1. Introduction
The excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) that surpasses the body’s natural antioxidant defenses leads to oxidative stress, which has significant implications for biological systems [
1,
2,
3]. As a result, oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the body’s oxidizing systems, mainly composed of free radicals, and the levels of ROS and RNS [
4,
5].
ROS are unstable molecules produced by all cells, including hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2), hydroxyl radical (•OH), singlet oxygen (
1O
2), and superoxide (O
−2). They are involved in deoxyribonucleotide formation, prostaglandin production, and reactions like oxidation, carboxylation, and hydroxylation, which are essential for cell function [
6]. ROS also participate in defending the host against microbial infections, regulating vascular tone and cell adhesion, and acting as sensors for oxygen levels [
7]. Moreover, they are involved in inflammation, not only as mediators but more importantly as regulators of cell signaling, promoting either cell proliferation and survival or cell death [
8]. ROS play a key role as signaling molecules in the development of inflammation, which is considered an immunoregulator [
9].
Recent findings emphasize the critical role of oxidative stress in initiating and maintaining inflammation, thereby affecting the development of many serious conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders [
2,
3,
10,
11,
12,
13]. The disruption of redox balance is linked to the development of various gastrointestinal disorders, such as Barrett’s esophagus, peptic ulcers, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and several types of adenocarcinomas [
3,
14]. Additionally, viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections are known to trigger ROS production, while also inducing and modulating antioxidant defense systems to create favorable environments for their spread [
15,
16]. For example, the gastrointestinal tract is a highly sensitive mucosal tissue exposed to external pathogens from food, which causes the stomach and intestines to produce oxidative stress; this response may be related to the emergence of gastrointestinal conditions including gastroenteritis, gastric ulcers, gastric and colon cancers, and functional disorders like functional dyspepsia [
17]. In fact, gastrointestinal pathogens significantly contribute to oxidative stress and the breakdown of mucosal barriers [
17,
18]. Some viruses can manipulate the body’s redox system; for example, coronaviruses cause downregulation of antioxidant genes like Nuclear Factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF 2), while increasing the expression of oxidative stress-related genes such as myeloperoxidase, potentially promoting both viral replication and inflammation [
19,
20]. Oxidative stress is also closely linked to aging and overall mortality [
10,
21], with reports indicating a positive correlation between oxidative stress levels and long-term as well as all-cause mortality [
21,
22]. Higher oxidative stress levels are also associated with increased mortality risk among older women [
23]. Despite the proven effectiveness of traditional treatments like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and synthetic antioxidants, their long-term use raises important clinical concerns. For example, PPIs have been linked to adverse effects, including hypomagnesemia, opportunistic infections, and poor nutrient absorption [
24]. NSAIDs and corticosteroids are known to cause gastrointestinal ulcers, bleeding, immunosuppression, and other serious systemic issues [
25,
26]. Furthermore, certain synthetic antioxidants, such as butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), have shown potential toxicity and are suspected of causing birth defects [
27].
These limitations highlight the urgent need for safer, more effective, and better-tolerated therapeutic options. In this context, medicinal plants have gained increasing attention due to their rich contents of natural bioactive compounds with proven anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and gastroprotective properties [
28,
29].
Recent interest in plant-based remedies for ulcer treatment has underscored the potential of natural immunomodulators [
30,
