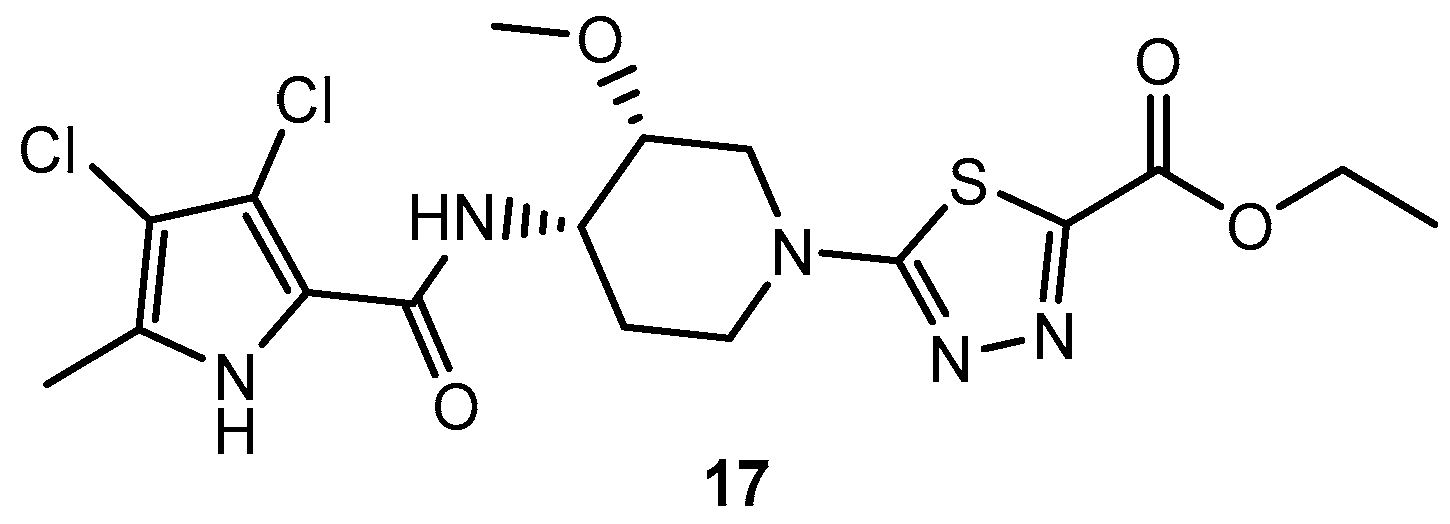
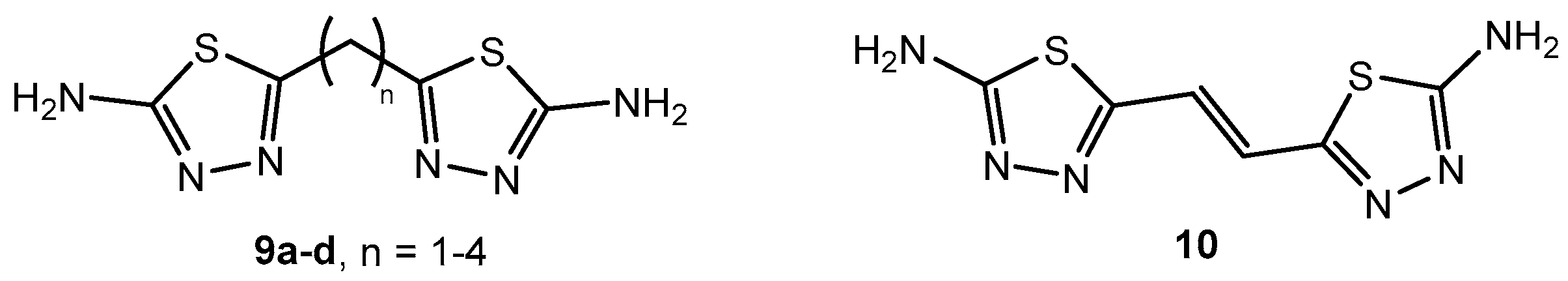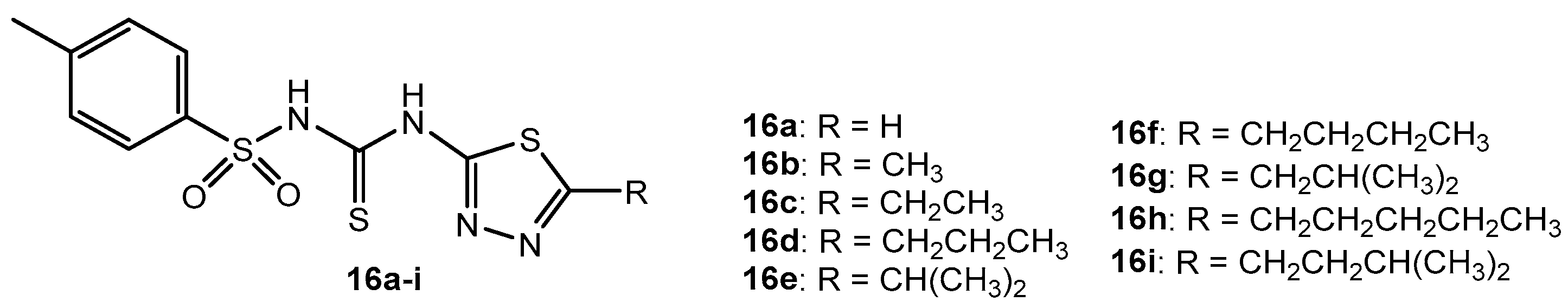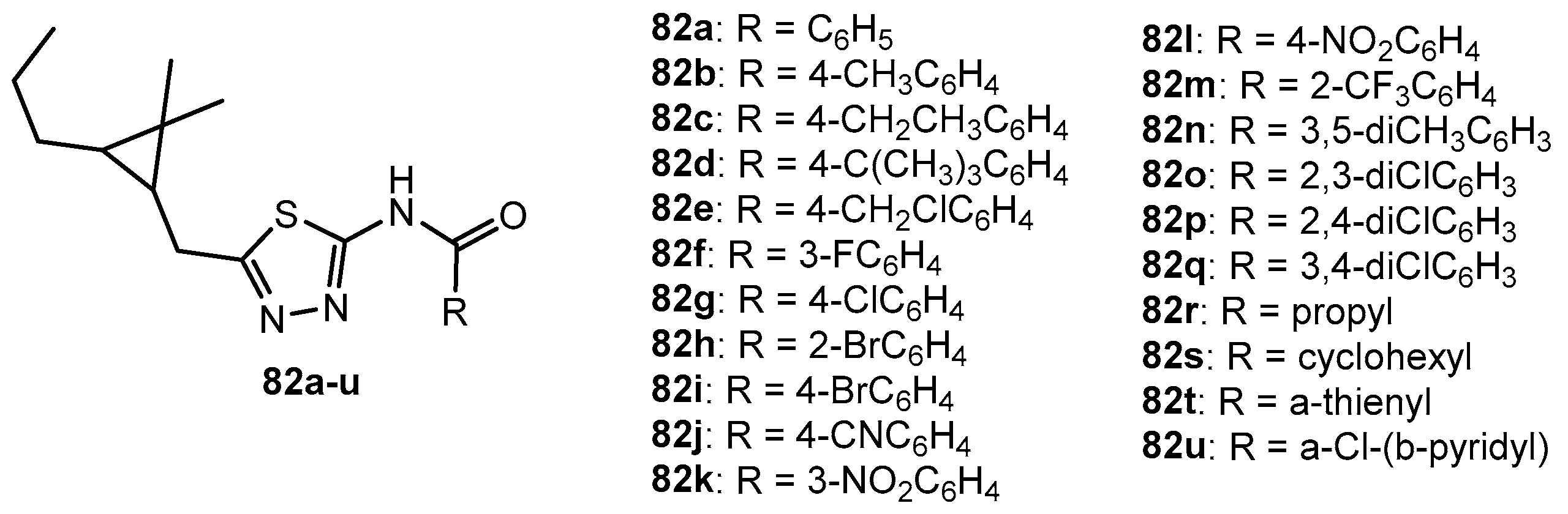Figure 1.
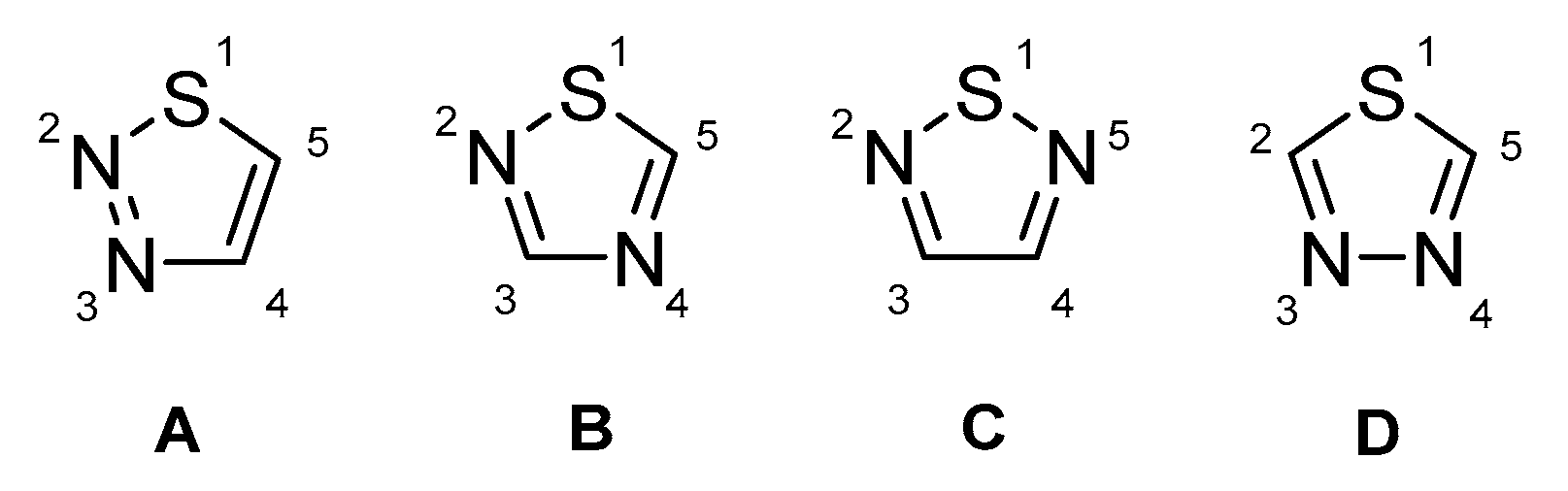
Possible isomers of thiadiazole core: A: 1,2,3-thiadiazole; B: 1,2,4-thiadiazole; C: 1,2,5-thiadiazole; D: 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 1.
Possible isomers of thiadiazole core: A: 1,2,3-thiadiazole; B: 1,2,4-thiadiazole; C: 1,2,5-thiadiazole; D: 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Scheme 1.
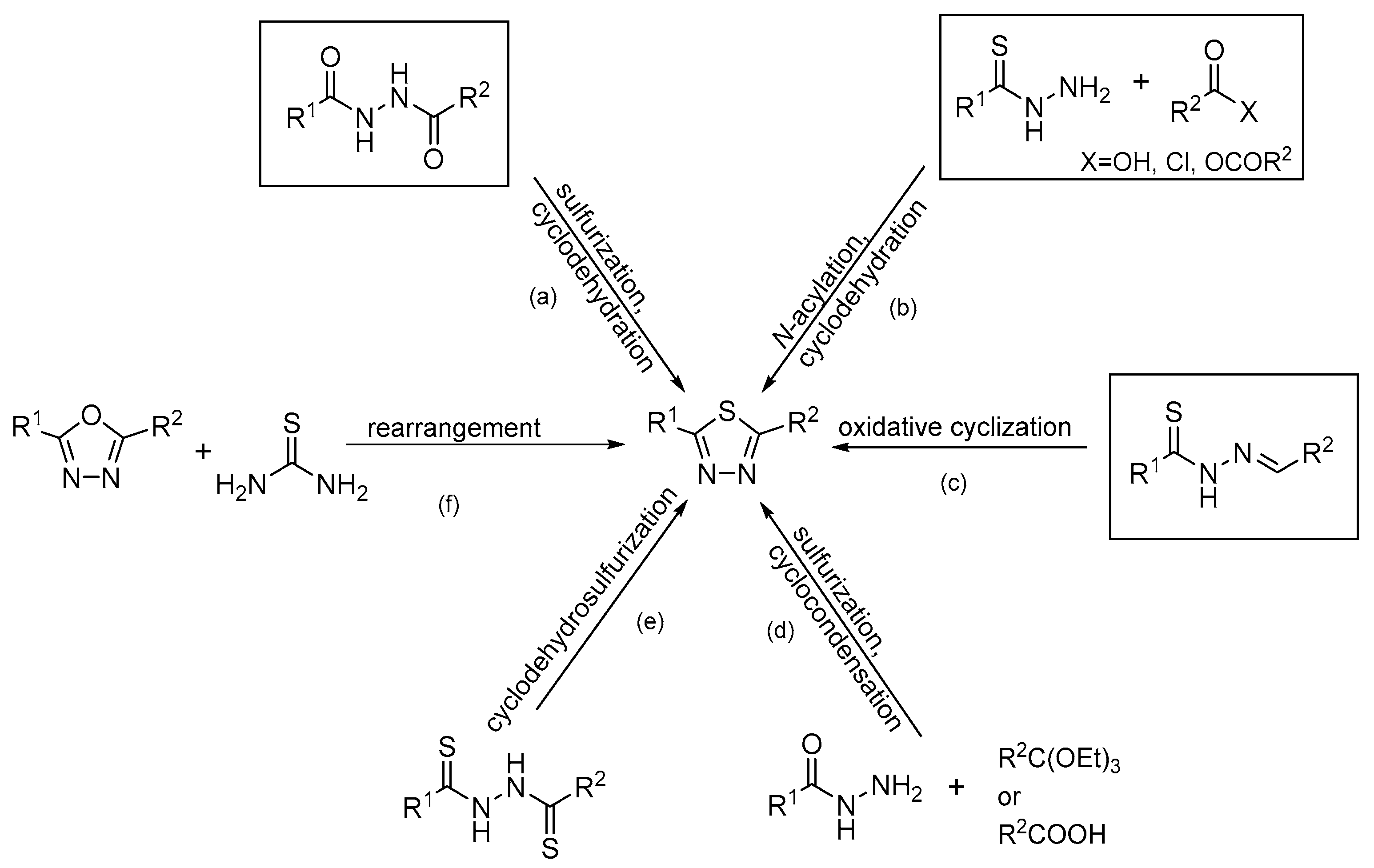
The most popular synthetic routes for the disubstituted 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivative: (a): sulfurization and cyclodehydration step; (b): N-acylation and cyclodehydration step; (c): oxidative cyclization step; (d): sulfurization and cyclocondensation step; (e): cyclodehydrosulfurization step; (f): rearrangement step.
Scheme 1.
The most popular synthetic routes for the disubstituted 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivative: (a): sulfurization and cyclodehydration step; (b): N-acylation and cyclodehydration step; (c): oxidative cyclization step; (d): sulfurization and cyclocondensation step; (e): cyclodehydrosulfurization step; (f): rearrangement step.
Figure 2.
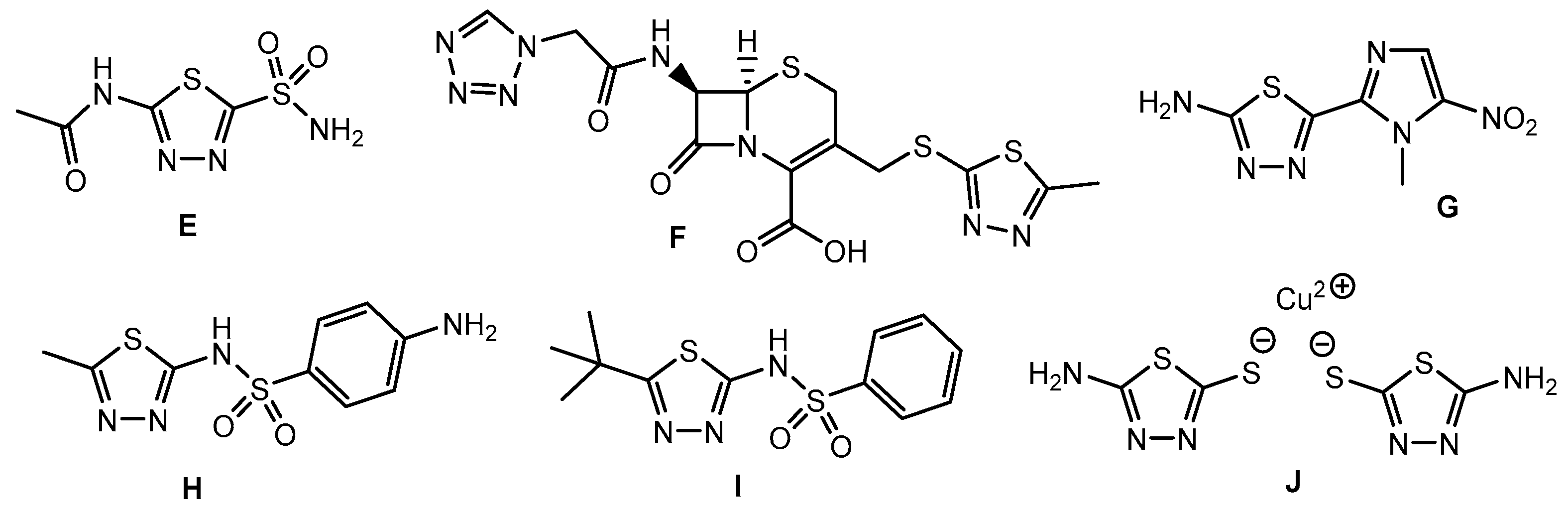
Representative drugs and reference standards characterized by the presence of the 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring. E: Acetazolamide—diuretic, antiglaucoma, anticonvulsant, and treatment for altitude sickness. F: Cefazolin—treats bacterial infections (especially Gram-positive). G: Megazol—antiparasitic agent (investigated for Chagas disease and sleeping sickness). H: Sulfamethizole—treats urinary tract infections (UTIs) and other bacterial infections. I: Gludiase—treats type 2 diabetes mellitus by stimulating insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. J: Thiodiazole copper—a type of copper-based antimicrobial compound often used to control a wide range of plant diseases caused by bacteria and fungi.
Figure 2.
Representative drugs and reference standards characterized by the presence of the 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring. E: Acetazolamide—diuretic, antiglaucoma, anticonvulsant, and treatment for altitude sickness. F: Cefazolin—treats bacterial infections (especially Gram-positive). G: Megazol—antiparasitic agent (investigated for Chagas disease and sleeping sickness). H: Sulfamethizole—treats urinary tract infections (UTIs) and other bacterial infections. I: Gludiase—treats type 2 diabetes mellitus by stimulating insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. J: Thiodiazole copper—a type of copper-based antimicrobial compound often used to control a wide range of plant diseases caused by bacteria and fungi.
Figure 3.
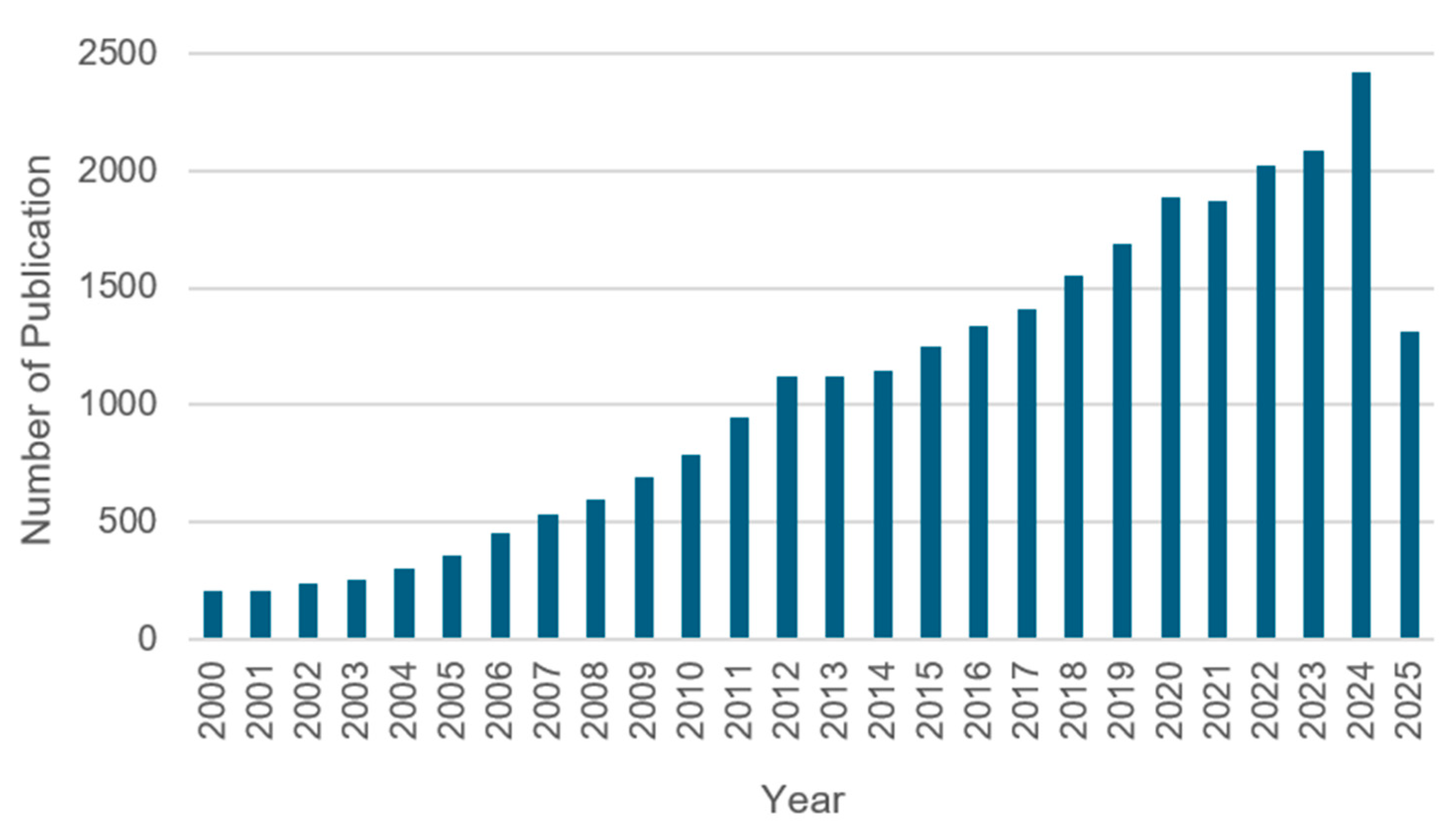
Number of relevant articles related to 1,3,4-thiadiazole published between 2000 and 2025. The data were obtained from Scopus. Search: 1,3,4-thiadiazole; all fields (accessed June 2025).
Figure 3.
Number of relevant articles related to 1,3,4-thiadiazole published between 2000 and 2025. The data were obtained from Scopus. Search: 1,3,4-thiadiazole; all fields (accessed June 2025).
Figure 4.
Oxazolidinones containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 4.
Oxazolidinones containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 5.
Dihydropyrrolidone derivatives with 1,3,4-thiadiazole core.
Figure 5.
Dihydropyrrolidone derivatives with 1,3,4-thiadiazole core.
Figure 6.
Two series of 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives containing (2H)-chromen-2-one moiety.
Figure 6.
Two series of 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives containing (2H)-chromen-2-one moiety.
Figure 7.
Phenylthiazole derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole thione moiety.
Figure 7.
Phenylthiazole derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole thione moiety.
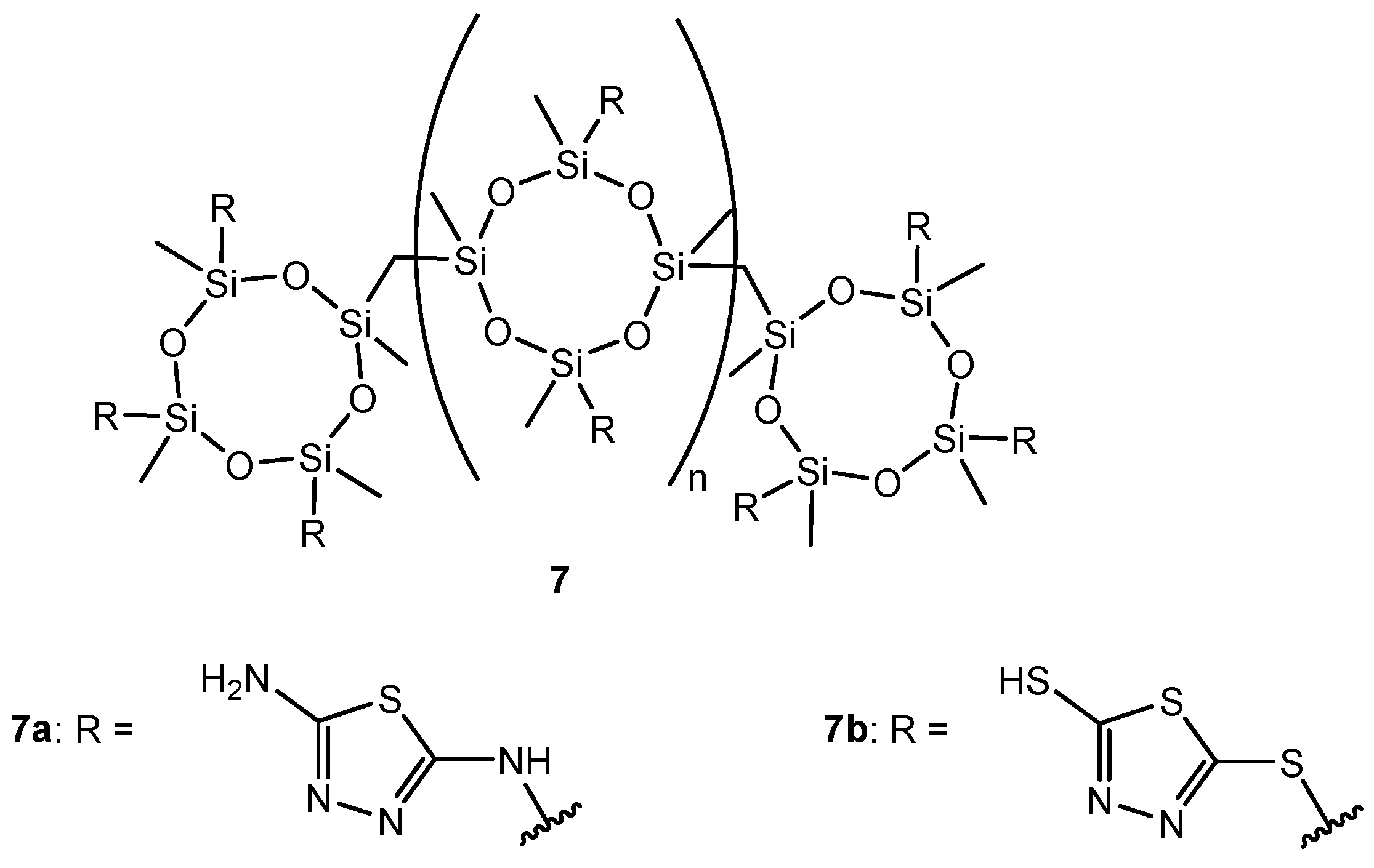
Figure 8.
The structure of mesostructured nanohybrids of thiadiazole.
Figure 8.
The structure of mesostructured nanohybrids of thiadiazole.
Figure 9.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole with benzo[d]imidazole scaffolds.
Figure 9.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole with benzo[d]imidazole scaffolds.
Figure 10.
The structure of bisaminothiadiazoles.
Figure 10.
The structure of bisaminothiadiazoles.
Figure 11.
The structure of thiadiazoles bearing Schiff base moiety.
Figure 11.
The structure of thiadiazoles bearing Schiff base moiety.
Figure 12.
The structure of pyrimidine derivatives incorporating amide and 1,3,4-thiadiazole thioether moiety.
Figure 12.
The structure of pyrimidine derivatives incorporating amide and 1,3,4-thiadiazole thioether moiety.
Figure 13.
The structure of 2-(pyrido[3,2-f]quinazolin-4(1H)-yl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 13.
The structure of 2-(pyrido[3,2-f]quinazolin-4(1H)-yl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
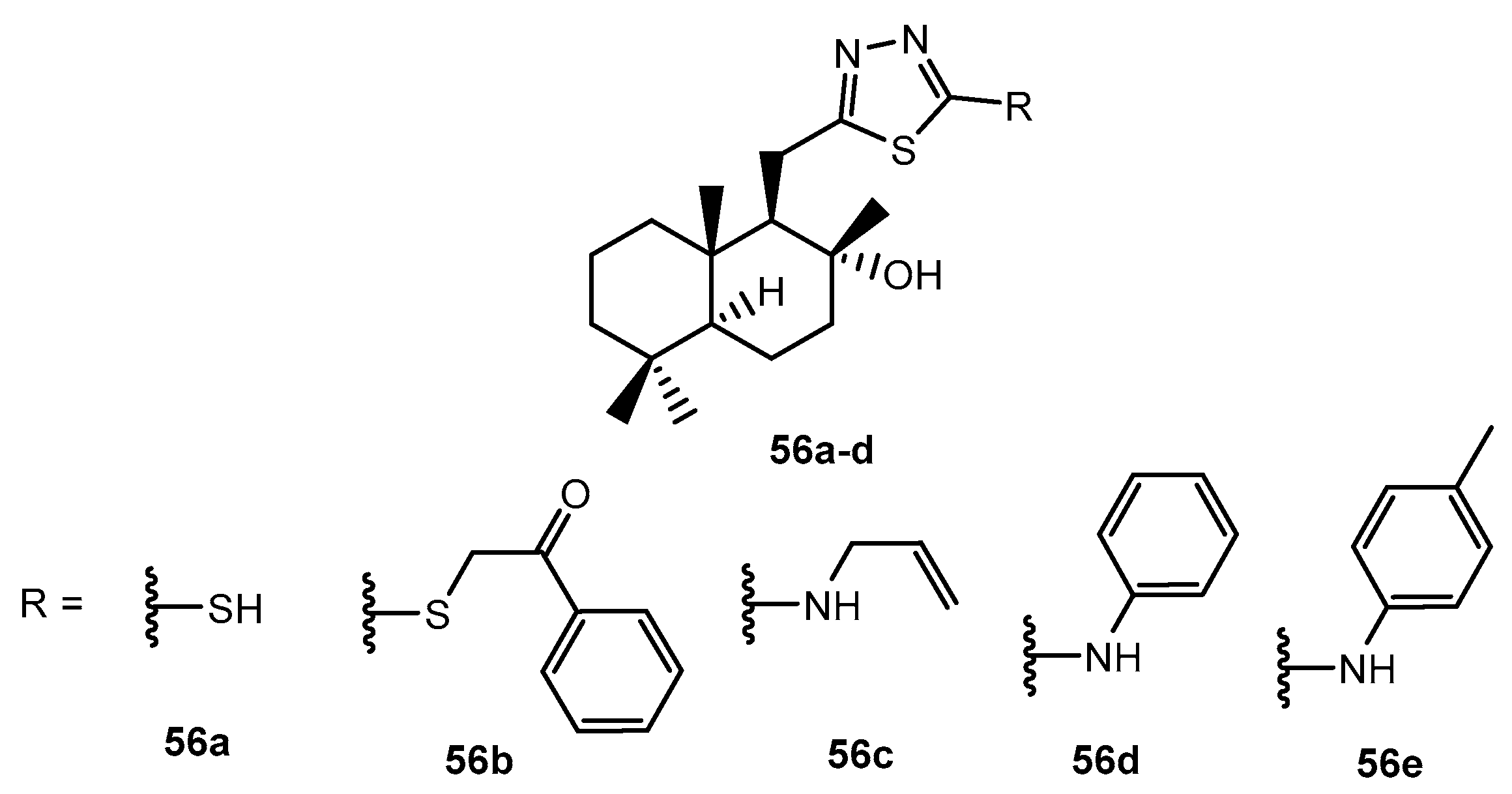
Figure 14.
The structure of tetranorlabdane-1,3,4-thiadiazole hybrid.
Figure 14.
The structure of tetranorlabdane-1,3,4-thiadiazole hybrid.
Figure 15.
The structure of functionalized chitosan with thio-thiadiazole scaffold.
Figure 15.
The structure of functionalized chitosan with thio-thiadiazole scaffold.
Figure 16.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole sulfonyl thiourea derivatives.
Figure 16.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole sulfonyl thiourea derivatives.
Figure 17.
The derivative of 1,3,4-thiadiazole connected to pyrroloamide.
Figure 17.
The derivative of 1,3,4-thiadiazole connected to pyrroloamide.
Figure 18.
The structure of the ligands containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 18.
The structure of the ligands containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 19.
Azetidin-2-one derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 19.
Azetidin-2-one derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 20.
Gallic acid amide derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 20.
Gallic acid amide derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 21.
Sparfloxacin derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 21.
Sparfloxacin derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 22.
The derivatives of 5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 22.
The derivatives of 5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 23.
S-Mercaptotriazolebenzothiazole-based derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 23.
S-Mercaptotriazolebenzothiazole-based derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 24.
2-Amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 24.
2-Amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 25.
Chiral derivative of 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 25.
Chiral derivative of 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 26.
1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives substituted with thiophene ring.
Figure 26.
1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives substituted with thiophene ring.
Figure 27.
The structure of 5-phenyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole azo dyes.
Figure 27.
The structure of 5-phenyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole azo dyes.
Figure 28.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole thioether derivatives.
Figure 28.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole thioether derivatives.
Figure 29.
The structure of galactosides containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 29.
The structure of galactosides containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 30.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole amine derivatives.
Figure 30.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole amine derivatives.
Figure 31.
The structure of benzimidazole-1,3,4-thiadiazole conjugates.
Figure 31.
The structure of benzimidazole-1,3,4-thiadiazole conjugates.
Figure 32.
Benzimidazole derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 32.
Benzimidazole derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 33.
A series of benzimidazoles containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 33.
A series of benzimidazoles containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 34.
Derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazole attached to thiazolidinone core.
Figure 34.
Derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazole attached to thiazolidinone core.
Figure 35.
The structure of a 2,5-dihydrazinyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole ligand.
Figure 35.
The structure of a 2,5-dihydrazinyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole ligand.
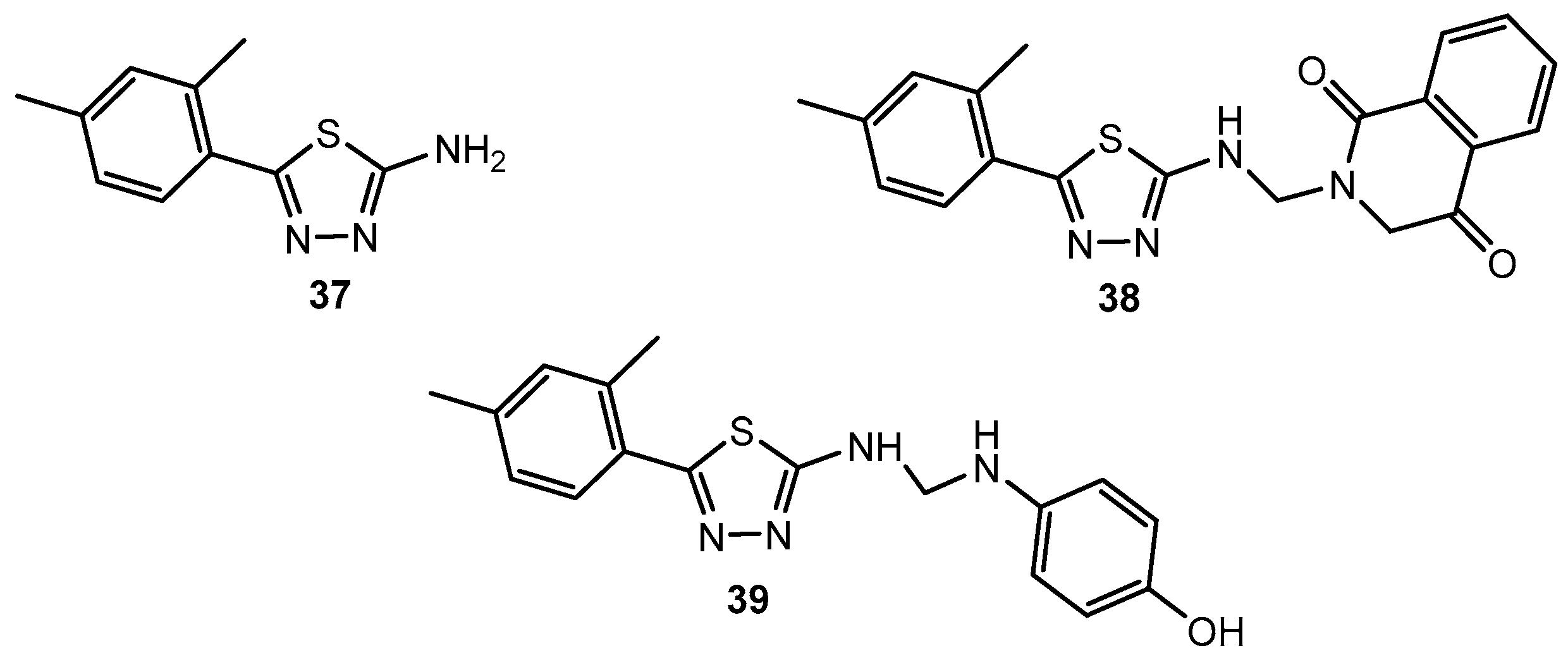
Figure 36.
