Self-Assembly 4-Butylresorcinol Deep Eutectic Solvent Nanoparticles for Efficient Transdermal Delivery and Whitening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
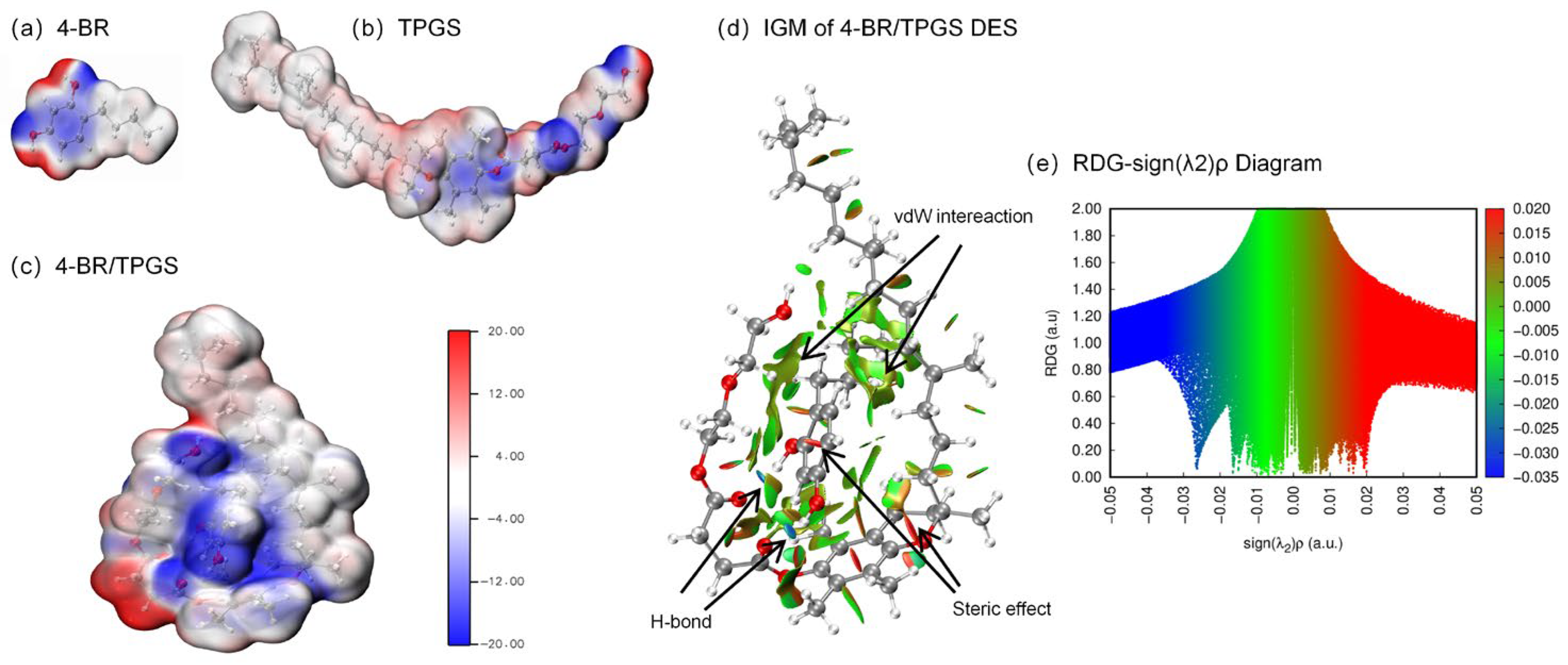
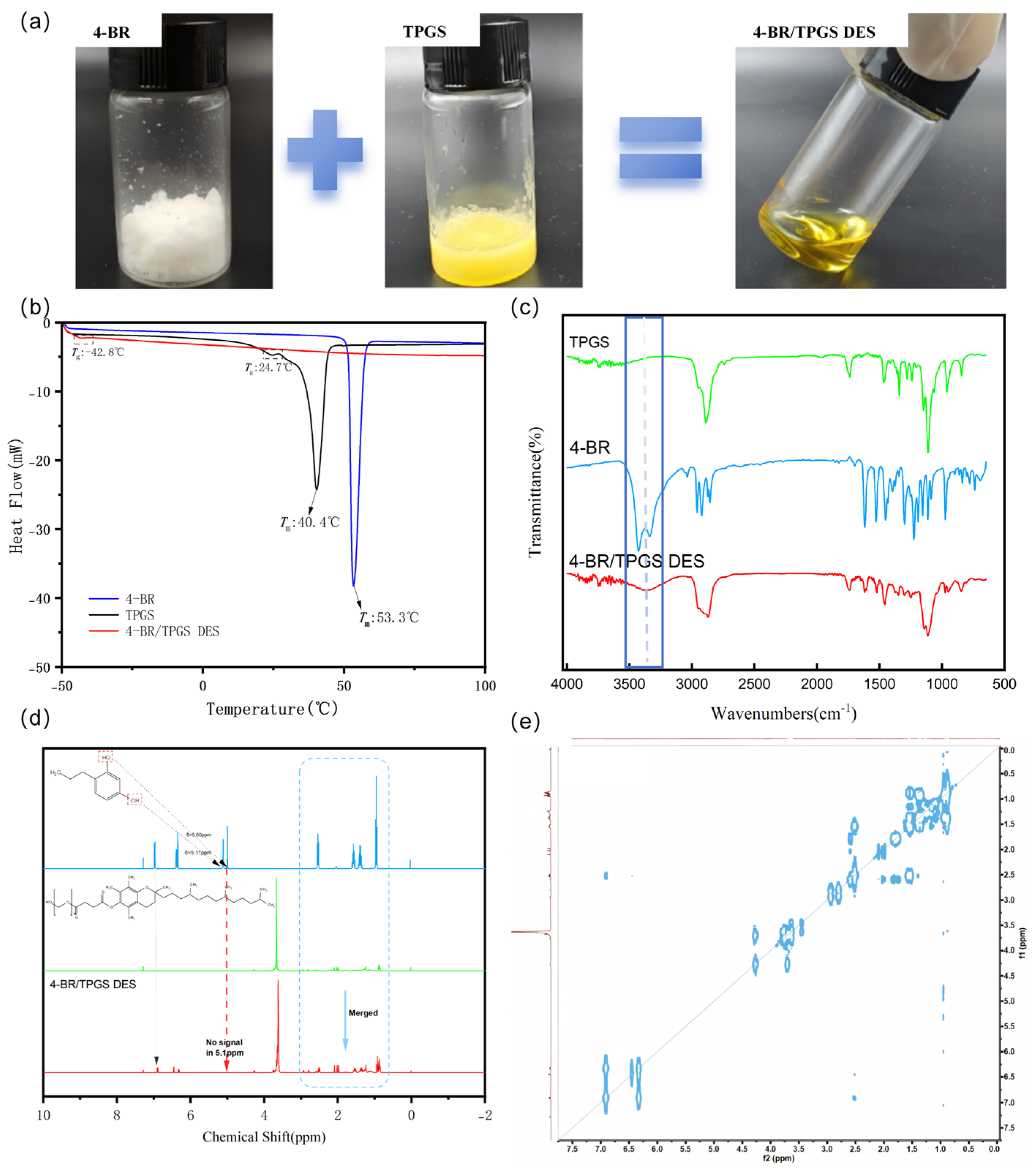
2.1. Properties of 4-BR/TPGS DES
2.2. Properties of 4-BR/TPGS DES NPs
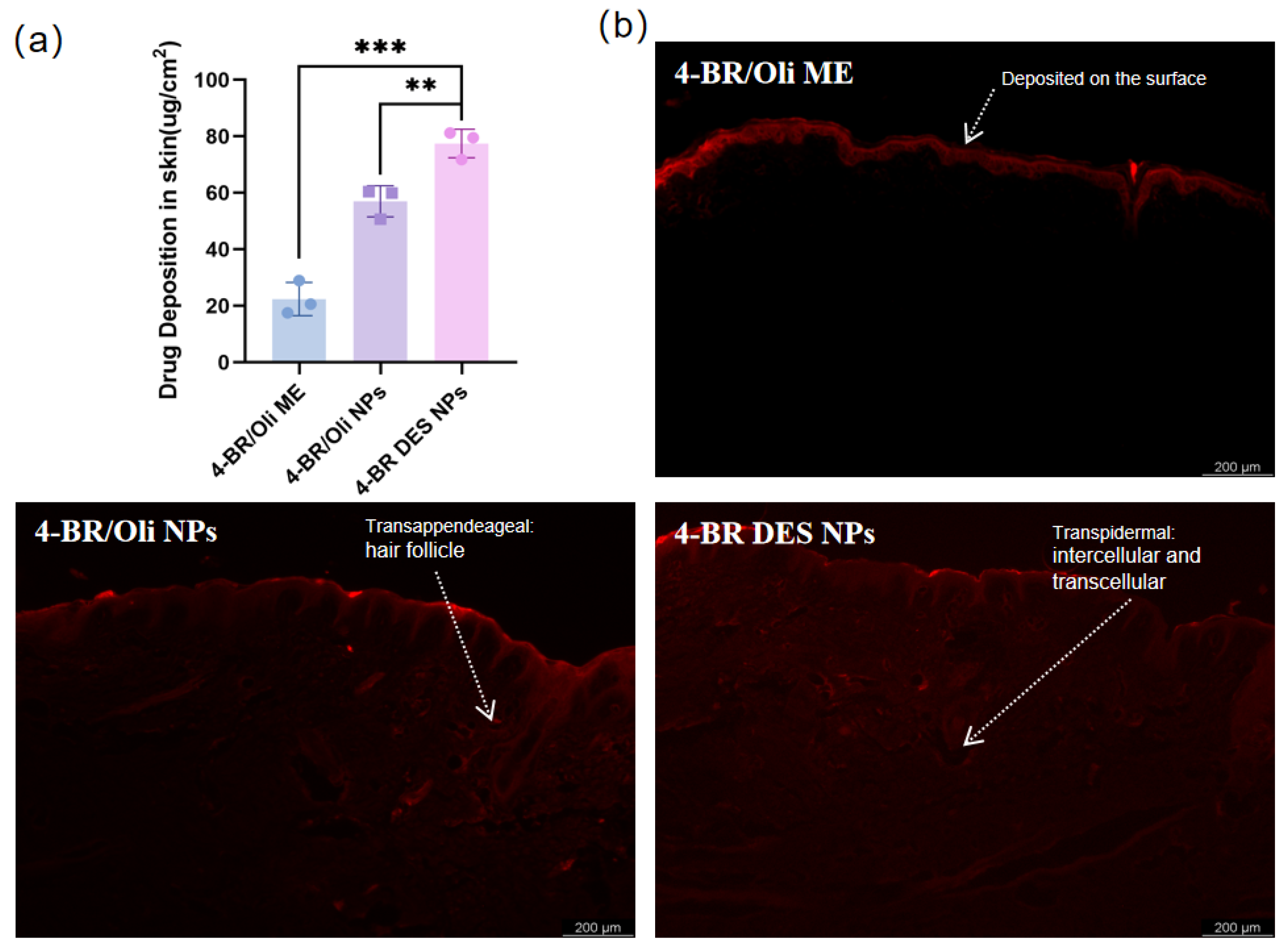