31]. Additionally, the use of natural products in cancer therapy and as antioxidants has gained recognition due to their effectiveness [
32,
33,
34]. Natural antioxidants have proven useful as medicinal supplements and alternative drugs that can prevent or protect the body against oxidative stress-related diseases, as well as food additives that inhibit lipid peroxidation [
34]. Plants offer sustainable, safer, and more effective antioxidant options, mainly due to their phenolic compounds, which are a notable strategy for reducing pathological conditions [
35,
36]. Exploring these natural resources could thus provide a promising pathway for developing complementary or alternative treatments with enhanced safety profiles.
P. biglobosa (Jacq.) Benth., also known as African locust bean, is a common plant in the Western African region that has been traditionally used for various medicinal purposes, such as antidiabetic, anti-hypertensive, anti-inflammatory, wound healing, antihelmintic, and antifungal applications [
37,
38,
39,
40]. In Benin, it has multiple uses, including medicinal, handicraft, domestic, medico-magic, veterinary, cultural, food, and commercial applications, with the most-used parts being pulp, seeds, and bark [
40,
41]. It is reported to contain phytochemicals such as saponins, tannins, flavonoids, terpenoids, alkaloids, cardiac glycosides, and coumarins [
40,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49]. Additionally, it possesses antidiabetic, antimalarial [
47], antioxidant [
44], antibacterial [
43,
50], antifungal [
51], antihypertensive, anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic, anti-nociceptive, and analgesic activities [
40,
49,
52]. Furthermore,
P. biglobosa is claimed to inhibit DPPH, ABTS, and CUPRAC, and also to inhibit several enzymes (α-Glucosidase; α-amylase and cholinesterase) in vitro [
42,
48,
53,
54]. Moreover, Ajibola et al. [
55] reported the hepatoprotective effect of
P. biglobosa stem bark methanolic extract against paracetamol-induced liver damage in Wistar rats.
In parallel,
V. paradoxa, also known as the shea tree, is a plant commonly found in West Africa. Reported to contain polyphenolic compounds [
39,
45,
46,
56,
57,
58], it is a plant traditionally used to treat diarrhea with blood, as a tonic and an appetizer, and to treat yellow fever, bee and wasp stings, waist pain, skin problems, rheumatism, bone dislocations and fractures, back pain, and arthritis, as well as being used as a pain-reliever [
59,
60]. Recent scientific studies have shown
V. paradoxa to demonstrate anticancer [
61,
62,
63], melanogenesis-inhibitory, antibacterial, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory [
64], anti-arthritic, anti-diarrheal, antimalarial, antigonorrheal (inhibition of Nesseria gonorrhoeae strains) [
61], antireverse transcriptase [
61], antioxidant activity (ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, CUPRAC, nitric oxide, and phosphomolybdenum assays) [
46,
62], enzyme inhibition (amylase, tyrosinase, and glucosidase), wound healing, intoxication prevention, antibacterial, antimycobacterial, and antifungal activities [
39,
56,
57,
63,
64,
65,
66,
67,
68,
69,
70,
71,
72,
73,
74,
75].
The aforementioned studies have assessed the various biological activities of
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa extracts. However, the integration of traditional medicinal plants such as
Vitellaria paradoxa (shea tree) and
Parkia biglobosa (African locust bean), along with phytochemical screenings, a determination of their antioxidant capacity, toxicological studies, and gastroprotective capacity evaluations, have not been demonstrated [
76]. The combination of
Vitellaria paradoxa and
Parkia biglobosa extracts, along with the specific assays conducted in this study, represent a novel contribution to the literature. This combination and the parameters tested have not been previously reported.
The aim of this research was to characterize the toxicity, gastroprotective effects, and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of V. paradoxa and P. biglobosa stem bark extracts using various solvents. We examined the phenolic contents, toxicity, in vitro antioxidant activity, and the in vitro anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective effects of the stem bark extracts from both plants.
3. Discussion
Shea (
V. paradoxa) and African locust bean (