The structure of 5-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-amine (37) and its derivatives.
Figure 36.
The structure of 5-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-amine (37) and its derivatives.
Figure 37.
Amoxicillin derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 37.
Amoxicillin derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 38.
The structure of the obtained 1,3,4-thiadiazole ligand bearing 2-(2-bromobenzylidene)hydrazinyl groups.
Figure 38.
The structure of the obtained 1,3,4-thiadiazole ligand bearing 2-(2-bromobenzylidene)hydrazinyl groups.
Figure 39.
2-sulfonamide-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 39.
2-sulfonamide-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
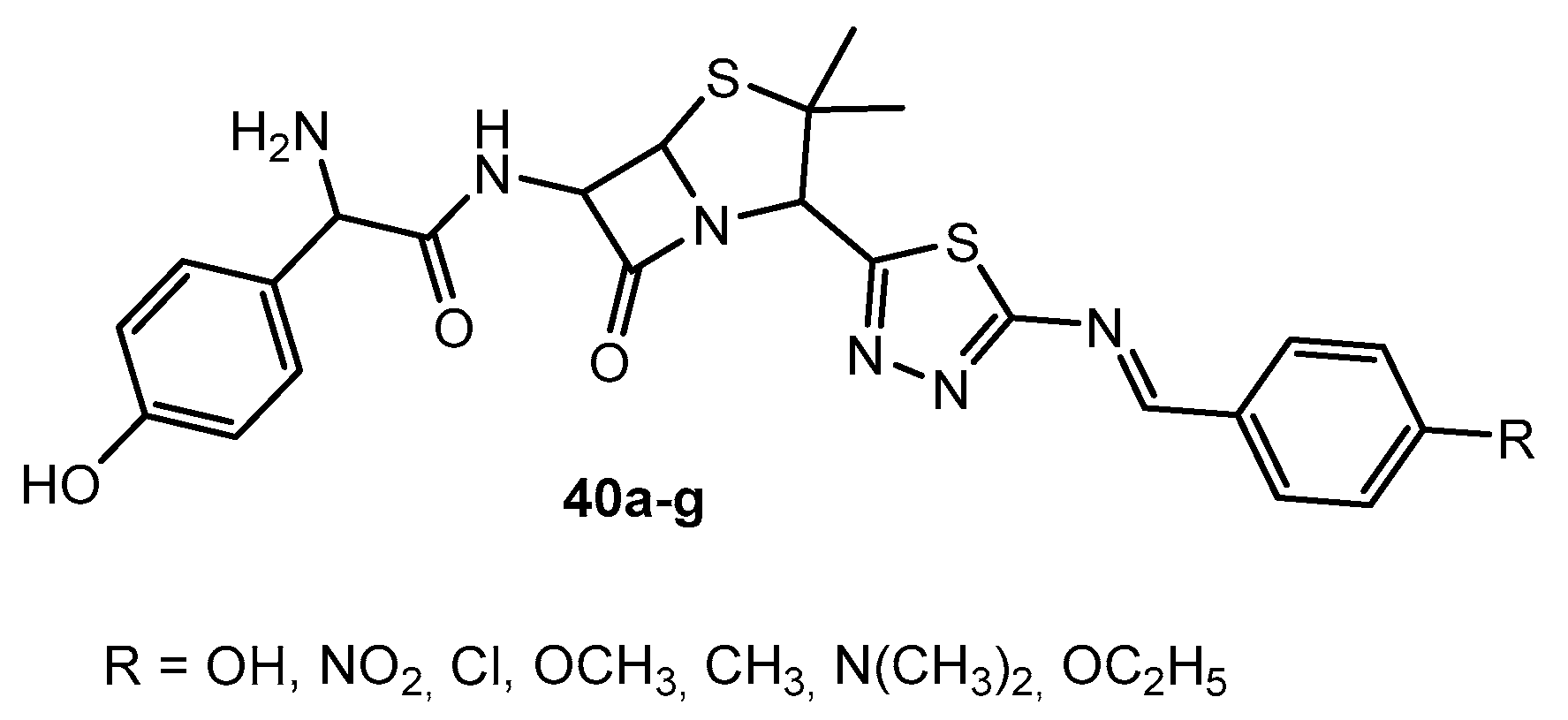
Figure 40.
The structures of the obtained 1,3,4-thiadiazole ligands and their metal complexes.
Figure 40.
The structures of the obtained 1,3,4-thiadiazole ligands and their metal complexes.
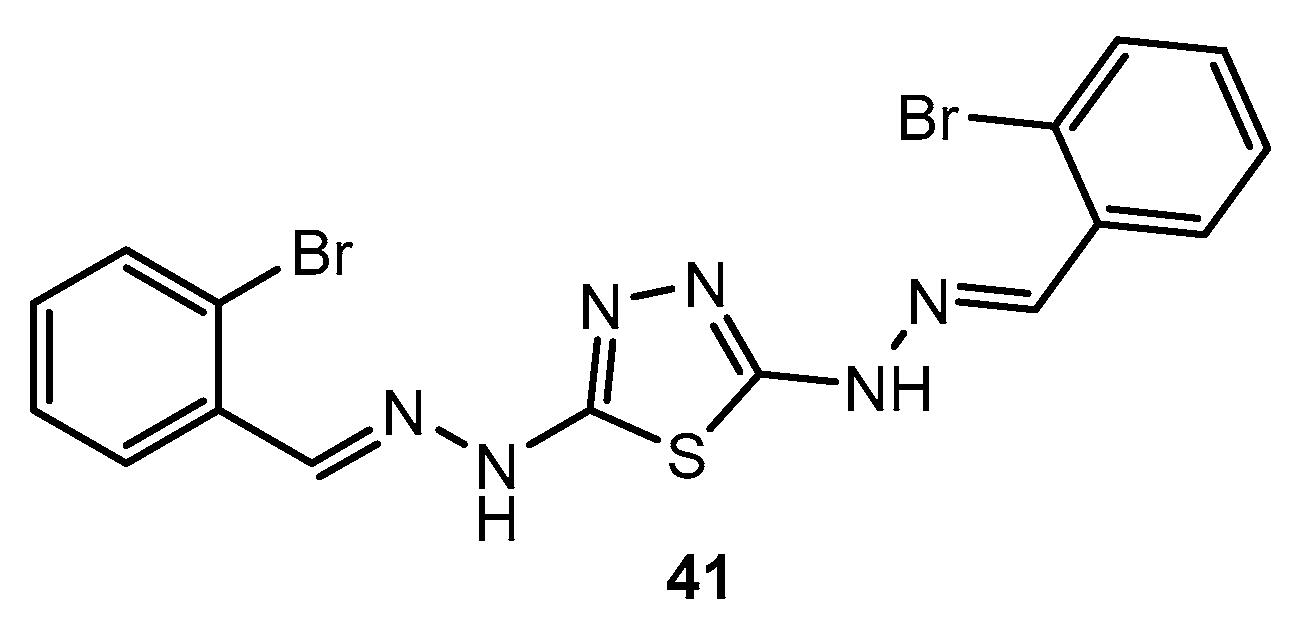
Figure 41.
A 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivative containing furan and benzimidazole scaffolds.
Figure 41.
A 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivative containing furan and benzimidazole scaffolds.
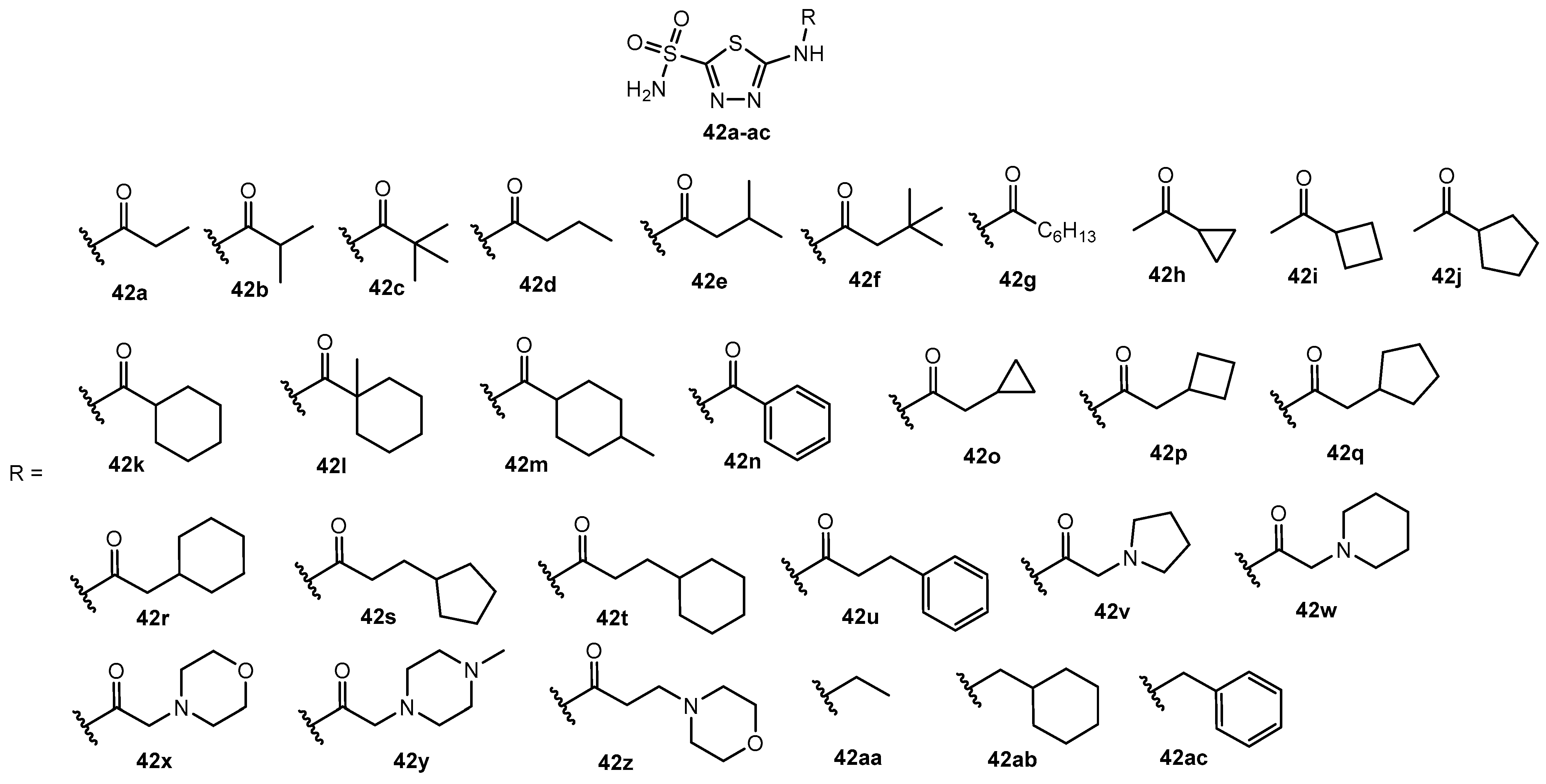
Figure 42.
A series of vanillin derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 42.
A series of vanillin derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 43.
Resveratrol derivatives bearing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 43.
Resveratrol derivatives bearing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 44.
Benzimidazole-based compounds bearing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 44.
Benzimidazole-based compounds bearing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 45.
The structure of novel homodrimane sesquiterpenoids bearing 1,3,4-thiadiazole units.
Figure 45.
The structure of novel homodrimane sesquiterpenoids bearing 1,3,4-thiadiazole units.
Figure 46.
Structures of benzamide derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 46.
Structures of benzamide derivatives containing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole ring.
Figure 47.
Ricinoleic acid derivatives bearing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
Figure 47.
Ricinoleic acid derivatives bearing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety.
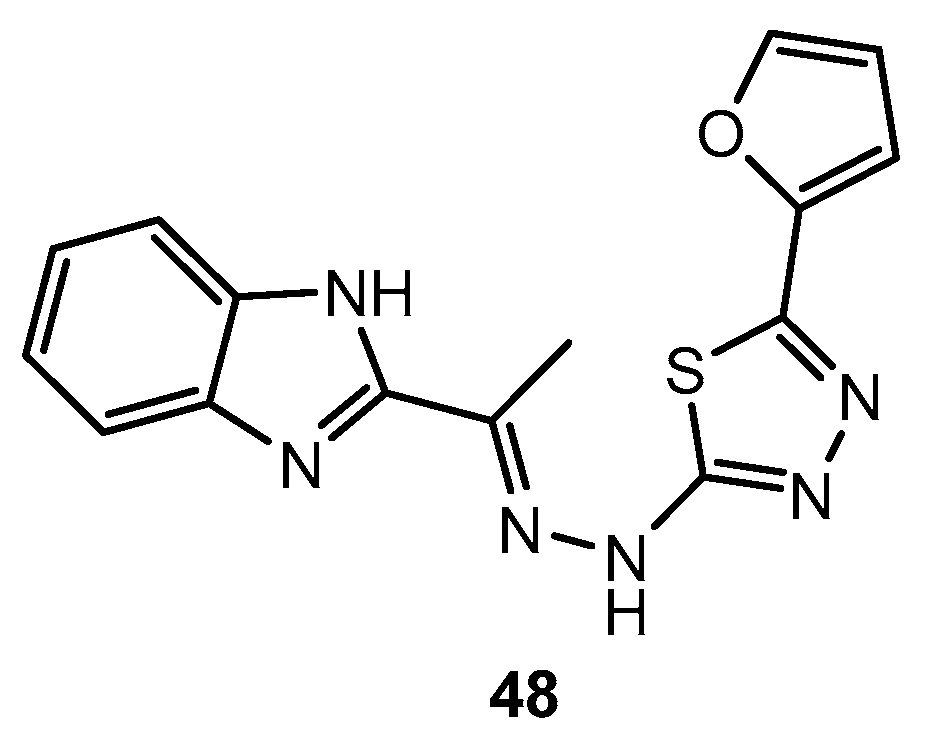
Figure 48.
Derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidin-5-one.
Figure 48.
Derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidin-5-one.
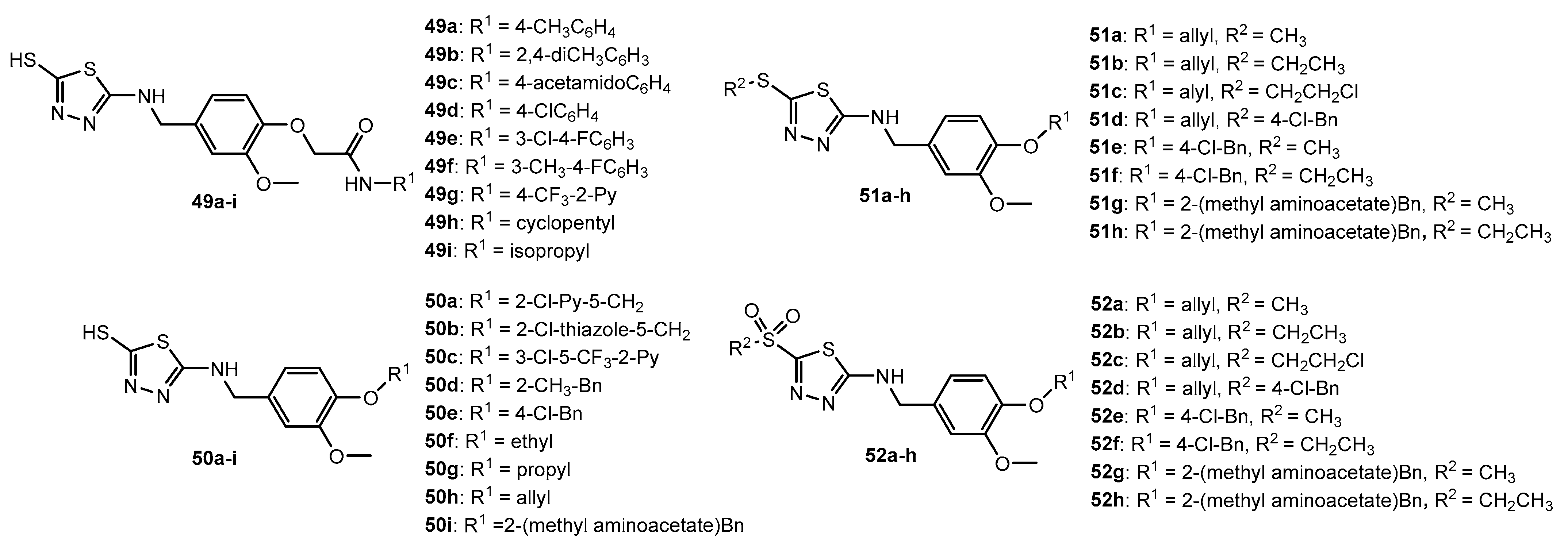
Figure 49.
Derivatives of [1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole bearing aryl substituents.
Figure 49.
Derivatives of [1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole bearing aryl substituents.
Figure 50.
The structure of quinazolin-4(3H)-one 1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole hybrids.
Figure 50.
The structure of quinazolin-4(3H)-one 1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole hybrids.
Figure 51.
Triazolo-based thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 51.
Triazolo-based thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 52.
The structure of bicyclic 1,3,4-thiadiazole-pyrimidine derivatives.
Figure 52.
The structure of bicyclic 1,3,4-thiadiazole-pyrimidine derivatives.
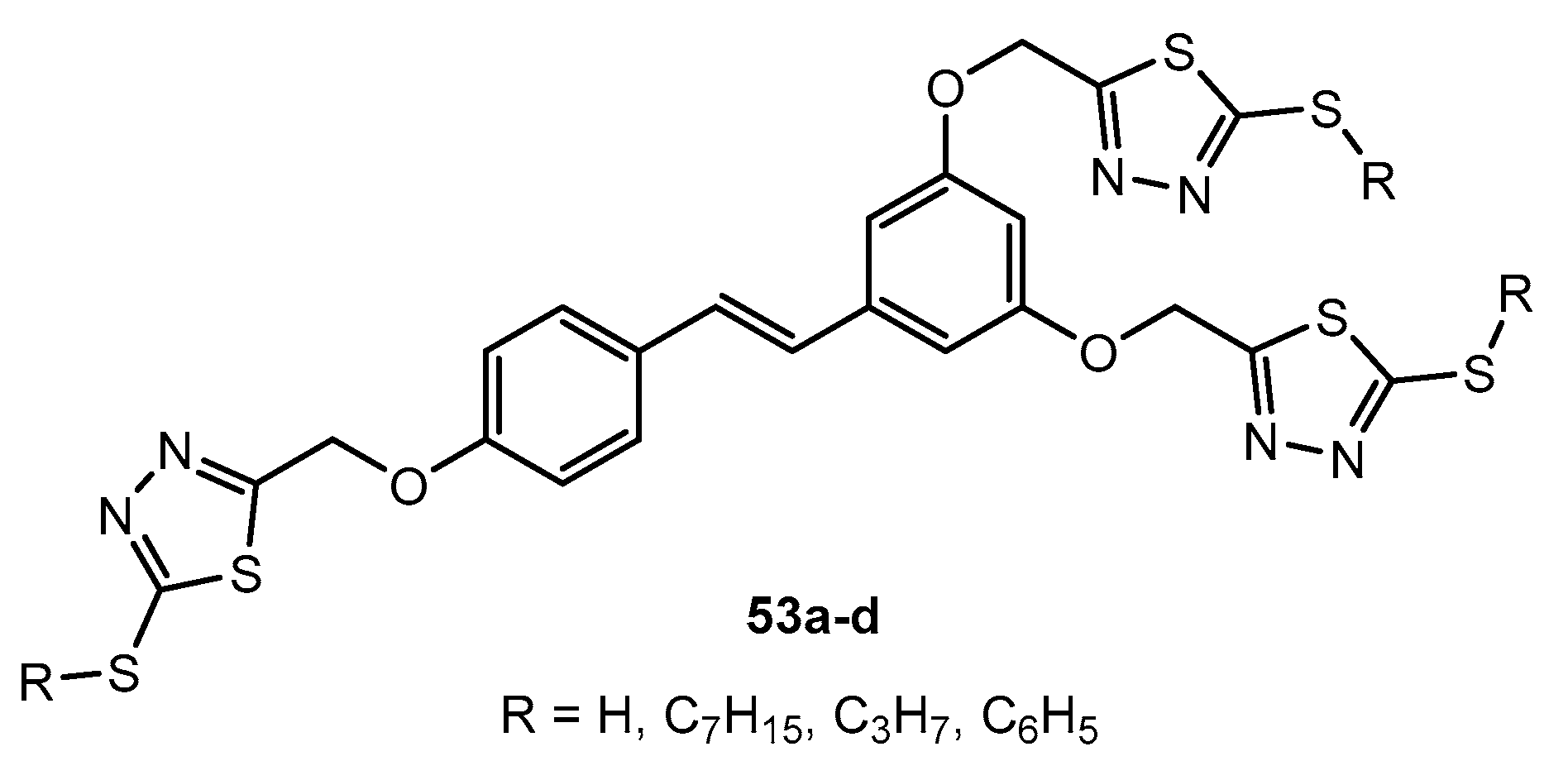
Figure 53.
Compounds containing the imidazo[2,1-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole scaffold.
Figure 53.
Compounds containing the imidazo[2,1-b][1,3,4]thiadiazole scaffold.
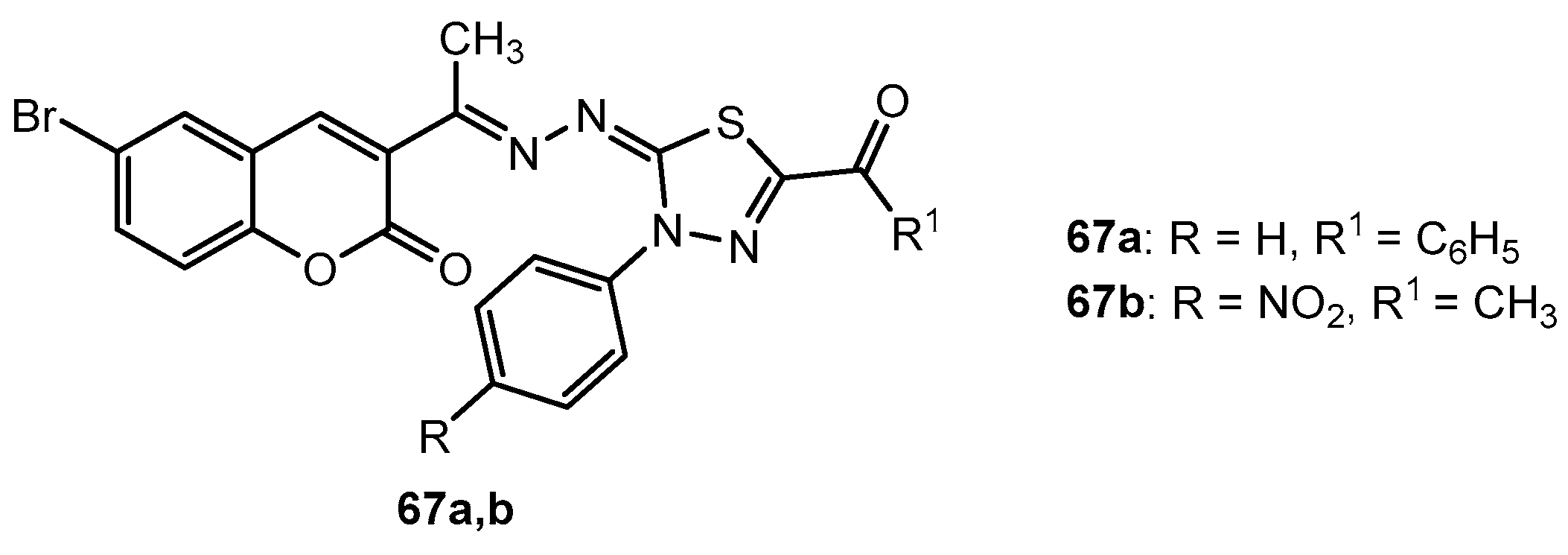
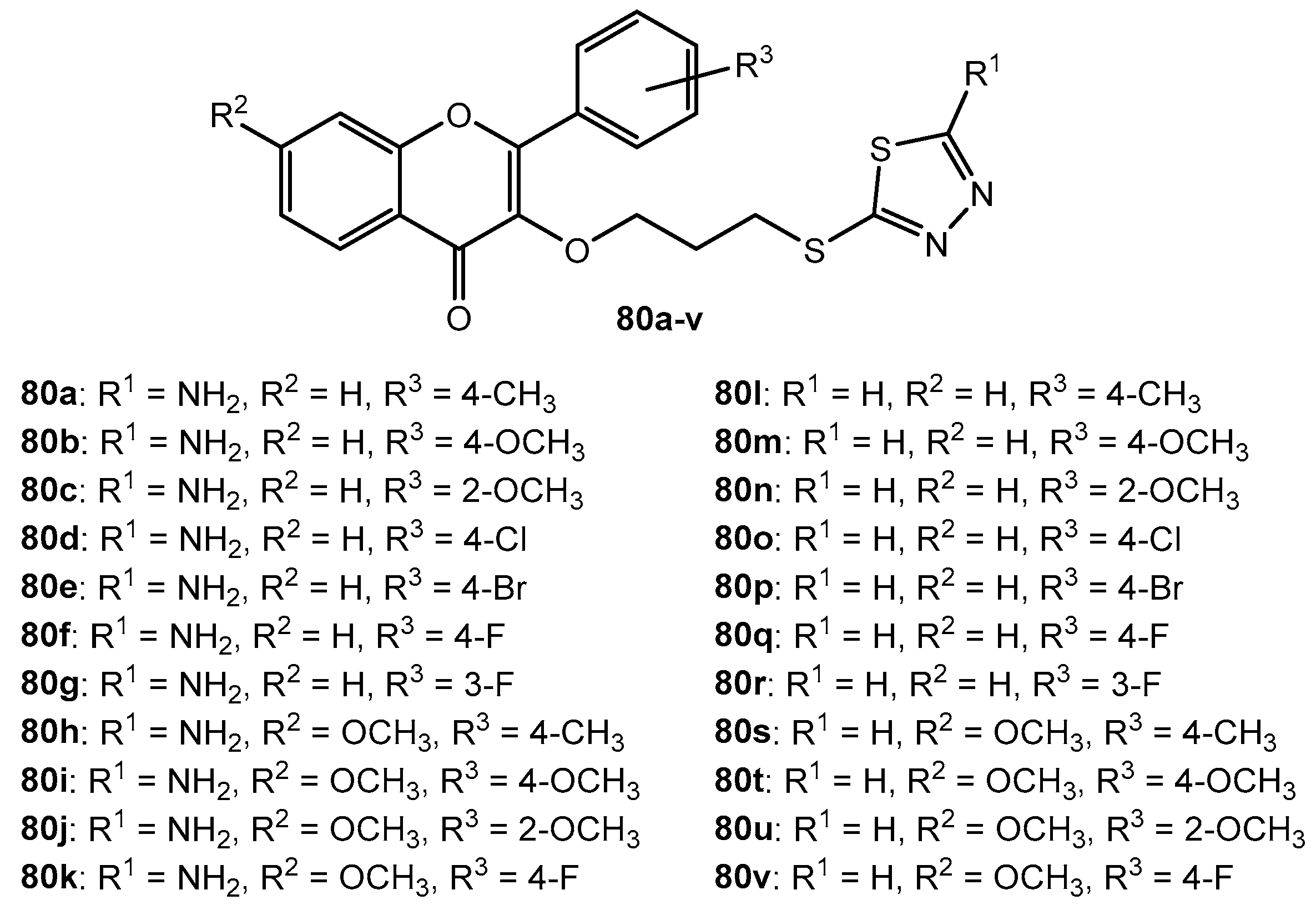
Figure 54.
The structure of tri-substituted 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives bearing acyl, aryl, and 2H-chromen-2-one scaffolds.
Figure 54.
The structure of tri-substituted 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives bearing acyl, aryl, and 2H-chromen-2-one scaffolds.
Figure 55.
The structure of 5-sulfonyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-substituted flavonoids.
Figure 55.
The structure of 5-sulfonyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-substituted flavonoids.
Figure 56.
The structure of 1,4-dihydropyridine hybrids with 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 56.
The structure of 1,4-dihydropyridine hybrids with 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 57.
The structure of the obtained tri-substituted 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 57.
The structure of the obtained tri-substituted 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 58.
The structure of tri-substituted 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 58.
The structure of tri-substituted 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 59.
The structure of L-carvone-based 1,3,4-thiadiazole-amide derivatives.
Figure 59.
The structure of L-carvone-based 1,3,4-thiadiazole-amide derivatives.
Figure 60.
The structure of indole derivatives containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 60.
The structure of indole derivatives containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 61.
The structure of chalcone derivatives containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 61.
The structure of chalcone derivatives containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 62.
The structure of 5-sulfonyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole flavonoids.
Figure 62.
The structure of 5-sulfonyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole flavonoids.
Figure 63.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl-benzamide derivatives.
Figure 63.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl-benzamide derivatives.
Figure 64.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-yl-pyrimidine derivatives.
Figure 64.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-yl-pyrimidine derivatives.
Figure 65.
Derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazole containing resorcinol moiety.
Figure 65.
Derivatives of 1,3,4-thiadiazole containing resorcinol moiety.
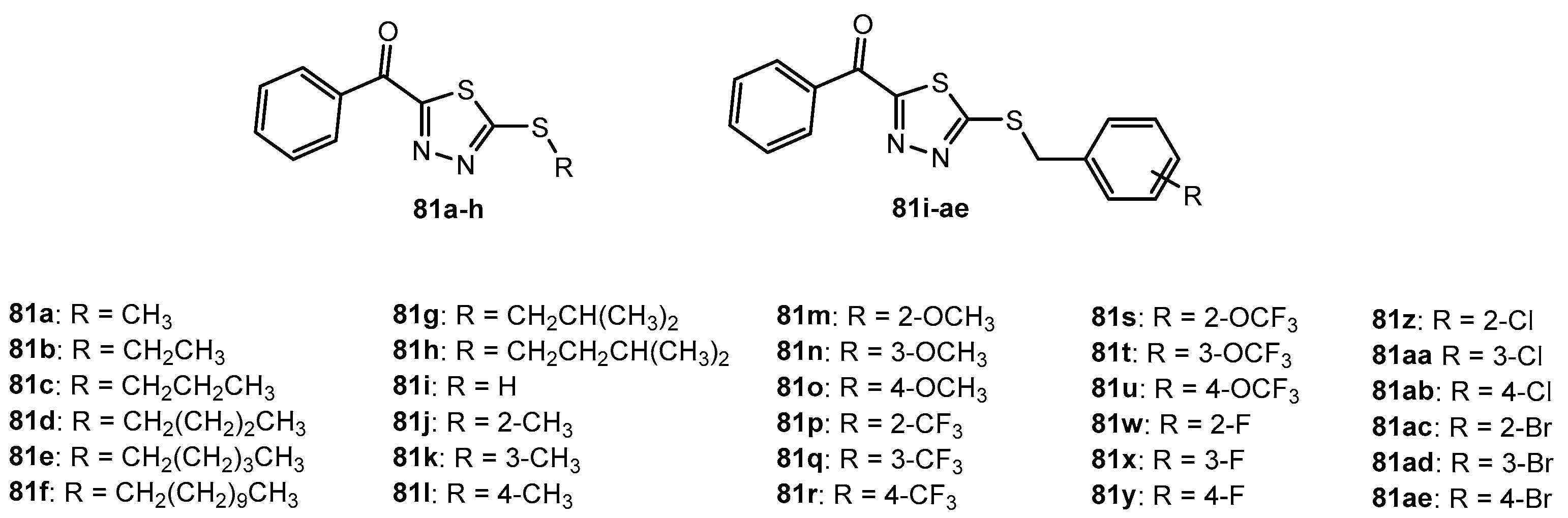
Figure 66.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole thioether derivatives.
Figure 66.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole thioether derivatives.
Figure 67.
The structure of flavanol derivatives containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole scaffold.
Figure 67.
The structure of flavanol derivatives containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole scaffold.
Figure 68.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thioethers.
Figure 68.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thioethers.
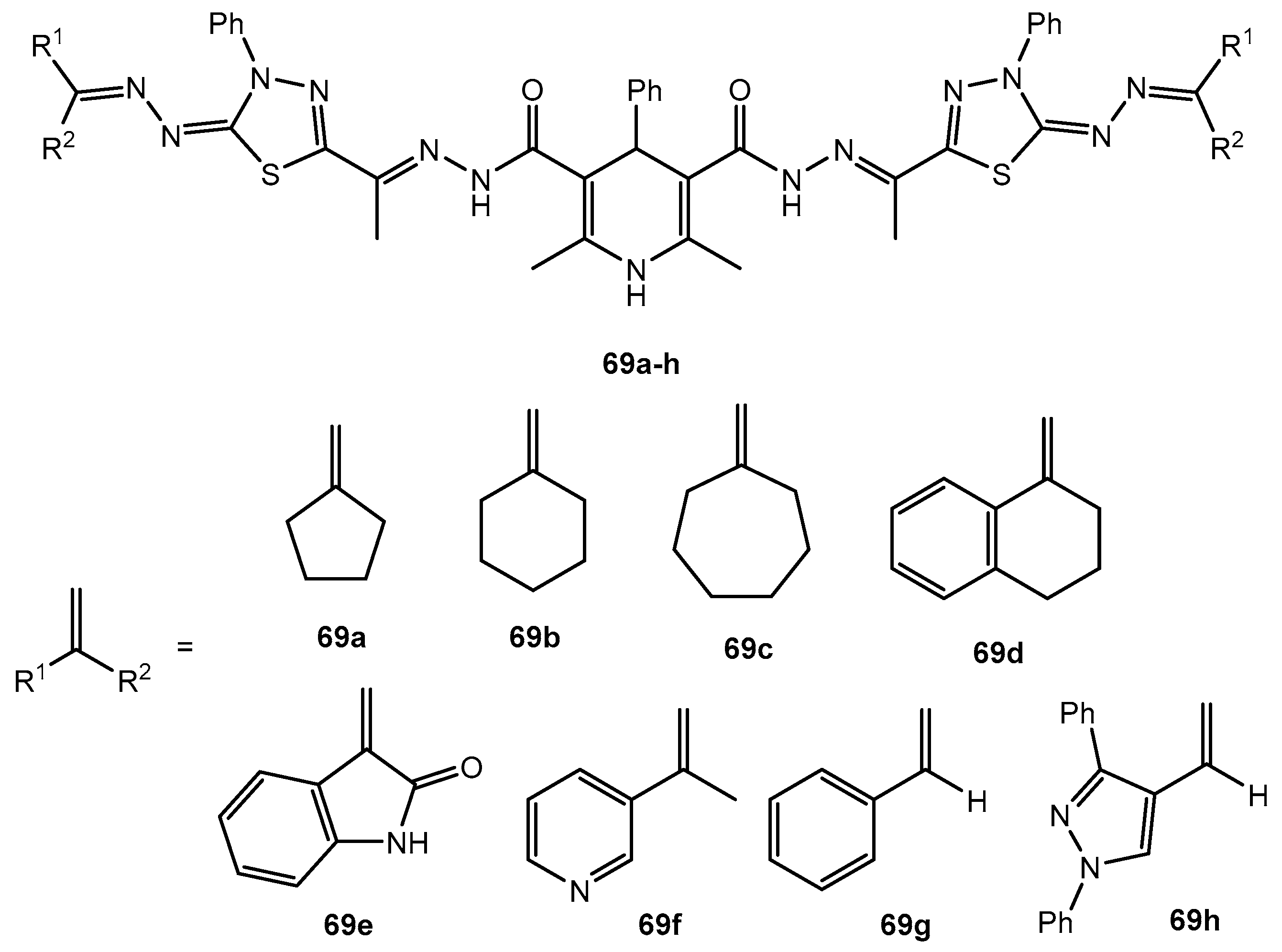
Figure 69.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-amide derivatives.
Figure 69.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-amide derivatives.
