Multiple Functions of the New Cytokine-Based Antimicrobial Peptide Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
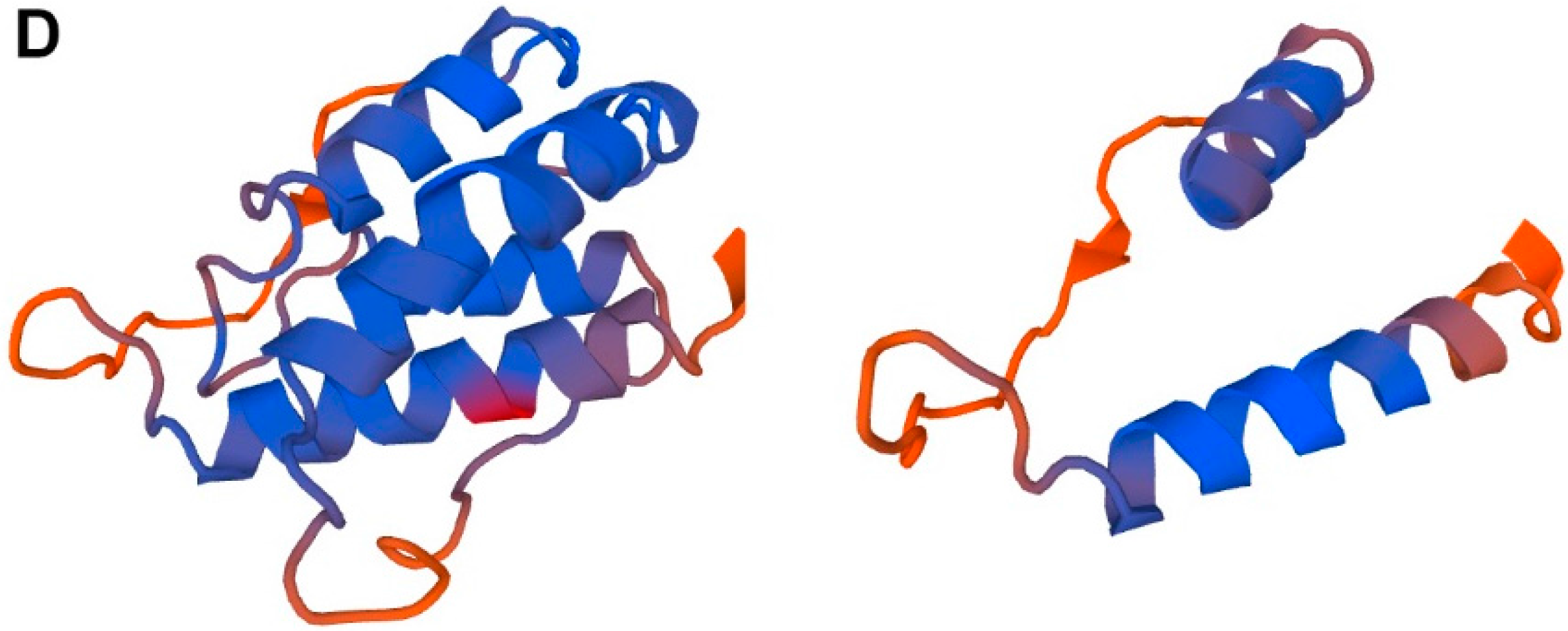
2. TSLP Variants
3. Expression and Regulation of TSLP Variants
4. Human TSLP Variants and Immunoregulation
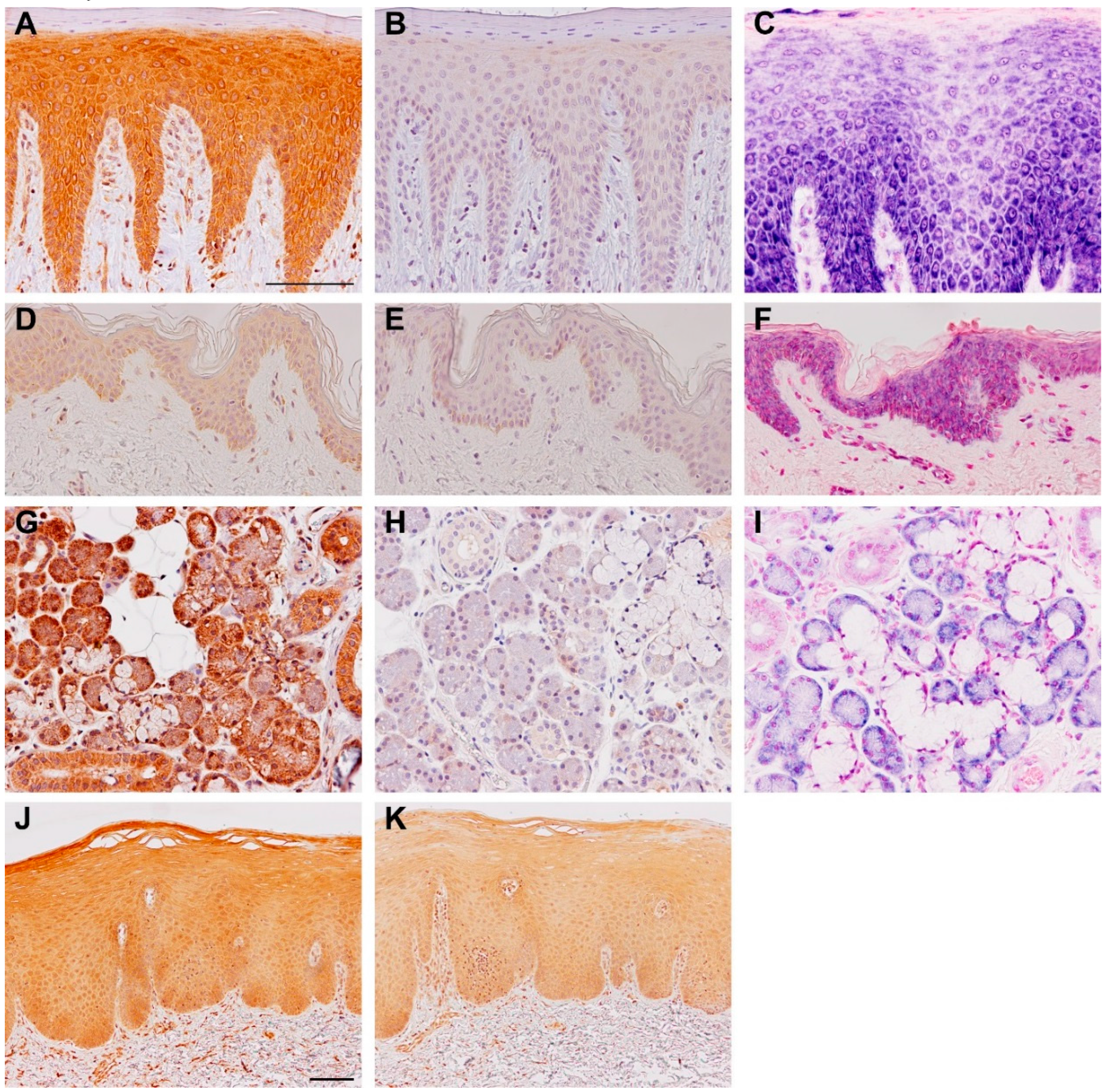
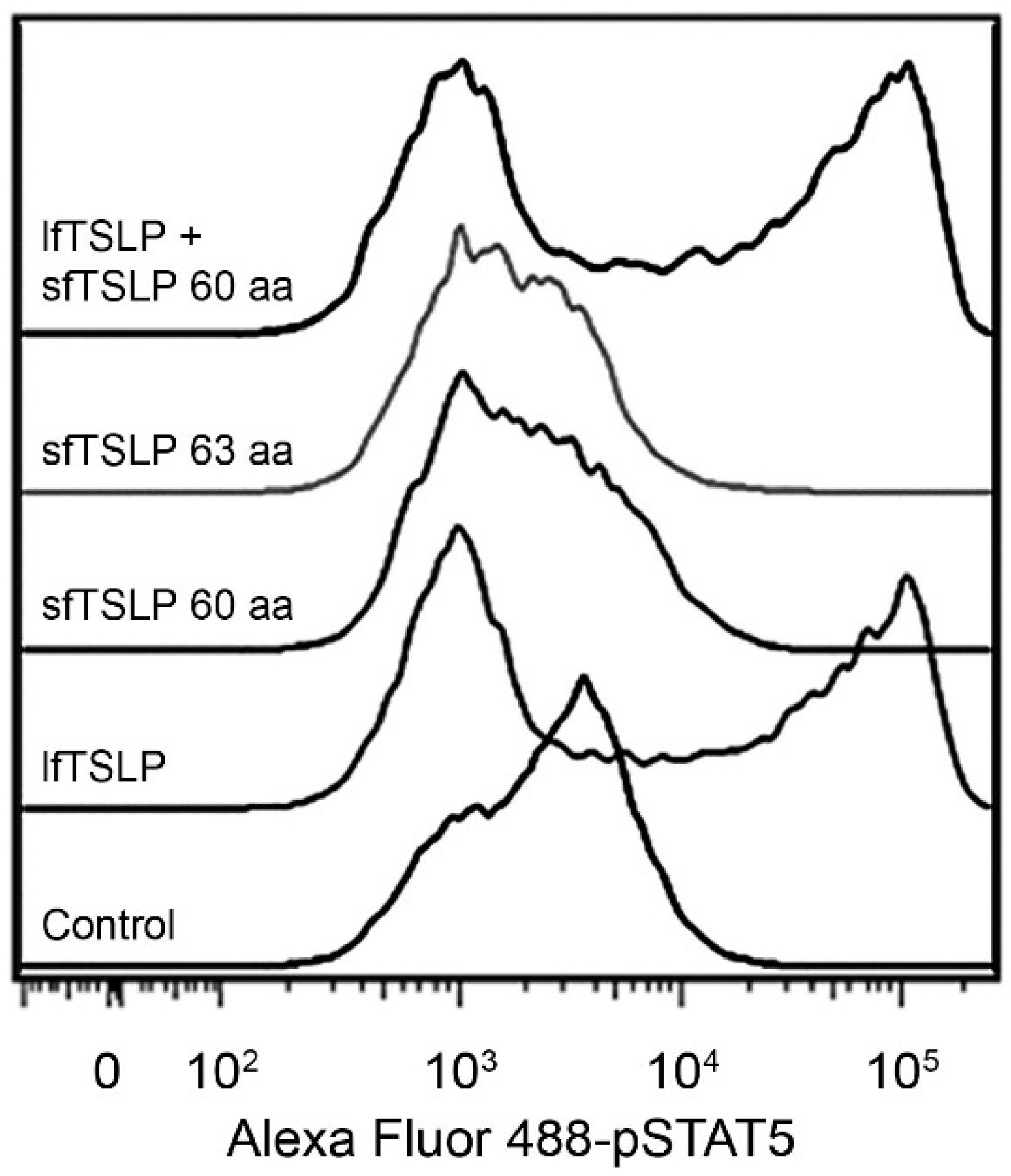
4.1. Long-Form TSLP (lfTSLP)
4.2. Short-Form TSLP (sfTSLP)
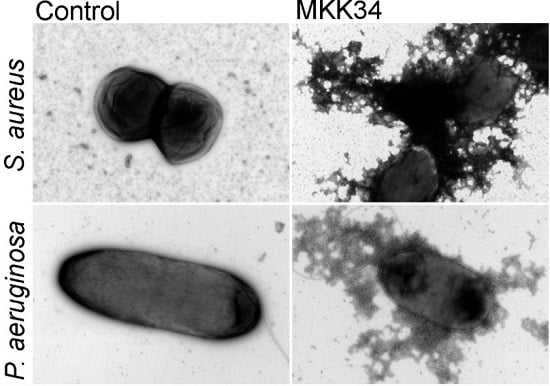
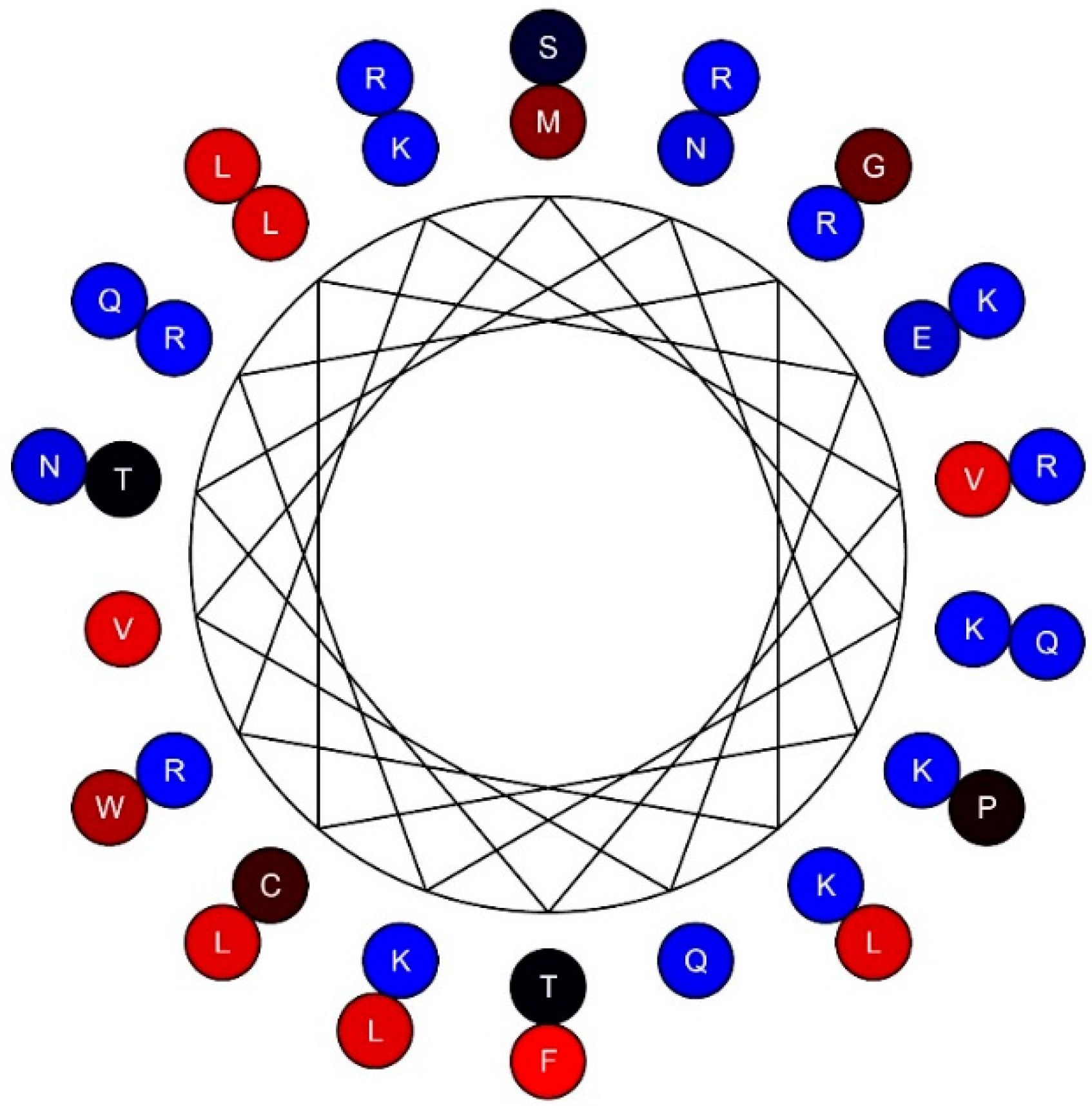
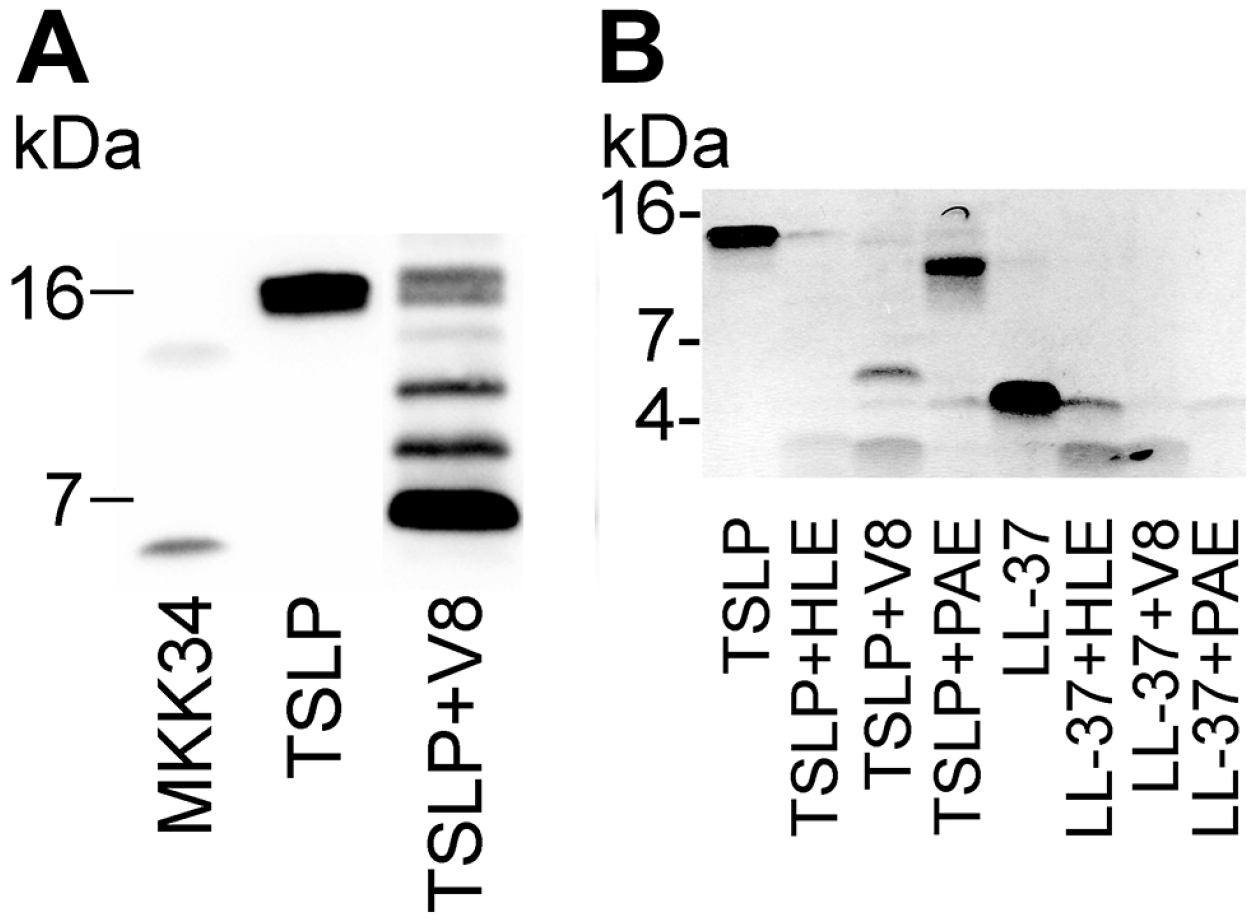
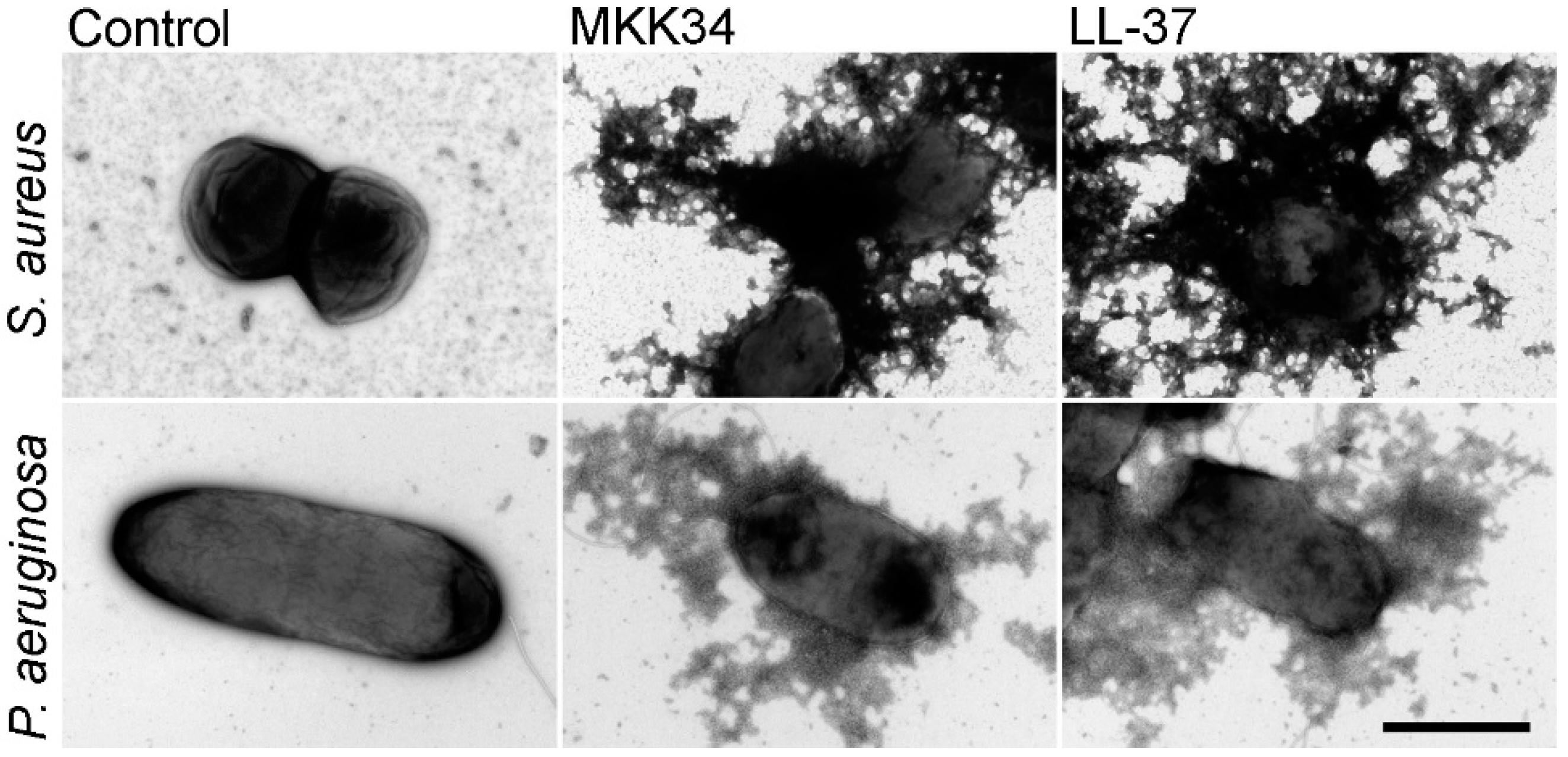
5. Human TSLP Variants as Antimicrobial Peptides
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friend, S.L.; Hosier, S.; Nelson, A.; Foxworthe, D.; Williams, D.E.; Farr, A. A thymic stromal cell line supports in vitro development of surface IgM+ B cells and produces a novel growth factor affecting B and T lineage cells. Exp. Hematol. 1994, 22, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quentmeier, H.; Drexler, H.G.; Fleckenstein, D.; Zaborski, M.; Armstrong, A.; Sims, J.E.; Lyman, S.D. Cloning of human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and signaling mechanisms leading to proliferation. Leukemia 2001, 15, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reche, P.A.; Soumelis, V.; Gorman, D.M.; Clifford, T.; Liu, M.; Travis, M.; Zurawski, S.M.; Johnston, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Spits, H.; et al. Human thymic stromal lymphopoietin preferentially stimulates myeloid cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, S.F.; Roan, F.; Bell, B.D.; Stoklasek, T.A.; Kitajima, M.; Han, H. The biology of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). Adv. Pharmacol. 