Purine–Hydrazone Scaffolds as Potential Dual EGFR/HER2 Inhibitors
Abstract
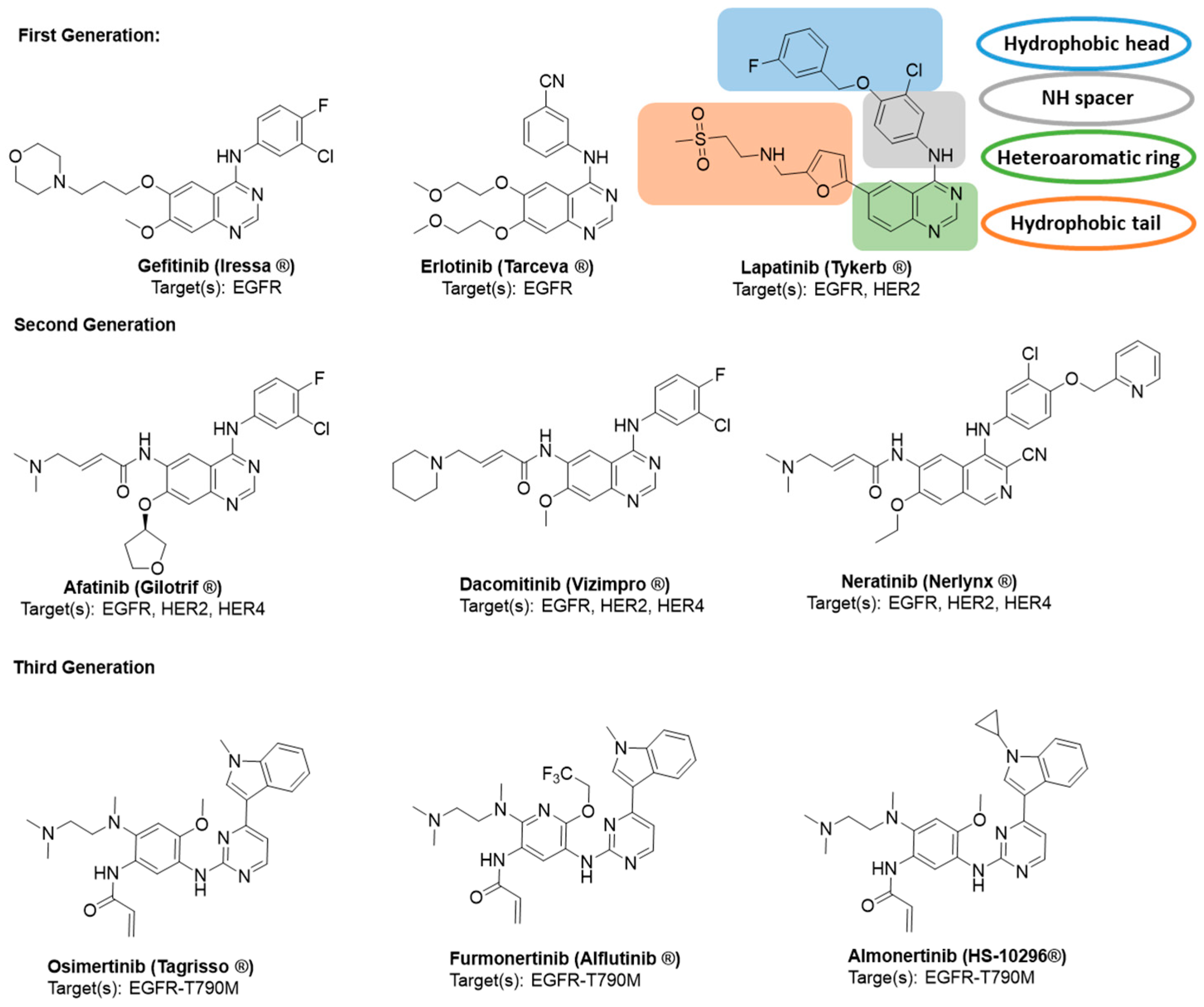
1. Introduction
2. Results
