Bisdemethoxycurcumin Induces Cell Apoptosis and Inhibits Human Brain Glioblastoma GBM 8401/Luc2 Cell Xenograft Tumor in Subcutaneous Nude Mice In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
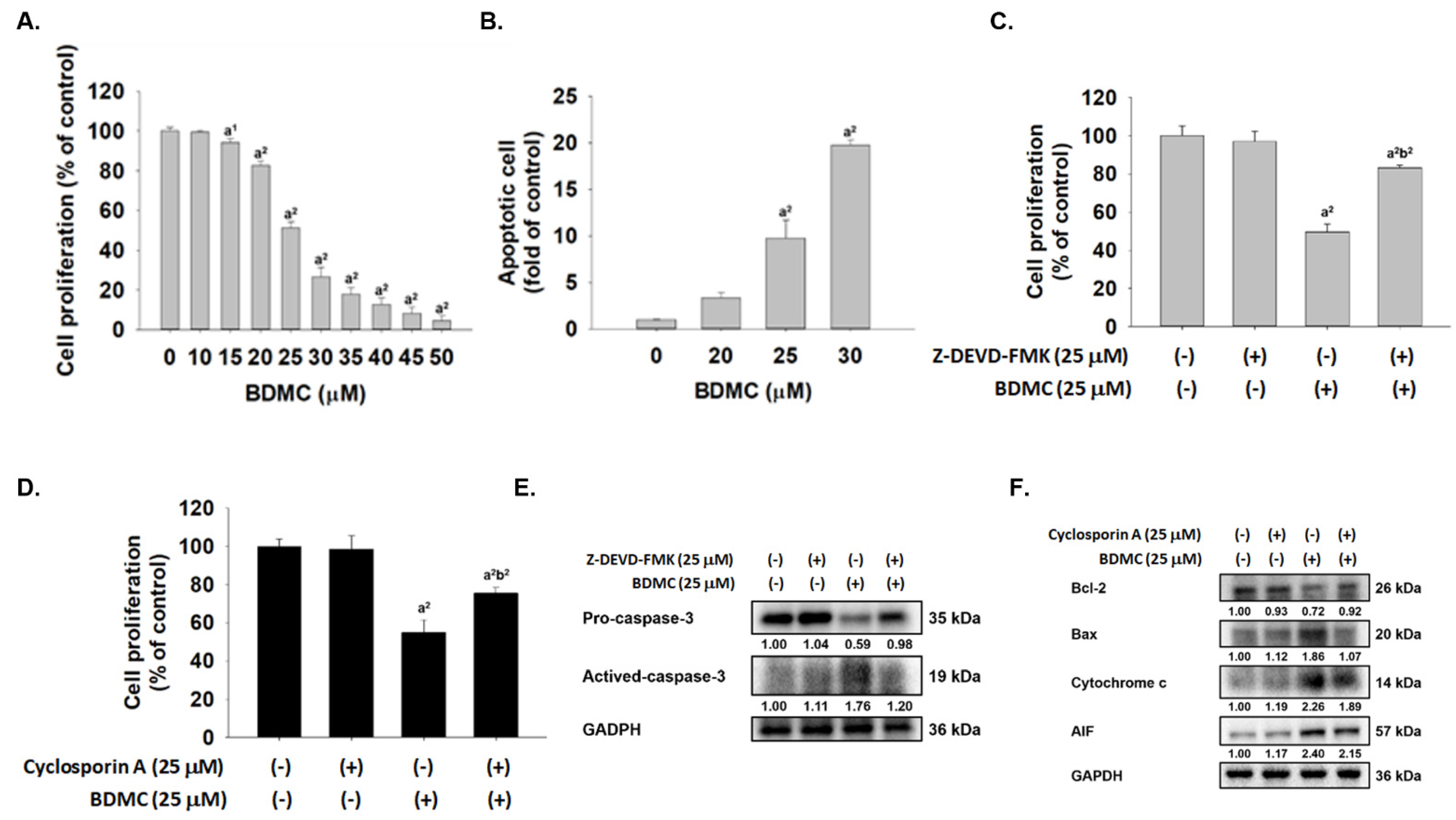
2.1. BDMC Reduced Cell Viability, Induced Apoptosis, and Affected Apoptosis-Associated Proteins in GBM 8401/luc2 Cells
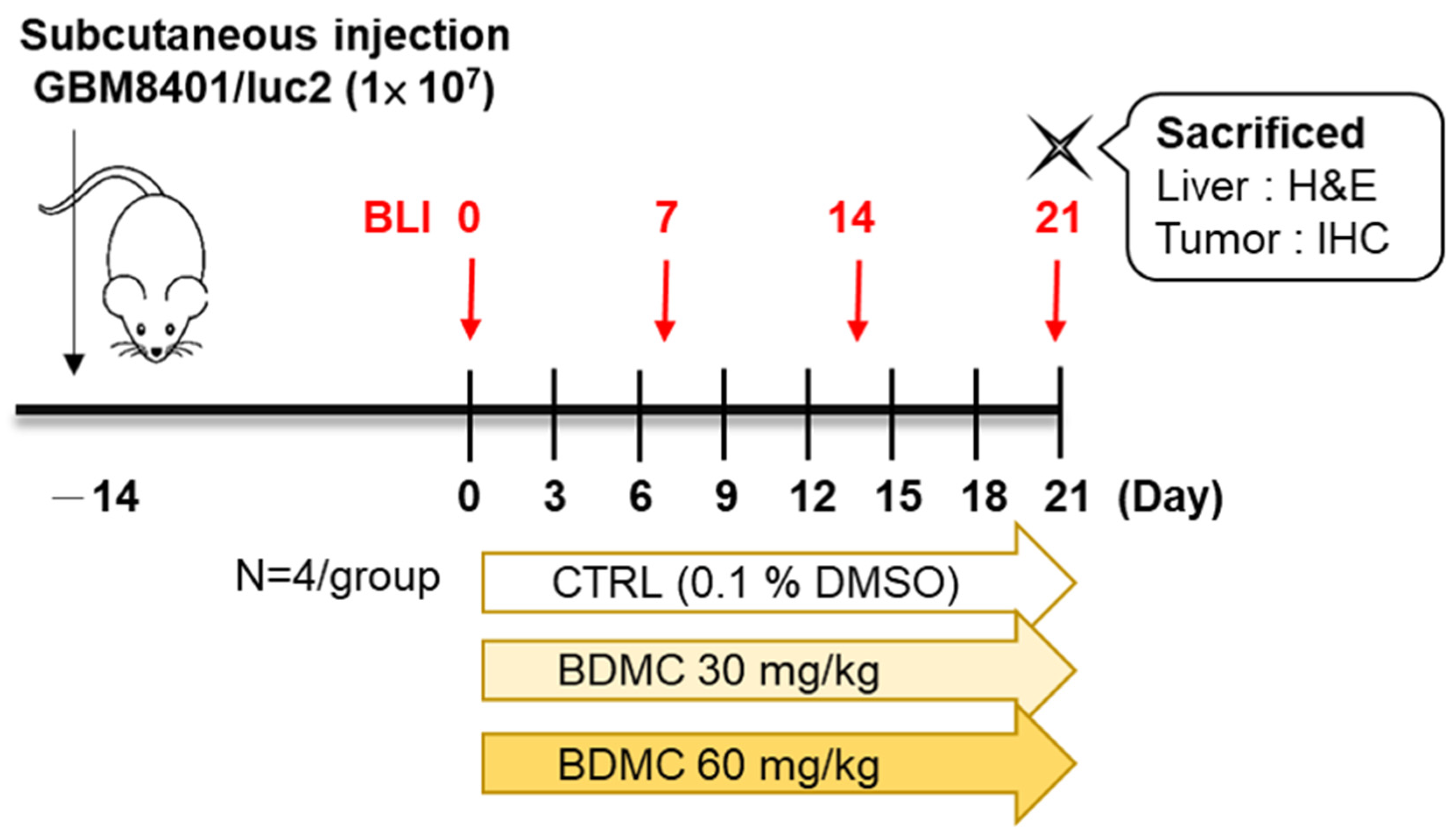
2.2. Flow Chart of In Vivo Experiments
2.3. BDMC Did Not Affect the Body Weight and Liver Pathology of Athymic BLAB/c nu/nu Nude Mice Bearing GBM 8401/luc2-Derived Tumors
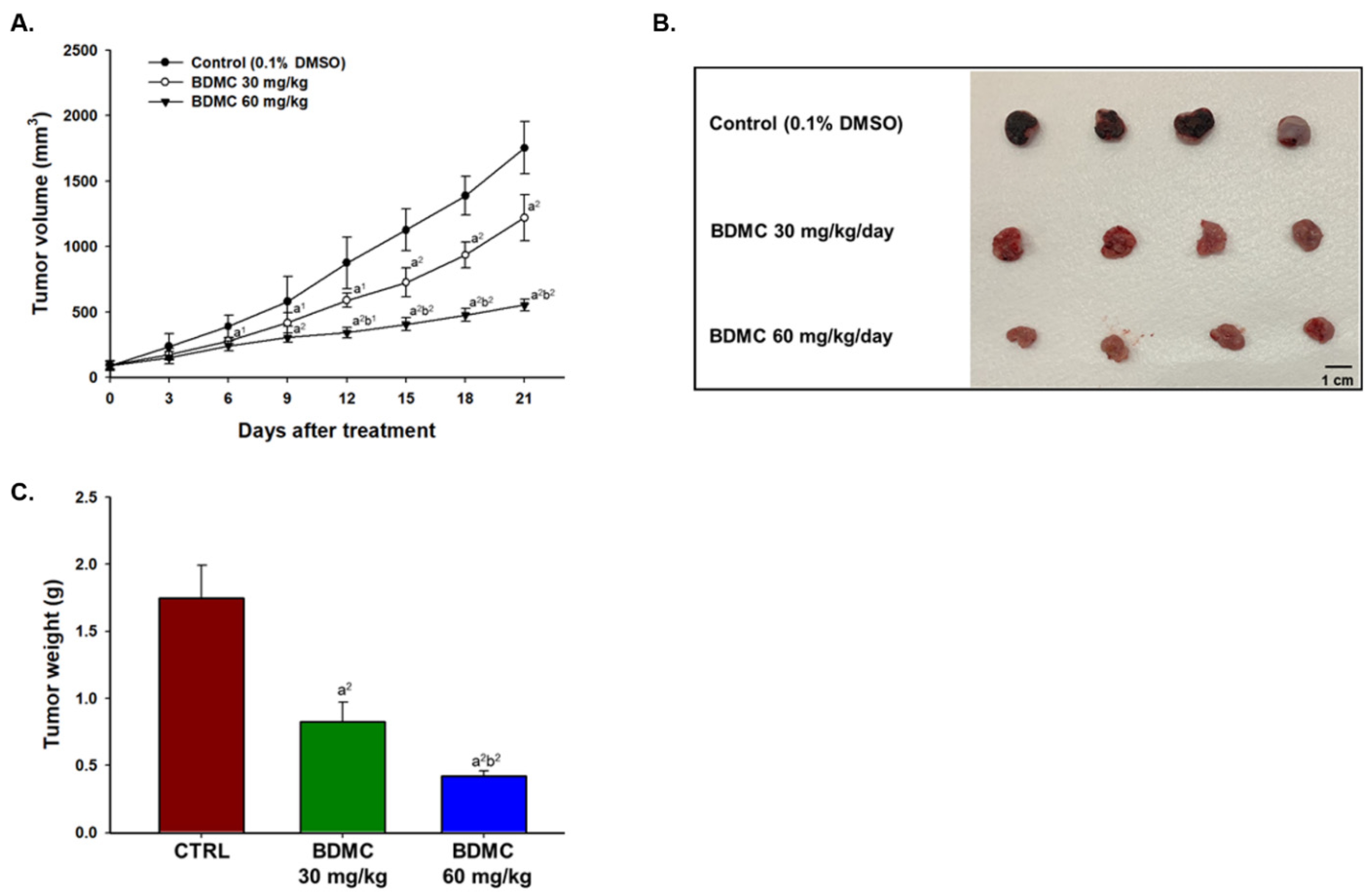
2.4. BDMC Inhibited GBM 8401/luc2 Cell Xenograft Tumor Growth in Nude Mice Bearing GBM 8401/luc2-Derived Tumors
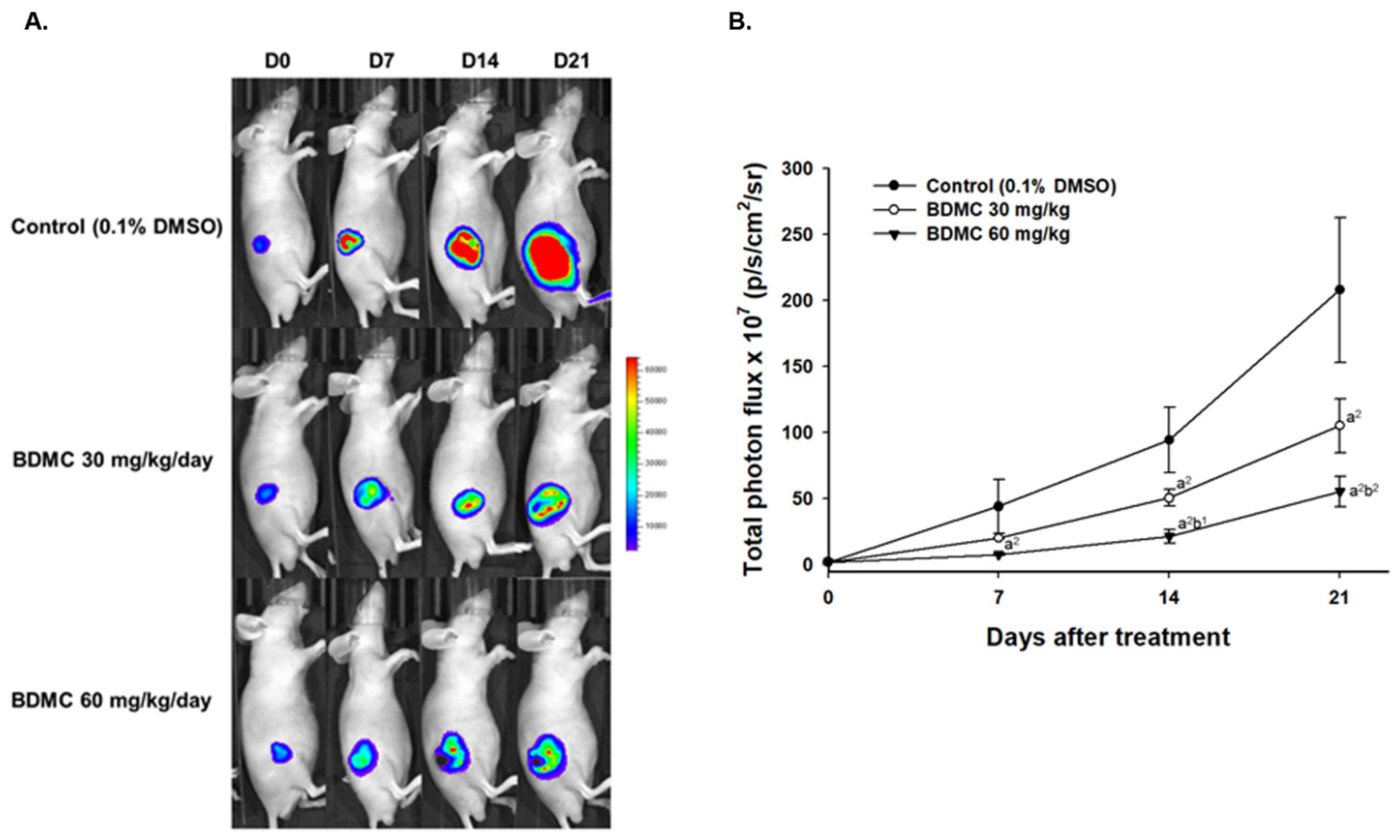
2.5. BDMC Reduced Living Cell Signal of Nude Mice Bearing GBM 8401/luc2-Derived Tumors
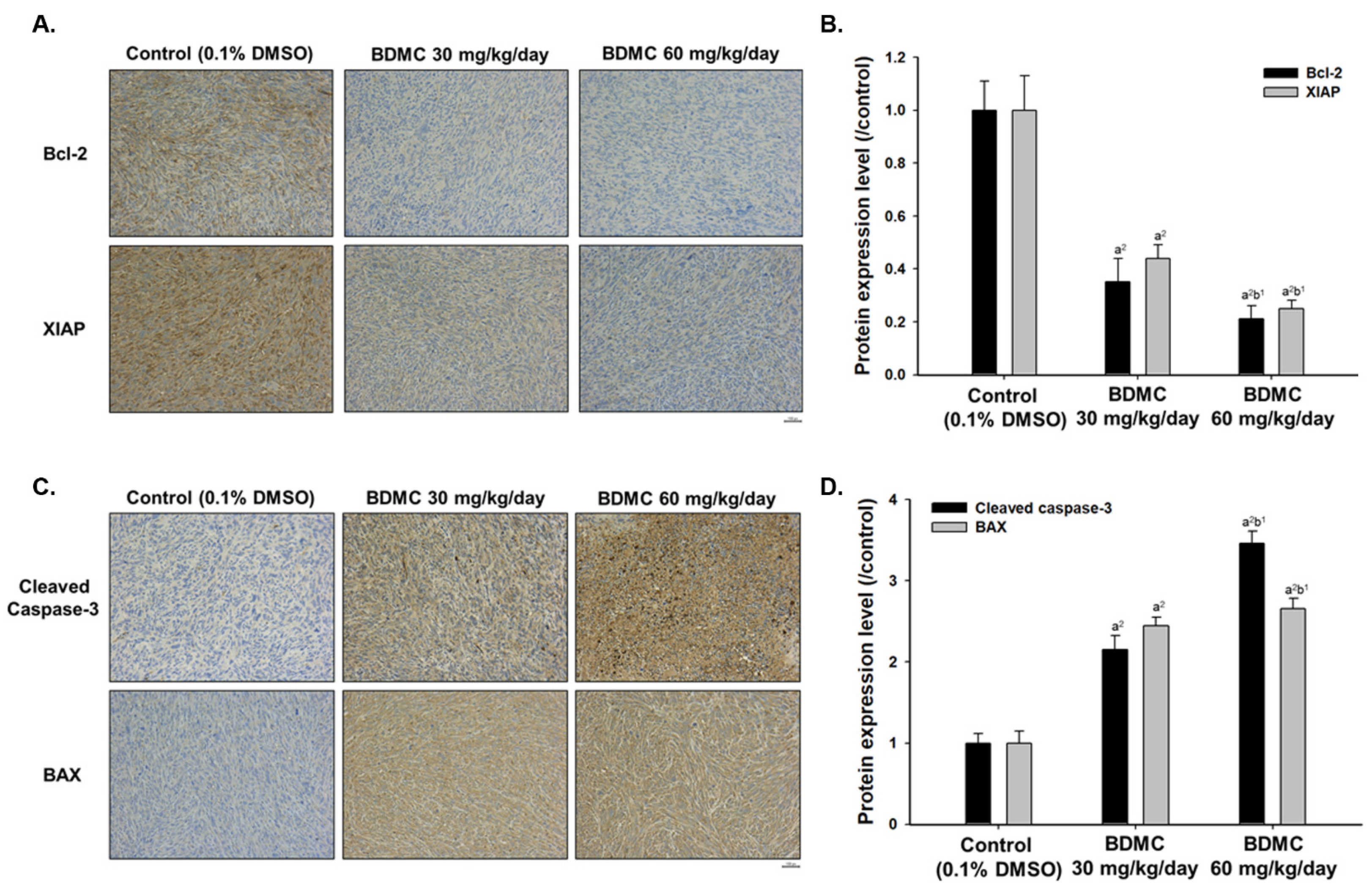
2.6. BDMC Affects the Expression of Apoptosis-Related Protein Signal Pathway of Nude Mice Bearing GBM 8401/luc2-Derived Tumors
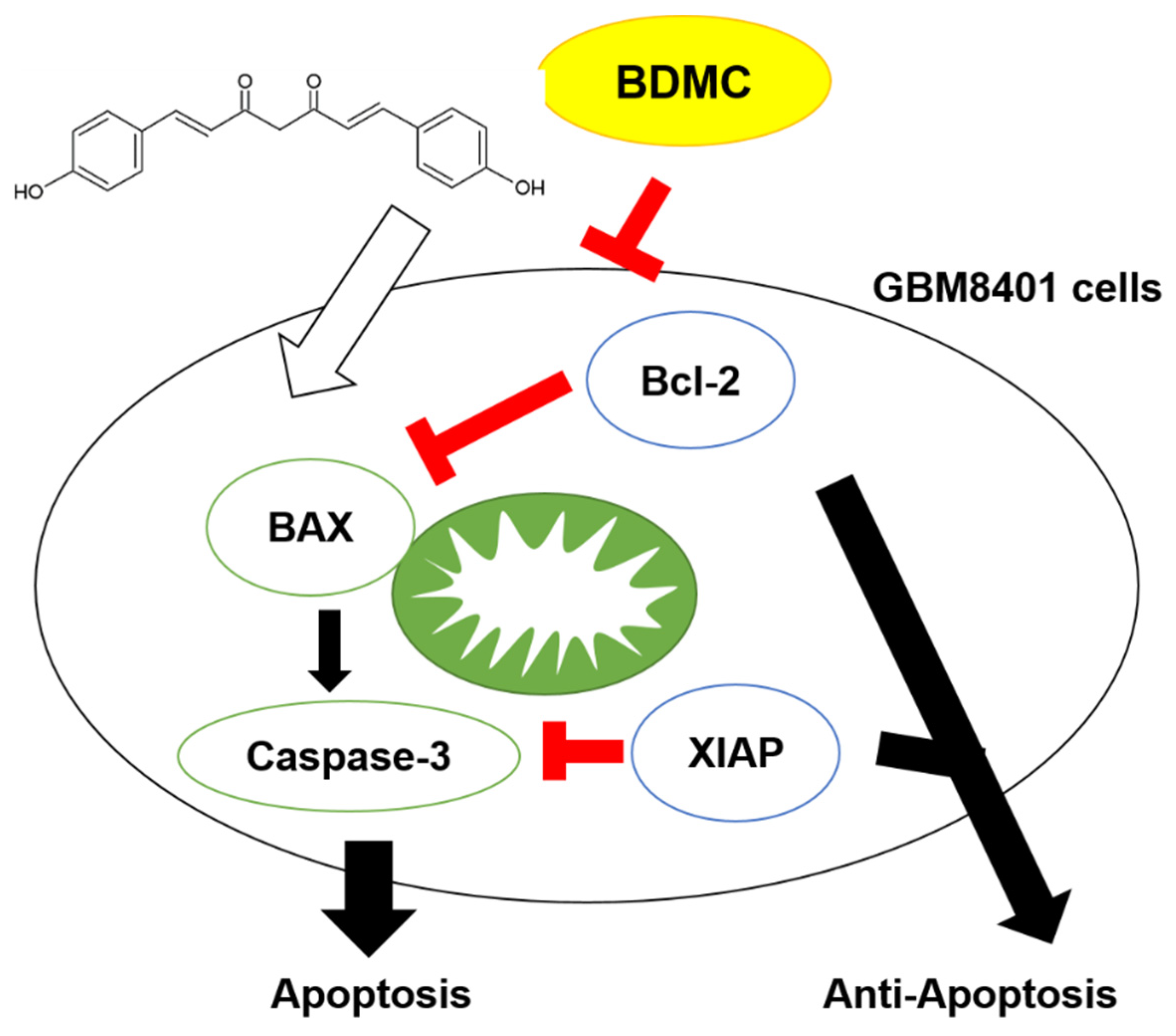
2.7. BDMC Effectively Triggers the Apoptosis Mechanism and Suppressed Glioblastoma Tumor Growth
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Test Compound, Reagents, Antibodies, and Culture Medium
4.2. Cell Culture of GBM 8401 Cells
4.3. Cell Culture, Transfection, and Stable Clone Selection
4.4. Measurements of Cytotoxicity
4.5. Annexin V/PI Staining for Cell Apoptosis Assay
4.6. Cytoxicity of Cotreatment BDMC with Caspase-3 or MMP Inhibitor
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Establishment of Glioblastoma Xenograft Bearing Mice and Treatments
4.9. Treatment Efficacy Evaluation and Animal Bioluminescent Imaging
4.10. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hess, K.R.; Broglio, K.R.; Bondy, M.L. Adult glioma incidence trends in the United States, 1977–2000. Cancer 2004, 101, 2293–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamson, C.; Kanu, O.O.; Mehta, A.I.; Di, C.; Lin, N.; Mattox, A.K.; Bigner, D.D. Glioblastoma multiforme: A review of where we have been and where we are going. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 1061–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Burger, P.C.; Jouvet, A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kleihues, P. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, J.M. Vasculogenesis: A crucial player in the resistance of solid tumours to radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20130686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; Van Den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, R.; Hayano, A.; Kanayama, T. Radiation-induced gliomas: A comprehensive review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Rev. 2018, 41, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, A.A.; Tosoni, A.; Franceschi, E.; Sotti, G.; Frezza, G.; Amistà, P.; Morandi, L.; Spagnolli, F.; Ermani, M. Recurrence pattern after temozolomide concomitant with and adjuvant to radiotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma: Correlation With MGMT promoter methylation status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallejo, M.J.; Salazar, L.; Grijalva, M. Oxidative Stress Modulation and ROS-Mediated Toxicity in Cancer: A Review on In Vitro Models for Plant-Derived Compounds. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4586068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chikara, S.; Nagaprashantha, L.D.; Singhal, J.; Horne, D.; Awasthi, S.; Singhal, S.S. Oxidative stress and dietary phytochemicals: Role in cancer chemoprevention and treatment. Cancer Lett. 2018, 413, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavamukulya, Y.; Wamunyokoli, F.; El-Shemy, H.A. Annona muricata: Is the natural therapy to most disease conditions including cancer growing in our backyard? A systematic review of its research history and future prospects. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapinova, A.; Stefanicka, P.; Kubatka, P.; Zubor, P.; Uramova, S.; Kello, M.; Mojzis, J.; Blahutova, D.; Qaradakhi, T.; Zulli, A.; et al. Are plant-based functional foods better choice against cancer than single phytochemicals? A critical review of current breast cancer research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayan, A.; Raiyn, J.; Falah, M. Nature is the best source of anticancer drugs: Indexing natural products for their anticancer bioactivity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.W.; Huang, H.C. Effect of curcumin on cell cycle progression and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 124, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orona-Ortiz, A.; Velázquez-Moyado, J.A.; Pineda-Peña, E.A.; Balderas-López, J.L.; Tavares Carvalho, J.C.; Navarrete, A. Effect of the proportion of curcuminoids on the gastroprotective action of Curcuma longa L. in rats. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 35, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongtao, C.; Youling, F.; Fang, H.; Huihua, P.; Jiying, Z.; Jun, Z. Curcumin alleviates ischemia reperfusion-induced late kidney fibrosis through the APPL1/Akt signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 8588–8596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Manikanta, K.; Hemshekhar, M.; Sundaram, M.S.; Naveen, S.; Ramesh, T.N.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Bisdemethoxycurcumin promotes apoptosis in human platelets via activation of ERK signaling pathway. Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 63, 104743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.Y.; Peng, S.F.; Huang, Y.P.; Tsai, C.H.; Tsai, F.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Tang, C.H.; Yang, J.S.; Hsu, Y.M.; Yin, M.C.; et al. Combinational treatment of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDMC)-induced apoptosis in liver cancer Hep3B cells. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lu, H.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, J.C.; Chou, W.H.; Huang, H.C. Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin induced caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis via Smad or Akt signaling pathways in HOS cells. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huo, C.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, R.; Liu, Y.; Jia, X.; Wang, X. Bisdemethoxycurcumin Protection of Cardiomyocyte Mainly Depends on Nrf2/HO-1 Activation Mediated by the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lee, P.S.; Kalyanam, N.; Ho, C.T.; Liou, W.S.; Yu, R.C.; Pan, M.H. Bisdemethoxycurcumin Inhibits Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes and Suppresses Obesity in High-Fat Diet-Fed C57BL/6 Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Chen, X.; Yan, H.; Xu, Z.; Yang, B.; Luo, P.; He, Q. Bisdemethoxycurcumin attenuates cisplatin-induced renal injury through anti-apoptosis, anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 874, 173026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dützmann, S.; Schiborr, C.; Kocher, A.; Pilatus, U.; Hattingen, E.; Weissenberger, J.; Geßler, F.; Quick-Weller, J.; Franz, K.; Seifert, V.; et al. Intratumoral Concentrations and Effects of Orally Administered Micellar Curcuminoids in Glioblastoma Patients. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, L.; Owens, K. Necrosis is not induced by gadolinium neutron capture in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2012, 88, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrigo, C.A.; Grivicich, I.; Schunemann, D.P.; Chemale, I.M.; dos Santos, D.; Jacovas, T.; Boschetti, P.S.; Jotz, G.P.; Braga Filho, A.; da Rocha, A.B. Radioresistance of human glioma spheroids and expression of HSP70, p53 and EGFr. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippi-Chiela, E.C.; Villodre, E.S.; Zamin, L.L.; Lenz, G. Autophagy interplay with apoptosis and cell cycle regulation in the growth inhibiting effect of resveratrol in glioma cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wei, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Xu, H. A systematic analysis of FDA-approved anticancer drugs. BMC Syst. Biol. 2017, 11 (Suppl. 