2013, 66, 129–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bjerkan, L.; Schreurs, O.; Engen, S.A.; Jahnsen, F.L.; Baekkevold, E.S.; Blix, I.J.; Schenck, K. The short form of TSLP is constitutively translated in human keratinocytes and has characteristics of an antimicrobial peptide. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornasa, G.; Tsilingiri, K.; Caprioli, F.; Botti, F.; Mapelli, M.; Meller, S.; Kislat, A.; Homey, B.; Di Sabatino, A.; Sonzogni, A.; et al. Dichotomy of short and long thymic stromal lymphopoietin isoforms in inflammatory disorders of the bowel and skin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonesson, A.; Kasetty, G.; Olin, A.I.; Malmsten, M.; Mörgelin, M.; Sørensen, O.E.; Schmidtchen, A. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin exerts antimicrobial activities. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M.; Hirota, T.; Jodo, A.I.; Doi, S.; Kameda, M.; Fujita, K.; Miyatake, A.; Enomoto, T.; Noguchi, E.; Yoshihara, S.; et al. Functional analysis of the thymic stromal lymphopoietin variants in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 40, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenberg, M.E.; Spergel, J.M.; Sherrill, J.D.; Annaiah, K.; Martin, L.J.; Cianferoni, A.; Gober, L.; Kim, C.; Glessner, J.; Frackelton, E.; et al. Common variants at 5q22 associate with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mjösberg, J.; Bernink, J.; Golebski, K.; Karrich, J.J.; Peters, C.P.; Blom, B.; te Velde, A.A.; Fokkens, W.J.; van Drunen, C.M.; Spits, H. The transcription factor GATA3 is essential for the function of human type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Immunity 2012, 37, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melum, G.R.; Farkas, L.; Scheel, C.; Van Dieren, B.; Gran, E.; Liu, Y.J.; Johansen, F.E.; Jahnsen, F.L.; Baekkevold, E.S. A thymic stromal lymphopoietin-responsive dendritic cell subset mediates allergic responses in the upper airway mucosa. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumelis, V.; Reche, P.A.; Kanzler, H.; Yuan, W.; Edward, G.; Homey, B.; Gilliet, M.; Ho, S.; Antonenko, S.; Lauerma, A.; et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, H.; Takai, T.; Le, T.A.; Kamijo, S.; Wang, X.L.; Ushio, H.; Hara, M.; Kawasaki, J.; Vu, A.T.; Ogawa, T.; et al. Cytokine milieu modulates release of thymic stromal lymphopoietin from human keratinocytes stimulated with double-stranded RNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Favoreto, S.; Avila, P.C.; Schleimer, R.P. TLR3- and Th2 cytokine-dependent production of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in human airway epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontenot, D.; He, H.; Hanabuchi, S.; Nehete, P.N.; Zhang, M.; Chang, M.; Nehete, B.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Ma, Z.M.; et al. TSLP production by epithelial cells exposed to immunodeficiency virus triggers DC-mediated mucosal infection of CD4+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16776–16781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allakhverdi, Z.; Comeau, M.R.; Jessup, H.K.; Yoon, B.R.; Brewer, A.; Chartier, S.; Paquette, N.; Ziegler, S.F.; Sarfati, M.; Delespesse, G. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is released by human epithelial cells in response to microbes, trauma, or inflammation and potently activates mast cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Comeau, M.R.; De Smedt, T.; Liggitt, H.D.; Dahl, M.E.; Lewis, D.B.; Gyarmati, D.; Aye, T.; Campbell, D.J.; Ziegler, S.F. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a key initiator of allergic airway inflammation in mice. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headley, M.B.; Zhou, B.; Shih, W.X.; Aye, T.; Comeau, M.R.; Ziegler, S.F. TSLP conditions the lung immune environment for the generation of pathogenic innate and antigen-specific adaptive immune responses. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Omori, M.; Gyarmati, D.; Zhou, B.; Aye, T.; Brewer, A.; Comeau, M.R.; Campbell, D.J.; Ziegler, S.F. Spontaneous atopic dermatitis in mice expressing an inducible thymic stromal lymphopoietin transgene specifically in the skin. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergot, A.S.; Monnet, N.; Le Tran, S.; Mittal, D.; Al-Kouba, J.; Steptoe, R.J.; Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Frazer, I.H.; Wells, J.W. HPV16 E7 expression in skin induces TSLP secretion, type 2 ILC infiltration and atopic dermatitis-like lesions. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmutovic-Persson, I.; Akbarshahi, H.; Bartlett, N.W.; Glanville, N.; Johnston, S.L.; Brandelius, A.; Uller, L. Inhaled dsRNA and rhinovirus evoke neutrophilic exacerbation and lung expression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in allergic mice with established experimental asthma. Allergy 2014, 69, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Messaddeq, N.; Teletin, M.; Pasquali, J.L.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P. Retinoid X receptor ablation in adult mouse keratinocytes generates an atopic dermatitis triggered by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14795–14800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lay, M.K.; Céspedes, P.F.; Palavecino, C.E.; León, M.A.; Díaz, R.A.; Salazar, F.J.; Méndez, G.P.; Bueno, S.M.; Kalergis, A.M. Human metapneumovirus infection activates the TSLP pathway that drives excessive pulmonary inflammation and viral replication in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 1680–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Geha, R.S. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1183, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, Y.; Kamijuku, H.; Taniguchi, M.; Ziegler, S.; Seino, K. Differential role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in the induction of airway hyperreactivity and Th2 immune response in antigen-induced asthma with respect to natural killer T cell function. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 144, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, I.; Watanabe, N.; Arima, K.; Liu, Y.J.; Leonard, W.J. Cutting edge: Direct action of thymic stromal lymphopoietin on activated human CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6720–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Hu, S.; Cheung, P.F.; Lam, C.W. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin induces chemotactic and prosurvival effects in eosinophils: Implications in allergic inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, S.F.; Artis, D. Sensing the outside world: TSLP regulates barrier immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, C.; Lechmann, M.; Brüstle, A.; Gareau, M.G.; Shuman, N.; Philpott, D.; Ziegler, S.F.; Mak, T.W. Thymic stromal lymphopoetin-induced expression of the endogenous inhibitory enzyme SLPI mediates recovery from colonic inflammation. Immunity 2011, 35, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, M.C.; Saenz, S.A.; Hill, D.A.; Kim, B.S.; Headley, M.B.; Doering, T.A.; Wherry, E.J.; Jessup, H.K.; Siegel, L.A.; Kambayashi, T.; et al. TSLP promotes interleukin-3-independent basophil haematopoiesis and type 2 inflammation. Nature 2011, 477, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arima, K.; Watanabe, N.; Hanabuchi, S.; Chang, M.; Sun, S.C.; Liu, Y.J. Distinct signal codes generate dendritic cell functional plasticity. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roan, F.; Bell, B.D.; Stoklasek, T.A.; Kitajima, M.; Han, H.; Ziegler, S.F. The multiple facets of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) during allergic inflammation and beyond. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Duramad, O.; Hori, T.; Delespesse, G.J.; Watanabe, N.; Qin, F.X.; Yao, Z.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.J. TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce an inflammatory T helper type 2 cell response through OX40 ligand. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimoldi, M.; Chieppa, M.; Salucci, V.; Avogadri, F.; Sonzogni, A.; Sampietro, G.M.; Nespoli, A.; Viale, G.; Allavena, P.; Rescigno, M. Intestinal immune homeostasis is regulated by the crosstalk between epithelial cells and dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 507–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliev, I.D.; Spadoni, I.; Mileti, E.; Matteoli, G.; Sonzogni, A.; Sampietro, G.M.; Foschi, D.; Caprioli, F.; Viale, G.; Rescigno, M. Human intestinal epithelial cells promote the differentiation of tolerogenic dendritic cells. Gut 2009, 58, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G. Improved methods for classification, prediction, and design of antimicrobial peptides. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1268, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brogden, K.A. Antimicrobial peptides: Pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.P.; Hancock, R.E. The relationship between peptide structure and antibacterial activity. Peptides 2003, 24, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schittek, B.; Hipfel, R.; Sauer, B.; Bauer, J.; Kalbacher, H.; Stevanovic, S.; Schirle, M.; Schroeder, K.; Blin, N.; Meier, F.; et al. Dermcidin: A novel human antibiotic peptide secreted by sweat glands. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, G.; Beckloff, N.; Weinberg, A.; Kisich, K.O. The roles of antimicrobial peptides in innate host defense. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2377–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guani-Guerra, E.; Santos-Mendoza, T.; Lugo-Reyes, S.O.; Teran, L.M. Antimicrobial peptides: General overview and clinical implications in human health and disease. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 135, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, R.; Harder, J.; Lange, H.; Bartels, J.; Christophers, E.; Schroder, J.M. Antimicrobial psoriasin (S100A7) protects human skin from Escherichia coli infection. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, O.E.; Follin, P.; Johnsen, A.H.; Calafat, J.; Tjabringa, G.S.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Borregaard, N. Human cathelicidin, hCAP-18, is processed to the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 by extracellular cleavage with proteinase 3. Blood 2001, 97, 3951–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordahl, E.A.; Rydengard, V.; Nyberg, P.; Nitsche, D.P.; Morgelin, M.; Malmsten, M.; Björck, L.; Schmidtchen, A. Activation of the complement system generates antibacterial peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16879–16884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papareddy, P.; Rydengard, V.; Pasupuleti, M.; Walse, B.; Morgelin, M.; Chalupka, A.; Malmsten, M.; Schmidtchen, A. Proteolysis of human thrombin generates novel host defense peptides. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papareddy, P.; Kalle, M.; Kasetty, G.; Mörgelin, M.; Rydengård, V.; Albiger, B.; Lundqvist, K.; Malmsten, M.; Schmidtchen, A. C-terminal peptides of tissue factor pathway inhibitor are novel host defense molecules. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 28387–28398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, B.S. The role of microorganisms in atopic dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 144, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Wu, Z.; Nuding, S.; Groscurth, S.; Marcinowski, M.; Beisner, J.; Buchner, J.; Schaller, M.; Stange, E.F.; Wehkamp, J. Reduction of disulphide bonds unmasks potent antimicrobial activity of human β-defensin 1. Nature 2011, 469, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bjerkan, L.; Sonesson, A.; Schenck, K. Multiple Functions of the New Cytokine-Based Antimicrobial Peptide Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP). Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030041
Bjerkan L, Sonesson A, Schenck K. Multiple Functions of the New Cytokine-Based Antimicrobial Peptide Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP). Pharmaceuticals. 2016; 9(3):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030041
Chicago/Turabian StyleBjerkan, Louise, Andreas Sonesson, and Karl Schenck. 2016. "Multiple Functions of the New Cytokine-Based Antimicrobial Peptide Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP)" Pharmaceuticals 9, no. 3: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030041
APA StyleBjerkan, L., Sonesson, A., & Schenck, K. (2016). Multiple Functions of the New Cytokine-Based Antimicrobial Peptide Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP). Pharmaceuticals, 9(3), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030041