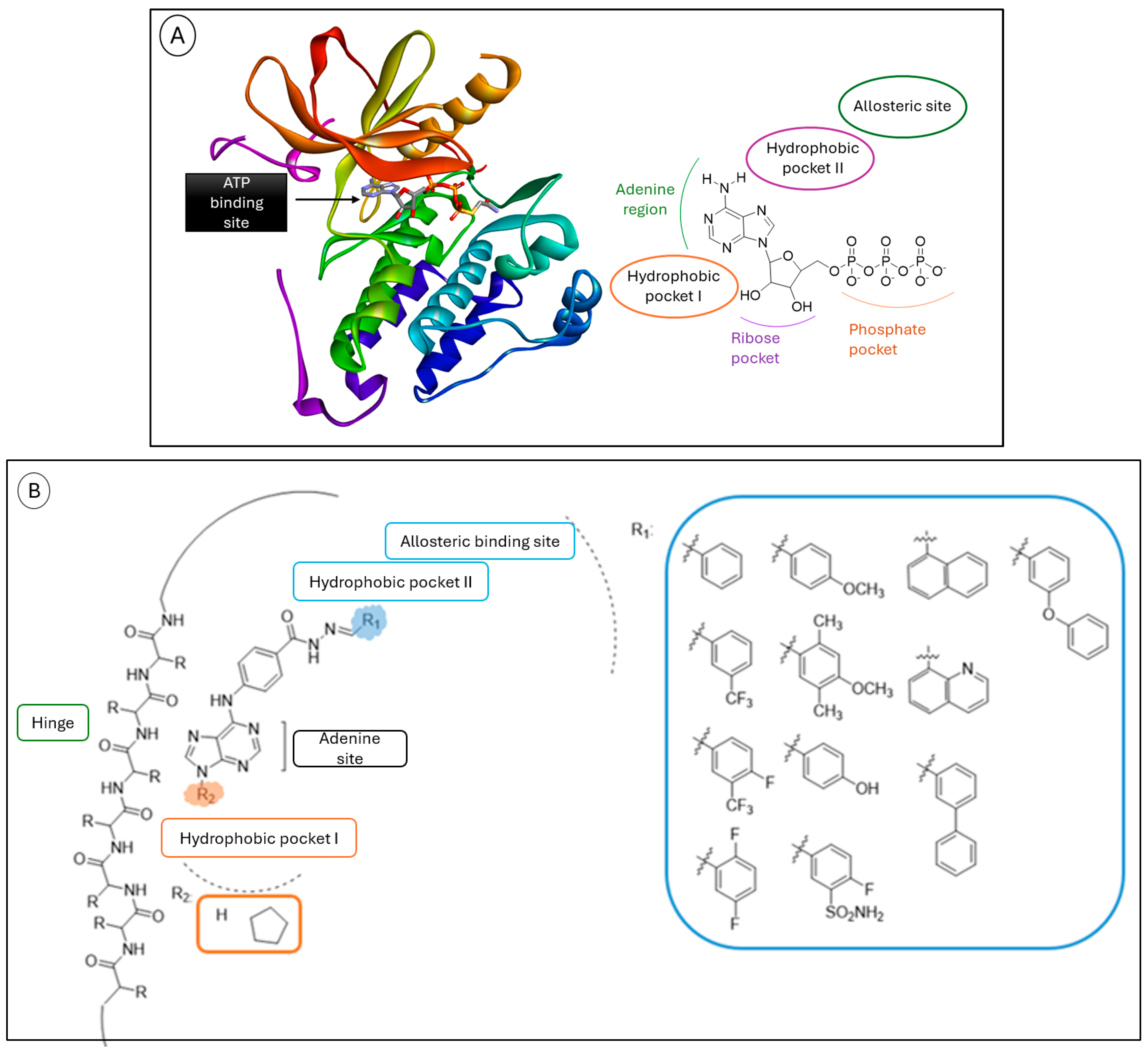
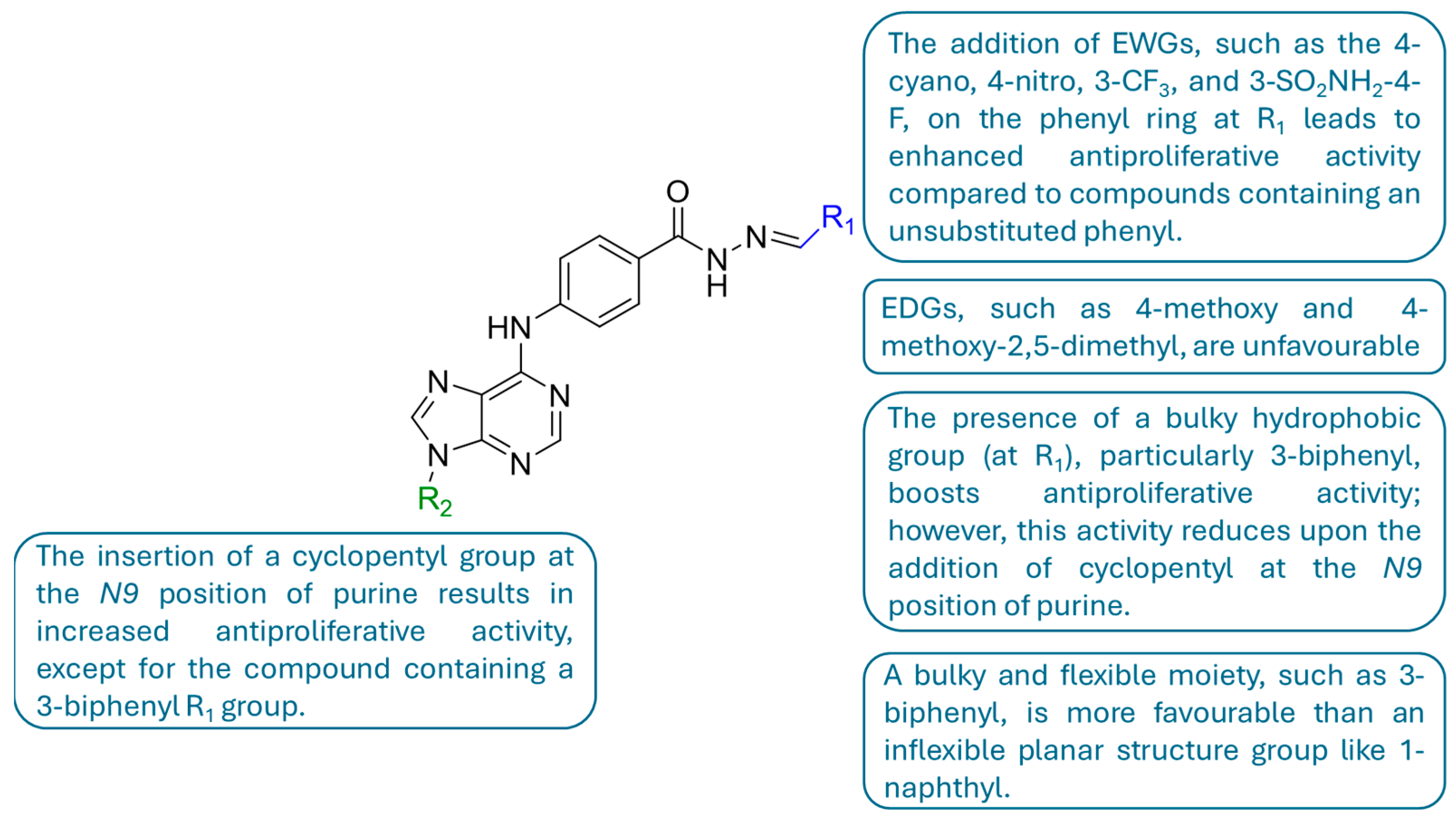
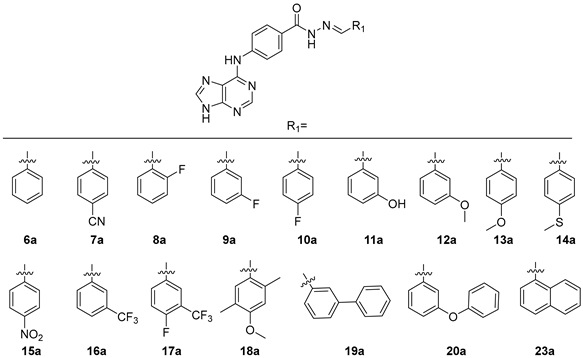