5), 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, I.F.; Gopalan, A.; Wood, S.; Chow, K.H.; Battelli, C.; George, J.; Blaszyk, H.; Florman, J.; Yun, K. Expression and function of ABCG2 and XIAP in glioblastomas. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellanki, S.H.; Grabrucker, A.; Liebau, S.; Proepper, C.; Eramo, A.; Braun, V.; Boeckers, T.; Debatin, K.M.; Fulda, S. Small-molecule XIAP inhibitors enhance gamma-irradiation-induced apoptosis in glioblastoma. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, F.A.; Zee, B.C.; Cheung, F.Y.; Kwong, P.; Chiang, C.L.; Leung, K.C.; Siu, S.W.; Lee, C.; Lai, M.; Kwok, C.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study of the X-linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis (XIAP) Antisense AEG35156 in Combination With Sorafenib in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, H.; Luo, Y. Anti-Aging Implications of Astragalus Membranaceus (Huangqi): A Well-Known Chinese Tonic. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 868–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.M.; Wu, Y.P.; Huang, L.C.; Huang, S.M.; Hueng, D.Y. The anti-cancer effect of four Curcumin Analogues on human glioma cells. Onco. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 4345–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattern, J.; Bak, M.; Hahn, E.W.; Volm, M. Human tumor xenografts as model for drug testing. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1988, 7, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.S.; Lin, J.J.; Lin, C.C.; Lien, J.C.; Peng, S.F.; Fan, M.J.; Hsu, F.T.; Chung, J.G. Benzyl isothiocyanate inhibits human brain glioblastoma multiforme GBM 8401 cell xenograft tumor in nude mice in vivo. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.C.; Chang, M.Y.; Lee, H.T.; Shen, C.C.; Harnod, T.; Liang, Y.J.; Wu, R.S.; Lai, K.C.; Hsu, F.T.; Chung, J.G. Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Inhibits In Vivo Growth of Xenograft Tumors of Human Glioblastoma Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, C.H.; Sheng, J.Q.; Fang, D.C.; Meng, Q.Z.; Fan, L.L.; Huang, Z.R. Involvement of VDAC1 and Bcl-2 family of proteins in VacA-induced cytochrome c release and apoptosis of gastric epithelial carcinoma cells. J. Dig. Dis. 2010, 11, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wan, G.; Yu, H.; Xiong, W. High-intensity focused ultrasound inhibits invasion and metastasis of colon cancer cells by enhancing microRNA-124-mediated suppression of STAT3. FEBS Open Biol. 2019, 9, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, R.S. Apoptosis in cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, S.K.; Patel, S.J.; Welsh, C.T.; Wilford, G.G.; Hogan, E.L.; Banik, N.L. Molecular evidence of apoptotic death in malignant brain tumors including glioblastoma multiforme: Upregulation of calpain and caspase-3. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 69, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.H.; Fang, W.L.; Li, A.F.; Liang, P.H.; Wu, C.W.; Shyr, Y.M.; Yang, M.H. Caspase-3, a key apoptotic protein, as a prognostic marker in gastric cancer after curative surgery. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 52, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.C. Caspase Allostery and Conformational Selection. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 6666–6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, C.; Galluzzi, L.; Brunet, M.; Puig, P.E.; Didelot, C.; Kroemer, G. Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cain, K. Chemical-induced apoptosis: Formation of the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Drug Metab. Rev. 2003, 35, 337–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvesen, G.S.; Duckett, C.S. IAP proteins: Blocking the road to death’s door. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirapelli, D.; Lustosa, I.L.; Menezes, S.B.; Franco, I.M.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Peria, F.M.; Marinho, A.; Serafini, L.N.; Carlotti, C.G., Jr.; Tirapelli, L.F. High expression of XIAP and Bcl-2 may inhibit programmed cell death in glioblastomas. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2017, 75, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.T.; Chen, Y.K.; Lin, S.S.; Hsu, F.T. Hyperforin Suppresses Tumor Growth and NF-kappaB-mediated Anti-apoptotic and Invasive Potential of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 2161–2167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weng, M.C.; Wang, M.H.; Tsai, J.J.; Kuo, Y.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Hsu, F.T.; Wang, H.E. Regorafenib inhibits tumor progression through suppression of ERK/NF-kappaB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma bearing mice. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maraming, P.; Klaynongsruang, S.; Boonsiri, P.; Peng, S.F.; Daduang, S.; Rungsa, P.; Tavichakorntrakool, R.; Chung, J.G.; Daduang, J. Anti-metastatic Effects of Cationic KT2 Peptide (a Lysine/Tryptophan-rich Peptide) on Human Melanoma A375.S2 Cells. In Vivo 2021, 35, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.C.; Kuo, C.L.; Lu, K.W.; Lin, J.J.; Yang, J.L.; Wu, R.S.; Wu, P.P.; Chung, J.G. 18alpha-Glycyrrhetinic Acid Induces Apoptosis of HL-60 Human Leukemia Cells through Caspases- and Mitochondria-Dependent Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2016, 21, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, F.T.; Chiang, I.T.; Kuo, Y.C.; Hsia, T.C.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Chung, J.G. Amentoflavone Effectively Blocked the Tumor Progression of Glioblastoma via Suppression of ERK/NF-kappa B Signaling Pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 913–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, W.C.; Yang, H.H.; Chiang, S.C.; Chou, Y.X.; Yang, H.T. Auricularia