P. biglobosa) are two indigenous plants from semi-arid and arid regions, and they have been reported for their traditional uses:
V. paradoxa [
59,
60],
P. biglobosa [
37,
38,
39,
40,
41]; their phytochemicals:
V. paradoxa [
39,
45,
46,
56,
58],
P. biglobosa [
42,
43,
44,
78]; and their various biological activities:
V. paradoxa [
39,
45,
51,
71,
72,
73,
74,
75,
79],
P. biglobosa [
37,
40,
42,
48,
49,
51,
52,
53,
54]. This study screened the phytochemical content and determined the phenolic content and structures of the stem bark of these two plants. In addition, the in vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of bark extracts were assessed, and the correlation between pharmacological activities and the phenolic content of the different extracts was analyzed.
A phytochemical screening of the bark powders of
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa revealed various groups of compounds in both plants. The bark of
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa contained phenolic compounds, including coumarins, tannins (gallic and catechin tannins), and flavonoids (anthocyanins and leuco-anthocyanins for
V. paradoxa and anthocyanins for
P. biglobosa). Other groups, such as saponins, terpenoid compounds (triterpenoids and mucilages), were detected. Alkaloids were found only in the bark powder of
V. paradoxa, while glycosides (O-heterosides with reduced genin and C-heterosides) were found only in the bark powder of
P. biglobosa. These results showed the rich phytochemical content of
V. paradoxa bark. This aligns with findings by Abdullahi et al. [
80], Manzoor et al. [
11], and Namadina et al. [
79], who detected classes of phytochemicals such as alkaloids, flavonoids, saponins, cardiac glycosides, tannins, steroids, triterpenes, phenols, and carbohydrates in
V. paradoxa bark. Amlabu and Nock [
70] did not detect flavonoids in
V. paradoxa bark samples.
P. biglobosa bark has been reported by Millogo-Kone et al. [
81] and Abioye et al. [
43] to contain major groups of secondary metabolites, including alkaloids, polyphenolics such as tannins, flavonoids, coumarins, anthocyanidins, saponins, steroids or sterols, glycosides, triterpenes, sugars, and reducing sugars.
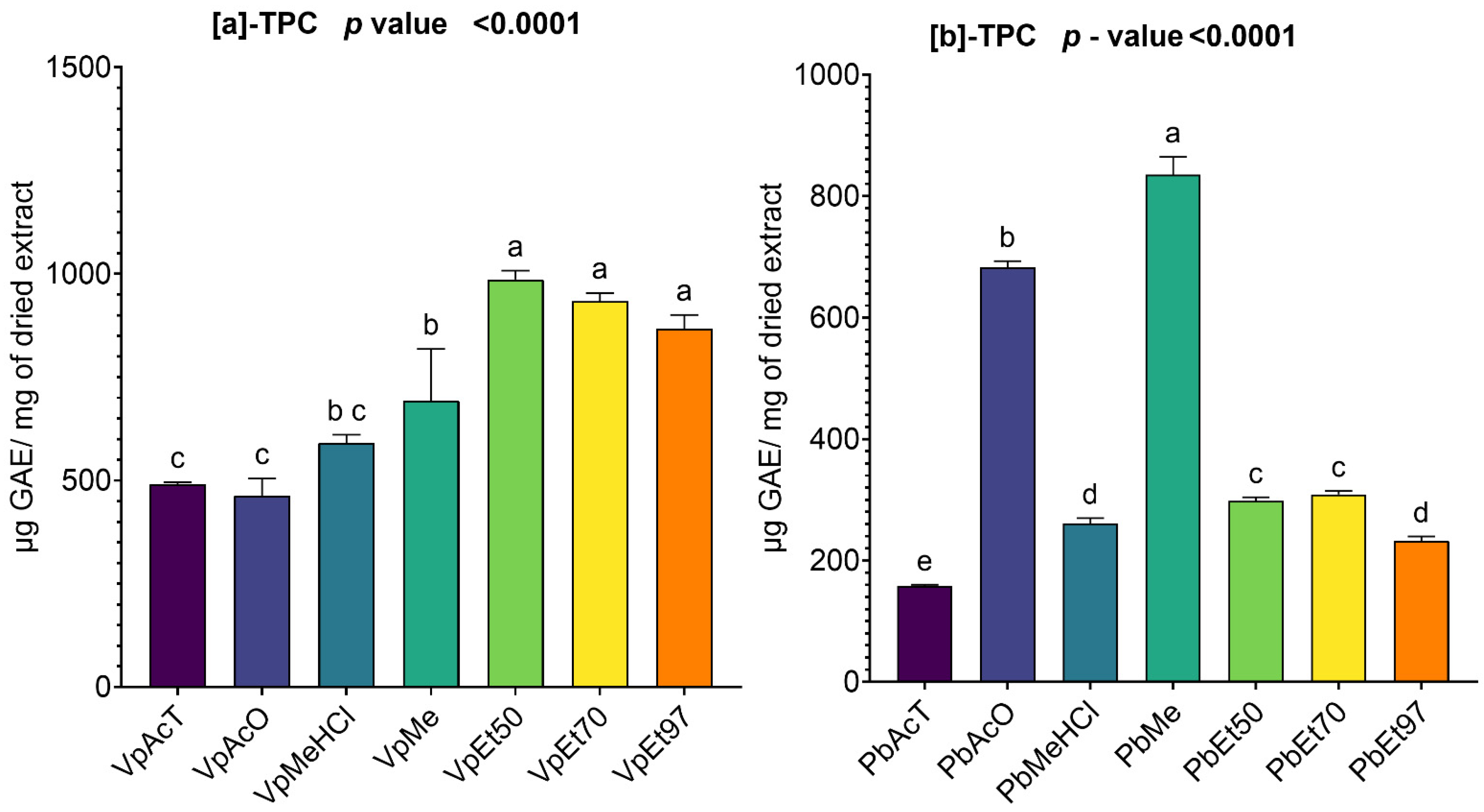
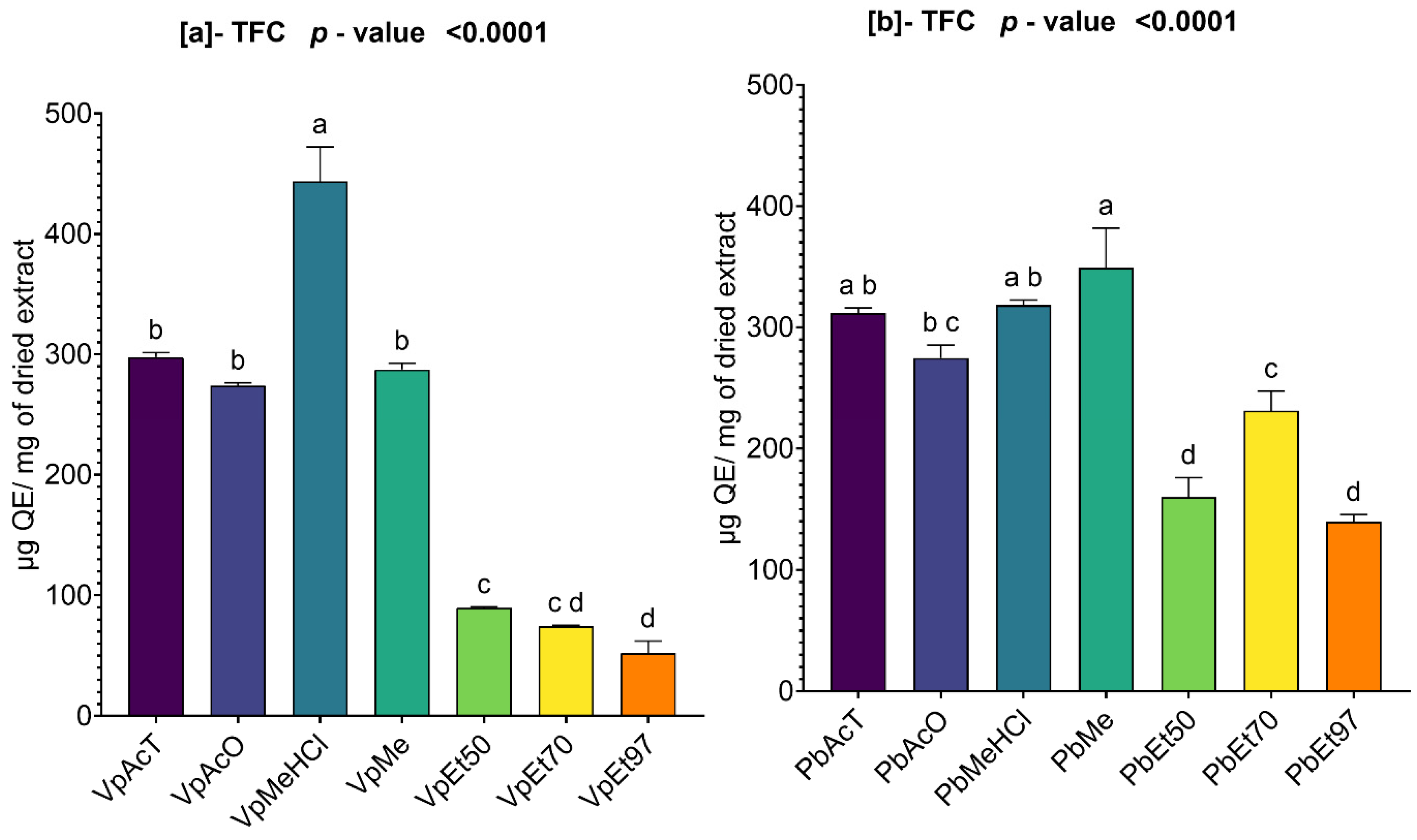
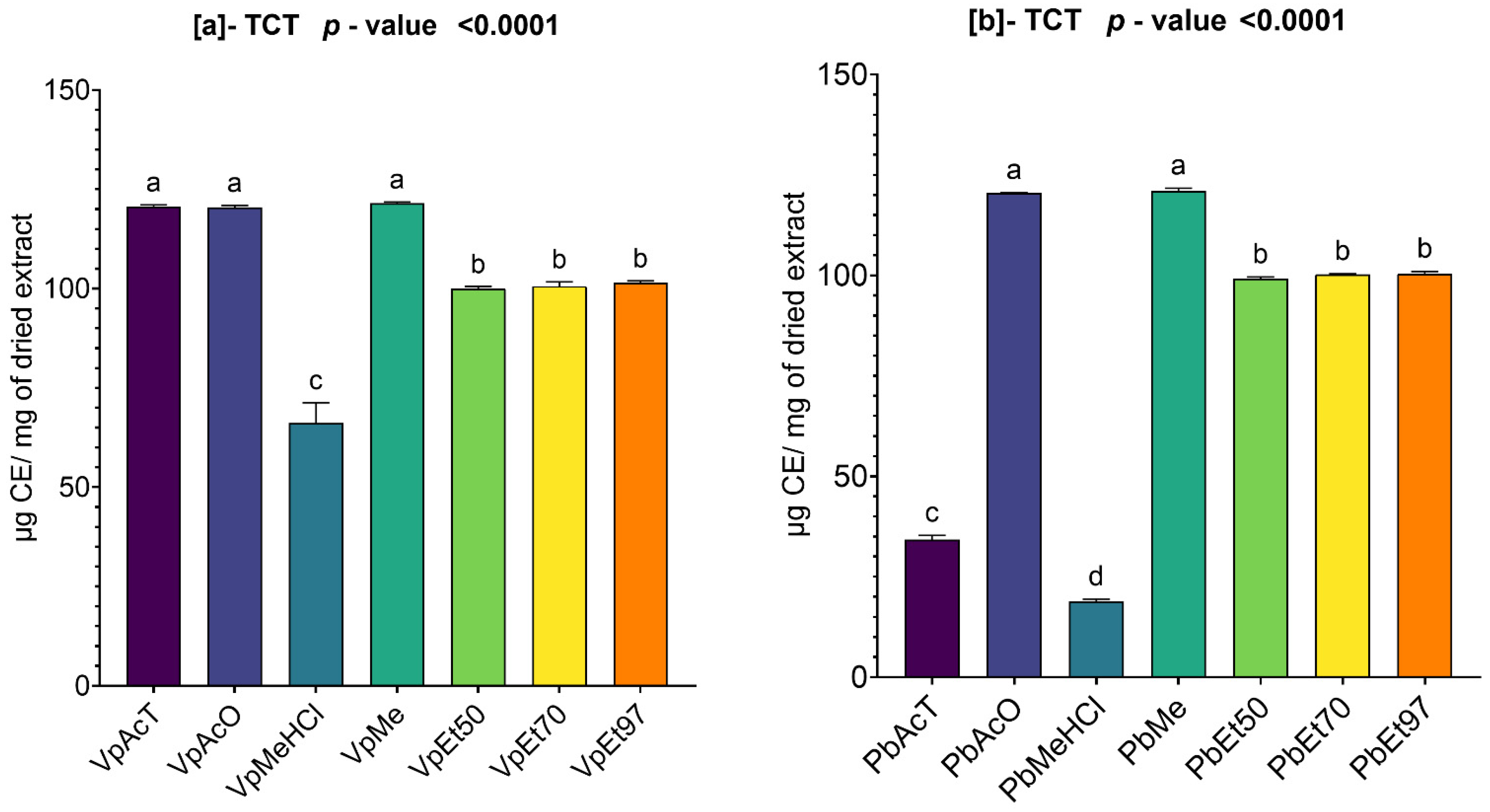
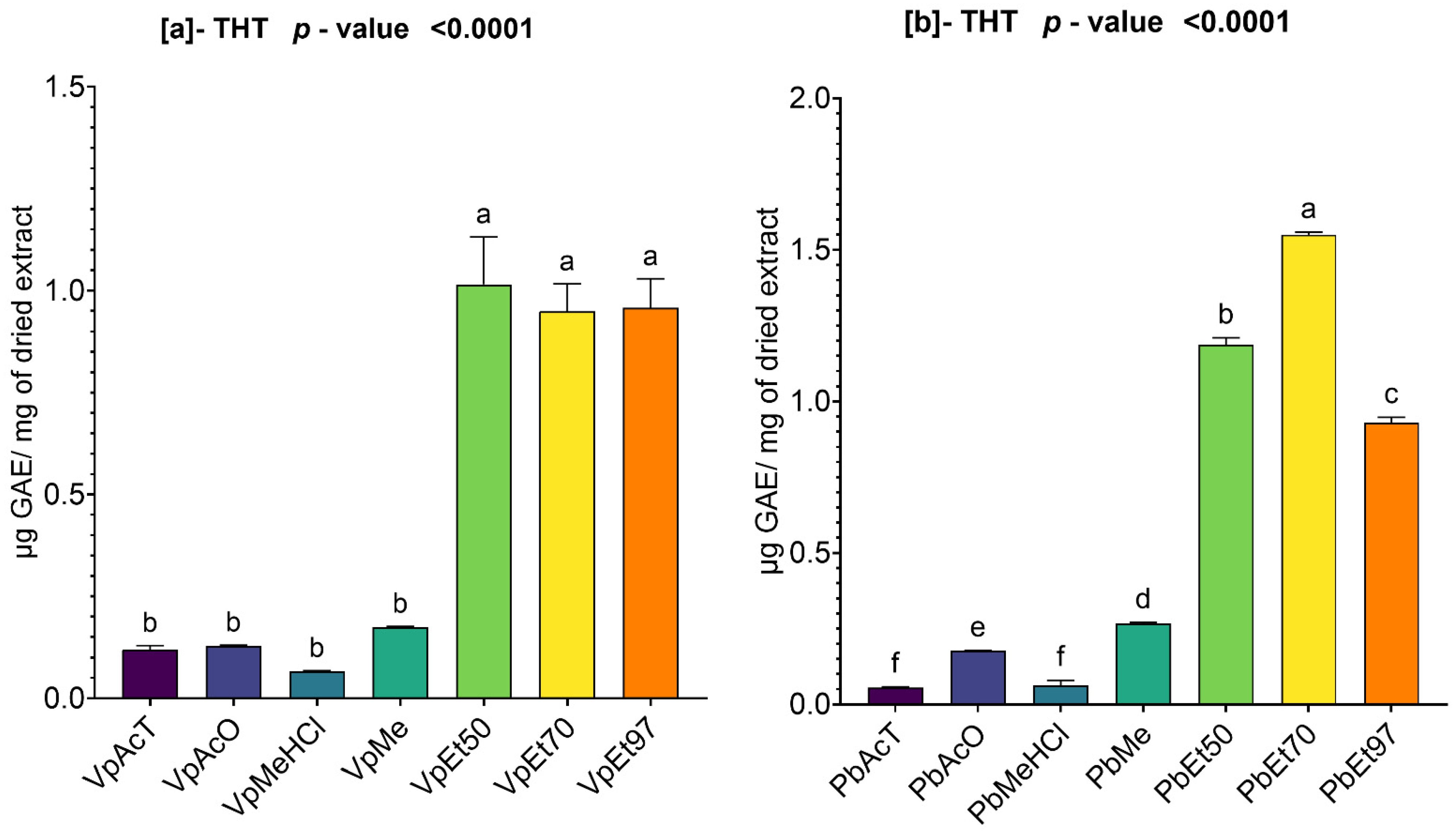
Among these phytochemical groups, phenolics were quantified using spectrophotometric assays. The bark extracts from both plants showed higher levels of total phenolics, flavonoids, hydrolyzable tannins, and condensed tannins. Ethanol, at all concentrations, extracted more total phenolics from
V. paradoxa bark than any other solvent, while methanol extracted more phenolics from
P. biglobosa bark. Flavonoids were more effectively extracted with methanol containing 1% HCl in
V. paradoxa bark, whereas they were better extracted with methanol, methanol with 1% HCl, and ethyl acetate in
P. biglobosa bark. Condensed tannins were most effectively extracted with ethyl acetate, acetone, and methanol in
V. paradoxa bark, while acetone and methanol were most effective in
P. biglobosa bark. The most hydrolyzable tannins were extracted with all ethanol concentrations in
V. paradoxa bark, and with 70% ethanol in
P. biglobosa bark. Kagambega et al. [
49] reported high polyphenol and flavonoid contents in methanolic and aqueous extracts of V. paradoxa bark. Similarly, Abdulazeez et al. [
82] observed high levels of polyphenols, flavonoids, tannins, saponins, and alkaloids in the methanolic extract of
V. paradoxa bark. Touré et al. [
44] found elevated polyphenol and flavonoid levels in aqueous decoctions and macerations of
P. biglobosa bark. However, these studies did not consider all extraction solvents, preventing them from identifying the optimal solvent for each phenolic group.
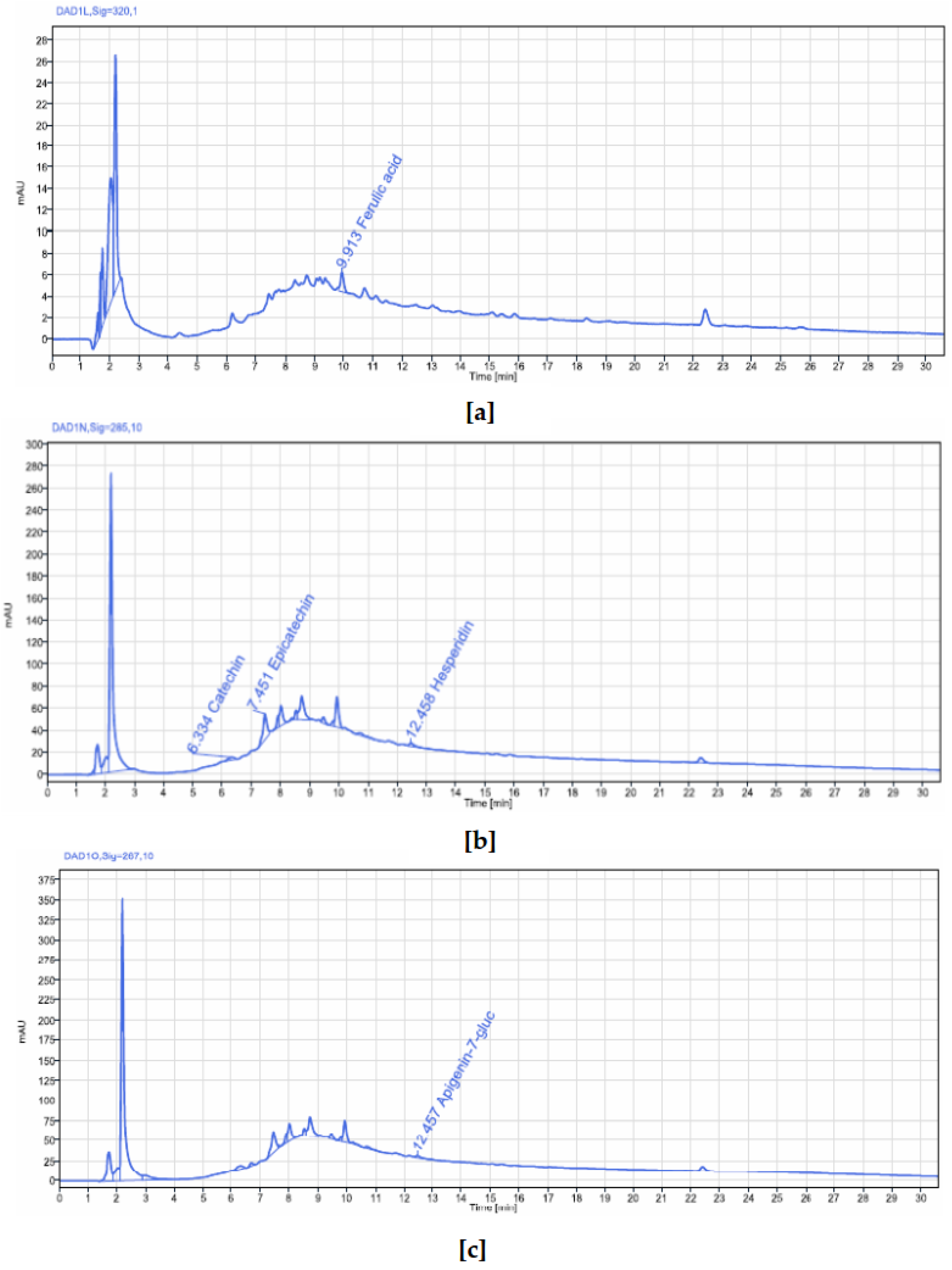
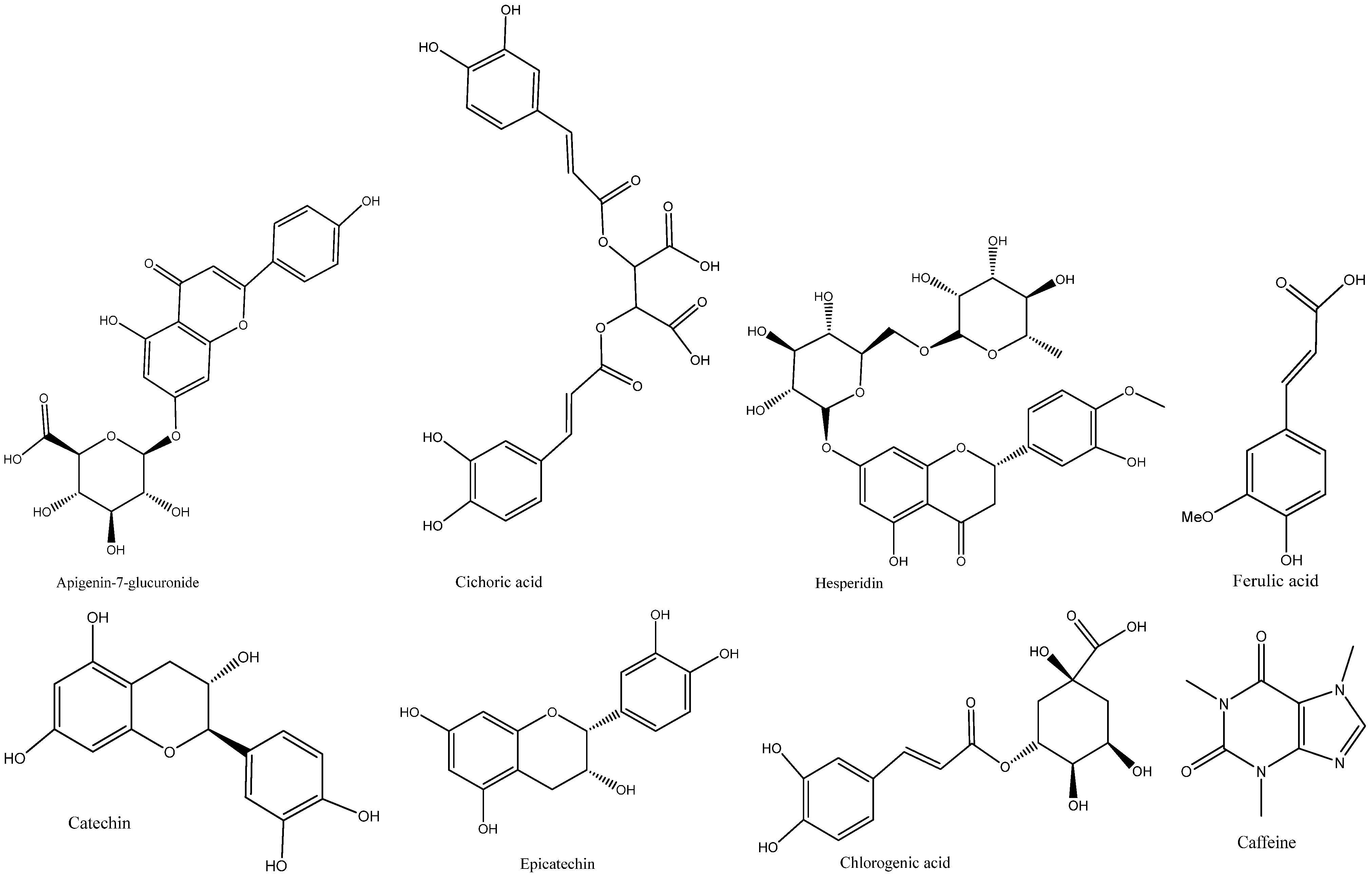
The bark extracts of both plants’ stem bark were analyzed, using HPLC-DAD for the accurate identification and measurement of phenolic compounds. The results revealed that
V. paradoxa bark contained catechin, epicatechin, ferulic acid, apigenin-7-glucuronide, and hesperidin. Other researchers, like Foyet et al. [
83], reported that
V. paradoxa bark was rich in epicatechin, gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, and anthocyanins. Additionally, Kagambega et al. [
