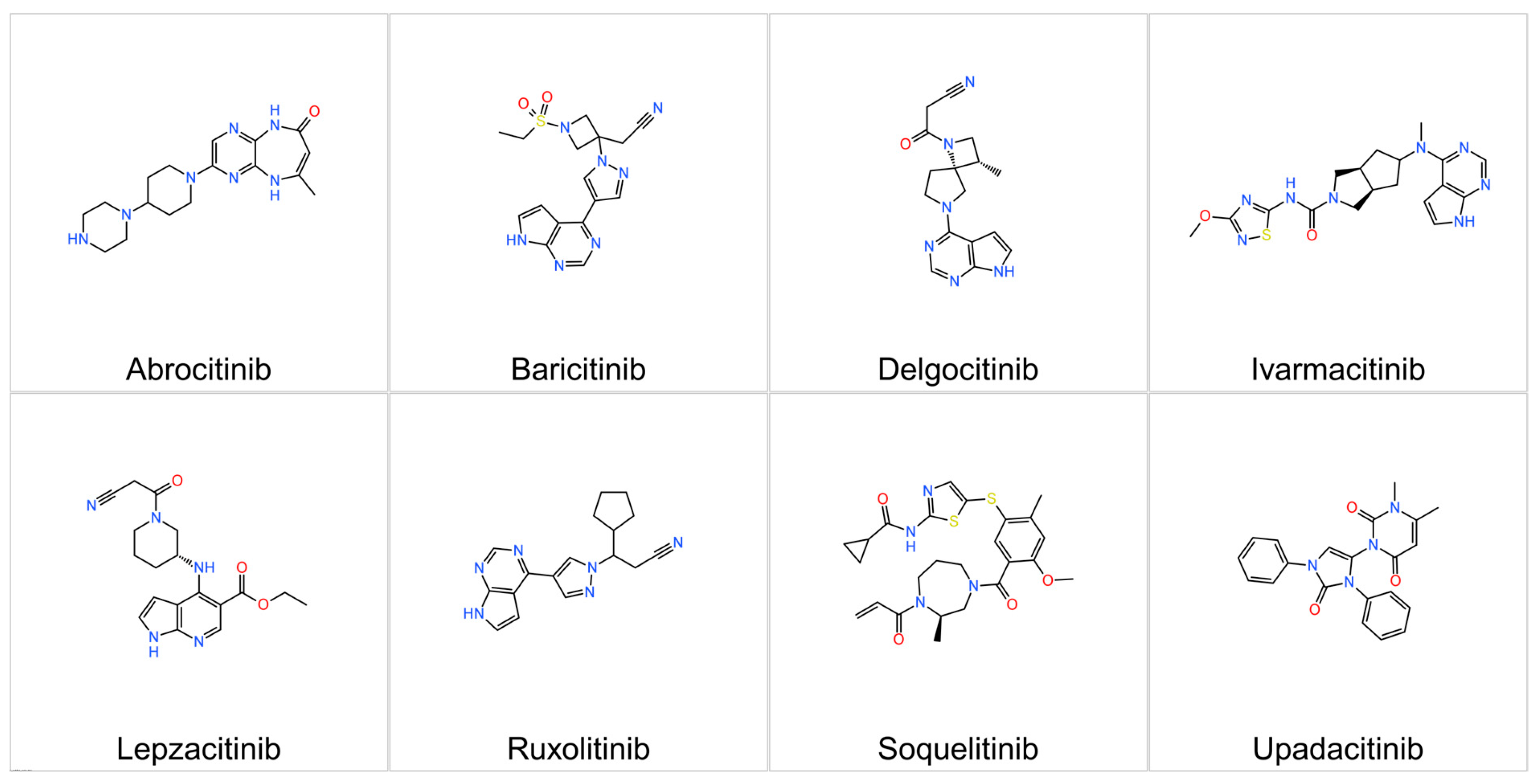
3.2.1. Upadacitinib
3.2.2. Abrocitinib
3.2.3. Baricitinib
3.2.4. Ruxolitinib
3.2.5. Delgocitinib
3.2.6. Ivarmacitinib
3.2.7. Lepzacitinib
3.2.8. Gusacitinib
3.2.9. Soquelitinib
3.2.10. Jaktinib
3.2.11. ATI-2138
3.3. Comparative Summary of JAK Inhibitors in AD
4. STAT6 Directed Therapies
4.1. Background
4.2. KT-621
4.3. REX-8756
4.4. NX-3911
5. Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors
5.1. Background
5.2. Mechanism of Action
5.3. Representatives
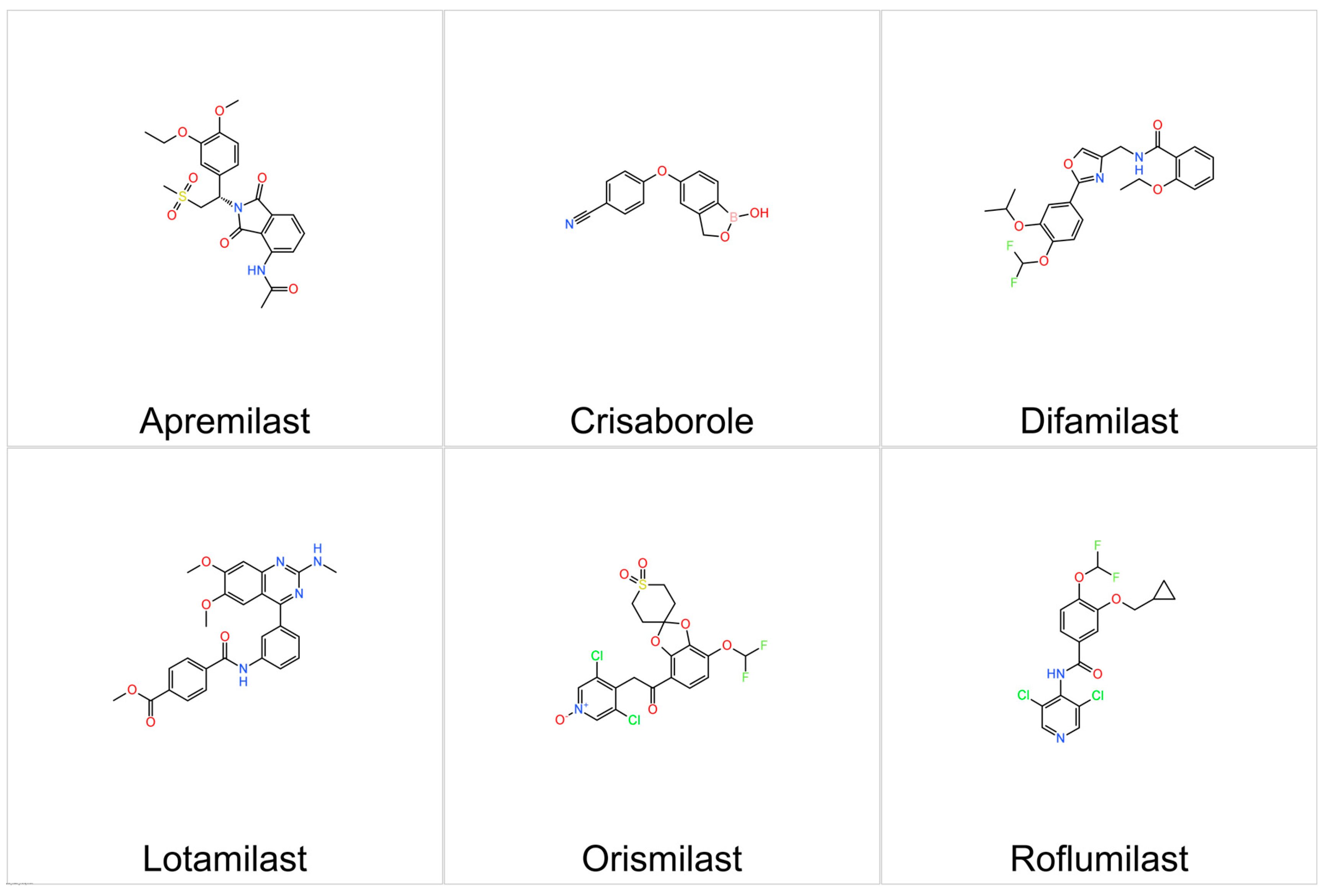
5.3.1. Crisaborole
5.3.2. Roflumilast
5.3.3. Difamilast
5.3.4. Apremilast
5.3.5. Orismilast
5.3.6. PF-07038124
5.3.7. Lotamilast
5.3.8. HSK44459
6. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Modulating Agents
6.1. Background
6.2. Mechanism of Action
6.3. Representatives
Tapinarof
7. Histamine H4 Receptor Antagonists
7.1. JNJ-39758979
7.2. Adriforant
7.3. Izuforant
8. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor Modulators
8.1. Etrasimod
8.2. BMS-986166
8.3. SCD-044
9. Discussion and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | atopic dermatitis |
| AhR | aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CPK | creatine phosphokinase |
| EASI | Eczema Area and Severity Index |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| FLG | filaggrin |
| H4R | histamine H4 receptor |
| IGA | Investigator’s Global Assessment |
| IL | interleukin |
| ITK | interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| mAb | monoclonal antibody |
| PASI | Psoriasis Area and Severity Index |
| PDE | phosphodiesterase |
| PROTACs | proteolysis-targeting chimeras |
| S1PR | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor |
| SCORAD | SCORing Atopic Dermatitis |
| SH2 | Src homology 2 |
| STAT | signal transducers and activators of transcription |
| TYK2 | tyrosine kinase 2 |
References
- Ujiie, H.; Rosmarin, D.; Schön, M.P.; Ständer, S.; Boch, K.; Metz, M.; Maurer, M.; Thaci, D.; Schmidt, E.; Cole, C.; et al. Unmet Medical Needs in Chronic, Non-Communicable Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 875492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolomoni, G.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Aoki, V.; Kabashima, K.; Deleuran, M.; Puig, L.; Bansal, A.; Rossi, A.B. Nomenclature and Clinical Phenotypes of Atopic Dermatitis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 20406223211002979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langan, S.M.; Mulick, A.R.; Rutter, C.E.; Silverwood, R.J.; Asher, I.; García-Marcos, L.; Ellwood, E.; Bissell, K.; Chiang, C.Y.; El Sony, A.; et al. Trends in Eczema Prevalence in Children and Adolescents: A Global Asthma Network Phase I Study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2023, 53, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, A.; Lembo, S. Atopic Dermatitis: Epidemiology and Clinical Phenotypes. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2021, 11, e2021146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dourmishev, L.; Mironova, N. Atopic Dermatitis: From Etiology and History to Treatment. Acta Medica Bulg. 2021, 48, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, S.; Novak, N. Atopic Dermatitis. Lancet 2016, 387, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanovic, N.; Irvine, A.D. Filaggrin and beyond: New Insights into the Skin Barrier in Atopic Dermatitis and Allergic Diseases, from Genetics to Therapeutic Perspectives. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024, 132, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. Atopic Dermatitis: An Expanding Therapeutic Pipeline for a Complex Disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, R.; Silverberg, J.I. Assessing the Severity of Atopic Dermatitis in Clinical Trials and Practice. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Bissonnette, R.; Paller, A.S.; King, B.; Silverberg, J.I.; Reich, K.; Thyssen, J.P.; Doll, H.; Sun, L.; DeLozier, A.M.; et al. The Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (VIGA-ADTM): A Clinical Outcome Measure for the Severity of Atopic Dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 187, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penton, H.; Jayade, S.; Selveindran, S.; Heisen, M.; Piketty, C.; Ulianov, L.; Jabbar-Lopez, Z.K.; Silverberg, J.I.; Puelles, J. Assessing Response in Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review of the Psychometric Performance of Measures Used in HTAs and Clinical Trials. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 2549–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, J.M.; Baghoomian, W.; Grinich, E.; Leshem, Y.A.; Jacobson, M.; Simpson, E.L. The Eczema Area and Severity Index-A Practical Guide. Dermat. Contact Atopic Occup. Drug 2022, 33, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, J.M.; Thurston, M.; Omoto, M.; Cherill, R.; Tofte, S.J.; Graeber, M.; Evaluator Group, T.E. The Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI): Assessment of Reliability in Atopic Dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2001, 10, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oranje, A.P. Practical Issues on Interpretation of Scoring Atopic Dermatitis: SCORAD Index, Objective SCORAD, Patient-Oriented SCORAD and Three-Item Severity Score. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2011, 41, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, T. Biologics in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis-Current Status and Future Prospects. Jpn. J. Allergol. 