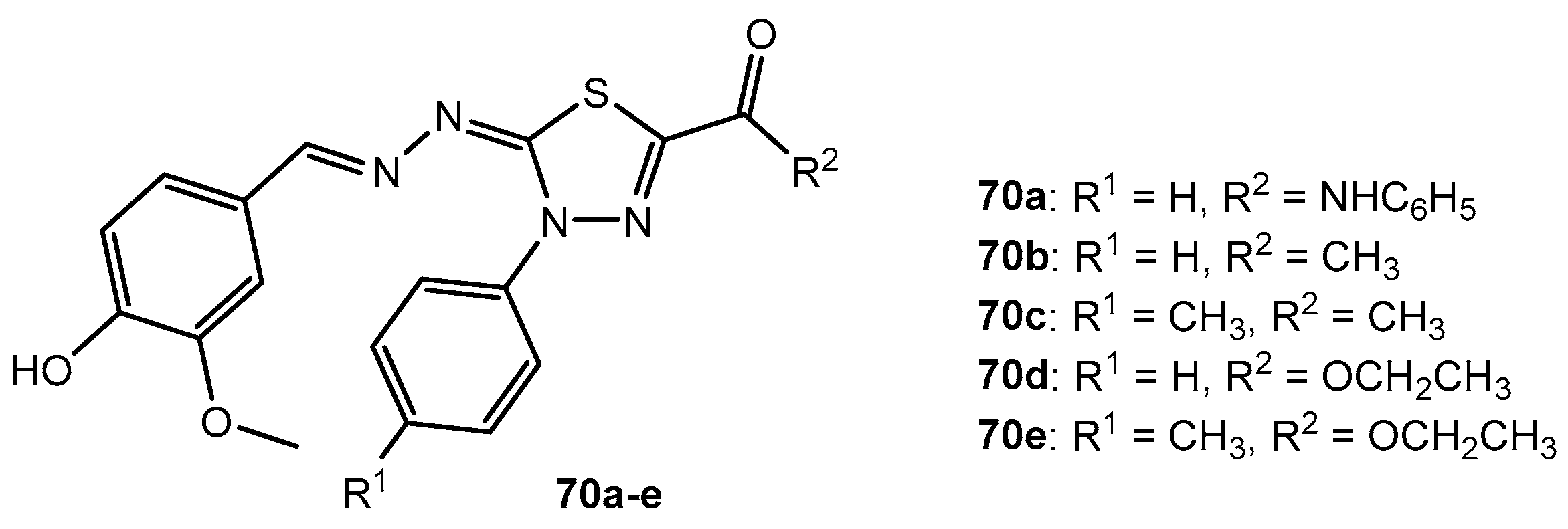
Figure 70.
The structure of pyrimidine-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 70.
The structure of pyrimidine-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
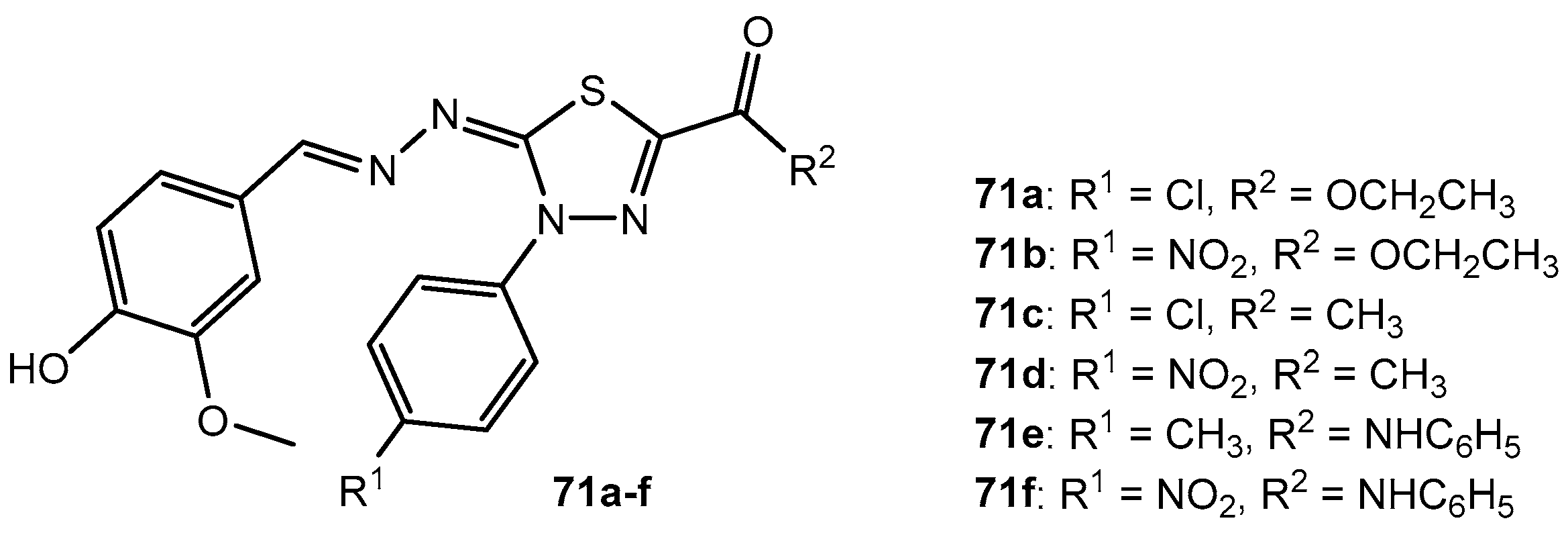
Figure 71.
The structure of terpene-derived 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 71.
The structure of terpene-derived 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
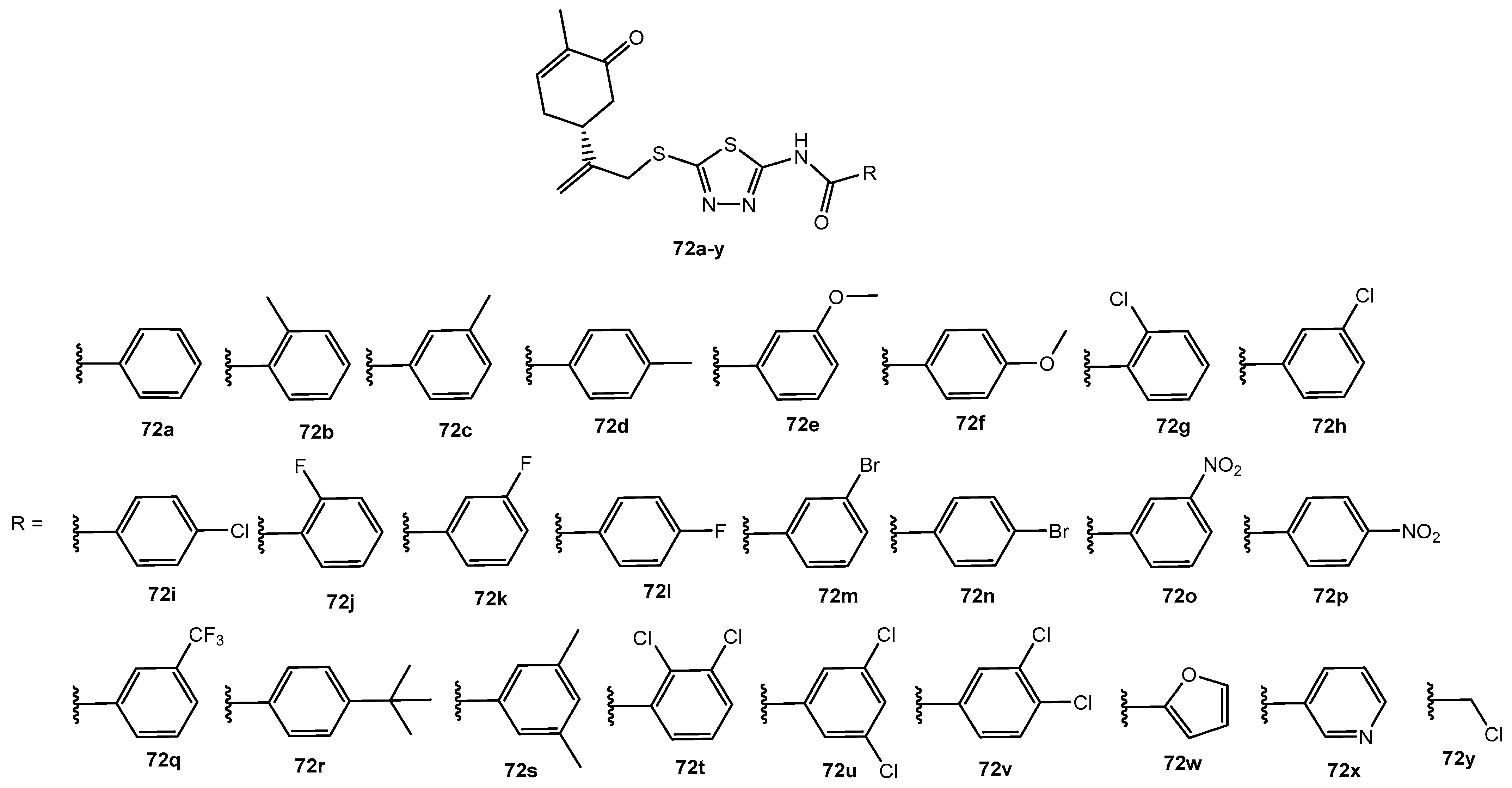
Figure 72.
The structure of dehydroabietyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-amide and dehydroabietyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-imine derivatives.
Figure 72.
The structure of dehydroabietyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-amide and dehydroabietyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-imine derivatives.
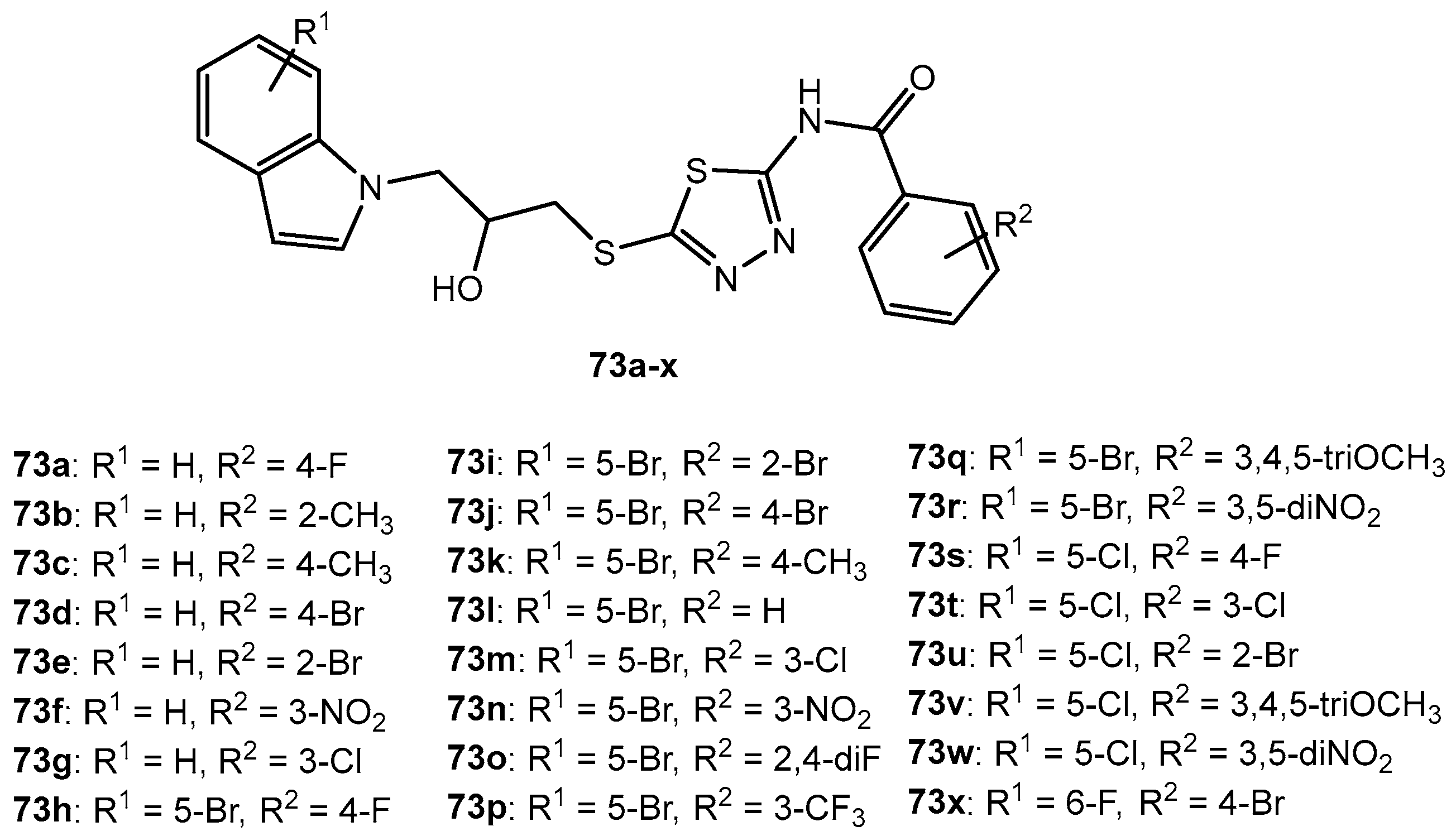
Figure 73.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-thioether compounds.
Figure 73.
The structure of 1,3,4-thiadiazole-thioether compounds.
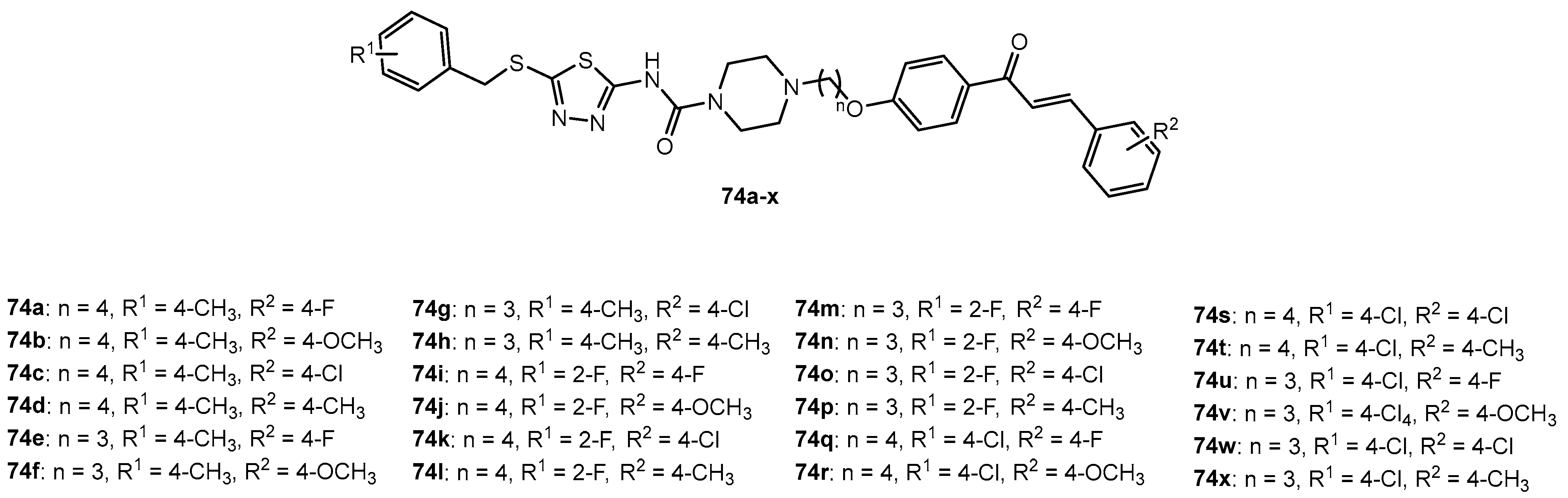
Figure 74.
The structure of nopol-derived 1,3,4-thiadiazole–thiourea compounds.
Figure 74.
The structure of nopol-derived 1,3,4-thiadiazole–thiourea compounds.
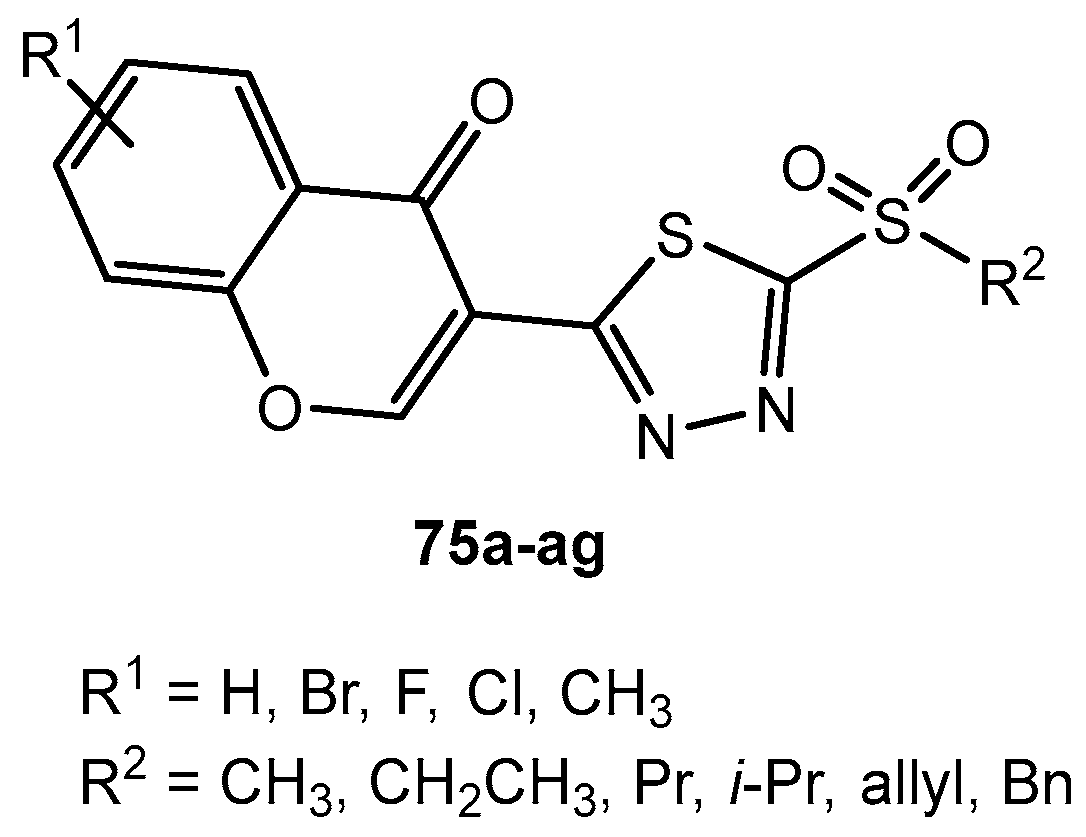
Figure 75.
The structure of 2-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 75.
The structure of 2-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
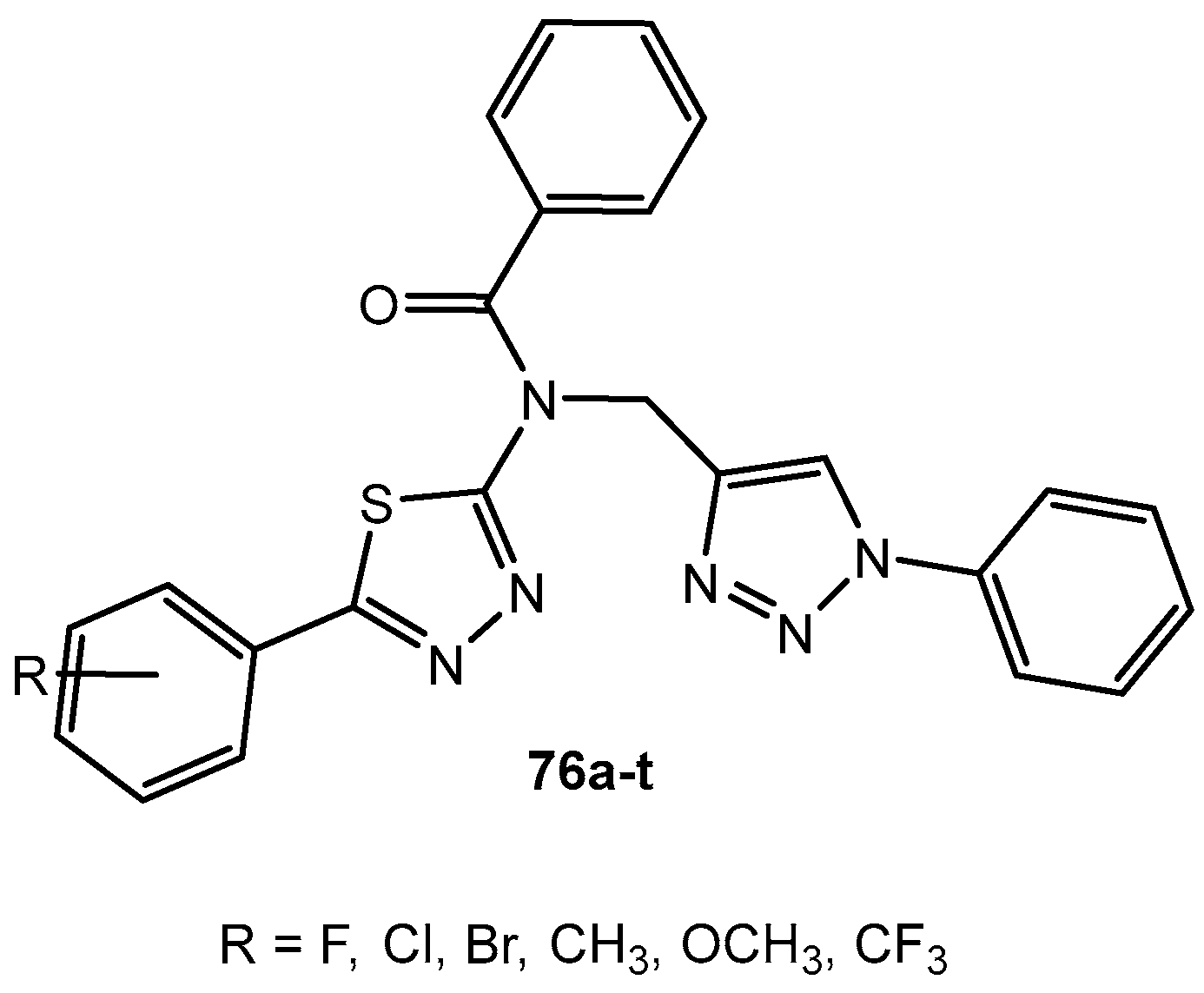
Figure 76.
The structure of the obtained ligand of 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 76.
The structure of the obtained ligand of 1,3,4-thiadiazole.
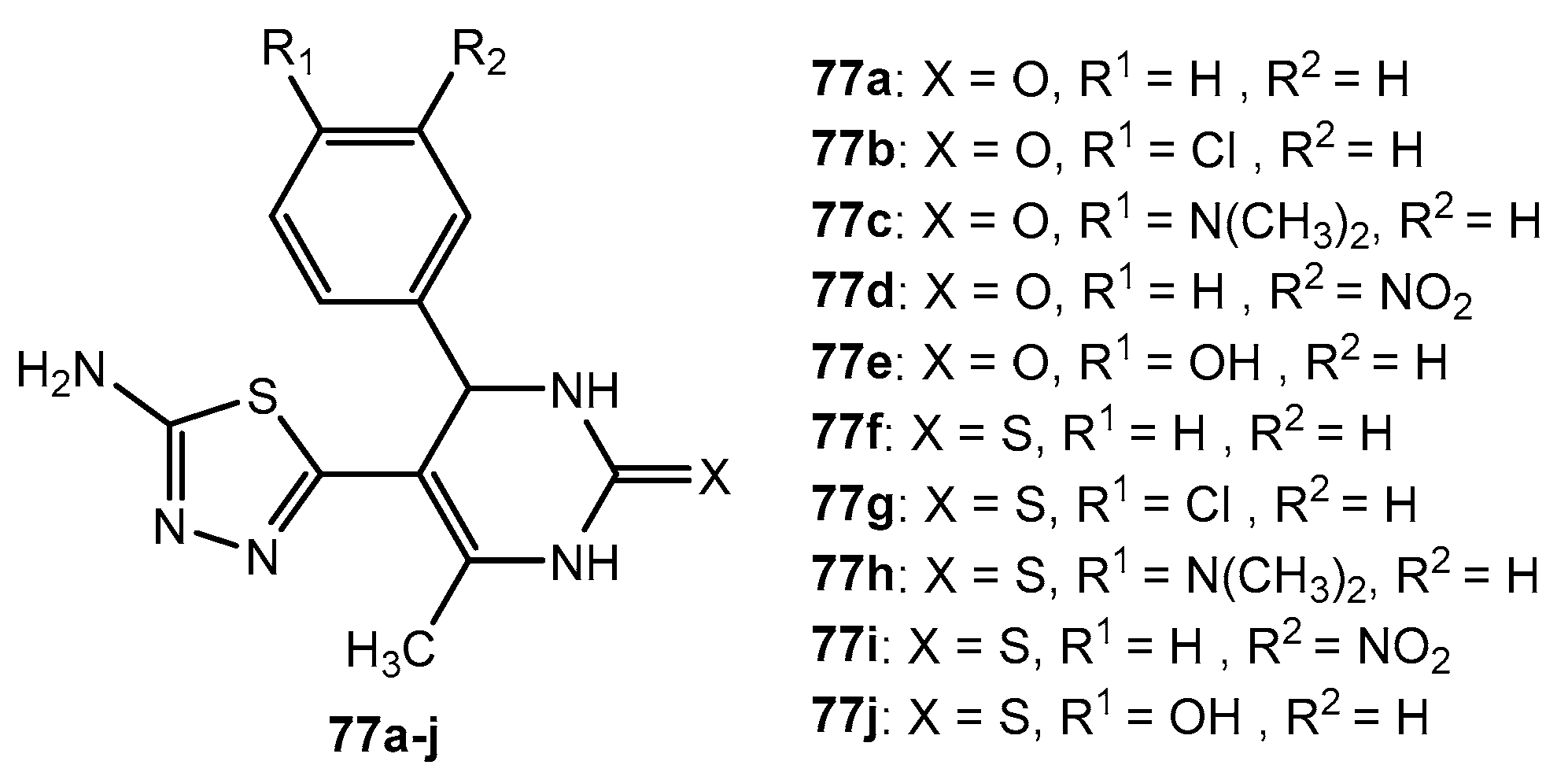
Figure 77.
The structure of chalcone derivatives containing 1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b]-1,3,4-thiadiazole.
Figure 77.
The structure of chalcone derivatives containing 1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b]-1,3,4-thiadiazole.
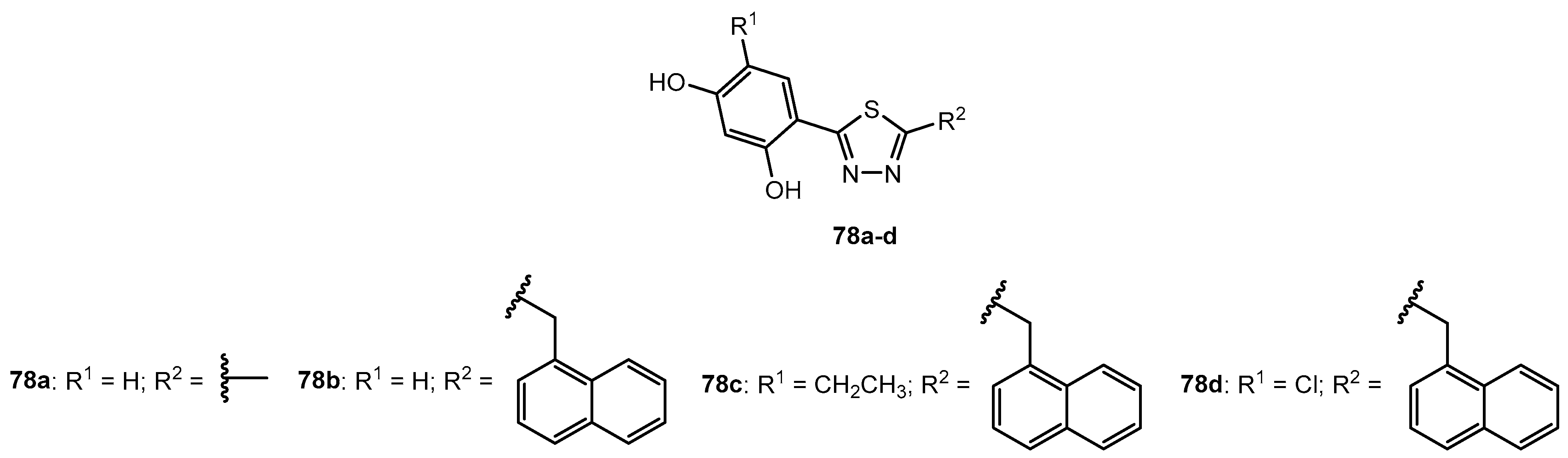
Figure 78.
The structure of [1,2,4]-triazolo-[3,4-b]-[1,3,4]-thiadiazoles.
Figure 78.
The structure of [1,2,4]-triazolo-[3,4-b]-[1,3,4]-thiadiazoles.
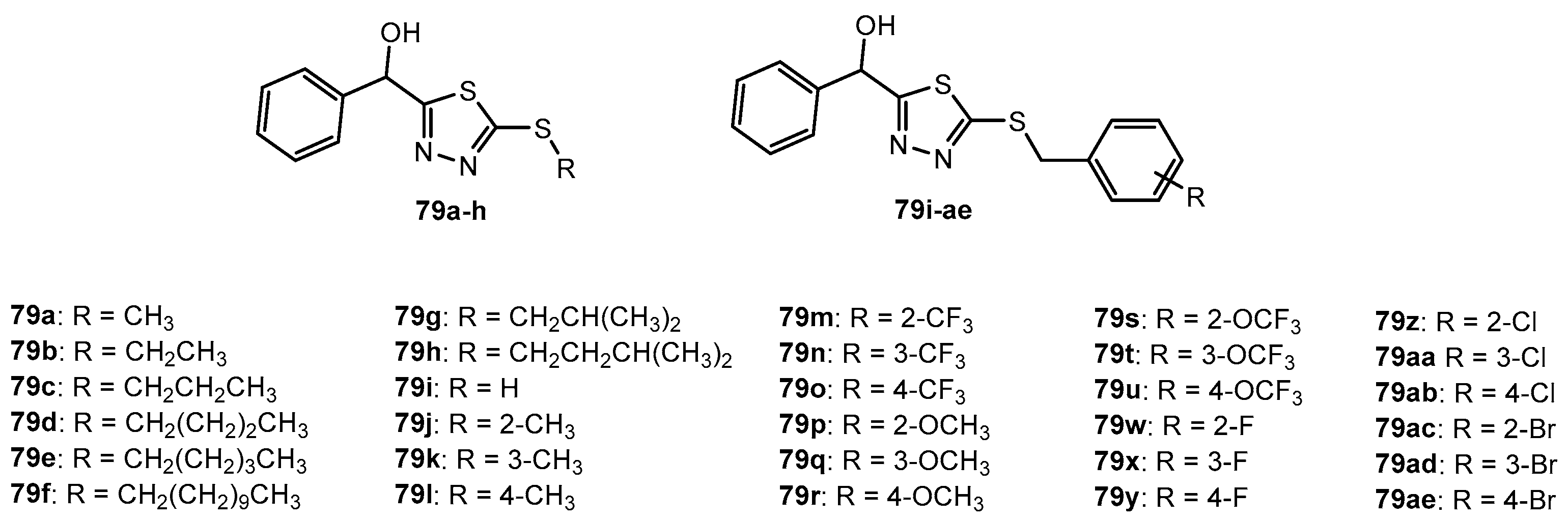
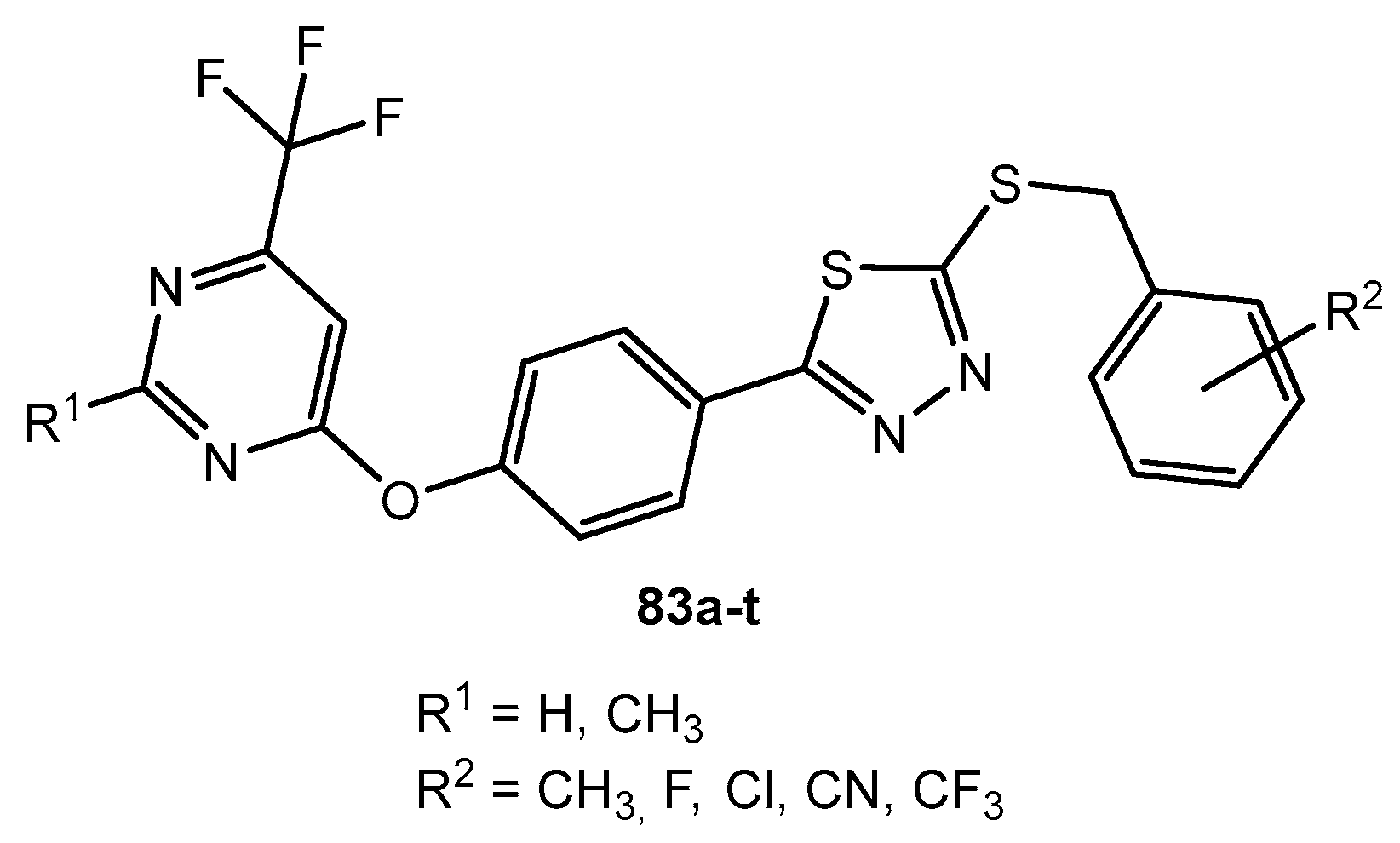
Figure 79.
The structure of bicyclic 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
Figure 79.
The structure of bicyclic 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives.
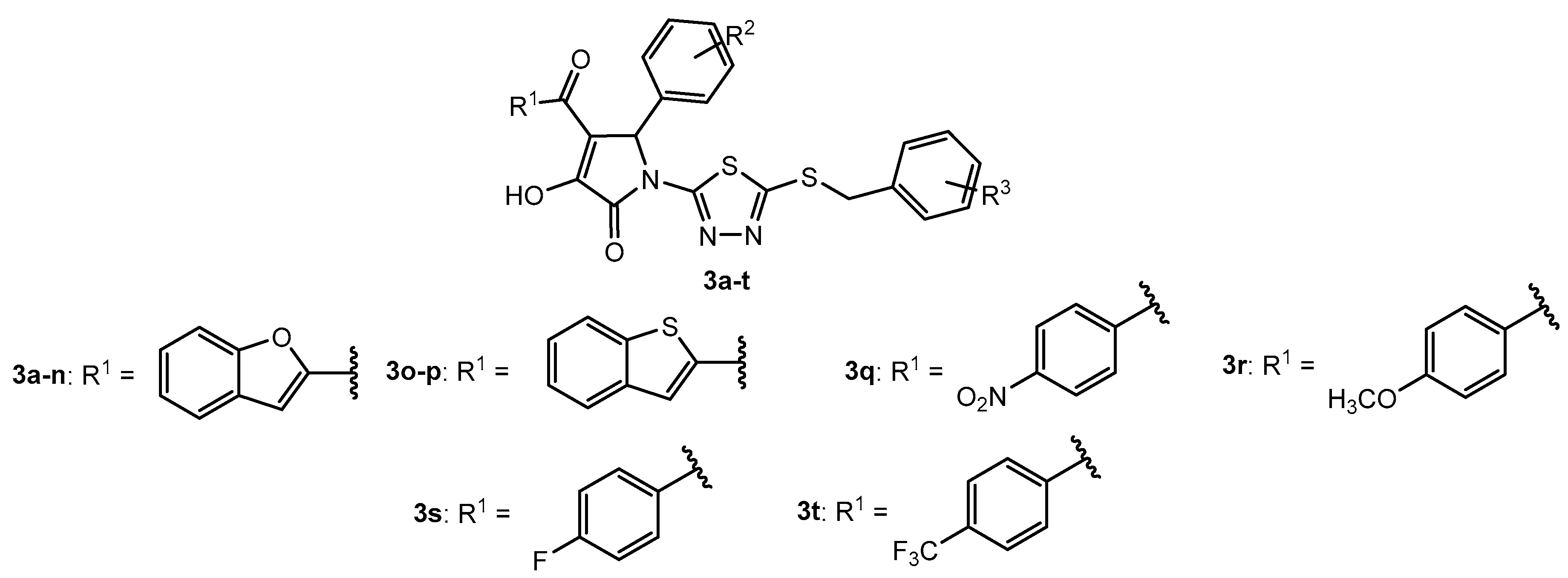
Table 1.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 3a–n.
