A High-Throughput Behavioral Assay for Screening Novel Anxiolytics in Larval Zebrafish
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Development of a Light-Dark Preference Assay in the 96-Well Format
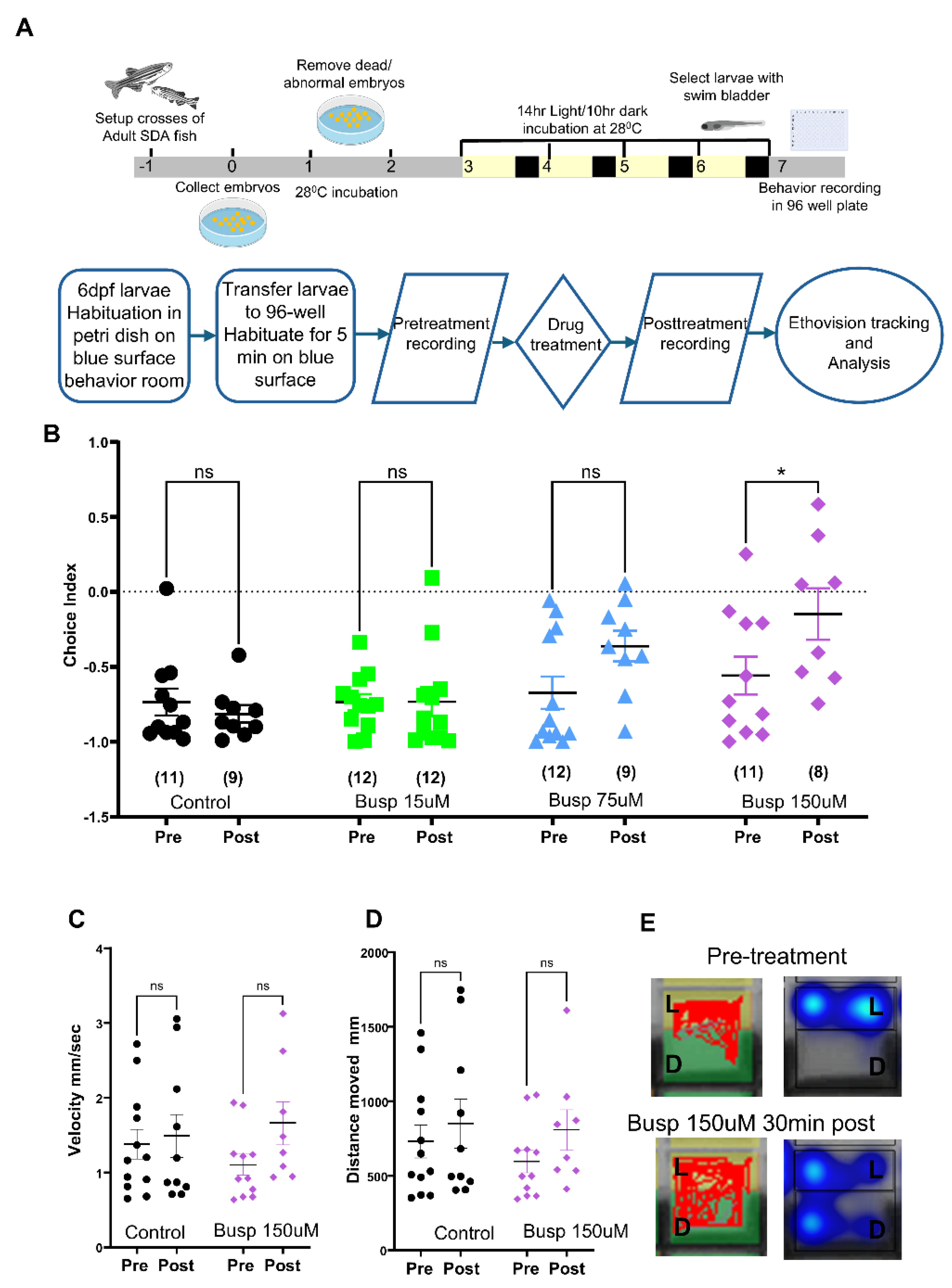
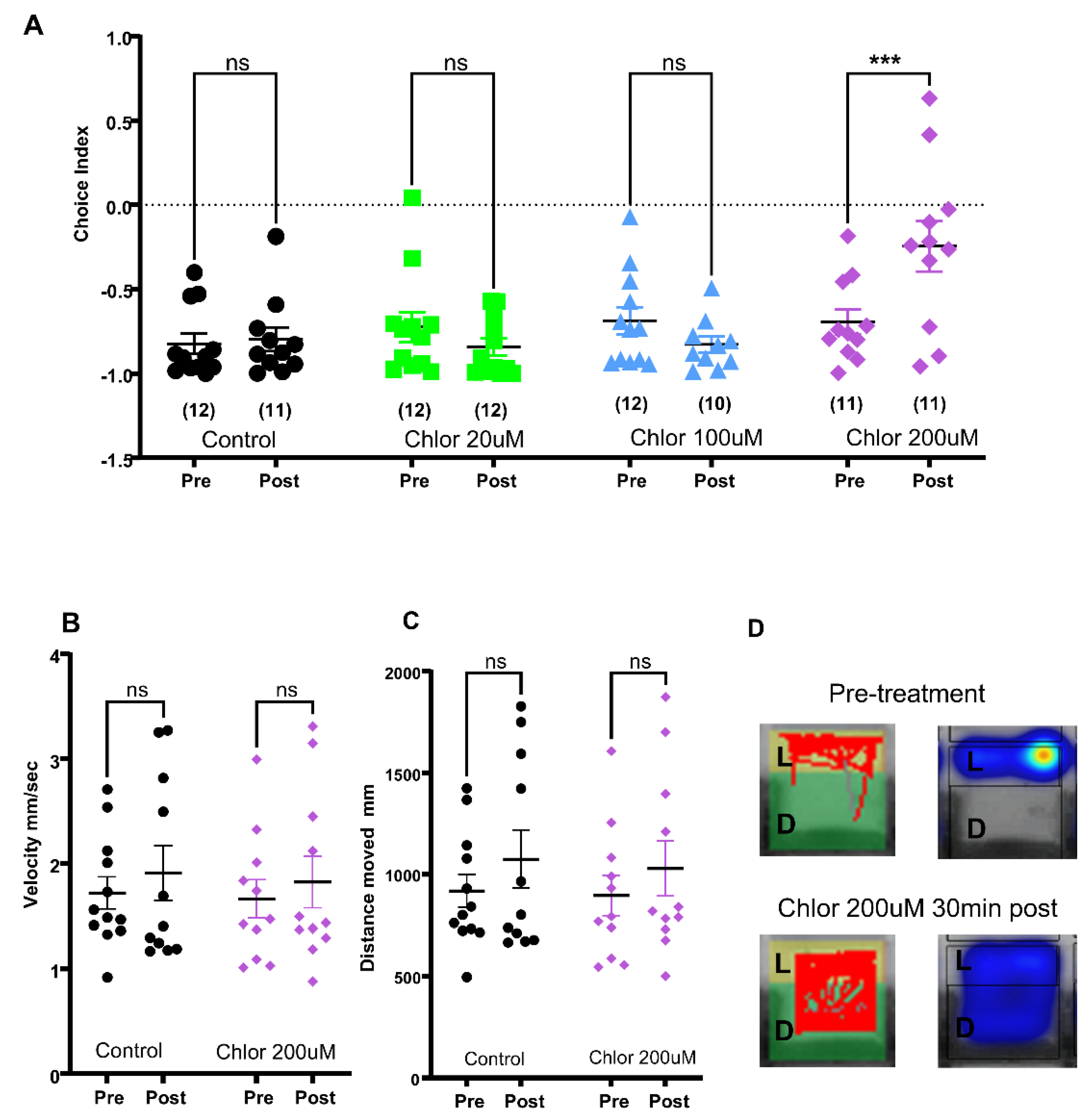
2.2. Effects of Known Anxiolytics in the 96-Well Light-Dark Preference Assay
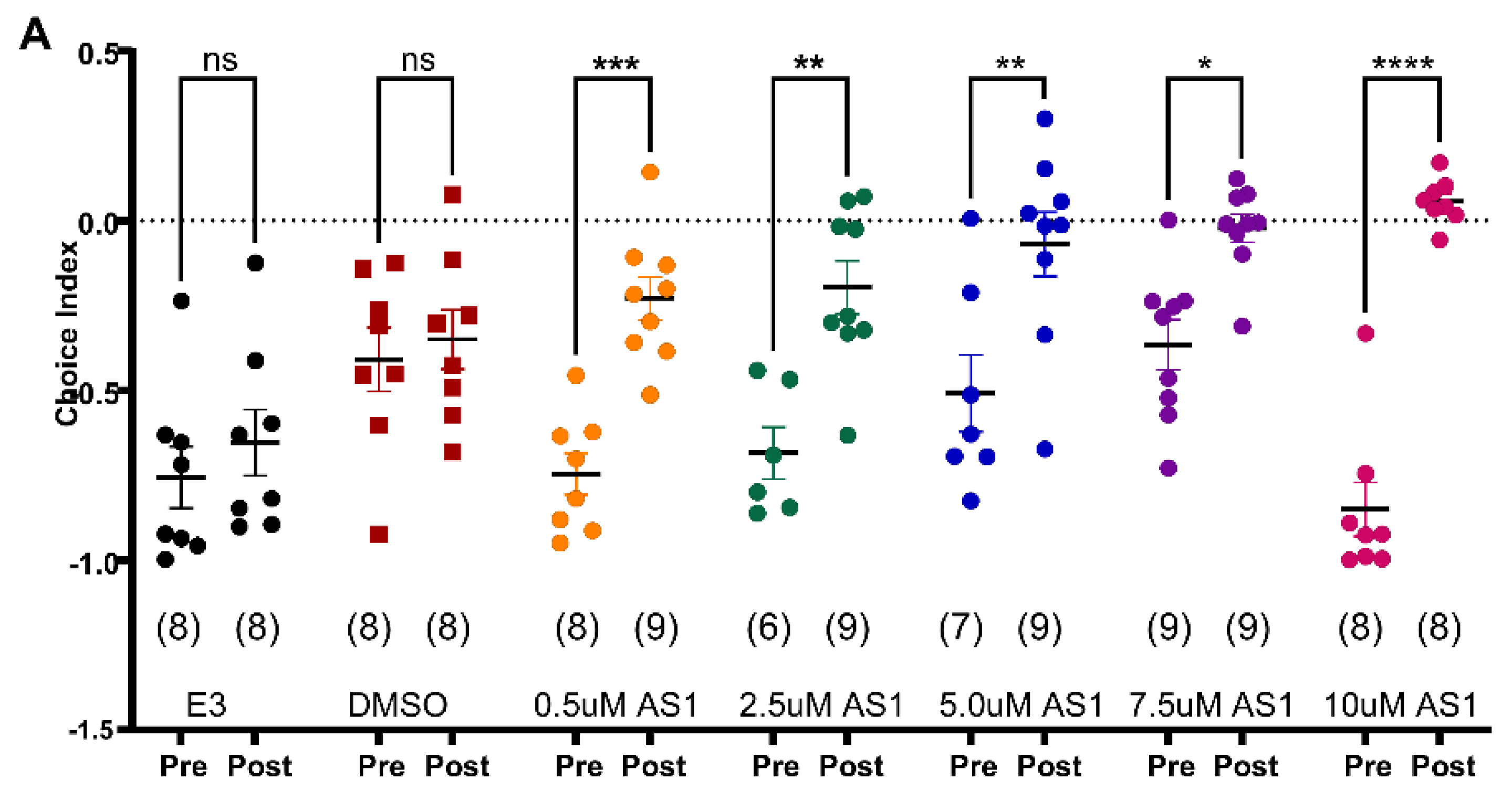
2.3. Discovery of a Novel Compound, AS1, for Its Anxiolytic Effects Using the 96-Well Light-Dark Preference Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Housing
4.2. High-Throughput Light/Dark Preference Assay Development
4.3. Drug Treatment
4.4. Behavioral Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SDA | Strong dark avoidance. |
| GAD | Generalized anxiety disorder |
| BZDs | Benzodiazepines |
| SSRIs | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors |
| SNRIs | Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors |
| 5-HT | 5-hydroxytryptamine, serotonin |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| CILD | Light/dark choice index |
References
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5TM, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013; pp. xliv, 947. ISBN 978-0-89042-554-1.
- Baldwin, D.S.; Anderson, I.M.; Nutt, D.J.; Allgulander, C.; Bandelow, B.; den Boer, J.A.; Christmas, D.M.; Davies, S.; Fineberg, N.; Lidbetter, N.; et al. Evidence-Based Pharmacological Treatment of Anxiety Disorders, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Revision of the 2005 Guidelines from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 28, 403–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griebel, G.; Holmes, A. 50 Years of Hurdles and Hope in Anxiolytic Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, U.; Knoflach, F. Beyond Classical Benzodiazepines: Novel Therapeutic Potential of GABAA Receptor Subtypes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)—Mayo Clinic. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/depression/in-depth/snris/art-20044970 (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Wilson, T.K.; Tripp, J. Buspirone. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Wheaton, M.; Murphy, D.L. What’s Wrong with My Mouse Model? Advances and Strategies in Animal Modeling of Anxiety and Depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 179, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Holmes, A. The Ascent of Mouse: Advances in Modelling Human Depression and Anxiety. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y. Recent Advances in Anxiety Disorders: Focus on Animal Models and Pathological Mechanisms. Anim. Model Exp. Med. 2023, 6, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Gebhardt, M.; Stewart, A.M.; Cachat, J.M.; Brimmer, M.; Chawla, J.S.; Craddock, C.; Kyzar, E.J.; Roth, A.; Landsman, S.; et al. Towards a Comprehensive Catalog of Zebrafish Behavior 1.0 and Beyond. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrinalini, R.; Tamilanban, T.; Naveen Kumar, V.; Manasa, K. Zebrafish—The Neurobehavioural Model in Trend. Neuroscience 2023, 520, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The Zebrafish Reference Genome Sequence and Its Relationship to the Human Genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Fang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Qu, L.; Yang, Q.; Wu, W.; Jin, L.; Sun, D. Advances in Zebrafish as a Comprehensive Model of Mental Disorders. Depress. Anxiety 2023, 2023, 6663141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.M.; Braubach, O.; Spitsbergen, J.; Gerlai, R.; Kalueff, A.V. Zebrafish Models for Translational Neuroscience Research: From Tank to Bedside. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, K.; Rt, P. Chemobehavioural Phenomics and Behaviour-Based Psychiatric Drug Discovery in the Zebrafish. Brief. Funct. Genom. Proteom. 2008, 7, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Wu, N.; Cachat, J.; Hart, P.; Gaikwad, S.; Wong, K.; Utterback, E.; Gilder, T.; Kyzar, E.; Newman, A.; et al. Pharmacological Modulation of Anxiety-like Phenotypes in Adult Zebrafish Behavioral Models. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacRae, C.A.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as Tools for Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRae, C.A.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as a Mainstream Model for In Vivo Systems Pharmacology and Toxicology. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.-K.; Krishnan, S.; Jesuthasan, S. Activation and Inhibition of Tph2 Serotonergic Neurons Operate in Tandem to Influence Larval Zebrafish Preference for Light over Darkness. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, M.; Zarei, M.; Lovett-Barron, M.; Poston, K.T.; Xu, J.; Ramey, V.; Pollard, K.S.; Prober, D.A.; Schulkin, J.; Deisseroth, K.; et al. Brain-Wide Perception of the Emotional Valence of Light Is Regulated by Distinct Hypothalamic Neurons. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 3777–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; Marques de Brito, T.; Dias, C.A.G.d.M.; Gouveia, A.; Morato, S. Scototaxis as Anxiety-like Behavior in Fish. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Peng, G. Effects of Lorazepam and WAY-200070 in Larval Zebrafish Light/Dark Choice Test. Neuropharmacology 2015, 95, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, B.; Wagle, M.; Guo, S. Identification of Environmental Stressors and Validation of Light Preference as a Measure of Anxiety in Larval Zebrafish. BMC Neurosci. 2016, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, M.; Nguyen, J.; Lee, S.; Zaitlen, N.; Guo, S. Heritable Natural Variation of an Anxiety-like Behavior in Larval Zebrafish. J. Neurogenet 2017, 31, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esancy, K.; Conceicao, L.L.; Curtright, A.; Tran, T.; Condon, L.; Lecamp, B.; Dhaka, A. A Novel Small Molecule, AS1, Reverses the Negative Hedonic Valence of Noxious Stimuli. BMC Biol. 2023, 21, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, A.S.; Cartwright, M.E.; Mahon, C.; Morrison, R.; Snyder, R.; McNamara, P.; Bradley, P.; Zhou, Y.