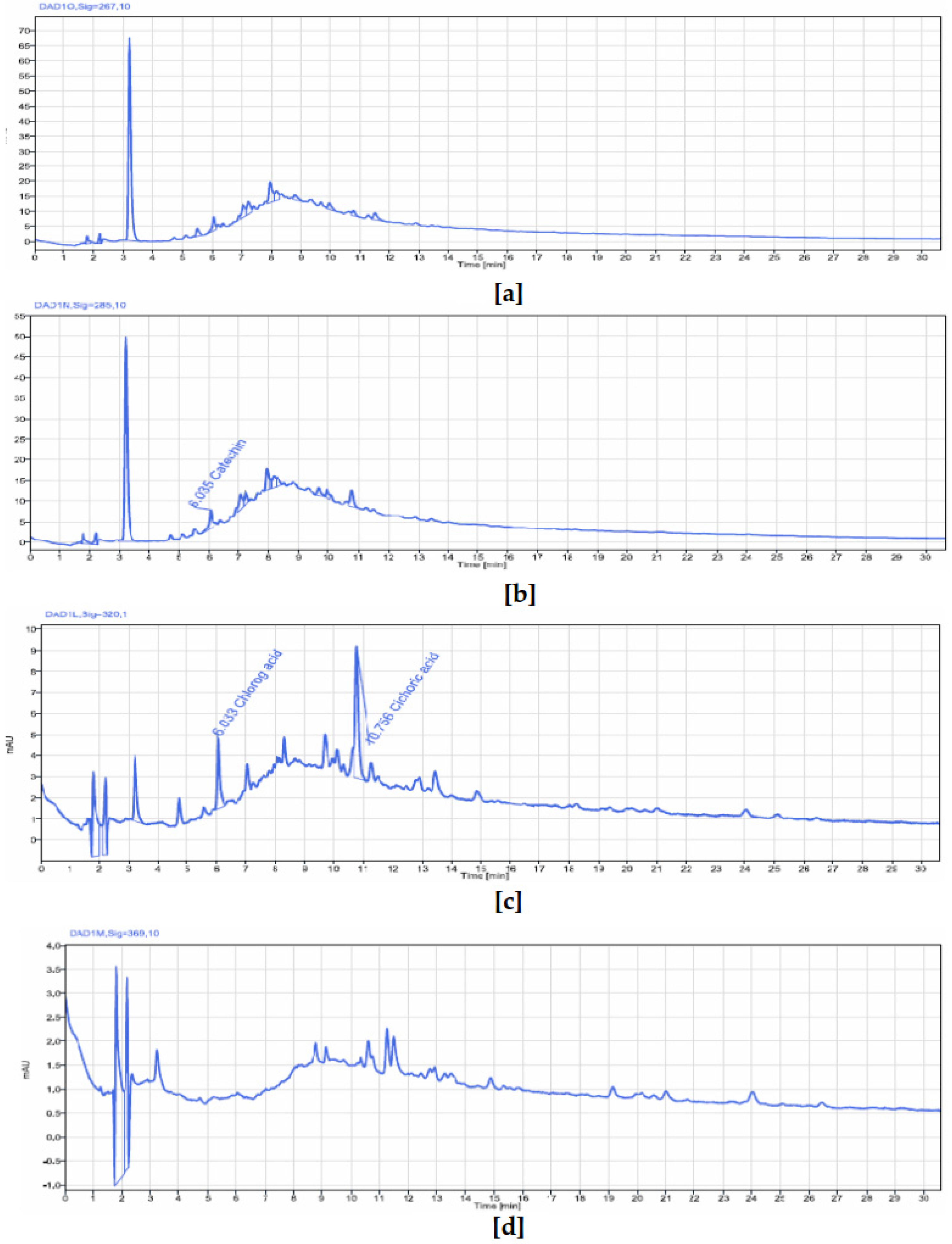
49], using HPLC-UV-MS, detected gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, gentisic acid, catechin, vanillic acid, syringic acid, epicatechin, p-coumaric acid, and quercitrin. These authors identified compounds absent in our samples, whereas ferulic acid, present in our samples, was not reported by them. These differences likely result from variations in environmental conditions faced by the plants in their natural ecosystems, as they were collected from different geographical locations. The extract of
P. biglobosa stem bark contained chlorogenic acid, catechin, caffeine, epicatechin, and cichoric acid. The catechins and epicatechins observed in
P. biglobosa extracts support the findings of Tala et al. [
42], who identified monomers and polymers of catechins using HPLC/ESI-IT-MS for proanthocyanidin analysis. Moreover, Kagambega et al. [
49] reported gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, catechin, vanillic acid, syringic acid, epicatechin, p-coumaric acid, and ferulic acid in their HPLC-UV-MS analysis of P. biglobosa stem bark, detecting compounds not found in our extract. These phytochemical differences likely depend on environmental factors specific to the collection sites. The accumulation of secondary metabolites is heavily influenced by environmental variables such as light, temperature, soil moisture, fertility, and salinity. Variations in a single factor can alter the secondary metabolite profile of most plants [
84,
85]. The compounds identified may also depend on the extraction solvent; in this study, HPLC was performed only on the 50% methanol extract to maximize the extraction of polyphenolics. Recent studies emphasize that solvent polarity significantly affects the efficiency of phytochemical extraction. Since methanol is more polar than ethanol, it is generally more effective at extracting polar compounds like phenolics and flavonoids, yielding higher amounts of these compounds compared to ethanol and acetone [
86,
87]. To better understand the biological potential of
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa bark extracts, it is crucial to conduct HPLC-based screenings using various solvents. This approach will enable a more comprehensive identification and quantification of bioactive compounds, facilitating the development of more effective plant-based therapies. While methanol is commonly used to extract polar compounds such as phenolics and flavonoids, relying solely on methanolic extracts for HPLC analysis may not capture the full spectrum of bioactive compounds present in
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa stem bark. As shown by our results, the phenolic content of both species depends on the choice of extraction solvent, highlighting that different solvents, due to their varying polarities, can extract distinct groups of phytochemicals.
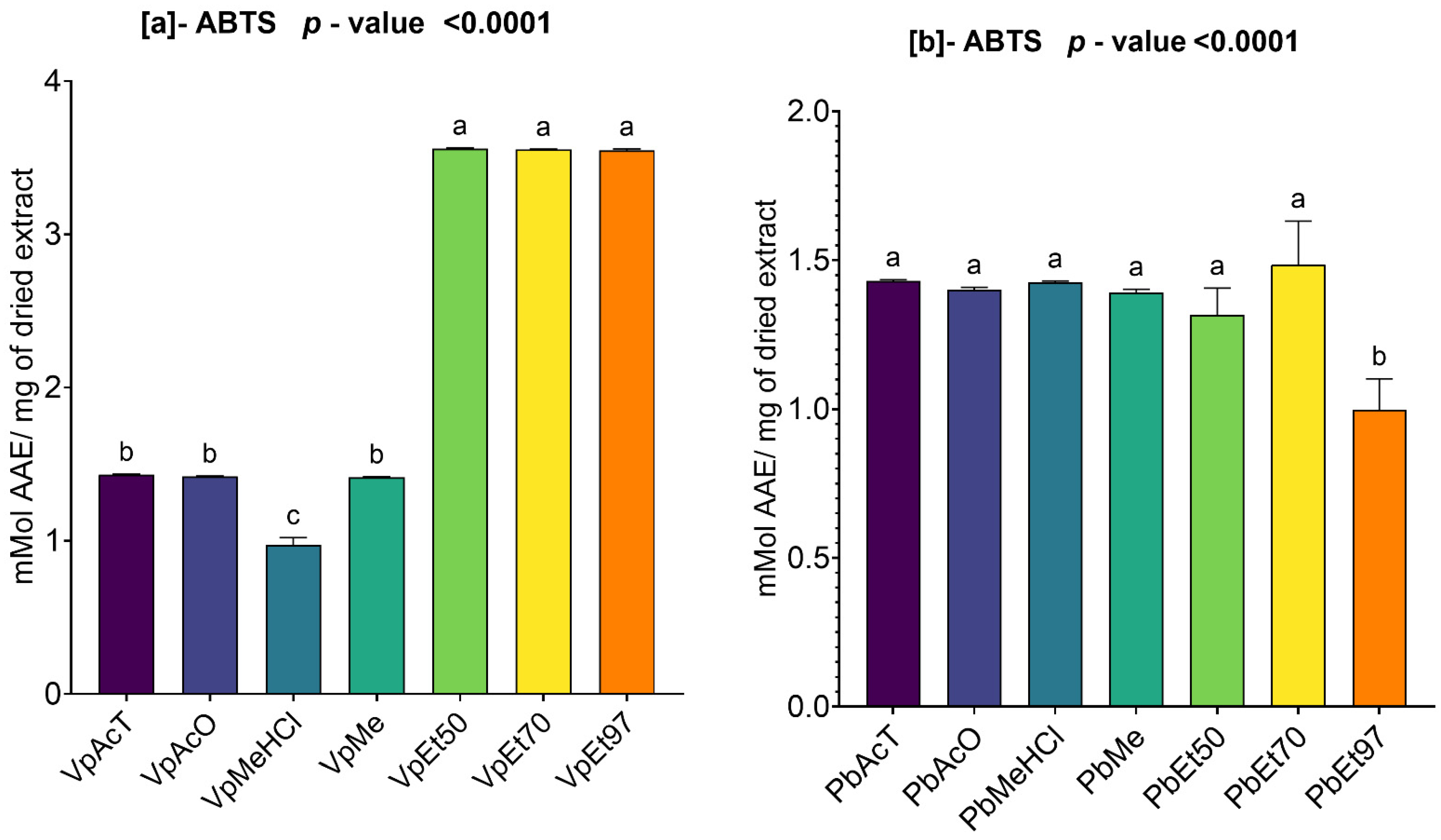
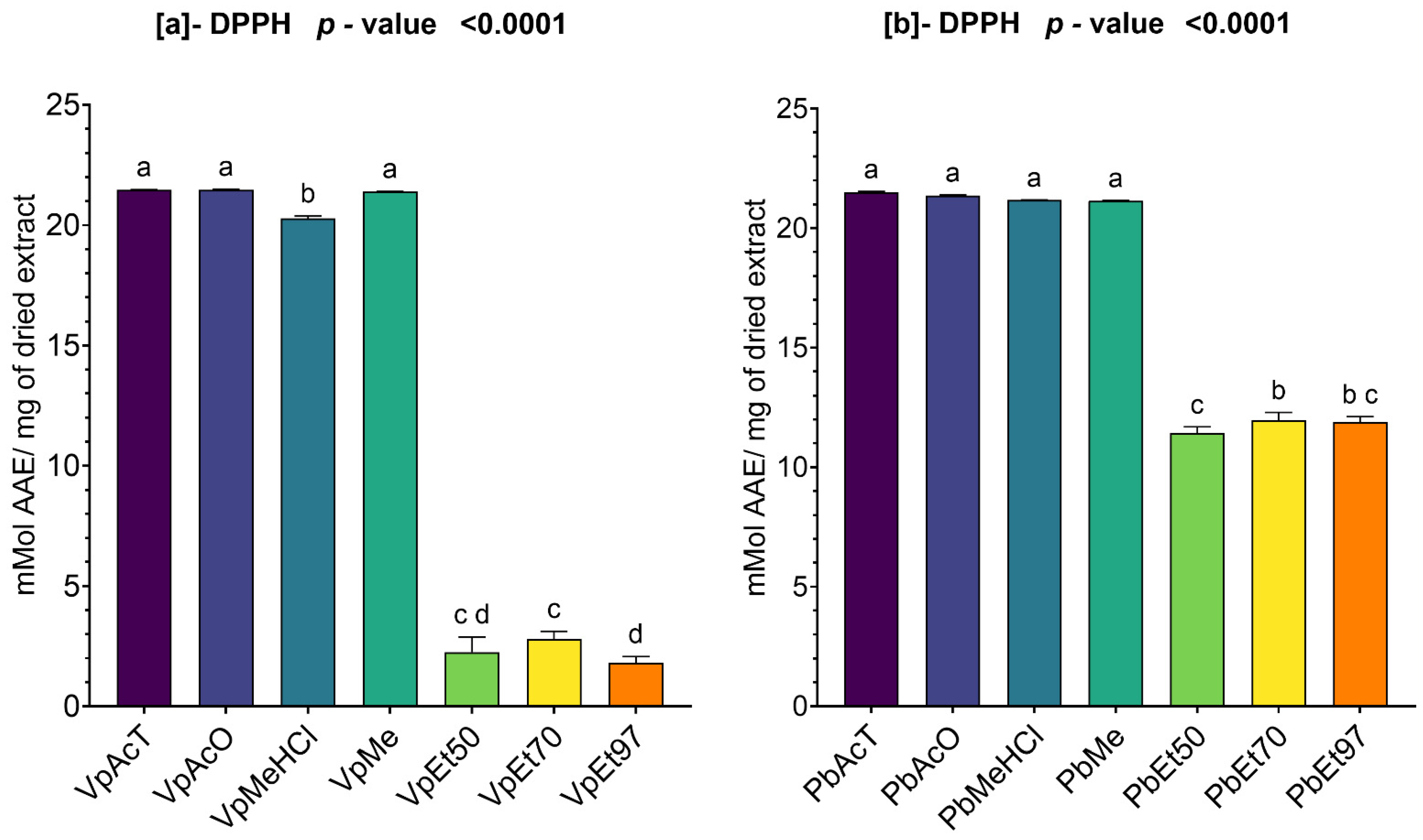
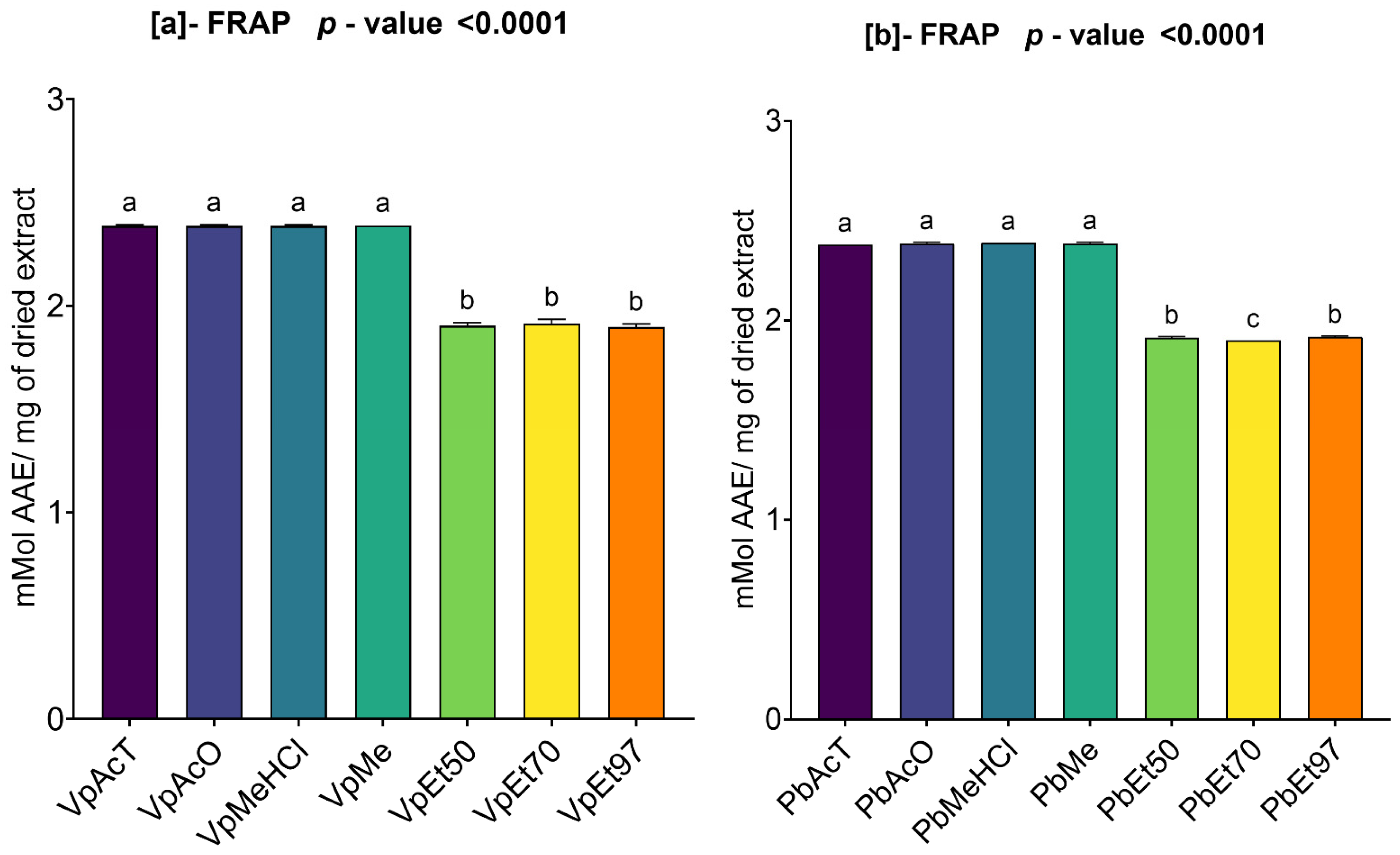
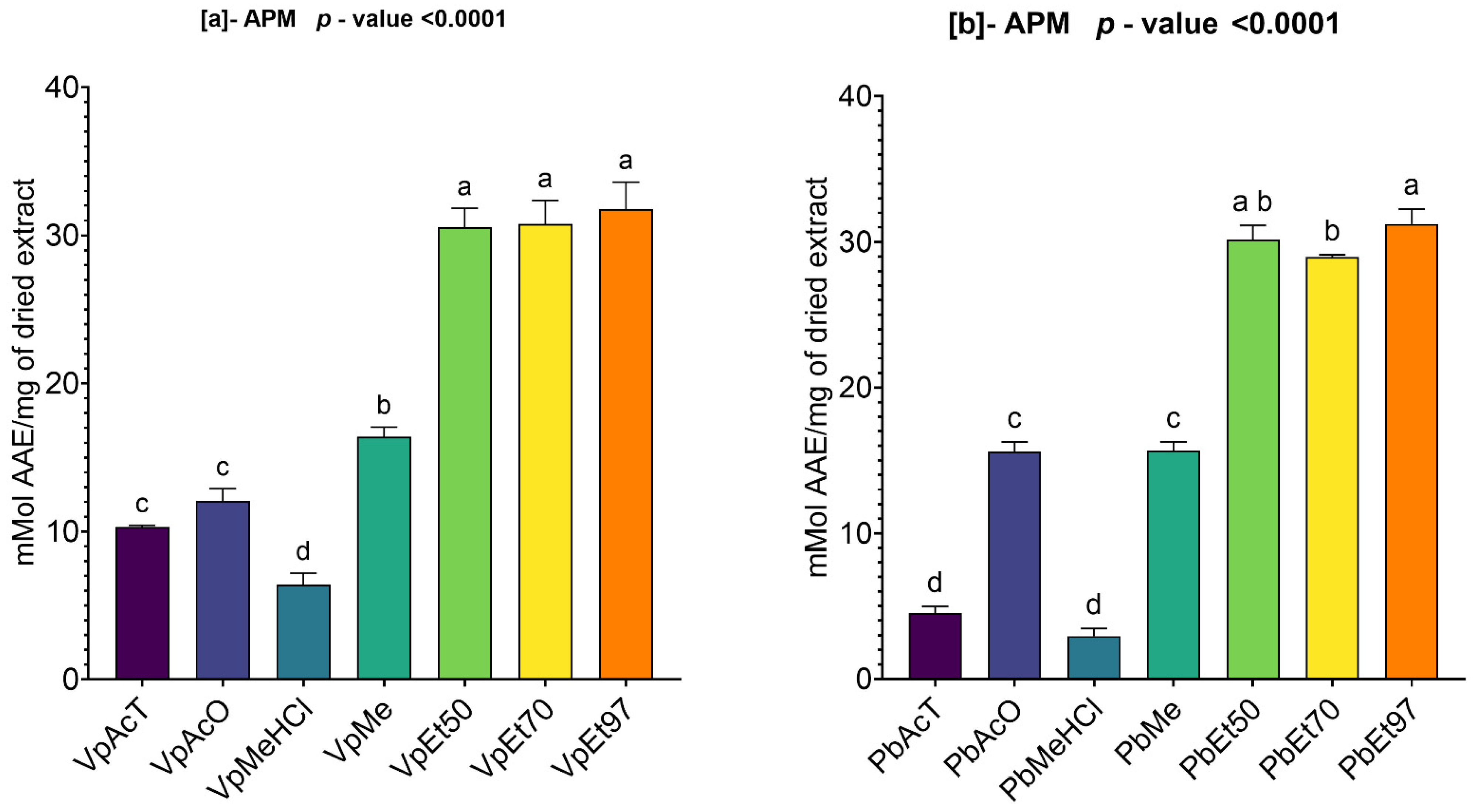
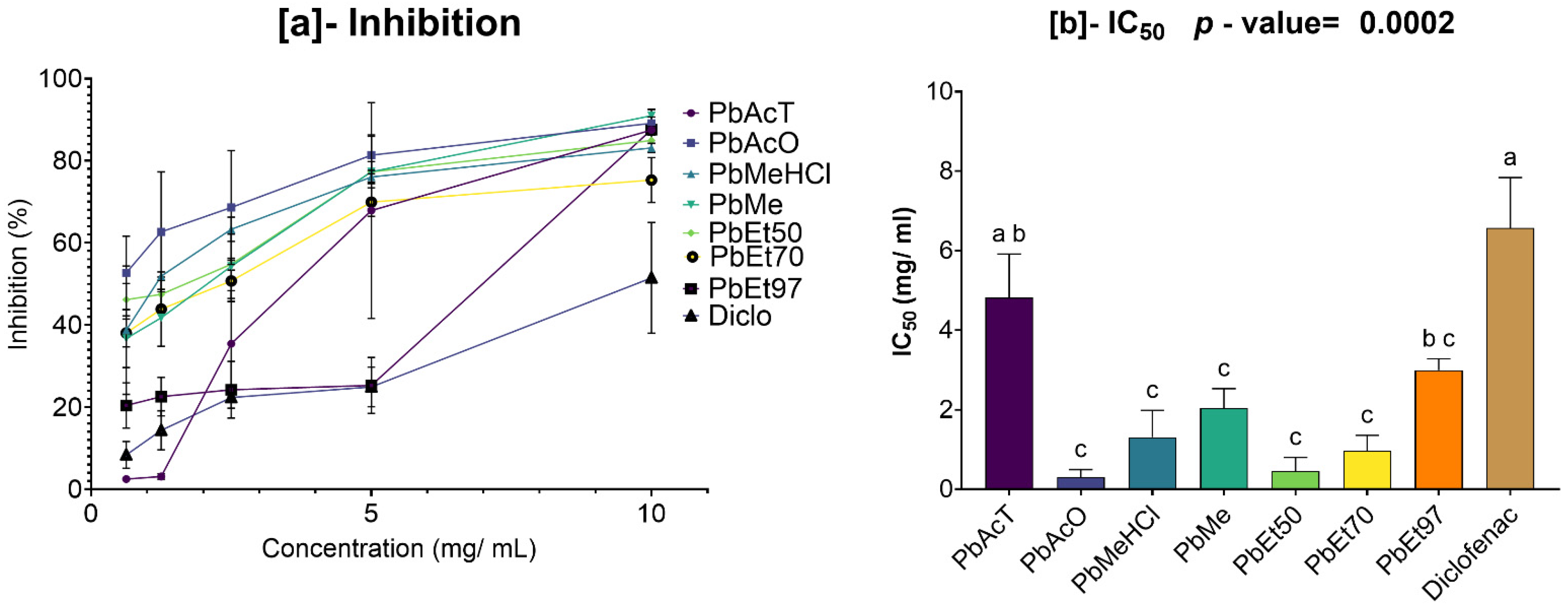
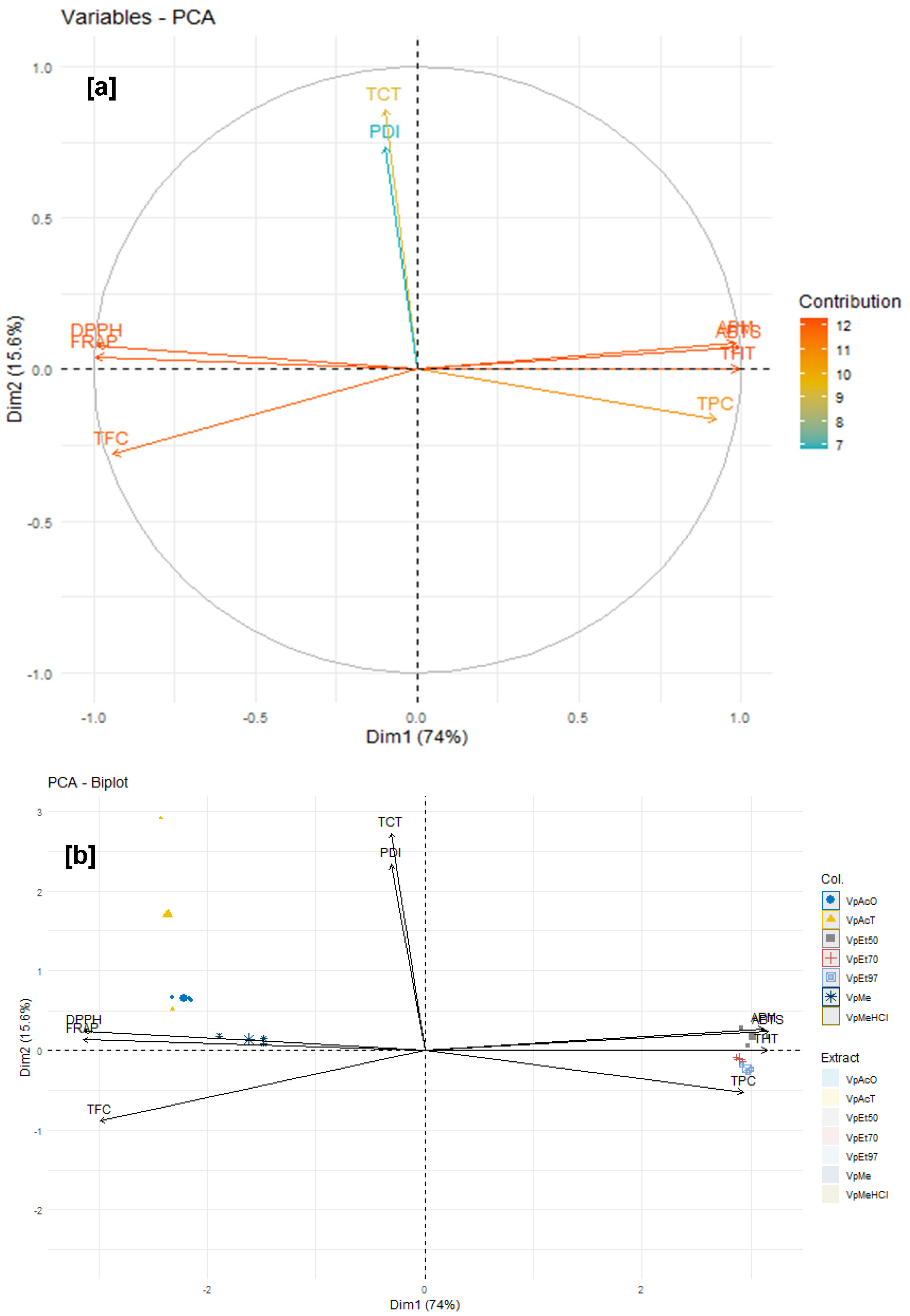
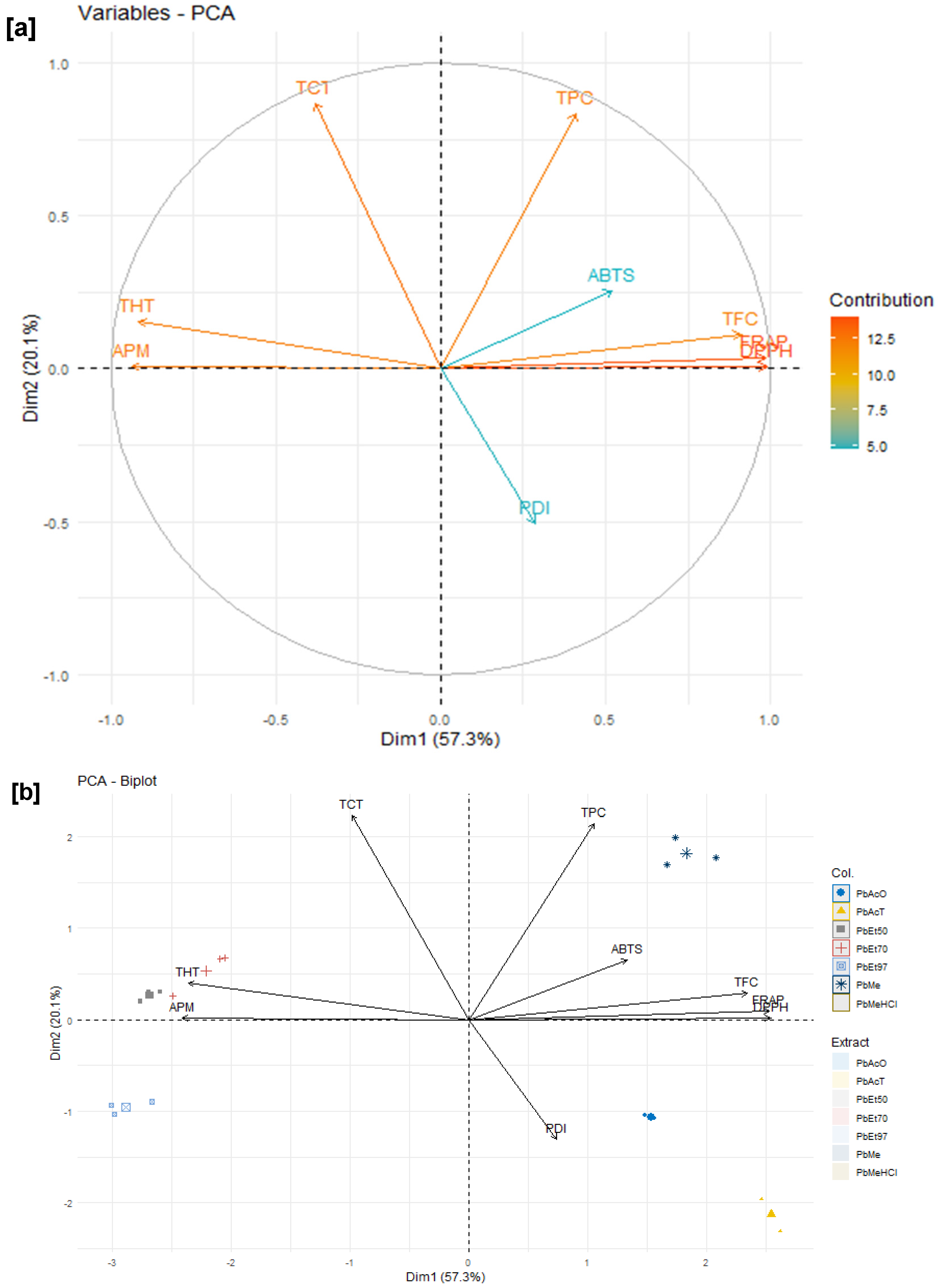
The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties were evaluated in vitro. Antioxidant activity was assessed using ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and APM methods. All extracts showed strong antioxidant activity by scavenging ABTS and DPPH, and by reducing ammonium phosphomolybdenum (APM) and ferric ions (FRAP). The highest ABTS scavenging capacities were observed in ethanolic extracts of
V. paradoxa bark, while
P. biglobosa stem bark showed high activity across all extracts except those based on 97% ethanol. DPPH scavenging activity was notably strong in the bark of both plants across all extracts, except for the ethanol-based ones. Regarding APM reduction activity, the highest reduction was found in the bark of both plants compared to ethanol extracts. Conversely, a ferric reduction capacity (FRAP) was evident in the bark of both plants across all extracts, except those based on ethanol. The broad antioxidant spectrum and potent activity of
V. paradoxa stem bark have been documented for aqueous and methanolic extracts, especially in terms of DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP scavenging properties [
49,