Table 1.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 3a–n.
| Entry | Compound | R2 | R3 | MIC (μM) |
|---|
| S. epidermidis | S. aureus | E. faecalis | E. faecium |
|---|
| 1 | 3a | H | 2-Cl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 2 | 3b | 4-OH | 2-Cl | 50 | 100 | >100 | >100 |
| 3 | 3c | 2-OH | 2-Cl | 6.25 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| 4 | 3d | 3-OH | 2-Cl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 5 | 3e | 3-Br-4-OH | 2-Cl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6 | 3f | 4-OCH2COOCH3 | 2-Cl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 7 | 3g | 4-OCH2COOCH3 | 2-Cl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 8 | 3h | 2-OH-5-OCH3 | H | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 9 | 3i | 2-OH | 4-Cl | 25 | 25 | 50 | 50 |
| 10 | 3j | 2-OH | 3-Cl | 25 | 50 | 25 | 25 |
| 11 | 3k | 2-OH-5-OCH3 | 2-Cl | 50 | 50 | 100 | 100 |
| 12 | 3l | 2,4-diOH | H | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 13 | 3m | 3,4-diOH | H | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 14 | 3n | 2,3-diOH | H | 50 | 50 | 25 | 25 |
| 15 | 3o | 2-OH | H | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 16 | 3p | 2-OH | 2-Cl | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 17 | 3q | 2-OH | H | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 18 | 3r | 2-OH | H | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 19 | 3s | 2-OH | H | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 20 | 3t | 2-OH | H | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 21 | Daptomycin | - | - | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
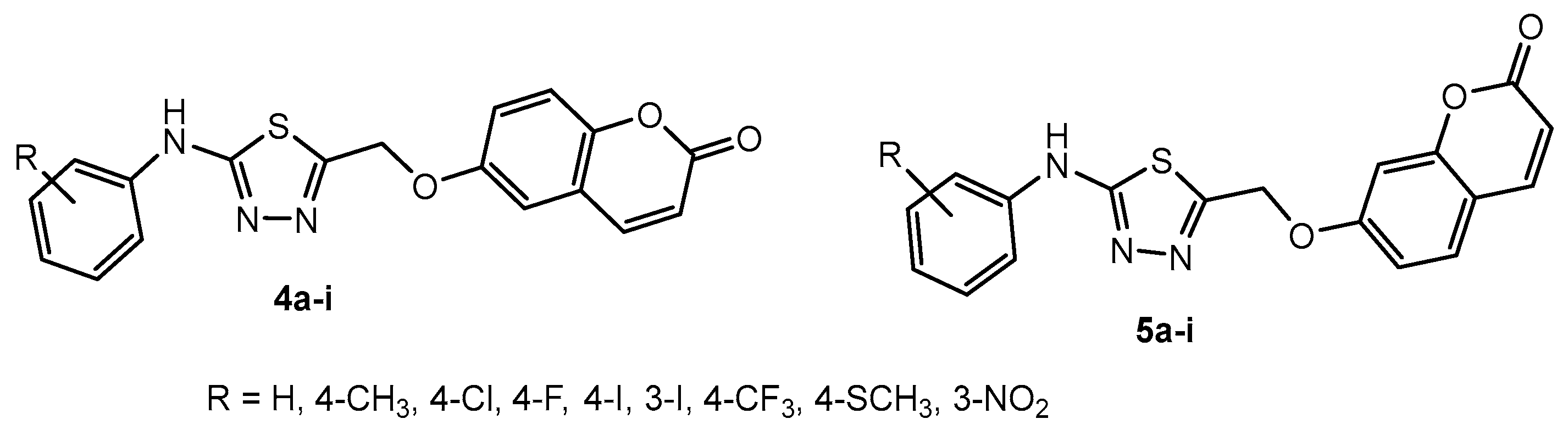
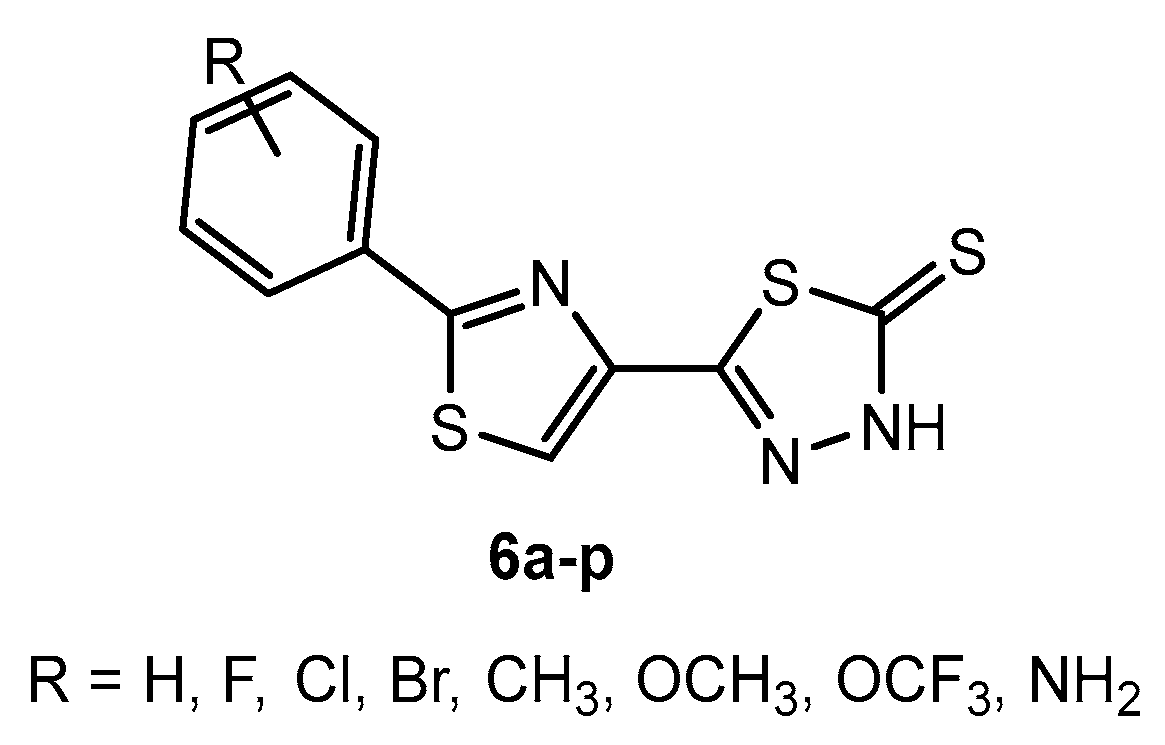
Table 2.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 6a–p.
Table 2.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 6a–p.
| Entry | Compound | R | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| R. solanacearum | Xoo |
|---|
| 200 μg/mL | 100 μg/mL | 200 μg/mL | 100 μg/mL |
|---|
| 1 | 6a | H | 100 | 42.45 | <10 | 17.24 |
| 2 | 6b | 2-F | 100 | 92.00 | 98.92 | 42.24 |
| 3 | 6c | 2-Cl | 100 | 87.04 | 34.30 | <10 |
| 4 | 6d | 2-Br | 82.09 | 74.37 | 47.08 | 13.48 |
| 5 | 6e | 2-CH3 | 78.63 | 45.96 | 32.33 | <10 |
| 6 | 6f | 2-OCH3 | 47.74 | 31.78 | 18.70 | <10 |
| 7 | 6g | 2-OCF3 | 80.08 | 48.26 | 28.65 | <10 |
| 8 | 6h | 3-F | 94.87 | 93.81 | 76.17 | 54.66 |
| 9 | 6i | 3-CH3 | 95.40 | 94.00 | 80.07 | 14.95 |
| 10 | 6j | 3-OCH3 | 70.57 | 67.56 | 45.34 | 31.37 |
| 11 | 6k | 3-OCF3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 72.63 |
| 12 | 6l | 4-F | 53.19 | 33.59 | 28.59 | 12.09 |
| 13 | 6m | 4-CH3 | 74.07 | 71.37 | 49.37 | 41.59 |
| 14 | 6n | 4-OCH3 | 64.10 | 53.41 | 48.40 | 44.61 |
| 15 | 6o | 4-OCF3 | 43.47 | 35.11 | <10 | <10 |
| 16 | 6p | 4-NH2 | 71.88 | 60.60 | 53.00 | 41.26 |
Table 3.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 7a,b.
Table 3.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 7a,b.
| Entry | Compound | MIC |
|---|
| E. coli | S. typhimurium | S. aureus | E. feacium |
|---|
| 1 | 7a a | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.12 |
| 2 | 7b a | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 0.25 |
| 3 | Gentamicin b | 7.81 | 7.81 | 3.91 | 7.81 |
Table 4.
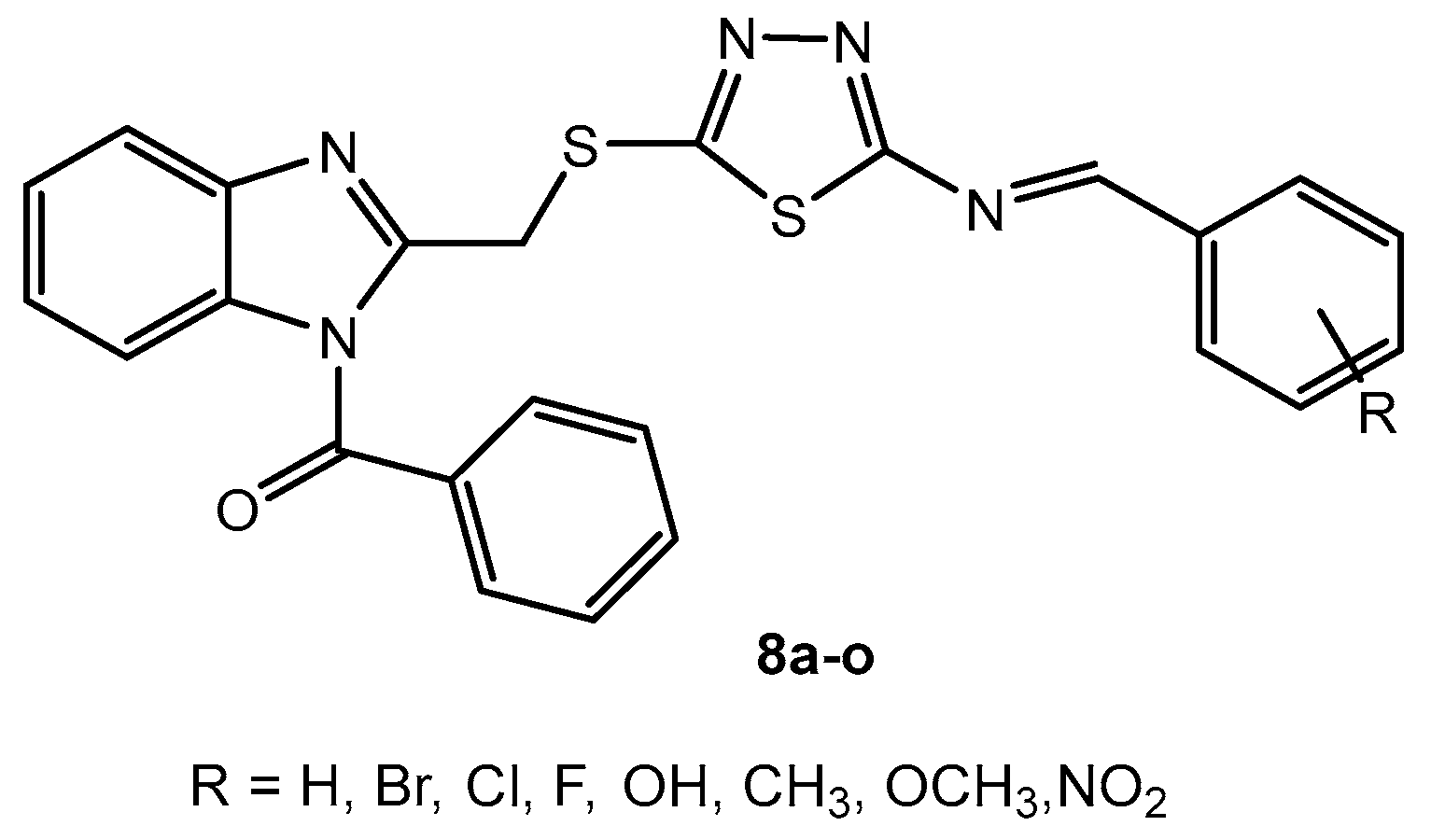
Antibacterial activity of compounds 8a–o.
Table 4.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 8a–o.
| Entry | Compound | R | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| E. coli | P. aeruginosa | S. aureus | S. pyogenes |
|---|
| 1 | 8a | H | 100 | 12.5 | 125 | 125 |
| 2 | 8b | 2-Br | 250 | 250 | 100 | 250 |
| 3 | 8c | 4-Br | 100 | 62.5 | 125 | 125 |
| 4 | 8d | 2-Cl | 50 | 125 | 250 | 100 |
| 5 | 8e | 4-Cl | 100 | 50 | 12.5 | 100 |
| 6 | 8f | 2-F | 125 | 250 | 250 | 250 |
| 7 | 8g | 3-F | 125 | 250 | 100 | 100 |
| 8 | 8h | 4-F | 100 | 62.5 | 100 | 125 |
| 9 | 8i | 2-OH | 100 | 100 | 62.5 | 100 |
| 10 | 8j | 4-OH | 50 | 12.5 | 100 | 100 |
| 11 | 8k | 4-CH3 | 100 | 125 | 250 | 100 |
| 12 | 8l | 4-OCH3 | 250 | 250 | 62.5 | 100 |
| 13 | 8m | 2-NO2 | 100 | 100 | 250 | 250 |
| 14 | 8n | 3-NO2 | 125 | 250 | 125 | 250 |
| 15 | 8o | 4-NO2 | 250 | 12.5 | 100 | 62.5 |
| 16 | Chloramphenicol | - | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| 17 | Ciprofloxacin | - | 25 | 25 | 50 | 50 |
| 18 | Norfloxacin | - | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
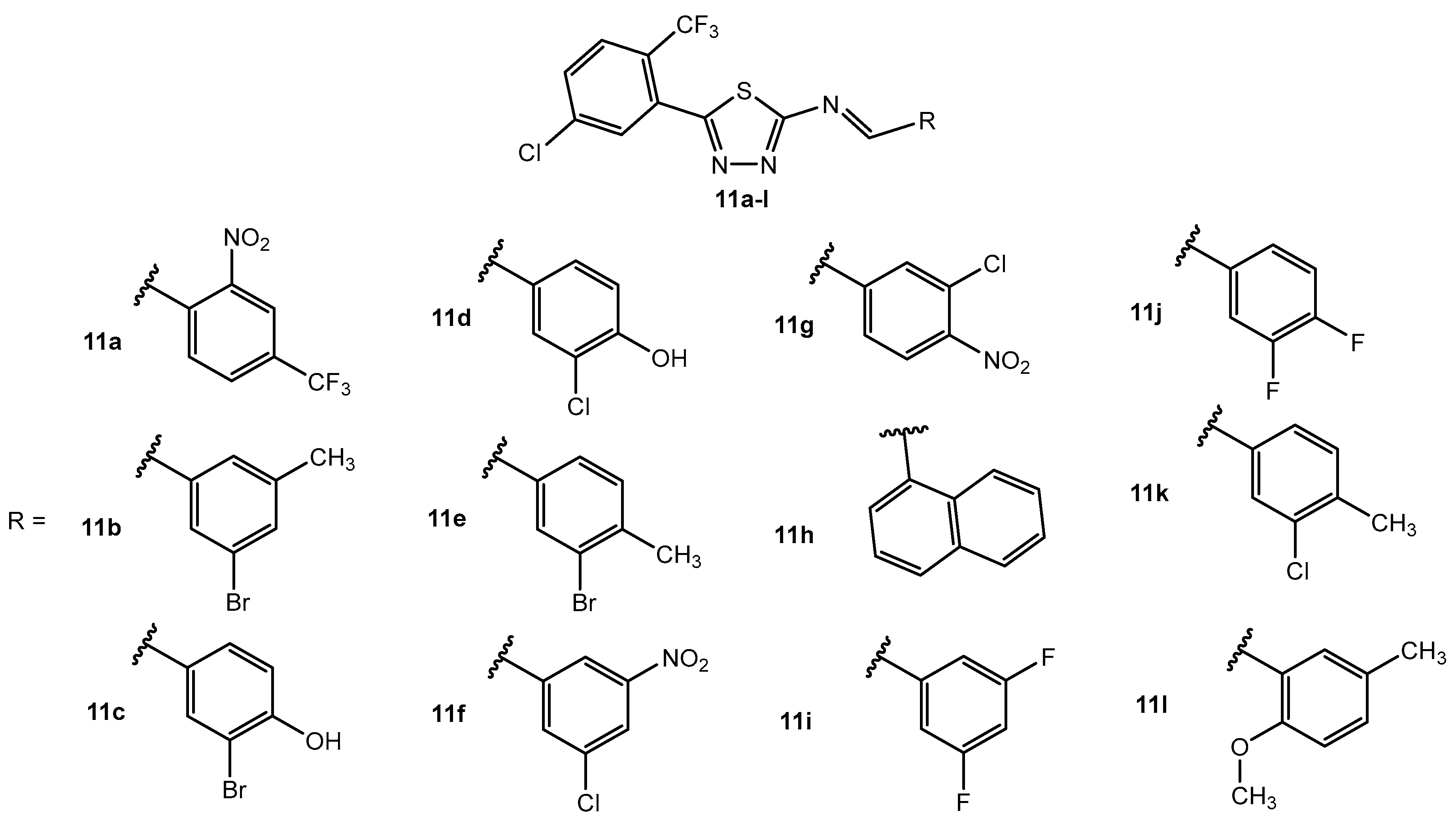
Table 5.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 11a–l.
Table 5.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 11a–l.
| Compound | 11a | 11b | 11c | 11d | 11e | 11f | 11g | 11h | 11i | 11j | 11k | 11l | Streptomycin |
|---|
| Inhibition rate (%) | 42.3 | 32.4 | 40.1 | 38.2 | 27.1 | 31 | 25.5 | 18.1 | 36.5 | 19.7 | 14.2 | 18.4 | 44 |
Table 6.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 12a–r.
Table 6.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 12a–r.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| 1 | 12a | CH3 | CH3 | 72 |
| 2 | 12b | CH3 | CH2CH3 | 72 |
| 3 | 12c | CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | 79 |
| 4 | 12d | CH3 | CH2C6H5 | 78 |
| 5 | 12e | CH3 | CH2C6H4-4-F | 63 |
| 6 | 12f | CH3 | CH2C6H4-4-Cl | 67 |
| 7 | 12g | CH3 | CH2C6H4-3-Cl | 61 |
| 8 | 12h | CH3 | CH2C6H4-2-Cl | 52 |
| 9 | 12i | CH3 | CH2C6H3-2,4-diCl | 76 |
| 10 | 12j | CF3 | CH3 | 72 |
| 11 | 12k | CF3 | CH2CH3 | 62 |
| 12 | 12l | CF3 | CH2CH2CH3 | 75 |
| 13 | 12m | CF3 | CH2C6H5 | 62 |
| 14 | 12n | CF3 | CH2C6H4-4-F | 68 |
| 15 | 12o | CF3 | CH2C6H4-4-Cl | 71 |
| 16 | 12p | CF3 | CH2C6H4-3-Cl | 83 |
| 17 | 12q | CF3 | CH2C6H4-2-Cl | 67 |
| 18 | 12r | CF3 | CH2C6H3-2,4-diCl | 76 |
Table 7.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 13a–i.
Table 7.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 13a–i.
| Entry | Compound | R | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | P. vulgaris |
|---|
| 1 | 13a | H | 6 | 0 | 6 |
| 2 | 13b | 2-Cl | 14 | 16 | 14 |
| 3 | 13c | 3-Cl | 12 | 16 | 12 |
| 4 | 13d | 4-Cl | 14 | 18 | 14 |
| 5 | 13e | 3-NO2 | 10 | 8 | 8 |
| 6 | 13f | 4-NO2 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| 7 | 13g | 3-OCH3-4-OH | 10 | 12 | 10 |
| 8 | 13h | 4-CH3 | 10 | 12 | 12 |
| 9 | 13i | 2-OH | 12 | 14 | 14 |
| 10 | Ampicillin trihydrate | - | 16 | 20 | 20 |
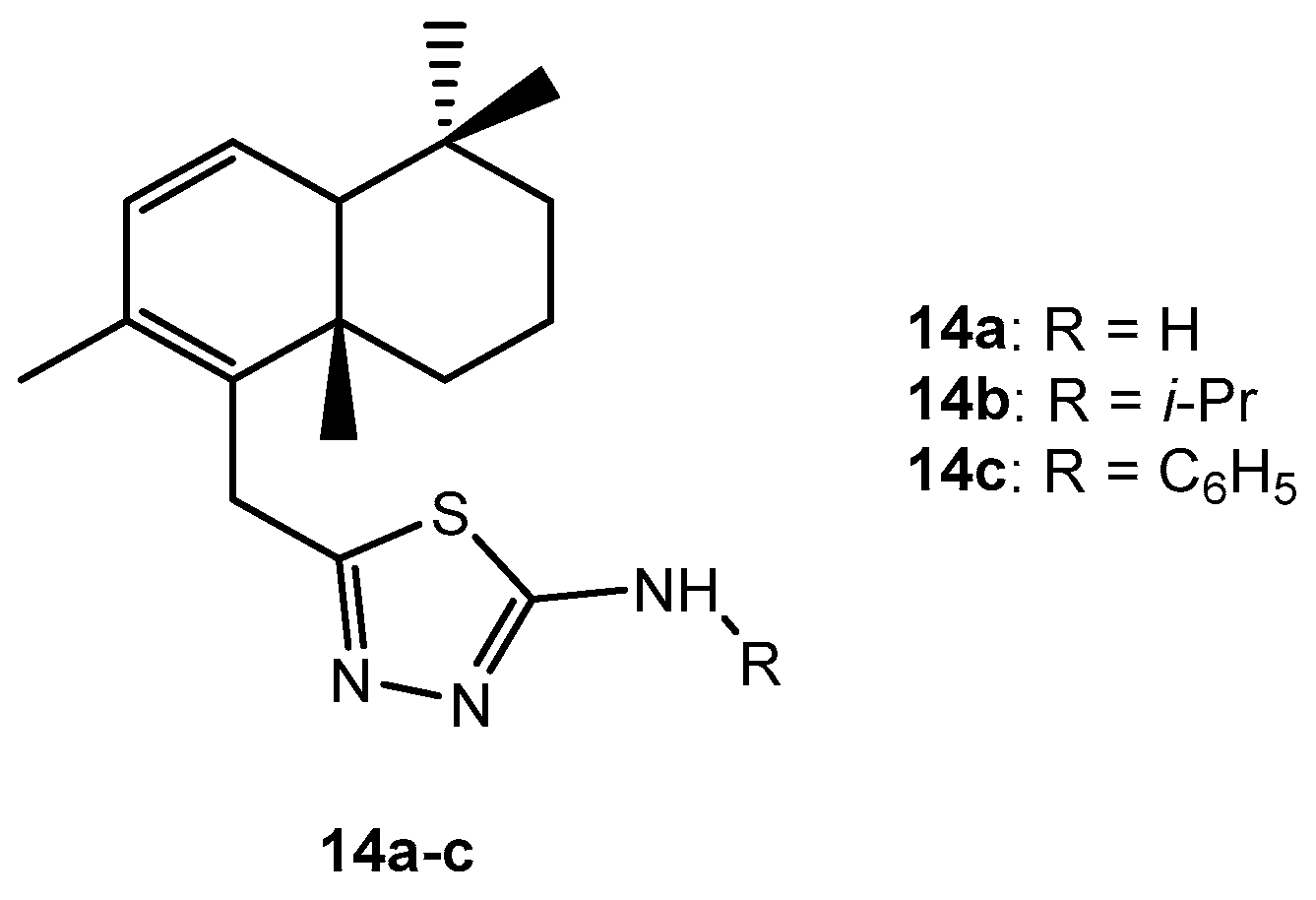
Table 8.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 14a–c.
Table 8.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 14a–c.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| B. polymyxa | P. aeruginosa |
|---|
| 1 | 14a | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 14b | >256 | >256 |
| 3 | 14c | >256 | >256 |
| 4 | Kanamycin | 4 | 4 |
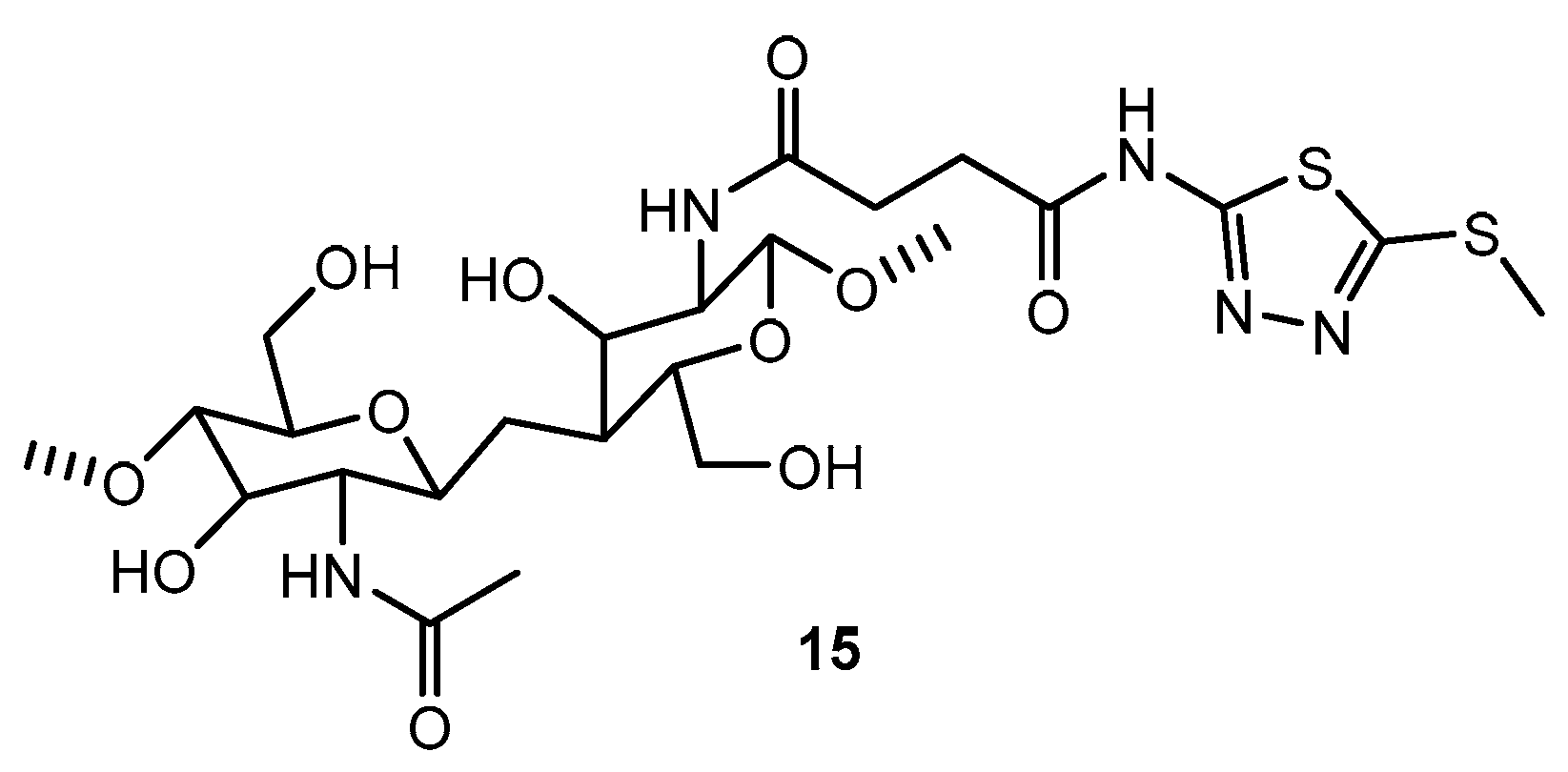
Table 9.
Antibacterial activity of compound 15.
Table 9.
Antibacterial activity of compound 15.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| E. coli | P. aeruginosa | B. subtilis | S. aureus |
|---|
| 1 | 15 | 11 | 11.5 | 11 | 8 |
Table 10.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 16a–i.
Table 10.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 16a–i.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| BS | CD | SA | SE | SP | EC | KP | PA | ST |
|---|
| 1 | 16a | 12.5 | 200 | 3.125 | 3.125 | 12.5 | 1.56 | 50 | 25 | 1.56 |
| 2 | 16b | 6.25 | 6.25 | 25 | 100 | 12.5 | 50 | 6.25 | 1.56 | 12.5 |
| 3 | 16c | 1.56 | 0.78 | 6.25 | 50 | 3.125 | 200 | 12.5 | 50 | 3.125 |
| 4 | 16d | 3.125 | 25 | 50 | 25 | 1.56 | 12.5 | 25 | 100 | 25 |
| 5 | 16e | 1.56 | 50 | 12.5 | 1.56 | 3.125 | 3.125 | 3.125 | 12.5 | 6.25 |
| 6 | 16f | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| 7 | 16g | 0.78 | 3.125 | 100 | 12.5 | 0.78 | 6.25 | 400 | 6.25 | 50 |
| 8 | 16h | 200 | 12.5 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 200 | 0.78 | 1.56 | 0.78 | 100 |
| 9 | 16i | 100 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 6.25 | 50 | 25 | 0.78 | 3.125 | 0.78 |
| 10 | Ciprofloxacin | 3.125 | 6.25 | 3.125 | 3.125 | 6.25 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 1.56 |
| 11 | Vancomycin | 1.56 | 1.56 | 1.56 | 0.78 | 1.56 | - | - | - | - |
Table 11.
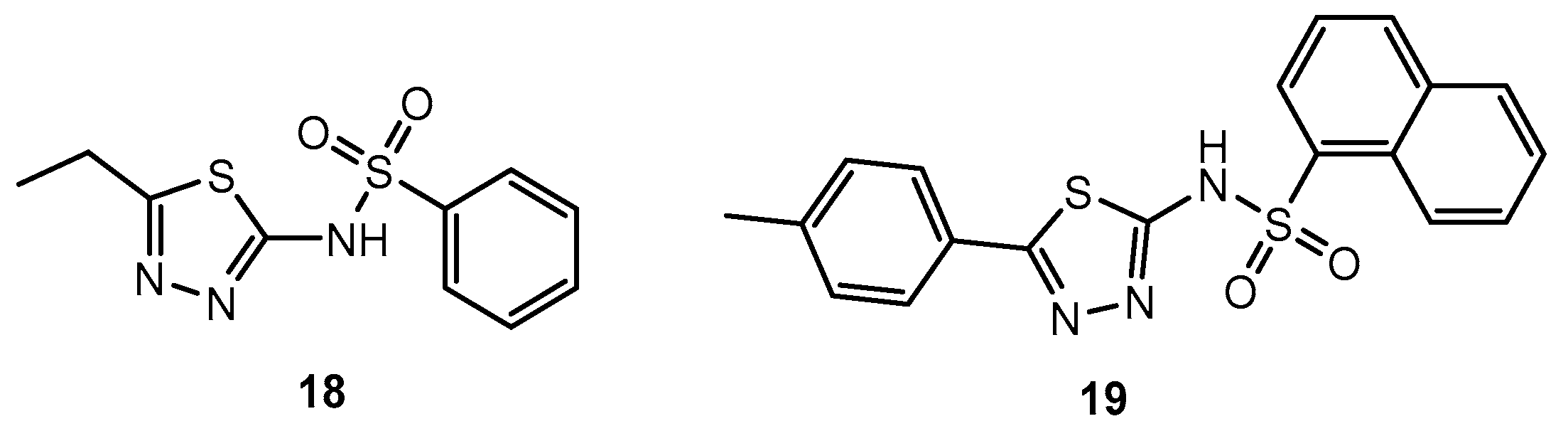
Antibacterial activity of compounds 18 and 19 and their complexes.
Table 11.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 18 and 19 and their complexes.
Bacterial
Strains | 18 Complex MIC
µM/L | 19 Complex MIC
µM/L | 18 MIC
µM/L | 19 MIC
µM/L |
|---|
| S. aureus MRSA | 2 | 2 | 25 | 12.5 |
| S. aureus MSSA | 2 | 2 | 12.5 | 12.5 |
| E. coli | 2 | 2 | 25 | 25 |
| E. faecium | n.a | 0.2 | n.a | 12.5 |
| P. aeruginosa | n.a | 0.2 | n.a | 25 |
| S. lentus | n.a | 2 | n.a | 25 |
Table 12.
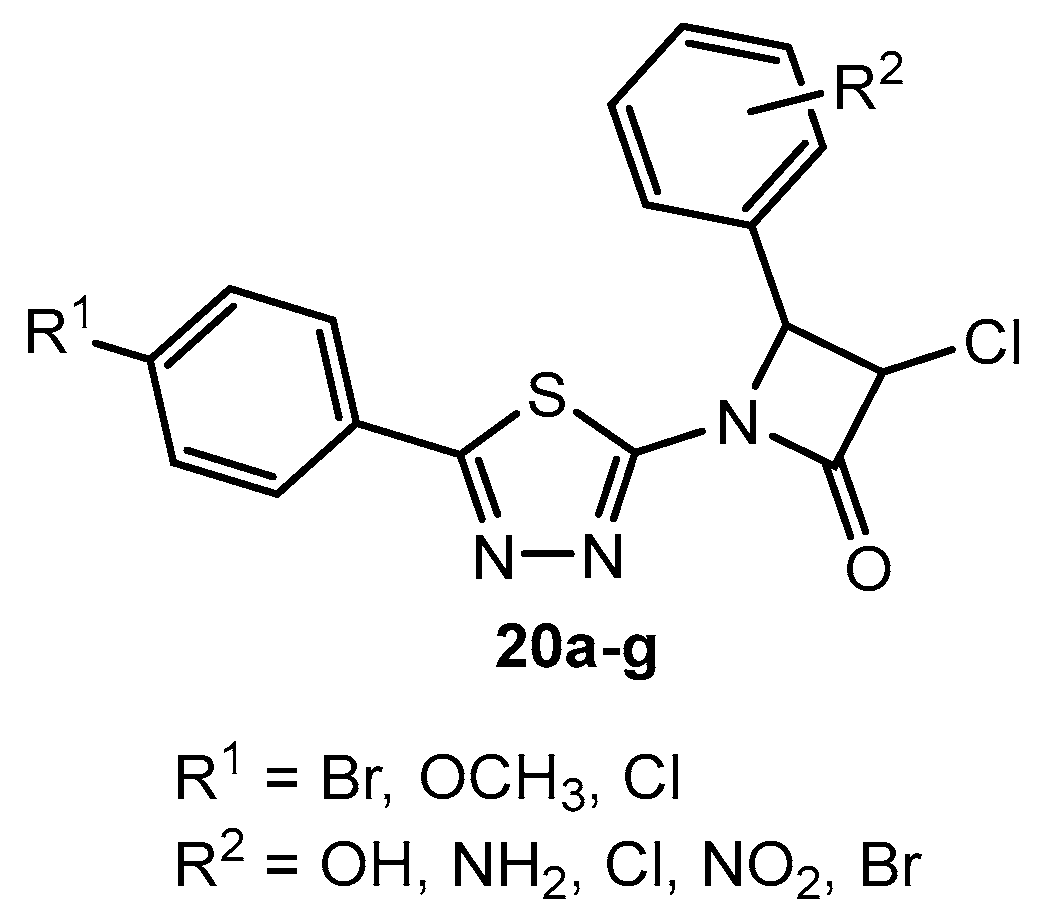
Antibacterial activity of compounds 20a–g.
Table 12.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 20a–g.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | MBC (µM) |
|---|
| SA | EF | PA | EC | KP |
|---|
| 1 | 20a | Br | 4-OH | 14.30 | 28.60 | 14.30 | 14.30 | 14.30 |
| 2 | 20b | Br | 4-NH2 | 14.33 | 28.67 | 14.33 | 43.10 | 14.33 |
| 3 | 20c | OCH3 | 3,5-diCl | 14.17 | 28.34 | 28.34 | 28.34 | 28.34 |
| 4 | 20d | OCH3 | 4-NO2 | 14.99 | 14.99 | 29.98 | 29.98 | 14.99 |
| 5 | 20e | OCH3 | 4-Br | 13.86 | 13.86 | 13.86 | 13.86 | 13.86 |
| 6 | 20f | Cl | 4-NO2 | 14.85 | 14.85 | 29.69 | 14.85 | 14.85 |
| 7 | 20g | Br | 4-Cl | 6.87 | 6.87 | 6.87 | 13.74 | 13.74 |
Table 13.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 21a–i.
Table 13.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 21a–i.
| Compound | 21a | 21b | 21c | 21d | 21e | 21f | 21g | 21h | 21i | Streptomycin Sulfate |
|---|
| MIC (mg/mL) | 0.0625 | 0.0313 | 0.0625 | - | 0.0625 | 0.0625 | 0.0625 | - | - | 44 |
Table 14.