-Y.; Hunter, J. Exploratory Drug Safety: A Discovery Strategy to Reduce Attrition in Development. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2009, 60, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.K.; Wang, Y.; Malany, S.; Deonarine, A.; Nguyen, K.; Vasile, S.; Choe, K.P. An Ultra High-Throughput, Whole-Animal Screen for Small Molecule Modulators of a Specific Genetic Pathway in Caenorhabditis Elegans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tsai, H.-J. Zebrafish, an In Vivo Platform to Screen Drugs and Proteins for Biomedical Use. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraban, S.C. A Zebrafish-Centric Approach to Antiepileptic Drug Development. Dis. Model Mech. 2021, 14, dmm049080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Casanave, R.; Chitre, A.S.; Wang, Q.; Nguyen, K.-M.; Blake, C.; Wagle, M.; Cheng, R.; Polesskaya, O.; Palmer, A.A.; et al. Causal Genetic Loci for a Motivated Behavior Spectrum Harbor Psychiatric Risk Genes. bioRxiv 2023, 2023, 2023.09.06.556529. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dang, A.; Zhao, G.; Xu, J.; Wagle, M.; Guo, S. A High-Throughput Behavioral Assay for Screening Novel Anxiolytics in Larval Zebrafish. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070968
Dang A, Zhao G, Xu J, Wagle M, Guo S. A High-Throughput Behavioral Assay for Screening Novel Anxiolytics in Larval Zebrafish. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070968
Chicago/Turabian StyleDang, Alice, Gina Zhao, Jiale Xu, Mahendra Wagle, and Su Guo. 2025. "A High-Throughput Behavioral Assay for Screening Novel Anxiolytics in Larval Zebrafish" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070968
APA StyleDang, A., Zhao, G., Xu, J., Wagle, M., & Guo, S. (2025). A High-Throughput Behavioral Assay for Screening Novel Anxiolytics in Larval Zebrafish. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070968