2.1. In Silico Molecular Docking Study
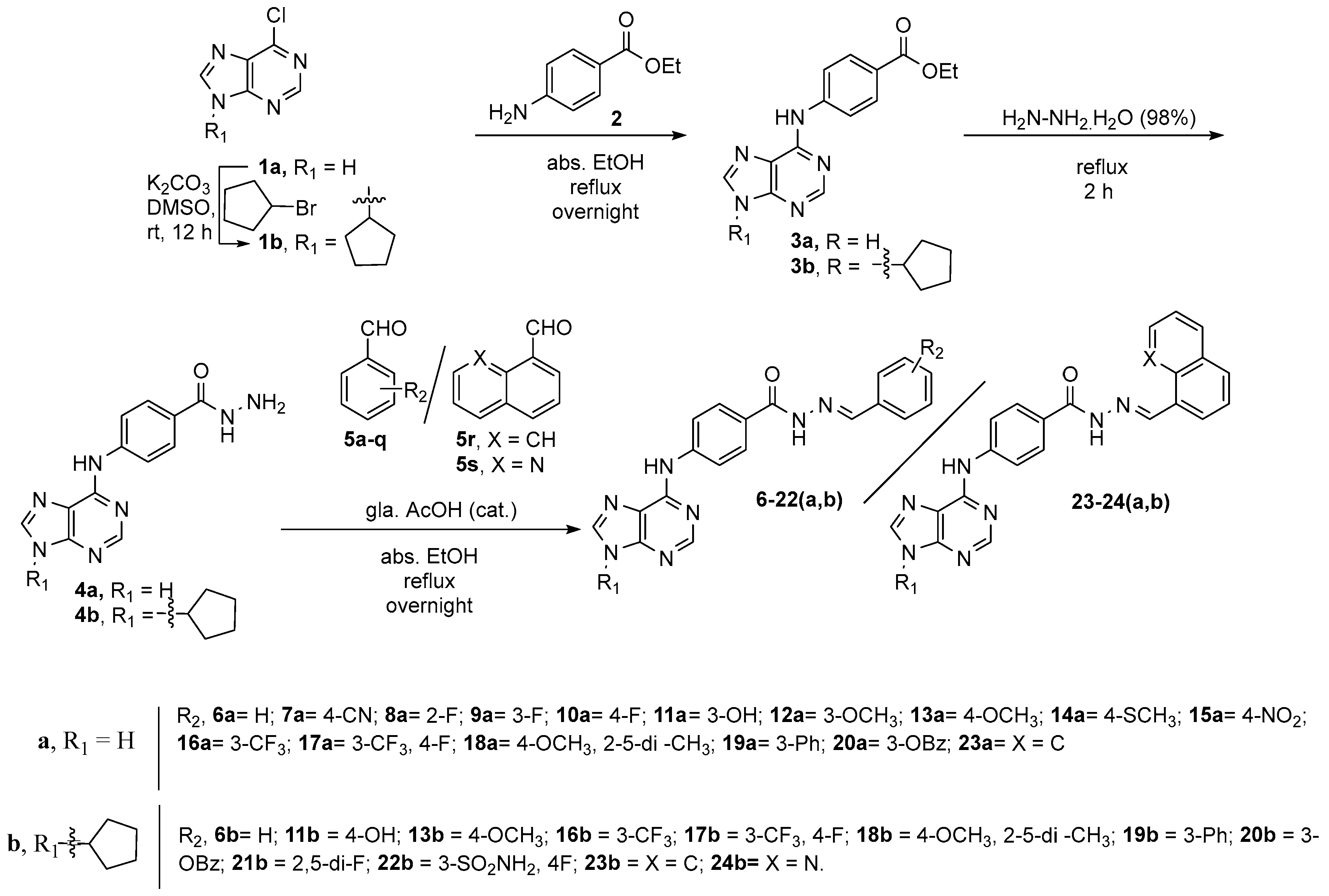
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assessment
