Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacometabolomics in Precision Tramadol Prescribing for Enhanced Pain Management: Evidence from QBB and EMR Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Prescription Trends of Tramadol in Qatar
2.2. General Characteristics of Participants
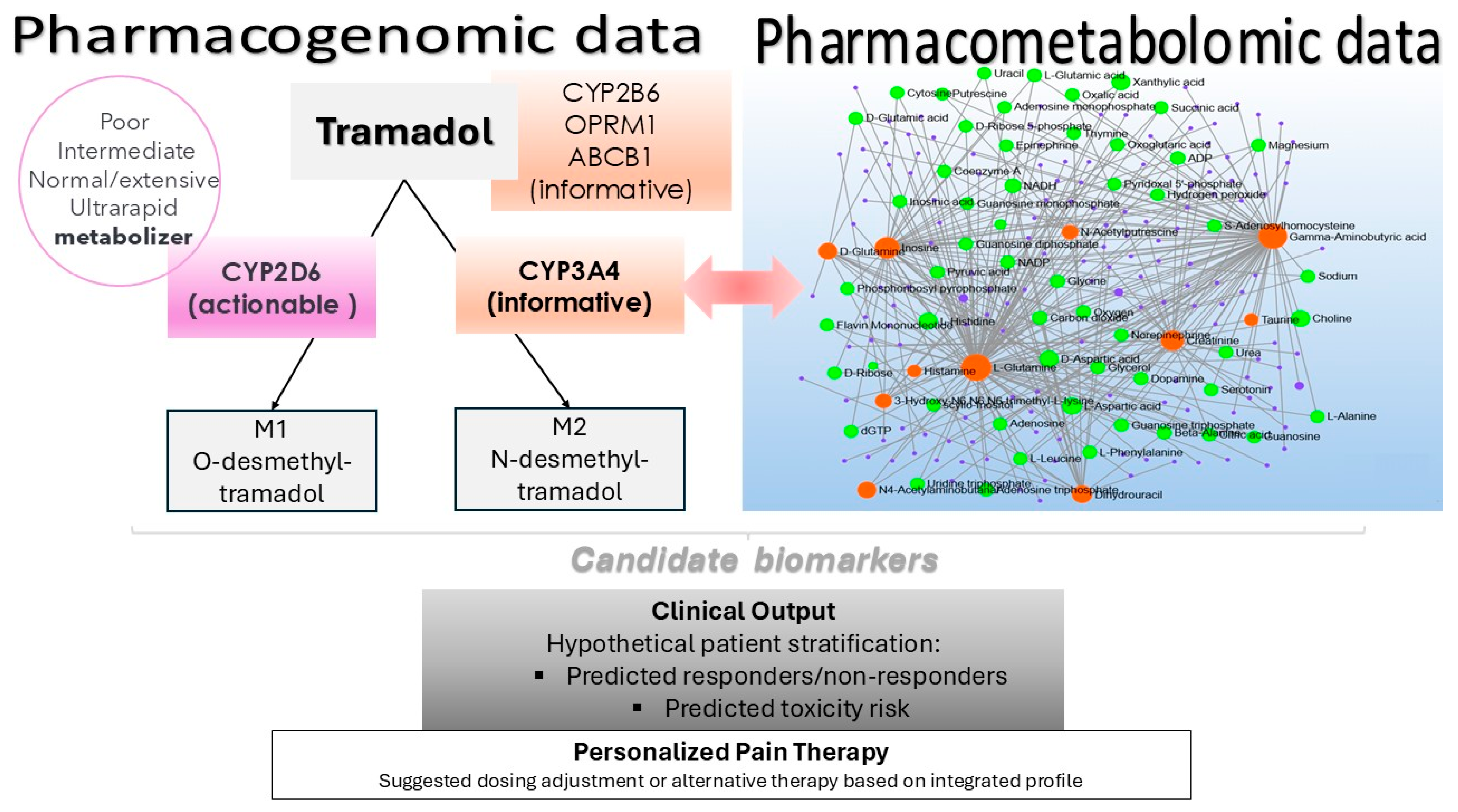
2.3. Pharmacogenomic Variation
2.4. Variability in Tramadol Metabolism: Correlation with CYP2D6 Activity and Metabolic Status
2.5. Multivariate Analysis of Differential Metabolites
2.6. Univariate Analysis of Differential Metabolites
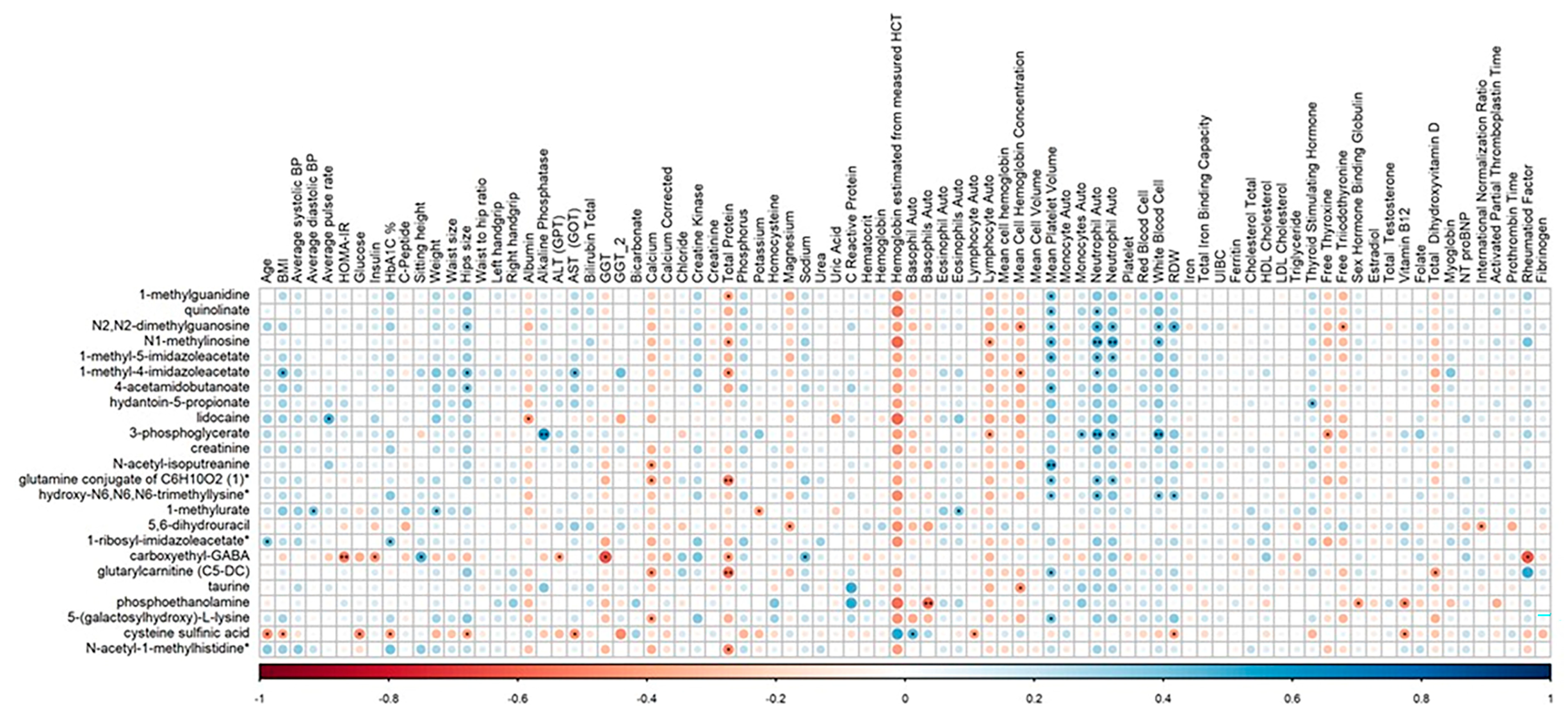
2.7. Correlation of Clinical Parameters with Identified Metabolites
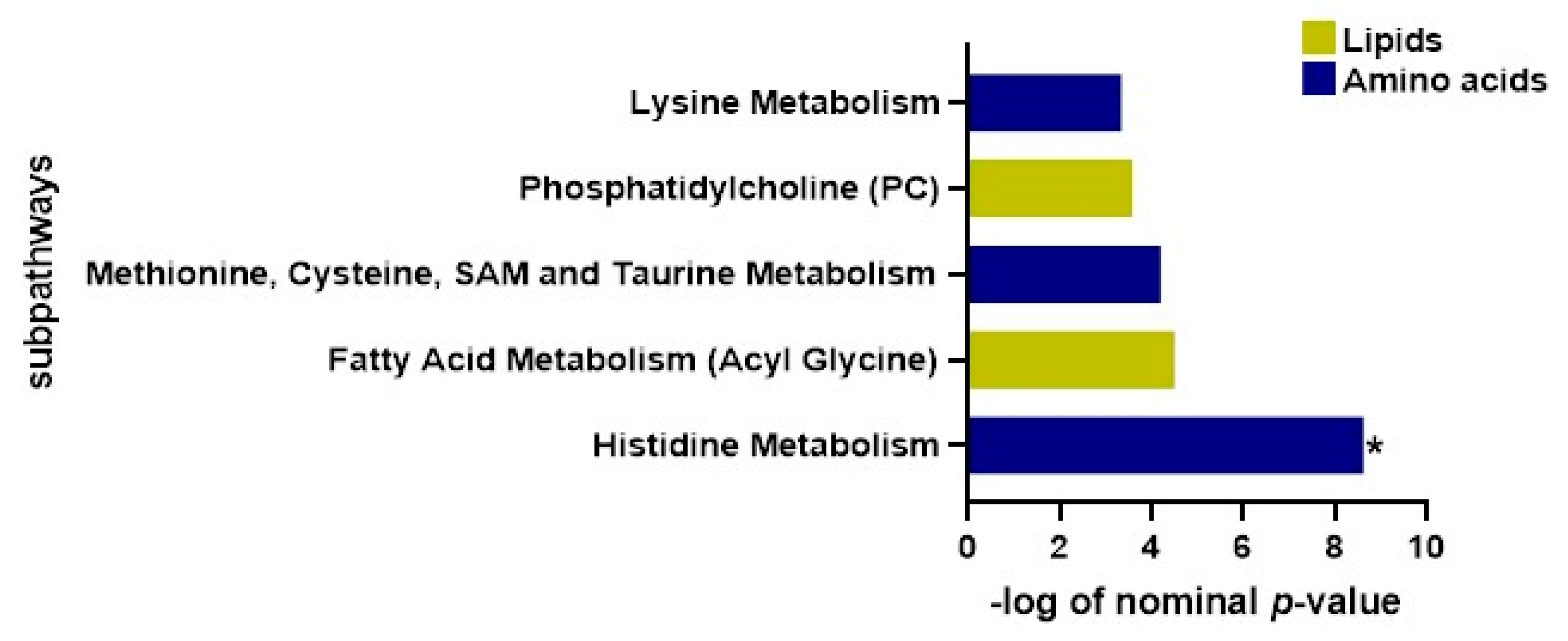
2.8. Functional Enrichment Investigation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source and Study Participants
4.2. Metabolomics
4.2.1. Metabolomics Measurements
4.2.2. Statistical Analysis
4.3. Genomics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QBB | Qatar Biobank |
| HMC | Hamad Medical Corporation |
| PGx | Pharmacogenomics |
| PMx | Pharmacometabolomics |
| EMR | Electronic medical records |
| PMs | Poor metabolizers |
| IMs | Intermediate metabolizers |
| NMs | Normal metabolizers |
| UMs | Ultra-rapid metabolizers |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyl transferase |
References
- Thiels, C.A.; Hanson, K.T.; Cima, R.R.; Habermann, E.B. From Data to Practice. Ann. Surg. 2018, 267, e46–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blendon, R.J.; Benson, J.M. The Public and the Opioid-Abuse Epidemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council of Economic Advisers Report: The Underestimated Cost of the Opioid Crisis. 20 November 2017. Available online: https://trumpwhitehouse.archives.gov/briefings-statements/cea-report-underestimated-cost-opioid-crisis/ (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Gaskin, D.J.; Richard, P. The economic costs of pain in the United States. J. Pain 2012, 13, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dydyk, A.M.; Conermann, T. Chronic Pain. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll, M.A.; Edwards, R.R.; Becker, W.C.; Kaptchuk, T.J.; Kerns, R.D. Psychological Interventions for the Treatment of Chronic Pain in Adults. Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 2021, 22, 52–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, B.L.; Langford, R.M.; Wodehouse, T. Arthritis and Pain. Current Approaches in the Treatment of Arthritic Pain. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2007, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauben, D.; Stacey, B.R. Pharmacologic Management of Chronic Non-Cancer Pain in Adults; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- US FDA Label Information for Tramadol. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/tramadol-information (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Edinoff, A.N.; Kaplan, L.A.; Khan, S.; Petersen, M.; Sauce, E.; Causey, C.D.; Cornett, E.M.; Imani, F.; Moradi Moghadam, O.; Kaye, A.M.; et al. Full Opioid Agonists and Tramadol: Pharmacological and Clinical Considerations. Anesthesiol. Pain Med. 2021, 11, e119156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, M.; Bajaj, S.; Kumar, M.S.; Yc, M. An Overview of Tramadol and Its Usage in Pain Management and Future Perspective. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestdagh, F.; Steyaert, A.; Lavand’homme, P. Cancer Pain Management: A Narrative Review of Current Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 6838–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayer, P.; Desmeules, J.; Collart, L. Pharmacologie Du Tramadol. Drugs 1997, 53, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grond, S.; Sablotzki, A. Clinical Pharmacology of Tramadol. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 879–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Stamer, U.M.; Tzvetkov, M.V.