73]. This activity has been shown in vivo by improving scopolamine-induced memory impairments and reducing oxidative stress in the hippocampus of rats with methanolic extract [
83]. Ethyl acetate, ethanolic, and aqueous extracts of
P. biglobosa stem bark have been reported for their DPPH, hydroxyl radical scavenging, nitric oxide inhibition, and FRAP properties [
53]. Additionally, aqueous decoctions and macerations of
P. biglobosa bark have been noted for their ABTS scavenging ability [
44].
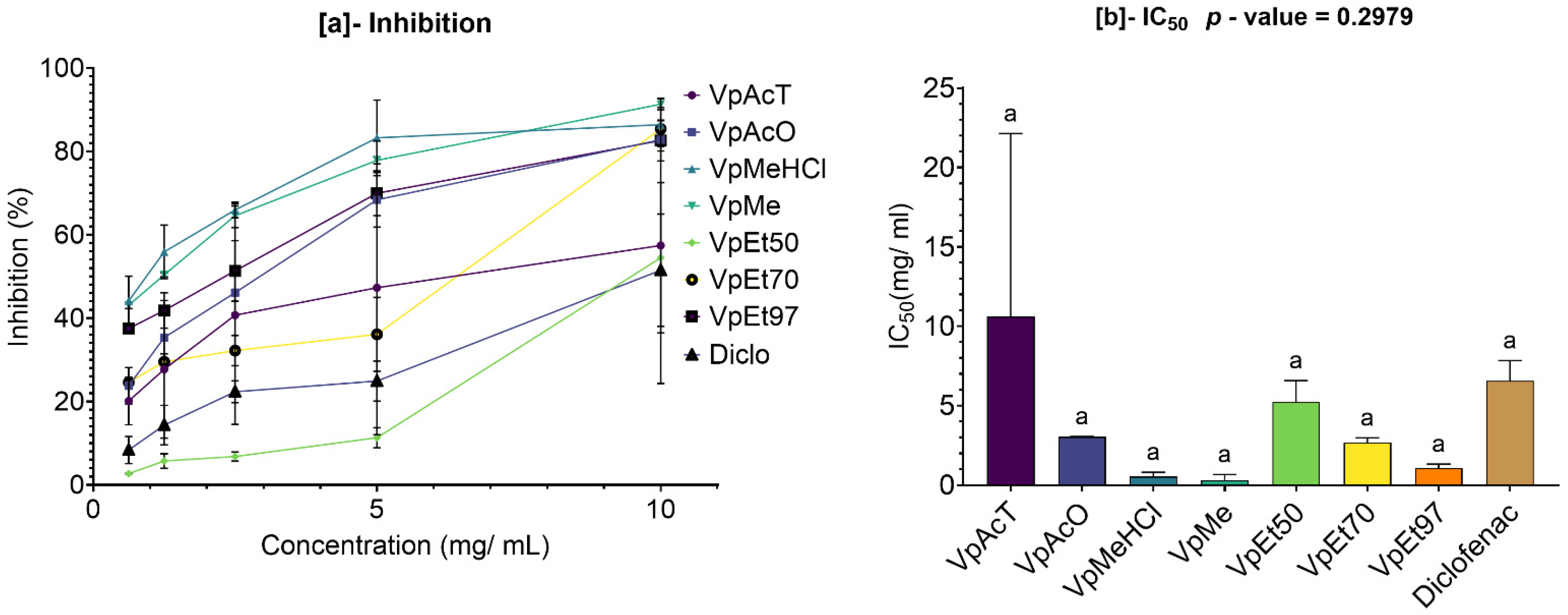
Anti-inflammatory activity was tested in vitro using a protein denaturation inhibition assay. The methanol extract and methanol with 1% HCl showed the best inhibition of protein denaturation among all
V. paradoxa bark extracts. However, for
P. biglobosa bark, acetone and 50% ethanol extracts exhibited the highest denaturation inhibition activity. The methanolic extract of
V. paradoxa bark has been previously reported for its anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects in rat models at doses starting from 75 mg/kg body weight [
64,
67]. The strong anti-inflammatory activity of
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa extracts has also been documented by Kagambega et al. [
49] in inflammation-induced rat models.
The reported link between antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity and the phenolic content of bark extracts from both plants emphasizes the important role of flavonoids, tannins, and phenolic compounds in the antioxidant properties of
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa bark extracts. Phenolic compounds are generally recognized for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects [
88]. For instance, catechin, found in the bark of both plants, is known for these effects [
89]. Additionally, the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of hesperidin are well-documented, as reported by Parhiz et al. [
90], Lorzadeh et al. [
91], and Tejada et al. [
92].
Phenolic compounds are not the only ones with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity; terpenoids are also studied, reported, and known for these activities [
93,
94,
95,
96,
97,
98,
99,
100,
101,
102]. Three modes of action have been identified so far. The main antioxidant mechanisms of terpenoids, such as carotenoids, include singlet oxygen-quenching, hydrogen transfer, and electron transfer [
94]. Although alkaloids can act as both pro- and antioxidants, recent studies have reported a correlation between antioxidant activity and alkaloid content [
103,
104,
105]. The anti-inflammatory effects of alkaloids have also been demonstrated and documented in recent research [
106,
107,
108,
109]. Additionally, glycosides can influence reduction and oxidation systems [
110]. Our study detected the presence of terpenoids in the bark powders of
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa. Furthermore, alkaloids were found in the stem bark powder of
Vitellaria paradoxa, while glycosides were identified in the stem bark powder of
Parkia biglobosa. The presence of these metabolites is significant when assessing the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of their extracts. To determine whether polyphenols are the sole contributors to these bioactivities, it is important to quantify these metabolite groups within the plant matrices and understand their specific roles in antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. The health benefits of these antioxidants, along with their immunomodulatory effects, make them suitable for developing antioxidant-based therapeutics [
111]. Yahfoufi et al. emphasized the importance of polyphenols as immunomodulators and anti-inflammatory agents [
112]. The fact that
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa stem bark extracts showed higher polyphenol content and exhibited strong antioxidant and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities provides a trustworthy basis for further research.
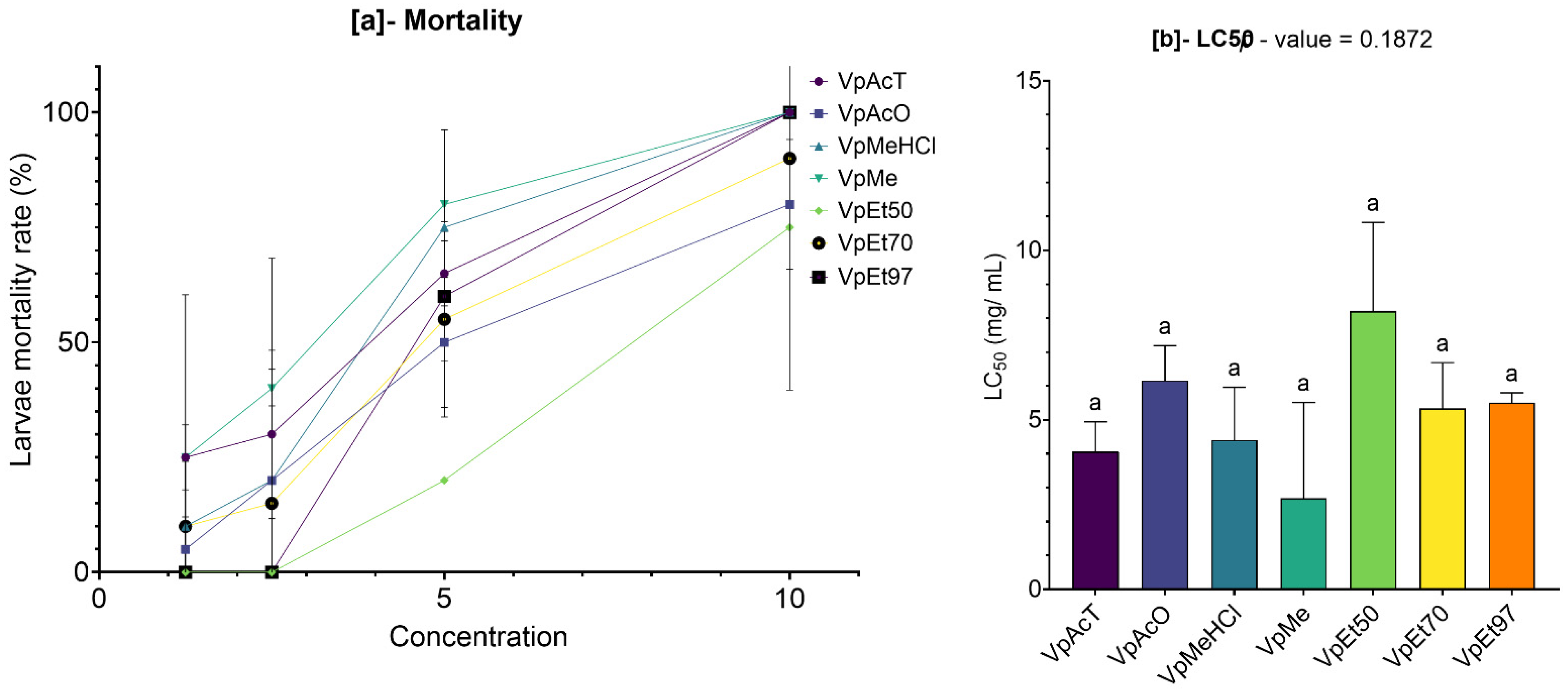
The cytotoxic potential of plant extracts is a vital factor in assessing their safety profile, especially when they are meant for therapeutic purposes. In this study, the cytotoxicity of stem bark extracts of V. paradoxa and P. biglobosa was evaluated using the Artemia salina larvae lethality bioassay, a dependable initial method for predicting cytotoxicity.