2.3. In Vitro Permeation Experiment
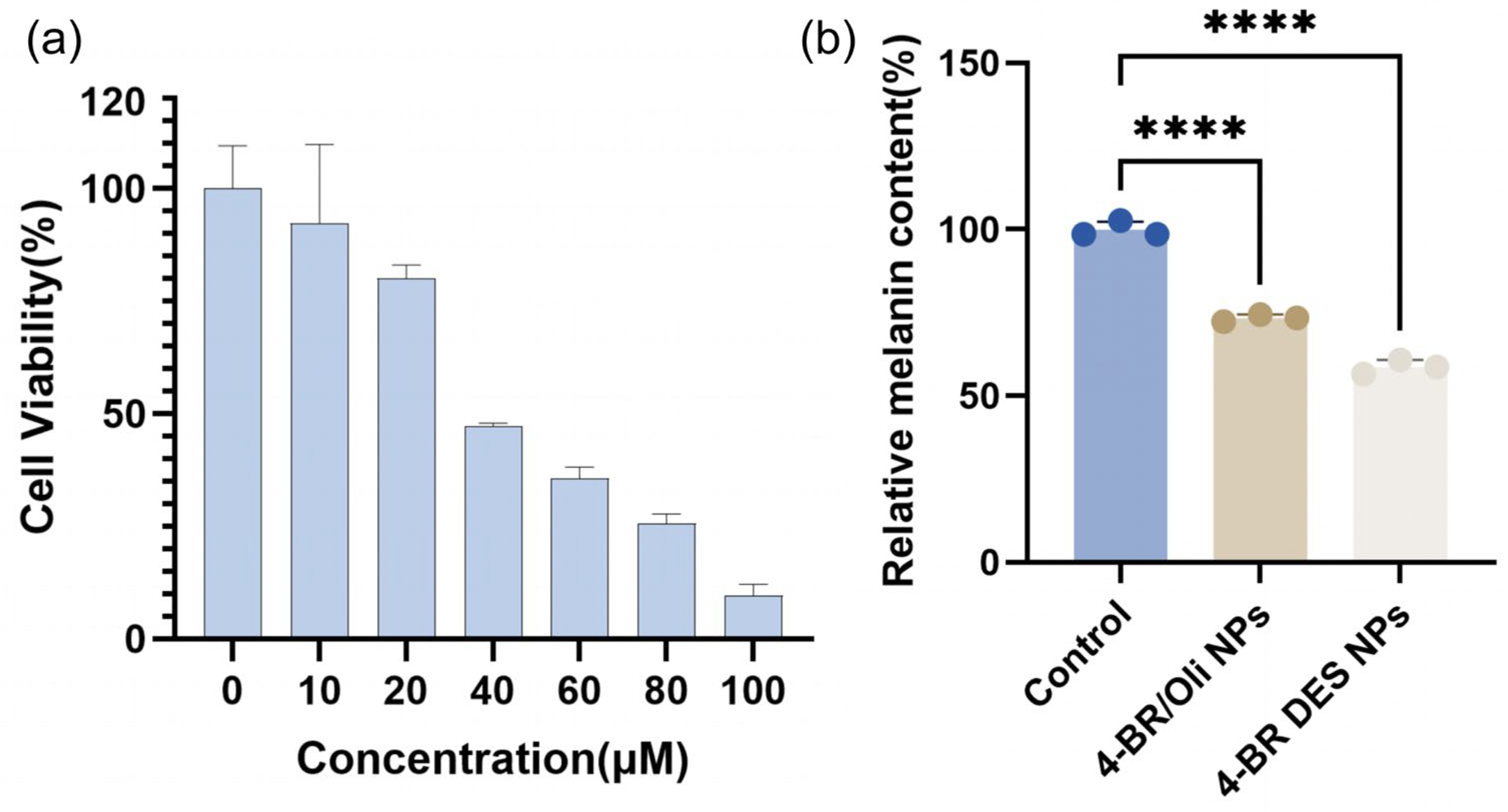
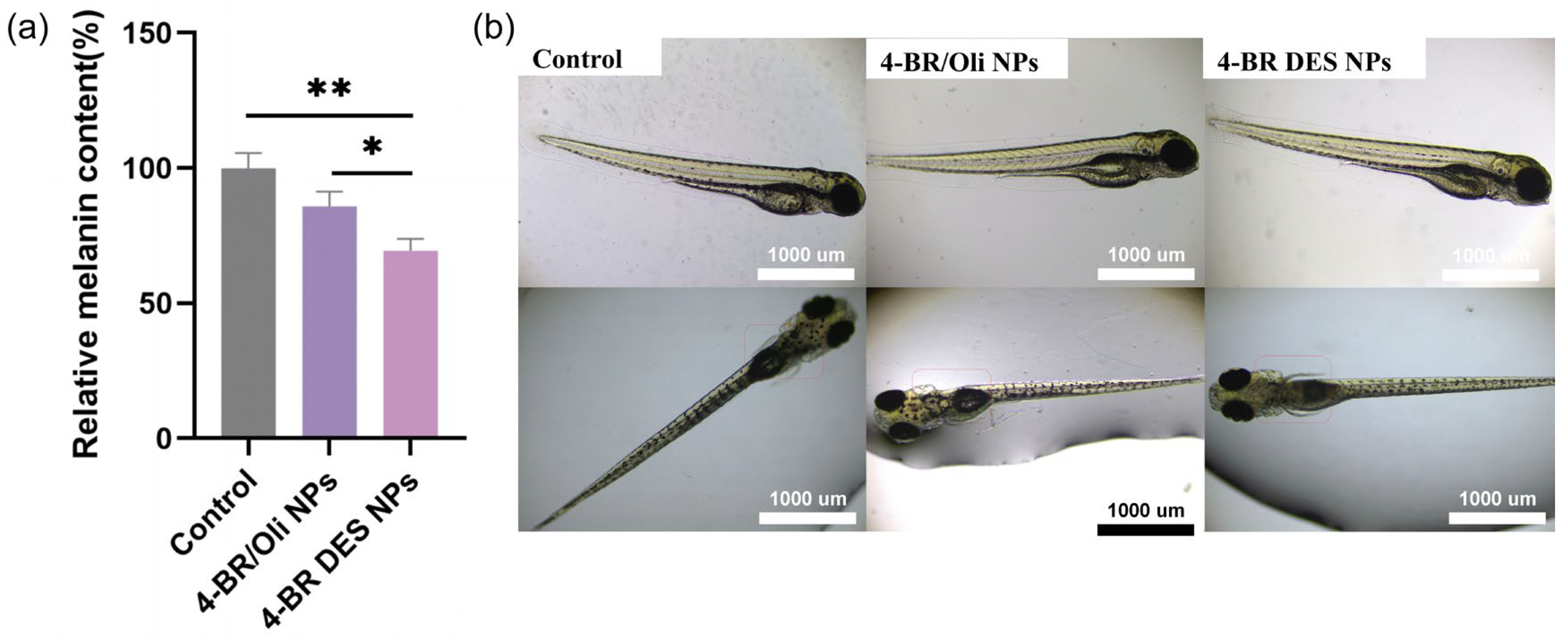
2.4. Whitening Activity of 4-BR/TPGS DES NPs
- (1)
- Properties of TPGS (a component of 4-BR/TPGS DES): As an FDA-approved pharmaceutical excipient, TPGS is a derivative of vitamin E with well-documented antioxidant properties and the ability to mitigate oxidative stress. Additionally, TPGS acts as an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated drug efflux. For instance, Pankaj Kumar Sharma et al. reviewed the antioxidant properties of TPGS in oxidative stress-mediated ocular diseases and its role as a P-gp inhibitor, which can prevent nasolacrimal drainage of drugs [6]. Similarly, Muhammad Asim Farooq et al. summarized that TPGS may bind to the non-transport active sites of P-gp, leading to conformational changes and disrupting its transport function, thereby enhancing its anticancer effects [23]. Given that elevated oxidative stress, higher ROS levels, increased intracellular accumulation of 4-BR (due to P-gp-mediated efflux inhibition) in B16 cells can lead to enhanced melanin production, the antioxidant and P-gp inhibitory properties of TPGS may contribute to the observed whitening effects [24,25]. Although there are currently no direct reports on the effects of TPGS on B16 cells and zebrafish, the aforementioned mechanisms provide a plausible explanation for the observed phenomenon.