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB Summary. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2014, 24, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotto, K.; Cho, A.K.; Khalil, M.A.; Blanco, K.; Sasaki, J.D.; Rawson, R. Trends in Tramadol: Pharmacology, Metabolism, and Misuse. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 124, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrigan TM Schedules of Controlled Substances: Placement of Tramadol into Schedule IV. Available online: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2014/07/02/2014-15548/schedules-of-controlled-substances-placement-of-tramadol-into-schedule-iv (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Dunn, K.E.; Bergeria, C.L.; Huhn, A.S.; Strain, E.C. A Systematic Review of Laboratory Evidence for the Abuse Potential of Tramadol in Humans. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, J.; Barbosa, J.; Moreira, R.; Queirós, O.; Carvalho, F.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Comparative Pharmacology and Toxicology of Tramadol and Tapentadol. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadpour, A.; Ashkezari, M.; Farahmand, B.; Shokrzadeh, M. Demographic Characteristics and Functional Performance of the Kidneys and Hearts of Patients with Acute Tramadol Toxicity. Drug Res. 2019, 69, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stassinos, G.L.; Gonzales, L.; Klein-Schwartz, W. Characterizing the Toxicity and Dose-Effect Profile of Tramadol Ingestions in Children. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2019, 35, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarikoski, T.; Saari, T.I.; Hagelberg, N.M.; Backman, J.T.; Neuvonen, P.J.; Scheinin, M.; Olkkola, K.T.; Laine, K. Effects of Terbinafine and Itraconazole on the Pharmacokinetics of Orally Administered Tramadol. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paar, W.D.; Frankus, P.; Dengler, H.J. The Metabolism of Tramadol by Human Liver Microsomes. Clin. Investig. 1992, 70, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paar, W.D.; Poche, S.; Gerloff, J.; Dengler, H.J. Polymorphic CYP2D6 Mediates O-Demethylation of the Opioid Analgesic Tramadol. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 53, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyam, V.; Renwick, A.B.; Walters, D.G.; Young, P.J.; Price, R.J.; Tonelli, A.P.; Lake, B.G. Identification of Cytochrome P-450 Isoforms Responsible for Cis-Tramadol Metabolism in Human Liver Microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, R.R.; Burke, R.S. Tramadol: Basic Pharmacology and Emerging Concepts. Drugs Today 2008, 44, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiz-Rodríguez, M.; Ochoa, D.; Román, M.; Zubiaur, P.; Koller, D.; Mejía, G.; Abad-Santos, F. Involvement of CYP2D6 and CYP2B6 on Tramadol Pharmacokinetics. Pharmacogenomics 2020, 21, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Pharmacogene Variation (PharmVar) Consortium. CYP2D6 Allele Nomenclature. Available online: https://www.pharmvar.org/gene/CYP2D6 (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Gaedigk, A.; Simon, S.; Pearce, R.; Bradford, L.; Kennedy, M.; Leeder, J. The CYP2D6 Activity Score: Translating Genotype Information into a Qualitative Measure of Phenotype. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudle, K.E.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Freimuth, R.R.; Peterson, J.F.; Burlison, J.D.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Scott, S.A.; Rehm, H.L.; Williams, M.S.; Klein, T.E.; et al. Standardizing Terms for Clinical Pharmacogenetic Test Results: Consensus Terms from the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC). Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musshoff, F.; Stamer, U.M.; Madea, B. Pharmacogenetics and Forensic Toxicology. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 203, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 41st ECDD Meeting Geneva: WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence. Critical Review Report: Tramadol. Geneva, 12–16 November 2018. Available online: https://ecddrepository.org/sites/default/files/2023-04/tramadol.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- El-Hadidy, M.A.; Helaly, A.M.N. Medical and Psychiatric Effects of Long-Term Dependence on High Dose of Tramadol. Subst. Use Misuse 2015, 50, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaddes Ardabili, H.; Akbari, A.; Rafei, P.; Butner, J.; Khan, R.; Khazaal, Y.; Arab, A.Z.; Qazizada, M.R.; Al-Ansari, B.; Baldacchino, A.M. Tramadol, Captagon and Khat Use in the Eastern Mediterranean Region: Opening Pandora’s Box. BJPsych Int. 2022, 19, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). Regional Overview Asia and Oceania. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/Regional_Overview_Asia_and_Oceania.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Zhang, R.; Lin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhang, H.; Liao, M.; Peng, Y. MvMRL: A Multi-View Molecular Representation Learning Method for Molecular Property Prediction. Brief Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Teschendorff, A.E.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Genomic and Epigenomic Regulation Reveals MiRNA Mediated Tumor Heterogeneity and Immune Evasion in Lower Grade Glioma. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Weitzel, K.W.; Elsey, A.R.; Langaee, T.; Gong, Y.; Wake, D.T.; Duong, B.Q.; Hagen, M.; Harle, C.A.; Mercado, E.; et al. CYP2D6-Guided Opioid Therapy Improves Pain Control in CYP2D6 Intermediate and Poor Metabolizers: A Pragmatic Clinical Trial. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, C.R.; Zang, Y.; Desta, Z.; Rosenman, M.B.; Holmes, A.M.; Decker, B.S.; Zhang, Y.; Callaghan, J.T.; Pratt, V.M.; Levy, K.D.; et al. Drug–Gene and Drug–Drug Interactions Associated with Tramadol and Codeine Therapy in the INGENIOUS Trial. Pharmacogenomics 2019, 20, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallari, L.H.; Lee, C.R.; Beitelshees, A.L.; Cooper-DeHoff, R.M.; Duarte, J.D.; Voora, D.; Kimmel, S.E.; McDonough, C.W.; Gong, Y.; Dave, C.V.; et al. Multisite Investigation of Outcomes With Implementation of CYP2C19 Genotype-Guided Antiplatelet Therapy After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, K.R.; Gaedigk, A.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Leeder, J.S.; Klein, T.E.; Caudle, K.E.; Haidar, C.E.; Shen, D.D.; Callaghan, J.T.; Sadhasivam, S.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guidelines for Cytochrome P450 2D6 Genotype and Codeine Therapy: 2014 Update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 95, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorina-Lichtenwalter, K.; Meloto, C.B.; Khoury, S.; Diatchenko, L. Genetic Predictors of Human Chronic Pain Conditions. Neuroscience 2016, 338, 36–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, K.J.A.; Huckins, L.M. Chronic Pain and Psychiatric Conditions. Complex. Psychiatry 2023, 9, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassiony, M.M.; Abdelghani, M.; Salah El-Deen, G.M.; Hassan, M.S.; El-Gohari, H.; Youssef, U.M. Opioid Use Disorders Attributed to Tramadol Among Egyptian University Students. J. Addict. Med. 2018, 12, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashirian, S.; Barati, M.; Fathi, Y. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Tramadol Abuse Among College Students in West of Iran: An Application of the Theory of Planned Behavior. Avicenna J. Neuro Psycho Physiol. 2014, 1, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, H.; Shin, J.-Y. Explosive Increase in Tramadol Use in Korea 2003–2013: Analysis of Patient Trends Based on the Korea National Health Insurance Database. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2020, 52, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näkkäläjärvi, I.; Hakko, H.; Riala, K.; Riipinen, P. Substance Dependence and Hepatitis among Tramadol Prescription Users: A Study of Former Adolescent Psychiatric Inpatients in Northern Finland. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2020, 52, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. The Investigation of Tramadol Dependence with No History of Substance Abuse: A Cross-Sectional Survey of Spontaneously Reported Cases in Guangzhou City, China. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 283425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J. Examining the Use of Tramadol Hydrochloride as an Antidepressant. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 19, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyn-St James, M.; Cooper, K.; Kaltenthaler, E.; Dickinson, K.; Cantrell, A.; Wylie, K.; Frodsham, L.; Hood, C. Tramadol for Premature Ejaculation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, M.; Mustafa, M. Tramadol-Induced Mood Elevation in a Patient with No Previous Psychiatric History. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2018, 2018, 9574395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, K.; Chawla, P.; Singh, S. Neurobehavioral Consequences Associated with Long Term Tramadol Utilization and Pathological Mechanisms. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 18, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arve, K.; Johnson, B. Drug Use Trajectories among Young People with Experiences of Problematic Tramadol Use. Drugs Educ. Prev. Policy 2023, 31, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Obata, H.; Saito, S. Antihypersensitivity Effects of Tramadol Hydrochloride in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 115, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.M.; Mahmoud, A.M. Chronic Exposure to the Opioid Tramadol Induces Oxidative Damage, Inflammation and Apoptosis, and Alters Cerebral Monoamine Neurotransmitters in Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, N.M.; Isbister, G.K. Tramadol Overdose Causes Seizures and Respiratory Depression but Serotonin Toxicity Appears Unlikely. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubhakaran, K.; Khichar, R. Tramadol Side Effects: Seizure and Hypoglycemia. Anesth. Essays Res. 2016, 10, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makunts, T.; U, A.; Atayee, R.S.; Abagyan, R. Retrospective Analysis Reveals Significant Association of Hypoglycemia with Tramadol and Methadone in Contrast to Other Opioids. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-W.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.-H.; Fu, S.-K.; Li, Q.; Lin, F.-Q. Neuronal Apoptosis in Morphine Addiction and Its Molecular Mechanism. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 6, 540–545. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, T.M.; Ghaffar, H.M.A.; El Husseiny, R.M. Effects of Tramadol, Clonazepam, and Their Combination on Brain Mitochondrial Complexes. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2015, 31, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.-Q.; Huang, L.; Huang, H.-Q.; Cai, Z. Effects of Chronic Tramadol Exposure on the Zebrafish Brain: A Proteomic Study. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 3351–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Liu, G.; Shao, Z.; Xu, E.; Yuan, H.; Liu, J.; Gao, L. Toxicology of Tramadol Following Chronic Exposure Based on Metabolomics of the Cerebrum in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, G.; Yuan, H.; Xu, E.; Xia, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Gao, L. Changes on Proteomic and Metabolomic Profile in Serum of Mice Induced by Chronic Exposure to Tramadol. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhn, S.; Amin, N.S.; Bardolia, C.; Del Toro-Pagán, N.; Pizzolato, K.; Thacker, D.; Turgeon, J.; Tomaino, C.; Michaud, V. Pharmacogenomics and Drug-Induced Phenoconversion Informed Medication Safety Review in the Management of Pain Control and Quality of Life: A Case Report. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, L.; Kane, M. Tramadol Therapy and CYP2D6 Genotype. In Medical Genetics Summaries [Internet]; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, S.; Polasek, T.M.; Sheffield, L.J.; Huppert, D.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.J. Quantifying the Impact of Phenoconversion on Medications With Actionable Pharmacogenomic Guideline Recommendations in an Acute Aged Persons Mental Health Setting. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 724170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klomp, S.D.; Manson, M.L.; Guchelaar, H.-J.; Swen, J.J. Phenoconversion of Cytochrome P450 Metabolism: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.R.; Smith, R.L. Addressing Phenoconversion: The Achilles’ Heel of Personalized Medicine. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 79, 222–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicali, E.J.; Elchynski, A.L.; Cook, K.J.; Houder, J.T.; Thomas, C.D.; Smith, D.M.; Elsey, A.; Johnson, J.A.; Cavallari, L.H.; Wiisanen, K. How to Integrate CYP2D6 Phenoconversion into Clinical Pharmacogenetics: A Tutorial. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheweita, S.A.; Almasmari, A.A.; El-Banna, S.G. Tramadol-Induced Hepato- and Nephrotoxicity in Rats: Role of Curcumin and Gallic Acid as Antioxidants. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, A.; Lan, J.; Ren, L.; Wei, Y.; Gao, L. Protective Mechanism of 1-Methylhydantoin against Lung Injury Induced by Paraquat Poisoning. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffa, R.B.; Friderichs, E.; Reimann, W.; Shank, R.P.; Codd, E.E.; Vaught, J.L. Opioid and Nonopioid Components Independently Contribute to the Mechanism of Action of Tramadol, an “atypical” Opioid Analgesic. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992, 260, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, H.L.; Sergeeva, O.A.; Selbach, O. Histamine in the Nervous System. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1183–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, S. Choline, Other Methyl-Donors and Epigenetics. Nutrients 2017, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestler, E.J. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Drug Addiction. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Oliveira, T.; Rego, A.C.; Oliveira, C.R. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Involved in the Neurotoxicity of Opioid and Psychostimulant Drugs. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 58, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.; Qiu, H.; Aleksic, M.; Glinka, Y.; Zhao, F.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Chakrabarti, R.; Ng, T.; et al. GABA Exerts Protective and Regenerative Effects on Islet Beta Cells and Reverses Diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11692–11697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandwitz, P. Neurotransmitter Modulation by the Gut Microbiota. Brain Res. 2018, 1693, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Nutt, D.J. Role of GABA in Anxiety and Depression. Depress. Anxiety 2007, 24, 495–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W.; Darlington, L.G. Endogenous Kynurenines as Targets for Drug Discovery and Development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Thani, A.; Fthenou, E.; Paparrodopoulos, S.; Al Marri, A.; Shi, Z.; Qafoud, F.; Afifi, N. Qatar Biobank Cohort Study: Study Design and First Results. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 1420–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhre, K.; Stephan, N.; Zaghlool, S.; Triggle, C.R.; Robinson, R.J.; Evans, A.M.; Halama, A. Matching Drug Metabolites from Non-Targeted Metabolomics to Self-Reported Medication in the Qatar Biobank Study. Metabolites 2022, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jithesh, P.V.; Abuhaliqa, M.; Syed, N.; Ahmed, I.; El Anbari, M.; Bastaki, K.; Sherif, S.; Umlai, U.