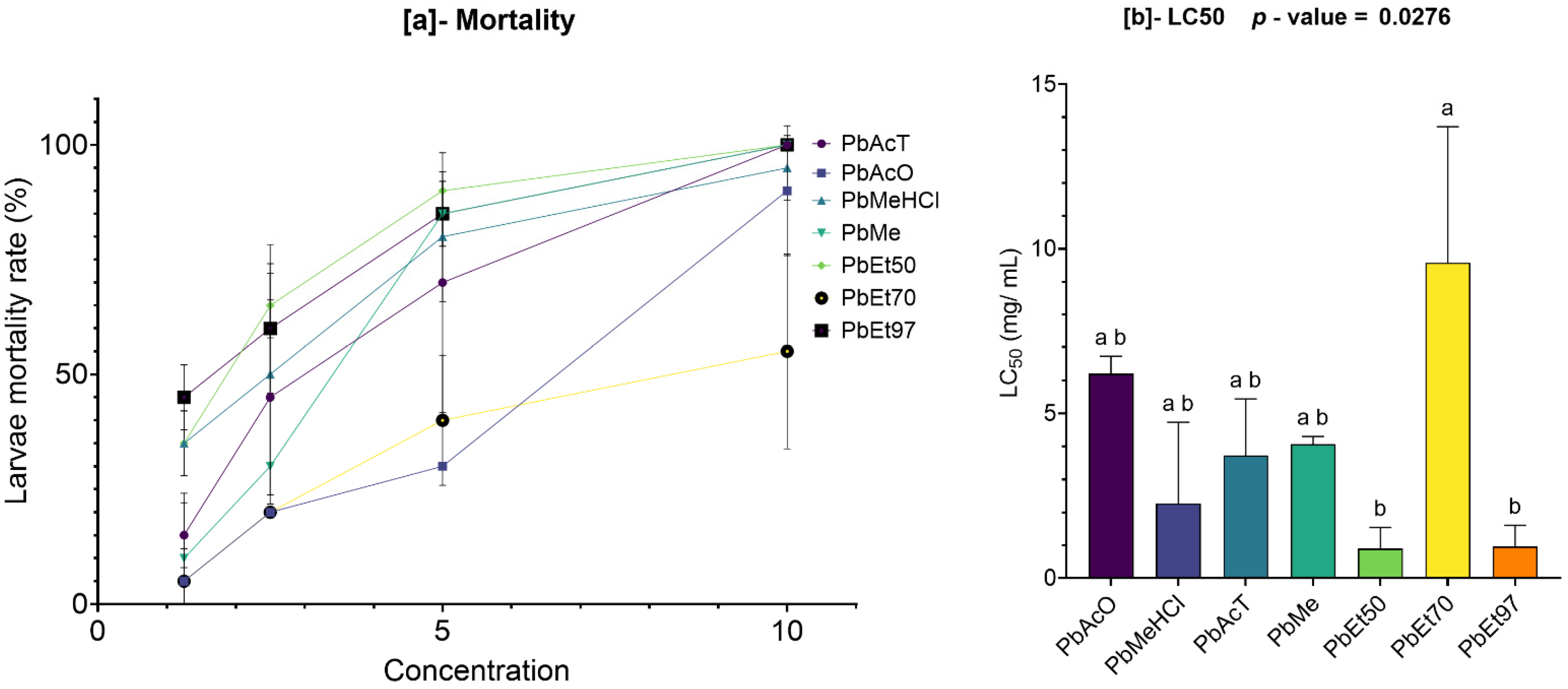
Our results showed that both
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa stem bark extracts, regardless of the solvent used, had LC
50 values significantly higher than the cytotoxicity threshold (LC
50 > 0.1 mg/mL) proposed by Moshi et al. [
77]. Although some extracts exhibited relatively low LC
50 values, none fell below the critical threshold of 0.1 mg/mL, confirming their non-toxic nature in this model. In contrast to our findings, Ibrahim et al. [
113] reported values well below this threshold and concluded that the methanolic extract of
Vitellaria paradoxa leaf and stem bark showed moderate cytotoxicity. As noted in a previous review, the safety and toxicity of different parts of
V. paradoxa remain unclear [
39]. These variations could be due to differences in the geographical location of samples and environmental conditions. Conversely, Nounagnon et al. [
114] reported LC50 values of 10.10 mg/mL and 19.90 mg/mL—slightly above the 0.1 mg/mL threshold—for ethanolic extracts of
Parkia biglobosa stem bark and leaves, respectively, against Artemia salina larvae. The lack of cytotoxicity in both plant species’ extracts supports their safe use for further in vivo studies and potential therapeutic applications. While the
Artemia salina assay offers valuable initial insights, it does not fully replicate mammalian toxicity; therefore, future toxicity evaluations using mammalian cell lines and long-term exposure models are essential to confirm these preliminary results.
After evaluating the cytotoxicity of the bark extracts using the
Artemia salina model, which showed no significant toxic effects at the cellular level, an in vivo acute toxicity study was performed to further assess the systemic safety of the extracts. This phase involved monitoring physiological, hematological, immunological, hepatic, and renal parameters in treated animals to thoroughly evaluate potential toxic effects under physiological conditions, following OECD guidelines [
115] for chemical safety assessments. Due to the potential toxicity linked to extracts prepared with solvents other than ethanol [
116], we chose to assess the in vivo toxicity of ethanol-based stem bark extracts of
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa as a safer, representative alternative.
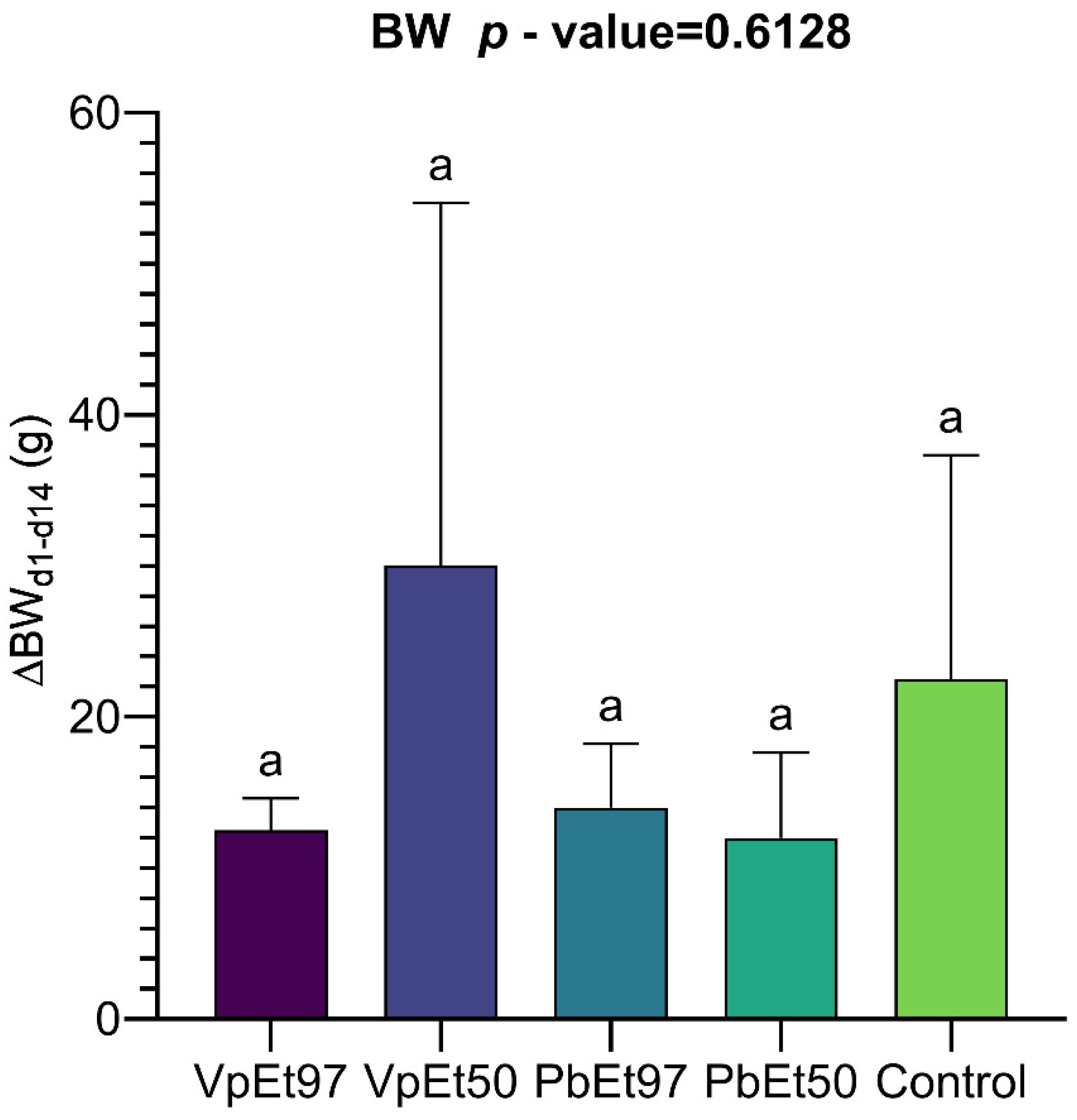
The evaluation of acute toxicity through weight-monitoring showed no significant adverse effects from the extracts of
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa. This supports the results reported by Mainasara et al. [
117] regarding the absence of adverse effects on the weight gain of
V. paradoxa stem bark extracts. The lack of significant differences in weight gain between treated and control groups suggests there is no acute systemic toxicity [
118]. Additionally, the absence of changes in physical characteristics or behavior further supports the biocompatibility of the extracts at the doses used. Mainasara et al. [
117] also reported no deaths or signs of toxicity in the oral acute toxicity test of
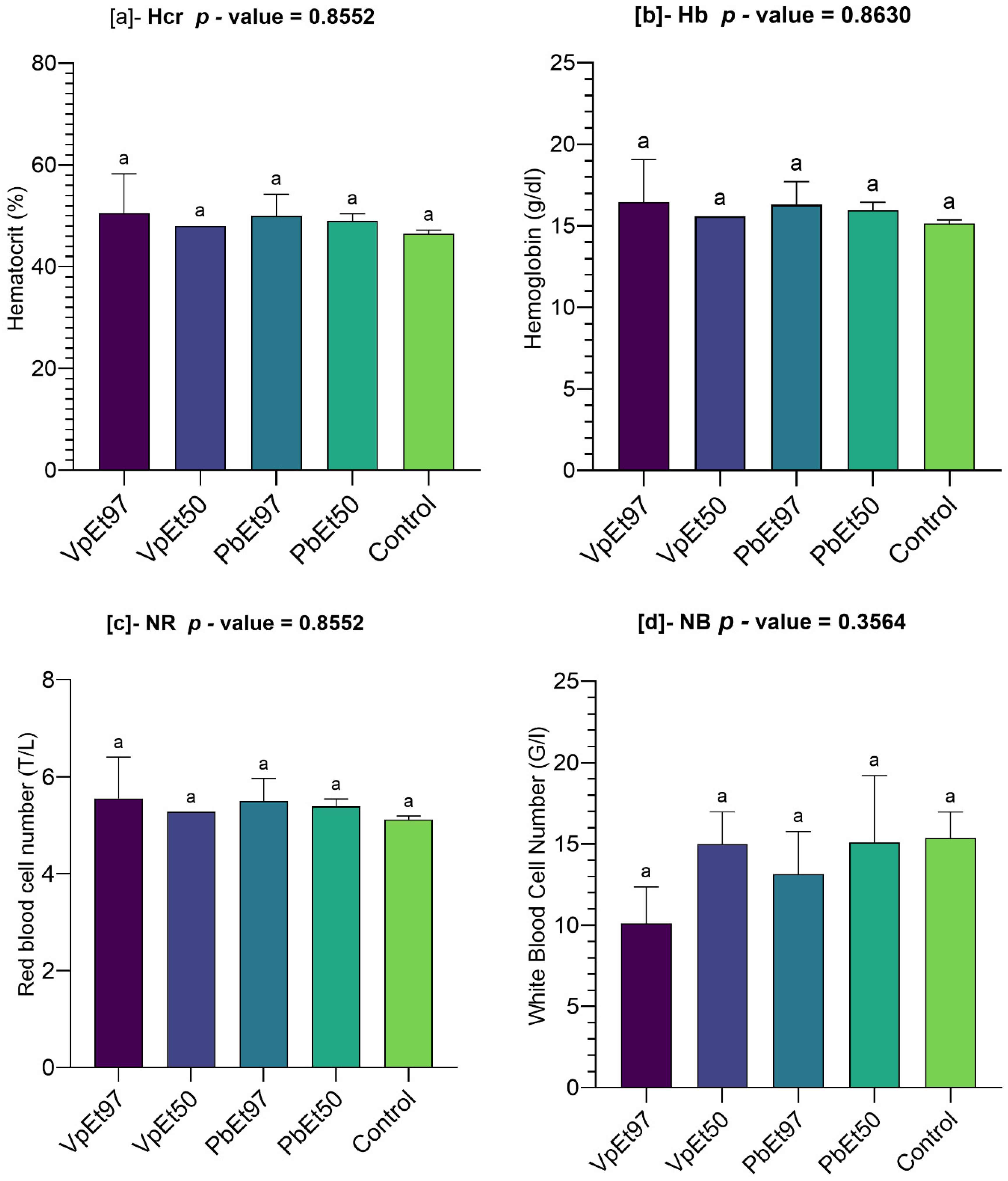
V. paradoxa stem bark extract. Hematological parameters, including hematocrit, hemoglobin, and red and white blood cell counts, showed no significant differences between the control and treated groups. This aligns with the findings of Ayankunle et al., who observed that, except for platelet count, the administration of ethanolic V. paradoxa stem bark extract did not alter hematological parameters in the experimental model [
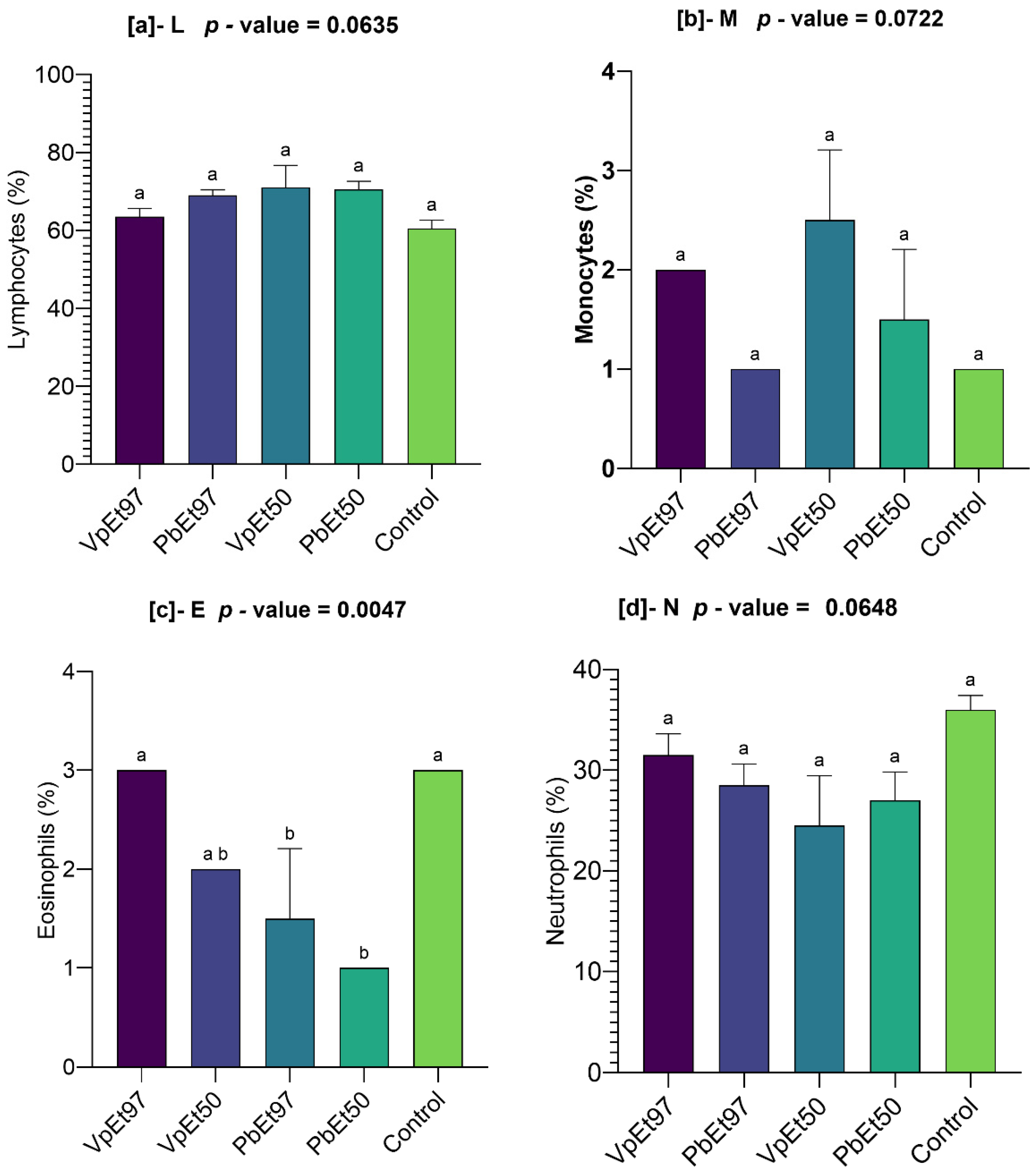
119]. These findings suggest that the ethanolic extracts of both plants do not impair the hematopoietic system. The slight increases in lymphocyte levels observed with certain extracts may indicate mild immunostimulatory effects, although the lack of statistical significance tempers this interpretation. Nevertheless, plant secondary metabolites are well-known for their immunomodulatory effects [
120,
121], and further studies are needed to confirm this activity. Monocyte and eosinophil levels remained comparable to the control. Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes are white blood cells that play a crucial role in defending against infection and protecting the body from external threats [