- (2)
- Higher cellular uptake rate: The higher cellular uptake rate of 4-BR DES NPs may also contribute to their enhanced whitening activity [26]. The primary distinction between 4-BR/TPGS DES NPs and 4-BR/Oil NPs lies in their formulation composition. For the former, the melanin-inhibiting component 4-BR is dissolved with TPGS in a DES, which enhances the solubility of 4-BR. These NPs are assembled through high-pressure homogenization, with TPGS acting as a surfactant. For the letter, 4-BR is dissolved in olive oil (due to its poor water solubility) and stabilized by the nonionic surfactant Tween 80. Similar to traditional 4-BR preparations, results in the simultaneous uptake of olive oil during cellular absorption by B16 cells and zebrafish, thereby hindering the efficient absorption of 4-BR.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Preparation of 4-BR/TPGS DES
3.2.2. Theoretical Calculation Methods
3.2.3. Characterization of 4-BR/TPGS DES
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.2.4. Preparation of 4-BR/TPGS DES Nanoparticles (4-BR/TPGS DES NPs)
3.2.5. Preparation of Olive-Oil Based Microemulsion (4-BR/Olive Oil ME)
3.2.6. Preparation of Olive-Oil Based Nanoparticles (4-BR/Olive Oil NPs)
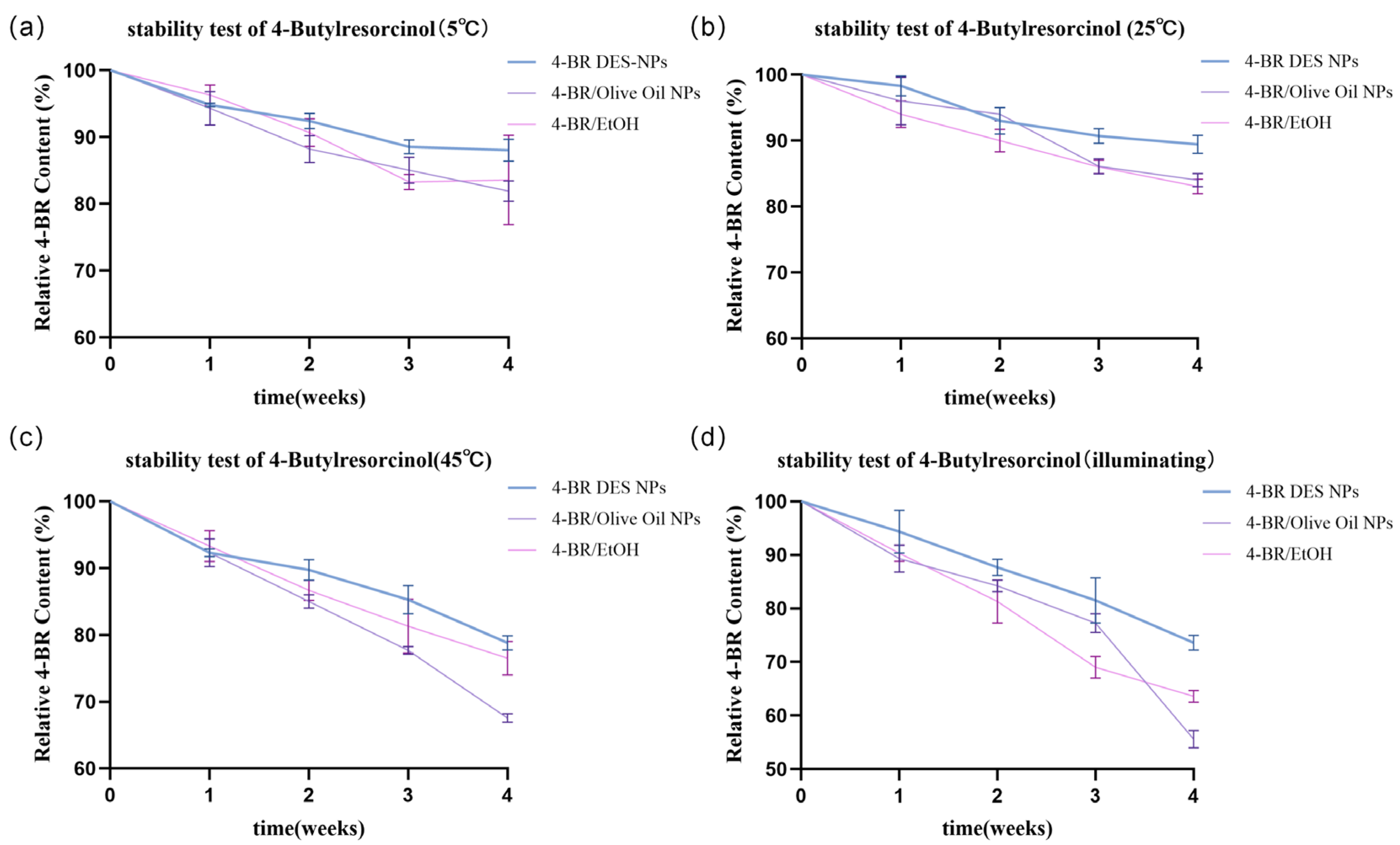
3.2.7. Stability Test of 4-BR in Above Formulations
3.3. Characterizations of 4-BR/TPGS DES NPs
3.3.1. Size, Zeta Potential and TEM of 4-BR/TPGS DES NPs
3.3.2. Ex Vivo Permeation Studies
3.3.3. In Vitro Assessment of Quantitative Permeation Using Intradermal Retention Test
3.3.4. In Vitro Assessment of Qualitative Permeation Using Inverted Fluorescence Microscope
3.4. Whitening Activity Assessment
3.4.1. Cell Culture
3.4.2. Cell Viability Assay of 4-BR/TPGS DES NPs in B16 Cells
3.4.3. Detection of Melanin Content in B16 Cells
3.4.4. Detection of Melanin Content in Zebrafish
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Vashi, N.A.; Kundu, R.V. Facial hyperpigmentation: Causes and treatment. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ephrem, E.; Elaissari, H.; Greige-Gerges, H. Improvement of skin whitening agents efficiency through encapsulation: Current state of knowledge. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbe, L.; Mann, T.; Gerwat, W.; Batzer, J.; Ahlheit, S.; Scherner, C.; Wenk, C.; Stäb, F. 4-n-butylresorcinol, a highly effective tyrosinase inhibitor for the topical treatment of hyperpigmentation. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Goswami, M.; Mittal, S.; Kundal, S. Recent Advancements in Transdermal Drug Delivery System: A Review: Pharmaceutical Science-Pharmaceutics. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharm. Res. 2023, 13, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan Mohan, N.T.; Gowda, A.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Sharath Kumar, B.C.; Shilpashree, P.; Gangaboraiah, B.; Shamanna, M. Assessment of efficacy, safety, and tolerability of 4-n-butylresorcinol 0.3% cream: An Indian multicentric study on melasma. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 9, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 205912, 4-Butylresorcinol; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.K.; Sharma, H.P.; Chakole, C.M.; Pandey, J.; Chauhan, M.K. Application of Vitamin E TPGS in ocular therapeutics—Attributes beyond excipient. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.N.; Liu, T.-S.; Zhu, X.-M.; Zhou, Y.-P.; Yao, J. Application of TPGS-based nano-drug delivery system in reversing P-gp mediated multidrug resistance. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2018, 53, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Ren, S.; Song, Y.; Quan, P.; Fang, L. Ionic liquids in transdermal drug delivery system: Current applications and future perspectives. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jiao, S.; Guo, S.; Xiao, T.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Xiong, S.; Xu, Y. Deep eutectic solvent self-assembled reverse nanomicelles for transdermal delivery of sparingly soluble drugs. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, M.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Cui, X.; Xu, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C. Noninvasive transdermal delivery of mesoporous silica nanoparticles using deep eutectic solvent. J. Control. Release 2022, 343, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, Q. Independent gradient model based on Hirshfeld partition: A new method for visual study of interactions in chemical systems. J. Comput. Chem. 2022, 43, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.N.; Yurek, G.J. Effect of alloy grain size and silicon content on the oxidation of austenitic Fe-Cr-Ni-Mn-Si alloys in pure O2. Oxid. Met. 1991, 36, 281–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xiao, T.; Guo, S.; Wu, Y.; Lai, R.; Liu, Z.; Luo, W.; Xu, Y. Oxymatrine-fatty acid deep eutectic solvents as novel penetration enhancers for transdermal drug delivery: Formation mechanism and enhancing effect. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 637, 122880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; An, Q.; Jin, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, L.; Du, G.; Lu, Y. Two Novel Co-Crystals of Naproxen: Comparison of Stability, Solubility and Intermolecular Interaction. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.; Pereira, C.V.; Mano, F.; Silva, E.; Castro, V.I.B.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Matias, A.A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Therapeutic Role of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Menthol and Saturated Fatty Acids on Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 4346–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadon, D.; McCrudden, M.T.; Courtenay, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Enhancement strategies for transdermal drug delivery systems: Current trends and applications. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 12, 758–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakamy, N.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Ahmed, O.A.A. Vitamin E TPGS based transferosomes augmented TAT as a promising delivery system for improved transdermal delivery of raloxifene. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ye, R.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Du, L.; Hu, F.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J. Retinoid-loaded ionic liquid nanoparticles: Decreased irritation, enhanced transdermal delivery and synergistic anti-wrinkle. Appl. Mater. Today 2025, 44, 102735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgheti-Cardoso, L.N.; Vicentini, F.T.M.D.C.; Gratieri, T.; Bentley, M.V.L.B. Liquid crystalline systems containing Vitamin E TPGS for the controlled transdermal nicotine delivery. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 52, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapierre-Landry, M.; Huckenpahler, A.L.; Link, B.A.; Collery, R.F.; Carroll, J.; Skala, M.C. Imaging Melanin Distribution in the Zebrafish Retina Using Photothermal Optical Coherence Tomography. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Trevaskis, N.L. TPGS Decorated Liposomes as Multifunctional Nano-Delivery Systems. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meira, W.V.; Heinrich, T.A.; Cadena, S.M.S.C.; Martinez, G.R. Melanogenesis inhibits respiration in B16-F10 melanoma cells whereas enhances mitochondrial cell content. Exp. Cell. Res. 2017, 350, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Son, Y.H.; Lee, K.B.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Jeong, E.M.; Park, S.C.; Kim, I.-G. 4-n-butylresorcinol enhances proteolytic degradation of tyrosinase in B16F10 melanoma cells. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Bai, Y. Cellulose nanocomposite modified conductive self-healing hydrogel with enhanced mechanical property. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 146, 110258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Revision A.03; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitragotri, S.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Transdermal Drug Delivery Using Low-Frequency Sonophoresis. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Shi, X.; Ma, Y. Spatiotemporal mapping of gene expression landscapes and developmental trajectories during zebrafish embryogenesis. Dev. Cell 2022, 57, 1284–1298.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Y.; Hu, Y.T.; Hu, J.Y.; Chang, W.C.; Huang, Q.; Hsieh, S.C. Nanoemulsified adlay bran oil reduces tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in B16F10 cells and zebrafish. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, H.; Hu, D.; Deng, Y.; Song, J.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, C.; Zeng, B. Self-Assembly 4-Butylresorcinol Deep Eutectic Solvent Nanoparticles for Efficient Transdermal Delivery and Whitening. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091383
Han H, Hu D, Deng Y, Song J, Sheng Y, Liu J, Wu C, Zeng B. Self-Assembly 4-Butylresorcinol Deep Eutectic Solvent Nanoparticles for Efficient Transdermal Delivery and Whitening. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(9):1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091383
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Hongtao, Dan Hu, Yaoming Deng, Jiayi Song, Yuyang Sheng, Jingxin Liu, Chengyu Wu, and Bin Zeng. 2025. "Self-Assembly 4-Butylresorcinol Deep Eutectic Solvent Nanoparticles for Efficient Transdermal Delivery and Whitening" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 9: 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091383
APA StyleHan, H., Hu, D., Deng, Y., Song, J., Sheng, Y., Liu, J., Wu, C., & Zeng, B. (2025). Self-Assembly 4-Butylresorcinol Deep Eutectic Solvent Nanoparticles for Efficient Transdermal Delivery and Whitening. Pharmaceuticals, 18(9), 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18091383