2023, 72, 1211–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.A.; Thaçi, D.; Hamilton, J.D.; Graham, N.M.; Bieber, T.; Rocklin, R.; Ming, J.E.; Ren, H.; Kao, R.; Simpson, E.; et al. Dupilumab Treatment in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Gao, X.-H.; Zhang, L. A Review of Dupilumab in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis in Infants and Children. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jing, D.; Cheng, J.; Chen, X.; Shen, M.; Liu, H. The Efficacy and Safety of IL-13 Inhibitors in Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 923362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Qi, F.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, B. Biological Therapies for Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review. Dermatology 2021, 237, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armario-Hita, J.C.; Galán-Gutiérrez, M.; Dodero-Anillo, J.M.; Carrascosa, J.M.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. Updated Review on Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 33, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, K.; Halperin-Goldstein, S.; Paller, A.S. New Treatments in Atopic Dermatitis Update. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waligóra-Dziwak, K.; Dańczak-Pazdrowska, A.; Jenerowicz, D. A Comprehensive Review of Biologics in Phase III and IV Clinical Trials for Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.L.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Pawlikowski, J.; Ghorayeb, E.G.; Ota, T.; Lebwohl, M.G. Interleukin-1α Inhibitor Bermekimab in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: Randomized and Nonrandomized Studies. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2024, 316, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koester, A.; Witcher, D.R.; Lee, M.; Demarest, S.J.; Potter, S.; Werle, K.; Bauer, S.; Ruiz, D.; Malherbe, L.; Poorbaugh, J.; et al. Ucenprubart Is an Agonistic Antibody to CD200R with the Potential to Treat Inflammatory Skin Disease: Preclinical Development and a Phase 1 Clinical Study. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lé, A.M.; Torres, T. OX40-OX40L Inhibition for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis—Focus on Rocatinlimab and Amlitelimab. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewerska, B.; Sher, L.D.; Alpizar, S.; Pauser, S.; Pulka, G.; Mozaffarian, N.; Salhi, Y.; Martinet, C.; Jabert, W.; Gudi, G.; et al. Phase 2b Randomized Trial of OX40 Inhibitor Telazorlimab for Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Glob. 2024, 3, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facheris, P.; Jeffery, J.; Del Duca, E.; Guttman-Yassky, E. The Translational Revolution in Atopic Dermatitis: The Paradigm Shift from Pathogenesis to Treatment. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 448–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.; Cheng, T.-T.; Huang, C.-J.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Chyuan, I.-T. Advancing Therapeutic Strategies in Atopic Dermatitis: Emerging Targets and Personalized Approaches. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perner, F.; Pahl, H.L.; Zeiser, R.; Heidel, F.H. Malignant JAK-Signaling: At the Interface of Inflammation and Malignant Transformation. Leukemia 2025, 39, 1011–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikhoune, L.; Poggi, C.; Moreau, J.; Dubucquoi, S.; Hachulla, E.; Collet, A.; Launay, D. JAK Inhibitors (JAKi): Mechanisms of Action and Perspectives in Systemic and Autoimmune Diseases. La Rev. Médecine Interne 2025, 46, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Oh, S.; Park, J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, J.H. Predicting Favorable Conditions for the Determination of Initial Use of Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.E.F.; Bhatnagar, S.; Parmentier, J.M.; Nakasato, P.; Wung, P. Upadacitinib: Mechanism of Action, Clinical, and Translational Science. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2023, 17, e13688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Irvine, A.D.; Brunner, P.M.; Kim, B.S.; Boguniewicz, M.; Parmentier, J.; Platt, A.M.; Kabashima, K. The Role of Janus Kinase Signaling in the Pathology of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.L.; Silverberg, J.I.; Prajapati, V.H.; Eyerich, K.; Katoh, N.; Boguniewicz, M.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Song, E.J.; Lee, W.-J.; Teixeira, H.D.; et al. Rapid Itch Improvement and Skin Clearance with Upadacitinib Versus Placebo (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2) and Versus Dupilumab (Heads Up): Results from Three Phase 3 Clinical Trials in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatol. Ther. 2025, 15, 2061–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Gooderham, M.J.; Paller, A.S.; Deleuran, M.; Bunick, C.G.; Gold, L.F.S.; Hijnen, D.; Calimlim, B.M.; Lee, W.-J.; Teixeira, H.D.; et al. Early and Sustained Improvements in Symptoms and Quality of Life with Upadacitinib in Adults and Adolescents with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: 52-Week Results from Two Phase III Randomized Clinical Trials (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2). Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2024, 25, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Fu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J. Safety Profile and Dose-Dependent Adverse Events of Upadacitinib in Randomized Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1598972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, N.; Ohya, Y.; Murota, H.; Ikeda, M.; Hu, X.; Ikeda, K.; Liu, J.; Sasaki, T.; Raymundo, E.M.; Teixeira, H.D.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Upadacitinib for Atopic Dermatitis in Japan: 2-Year Interim Results from the Phase 3 Rising Up Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezamololama, N.; Fieldhouse, K.; Metzger, K.; Gooderham, M. Emerging Systemic JAK Inhibitors in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: A Review of Abrocitinib, Baricitinib, and Upadacitinib. Drugs Context 2020, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, A.M.; Almalki, F.A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Abdelazeem, A.H.; Gouda, A.M. A Comprehensive Overview of Globally Approved JAK Inhibitors. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, E.D.; Duggan, S. Abrocitinib: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooderham, M.J.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Weidinger, S.; Cork, M.J.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Simpson, E.L.; Tsianakas, A.; Kerkmann, U.; Feeney, C.; Romero, W. Practical Management of the JAK1 Inhibitor Abrocitinib for Atopic Dermatitis in Clinical Practice: Special Safety Considerations. Dermatol. Ther. 2024, 14, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, K.; Silverberg, J.I.; Papp, K.A.; Deleuran, M.; Katoh, N.; Strober, B.; Beck, L.A.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Werfel, T.; Zhang, F.; et al. Abrocitinib Efficacy and Safety in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: Results from Phase 3 Studies, Including the Long-Term Extension JADE EXTEND Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 2056–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lé, A.M.; Gooderham, M.; Torres, T. Abrocitinib for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Immunotherapy 2023, 15, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, S.M. Baricitinib: A Review in Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayence, A.; Vanden Eynde, J.J. Baricitinib: A 2018 Novel FDA-Approved Small Molecule Inhibiting Janus Kinases. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, F.; Gao, G.; Lu, S.; Wei, Q.; Hu, H.; Wu, Z.; Fang, M.; Wang, X. Approved Small-Molecule ATP-Competitive Kinases Drugs Containing Indole/Azaindole/Oxindole Scaffolds: R&D and Binding Patterns Profiling. Molecules 2023, 28, 943. [Google Scholar]
- Eichner, A.; Wohlrab, J. Pharmacology of Inhibitors of Janus Kinases—Part 1: Pharmacokinetics. JDDG J. Der Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2022, 20, 1485–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Lacour, J.-P.; Spelman, L.; Galimberti, R.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Bissonnette, R.; King, B.A.; Thyssen, J.P.; Silverberg, J.I.; Bieber, T.; et al. Baricitinib in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis and Inadequate Response to Topical Corticosteroids: Results from Two Randomized Monotherapy Phase III Trials. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoghayer, I.H.I.; Soomro, A.M.; Dev, S.; Turesh, M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, R.; Meghjiani, A.; Lamiya Mir, S.; Hassaan, M.; Qureshi, R.; et al. Baricitinib as Monotherapy and with Topical Corticosteroids in Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Dose-Response. Front. Allergy 2024, 5, 1486271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Jia, H.; Xia, T.; Zhang, D. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Abrocitinib, Baricitinib, and Upadacitinib for Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Network Meta-Analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, F.; Malvaso, D.; Caldarola, G.; De Simone, C.; Peris, K.; Chiricozzi, A. Infectious Adverse Events in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Treated with Baricitinib. Immunotherapy 2023, 15, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, B.; Maari, C.; Lain, E.; Silverberg, J.I.; Issa, M.; Holzwarth, K.; Brinker, D.; Cardillo, T.; Nunes, F.P.; Simpson, E.L. Extended Safety Analysis of Baricitinib 2 Mg in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: An Integrated Analysis from Eight Randomized Clinical Trials. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitulescu, G.M.; Stancov, G.; Seremet, O.C.; Nitulescu, G.; Mihai, D.P.; Duta-Bratu, C.G.; Barbuceanu, S.F.; Olaru, O.T. The Importance of the Pyrazole Scaffold in the Design of Protein Kinases Inhibitors as Targeted Anticancer Therapies. Molecules 2023, 28, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.R.; Li, B.; Yun, S.Y.; Chan, A.; Nareddy, P.; Gunawan, S.; Ayaz, M.; Lawrence, H.R.; Reuther, G.W.; Lawrence, N.J.; et al. Structural Insights into JAK2 Inhibition by Ruxolitinib, Fedratinib, and Derivatives Thereof. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2228–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassani, C.; Leite Pértile, G.; Scaravonatto Baldo Cunha, S.L.; de Castro Wordell, F.; Gobbi Cazarotto, L.F.; Magalhães Pinheiro Almeida, A.; Kase Tanno, L. Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Topical Ruxolitinib in Mild-to-Moderate Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review. J. Allergy Hypersensitivity Dis. 2025, 5, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Ruxolitinib Cream 1.5%: A Review in Mild to Moderate Atopic Dermatitis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2023, 24, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Chen, G.; Ye, L. Current Application Status and Structure–Activity Relationship of Selective and Non-Selective JAK Inhibitors in Diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 122, 110660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kambe, N.; Takimoto-Ito, R.; Kabashima, K. Advances in the Pathophysiology of Atopic Dermatitis Revealed by Novel Therapeutics and Clinical Trials. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 224, 107830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, M.; Thyssen, J.P.; Schliemann, S.; Bauer, A.; Shi, V.Y.; Ehst, B.; Tillmann, S.; Korn, S.; Resen, K.; Agner, T. The Pan-JAK Inhibitor Delgocitinib in a Cream Formulation Demonstrates Dose Response in Chronic Hand Eczema in a 16-Week Randomized Phase IIb Trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 187, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaçi, D.; Gooderham, M.; Lovato, P.; Madsen, D.E.; Soehoel, A.; Bissonnette, R. Systemic Exposure and Bioavailability of Delgocitinib Cream in Adults with Moderate to Severe Chronic Hand Eczema. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Delgocitinib: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhalim, A.; Yilmaz, O.; Elshaikh Berair, M.; Torres, T. Topical Delgocitinib for the Treatment of Chronic Hand Eczema. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2025, 36, 2479126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, S.J. Ivarmacitinib Sulfate: First Approval. Drugs 2025, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gooderham, M.; Yang, B.; Wu, J.; Wu, L.; Loo, W.J.; Toth, D.; Sauder, M.; Li, J.; Chen, A.; et al. Ivarmacitinib for Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis in Adults and Adolescents: A Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2025, 161, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changelian, P.; Xu, C.; Mnich, S.; Hope, H.; Kostecki, K.; Hirsch, J.; Loh, C.-Y.; Anderson, D.; Blinn, J.; Hockerman, S.; et al. ATI-1777, a Topical Jak1/3 Inhibitor, May Benefit Atopic Dermatitis without Systemic Drug Exposure: Results from Preclinical Development and Phase 2a Randomized Control Study ATI-1777-AD-201. JID Innov. 2024, 4, 100251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, M.; Berman-Rosa, M.; Ghazawi, F.M.; Bourcier, M.; Fiorillo, L.; Gooderham, M.; Guenther, L.; Hanna, S.; Hong, H.C.-H.; Landells, I.; et al. Systematic Review on the Efficacy and Safety of Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 682547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatmaitan, J.G.; Lee, J.H. Challenges and Future Trends in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.-Y.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Verner, E.; Jones, W.B.; Hill, C.M.; Janc, J.W.; Buggy, J.J.; Pawar, R.D.; Ghosh, P.; Li, D.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Soquelitinib a Selective ITK Inhibitor That Modulates Tumor Immunity. npj Drug Discov. 2024, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvus Pharmaceuticals; Stanford University Safety. Tolerability, and Preliminary Efficacy of Soquelitinib in Participants with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis 2025. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06345404?term=NCT06345404&rank=1 (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhuang, J.; Li, W.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhu, H.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Jaktinib in the Treatment of Janus Kinase Inhibitor-Naïve Patients with Myelofibrosis: Results of a Phase II Trial. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, A.; Hope, H.; Xu, C.; Basavalingappa, R.; Binz, S.K.; Boily, C.; Bradley, Z.; Burt, D.; Emanuel, C.; Fairchild, J.; et al. Characterization of the Dual ITK/JAK3 Small Molecule Covalent Inhibitor ATI-2138. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2025, 392, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, D. Turning Off STAT6 with a Targeted Degrader. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 5123–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matucci, A.; Vivarelli, E.; Nencini, F.; Maggi, E.; Vultaggio, A. Strategies Targeting Type 2 Inflammation: From Monoclonal Antibodies to JAK-Inhibitors. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneshige, A.; Yang, Y.; Bai, L.; Wang, M.; Xu, R.; Mallik, L.; Chinnaswamy, K.; Metwally, H.; Wang, Y.; McEachern, D.; et al. Discovery of AK-1690: A Potent and Highly Selective STAT6 PROTAC Degrader. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 5125–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therapeutics, K. A Study to Assess the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of KT-621 in Healthy Adult Participants; ClinicalTrials.gov: Bethesda, MD, USA; National Library of Medicine (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Metz, P.; Bregman, H.; Vaswani, R.; Kim, J.H.; Moreno, A.; Park, D.; Bozek, K.; Reznik, S.; Sutherland, A.; Holdeman, K.; et al. Highly Selective and Reversible STAT6 Inhibition Demonstrates Potential for Differentiated Efficacy and Safety Profile in Type 2 Allergic Inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2025, 211, A1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therapeutics, N. Sanofi Exercises License Extension Option to Nurix’s STAT6 Program. Nurix Ther. Press Release. 