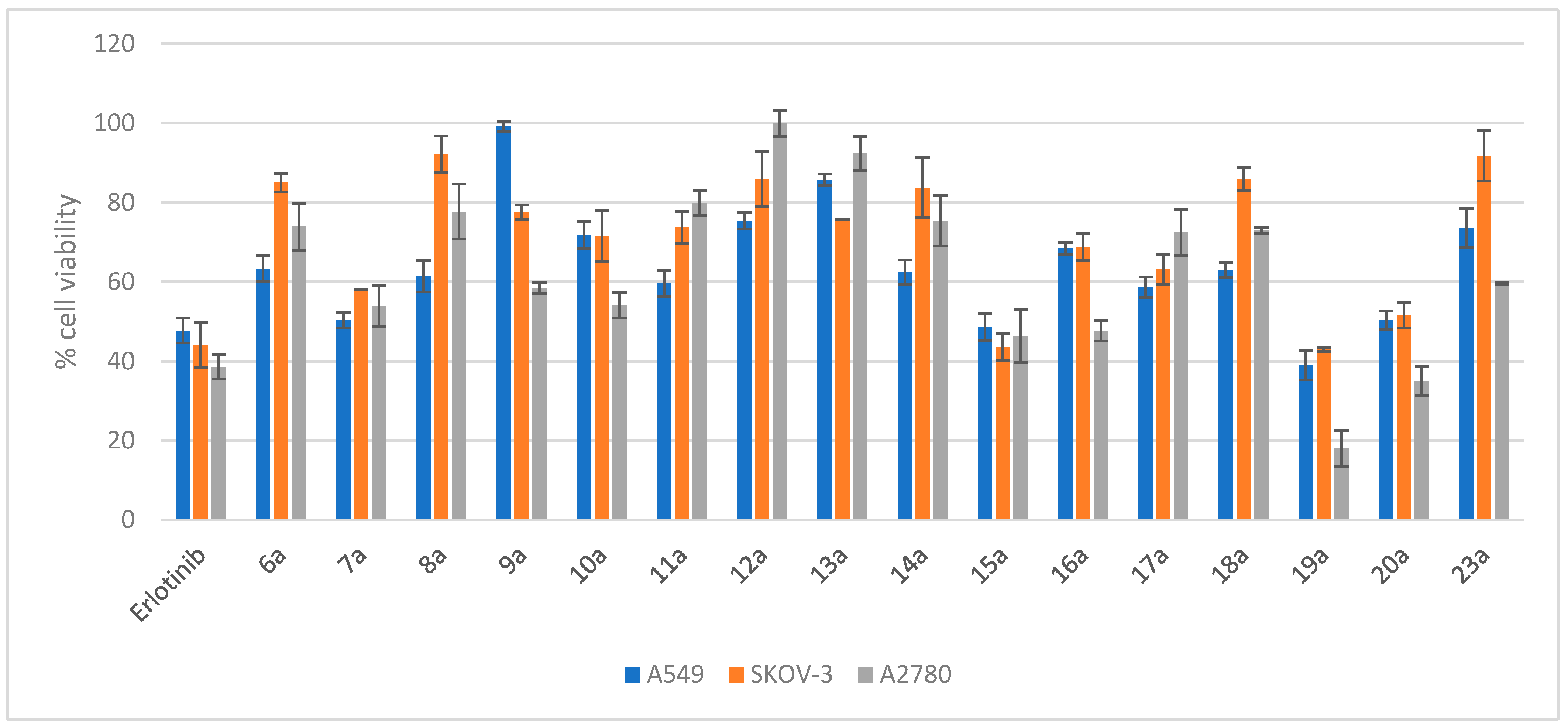
2.3.1. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of Compounds 6a–20a and 23a
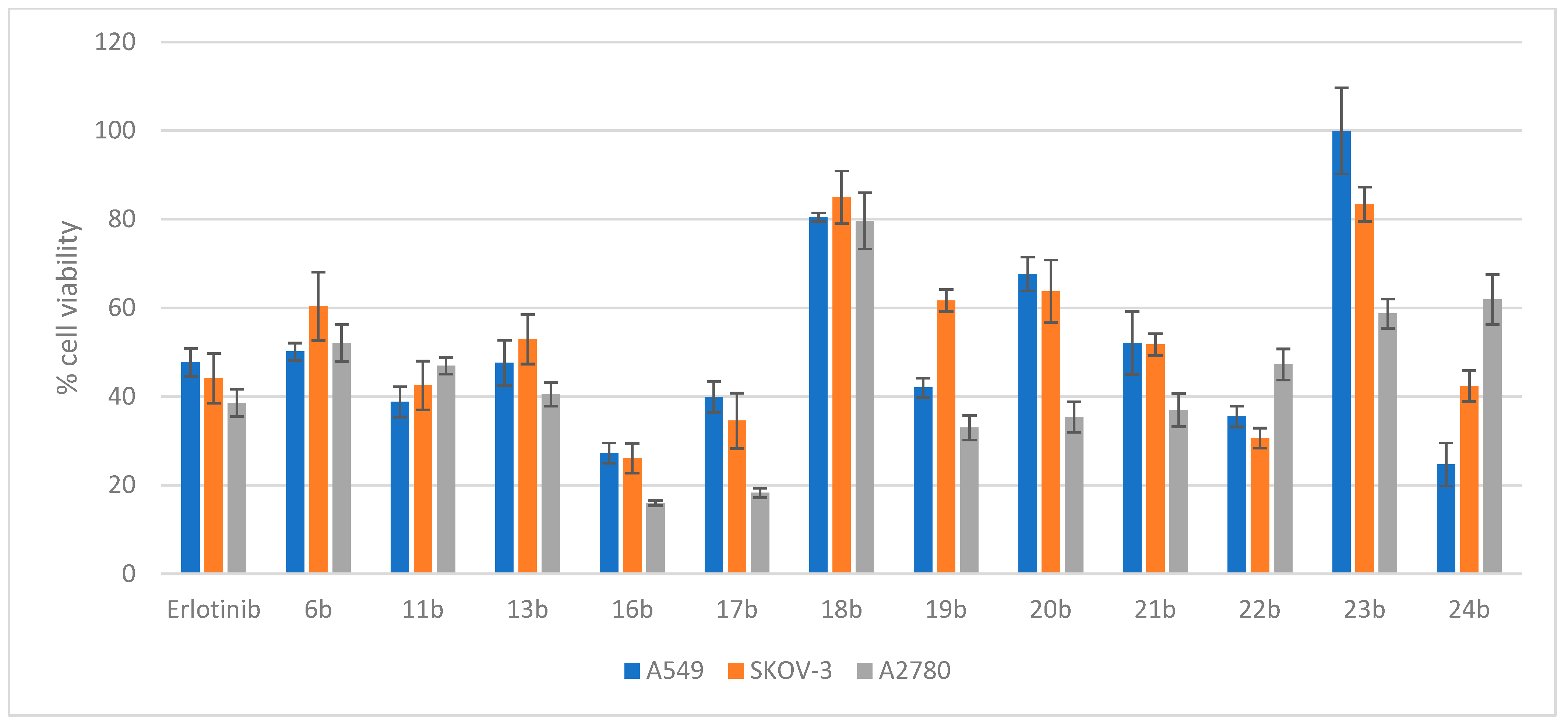