-K.; Jan, Z.; Gandhi, G.; et al. A Population Study of Clinically Actionable Genetic Variation Affecting Drug Response from the Middle East. NPJ Genom. Med. 2022, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thareja, G.; Al-Sarraj, Y.; Belkadi, A.; Almotawa, M.; Ismail, S.; Al-Muftah, W.; Badji, R.; Mbarek, H.; Darwish, D.; Fadl, T.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing in the Middle Eastern Qatari Population Identifies Genetic Associations with 45 Clinically Relevant Traits. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Tramadol (−) | Tramadol (+) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 54 | 27 | |
| Diabetes status | 0.482 | ||
| Yes | 8 (14.81%) | 2 (7.41%) | |
| No | 46 (85.19%) | 25 (92.59%) | |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 18 (33.33%) | 10 (37.04%) | 0.934 |
| Female | 36 (66.67%) | 17 (62.96%) | |
| Age | 41.259 (12.407) | 39 (13.89) | 0.478 |
| BMI | 29.376 (5.563) | 28.227 (5.819) | 0.399 |
| Average systolic BP | 112.87 (14.721) | 112.704 (12.892) | 0.958 |
| Average diastolic BP | 74.963 (11.535) | 73.148 (8.47) | 0.425 |
| Average pulse rate | 70.574 (10.785) | 72.593 (10.778) | 0.431 |
| Homa | 2.445 (1.528–5.138) | 2.08 (1.455–6.13) | 0.845 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.1 (4.6–5.6) | 5.1 (4.935–5.5) | 0.821 |
| Insulin (μU/mL) | 11.25 (7.1–17) | 10 (6.6–25.55) | 0.837 |
| HBA 1C | 5.5 (5.3–5.8) | 5.4 (5–5.6) | 0.130 |
| C Peptide (ng/mL) | 2.68 (1.912–3.808) | 2.61 (1.67–3.607) | 0.731 |
| Sitting height | 127.2 (86.1–135.8) | 87.3 (84.95–110.3) | 0.052 |
| Weight | 78.048 (16.846) | 74.089 (16.678) | 0.320 |
| Waist size | 89.019 (14.423) | 86.333 (16.117) | 0.468 |
| Hip size | 108.13 (9.695) | 104.259 (11.651) | 0.144 |
| Waist to hip ratio | 0.822 (0.102) | 0.825 (0.102) | 0.903 |
| Left handgrip | 23 (20–34) | 24 (20–35) | 0.876 |
| Right handgrip | 30.204 (11.21) | 31.231 (10.558) | 0.691 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 44.907 (2.87) | 44.963 (2.361) | 0.926 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 66 (54.5–82.25) | 63 (55.5–82.5) | 0.992 |
| ALT (GPT) (U/L) | 18 (13–27.5) | 18 (13.5–21.5) | 0.688 |
| AST GOT (U/L) | 17 (15–20.75) | 18 (13.5–21) | 0.718 |
| Bilirubin total (μmol/L) | 6 (4.85–8.25) | 6 (4.95–7.25) | 0.963 |
| GGT (U/L) | 21 (13–30.5) | 13.5 (12–24) | 0.197 |
| GGT-2 (U/L) | 19 (14–30) | 24 (14–37) | 0.663 |
| Bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 26.093 (2.113) | 26.741 (1.953) | 0.176 |
| Calcium (mmol/L) | 2.36 (2.292–2.42) | 2.41 (2.34–2.43) | 0.091 |
| Calcium corrected (mmol/L) | 2.26 (2.2–2.31) | 2.3 (2.25–2.325) | 0.083 |
| Chloride (mmol/L) | 101.389 (2.422) | 101.185 (2.512) | 0.729 |
| Creatine kinase (μ/L) | 75 (56–118) | 83.5 (45–130.25) | 0.814 |
| Creatine kinase_1 (ng/mL) | 1.15 (0.76–1.73) | 1.43 (1.15–1.71) | 0.927 |
| Creatine kinase_2 (U/L) | 69 (55–83.5) | 64.5 (63.75–65.25) | 0.884 |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 64.796 (13.273) | 67.556 (14.148) | 0.402 |
| Total protein (g/L) | 72.889 (3.694) | 73.593 (3.238) | 0.383 |
| Phosphorus (mmol/L) | 1.104 (0.165) | 1.108 (0.177) | 0.914 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.369 (0.367) | 4.333 (0.385) | 0.696 |
| Homocysteine (μmol/L) | 8.5 (7.025–9.475) | 7.8 (6.55–8.675) | 0.079 |
| Magnesium (mmol/L) | 0.834 (0.055) | 0.834 (0.064) | 0.969 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 140 (139–141) | 140 (139–141.5) | 0.819 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 4.25 (3.5–4.825) | 3.7 (3.35–4.7) | 0.637 |
| Uric acid (μmol/L) | 297.407 (73.841) | 285.407 (93.336) | 0.563 |