2025. Available online: https://ir.nurixtx.com/news-releases/news-release-details/sanofi-exercises-license-extension-option-nurixs-stat6-program (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Hanifin, J.M.; Boguniewicz, M.; Wollenberg, A.; Bissonnette, R.; Purohit, V.; Kilty, I.; Tallman, A.M.; Zielinski, M.A. The Role of Phosphodiesterase 4 in the Pathophysiology of Atopic Dermatitis and the Perspective for Its Inhibition. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Card, G.L.; England, B.P.; Suzuki, Y.; Fong, D.; Powell, B.; Lee, B.; Luu, C.; Tabrizizad, M.; Gillette, S.; Ibrahim, P.N.; et al. Structural Basis for the Activity of Drugs That Inhibit Phosphodiesterases. Structure 2004, 12, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, H.R.; Rashed, L.A.; Shehada, J.; Mostafa, P.I.N. Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) Gene Expression in Atopic Dermatitis Patients, before and after Treatment with Topical Mometasone Cream. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2022, 32, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serezani, C.H.; Ballinger, M.N.; Aronoff, D.M.; Peters-Golden, M. Cyclic AMP: Master Regulator of Innate Immune Cell Function. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Novak, N. Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.W.L.; Bowman, E.P.; McElwee, J.J.; Smyth, M.J.; Casanova, J.L.; Cooper, A.M.; Cua, D.J. IL-12 and IL-23 Cytokines: From Discovery to Targeted Therapies for Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L. PDE4 Inhibitors: Potential Protective Effects in Inflammation and Vascular Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1407871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, E.L.; Gooderham, M.J. Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibition in the Management of Psoriasis. Pharmaceutics 2023, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; Langley, R.G.; Gordon, K.B.; Silverberg, J.I.; Eyerich, K.; Sommer, M.O.A.; Felding, J.; Warren, R.B. Next Generation PDE4 Inhibitors That Selectively Target PDE4B/D Subtypes: A Narrative Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 3031–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.R.; Akama, T.; Alley, M.R.K.; Antunes, J.; Dong, C.; Jarnagin, K.; Kimura, R.; Nieman, J.A.; Maples, K.R.; Plattner, J.J.; et al. Boron-Based Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors Show Novel Binding of Boron to PDE4 Bimetal Center. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3410–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, H.; Imamura, T.; Yokota, D.; Tsubouchi, H. Difamilast Ointment in Japanese Adult and Pediatric Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Phase III, Long-Term, Open-Label Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocetti, L.; Floresta, G.; Cilibrizzi, A.; Giovannoni, M.P. An Overview of PDE4 Inhibitors in Clinical Trials: 2010 to Early 2022. Molecules 2022, 27, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton, D.M. Crisaborole: Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor for Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Drugs Today 2017, 53, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callender, V.D.; Alexis, A.F.; Stein Gold, L.F.; Lebwohl, M.G.; Paller, A.S.; Desai, S.R.; Tan, H.; Ports, W.C.; Zielinski, M.A.; Tallman, A.M. Efficacy and Safety of Crisaborole Ointment, 2%, for the Treatment of Mild-to-Moderate Atopic Dermatitis Across Racial and Ethnic Groups. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 20, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, R.; Pavel, A.B.; Diaz, A.; Werth, J.L.; Zang, C.; Vranic, I.; Purohit, V.S.; Zielinski, M.A.; Vlahos, B.; Estrada, Y.D.; et al. Crisaborole and Atopic Dermatitis Skin Biomarkers: An Intrapatient Randomized Trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1274–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlessinger, J.; Shepard, J.S.; Gower, R.; Su, J.C.; Lynde, C.; Cha, A.; Ports, W.C.; Purohit, V.; Takiya, L.; Werth, J.L.; et al. Safety, Effectiveness, and Pharmacokinetics of Crisaborole in Infants Aged 3 to <24 Months with Mild-to-Moderate Atopic Dermatitis: A Phase IV Open-Label Study (CrisADe CARE 1). Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Hebert, A.A.; Takiya, L.; Miller, L.; Werth, J.L.; Zang, C.; Sanders, P.; Lebwohl, M.G. Efficacy and Safety Trends with Continuous, Long-Term Crisaborole Use in Patients Aged ≥ 2 Years with Mild-to-Moderate Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.J.; Nam, K.H. Molecular Properties of Phosphodiesterase 4 and Its Inhibition by Roflumilast and Cilomilast. Molecules 2025, 30, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, A.W.; Osborne, D.W.; Snyder, S.; Higham, R.C.; Burnett, P.; Berk, D.R. Pharmacokinetics of Roflumilast Cream in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: Data from Phase I to Phase III Studies. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2023, 24, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooderham, M.; Kircik, L.; Zirwas, M.; Lee, M.; Kempers, S.; Draelos, Z.; Ferris, L.; Jones, T.; Saint-Cyr Proulx, E.; Bissonnette, R.; et al. The Safety and Efficacy of Roflumilast Cream 0.15% and 0.05% in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis: Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 2 Proof of Concept Study. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2023, 22, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, E.; Gooderham, M.; Torres, T. New Topical Therapies in Development for Atopic Dermatitis. Drugs 2022, 82, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenfield, L.F.; Serrao, R.; Prajapati, V.H.; Browning, J.C.; Swanson, L.; Funk, T.; Gonzalez, M.E.; Hebert, A.A.; Lee, M.; Boguniewicz, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Once-Daily Roflumilast Cream 0.05% in Pediatric Patients Aged 2–5 Years With Mild-to-Moderate Atopic Dermatitis (INTEGUMENT-PED): A Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Trial. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2025, 42, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Rocha, E.; Rusiñol, L.; Puig, L. Exploring the Therapeutic Landscape: A Narrative Review on Topical and Oral Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors in Dermatology. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiyama, H.; Arichika, N.; Okada, M.; Koyama, N.; Tahara, T.; Haruta, J. Pharmacological Profile of Difamilast, a Novel Selective Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor, for Topical Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2023, 386, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, H.; Baba, N.; Oshiden, K.; Abe, Y.; Tsubouchi, H. Phase 2, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, 4-Week Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of OPA-15406 (Difamilast), a New Topical Selective Phosphodiesterase Type-4 Inhibitor, in Japanese Pediatric Patients Aged 2–14 Years with Atopic Derm. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, H.; Ito, K.; Yokota, D.; Tsubouchi, H. Difamilast Ointment in Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Phase 3 Randomized, Double-Blind, Vehicle-Controlled Trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.C.; Chao, C.M.; Chang, S.P.; Lan, S.H.; Lai, C.C. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Topical Difamilast in the Treatment of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 15, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samrao, A.; Berry, T.M.; Goreshi, R.; Simpson, E.L. A Pilot Study of an Oral Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor (Apremilast) for Atopic Dermatitis in Adults. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Imafuku, S.; Poulin, Y.; Ungar, B.; Zhou, L.; Malik, K.; Wen, H.C.; Xu, H.; Estrada, Y.D.; Peng, X.; et al. A Phase 2 Randomized Trial of Apremilast in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, J.I.; French, L.E.; Warren, R.B.; Strober, B.; Kjøller, K.; Sommer, M.O.A.; Andres, P.; Felding, J.; Weiss, A.; Tutkunkardas, D.; et al. Pharmacology of Orismilast, a Potent and Selective PDE4 Inhibitor. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.; Eichenfield, L.; Blauvelt, A.; Irvine, A.D.; Langley, R.; Guttman, E.; Warren, R.; French, L.; Pedersen, C.B.; Carlsson, A.; et al. 693-Efficacy and Safety of Orismilast, a Potent PDE4B/D Inhibitor, in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Phase 2b Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial (ADESOS). Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 191, ljae266.067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenfield, L.F.; Tarabar, S.; Forman, S.; García-Bello, A.; Feng, G.; Fetterly, G.; Mahling, P.; Peeva, E.; Vincent, M.S.; Chandra, D.E. Efficacy and Safety of PF-07038124 in Patients With Atopic Dermatitis and Plaque Psoriasis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.M.; Chiricozzi, A.; Calabrese, L.; Mannino, M.; Peris, K. Novel Therapeutic Strategies in the Topical Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, N.; Shirato, M.; Wakita, H.; Miyazaki, K.; Takase, Y.; Asano, O.; Kusano, K.; Yamamoto, E.; Inoue, C.; Hishinuma, I. Antipruritic Effect of the Topical Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor E6005 Ameliorates Skin Lesions in a Mouse Atopic Dermatitis Model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 346, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, T.; Kuraishi, Y. Antipruritic Mechanisms of Topical E6005, a Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor: Inhibition of Responses to Proteinase-Activated Receptor 2 Stimulation Mediated by Increase in Intracellular Cyclic AMP. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 76, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, H.; Ohkuro, M.; Ishii, N.; Hishinuma, I.; Shirato, M. A Putative Antipruritic Mechanism of the Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitor E6005 by Attenuating Capsaicin-Induced Depolarization of C-Fibre Nerves. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M.; Kitahara, Y.; Akama, H.; Hojo, S.; Hayashi, N.; Nakagawa, H. Safety and Efficacy of Topical E6005, a Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor, in Japanese Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: Results of a Randomized, Vehicle-Controlled, Multicenter Clinical Trial. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, O.; Hayashi, N.; Kitahara, Y.; Furue, M.; Hojo, S.; Nomoto, M.; Shima, S.; Investigators, T.J.E.S. Effect of Topical Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitor E6005 on Japanese Children with Atopic Dermatitis: Results from a Randomized, Vehicle-Controlled Exploratory Trial. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xizang Haisco Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. A Study for HSK44459 in Participants with Atopic Dermatitis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT07070739 (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Edwards, H.E.; Gorelick, D.A. The Evolution and Structure/Function of BHLH-PAS Transcription Factor Family. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2022, 50, 1227–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Gallego, N.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; Cibrian, D. Role of AHR Ligands in Skin Homeostasis and Cutaneous Inflammation. Cells 2021, 10, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawe, H.R.; Di Meglio, P. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR): Peacekeeper of the Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiering, C.; Vonk, A.; Das, S.; Stockinger, B.; Wincent, E. Cytochrome P4501-Inhibiting Chemicals Amplify Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation and IL-22 Production in T Helper 17 Cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 151, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.V.; Kongsbak-Wismann, M. Role of IL-22 in Homeostasis and Diseases of the Skin. APMIS 2022, 130, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.H.G. IL-17 and IL-17-Producing Cells in Protection versus Pathology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, R.; Stein Gold, L.; Rubenstein, D.S.; Tallman, A.M.; Armstrong, A. Tapinarof in the Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review of the Unique Mechanism of Action of a Novel Therapeutic Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor–Modulating Agent. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, A.S.; Stein Gold, L.; Soung, J.; Tallman, A.M.; Rubenstein, D.S.; Gooderham, M. Efficacy and Patient-Reported Outcomes from a Phase 2b, Randomized Clinical Trial of Tapinarof Cream for the Treatment of Adolescents and Adults with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 36, 2444489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, L.S.; Del Rosso, J.; Ehst, B.D.; Zirwas, M.J.; Green, L.J.; Brown, P.M.; Rubenstein, D.S.; Piscitelli, S.C.; Tallman, A.M. Tapinarof Cream 1% Once Daily Was Well Tolerated in Adults and Children with Atopic Dermatitis in Two Phase 3 Randomized Trials. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2025, 36, 2444489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, F.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Q.; Hu, J.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J. A Multi-Center, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo- and Positive-Controlled Phase II Clinical Study of Benvitimod for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Chin. Med. J. 2023, 136, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, X.; Cai, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Jing, S.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Fang, Y. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multiple-Dose Study of the Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Benvitimod, a Candidate Drug for the Treatment of Psoriasis. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 39, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaura, K.; Shigemori, A.; Suwa, E.; Ueno, K. Expression of the Histamine H4 Receptor in Dermal and Articular Tissues. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaper-Gerhardt, K.; Rossbach, K.; Nikolouli, E.; Werfel, T.; Gutzmer, R.; Mommert, S. The Role of the Histamine H(4) Receptor in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.H.; Hong, T.; Yoo, B.W.; Kim, C.O.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.N.; Park, M.S. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Safety of Izuforant, an H4R Inhibitor, in Healthy Subjects: A Phase I Single and Multiple Ascending Dose Study. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e70032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JW Pharmaceutical. A Phase 2 Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Orally Administered LEO 152020 Tablets Compared with Placebo Tablets for up to 16 Weeks of Treatment in Adults with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. ClinicalTrials.gov. 2023. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05117060 (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Bell, M.; Foley, D.; Naylor, C.; Wood, G.; Robinson, C.; Riley, J.; Epemolu, O.; Ellis, L.; Scullion, P.; Shishikura, Y.; et al. Discovery of Soft-Drug Topical Tool Modulators of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 1 (S1PR1). ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Bissonnette, R.; Kircik, L.; Murrell, D.F.; Selfridge, A.; Liu, K.; Ahluwalia, G.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Efficacy and Safety of Etrasimod, a Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Modulator, in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis (ADVISE). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfizer. A Study to Learn About the Study Medicine Etrasimod in Adults with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Who Have Already Tried Treatments Taken by Mouth or by Injection 2023. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05732454 (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Bihorel, S.; Singhal, S.; Shevell, D.; Sun, H.; Xie, J.; Basdeo, S.; Liu, A.; Dutta, S.; Ludwig, E.; Huang, H.; et al. Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis of BMS-986166, a Novel Selective Sphingosine-1-Phosphate-1 Receptor Modulator, and Exposure-Response Assessment of Lymphocyte Counts and Heart Rate in Healthy Participants. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2021, 10, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakos, A.; Torres, T.; Vender, R. Emerging Oral Therapies for the Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review of Pipeline Agents. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A. Sun Pharma Halts Development of SCD-044 Skin Drug after Trial Failure. Bus. Stand. 2025. Available online: https://www.business-standard.com/companies/news/sun-pharma-halts-development-scd044-skin-drug-after-trial-failure-125060300966_1.html (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Sato, M.; Matsuo, K.; Susami, Y.; Yamashita, A.; Hayasaka, H.; Hara, Y.; Nishiwaki, K.; Oiso, N.; Kawada, A.; Otsuka, A.; et al. A CCR4 Antagonist Attenuates Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Inflammation by Inhibiting the Recruitment and Expansion of Th2 Cells and Th17 Cells. Int. Immunol. 2023, 35, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, R.; DuBois, J.; Facheris, P.; Del Duca, E.; Kim, M.; Correa Da Rosa, J.; Trujillo, D.L.; Bose, S.; Pagan, A.D.; Wustrow, D.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Effects of Oral CCR4 Antagonist RPT193 in Atopic Dermatitis: A Phase 1 Study. Allergy 2024, 79, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Endpoint | Description | Strengths | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) | a clinician-rated scale assessing overall atopic dermatitis severity on a 5-point scale: 0 = clear (no inflammatory signs), 1 = almost clear (minimal signs of erythema and infiltration), 2 = mild (mild erythema, infiltration, and possibly minimal oozing), 3 = moderate (distinct erythema, infiltration, oozing/crusting), 4 = severe (severe erythema and infiltration with extensive oozing/crusting and/or lichenification). |
|
| [10,11] |
| Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) |
|
|
| [12,13] |
| SCORAD (Scoring Atopic Dermatitis) | a composite index (0–103) combining three components:
|
|
| [14] |
| Drug | Mechanism | Approved Dose | Efficacy Endpoints | Adverse Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upadacitinib | JAK1 inhibitor | 15 mg or 30 mg oral, once daily | Measure Up 1: EASI-75 achieved by 70% (15 mg) and 80% (30 mg) vs. 16% on placebo Measure Up 2: EASI-75 achieved by 60% (15 mg) and 73% (30 mg) vs. 13% on placebo | very common: acne, upper respiratory infections, nasopharyngitis, headache, elevated CPK—frequently observed across trials common: neutropenia, herpes simplex/zoster, lab changes (CPK, liver enzymes)—dose-dependent but generally mild |
| Abrocitinib | JAK1 inhibitor | 100 mg or 200 mg, oral, once daily | JADE MONO-1, MONO-2, COMPARE: EASI-75 at week 12 achieved in 40–69% of patients with 100 mg | very common: headache, nausea, acne, nasopharyngitis, herpes simplex, elevated CPK, vomiting, dizziness, abdominal pain common: infections, hematologic lab changes, diarrhea, conjunctivitis |
| Baricitinib | JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor | 2 mg or 4 mg, oral, once daily | BREEZE-AD: EASI-75 EASI-75 at week 16 achieved in 13% (1 mg) and 24% (2 mg) | very common: nasopharyngitis common: headache, upper respiratory tract infections, herpes simplex |
| Ruxolitinib | JAK1/JAK2 Inhibitor | 1.5% topical cream, twice daily | TRuE-AD1: EASI-75 at week 8 achieved by 56.0% (0.75%), 62.1% (1.5%) TRuE-AD1: EASI-75 at week 8 achieved by 51.5% (0.75%), 61.8% (1.5%) | common: naso- pharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, application site burning, application site pruritus |
| Delgocitinib | pan-JAK inhibitor | 2%, 0.5%, and 0.25% topical formulation | QBA4-1: mEASI-75 at week 4 achieved by 10.9% and at week 24 by 22.7% QBA4-2: mEASI-75 at week 52 achieved by 27.5% | common: nasopharyngitis, contact dermatitis, acne, application site folliculitis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nitulescu, G.; Olaru, O.T.; Andrei, C.; Nitulescu, G.M.; Zanfirescu, A. Targeting Intracellular Pathways in Atopic Dermatitis with Small Molecule Therapeutics. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080659
Nitulescu G, Olaru OT, Andrei C, Nitulescu GM, Zanfirescu A. Targeting Intracellular Pathways in Atopic Dermatitis with Small Molecule Therapeutics. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(8):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080659
Chicago/Turabian StyleNitulescu, Georgiana, Octavian Tudorel Olaru, Corina Andrei, George Mihai Nitulescu, and Anca Zanfirescu. 2025. "Targeting Intracellular Pathways in Atopic Dermatitis with Small Molecule Therapeutics" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 8: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080659
APA StyleNitulescu, G., Olaru, O. T., Andrei, C., Nitulescu, G. M., & Zanfirescu, A. (2025). Targeting Intracellular Pathways in Atopic Dermatitis with Small Molecule Therapeutics. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(8), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47080659