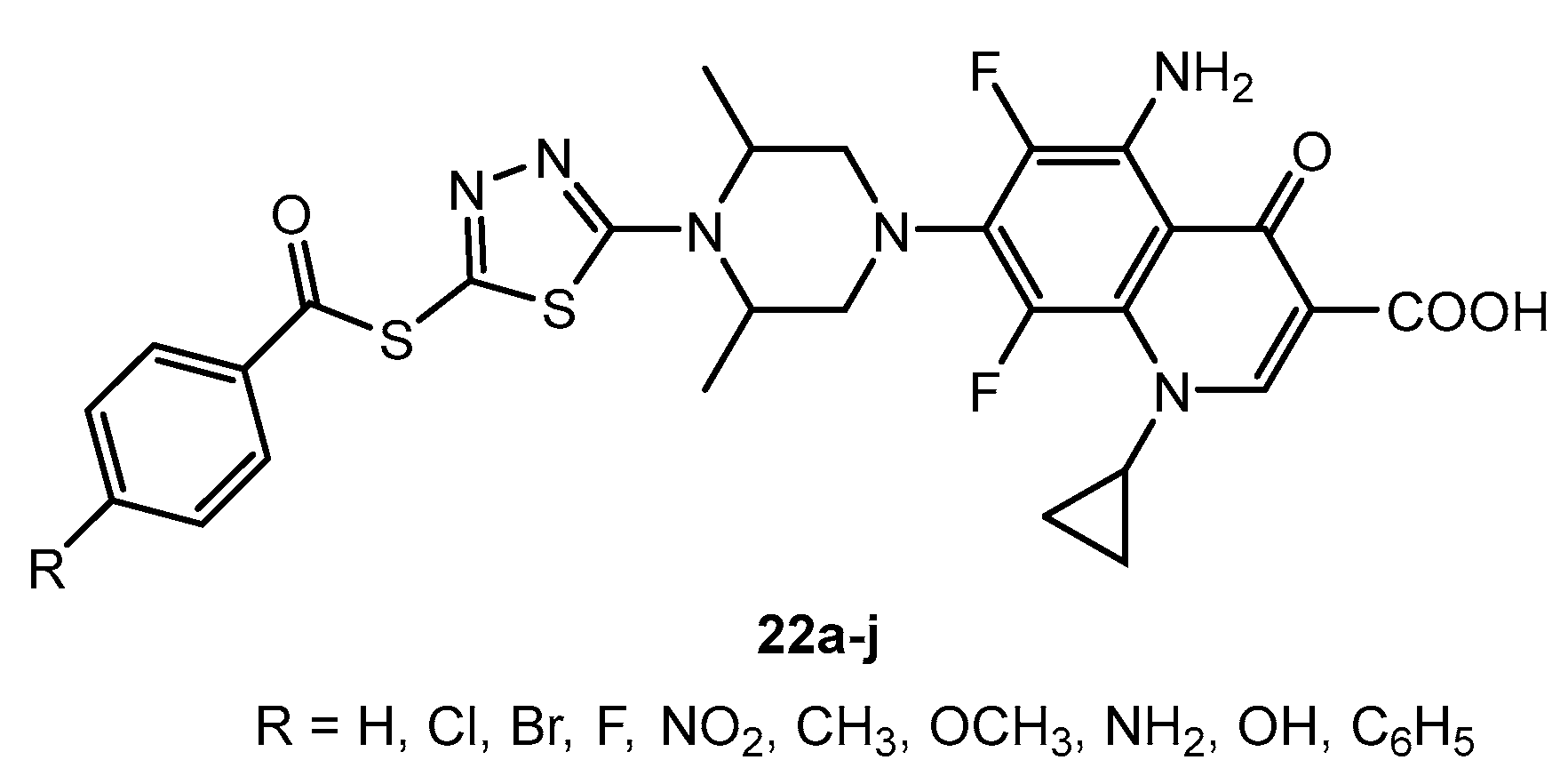
Antibacterial activity of compounds 22a–j.
Table 14.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 22a–j.
| Entry | Compound | R | MIC [μg/mL] |
|---|
| S. aureus | B. subtilis | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | M. tuberculosis |
|---|
| 1 | 22a | H | 15.67 | 16.67 | 31.00 | 65.33 | Resist |
| 2 | 22b | Cl | 1.62 | 1.33 | 8.67 | 8.67 | 3.12 |
| 3 | 22c | Br | 2.00 | 2.00 | 3.33 | 5.00 | 6.25 |
| 4 | 22d | F | 4.67 | 7.33 | 7.67 | 7.33 | 3.12 |
| 5 | 22e | NO2 | 1.67 | 1.67 | 4.67 | 2.67 | Resist |
| 6 | 22f | CH3 | 8.00 | 16.33 | 17.33 | 32.67 | 6.25 |
| 7 | 22g | OCH3 | 8.67 | 8.33 | 16.67 | 16.67 | 1.60 |
| 8 | 22h | NH2 | 5.33 | 4.00 | 16.00 | 8.00 | 1.60 |
| 9 | 22i | OH | 7.33 | 9.00 | 15.33 | 16.33 | Resist |
| 10 | 22j | C6H5 | 1.33 | 2.00 | 4.00 | 9.00 | 0.8 |
Table 15.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 28a–e.
Table 15.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 28a–e.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| S. aureus | B. subtilis | K. pneumonia | E. coli |
|---|
| 1 | 28a | 10 | 9 | 12 | 8 |
| 2 | 28b | 14 | 15 | 12 | 13 |
| 3 | 28c | 10 | 11 | - | 8 |
| 4 | 28d | - | 11 | 9 | 12 |
| 5 | 28e | 8 | 13 | - | 14 |
| 6 | Streptomycin | 17 | 16 | 15 | 15 |
Table 16.
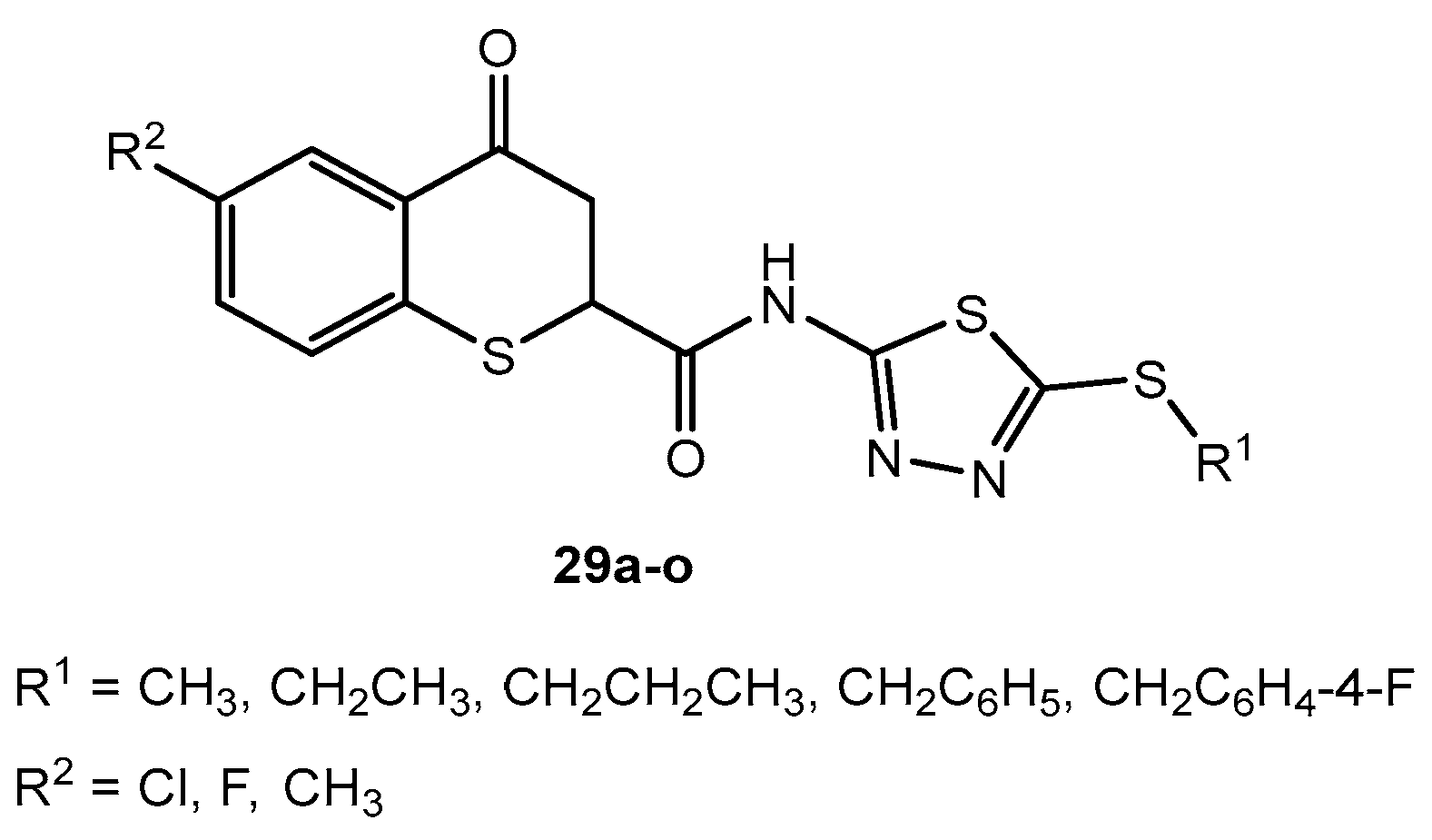
Antibacterial activity of compounds 29a–o.
Table 16.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 29a–o.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| Xoo | Xac |
|---|
| 200 μg/mL | 100 μg/mL | 200 μg/mL | 100 μg/mL |
|---|
| 1 | 29a | CH3 | Cl | 100 | 94 | 90 | 78 |
| 2 | 29b | CH2CH3 | Cl | 92 | 78 | 86 | 70 |
| 3 | 29c | CH2CH2CH3 | Cl | 81 | 70 | 74 | 61 |
| 4 | 29d | CH2C6H5 | Cl | 60 | 44 | 51 | 40 |
| 5 | 29e | CH2C6H4-4-F | Cl | 64 | 50 | 57 | 45 |
| 6 | 29f | CH3 | F | 90 | 75 | 80 | 61 |
| 7 | 29g | CH2CH3 | F | 74 | 60 | 68 | 54 |
| 8 | 29h | CH2CH2CH3 | F | 68 | 54 | 60 | 48 |
| 9 | 29i | CH2C6H5 | F | 51 | 38 | 47 | 31 |
| 10 | 29j | CH2C6H4-4-F | F | 54 | 41 | 51 | 39 |
| 11 | 29k | CH3 | CH3 | 45 | 32 | 40 | 30 |
| 12 | 29l | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 37 | 28 | 32 | 20 |
| 13 | 29m | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 30 | 20 | 25 | 14 |
| 14 | 29n | CH2C6H5 | CH3 | 24 | 16 | 16 | 8 |
| 15 | 29o | CH2C6H4-4-F | CH3 | 28 | 18 | 21 | 12 |
| 16 | Bismerthiazol | - | - | 70 | 52 | 57 | 35 |
| 17 | Thiodiazole copper | - | - | 63 | 45 | 35 | 15 |
Table 17.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 32a–k.
Table 17.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 32a–k.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| EC | KP | PA | EF | BS | SA |
|---|
| 1 | 32a | 125 | 125 | 250 | 7.81 | 15.63 | 125 |
| 2 | 32b | 125 | 125 | 125 | 7.81 | 31.25 | 125 |
| 3 | 32c | 125 | 125 | 125 | 31.25 | 125 | 125 |
| 4 | 32d | 62.5 | 62.5 | 125 | 3.9 | 125 | 125 |
| 5 | 32e | 125 | 62.5 | 125 | 7.81 | 125 | 125 |
| 6 | 32f | <0.97 | 31.25 | 125 | 7.81 | 125 | 31.25 |
| 7 | 32g | 7.81 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 7.81 | 62.5 | 31.25 |
| 8 | 32h | 1.95 | 15.63 | 31.25 | 7.81 | 31.25 | 7.81 |
| 9 | 32i | <0.97 | 125 | 125 | 3.9 | 125 | 250 |
| 10 | 32j | 3.9 | 125 | 125 | 7.81 | 125 | 125 |
| 11 | 32k | 3.9 | 125 | 125 | 3.9 | 125 | 62.5 |
| 12 | Azithromycin | <0.97 | <0.97 | <0.97 | <0.97 | <0.97 | <0.97 |
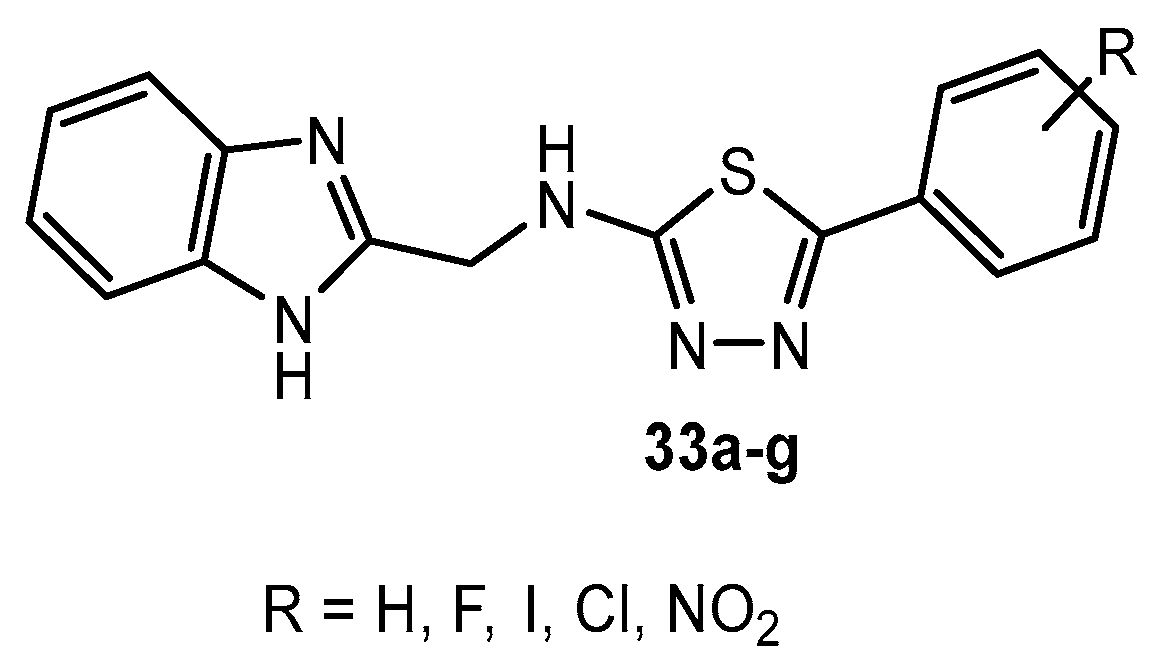
Table 18.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 33a–g.
Table 18.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 33a–g.
| Entry | Compound | R | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| S. aureus | S. epidermidis | P. aeruginosa | E. coli |
|---|
| 1 | 33a | H | 18 | 19 | 11 | 22 |
| 2 | 33b | 2-F | 20 | 19 | 11 | 18 |
| 3 | 33c | 2-I | 16 | 15 | 13 | - |
| 4 | 33d | 2-Cl | 20 | 19 | - | - |
| 5 | 33e | 3-Cl | 16 | 15 | - | 15 |
| 6 | 33f | 4-Cl | 20 | 18 | - | 17 |
| 7 | 33g | 4-NO2 | 24 | 23 | - | 15 |
Table 19.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 34a–e.
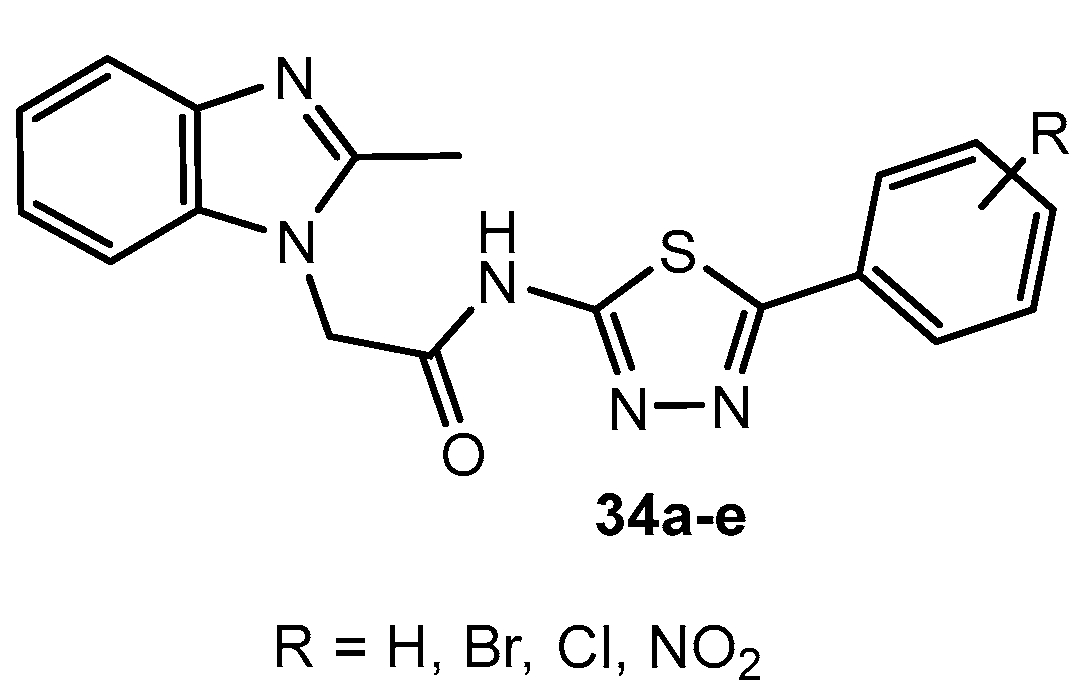
Table 19.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 34a–e.
| Entry | Compound | R | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| S. aureus | S. epidermidis | P. aeruginosa | E. coli |
|---|
| 1 | 34a | H | 14 | 12 | 17 | 15 |
| 2 | 34b | 2-Br | 13 | 12 | 14 | 15 |
| 3 | 34c | 2-Cl | 11 | 13 | 20 | 16 |
| 4 | 34d | 3-NO2 | 14 | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 5 | 34e | 3,5-diNO2 | 21 | 11 | 27 | 18 |
Table 20.
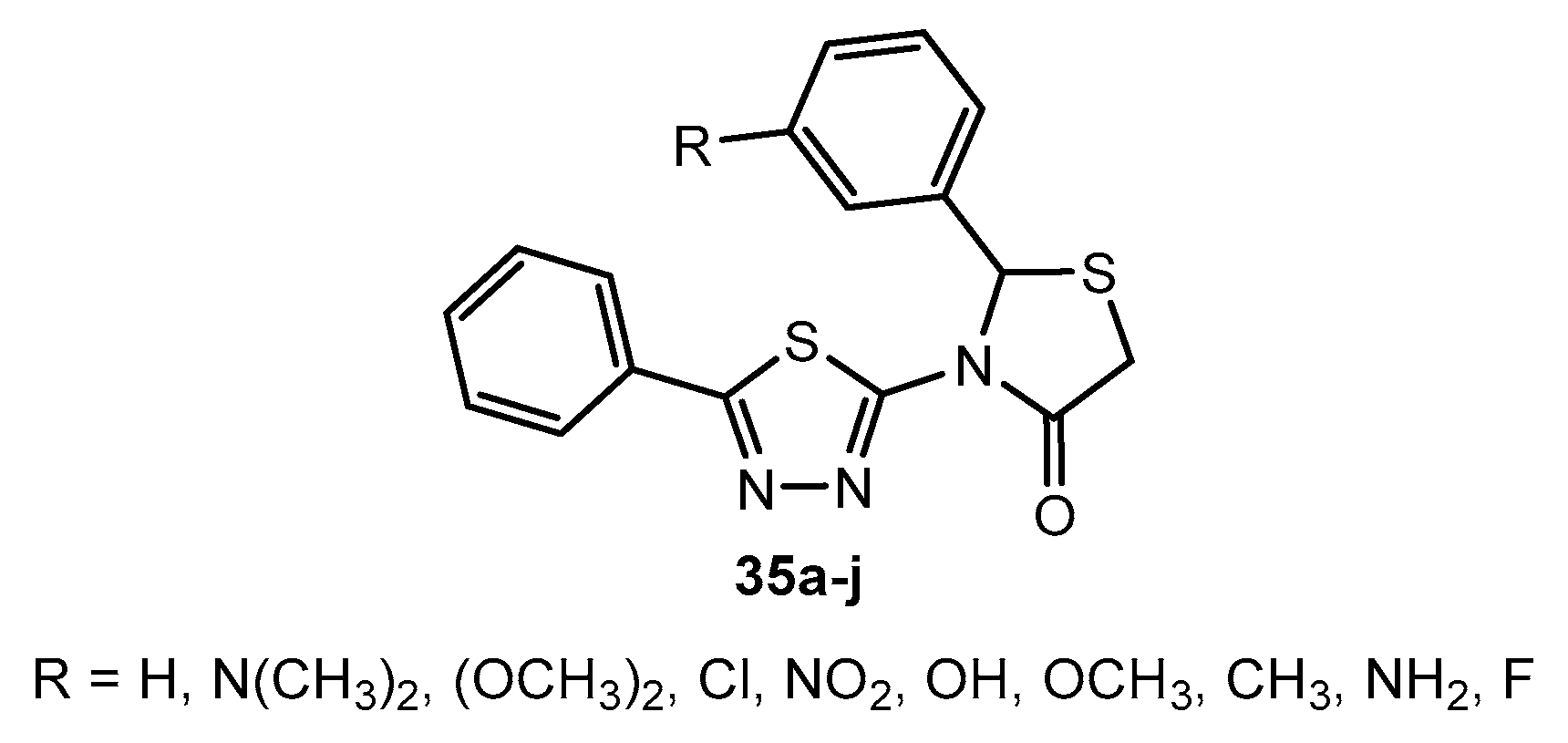
Antibacterial activity of compounds 35a–j.
Table 20.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 35a–j.
| Entry | Compound | R | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| S. aureus | S. pyogenes | P. aeruginosa | E. coli |
|---|
| 1 | 35a | H | 21 | 20 | 22 | 20 |
| 2 | 35b | N(CH3)2 | 23 | 24 | 26 | 22 |
| 3 | 35c | (OCH3)2 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 19 |
| 4 | 35d | Cl | 17 | 17 | 21 | 18 |
| 5 | 35e | NO2 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 15 |
| 6 | 35f | OH | 21 | 23 | 23 | 22 |
| 7 | 35g | OCH3 | 19 | 21 | 20 | 20 |
| 8 | 35h | CH3 | 20 | 18 | 19 | 19 |
| 9 | 35i | NH2 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 26 |
| 10 | 35j | F | 20 | 19 | 19 | 18 |
| 11 | Ampicillin | - | 25 | 25 | 26 | 24 |
Table 21.
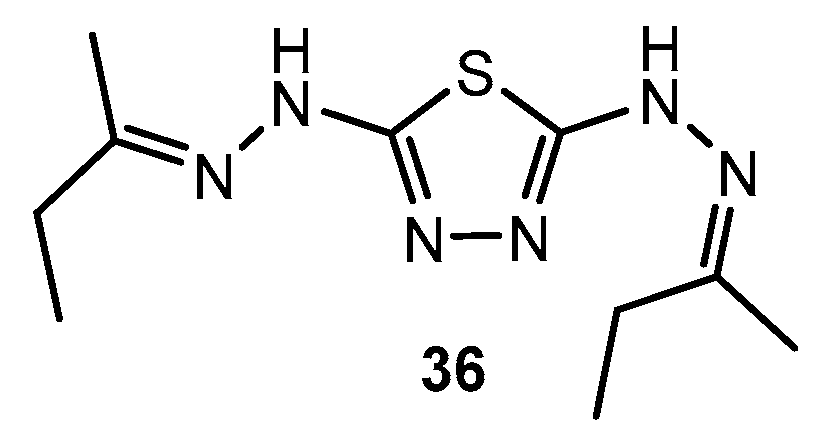
Antibacterial activity of compound 36 and its complexes.
Table 21.
Antibacterial activity of compound 36 and its complexes.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| E. coli | S. aureus |
|---|
| 1 | 36 | 11 | 22 |
| 2 | Cr(36)2Cl2]Cl] | 21 | 26 |
| 3 | [Co(36)2Cl2]Cl | 28 | 15 |
| 4 | [Cu(36)Cl2] | 32 | 27 |
| 5 | Ciprofloxacin | 30 | 25 |
Table 22.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 40a–g.
Table 22.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 40a–g.
| Entry | Compound | R | Zone of Inhibition in (mm) |
|---|
| E. coli | M. tuberculosis | P. mirabilis |
|---|
| 1 | 40a | OH | 24 | 18 | 19 |
| 2 | 40b | NO2 | 18 | 12 | 17 |
| 3 | 40c | Cl | 22 | 16 | 15 |
| 4 | 40d | OCH3 | 17 | 15 | 18 |
| 5 | 40e | CH3 | 12 | 10 | 11 |
| 6 | 40f | N(CH3)2 | 16 | 14 | 12 |
| 7 | 40g | OC2H5 | 21 | 19 | 14 |
| 8 | Amoxicillin | - | 20 | 17 | 18 |
Table 23.
Antibacterial activity of compound 41 and its complexes.
Table 23.
Antibacterial activity of compound 41 and its complexes.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| E. coli | S. aureus |
|---|
| 1 | 41 | 13 | 15 |
| 2 | [Fe(41)2Cl2]Cl | 31 | 29 |
| 3 | [Ni(41)Cl2] | 20 | 27 |
| 4 | [Cu(41)Cl2] | 33 | 23 |
| 5 | Ciprofloxacin | 30 | 25 |
Table 24.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 42a–ac.
Table 24.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 42a–ac.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) | Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| 1 | 42a | 1 | 16 | 42p | 0.25 |
| 2 | 42b | 1 | 17 | 42q | 0.06 |
| 3 | 42c | 0.25 | 18 | 42r | 0.06 |
| 4 | 42d | 0.5 | 19 | 42s | 0.06 |
| 5 | 42e | 0.125 | 20 | 42t | 0.007 |
| 6 | 42f | 0.015 | 21 | 42u | 0.06 |
| 7 | 42g | 0.015 | 22 | 42v | 1 |
| 8 | 42h | 2 | 23 | 42w | 1 |
| 9 | 42i | 0.5 | 24 | 42x | 1 |
| 10 | 42j | 0.25 | 25 | 42y | 8 |
| 11 | 42k | 0.25 | 26 | 42z | 2 |
| 12 | 42l | 0.25 | 27 | 42aa | >64 |
| 13 | 42m | 0.25 | 28 | 42ab | >64 |
| 14 | 42n | 2 | 29 | 42ac | >64 |
| 15 | 42o | 0.25 | 30 | Acetazolamide | 2 |
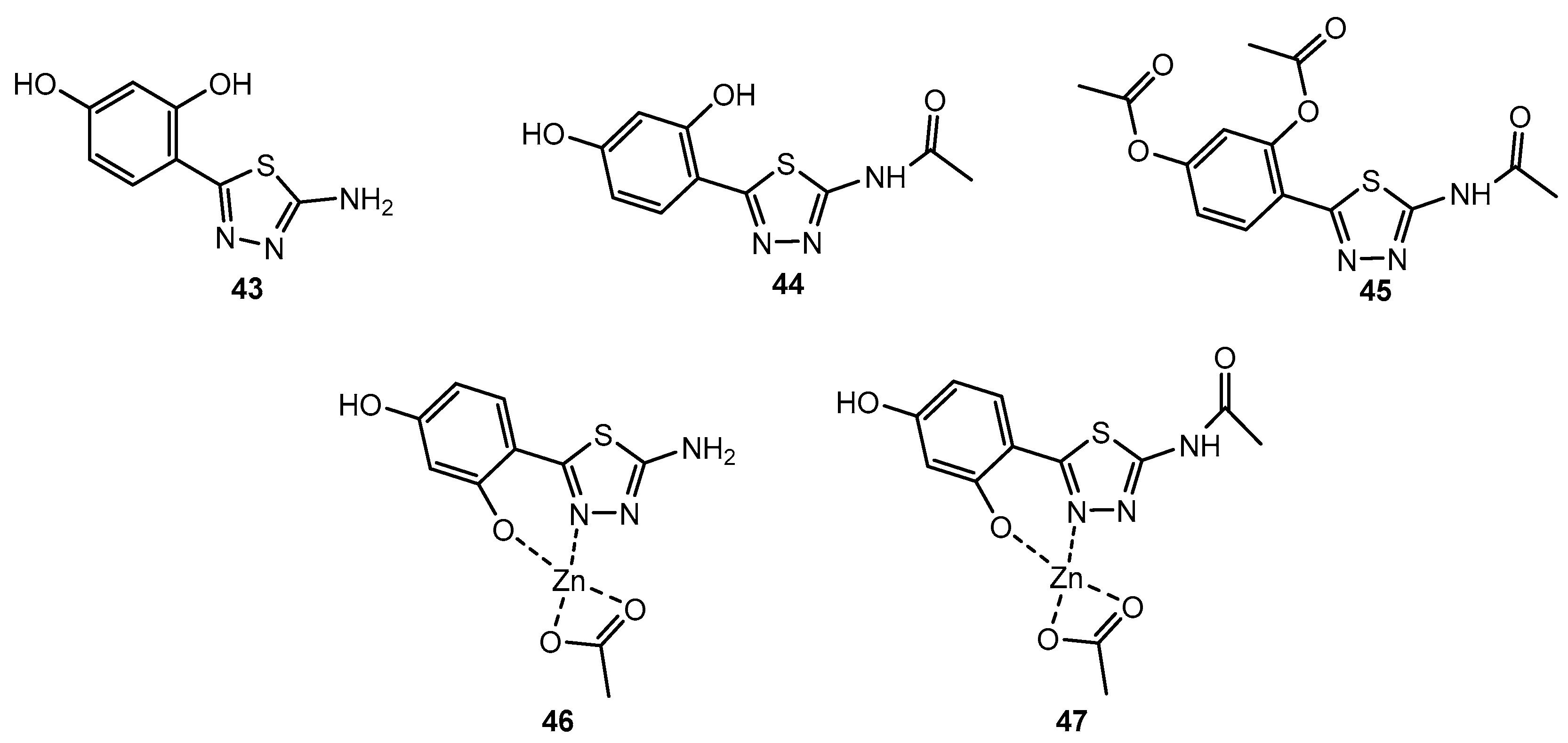
Table 25.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 43–45 and their complexes 46 and 47.
Table 25.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 43–45 and their complexes 46 and 47.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| S. aureus | P. aeruginosa | E. coli |
|---|
| 1 | 43 | 500 | - | 1000 |
| 2 | 44 | - | - | - |
| 3 | 45 | - | - | - |
| 4 | 46 | 500 | - | 1000 |
| 5 | 47 | 500 | - | 1000 |
Table 26.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 49a–i, 50a–i, 51a–h, and 52a–h.
Table 26.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 49a–i, 50a–i, 51a–h, and 52a–h.
| Entry | Compound | EC50 (μg/mL) | Entry | Compound | EC50 (μg/mL) |
|---|
| Xoo | Xoc | Xoo | Xoc |
|---|
| 1 | 49a | 51.02 | 51.81 | 18 | 50i | 31.78 | 26.54 |
| 2 | 49b | 55.9 | 63.50 | 19 | 51a | 100.39 | 107.15 |
| 3 | 49c | 54.78 | 62.12 | 20 | 51b | 107.8 | 118.91 |
| 4 | 49d | 40.6 | 42.53 | 21 | 51c | 61.66 | 61.20 |
| 5 | 49e | 47.6 | 86.29 | 22 | 51d | 190.41 | 163.17 |
| 6 | 49f | 95.37 | 64.08 | 23 | 51e | 182.31 | 167.98 |
| 7 | 49g | 51.73 | 72.13 | 24 | 51f | 175.29 | 176.67 |
| 8 | 49h | 48.63 | 47.62 | 25 | 51g | 138.08 | 140.29 |
| 9 | 494i | 44.45 | 45.80 | 26 | 51h | 143.93 | 147.33 |
| 10 | 50a | 51.34 | 60.72 | 27 | 52a | 16.03 | 27.69 |
| 11 | 50b | 78.94 | 77.23 | 28 | 52b | 28.47 | 36.47 |
| 12 | 50c | 38.74 | 46.97 | 29 | 52c | 3.14 | 8.83 |
| 13 | 50d | 40.52 | 48.17 | 30 | 52d | 51.83 | 70.02 |
| 14 | 50e | 33.73 | 40.23 | 31 | 52e | 31.13 | 44.20 |
| 15 | 50f | 88.08 | 89.66 | 32 | 52f | 41.31 | 66.12 |
| 16 | 50g | 80.52 | 65.66 | 33 | 52g | 44.66 | 44.59 |
| 17 | 50h | 33.25 | 35.49 | 34 | 52h | 59.56 | 61.33 |
Table 27.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 53a–d.
Table 27.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 53a–d.
| Entry | Compound | R | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| S. aureus | S. pyougenes | K. pneumoniae | E. coli |
|---|
| 1 | 53a | H | 15 | 6 | 8 | 17 |
| 2 | 53b | C7H15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 12 |
| 3 | 53c | C3H7 | 15 | 8 | 10 | 13 |
| 4 | 53d | C6H5 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 12 |
Table 28.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 57a–l.
Table 28.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 57a–l.
| Entry | Compound | R | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| S. aureus | B. subtilis | E. coli | P. aeruginosa |
|---|
| 1 | 57a | H | 14 | 13 | 15 | 14 |
| 2 | 57b | 4-CH3 | 12 | 13 | 12 | 15 |
| 3 | 57c | 4-OCH3 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 10 |
| 4 | 57d | 3-CH3 | 15 | 14 | 16 | 14 |
| 5 | 57e | 3-OCH3 | 15 | 16 | 15 | 14 |
| 6 | 57f | 4-C2H5 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 14 |
| 7 | 57g | 3-CH3-4-OCH3 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 12 |
| 8 | 57h | 4-Cl-3-CH3 | 11 | 11 | 13 | 12 |
| 9 | 57i | 4-Cl | 12 | 12 | 11 | 12 |
| 10 | 57j | 4-Br | 10 | 11 | 12 | 11 |
| 11 | 57k | 4-Cl-2-CH3 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 13 |
| 12 | 57l | 4-Br-2-CH3 | 15 | 13 | 14 | 12 |
| 13 | Streptomycin | - | 17 | 18 | 20 | 18 |
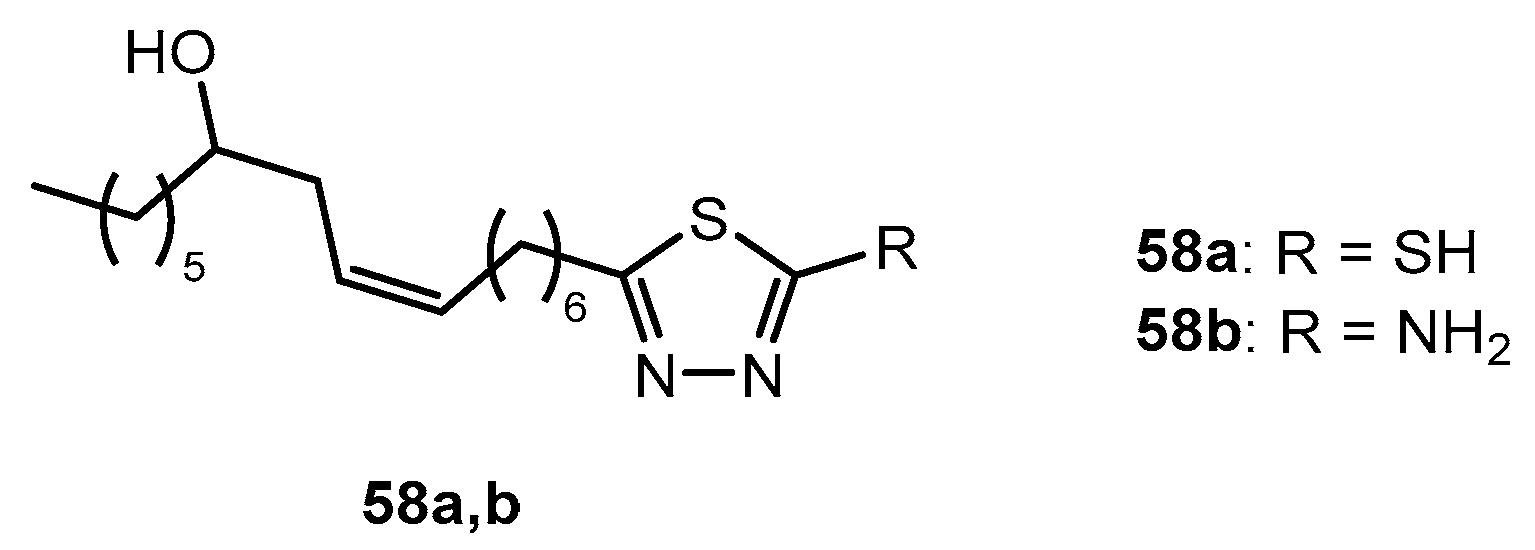
Table 29.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 58a,b.