122]. This further supports the hematological safety of
P. biglobosa and
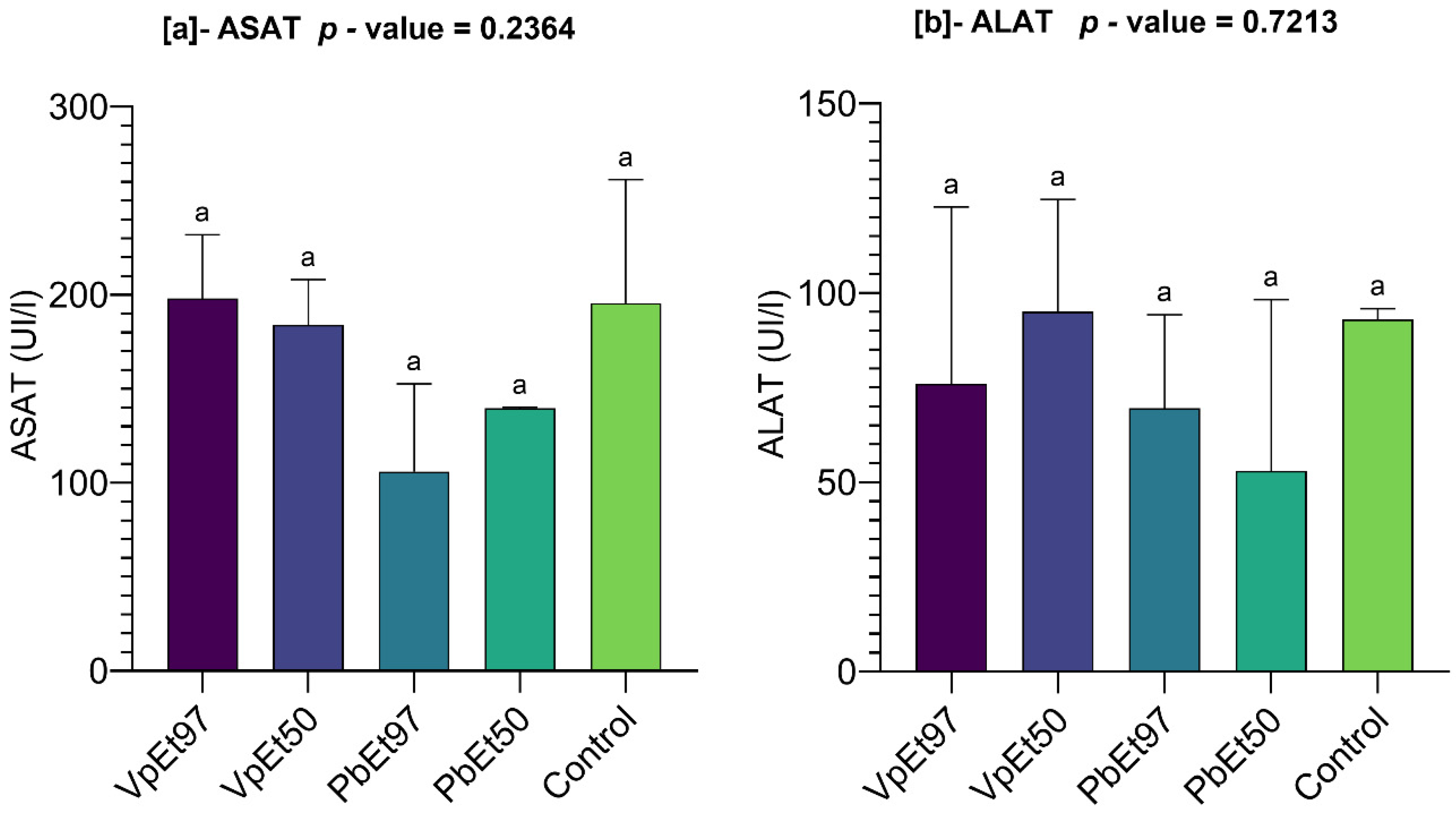
V. paradoxa stem bark extracts. Liver function markers (AST and ALT) remained within normal ranges, with no statistically significant differences across groups. Although there was a slight elevation in AST in animals treated with the 97% ethanolic
V. paradoxa extract, the levels were comparable to the control. Overall, the data suggest that the extracts do not cause hepatotoxicity under the conditions of this study. This contradicts Ayankunle et al. [
119], who reported that serum levels of creatinine, urea, ALAT, ASAT, and ALP were significantly higher in treated rats compared to controls when administered with ethanol extract of
V. paradoxa. The non-toxic effects of
P. biglobosa observed in this study are supported by the findings of Josiah et al. [
123], who reported in a toxicity study of aqueous fractions of methanolic
P. biglobosa stem bark extract in goats that there were no significant effects on biochemical parameters or changes in glucose, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Additionally, Udobi and Onaolapo [
124] reported that the LD
50 of
P. biglobosa leaf and root extracts falls within 500–5000 mg/kg body weight, indicating slight toxicity but overall suggesting they are potentially safe [
124]. However, seed extracts of
P. biglobosa have been reported to cause a significant increase in hematological parameters such as white blood cells, lymphocytes, and neutrophils, as well as total protein, albumin, and aspartate aminotransferase, and a significant decrease in blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels [
125].
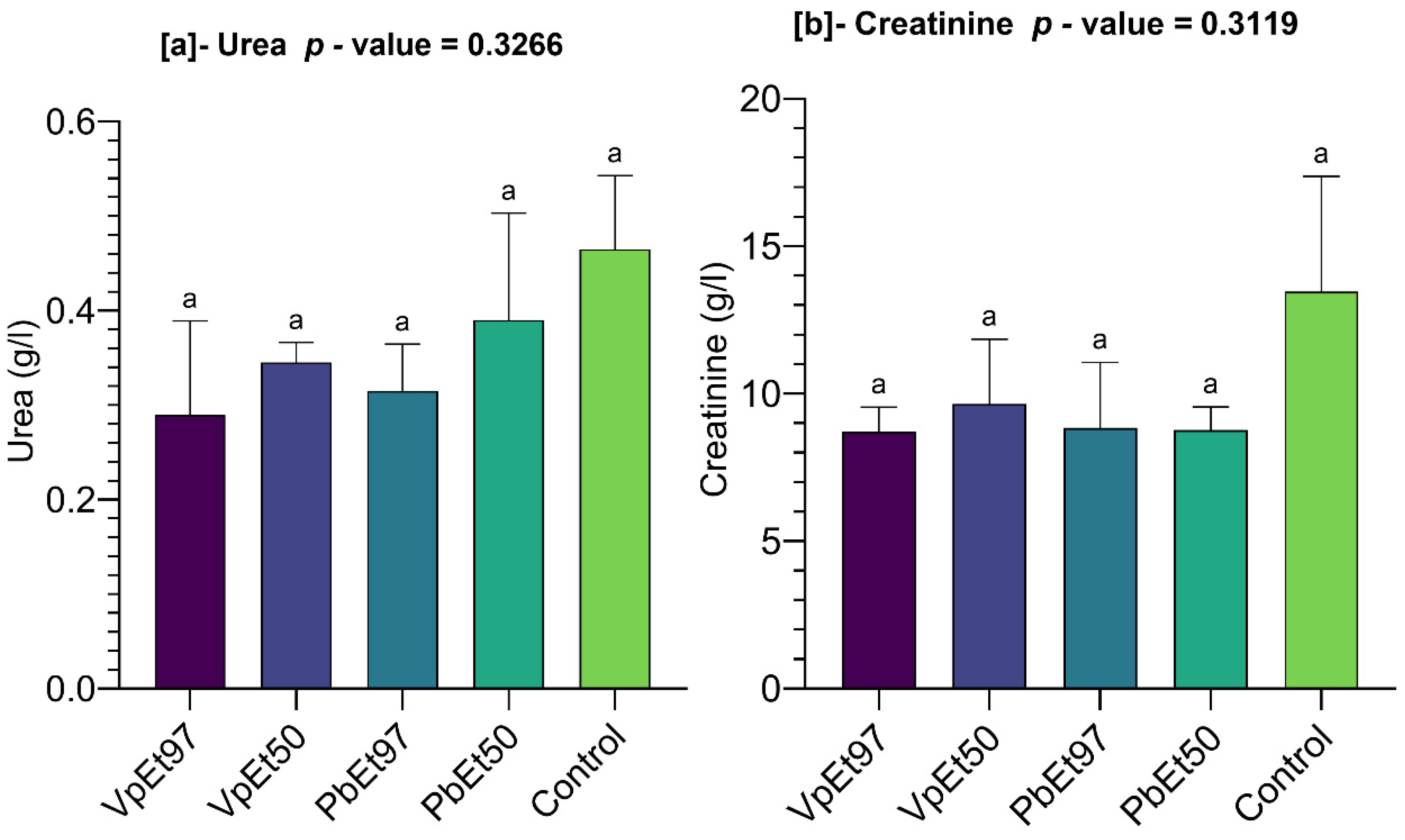
An assessment of kidney function showed no significant changes in urea and creatinine levels, which remained below those of the control group. This indicates preserved renal function and suggests that the tested doses of bark extracts did not harm kidney physiology. These findings are consistent with those of Mainasara et al. [
126] and Ajibade and Soetan [
125], who reported no significant differences between control and test groups except for urea and creatinine levels and indicated no harmful effects on kidney function in Wistar rats administered
P. biglobosa leaf extracts and
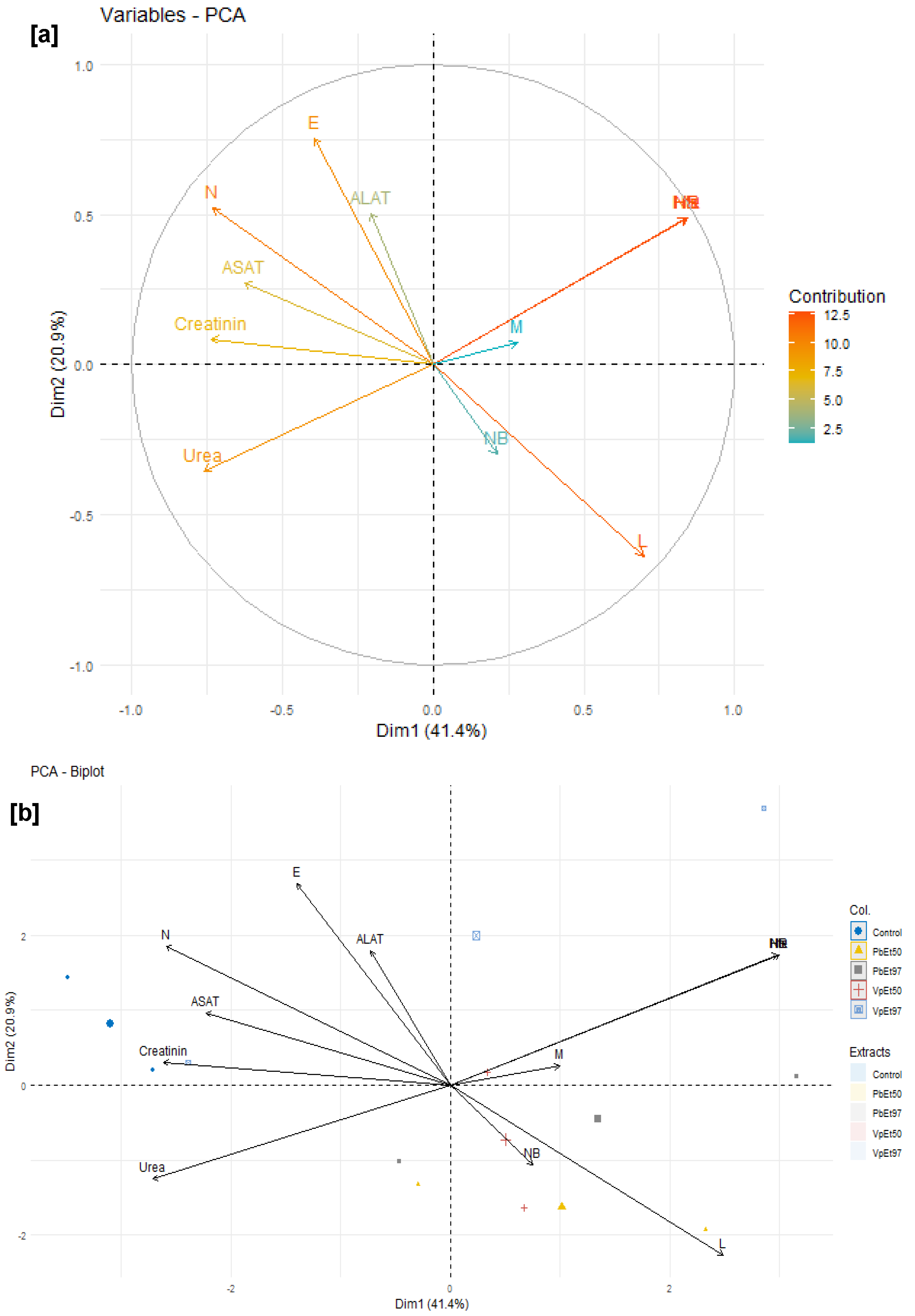
V. paradoxa stem bark extracts. Principal component analysis identified hemoglobin, hematocrit, and red blood cell count as the most influential parameters. These positively correlated parameters, which increase with plant extract administration, support the safety of the extracts. Conversely, higher levels of neutrophils, eosinophils, and liver/kidney function markers in the placebo group suggest no toxic effects from the extracts. Overall, these results support the non-toxic nature of
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa ethanolic bark extracts at the tested doses. This safety profile, combined with their previously shown biological activities, enhances the case for their potential use in therapy pending further sub-chronic and chronic toxicity studies. Our findings align with the study by Mainasara et al. [
117] on the acute hepatotoxicity of methanol extract of
V. paradoxa stem bark at doses of 5, 50, 300, 2000, and 5000 mg/kg, where no behavioral changes or mortality were observed in rats within 24 h and up to 14 days after treatment. Similarly, Ajibade and Soetan [
125] reported that
P. biglobosa leaf methanolic extract has no harmful effect on rat liver.
The low cytotoxicity observed in the
Artemia salina model and the unremarkable acute toxicity reported for
V. paradoxa indicate that the plant appears to be safe, as it has been shown to inhibit sodium arsenic toxicity in rats and Harwich fruit flies and to exhibit antiproliferative activity in cancer cell models [
127]. A similar observation was made with
P. biglobosa stem bark extract, which demonstrated hepatoprotective effects in preventing paracetamol-induced liver damage in Wistar rats [
55].