| C reactive protein (mg/L) | 5 (5–5.25) | 5 (5–8) | 0.200 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 40.207 (4.622) | 40.456 (4.243) | 0.811 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.2 (1.689) | 13.374 (1.593) | 0.653 |
| Hemoglobin estimated from measured HCT | 17.148 (3.509) | 16.478 (3.391) | 0.595 |
| Basophil auto (%) | 0.7 (0.5–0.8) | 0.7 (0.45–0.8) | 0.818 |
| Basophils auto (×103 μL) | 0 (0–0.1) | 0 (0–0.06) | 0.407 |
| Eosinophil auto (%) | 2.5 (1.425–3.875) | 3.2 (1.85–4.2) | 0.205 |
| Eosinophils auto (×103 μL) | 0.15 (0.1–0.275) | 0.2 (0.1–0.3) | 0.404 |
| Lymphocyte auto (×103 μL) | 2 (1.9–2.475) | 2.2 (1.7–2.6) | 0.928 |
| Lymphocyte auto (%) | 34.183 (7.02) | 37.078 (10.802) | 0.214 |
| Mean cell hemoglobin (pg) | 27.5 (25.625–29.2) | 27.9 (26.4–29.15) | 0.458 |
| Mean cell hemoglobin concentration (g/dL) | 32.88 (0.965) | 33.052 (1.171) | 0.513 |
| Mean cell volume (fl) | 83.25 (78.35–87.8) | 84.7 (80.4–87.6) | 0.558 |
| Mean platelet volume (fl) | 9.104 (1.074) | 9.481 (1.037) | 0.133 |
| Monocyte auto (%) | 7.15 (5.6–8.775) | 7.6 (6.5–9.8) | 0.290 |
| Monocytes auto (×103 μL) | 0.45 (0.4–0.5) | 0.4 (0.4–0.6) | 0.984 |
| Neutrophil auto (×103 μL) | 3.6 (3–4.3) | 3 (2.3–3.65) | 0.060 |
| Neutrophil auto (%) | 55.067 (8.329) | 51.052 (10.87) | 0.099 |
| Platelet (×103 uL) | 247.868 (48.249) | 243.889 (71.005) | 0.795 |
| Red blood cell (×106 μL) | 4.907 (0.611) | 4.848 (0.454) | 0.625 |
| White blood cell (×103 μL) | 6.4 (5.525–7.5) | 5.7 (5.2–6.55) | 0.096 |
| RDW | 13.9 (13.325–15.275) | 13.9 (13.25–14.75) | 0.616 |
| Iron (μmol/L) | 15.449 (5.896) | 15.124 (5.72) | 0.812 |
| Total iron binding capacity (μmol/L) | 59.5 (54–63.75) | 57 (55–62) | 0.710 |
| UIBC (μmol/L) | 43 (35.15–50) | 41.2 (36.6–50.1) | 0.924 |
| Ferritin (μg/L) | 39.5 (18.5–103.5) | 29 (12–96) | 0.620 |
| Cholesterol total (mmol/L) | 4.966 (0.922) | 4.949 (1.061) | 0.943 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) | 1.195 (1.062–1.485) | 1.33 (1.08–1.585) | 0.455 |
| LDL cholesterol calc (mmol/L) | 2.998 (0.838) | 2.979 (0.934) | 0.932 |
| Triglyceride (mmol/L) | 1.22 (0.957–1.895) | 1.06 (0.705–1.85) | 0.198 |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone (mIU/L) | 1.42 (0.952–2.175) | 1.36 (1.05–2.125) | 0.900 |
| Free thyroxine (pmol/L) | 12.7 (12.125–14.687) | 12.76 (11.555–14.845) | 0.768 |
| Free triiodothyronine (pmol/L) | 4.421 (0.629) | 4.298 (0.566) | 0.394 |
| Sex hormone binding globulin (nmol/L) | 44.95 (32.65–60.75) | 41.1 (32.25–56.5) | 0.544 |
| Estradiol (pmol/L) | 127 (76–318) | 112.5 (68.25–356.75) | 0.929 |
| Testosterone total (nmol/L) | 1.54 (0.88–10.91) | 1.71 (0.863–11.835) | 0.900 |
| Vitamin B12 (pmol/L) | 253.5 (194.5–314.5) | 277 (223–342.5) | 0.213 |
| Folate (nmol/L) | 25.05 (19.225–29.95) | 25.35 (22.325–30.625) | 0.583 |
| Dihydroxyvitamin D total (ng/mL) | 17.5 (13–24) | 16 (12–21) | 0.648 |
| Myoglobin (ng/mL) | 21 (21–21.75) | 21 (20–25) | 0.937 |
| NT proBNP (pg mL) | 27 (12.86–43.25) | 21.3 (10–37.65) | 0.376 |
| International normalization ratio | 1 (1–1.1) | 1.1 (1–1.1) | 0.040 |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time (seconds) | 33.8 (32–36.175) | 34.7 (32.85–36.85) | 0.247 |
| Prothrombin time PT (seconds) | 11.05 (10.625–11.875) | 11.8 (10.9–12.7) | 0.032 |
| Rheumatoid factor (IU/mL) | 10 (9.825–10) | 10.35 (9.875–11.1) | 0.280 |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | 3.17 (2.725–3.7) | 3.1 (2.885–3.55) | 0.984 |
| Metabolite | Superpathway | Subpathway | Estimate | SE | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-methylguanidine | Amino Acid | Guanidino and Acetamido Metabolism | 1.752 | 0.221 | 5.10 × 10−11 | 4.16 × 10−8 |
| quinolinate | Cofactors and Vitamins | Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism | 1.268 | 0.178 | 5.80 × 10−10 | 2.15 × 10−7 |
| N2,N2-dimethylguanosine | Nucleotide | Purine Metabolism, Guanine Containing | 1.266 | 0.179 | 7.91 × 10−10 | 2.15 × 10−7 |