Table 29.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 58a,b.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition in mm and (MIC) in µg/mL |
|---|
| SA | EF | BC | PA | EC | KP | S | PV |
|---|
| 1 | 58a | 10 (6.25) | 12 (25) | - | - | 8 (25) | 10 (25) | 10 (6.25) | 8 (25) |
| 2 | 58b | 8 (50) | 8 (50) | 7 (100) | 7 (100) | - | 10 (25) | 10 (25) | - |
| 3 | Ampicillin | 25 | 8 | 32 | 15 | 20 | 32 | 18 | 22 |
Table 30.
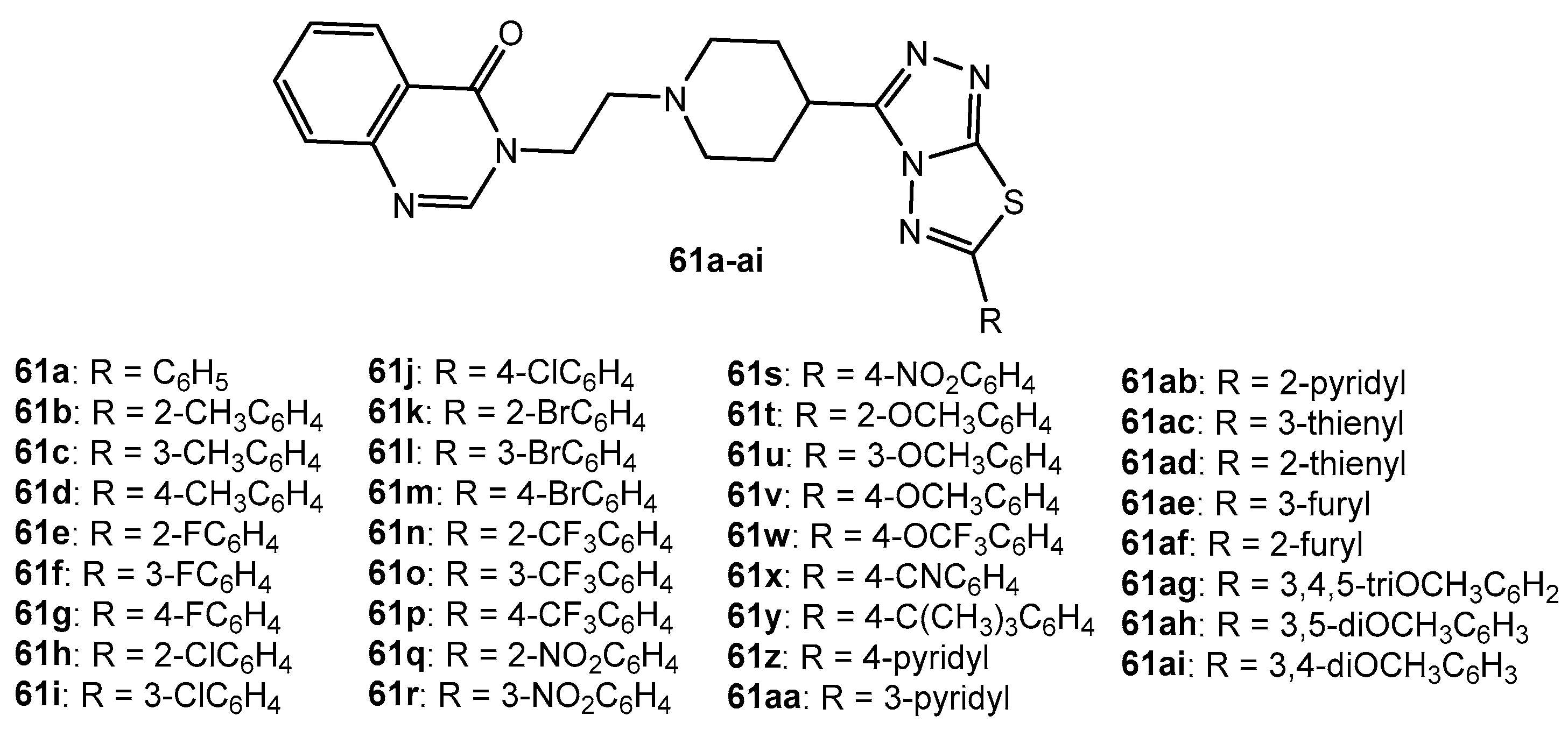
Antibacterial activity of compounds 61a–ai.
Table 30.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 61a–ai.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| Xac | Xoc | Xoo | Psa |
|---|
| 1 | 61a | 77.3 | 27.1 | 30.3 | 87.5 |
| 2 | 61b | 78.3 | 51.1 | 39.5 | 42.0 |
| 3 | 61c | 69.1 | 52.7 | 37.8 | 41.5 |
| 4 | 61d | 66.0 | 42.4 | 53.1 | 49.9 |
| 5 | 61e | 63.9 | 98.4 | 87.6 | 32.1 |
| 6 | 61f | 74.9 | 99.3 | 100 | 38.6 |
| 7 | 61g | 78.9 | 93.0 | 100 | 47.7 |
| 8 | 61h | 72.9 | 44.0 | 92.8 | 34.1 |
| 9 | 61i | 76.9 | 23.3 | 31.7 | 27.1 |
| 10 | 61j | 78.8 | 21.9 | 34.9 | 55.0 |
| 11 | 61k | 69.4 | 47.2 | 32.2 | 24.6 |
| 12 | 61l | 71.3 | 49.1 | 15.7 | 43.9 |
| 13 | 61m | 80.9 | 15.1 | 26.0 | 52.3 |
| 14 | 61n | 83.9 | 47.1 | 28.4 | 27.7 |
| 15 | 61o | 74.6 | 58.6 | 20.9 | 32.1 |
| 16 | 61p | 72.8 | 53.3 | 96.1 | 34.9 |
| 17 | 61q | 79.4 | 13.8 | 6.3 | 57.7 |
| 18 | 61r | 59.6 | 40.3 | 13.7 | 35.4 |
| 19 | 61s | 68.5 | 33.2 | 21.5 | 28.2 |
| 20 | 61t | 69.2 | 72.8 | 74.9 | 28.7 |
| 21 | 61u | 66.7 | 18.6 | 34.0 | 33.2 |
| 22 | 61v | 48.9 | 98.6 | 90.9 | 28.4 |
| 23 | 61w | 53.2 | 73.1 | 17.5 | 51.0 |
| 24 | 61x | 71.2 | 60.7 | 10.5 | 47.9 |
| 25 | 61y | 70.7 | 46.3 | 100 | 34.2 |
| 26 | 61z | 76.9 | 26.6 | 18.8 | 24.2 |
| 27 | 61aa | 75.2 | 43.9 | 13.7 | 34.3 |
| 28 | 61ab | 70.1 | 42.9 | 17.0 | 38.1 |
| 29 | 61ac | 76.3 | 38.1 | 6.7 | 31.1 |
| 30 | 61ad | 70.4 | 99.9 | 97.6 | 31.0 |
| 31 | 61ae | 67.6 | 32.5 | 25.4 | 25.0 |
| 32 | 61af | 21.9 | 100 | 98.1 | 38.4 |
| 33 | 61ag | 53.1 | 99.7 | 95.1 | 45.4 |
| 34 | 61ah | 48.7 | 87.2 | 82.5 | 37.5 |
| 35 | 61ai | 74.9 | 77.7 | 93.3 | 47.0 |
| 36 | BMT | 58.8 | 56.6 | 60.0 | 64.5 |
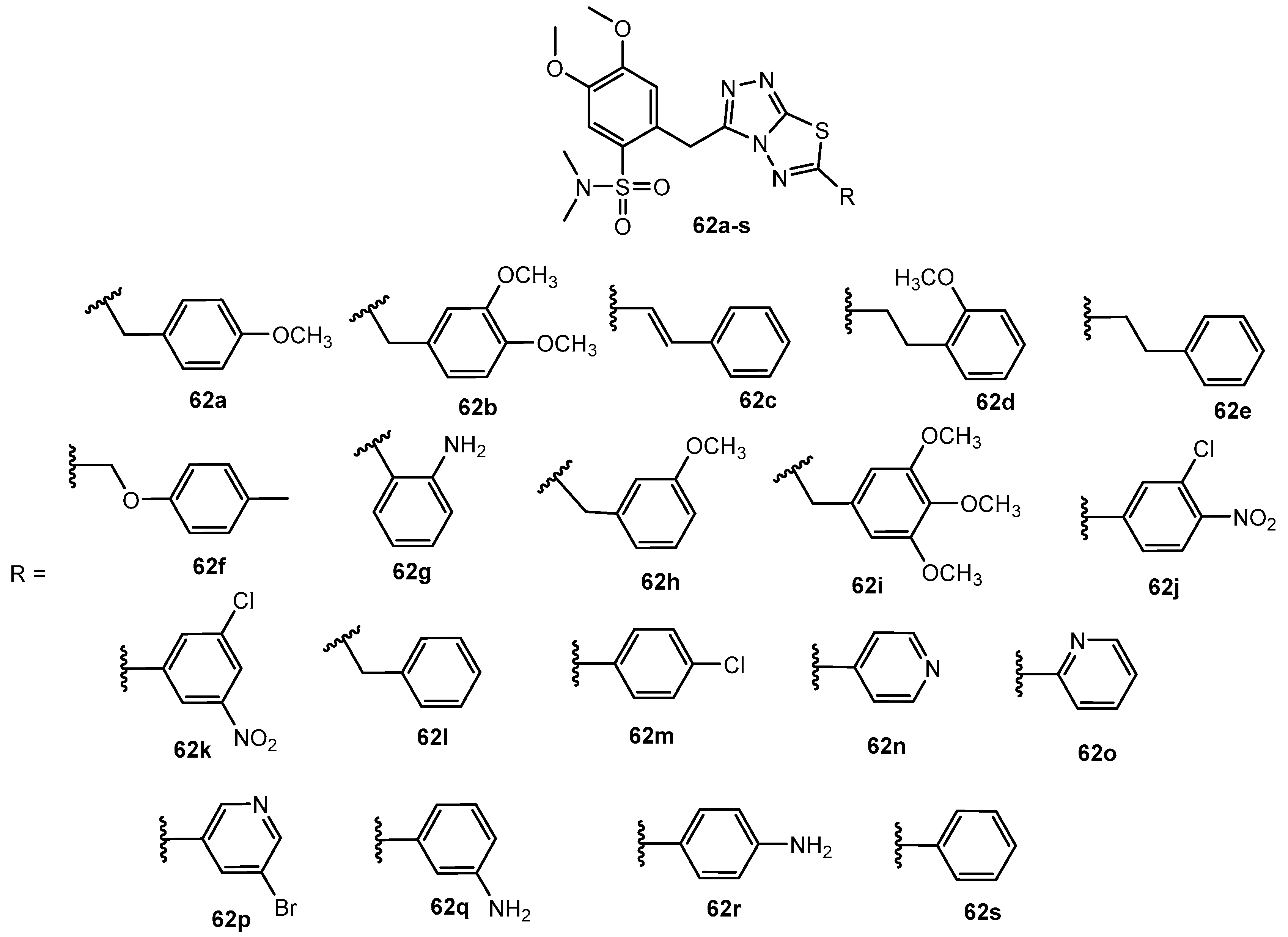
Table 31.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 62a–s.
Table 31.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 62a–s.
| Entry | Compound | MBC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| BC | SA | LM | PA | EC | ST |
|---|
| 1 | 62a | 20 | 40 | 20 | 200 | 10 | 20 |
| 2 | 62b | 20 | 20 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 20 |
| 3 | 62c | 20 | 40 | 10 | 20 | 10 | 20 |
| 4 | 62d | 20 | 0.20 | 0.020 | 0.040 | 0.020 | 0.020 |
| 5 | 62e | 20 | 36 | 40 | 20 | 10 | 40 |
| 6 | 62f | 20 | 20 | 36 | 40 | 10 | 10 |
| 7 | 62g | 20 | 40 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| 8 | 62h | 36 | 40 | 40 | 73 | 20 | 20 |
| 9 | 62i | 40 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 20 |
| 10 | 62j | 20 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 10 | 10 |
| 11 | 62k | 23 | 40 | 20 | 67 | 10 | 20 |
| 12 | 62l | 40 | 37 | 20 | 150 | 10 | 10 |
| 13 | 62m | 20 | 40 | 20 | 200 | 47 | 20 |
| 14 | 62n | 20 | 60 | 80 | 80 | 13 | 20 |
| 15 | 62o | 10 | 40 | 20 | 60 | 10 | 20 |
| 16 | 62p | 20 | 80 | 20 | 80 | 10 | 20 |
| 17 | 62q | 20 | 40 | 20 | 80 | 10 | 20 |
| 18 | 62r | 20 | 40 | 20 | 60 | 10 | 20 |
| 19 | 62s | 10 | 20 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 10 |
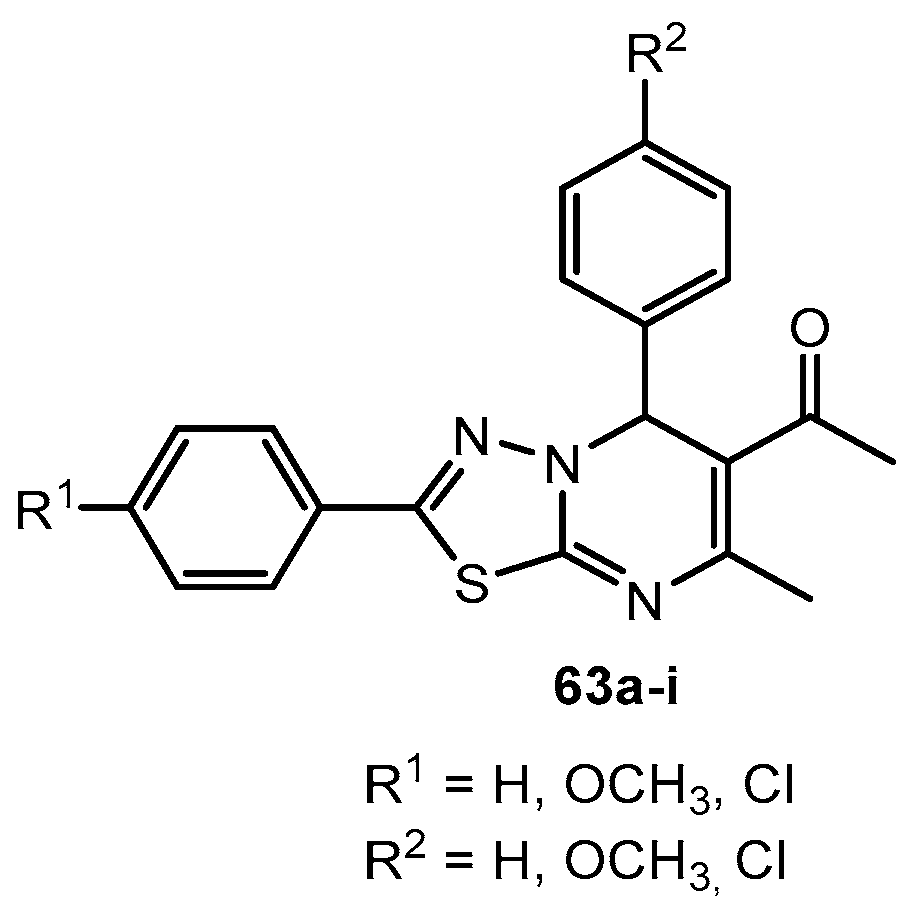
Table 32.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 63a–i.
Table 32.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 63a–i.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | MBC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| B. cereus | S. aureus | E. coli | K. pneumoniae |
|---|
| 1 | 63a | H | H | 280 | 260 | 250 | 265 |
| 2 | 63b | H | OCH3 | 130 | 140 | 145 | 135 |
| 3 | 63c | H | Cl | 250 | 255 | 260 | 240 |
| 4 | 63d | OCH3 | H | 150 | 165 | 210 | 195 |
| 5 | 63e | OCH3 | OCH3 | 130 | 145 | 120 | 135 |
| 6 | 63f | OCH3 | Cl | 150 | 140 | 160 | 210 |
| 7 | 63g | Cl | H | 280 | 290 | 275 | 270 |
| 8 | 63h | Cl | OCH3 | 185 | 215 | 200 | 210 |
| 9 | 63i | Cl | Cl | 240 | 260 | 250 | 250 |
Table 33.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 67a,b.
Table 33.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 67a,b.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| B. pumilis | S. faecalis | E. coli | E. cloacae |
| 1 | 67a | 19 | 21 | 20 | 17 |
| 2 | 67b | 21 | 16 | 19 | 18 |
| 3 | Penicillin G | 25 | 19 | - | - |
| 4 | Ciprofloxacin | - | - | 30 | 27 |
Table 34.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 68a–ah.
Table 34.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 68a–ah.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| Xac | Xoo |
|---|
| 1 | 68a | H | CH3 | CH3 | 0 | 93.91 |
| 2 | 68b | 6-Br | CH3 | CH3 | 48.28 | 70.30 |
| 3 | 68c | 6-F | CH3 | CH3 | 22.99 | 88.34 |
| 4 | 68d | 6-Cl | CH3 | CH3 | 43.03 | 91.57 |
| 5 | 68e | 6-CH3 | CH3 | CH3 | 43.10 | 82.61 |
| 6 | 68f | 7-Br | CH3 | CH3 | 46.51 | 80.95 |
| 7 | 68g | H | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 27.30 | 97.01 |
| 8 | 68h | 6-Br | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 67.96 | 83.62 |
| 9 | 68i | 6-F | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 46.98 | 98.99 |
| 10 | 68j | 6-Cl | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 59.99 | 93.42 |
| 11 | 68k | 6-CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 63.43 | 97.62 |
| 12 | 68l | H | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 69.68 | 65.17 |
| 13 | 68m | 6-Br | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 31.39 | 90.31 |
| 14 | 68n | 6-F | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 29.60 | 98.14 |
| 15 | 68o | 6-Cl | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 57.04 | 62.75 |
| 16 | 68p | 6-CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 36.71 | 61.30 |
| 17 | 68q | 7-Br | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 40.52 | 48.02 |
| 18 | 68r | H | CH3CHCH3 | CH3 | 44.11 | 97.22 |
| 19 | 68s | 6-Br | CH3CHCH3 | CH3 | 48.99 | 37.73 |
| 20 | 68t | 6-F | CH3CHCH3 | CH3 | 18.75 | 98.06 |
| 21 | 68u | 6-Cl | CH3CHCH3 | CH3 | 37.57. | 45.04 |
| 22 | 68v | 7-Br | CH3CHCH3 | CH3 | 57.26 | 9.64 |
| 23 | 68w | 6-F | allyl | CH3 | 57.40 | 99.39 |
| 24 | 68x | 6-CH3 | allyl | CH3 | 39.94 | 1.49 |
| 25 | 68y | H | Bn | CH3 | 45.19 | 36.92 |
| 26 | 68z | 6-Br | Bn | CH3 | 34.34 | 47.66 |
| 27 | 68aa | 6-F | Bn | CH3 | 29.02 | 46.53 |
| 28 | 68ab | 6-Cl | Bn | CH3 | 66.52 | 83.21 |
| 29 | 68ac | 6-CH3 | Bn | CH3 | 29.09. | 38.58 |
| 30 | 68ad | 7-Br | Bn | CH3 | 42.31 | 54.08 |
| 31 | 68ae | 6-F | CH3 | CH2CH3 | 55.82 | 70.22 |
| 32 | 68af | 6-Cl | CH3 | CH2CH3 | 87.43 | 78.29 |
| 33 | 68ag | H | i-Pr | CH2CH3 | 38.43 | 96.81 |
| 34 | 68ah | 6-CH3 | i-Pr | CH2CH3 | 46.48 | 8.80 |
| 35 | Bismerthiazole | - | - | - | 35.85 | 31.6 |
Table 35.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 69a–h.
Table 35.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 69a–h.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| SA | SE | BS | SP | PA | EC | KP | ST |
|---|
| 1 | 69a | 19.3 | 19.4 | 22.7 | - | - | 22.3 | 18.2 | 20.4 |
| 2 | 69b | 18.1 | 18.7 | 20.1 | - | - | 19.3 | 19.2 | 18.4 |
| 3 | 69c | 19.4 | 22.7 | 18.3 | - | - | 25.2 | 21.2 | 20.6 |
| 4 | 69d | 19.9 | 22.0 | 17.6 | - | - | 23.1 | 22.4 | 23.0 |
| 5 | 69e | 23.6 | 22.4 | 25.5 | - | - | 26.9 | 26.3 | 27.2 |
| 6 | 69f | 22.4 | 20.9 | 23.8 | - | - | 24.3 | 22.5 | 26.3 |
| 7 | 69g | 20.1 | 19.2 | 24.3 | - | - | 23.7 | 19.3 | 21.6 |
| 8 | 69h | 22.1 | 19.8 | 24.3 | - | - | 24.2 | 21.3 | 23.3 |
| 9 | Ampicillin | 23.7 | 22.4 | 32.4 | 24.5 | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | Gentamicin | - | - | - | - | 22.3 | 25.4 | 22.6 | 23.3 |
Table 36.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 70a–e.
Table 36.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 70a–e.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| E. coli | P. aeruginosa | P. vulgaris | B. subtilis | S. aureus |
|---|
| 1 | 70a | 20 | 40 | 20 | 10 | 20 |
| 2 | 70b | - | - | - | 40 | 80 |
| 3 | 70c | 40 | 160 | 80 | 40 | 20 |
| 4 | 70d | 160 | - | - | 80 | 160 |
| 5 | 70e | - | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | Ciprofloxacin | 5 | 7 | 1.25 | 2.5 | 1.25 |
Table 37.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 71a–f.
Table 37.
Antibacterial activity of compounds 71a–f.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| K. pneumoniae | P. aeruginosa | S. aureus | B. subtilis |
|---|
| 1 | 71a | 19 | 20 | 13 | 15 |
| 2 | 71b | 13 | 15 | 10 | 12 |
| 3 | 71c | 16 | 18 | 13 | 15 |
| 4 | 71d | 15 | 17 | 12 | 14 |
| 5 | 71e | 20 | 22 | 15 | 17 |
| 6 | 71f | 22 | 25 | 18 | 20 |
| 7 | Ciprofloxacin | 18 | 20 | 15 | 17 |
Table 38.
Antifungal activity of compounds 6a–p.
Table 38.
Antifungal activity of compounds 6a–p.
| Entry | Compound | R | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| S. sclerotiorum | R. solani | M. oryzae | C. gloeosporioides |
|---|
| 1 | 6a | H | 32.14 | 30.65 | 28.57 | 28.27 |
| 2 | 6b | 2-F | 90.48 | 72.32 | 55.36 | 52.98 |
| 3 | 6c | 2-Cl | 67.85 | 40.78 | 15.70 | 16.12 |
| 4 | 6d | 2-Br | 33.04 | 23.21 | 29.46 | 26.19 |
| 5 | 6e | 2-CH3 | 17.81 | 52.85 | 19.11 | 33.22 |
| 6 | 6f | 2-OCH3 | 50.00 | 38.69 | 31.25 | 25.89 |
| 7 | 6g | 2-OCF3 | <10 | 31.78 | 34.13 | 24.34 |
| 8 | 6h | 3-F | 82.14 | 57.44 | 38.99 | 45.83 |
| 9 | 6i | 3-CH3 | 83.63 | 52.98 | 31.85 | 38.69 |
| 10 | 6j | 3-OCH3 | 69.05 | 54.76 | 30.95 | 42.56 |
| 11 | 6k | 3-OCF3 | 59.52 | 40.48 | 41.96 | 43.15 |
| 12 | 6l | 4-F | 32.14 | 39.88 | 26.49 | 35.42 |
| 13 | 6m | 4-CH3 | 50.00 | 27.98 | 22.02 | 33.04 |
| 14 | 6n | 4-OCH3 | 55.36 | 49.40 | 33.63 | 33.93 |
| 15 | 6o | 4-OCF3 | 23.51 | 33.63 | 48.51 | 41.37 |
| 16 | 6p | 4-NH2 | 80.06 | 31.55 | 22.62 | 31.85 |
| 17 | Thifluzamide | - | 72.92 | 98.51 | 25.89 | 26.49 |
| 18 | Carbendazim | - | 98.21 | 100 | 100 | 96.13 |
Table 39.
Antifungal activity of compounds 72a–y.
Table 39.
Antifungal activity of compounds 72a–y.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| PP | CO | CA | GZ | AS | RS | FO | BM |
|---|
| 1 | 72a | 43 | 7 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 45 | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | 72b | 89 | 80 | 70 | 67 | 70 | 74 | 69 | 74 |
| 3 | 72c | 53 | 10 | 45 | 40 | 33 | 21 | 11 | 18 |
| 4 | 72d | 42 | 0 | 85 | 83 | 77 | 18 | 6 | 3 |
| 5 | 72e | 51 | 13 | 60 | 60 | 63 | 68 | 17 | 18 |
| 6 | 72f | 74 | 50 | 55 | 62 | 57 | 39 | 40 | 41 |
| 7 | 72g | 68 | 30 | 10 | 30 | 47 | 17 | 23 | 27 |
| 8 | 72h | 42 | 7 | 70 | 25 | 43 | 13 | 14 | 21 |
| 9 | 72i | 49 | 3 | 20 | 25 | 20 | 11 | 11 | 9 |
| 10 | 72j | 74 | 27 | 45 | 49 | 57 | 45 | 26 | 24 |
| 11 | 72k | 79 | 57 | 30 | 37 | 47 | 27 | 43 | 41 |
| 12 | 72l | 30 | 0 | 25 | 19 | 17 | 16 | 9 | 0 |
| 13 | 72m | 47 | 40 | 40 | 25 | 37 | 12 | 31 | 35 |
| 14 | 72n | 79 | 47 | 45 | 43 | 33 | 16 | 31 | 32 |
| 15 | 72o | 49 | 13 | 30 | 27 | 33 | 16 | 20 | 21 |
| 16 | 72p | 70 | 40 | 45 | 57 | 53 | 62 | 34 | 32 |
| 17 | 72q | 42 | 0 | 50 | 37 | 27 | 16 | 11 | 9 |
| 18 | 72r | 70 | 53 | 70 | 49 | 47 | 19 | 46 | 41 |
| 19 | 72s | 77 | 53 | 45 | 32 | 33 | 12 | 43 | 47 |
| 20 | 72t | 42 | 13 | 35 | 35 | 33 | 12 | 11 | 24 |
| 21 | 72u | 15 | 0 | 55 | 48 | 23 | 12 | 0 | 12 |
| 22 | 72v | 42 | 7 | 55 | 40 | 63 | 33 | 9 | 18 |
| 23 | 72w | 57 | 0 | 55 | 24 | 40 | 10 | 14 | 9 |
| 24 | 72x | 51 | 17 | 45 | 27 | 27 | 10 | 11 | 24 |
| 25 | 72y | 79 | 57 | 55 | 35 | 60 | 31 | 46 | 38 |
| 26 | Boscalid | 89 | 50 | 90 | 18 | 67 | 87 | 40 | 38 |
Table 40.
Antifungal activity of compounds 8a–o.
Table 40.
Antifungal activity of compounds 8a–o.
| Entry | Compound | R | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| C. albicans | A. niger | A. clavatus |
|---|
| 1 | 8a | H | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| 2 | 8b | 2-Br | 1000 | >1000 | >1000 |
| 3 | 8c | 4-Br | 250 | 100 | 500 |
| 4 | 8d | 2-Cl | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 5 | 8e | 4-Cl | 100 | >1000 | 100 |
| 6 | 8f | 2-F | 250 | 500 | 500 |
| 7 | 8g | 3-F | 500 | 1000 | >1000 |
| 8 | 8h | 4-F | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 9 | 8i | 2-OH | 250 | 100 | 500 |
| 10 | 8j | 4-OH | 1000 | 100 | 1000 |
| 11 | 8k | 4-CH3 | 500 | 1000 | 1000 |
| 12 | 8l | 4-OCH3 | 250 | >1000 | >1000 |
| 13 | 8m | 2-NO2 | 1000 | 500 | 500 |
| 14 | 8n | 3-NO2 | >1000 | 500 | 500 |
| 15 | 8o | 4-NO2 | 1000 | 100 | 250 |
| 16 | Nystatin | - | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 17 | Griseofulvin | - | 500 | 100 | 100 |
Table 41.
Antifungal activity of selected compounds 73a–x.
Table 41.
Antifungal activity of selected compounds 73a–x.
| Entry | Compound | Pathogens | EC50 (μg/mL) |
|---|
| 1 | 73b | Botrytis cinerea | 2.7 |
| 2 | 73g | Botrytis cinerea | 2.9 |
| 3 | 73o | Botrytis cinerea | 5.2 |
| 4 | Azoxystrobin | Botrytis cinerea | 14.5 |
| 5 | 73d | Tomato Botrytis cinerea | 3.5 |
| 6 | 73e | Tomato Botrytis cinerea | 14.1 |
| 7 | 73v | Tomato Botrytis cinerea | 25.9 |
| 8 | Azoxystrobin | Tomato Botrytis cinerea | 26.5 |
| 9 | 73b | Phomopsis sp. | 6.4 |
| 10 | 73d | Phomopsis sp. | 5.3 |
| 11 | 73o | Phomopsis sp. | 7.8 |
| 12 | Azoxystrobin | Phomopsis sp. | 10.4 |
Table 42.
Antifungal activity of compounds 74a–x.
Table 42.
Antifungal activity of compounds 74a–x.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| R. solani | Phomopsis sp. | P. capsici |
|---|
| 1 | 74a | 73.2 | 83.9 | 63.1 |
| 2 | 74b | 59.4 | 82.6 | 39.5 |
| 3 | 74c | 76.2 | 71.3 | 83.3 |
| 4 | 74d | 83.7 | 91.3 | 73.0 |
| 5 | 74e | 73.6 | 71.3 | 74.7 |
| 6 | 74f | 78.2 | 81.3 | 41.2 |
| 7 | 74g | 35.6 | 15.7 | 21.9 |
| 8 | 74h | 72.8 | 60.9 | 82.8 |
| 9 | 74i | 61.5 | 70.0 | 68.2 |
| 10 | 74j | 54.0 | 59.1 | 50.6 |
| 11 | 74k | 60.3 | 57.4 | 59.7 |
| 12 | 74l | 67.4 | 80.0 | 75.5 |
| 13 | 74m | 58.6 | 56.1 | 85.0 |
| 14 | 74n | 46.4 | 60.9 | 84.1 |
| 15 | 74o | 59.4 | 30.4 | 75.1 |
| 16 | 74p | 71.6 | 82.6 | 77.7 |
| 17 | 74q | 32.2 | 29.6 | 30.5 |
| 18 | 74r | 53.1 | 75.2 | 60.1 |
| 19 | 74s | 71.6 | 67.2 | 84.5 |
| 20 | 74t | 73.2 | 39.1 | 85.0 |
| 21 | 74u | 67.8 | 47.8 | 41.2 |
| 22 | 74v | 52.7 | 39.1 | 71.7 |
| 23 | 74w | 40.2 | 35.7 | 55.8 |
| 24 | 74x | 73.6 | 75.7 | 82.4 |
Table 43.
Antifungal activity of compounds 11a–l.
Table 43.
Antifungal activity of compounds 11a–l.
| Compound | 11a | 11b | 11c | 11d | 11e | 11f | 11g | 11h | 11i | 11j | 11k | 11l | Terinafine |
|---|
| Inhibition rate (%) | 43.4 | 3.4 | 25.8 | 31.9 | 4.3 | 7.3 | 11.1 | 14.2 | 34.3 | 21.2 | 9.4 | 0 | 50.7 |
Table 44.
Antifungal activity of compounds 75a–ag.
Table 44.
Antifungal activity of compounds 75a–ag.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| B. cinerea | A. solani | R. solani | F. graminearum | C. orbiculare |
|---|
| 1 | 75a | H | CH3 | 62.1 | 43.4 | 64.8 | 32.3 | 51.1 |
| 2 | 75b | 6-Br | CH3 | 100 | 87.0 | 92.4 | 70.0 | 87.4 |
| 3 | 75c | 6-F | CH3 | 34.4 | 43.7 | 50.4 | 28.7 | 43.8 |
| 4 | 75d | 6-Cl | CH3 | 100 | 81.7 | 83.0 | 44.5 | 75.1 |
| 5 | 75e | 6-CH3 | CH3 | 59.3 | 41.3 | 53.7 | 28.7 | 48.6 |
| 6 | 75f | 7-Br | CH3 | 11.0 | 32.3 | 75.4 | 38.3 | 13.3 |
| 7 | 75g | H | CH2CH3 | 100 | 65.6 | 85.6 | 48.7 | 100 |
| 8 | 75h | 6-Br | CH2CH3 | 100 | 84.9 | 91.8 | 71.8 | 100 |
| 9 | 75i | 6-F | CH2CH3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 49.4 | 100 |
| 10 | 75j | 6-Cl | CH2CH3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 73.9 | 100 |
| 11 | 75k | 6-CH3 | CH2CH3 | 59.9 | 50.4 | 62.6 | 41.1 | 61.2 |
| 12 | 75l | H | Pr | 64.3 | 53.9 | 76.3 | 36.1 | 77.4 |
| 13 | 75m | 6-Br | Pr | 100 | 71.4 | 91.2 | 79.0 | 93.2 |
| 14 | 75n | 6-F | Pr | 84.9 | 63.6 | 86.8 | 76.1 | 98.9 |
| 15 | 75o | 6-Cl | Pr | 82.7 | 69.2 | 100 | 59.4 | 95.4 |
| 16 | 75p | 6-CH3 | Pr | 39.8 | 36.6 | 38.9 | 28.3 | 48.8 |
| 17 | 75q | 7-Br | Pr | 16.1 | 23.9 | 23.9 | 14.7 | 16.9 |
| 18 | 75r | H | i-Pr | 49.1 | 79.1 | 89.1 | 40.6 | 100 |
| 19 | 75s | 6-Br | i-Pr | 100 | 98.5 | 100 | 65.6 | 100 |
| 20 | 75t | 6-F | i-Pr | 44.8 | 84.9 | 93.5 | 51.0 | 100 |
| 21 | 75u | 6-Cl | i-Pr | 100 | 66.2 | 100 | 75.6 | 100 |
| 22 | 75v | 6-CH3 | i-Pr | 51.8 | 46.3 | 45.8 | 40.0 | 68.6 |
| 23 | 75w | 7-Br | i-Pr | 22.0 | 36.1 | 62.1 | 26.1 | 27.1 |
| 24 | 75x | H | allyl | 85.3 | 59.0 | 93.9 | 35.0 | 83.3 |
| 25 | 75y | 6-Cl | allyl | 100 | 84.0 | 100 | 21.4 | 30.2 |
| 26 | 75z | 6-CH3 | allyl | 24.9 | 19.0 | 57.4 | 36.2 | 32.8 |
| 27 | 75aa | 7-Br | allyl | 33.9 | 41.7 | 70.7 | 17.5 | 20.0 |
| 28 | 75ab | H | Bn | 13.9 | 27.0 | 23.7 | 17.3 | 16.7 |
| 29 | 75ac | 6-Br | Bn | 13.6 | 39.2 | 73.6 | 54.6 | 39.0 |
| 30 | 75ad | 6-F | Bn | 20.2 | 25.4 | 31.7 | 40.1 | 33.1 |
| 31 | 75ae | 6-Cl | Bn | 13.7 | 5.3 | 12.9 | 14.7 | 5.1 |
| 32 | 75af | 6-CH3 | Bn | 10.7 | 0 | 24.0 | 19.6 | 11.9 |
| 33 | 75ag | 7-Br | Bn | 6.8 | 0 | 14.1 | 9.5 | 5.1 |
| 34 | Carbendazim | - | - | 97.1 | 65.3 | 100 | 100 | 84.3 |
| 35 | Boscalid | - | - | 83.7 | 35.7 | 81.9 | 17.5 | - |
Table 45.
Antifungal activity of compounds 12a–r.
Table 45.
Antifungal activity of compounds 12a–r.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| C. gloeosporioides | N. ishiwadae | G. persicaria | Fusarium sp. |
|---|
| 1 | 12a | CH3 | CH3 | 62 | 74 | 85 | 65 |
| 2 | 12b | CH3 | CH2CH3 | 83 | 74 | 81 | 59 |
| 3 | 12c | CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | 87 | 66 | 77 | 56 |
| 4 | 12d | CH3 | CH2C6H5 | 85 | 75 | 79 | 74 |
| 5 | 12e | CH3 | CH2C6H4-4-F | 60 | 60 | 65 | 45 |
| 6 | 12f | CH3 | CH2C6H4-4-Cl | 76 | 62 | 72 | 49 |
| 7 | 12g | CH3 | CH2C6H4-3-Cl | 70 | 51 | 74 | 35 |
| 8 | 12h | CH3 | CH2C6H4-2-Cl | 56 | 46 | 64 | 34 |
| 9 | 12i | CH3 | CH2C6H3-2,4-diCl | 63 | 70 | 59 | 59 |
| 10 | 12j | CF3 | CH3 | 64 | 74 | 75 | 57 |
| 11 | 12k | CF3 | CH2CH3 | 79 | 55 | 65 | 43 |
| 12 | 12l | CF3 | CH2CH2CH3 | 66 | 63 | 77 | 51 |
| 13 | 12m | CF3 | CH2C6H5 | 68 | 34 | 60 | 23 |
| 14 | 12n | CF3 | CH2C6H4-4-F | 78 | 61 | 74 | 51 |
| 15 | 12o | CF3 | CH2C6H4-4-Cl | 74 | 71 | 72 | 63 |
| 16 | 12p | CF3 | CH2C6H4-3-Cl | 90 | 37 | 41 | 54 |
| 17 | 12q | CF3 | CH2C6H4-2-Cl | 77 | 51 | 74 | 39 |
| 18 | 12r | CF3 | CH2C6H3-2,4-diCl | 73 | 66 | 70 | 49 |
| 19 | Prochloraz | - | - | 87 | 98 | 95 | 91 |
Table 46.