Vitellaria paradoxa and
Parkia biglobosa stem bark extracts showed significant polyphenolic content, which depended on the solvent’s nature and polarity. This content was strongly correlated with antioxidant activity and protein denaturation inhibition, likely due to their chemical structures. Given the absence of significant cytotoxic and acute toxic effects, we next evaluated the therapeutic potential of the ethanol-based extracts by testing their anti-ulcer effects in vivo. The stem bark extracts of
Vitellaria paradoxa and
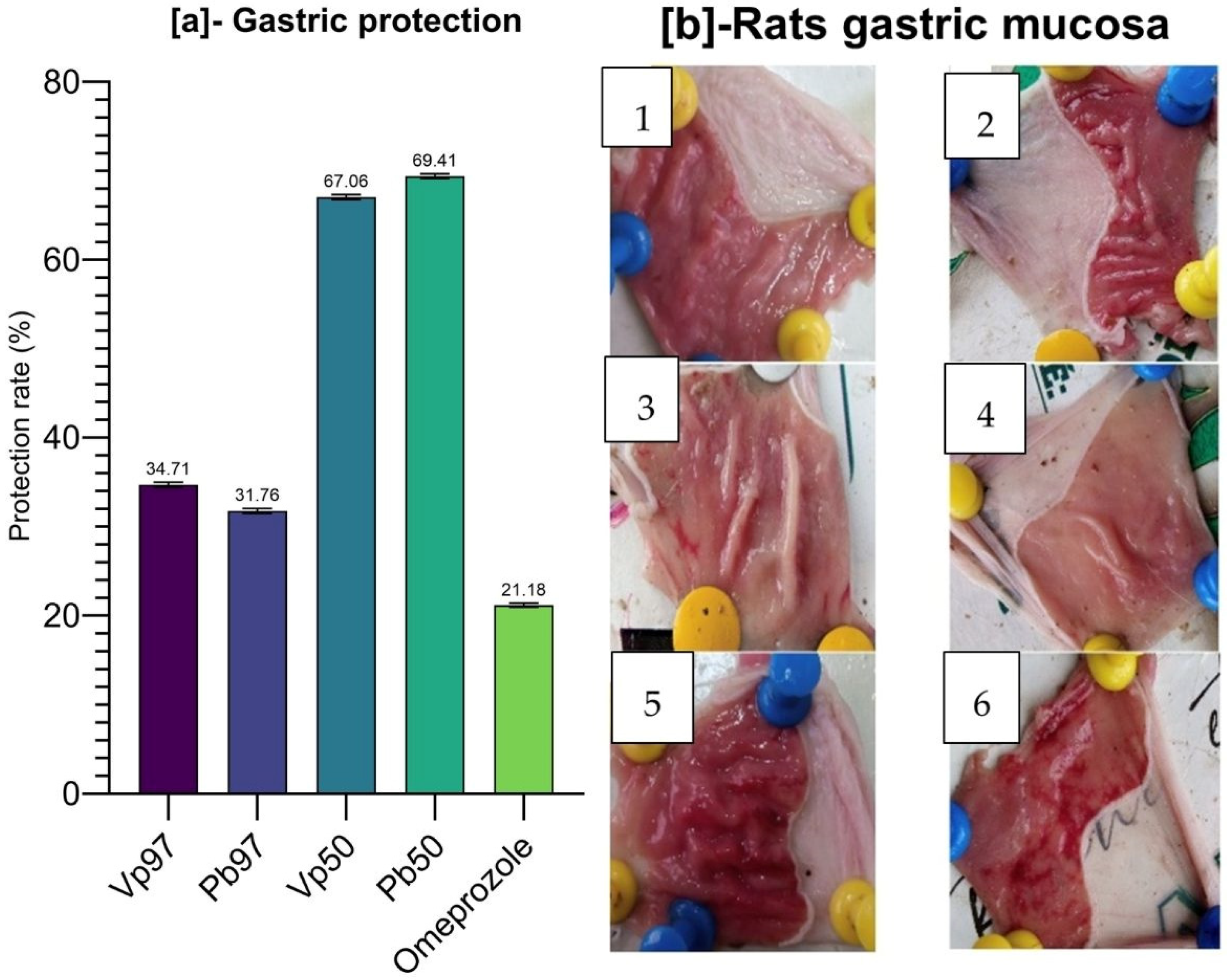
Parkia biglobosa demonstrated promising gastroprotective properties in the ethanol-induced ulcer model. Notably, the 50% ethanolic extracts of both plants showed the highest stomach protection rates—67.06% for
V. paradoxa and 69.41% for
P. biglobosa—surpassing even the reference drug, omeprazole, which had a protection rate of only 21.18%. These results indicate a strong therapeutic potential for these extracts against gastric mucosal injury. Both
V. paradoxa and
P. biglobosa have been reported to exhibit remarkable biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antioxidant effects, both in vitro and in vivo [
38,
39].
The observed gastroprotective effect may be linked to the presence of bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, tannins, and saponins, which are known for their antioxidant and cytoprotective properties [
128,
129,
130]. Flavonoids, in particular, are recognized as strengthening the gastric mucosal barrier, inhibiting acid secretion, and scavenging free radicals, thus helping to reduce ulcer formation [
129,
130,
131]. Tannins can precipitate proteins on the gastric lining, creating a protective layer that resists further irritation [
129,
130].
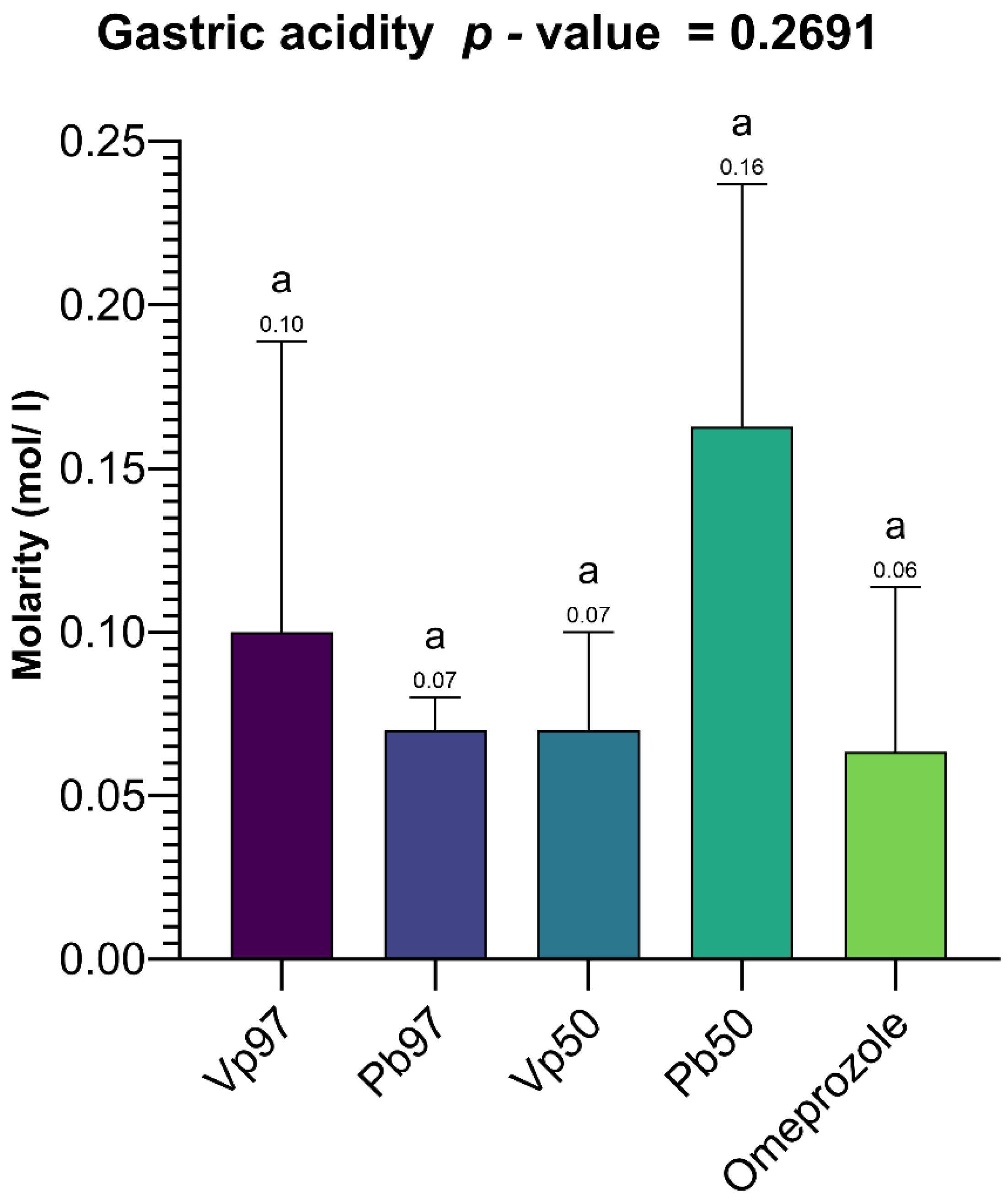
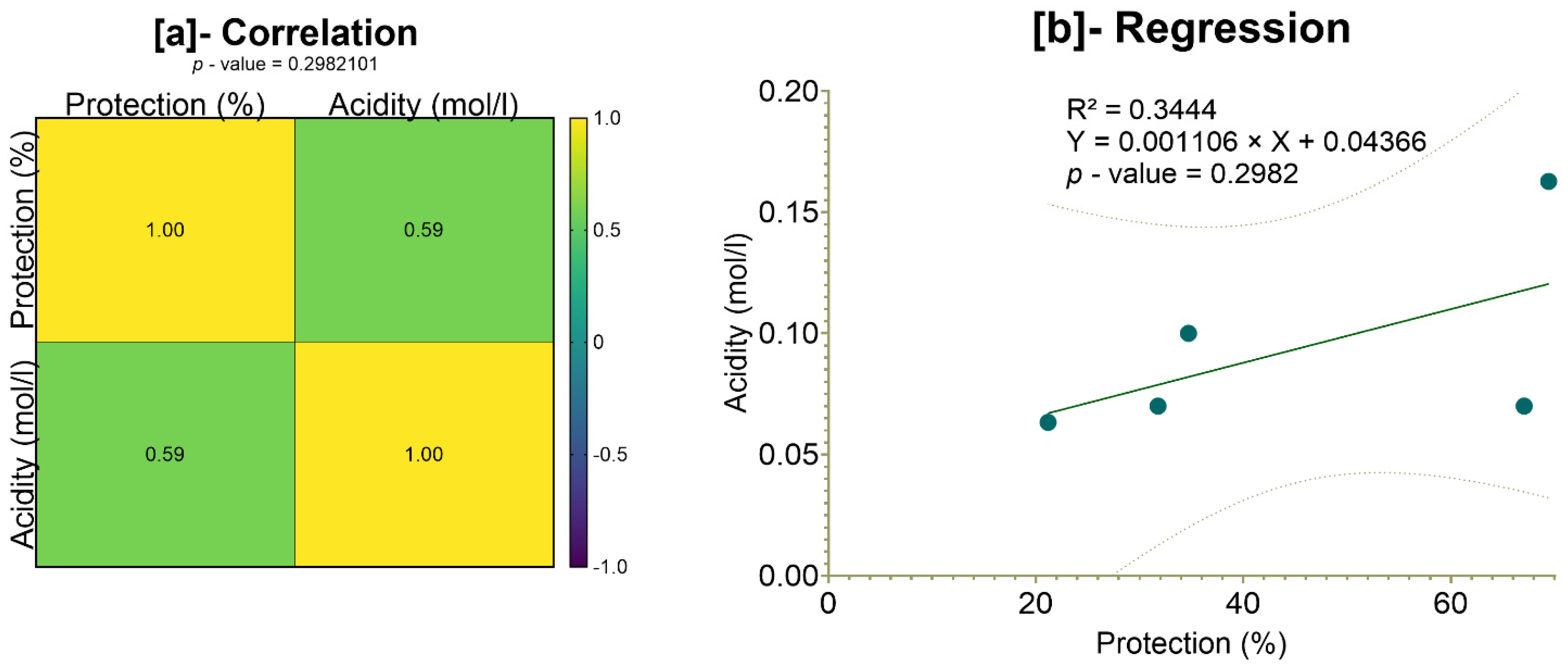
Although a moderate correlation (59%) was observed between total gastric acidity and the protection rate, the lack of statistical significance (
p = 0.2982 > 0.05) suggests that acidity alone does not fully explain the extracts’ protective effects. This indicates the involvement of multiple mechanisms, potentially including enhanced gastric mucus secretion, antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effects, Gastric H
+, K
+ ATPase inhibition, H
2-antagonism, increased prostaglandin synthesis, gastric mucosa protection, and a combined or unknown mechanism of action [
132], which warrants further investigation. Notably, the greater protection offered by the plant extracts compared to omeprazole highlights the potential of these natural compounds as effective alternatives or complementary agents in ulcer treatment. However, additional studies, including histopathological analyses, measurements of gastric mucus, and an assessment of inflammatory mediators, are needed to clarify the underlying mechanisms and establish their clinical relevance.