polytricha aqueous extract supplementation decreases hepatic lipid accumulation and improves antioxidative status in animal model of nonalcoholic fatty liver. BioMedicine 2014, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, J.J.; Hsu, F.T.; Pan, P.J.; Chen, C.W.; Kuo, Y.C. Amentoflavone Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sorafenib by Inhibiting Anti-apoptotic Potential and Potentiating Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vivo. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsia, T.-C.; Peng, S.-F.; Chueh, F.-S.; Lu, K.-W.; Yang, J.-L.; Huang, A.-C.; Hsu, F.-T.; Wu, R.S.-C. Bisdemethoxycurcumin Induces Cell Apoptosis and Inhibits Human Brain Glioblastoma GBM 8401/Luc2 Cell Xenograft Tumor in Subcutaneous Nude Mice In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010538
Hsia T-C, Peng S-F, Chueh F-S, Lu K-W, Yang J-L, Huang A-C, Hsu F-T, Wu RS-C. Bisdemethoxycurcumin Induces Cell Apoptosis and Inhibits Human Brain Glioblastoma GBM 8401/Luc2 Cell Xenograft Tumor in Subcutaneous Nude Mice In Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(1):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010538
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsia, Te-Chun, Shu-Fen Peng, Fu-Shin Chueh, Kung-Wen Lu, Jiun-Long Yang, An-Cheng Huang, Fei-Ting Hsu, and Rick Sai-Chuen Wu. 2022. "Bisdemethoxycurcumin Induces Cell Apoptosis and Inhibits Human Brain Glioblastoma GBM 8401/Luc2 Cell Xenograft Tumor in Subcutaneous Nude Mice In Vivo" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 1: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010538
APA StyleHsia, T.-C., Peng, S.-F., Chueh, F.-S., Lu, K.-W., Yang, J.-L., Huang, A.-C., Hsu, F.-T., & Wu, R. S.-C. (2022). Bisdemethoxycurcumin Induces Cell Apoptosis and Inhibits Human Brain Glioblastoma GBM 8401/Luc2 Cell Xenograft Tumor in Subcutaneous Nude Mice In Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(1), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010538