Antifungal activity of compounds 76a–t.
Table 46.
Antifungal activity of compounds 76a–t.
| Entry | Compound | R | EC50 (95% Cl, μmol/L) |
|---|
| R. solani | B. cinerea | S. lycopersici | C. lunata | P. aphanidermatum |
|---|
| 1 | 76a | 2-F | 0.0285 | 0.8424 | 0.1432 | 0.4226 | --- |
| 2 | 76b | 3-F | 2.4311 | --- | 0.0374 | 0.0237 | --- |
| 3 | 76c | 4-F | 0.1297 | 7.7911 | 1.2300 | --- | --- |
| 4 | 76d | 2-Cl | 0.1586 | 1.2954 | --- | --- | --- |
| 5 | 76e | 3-Cl | 0.0466 | --- | 0.0105 | 0.0051 | 0.1603 |
| 6 | 76f | 4-Cl | 0.0415 | 0.1422 | 1.0919 | 1.1636 | 0.7236 |
| 7 | 76g | 2-Br | --- | 0.0045 | --- | --- | 0.2273 |
| 8 | 76h | 4-Br | --- | --- | 0.0590 | 0.0359 | 0.2717 |
| 9 | 76i | 2-CH3 | 0.1303 | 0.1169 | 1.8938 | 0.2065 | --- |
| 10 | 76j | 3-CH3 | 0.0107 | --- | 3.6669 | 0.3369 | --- |
| 11 | 76k | 4-CH3 | 0.0328 | 0.9588 | --- | --- | 0.0334 |
| 12 | 76l | 2-OCH3 | 1.5904 | 0.0024 | 2.9342 | 0.4719 | - |
| 13 | 76m | 3-OCH3 | 0.0079 | 0.9994 | 0.0993 | 0.0119 | 0.0355 |
| 14 | 76n | 4-OCH3 | 0.0857 | --- | --- | - | 0.0180 |
| 15 | 76o | 3-CF3 | 0.0160 | 0.1465 | 0.0481 | 0.3058 | 0.0270 |
| 16 | 76p | 4-CF3 | 0.0028 | --- | 0.0359 | 1.0790 | 1.9811 |
| 17 | 76q | 2,4-diCl | 0.0547 | 0.0347 | 0.2990 | 0.2019 | - |
| 18 | 76r | 2,4-diF | 0.0155 | 0.1419 | 8.2794 | - | 0.4482 |
| 19 | 76s | 3,4-diOCH3 | 0.0189 | 0.1708 | 0.2725 | 0.0318 | 3.5046 |
| 20 | 76t | 3,4,5-triOCH3 | 1.8869 | 1.1614 | 0.1054 | 0.0198 | 1.1971 |
| 21 | Difenoconazole | - | 0.0019 | 0.0042 | 0.0124 | 0.0014 | 0.0001 |
Table 47.
Antifungal activity of compounds 77a–j.
Table 47.
Antifungal activity of compounds 77a–j.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| C. albicans | P. species | A. Niger |
|---|
| 1 | 77a | - | - | - |
| 2 | 77b | - | 9 | 5 |
| 3 | 77c | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| 4 | 77d | - | 6 | - |
| 5 | 77e | - | 8 | - |
| 6 | 77f | - | 8 | - |
| 7 | 77g | 7 | 10 | 8 |
| 8 | 77h | - | 5 | - |
| 9 | 77i | - | - | - |
| 10 | 77j | - | 8 | - |
Table 48.
Antifungal activity of compounds 78a–d.
Table 48.
Antifungal activity of compounds 78a–d.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| C. albicans | C. parapsilosis |
|---|
| 1 | 78a | 128 | 64 |
| 2 | 78b | >128 | >128 |
| 3 | 78c | >128 | 16 |
| 4 | 78d | 128 | 64 |
Table 49.
Antifungal activity of compounds 13a–i.
Table 49.
Antifungal activity of compounds 13a–i.
| Entry | Compound | R | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| A. fumigatus | C. albicans | C. krusei |
|---|
| 1 | 13a | H | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 13b | 2-Cl | 6 | 16 | 16 |
| 3 | 13c | 3-Cl | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| 4 | 13d | 4-Cl | 12 | 16 | 18 |
| 5 | 13e | 3-NO2 | 10 | 12 | 12 |
| 6 | 13f | 4-NO2 | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 7 | 13g | 3-OCH3-4-OH | 0 | 10 | 8 |
| 8 | 13h | 4-CH3 | 6 | 6 | 8 |
| 9 | 13i | 2-OH | 8 | 12 | 16 |
| 10 | Fluconazole | - | 0 | 29 | 20 |
Table 50.
Antifungal activity of compounds 14a–c.
Table 50.
Antifungal activity of compounds 14a–c.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| A. niger | F. solani | P. chrysogenum | P. frequentans | A. alternata |
|---|
| 1 | 14a | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.125 |
| 2 | 14b | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 |
| 3 | 14c | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 | >32 |
| 4 | Caspofungin | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
Table 51.
Antifungal activity of selected compounds 79a–ae.
Table 51.
Antifungal activity of selected compounds 79a–ae.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| G. saubinetii | A. solani | V. dahliae | G. zeae | T. cucumeris |
|---|
| 1 | 79c | 102.8 | 91.9 | - | - | 31.3 |
| 2 | 79d | 84.2 | 119.0 | - | - | 15.3 |
| 3 | 79i | 86.8 | 62.5 | - | 87.3 | 11.8 |
| 4 | 79j | 23.3 | 50.0 | 88.4 | 63.0 | 9.7 |
| 5 | 79k | 28.0 | 45.9 | 89.2 | 54.9 | 18.7 |
| 6 | 79m | 43.3 | 42.3 | 58.7 | 104.0 | 35.4 |
| 7 | 79n | 52.2 | 37.1 | 73.4 | 112.7 | 27.7 |
| 8 | 79o | 11.4 | 36.6 | 69.6 | 167.5 | 46.1 |
| 9 | 79p | 92.7 | 37.0 | - | - | - |
| 10 | 79q | 90.1 | 63.8 | - | 108.1 | 25.7 |
| 11 | 79s | 47.6 | 56.4 | 66.2 | 55.3 | 51.2 |
| 12 | 79t | 37.6 | 42.1 | 72.1 | 49.1 | 20.0 |
| 13 | 79u | 23.6 | 41.2 | 72.9 | 33.7 | 24.3 |
| 14 | 79w | 69.2 | 70.5 | - | - | - |
| 15 | 79x | 37.1 | 49.6 | 110.6 | 81.4 | 34.9 |
| 16 | 79y | 47.7 | 76.4 | 102.9 | 119.9 | 32.7 |
| 17 | 79z | 43.9 | 35.8 | - | 93.8 | 60.6 |
| 18 | 79aa | 31.4 | 47.1 | 95.8 | 86.3 | 32.3 |
| 19 | 79ac | 49.2 | 53.2 | 175.8 | 92.3 | 116.4 |
| 20 | 79ad | 91.0 | 48.2 | - | 112.9 | 53.9 |
| 21 | Triadimefon | 14.8 | 45.3 | 2.9 | 16.9 | 11.0 |
Table 52.
Antifungal activity of compounds 80a–v.
Table 52.
Antifungal activity of compounds 80a–v.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| BC | PS | CG | RS | PC | SS | FcU | FG | AB | FcA |
|---|
| 1 | 80a | 55.5 | 32.2 | 47.7 | 54.0 | 30.0 | 40.6 | 20.5 | 33.2 | 44.4 | 44.4 |
| 2 | 80b | 61.3 | 40.4 | 46.0 | 55.5 | 38.4 | 38.2 | 18.9 | 36.5 | 46.0 | 33.9 |
| 3 | 80c | 65.1 | 37.2 | 47.7 | 59.3 | 34.5 | 63.6 | 32.3 | 24.9 | 51.7 | 48.8 |
| 4 | 80d | 36.6 | 34.1 | 42.7 | 38.6 | 41.8 | 43.8 | 35.0 | 38.5 | 51.0 | 40.3 |
| 5 | 80e | 38.7 | 60.2 | 41.8 | 43.8 | 36.3 | 44.6 | 32.7 | 31.6 | 49.8 | 42.3 |
| 6 | 80f | 60.1 | 51.7 | 32.2 | 48.5 | 28.7 | 10.7 | 41.7 | 32.8 | 35.6 | 42.3 |
| 7 | 80g | 74.6 | 36.8 | 30.1 | 55.3 | 32.1 | 51.2 | 29.1 | 35.7 | 32.6 | 39.1 |
| 8 | 80h | 62.2 | 53.5 | 35.6 | 51.5 | 31.2 | 52.6 | 30.7 | 28.3 | 42.9 | 42.7 |
| 9 | 80i | 54.4 | 55.0 | 36.0 | 52.2 | 49.4 | 53.8 | 31.1 | 31.6 | 39.8 | 47.6 |
| 10 | 80j | 56.7 | 37.2 | 38.9 | 47.1 | 51.9 | 45.0 | 30.3 | 33.2 | 28.7 | 41.5 |
| 11 | 80k | 33.3 | 27.1 | 24.3 | 57.4 | 35.7 | 45.7 | 46.5 | 33.5 | 36.8 | 47.6 |
| 12 | 80l | 91.7 | 59.6 | 36.0 | 55.5 | 24.5 | 54.2 | 37.8 | 35.7 | 39.5 | 45.6 |
| 13 | 80m | 83.2 | 42.8 | 41.8 | 54.0 | 34.2 | 47.0 | 46.5 | 35.7 | 39.8 | 52.4 |
| 14 | 80n | 69.1 | 73.8 | 54.0 | 65.6 | 16.8 | 71.5 | 40.9 | 20.2 | 47.9 | 50.8 |
| 15 | 80o | 58.8 | 59.0 | 36.0 | 40.1 | 32.9 | 57.4 | 39.4 | 51.6 | 34.5 | 47.6 |
| 16 | 80p | 50.4 | 50.2 | 23.9 | 40.8 | 32.5 | 48.8 | 39.4 | 31.2 | 30.3 | 51.6 |
| 17 | 80q | 87.3 | 66.1 | 46.4 | 65.2 | 22.4 | 65.3 | 34.3 | 28.4 | 48.3 | 50.4 |
| 18 | 80r | 96.2 | 65.3 | 45.2 | 63.4 | 22.4 | 58.7 | 29.5 | 18.0 | 47.1 | 51.2 |
| 19 | 80s | 60.1 | 49.4 | 41.0 | 45.6 | 28.3 | 47.0 | 41.3 | 32.0 | 40.2 | 46.4 |
| 20 | 80t | 65.9 | 42.8 | 34.3 | 45.2 | 49.8 | 45.0 | 26.0 | 26.6 | 31.4 | 46.4 |
| 21 | 80u | 58.4 | 72.8 | 45.2 | 46.3 | 46.8 | 66.9 | 35.4 | 44.3 | 42.5 | 48.4 |
| 22 | 80v | 52.7 | 38.0 | 37.7 | 52.8 | 52.7 | 41.7 | 28.7 | 37.7 | 36.8 | 44.4 |
| 23 | Azoxystrobin | 80.7 | 58.1 | 56.1 | 75.7 | 75.5 | 71.9 | 48.0 | 36.6 | 24.5 | 60.9 |
Table 53.
Antifungal activity of compounds 16a–i.
Table 53.
Antifungal activity of compounds 16a–i.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| A. niger | A. flavus | C. albicans | S. cerevisiae | F. oxysporum |
|---|
| 1 | 16a | 200 | 50 | 25 | 12.5 | 25 |
| 2 | 16b | 50 | 25 | 0.78 | 6.25 | 25 |
| 3 | 16c | 100 | 6.25 | 1.56 | 25 | 6.25 |
| 4 | 16d | 12.5 | 1.56 | 3.125 | 1.56 | 200 |
| 5 | 16e | 6.25 | 200 | 6.25 | 100 | 6.25 |
| 6 | 16f | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| 7 | 16g | 50 | 0.78 | 3.125 | 3.125 | 1.56 |
| 8 | 16h | 3.125 | 12.5 | 200 | 400 | 1.56 |
| 9 | 16i | 0.78 | 3.125 | 12.5 | 0.78 | 0.78 |
| 10 | Miconazole | 1.56 | 1.56 | 3.125 | 3.125 | 3.125 |
| 11 | Fluconazole | 1.56 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 |
Table 54.
Antifungal activity of compounds 20a–g.
Table 54.
Antifungal activity of compounds 20a–g.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | MIC (µM) |
|---|
| T. harzianum | A. niger |
|---|
| 1 | 20a | Br | 4-OH | 7.15 | 28.60 |
| 2 | 20b | Br | 4-NH2 | 28.67 | 28.67 |
| 3 | 20c | OCH3 | 3,5-diCl | 14.17 | 28.34 |
| 4 | 20d | OCH3 | 4-NO2 | 14.99 | 14.99 |
| 5 | 20e | OCH3 | 4-Br | 6.93 | 13.86 |
| 6 | 20f | Cl | 4-NO2 | 3.71 | 29.69 |
| 7 | 20g | Br | 4-Cl | 6.87 | 3.43 |
| 8 | Fluconazole | - | - | 5.10 | 5.10 |
Table 55.
Antifungal activity of compounds 24a–c.
Table 55.
Antifungal activity of compounds 24a–c.
| Entry | Compound | R | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| C. albicans | A. fumigatus | P. chrysogenum |
|---|
| 1 | 24a | H | 64 | 128 | 64 |
| 2 | 24b | Br | 8 | 16 | 8 |
| 3 | 24c | CH3 | 16 | 32 | 16 |
| 4 | Fluconazole | - | 4 | 8 | 8 |
Table 56.
Antifungal activity of selected compounds 81a–ae.
Table 56.
Antifungal activity of selected compounds 81a–ae.
| Entry | Compound | EC50 (100 μg/mL) |
|---|
| G. saubinetii | V. dahliae | A. solani | G. zeae | T. cucumeris |
|---|
| 1 | 81a | 30.5 | 48.1 | 61.7 | 59.8 | 32.8 |
| 2 | 81b | 21.9 | 45.4 | 67.5 | 42.8 | 22.2 |
| 3 | 81c | 21.5 | 41.6 | 63.4 | 37.3 | 39.6 |
| 4 | Triadimefon | 14.8 | 2.9 | 45.3 | 16.9 | 11.0 |
| 5 | Tebuconazole | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
Table 57.
Antifungal activity of compounds 25a–l.
Table 57.
Antifungal activity of compounds 25a–l.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| C. albicans | A. niger |
|---|
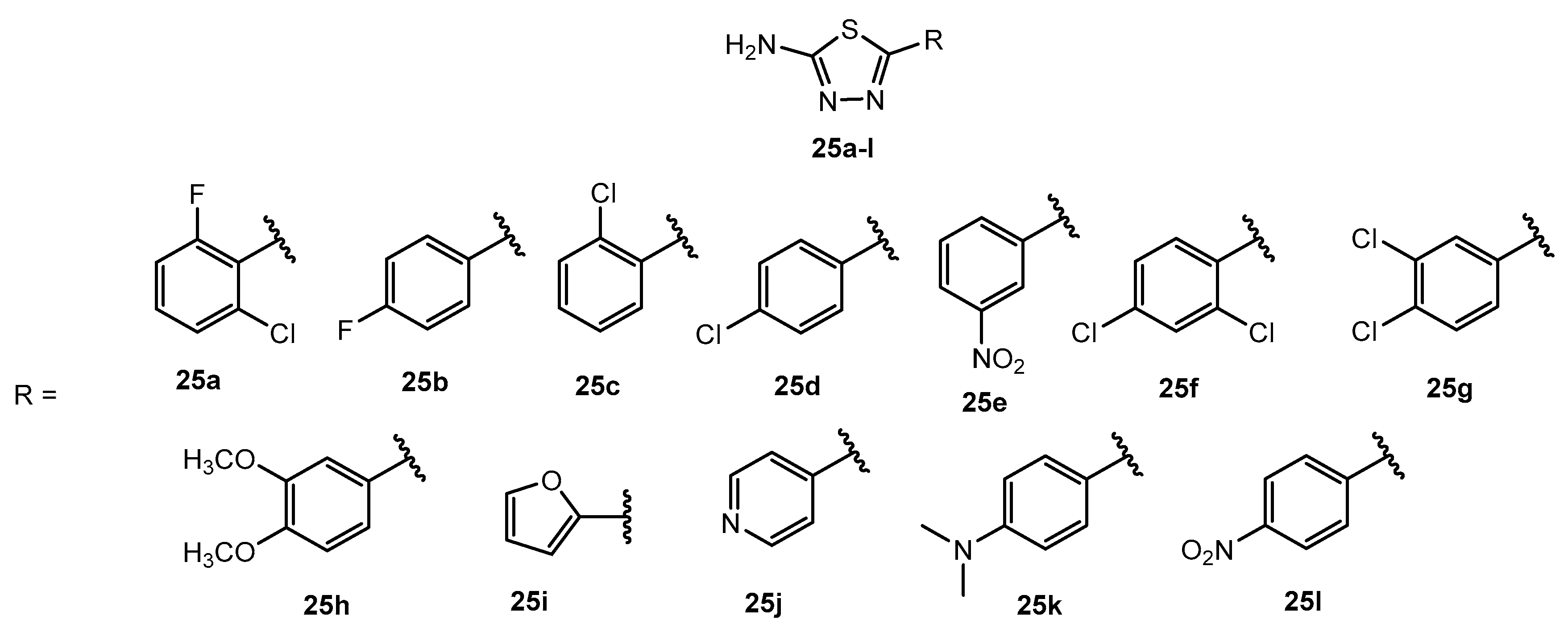
| 1 | 25a | - | - |
| 2 | 25b | 1024 | 512 |
| 3 | 25c | 512 | >1024 |
| 4 | 25d | 128 | 128 |
| 5 | 25e | - | - |
| 6 | 25f | - | - |
| 7 | 25g | 8 | 64 |
| 8 | 25h | - | - |
| 9 | 25i | - | - |
| 10 | 25j | 128 | 128 |
| 11 | 25k | 1024 | >1024 |
| 12 | 25l | 512 | 512 |
| 13 | Fluconazole | 4 | 256 |
Table 58.
Antifungal activity of compounds 82a–u.
Table 58.
Antifungal activity of compounds 82a–u.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| FO | CA | PP | AS | GZ | RS | BM | CO |
|---|
| 1 | 82a | 19.1 | 23.0 | 33.1 | 57.6 | 31.2 | 12.2 | 19.5 | 14.5 |
| 2 | 82b | 23.6 | 31.7 | 48.5 | 43.3 | 28.2 | 12.2 | 19.5 | 14.5 |
| 3 | 82c | 34.1 | 64.3 | 94.8 | 56.2 | 56.6 | 19.8 | 31.3 | 31.6 |
| 4 | 82d | 28.2 | 14.3 | 48.5 | 57.6 | 25.2 | 38.3 | 19.5 | 14.5 |
| 5 | 82e | 14.5 | 14.3 | 25.4 | 48.1 | 40.3 | 14.3 | 19.5 | 14.5 |
| 6 | 82f | 28.2 | 31.7 | 33.1 | 24.3 | 25.2 | 12.2 | 33.8 | 28.2 |
| 7 | 82g | 23.6 | 14.3 | 17.7 | 52.9 | 31.2 | 31.7 | 19.5 | 14.5 |
| 8 | 82h | 32.7 | 40.4 | 33.1 | 67.1 | 31.2 | 47.0 | 33.8 | 37.3 |
| 9 | 82i | 69.1 | 83.9 | 79.2 | 76.7 | 70.6 | 86.1 | 71.9 | 73.6 |
| 10 | 82j | 23.6 | 31.7 | 17.7 | 57.6 | 34.2 | 62.2 | 29.0 | 32.7 |
| 11 | 82k | 28.2 | 23.0 | 17.7 | 52.9 | 25.2 | 53.5 | 24.3 | 23.6 |
| 12 | 82l | 28.2 | 14.3 | 17.7 | 57.6 | 25.2 | 31.7 | 19.5 | 23.6 |
| 13 | 82m | 23.6 | 23.0 | 17.7 | 52.9 | 28.2 | 31.7 | 29.0 | 37.3 |
| 14 | 82n | 35.9 | 64.3 | 33.9 | 45.9 | 51.4 | 17.3 | 35.5 | 33.5 |
| 15 | 82o | 28.2 | 57.8 | 48.5 | 52.9 | 52.4 | 53.5 | 33.8 | 32.7 |
| 16 | 82p | 14.5 | 23.0 | 17.7 | 33.8 | 40.3 | 31.7 | 19.5 | 23.6 |
| 17 | 82q | 23.6 | 14.3 | 17.7 | 43.3 | 31.2 | 42.6 | 15.5 | 23.6 |
| 18 | 82r | 46.4 | 66.5 | 48.5 | 67.1 | 52.4 | 70.9 | 43.3 | 46.4 |
| 19 | 82s | 18.2 | 14.3 | 33.1 | 43.3 | 43.3 | 62.2 | 33.8 | 32.7 |
| 20 | 82t | 18.2 | 14.3 | 33.1 | 57.6 | 31.2 | 25.2 | 33.8 | 23.6 |
| 21 | 82u | 13.6 | 14.3 | 17.7 | 38.6 | 43.3 | 42.6 | 29.0 | 23.6 |
| 23 | Chlorothalonil | 100 | 73.3 | 75.0 | 73.9 | 73.1 | 96.1 | 90.4 | 91.3 |
Table 59.
Antifungal activity of compounds 28a–e.
Table 59.
Antifungal activity of compounds 28a–e.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| A. flavus | A. niger | R. stolonifera |
|---|
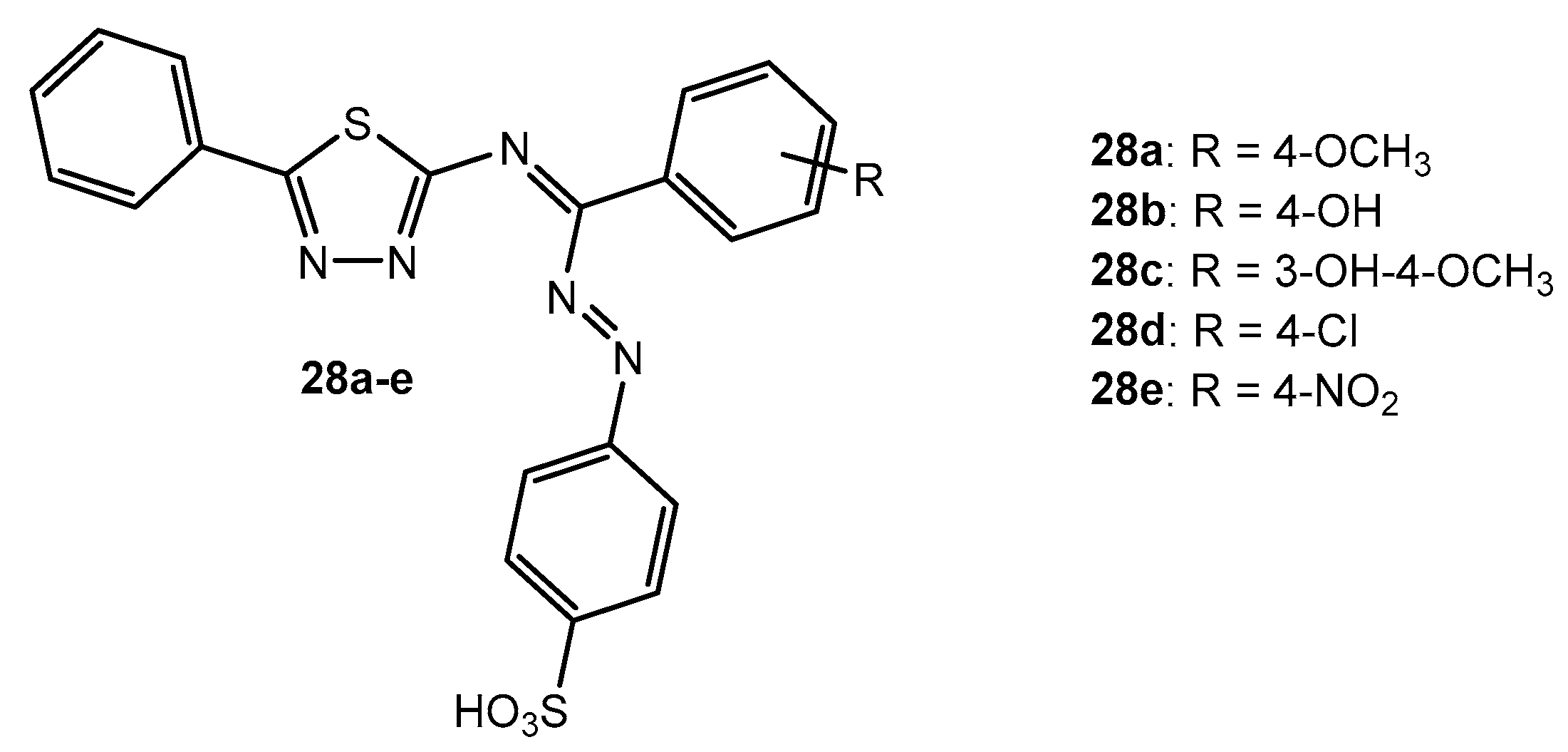
| 1 | 28a | 8 | - | - |
| 2 | 28b | 8 | 7 | 8 |
| 3 | 28c | 10 | 16 | 12 |
| 4 | 28d | 8 | - | - |
| 5 | 28e | - | - | - |
| 6 | Fluconazole | 20 | 19 | 21 |
Table 60.
Antifungal activity of compounds 83a–t.
Table 60.
Antifungal activity of compounds 83a–t.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| B. dothidea | Phomopsis sp. | B. cinerea |
|---|
| 1 | 83a | H | 2-CH3 | 41.8 | 50.6 | 73.2 |
| 2 | 83b | H | 2-F | 63.0 | 83.2 | 78.7 |
| 3 | 83c | H | 4-F | 75.6 | 89.6 | 85.1 |
| 4 | 83d | H | 2-Cl | 57.4 | 74.6 | 71.1 |
| 5 | 83e | H | 3-Cl | 65.9 | 79.4 | 79.2 |
| 6 | 83f | H | 4-Cl | 72.4 | 84.5 | 84.9 |
| 7 | 83g | H | 2-CN | 80.0 | 88.7 | 86.1 |
| 8 | 83h | H | 4-CF3 | 82.6 | 89.2 | 90.7 |
| 9 | 83i | H | 3,4-diCl | 70.8 | 84.6 | 85.4 |
| 10 | 83j | CH3 | 2-CH3 | 36.2 | 42.9 | 65.3 |
| 11 | 83k | CH3 | 4-F | 59.0 | 71.6 | 74.0 |
| 12 | 83l | CH3 | 2-Cl | 51.5 | 64.5 | 65.7 |
| 13 | 83m | CH3 | 3-Cl | 57.4 | 71.9 | 73.3 |
| 14 | 83n | CH3 | 4-Cl | 65.4 | 78.4 | 80.4 |
| 15 | 83o | CH3 | 2-CN | 73.7 | 76.7 | 78.8 |
| 16 | 83p | CH3 | 2-CF3 | 68.4 | 80.3 | 81.8 |
| 17 | 83q | CH3 | 4-CF3 | 75.7 | 86.8 | 88.3 |
| 18 | 83r | CH3 | 2,3-diCl | 58.2 | 69.0 | 66.5 |
| 19 | 83s | CH3 | 2,4-diCl | 75.6 | 82.4 | 83.9 |
| 20 | 83t | CH3 | 3,4-diCl | 65.7 | 78.0 | 80.8 |
| 21 | Pyrimethanil | - | - | 84.4 | 85.1 | 82.8 |
Table 61.
Antifungal activity of compounds 29a–o.
Table 61.
Antifungal activity of compounds 29a–o.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| B. cinerea | V. dahliae | F. oxysporum |
|---|
| 1 | 29a | CH3 | Cl | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 2 | 29b | CH2CH3 | Cl | 17 | 8 | 5 |
| 3 | 29c | CH2CH2CH3 | Cl | 21 | 15 | 12 |
| 4 | 29d | CH2C6H5 | Cl | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | 29e | CH2C6H4-4-F | Cl | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 29f | CH3 | F | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 29g | CH2CH3 | F | 48 | 24 | 16 |
| 8 | 29h | CH2CH2CH3 | F | 55 | 36 | 26 |
| 9 | 29i | CH2C6H5 | F | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 29j | CH2C6H4-4-F | F | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | 29k | CH3 | CH3 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
| 12 | 29l | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 61 | 45 | 32 |
| 13 | 29m | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 69 | 54 | 40 |
| 14 | 29n | CH2C6H5 | CH3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | 29o | CH2C6H4-4-F | CH3 | 9 | 6 | 0 |
| 16 | Carbendazim | - | - | 57 | 79 | 100 |
Table 62.
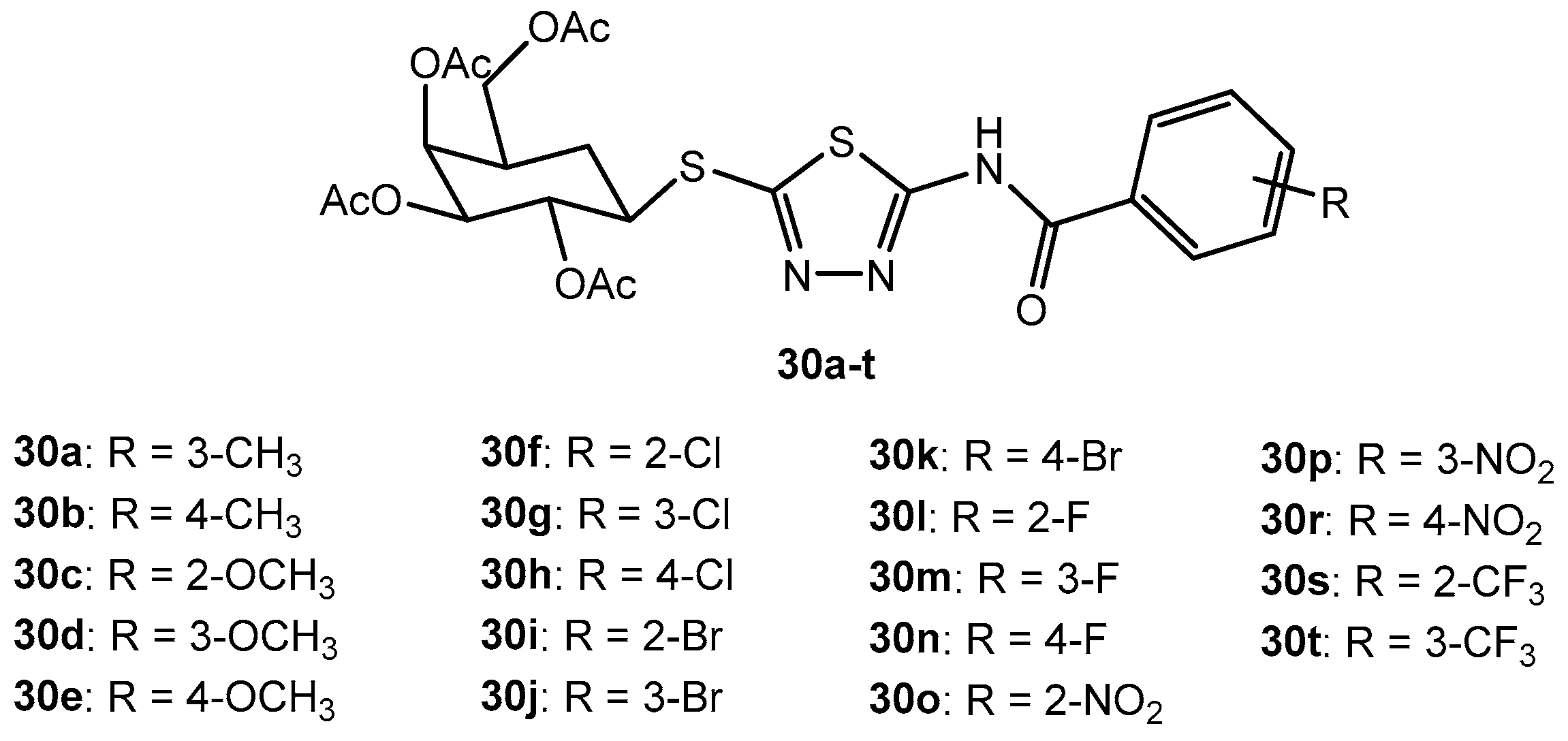
Antifungal activity of compounds 30a–t.
Table 62.
Antifungal activity of compounds 30a–t.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| G. zeae | B. dothidea | P. infestans | Phompsis sp. | T. cucumeris |
|---|
| 1 | 30a | 28.8 | 24.5 | 23.6 | 49.2 | 45.2 |
| 2 | 30b | 34.5 | 32.0 | 28.1 | 36.3 | 33.4 |
| 3 | 30c | 37.6 | 31.0 | 25.6 | 32.5 | 56.3 |
| 4 | 30d | 45.4 | 25.8 | 24.7 | 36.2 | 42.6 |
| 5 | 30e | 40.1 | 26.8 | 25.3 | 47.5 | 47.5 |
| 6 | 30f | 36.2 | 21.6 | 56.4 | 34.2 | 43.4 |
| 7 | 30g | 47.0 | 33.2 | 56.7 | 55.6 | 46.3 |
| 8 | 30h | 34.2 | 48.5 | 56.1 | 35.2 | 35.7 |
| 9 | 30i | 38.6 | 54.8 | 59.8 | 33.5 | 45.6 |
| 10 | 30j | 43.0 | 51.6 | 57.5 | 37.3 | 55.4 |
| 11 | 30k | 45.4 | 50.7 | 57.6 | 45.1 | 43.0 |
| 12 | 30l | 63.4 | 50.5 | 73.5 | 34.5 | 59.7 |
| 13 | 30m | 53.8 | 46.4 | 73.1 | 48.1 | 68.3 |
| 14 | 30n | 52.3 | 66.4 | 77.5 | 42.6 | 56.5 |
| 15 | 30o | 61.0 | 65.3 | 75.1 | 45.2 | 56.3 |
| 16 | 30p | 52.2 | 66.0 | 80.1 | 58.1 | 56.5 |
| 17 | 30r | 45.2 | 54.3 | 79.7 | 43.2 | 58.7 |
| 18 | 30s | 55.4 | 55.2 | 78.0 | 44.5 | 65.3 |
| 19 | 30t | 57.2 | 54.7 | 79.3 | 48.2 | 68.4 |
| 20 | Dimethomorph | 74.3 | 72.3 | 78.2 | 69.3 | 68.3 |
Table 63.
Antifungal activity of compounds 84a–ab.
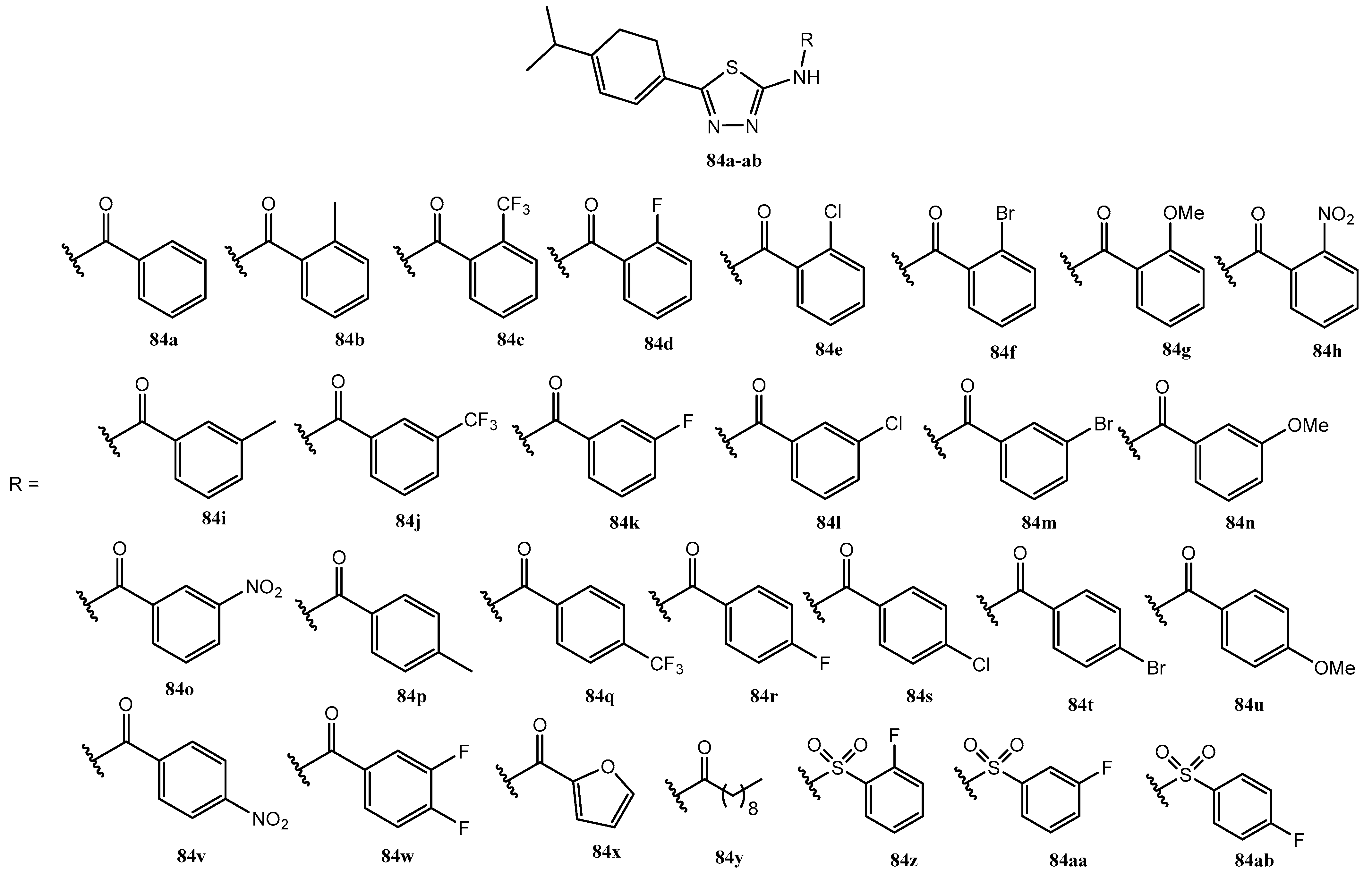
Table 63.