| N1-methylinosine | Nucleotide | Purine Metabolism, (Hypo)Xanthine/Inosine Containing | 1.247 | 0.192 | 9.06 × 10−9 | 1.85 × 10−6 |
| 1-methyl-5-imidazoleacetate | Amino Acid | Histidine Metabolism | 1.326 | 0.207 | 1.30 × 10−8 | 2.12 × 10−6 |
| 1-methyl-4-imidazoleacetate | Amino Acid | Histidine Metabolism | 1.008 | 0.174 | 1.52 × 10−7 | 2.07 × 10−5 |
| 4-acetamidobutanoate | Amino Acid | Polyamine Metabolism | 1.138 | 0.203 | 3.56 × 10−7 | 3.76 × 10−5 |
| hydantoin-5-propionate | Amino Acid | Histidine Metabolism | 1.384 | 0.238 | 3.68 × 10−7 | 3.76 × 10−5 |
| 3-phosphoglycerate | Carbohydrate | Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, and Pyruvate Metabolism | 1.030 | 0.198 | 1.83 × 10−6 | 1.50 × 10−4 |
| creatinine | Amino Acid | Creatine Metabolism | 0.836 | 0.173 | 6.79 × 10−6 | 5.04 × 10−4 |
| N-acetyl-isoputreanine | Amino Acid | Polyamine Metabolism | 0.934 | 0.197 | 1.03 × 10−5 | 6.97 × 10−4 |
| glutamine conjugate of C6H10O2 (1)* | Partially Characterized Molecules | Partially Characterized Molecules | 0.882 | 0.186 | 1.28 × 10−5 | 8.02 × 10−4 |
| hydroxy-N6,N6,N6-trimethyllysine* | Amino Acid | Lysine Metabolism | 0.741 | 0.167 | 3.21 × 10−5 | 1.87 × 10−3 |
| 1-methylurate | Xenobiotics | Xanthine Metabolism | 0.902 | 0.205 | 3.73 × 10−5 | 2.03 × 10−3 |
| 5,6-dihydrouracil | Nucleotide | Pyrimidine Metabolism, Uracil Containing | −0.974 | 0.243 | 1.76 × 10−4 | 8.65 × 10−3 |
| 1-ribosyl-imidazoleacetate* | Amino Acid | Histidine Metabolism | 0.675 | 0.171 | 1.80 × 10−4 | 8.65 × 10−3 |
| carboxyethyl-GABA | Amino Acid | Glutamate Metabolism | 0.843 | 0.226 | 3.77 × 10−4 | 1.71 × 10−2 |
| glutarylcarnitine (C5-DC) | Amino Acid | Lysine Metabolism | 0.789 | 0.212 | 4.45 × 10−4 | 1.91 × 10−2 |
| taurine | Amino Acid | Methionine, Cysteine, SAM and Taurine Metabolism | 0.775 | 0.223 | 8.57 × 10−4 | 3.50 × 10−2 |
| phosphoethanolamine | Lipid | Phospholipid Metabolism | 0.736 | 0.216 | 1.06 × 10−3 | 4.14 × 10−2 |
| 5-(galactosylhydroxy)-L-lysine | Amino Acid | Lysine Metabolism | 0.788 | 0.235 | 1.27 × 10−3 | 4.57 × 10−2 |
| cysteine sulfinic acid | Amino Acid | Methionine, Cysteine, SAM and Taurine Metabolism | 0.751 | 0.223 | 1.29 × 10−3 | 4.57 × 10−2 |
| N-acetyl-1-methylhistidine* | Amino Acid | Histidine Metabolism | 0.590 | 0.178 | 1.43 × 10−3 | 4.88 × 10−2 |
| Subpathways | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|
| Histidine Metabolism | 0.000178 | 0.018 |
| Fatty Acid Metabolism (Acyl Glycine) | 0.011 | 0.499 |
| Methionine, Cysteine, SAM and Taurine Metabolism | 0.015 | 0.499 |
| Phosphatidylcholine (PC) | 0.028 | 0.692 |
| Lysine Metabolism | 0.035 | 0.700 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhieb, D.; Anwardeen, N.; Velayutham, D.; Elrayess, M.A.; Jithesh, P.V.; Bastaki, K. Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacometabolomics in Precision Tramadol Prescribing for Enhanced Pain Management: Evidence from QBB and EMR Data. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070971
Dhieb D, Anwardeen N, Velayutham D, Elrayess MA, Jithesh PV, Bastaki K. Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacometabolomics in Precision Tramadol Prescribing for Enhanced Pain Management: Evidence from QBB and EMR Data. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070971
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhieb, Dhoha, Najeha Anwardeen, Dinesh Velayutham, Mohamed A. Elrayess, Puthen Veettil Jithesh, and Kholoud Bastaki. 2025. "Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacometabolomics in Precision Tramadol Prescribing for Enhanced Pain Management: Evidence from QBB and EMR Data" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070971
APA StyleDhieb, D., Anwardeen, N., Velayutham, D., Elrayess, M. A., Jithesh, P. V., & Bastaki, K. (2025). Pharmacogenomics and Pharmacometabolomics in Precision Tramadol Prescribing for Enhanced Pain Management: Evidence from QBB and EMR Data. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18070971