Antifungal activity of compounds 84a–ab.
| Entry | Compound | EC50 (μg/mL) | Entry | Compound | EC50 (μg/mL) |
|---|
| 1 | 84a | 83.450 | 16 | 84p | 114.00 |
| 2 | 84b | 70.725 | 17 | 84q | 82.085 |
| 3 | 84c | 29.924 | 18 | 84r | 89.406 |
| 4 | 84d | 41.398 | 19 | 84s | 107.633 |
| 5 | 84e | 45.246 | 20 | 84t | 90.859 |
| 6 | 84f | 50.608 | 21 | 84u | 52.089 |
| 7 | 84g | 43.570 | 22 | 84v | 126.441 |
| 8 | 84h | 84.770 | 23 | 84w | 101.486 |
| 9 | 84i | 79.635 | 24 | 84x | 66.656 |
| 10 | 84j | 40.969 | 25 | 84y | 205.857 |
| 11 | 84k | 55.469 | 26 | 84z | 9.911 |
| 12 | 84l | 58.441 | 27 | 84aa | 3.785 |
| 13 | 84m | 50.201 | 28 | 84ab | 6.049 |
| 14 | 84n | 43.448 | 29 | Boscalid | 47.356 |
| 15 | 84o | 62.553 | |
Table 64.
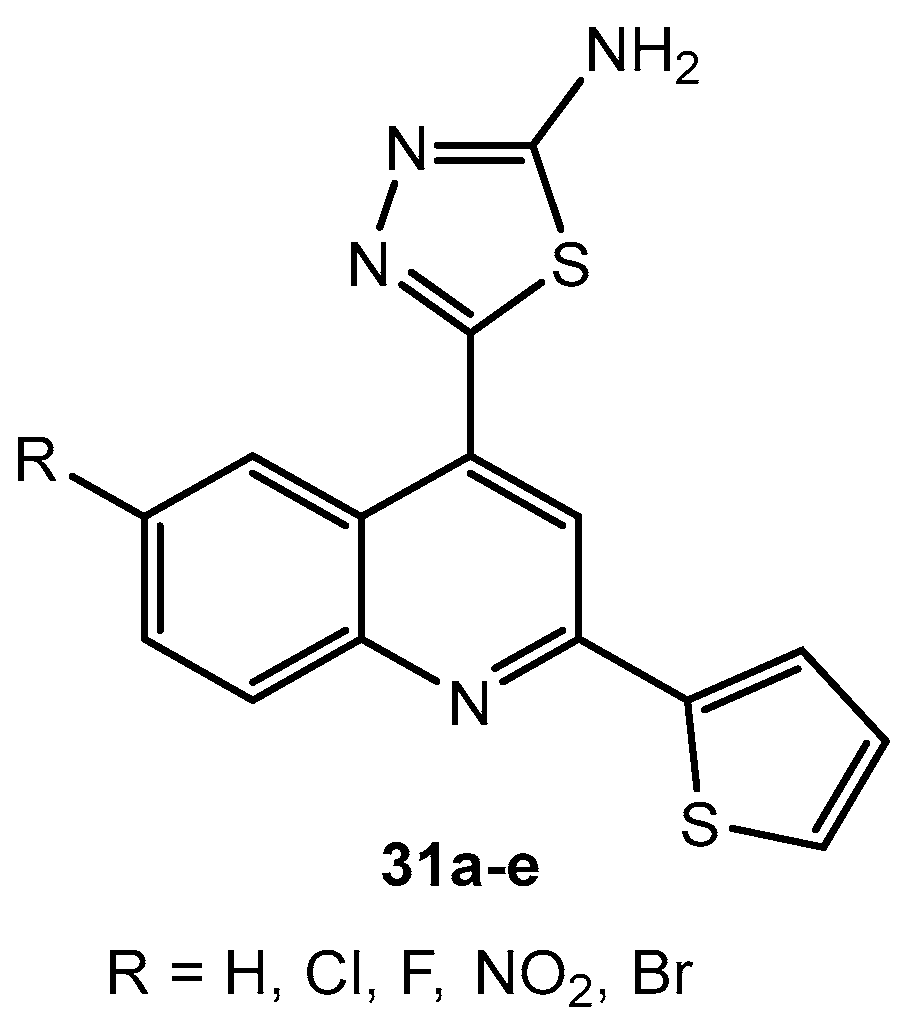
Antifungal activity of compounds 31a–e.
Table 64.
Antifungal activity of compounds 31a–e.
| Entry | Compound | R | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| A. niger | A. flavus |
|---|
| 1 | 31a | H | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 31b | Cl | 6 | 10 |
| 3 | 31c | F | 12 | 6 |
| 4 | 31d | NO2 | 20.5 | 6 |
| 5 | 31e | Br | 9 | 6 |
| 6 | Fluconazole | - | 19.5 | 25 |
Table 65.
Antifungal activity of compounds 32a–k.
Table 65.
Antifungal activity of compounds 32a–k.
| Entry | Compound | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| C. albicans | C. krusei | C. glabrata | C. parapsilosis |
|---|
| 1 | 32a | 1.95 | 62.5 | 3.9 | 62.5 |
| 2 | 32b | 15.625 | 62.5 | 3.9 | 62.5 |
| 3 | 32c | 15.625 | 62.5 | 3.9 | 125 |
| 4 | 32d | 15.625 | 125 | 125 | 125 |
| 5 | 32e | 31.25 | 125 | 7.81 | 125 |
| 6 | 32f | 15.625 | 125 | 31.25 | 125 |
| 7 | 32g | 7.81 | 62.5 | 3.9 | 62.5 |
| 8 | 32h | 1.95 | 7.81 | 1.95 | 7.81 |
| 9 | 32i | 7.81 | 125 | 125 | 62.5 |
| 10 | 32j | 15.625 | 125 | 62.5 | 62.5 |
| 11 | 32k | 3.9 | 125 | 62.5 | 62.5 |
| 12 | Voriconazole | 3.9 | 3.9 | 1.95 | 3.9 |
| 13 | Fluconazole | 7.81 | 7.81 | 3.9 | 3.9 |
Table 66.
Antifungal activity of compounds 35a–j.
Table 66.
Antifungal activity of compounds 35a–j.
| Entry | Compound | R | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| A. niger | C. albicans |
|---|
| 250 μg/mL | 25 μg/mL | 250 μg/mL | 25 μg/mL |
|---|
| 1 | 35a | H | 16 | 11 | 17 | 13 |
| 2 | 35b | N(CH3)2 | 20 | 15 | 18 | 12 |
| 3 | 35c | (OCH3)2 | 15 | - | 14 | 10 |
| 4 | 35d | Cl | 15 | - | 14 | 10 |
| 5 | 35e | NO2 | 15 | 10 | 16 | 11 |
| 6 | 35f | OH | 16 | 12 | 15 | 12 |
| 7 | 35g | OCH3 | 18 | 11 | 17 | 13 |
| 8 | 35h | CH3 | 17 | 12 | 14 | 10 |
| 9 | 35i | NH2 | 19 | 13 | 17 | 12 |
| 10 | 35j | F | 14 | 10 | 17 | 11 |
| 11 | Miconazole | - | 19 | 14 | 17 | 14 |
Table 67.
Antifungal activity of compounds 89a–w.
Table 67.
Antifungal activity of compounds 89a–w.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| FC | CA | PP | AS | GZ | RS | BM | CO |
|---|
| 1 | 89a | 62.2 | 54.2 | 59.3 | 40.9 | 23.8 | 50.6 | 31.6 | 21.6 |
| 2 | 89b | 8.1 | 20.8 | 33.3 | 0 | 23.8 | 50.6 | 31.6 | 29.7 |
| 3 | 89c | 29.7 | 25.0 | 59.3 | 22.7 | 33.3 | 44.6 | 28.9 | 21.6 |
| 4 | 89d | 45.9 | 54.2 | 40.7 | 36.4 | 14.3 | 62.7 | 57.9 | 21.6 |
| 5 | 89e | 21.6 | 29.2 | 59.3 | 9.1 | 23.8 | 53.0 | 34.2 | 35.1 |
| 6 | 89f | 54.1 | 54.2 | 77.8 | 63.6 | 33.3 | 32.5 | 23.7 | 16.2 |
| 7 | 89g | 51.4 | 50.0 | 29.6 | 18.2 | 33.3 | 53.0 | 31.6 | 27.0 |
| 8 | 89h | 43.2 | 45.8 | 59.3 | 45.5 | 19.0 | 44.6 | 34.2 | 32.4 |
| 9 | 89i | 37.8 | 33.3 | 88.9 | 27.3 | 38.1 | 8.4 | 13.2 | 29.7 |
| 10 | 89j | 24.3 | 25.0 | 51.9 | 4.5 | 28.6 | 8.4 | 18.4 | 18.9 |
| 11 | 89k | 29.7 | 33.3 | 25.9 | 22.7 | 33.3 | 38.6 | 18.4 | 21.6 |
| 12 | 89l | 21.6 | 54.2 | 59.3 | 0 | 14.3 | 14.5 | 42.1 | 21.6 |
| 13 | 89m | 16.2 | 25.0 | 22.2 | 0 | 52.4 | 80.7 | 60.5 | 62.2 |
| 14 | 89n | 40.5 | 41.7 | 28.5 | 40.9 | 38.1 | 38.6 | 31.6 | 40.5 |
| 15 | 89o | 56.8 | 54.2 | 29.6 | 27.3 | 19.0 | 62.7 | 39.5 | 45.9 |
| 16 | 89p | 56.8 | 54.2 | 33.3 | 40.9 | 47.6 | 68.7 | 50.0 | 35.1 |
| 17 | 89q | 54.1 | 62.5 | 77.8 | 50.0 | 23.8 | 36.1 | 21.1 | 10.8 |
| 18 | 89r | 10.8 | 16.7 | 40.7 | 9.1 | 47.6 | 60.2 | 36.8 | 29.7 |
| 19 | 89s | 27.1 | 35.7 | 50.1 | 24.1 | 22.8 | 16.8 | 24.9 | 46.7 |
| 20 | 89t | 28.6 | 51.6 | 47.3 | 28.6 | 27.4 | 46.2 | 39.5 | 44.3 |
| 21 | 89u | 18.9 | 45.8 | 59.3 | 0 | 23.8 | 26.5 | 21.1 | 10.8 |
| 22 | 89v | 51.4 | 54.2 | 29.6 | 50.0 | 47.6 | 62.7 | 52.6 | 29.7 |
| 23 | 89w | 43.2 | 66.7 | 31.1 | 45.5 | 33.3 | 62.7 | 34.2 | 29.7 |
| 24 | Chlorothalonil | 100 | 73.3 | 75.0 | 73.9 | 73.1 | 96.1 | 90.4 | 91.3 |
Table 68.
Antifungal activity of compounds 90a–r.
Table 68.
Antifungal activity of compounds 90a–r.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| FC | CA | PP | AS | GZ | RS | BM | CO |
|---|
| 1 | 90a | 34.1 | 64.3 | 64.3 | 60.6 | 54.8 | 19.8 | 37.7 | 35.5 |
| 2 | 90b | 37.8 | 67.1 | 75.2 | 72.3 | 47.9 | 19.8 | 29.1 | 35.5 |
| 3 | 90c | 28.5 | 52.9 | 86.1 | 61.3 | 56.6 | 17.3 | 33.4 | 25.7 |
| 4 | 90d | 30.4 | 50.0 | 66.5 | 33.1 | 47.9 | 53.9 | 24.9 | 29.6 |
| 5 | 90e | 28.5 | 64.3 | 55.7 | 65.0 | 58.3 | 14.9 | 24.9 | 27.6 |
| 6 | 90f | 21.1 | 50.5 | 68.7 | 50.9 | 39.3 | 17.3 | 22.8 | 25.7 |
| 7 | 90g | 21.1 | 70.0 | 64.3 | 77.3 | 56.6 | 17.3 | 27.0 | 27.6 |
| 8 | 90h | 30.5 | 80.6 | 55.5 | 69.7 | 56.8 | 19.3 | 36.5 | 33.6 |
| 9 | 90i | 29.8 | 69.3 | 80.2 | 61.3 | 58.1 | 22.3 | 38.4 | 28.7 |
| 10 | 90j | 36.1 | 66.3 | 66.3 | 70.3 | 65.4 | 21.8 | 39.7 | 49.3 |
| 11 | 90k | 32.2 | 64.3 | 75.2 | 69.0 | 47.9 | 14.9 | 35.5 | 33.5 |
| 12 | 90l | 26.7 | 52.9 | 51.3 | 71.0 | 30.7 | 19.8 | 35.5 | 29.6 |
| 13 | 90m | 34.1 | 67.1 | 64.3 | 61.3 | 27.2 | 17.3 | 29.1 | 31.6 |
| 14 | 90n | 34.1 | 61.4 | 57.8 | 72.8 | 79.0 | 16.1 | 31.3 | 37.5 |
| 15 | 90o | 26.7 | 72.9 | 53.5 | 70.9 | 56.6 | 17.3 | 29.1 | 25.7 |
| 16 | 90p | 35.9 | 72.9 | 36.1 | 63.8 | 51.4 | 17.3 | 35.5 | 37.5 |
| 17 | 90q | 34.1 | 70.0 | 86.1 | 60.6 | 58.3 | 17.3 | 22.8 | 29.6 |
| 18 | 90r | 28.5 | 61.4 | 75.2 | 63.8 | 51.4 | 14.9 | 24.9 | 27.6 |
| 19 | Chlorothalonil | 100 | 73.3 | 75.0 | 73.9 | 73.1 | 96.1 | 90.4 | 91.3 |
Table 69.
Antifungal activity of compounds 91a,b.
Table 69.
Antifungal activity of compounds 91a,b.
| Entry | Compound | (LD50 a/MIC b/MFC c μg/mL) |
|---|
| A. solani | F. melonis | V. dahliae |
|---|
| 1 | 91a | 28.7/<1.25/<40 | 80.3/0.625/>40 | 14.3/<0.625/20 |
| 2 | 91b | 26.1/<1.25/<40 | 27.9/<1.25/>40 | 23.5/<0.625/>20 |
| 3 | Thiram 80% d | 11.9/>0.625/<3000 | 11.3/>0.625/<3000 | 14.34/<1.25/<3000 |
Table 70.
Antifungal activity of compounds 93a–am.
Table 70.
Antifungal activity of compounds 93a–am.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| RS | PS | FG | CC | PC | BD | SS |
|---|
| 1 | 93a | 53.7 | 27.0 | 16.4 | 19.3 | 24.6 | 14.2 | 34.1 |
| 2 | 93b | 6.3 | 21.8 | 16.2 | 24.1 | 30.6 | 19.8 | 33.7 |
| 3 | 93c | 10.7 | 27.4 | 15.6 | 26.6 | 35.8 | 26.3 | 27.2 |
| 4 | 93d | 20.0 | 12.9 | 9.3 | 12.9 | 6.9 | 12.6 | 12.2 |
| 5 | 93e | 11.5 | 19.8 | 16.0 | 21.4 | 36.2 | 5.7 | 39.0 |
| 6 | 93f | 11.1 | 12.5 | 17.7 | 31.5 | 30.6 | 3.2 | 35.7 |
| 7 | 93g | 22.9 | 30.2 | 31.5 | 30.2 | 34.9 | 5.2 | 48.3 |
| 8 | 93h | 27.0 | 34.7 | 24.8 | 25.4 | 36.6 | 14.9 | 41.8 |
| 9 | 93i | 22.6 | 29.4 | 28.6 | 19.3 | 37.1 | 3.6 | 36.9 |
| 10 | 93j | 28.5 | 32.7 | 38.2 | 24.6 | 31.0 | 4.8 | 49.5 |
| 11 | 93k | 26.3 | 23.0 | 19.8 | 25.4 | 32.0 | 6.0 | 35.7 |
| 12 | 93l | 21.1 | 12.5 | 27.3 | 21.4 | 27.6 | 3.6 | 33.3 |
| 13 | 93m | 27.0 | 12.9 | 5.9 | 22.2 | 28.5 | 2.4 | 41.6 |
| 14 | 93n | 21.5 | 14.1 | 24.4 | 17.7 | 35.4 | 2.8 | 36.5 |
| 15 | 93o | 26.3 | 13.7 | 26.9 | 19.7 | 34. | 3.6 | 33.3 |
| 16 | 93p | 18.9 | 5.2 | 17.7 | 19.4 | 30.6 | 3.5 | 31.7 |
| 17 | 93q | 27.0 | 6.8 | 21.0 | 16.5 | 25.9 | 26.7 | 33.7 |
| 18 | 93r | 21.9 | 23.0 | 47.5 | 26.6 | 25.4 | 3.2 | 36.5 |
| 19 | 93s | 19.2 | 15.7 | 34.5 | 25.4 | 31.0 | 9.7 | 40.2 |
| 20 | 93t | 17.4 | 18.2 | 26.5 | 29.4 | 31.5 | 8.1 | 34.9 |
| 21 | 93u | 16.3 | 14.5 | 32.4 | 14.1 | 28.5 | 15.3 | 34.9 |
| 22 | 93v | 15.2 | 20.2 | 34.9 | 13.3 | 26.7 | 6.0 | 34.5 |
| 23 | 93w | 22.2 | 20.3 | 42.4 | 14.9 | 31.5 | 17.0 | 27.6 |
| 24 | 93x | 22.6 | 19.1 | 31.1 | 25.0 | 32.3 | 22.2 | 36.1 |
| 25 | 93y | 25.2 | 12.0 | 25.6 | 12.9 | 33.2 | 3.2 | 37.4 |
| 26 | 93z | 6.1 | 10.4 | 9.3 | 12.9 | 6.9 | 12.5 | 46.7 |
| 27 | 93aa | 23.5 | 24.5 | 34.5 | 37.1 | 35.4 | 16.2 | 12.2 |
| 28 | 93ab | 21.3 | 21.6 | 30.7 | 11.7 | 39.2 | 27.9 | 33.3 |
| 29 | 93ac | 19.1 | 27.8 | 41.2 | 33.9 | 53.5 | 21.4 | 41.4 |
| 30 | 93ad | 22.6 | 49.0 | 26.9 | 29.4 | 55.1 | 15.8 | 47.5 |
| 31 | 93ae | 28.3 | 73.1 | 15.5 | 48.4 | 25.9 | 28.7 | 49.5 |
| 32 | 93af | 30.4 | 64.4 | 27.7 | 48.4 | 19.5 | 17.4 | 49.9 |
| 33 | 93ag | 22.2 | 29.1 | 28.6 | 32.3 | 34.3 | 10.1 | 39.0 |
| 34 | 93ah | 19.9 | 21.6 | 27.3 | 20.2 | 28.7 | 3.6 | 47.9 |
| 35 | 93ai | 24.3 | 10.8 | 27.3 | 30.5 | 26.7 | 3.8 | 41.8 |
| 36 | 93aj | 21.3 | 17.9 | 23.1 | 25.7 | 36.3 | 3.8 | 45.9 |
| 37 | 93ak | 19.5 | 14.1 | 28.6 | 27.8 | 35.8 | 16.2 | 47.9 |
| 38 | 93al | 23.5 | 36.1 | 46.2 | 27.8 | 31.9 | 12.4 | 50.8 |
| 39 | 93am | 22.6 | 15.4 | 16.5 | 32.8 | 19.5 | 4.2 | 50.4 |
| 40 | Azoxystrobin | 58.2 | 55.6 | 56.6 | 52.6 | 64.7 | 71.9 | 73.5 |
Table 71.
Antifungal activity of compounds 94a–m.
Table 71.
Antifungal activity of compounds 94a–m.
| Entry | Compounds | R | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| F. oxysporum | P. citrinum |
|---|
| 1 | 94a | H | 42 | 33 |
| 2 | 94b | 4-Br | 56 | 44 |
| 3 | 94c | 4-Cl | 90 | 95 |
| 4 | 94d | 4-F | 51 | 40 |
| 5 | 94e | 4-NO2 | 48 | 38 |
| 6 | 94f | 3,4-diCl | 38 | 28 |
| 7 | 94g | 3-Br | 50 | 38 |
| 8 | 94h | 3-Cl | 67 | 64 |
| 9 | 94i | 3-F | 68 | 62 |
| 10 | 94j | 3-CH3 | 52 | 48 |
| 11 | 94k | 2-Br | 35 | 26 |
| 12 | 94l | 2-Cl | 59 | 61 |
| 13 | 94m | 2-CH3 | 63 | 42 |
| 14 | Dithane M-45 | - | 96 | 97 |
| 15 | Griseofulvin | | 99 | 98 |
Table 72.
Antifungal activity of compounds 60-n.
Table 72.
Antifungal activity of compounds 60-n.
| Entry | Compound | R | MIC (µg/mL) |
|---|
| 1 | 60a | H | >256 |
| 2 | 60b | 2-F | >256 |
| 3 | 60c | 3-F | >256 |
| 4 | 60d | 4-F | >256 |
| 5 | 60e | 2-Cl | >256 |
| 6 | 60f | 3-Cl | 1 |
| 7 | 60g | 4-Cl | 2 |
| 8 | 60h | 3,4-diCl | 0.5 |
| 9 | 60i | 2-Br | >256 |
| 10 | 60j | 3-Br | >256 |
| 11 | 60k | 4-Br | >256 |
| 12 | 60l | 4-NO2 | >256 |
| 13 | 60m | 2-CH3 | >256 |
| 14 | 60n | 3-CH3 | >256 |
| 15 | Fluconazole | - | 2 |
Table 73.
Antifungal activity of compounds 61a–ai.
Table 73.
Antifungal activity of compounds 61a–ai.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| PN | GZ | VD | FS | AT | SS | FO |
|---|
| 1 | 61a | 26.3 | 37.2 | 18.1 | 10.9 | 13.1 | 7.2 | 23.0 |
| 2 | 61b | 33.7 | 32.6 | 18.3 | 0 | 25.3 | 20.1 | 10.0 |
| 3 | 61c | 33.5 | 35.7 | 26.5 | 8.3 | 19.6 | 25.4 | 14.3 |
| 4 | 61d | 24.7 | 20.9 | 15.8 | 0 | 12.0 | 7.6 | 16.8 |
| 5 | 61e | 11.7 | 45.0 | 6.0 | 3.6 | 15.5 | 4.8 | 11.7 |
| 6 | 61f | 31.8 | 37.8 | 19.0 | 9.6 | 14.6 | 17.9 | 8.9 |
| 7 | 61g | 34.8 | 41.5 | 24.2 | 7.8 | 16.4 | 8.7 | 30.1 |
| 8 | 61h | 35.2 | 17.4 | 10.4 | 6.9 | 19.9 | 9.8 | 11.7 |
| 9 | 61i | 29.6 | 24.3 | 13.6 | 5.1 | 18.2 | 16.1 | 17.4 |
| 10 | 61j | 23.6 | 25.7 | 14.5 | 8.6 | 16.5 | 14.8 | 28.9 |
| 11 | 61k | 31.2 | 23.8 | 21.4 | 0 | 14.2 | 10.4 | 0 |
| 12 | 61l | 36.4 | 48.3 | 24.8 | 12.6 | 13.6 | 9.3 | 33.5 |
| 13 | 61m | 23.5 | 35.0 | 14.8 | 8.1 | 13.8 | 21.5 | 15.7 |
| 14 | 61n | 44.0 | 21.7 | 8.5 | 8.8 | 12.8 | 23.4 | 11.5 |
| 15 | 61o | 62.7 | 19.6 | 41.0 | 12.1 | 21.2 | 24.5 | 17.9 |
| 16 | 61p | 39.0 | 43.4 | 33.6 | 6.6 | 15.9 | 26.8 | 21.9 |
| 17 | 61q | 18.8 | 18.4 | 11.4 | 0 | 9.6 | 0 | 11.5 |
| 18 | 61r | 26.7 | 16.5 | 0 | 10.4 | 9.8 | 8.2 | 9.7 |
| 19 | 61s | 67.2 | 15.7 | 15.5 | 8.9 | 10.3 | 5.0 | 8.3 |
| 20 | 61t | 0 | 12.7 | 0 | 9.6 | 0 | 7.1 | 11.3 |
| 21 | 61u | 19.9 | 36.1 | 13.1 | 0 | 12.0 | 12.6 | 0 |
| 22 | 61v | 47.2 | 4.4 | 5.8 | 6.4 | 8.3 | 5.3 | 13.1 |
| 23 | 61w | 52.8 | 47.0 | 40.6 | 11.2 | 20.5 | 28.4 | 35.8 |
| 24 | 61x | 6.1 | 9.4 | 6.8 | 8.6 | 11.9 | 0 | 0 |
| 25 | 61y | 41.6 | 19.6 | 36.2 | 21.7 | 33.6 | 50.4 | 17.6 |
| 26 | 61z | 41.1 | 16.5 | 0 | 7.8 | 10.5 | 0 | 10.7 |
| 27 | 61aa | 51.2 | 22.2 | 4.8 | 8.8 | 18.1 | 38.6 | 20.7 |
| 28 | 61ab | 50.1 | 23.9 | 1.8 | 10.2 | 10.1 | 0 | 8.3 |
| 29 | 61ac | 29.3 | 25.0 | 8.5 | 12.3 | 13.4 | 6.2 | 13.3 |
| 30 | 61ad | 48.8 | 19.6 | 7.5 | 8.3 | 14.0 | 7.9 | 10.0 |
| 31 | 61ae | 34.4 | 12.9 | 0 | 6.1 | 8.5 | 0 | 11.4 |
| 32 | 61af | 11.6 | 20.2 | 8.5 | 7.8 | 5.9 | 8.3 | 8.6 |
| 33 | 61ag | 0 | 12.8 | 4.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12.3 |
| 34 | 61ah | 0 | 11.9 | 5.6 | 7.7 | 0 | 4.9 | 12.1 |
| 35 | 61ai | 0 | 12.4 | 3.8 | 7.4 | 0 | 5.2 | 15.5 |
| 36 | Chlorothalonil | 84.5 | 75.1 | 67.1 | 64.7 | 73.5 | 100 | 67.5 |
| 37 | Carbendazim | 81.1 | 100 | 73.5 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
Table 74.
Antifungal activity of compounds 62a–s.
Table 74.
Antifungal activity of compounds 62a–s.
| Entry | Compound | MIC/MFC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| AF | AV | AN | TV | PF | PC |
|---|
| 1 | 62a | 5/10 | 2/5 | 10/20 | 2/5 | 20/40 | 10/20 |
| 2 | 62b | 10/20 | 5/10 | 10/20 | 2/5 | 10/20 | 10/20 |
| 3 | 62c | 20/40 | 10/20 | 15/20 | 2/5 | 20/36 | 20/36 |
| 4 | 62d | 2/5 | 2/5 | 5/1 | 5/1 | 10/20 | 10/20 |
| 5 | 62e | 20/36 | 10/20 | 15/20 | 8/10 | 33/40 | 20/40 |
| 6 | 62f | 5/10 | 5/10 | 5/10 | 2/5 | 10/20 | 10/20 |
| 7 | 62g | 10/20 | 10/20 | 5/10 | 5/10 | 5/10 | 20/36 |
| 8 | 62h | 10/20 | 10/20 | 15/20 | 5/10 | 10/20 | 15/20 |
| 9 | 62i | 5/10 | 5/10 | 10/20 | 5/10 | 36/80 | 30/40 |
| 10 | 62j | 32/40 | 20/40 | 10/20 | 5/10 | 10/20 | 20/40 |
| 11 | 62k | 20/40 | 5/10 | 20/32 | 2/5 | 2/5 | 2/5 |
| 12 | 62l | 5/20 | 10/20 | 15/20 | 5/10 | 40/67 | 20/40 |
| 13 | 62m | 40/67 | 20/36 | 20/40 | 2/5 | 40/80 | 32/40 |
| 14 | 62n | 10/36 | 10/20 | 10/20 | 5/10 | 30/40 | 32/40 |
| 15 | 62o | 15/20 | 10/20 | 20/37 | 5/10 | 30/40 | 30/36 |
| 16 | 62p | 20/40 | 10/20 | 5/1 | 5/8 | 10/20 | 20/40 |
| 17 | 62q | 20/40 | 20/40 | 20/32 | 5/10 | 30/40 | 30/40 |
| 18 | 62r | 20/32 | 10/20 | 10/20 | 8/10 | 20/40 | 30/36 |
| 19 | 62s | 20/40 | 20/36 | 10/20 | 8/10 | 20/40 | 20/40 |
| 20 | Ketoconazole | 20/500 | 200/500 | 200/500 | 1000/1500 | 200/500 | 200/300 |
| 21 | Bifonazole | 150/200 | 100/200 | 150/200 | 150/200 | 200/250 | 100/200 |
Table 75.
Antifungal activity of compounds 95a–h.
Table 75.
Antifungal activity of compounds 95a–h.
| Entry | Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| R. solani | D. orazae |
|---|
Concentration
50 (ppm) | Concentration
100 (ppm) | Concentration
50 (ppm) | Concentration
100 (ppm) |
|---|
| 1 | 95a | 33.25 | 50.15 | 36.12 | 52.19 |
| 2 | 95b | 46.21 | 74.80 | 42.14 | 76.20 |
| 3 | 95c | 31.46 | 50.12 | 42.09 | 57.20 |
| 4 | 95d | 35.34 | 59.84 | 30.86 | 68.76 |
| 5 | 95e | 40.74 | 59.35 | 36.75 | 49.45 |
| 6 | 95f | 46.75 | 52.76 | 46.54 | 61.95 |
| 7 | 95g | 47.37 | 75.38 | 38.45 | 55.20 |
| 8 | 95h | 38.56 | 62.24 | 42.24 | 60.24 |
| 9 | carbendazim | 96.67 | 98.56 | 95.45 | 98.26 |
Table 76.
Antifungal activity of compounds 63a–i.
Table 76.
Antifungal activity of compounds 63a–i.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | MFC (μg/mL) |
|---|
| A. flavus | A. niger | F. oxysporum | F. monaliforme |
|---|
| 1 | 63a | H | H | 250 | 265 | 270 | 280 |
| 2 | 63b | H | OCH3 | 290 | 285 | 280 | 275 |
| 3 | 63c | H | Cl | 135 | 120 | 125 | 120 |
| 4 | 63d | OCH3 | H | 250 | 220 | 270 | 230 |
| 5 | 63e | OCH3 | OCH3 | 135 | 155 | 150 | 165 |
| 6 | 63f | OCH3 | Cl | 285 | 275 | 280 | 260 |
| 7 | 63g | Cl | H | 135 | 155 | 140 | 165 |
| 8 | 63h | Cl | OCH3 | 215 | 220 | 210 | 215 |
| 9 | 63i | Cl | Cl | 120 | 125 | 130 | 130 |
| 10 | Nystatin | - | - | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
Table 77.
Antifungal activity of compounds 68a–ah.
Table 77.
Antifungal activity of compounds 68a–ah.
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|
| B. cinerea | A. solani | R. solani | G. zeae | C. orbiculare |
|---|
| 1 | 68a | H | CH3 | CH3 | 69.36 | 47.71 | 82.53 | 54.59 | 46.88 |
| 2 | 68b | 6-Br | CH3 | CH3 | 98.57 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 77.32 | 92.90 |
| 3 | 68c | 6-F | CH3 | CH3 | 69.84 | 70.00 | 91.67 | 71.46 | 86.53 |
| 4 | 68d | 6-Cl | CH3 | CH3 | 89.07 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 81.41 | 94.67 |
| 5 | 68e | 6-CH3 | CH3 | CH3 | 29.82 | 48.02 | 79.13 | 51.13 | 65.43 |
| 6 | 68f | 7-Br | CH3 | CH3 | 38.37 | 89.17 | 100.00 | 33.37 | 59.62 |
| 7 | 68g | H | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 43.00 | 59.94 | 95.57 | 54.08 | 92.21 |
| 8 | 68h | 6-Br | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 84.56 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 81.60 | 100.00 |
| 9 | 68i | 6-F | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 42.52 | 74.01 | 90.08 | 67.02 | 100.00 |
| 10 | 68j | 6-Cl | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 78.29 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 68.22 | 100.00 |
| 11 | 68k | 6-CH3 | CH2CH3 | CH3 | 31.66 | 62.44 | 84.33 | 46.91 | 90.87 |
| 12 | 68l | H | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 60.38 | 56.88 | 87.48 | 38.13 | 78.14 |
| 13 | 68m | 6-Br | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 80.82 | 95.72 | 100.00 | 51.11 | 84.84 |
| 14 | 68n | 6-F | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 42.51 | 90.70 | 100.00 | 39.56 | 97.73 |
| 15 | 68o | 6-Cl | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 81.33 | 92.68 | 100.00 | 50.52 | 92.56 |
| 16 | 68p | 6-CH3 | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 32.72 | 25.73 | 47.28 | 20.89 | 32.22 |
| 17 | 68q | 7-Br | CH2CH2CH3 | CH3 | 32.51 | 35.03 | 60.62 | 17.83 | 33.09 |
| 18 | 68r | H | CH3CHCH3 | CH3 | 33.55 | 65.77 | 87.77 | 47.81 | 67.93 |
| 19 | 68s | 6-Br | CH3CHCH3 | CH3 | 72.86 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 50.03 | 100.00 |
| 20 | 68t | 6-F | CH3CHCH3 | CH3 | 5.44 | 94.47 | 89.17 | 50.33 | 79.39 |
| 21 | 68u | 6-Cl | CH3CHCH3 | CH3 | 72.31 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 55.77 | 97.06 |
| 22 | 68v | 7-Br | CH3CHCH3 | CH3 | 22.18 | 64.92 | 100.00 | 70.02 | 21.12 |
| 23 | 68w | 6-F | allyl | CH3 | 59.09 | 39.18 | 77.34 | 38.37 | 91.38 |
| 24 | 68x | 6-CH3 | allyl | CH3 | 35.77 | 17.69 | 61.59 | 14.74 | 37.90 |
| 25 | 68y | H | Bn | CH3 | 14.52 | 26.04 | 47.78 | 21.93 | 11.03 |
| 26 | 68z | 6-Br | Bn | CH3 | 5.50 | 39.18 | 60.28 | 22.48 | 13.01 |
| 27 | 68aa | 6-F | Bn | CH3 | 19.13 | 18.54 | 62.60 | 22.51 | 20.27 |
| 28 | 68ab | 6-Cl | Bn | CH3 | 13.61 | 18.78 | 1.54 | 5.89 | 0.80 |
| 29 | 68ac | 6-CH3 | Bn | CH3 | 14.33 | 0.00 | 47.46 | 7.54 | 6.88 |
| 30 | 68ad | 7-Br | Bn | CH3 | 11.82 | 0.00 | 16.52 | 3.93 | 1.38 |
| 31 | 68ae | 6-F | CH3 | CH2CH3 | 16.04 | 71.83 | 100.00 | 50.47 | 87.39 |
| 32 | 68af | 6-Cl | CH3 | CH2CH3 | 85.61 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 66.48 | 94.80 |
| 33 | 68ag | H | i-Pr | CH2CH3 | 27.38 | 94.17 | 94.08 | 10.62 | 89.66 |
| 34 | 68ah | 6-CH3 | i-Pr | CH2CH3 | 67.48 | 83.44 | 69.72 | 31.83 | 82.86 |
Table 78.
Antifungal activity of compounds 69a–h.
Table 78.
Antifungal activity of compounds 69a–h.
| Entry | Compound | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
|---|
| A. niger | G. candidum |
|---|
| 1 | 69a | 21.1 | 19.8 |
| 2 | 69b | 22.3 | 23.4 |
| 3 | 69c | 18.5 | 23.2 |
| 4 | 69d | 19.9 | 24.1 |
| 5 | 69e | 25.3 | 24.2 |
| 6 | 69f | 24.1 | 23.6 |
| 7 | 69g | 23.3 | 22.3 |
| 8 | 69h | 25.5 | 23.2 |
| 9 | Amphotericin B | 23.3 | 25.2 |
Table 79.
Antifungal activity of compounds 71a–f.
Table 79.
Antifungal activity of compounds 71a–f.
| Compound | 71a | 71b | 71c | 71d | 71e | 71f | Amphotericin |
|---|
| Zone of inhibition (mm) | 9.7 | 10 | 12 | 11 | 14 | 17 | 21 |