2.3.2. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of Compounds 6b, 11b, 13b, and 16b–24b
2.4. In Vitro EGFR and HER2 Kinase Inhibition Assays
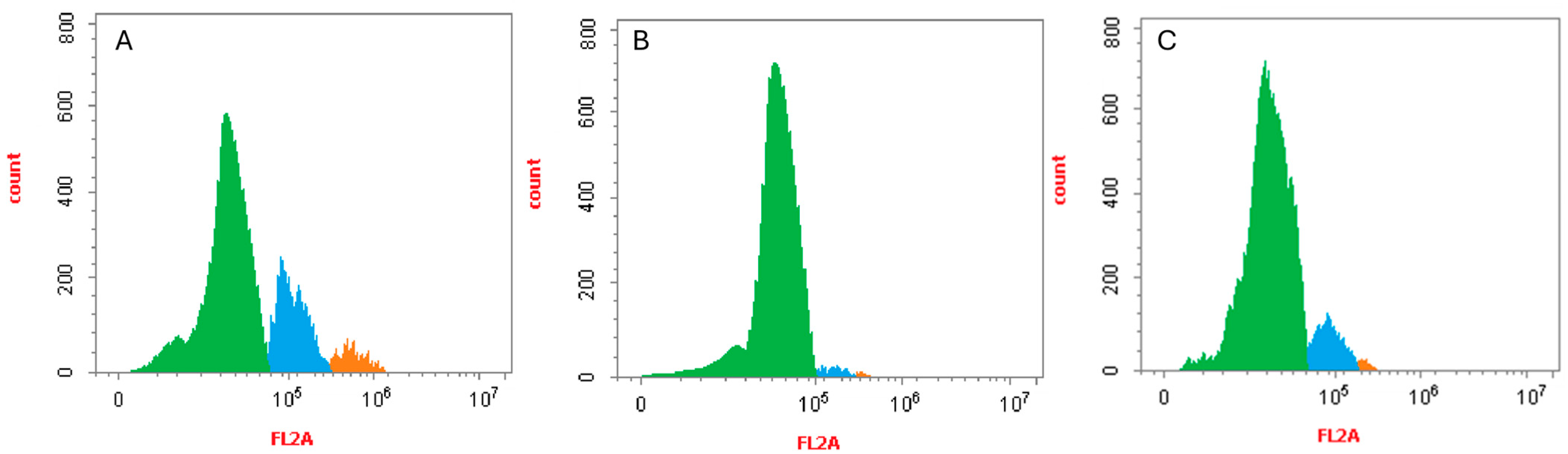
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis of Compounds 19a and 22b
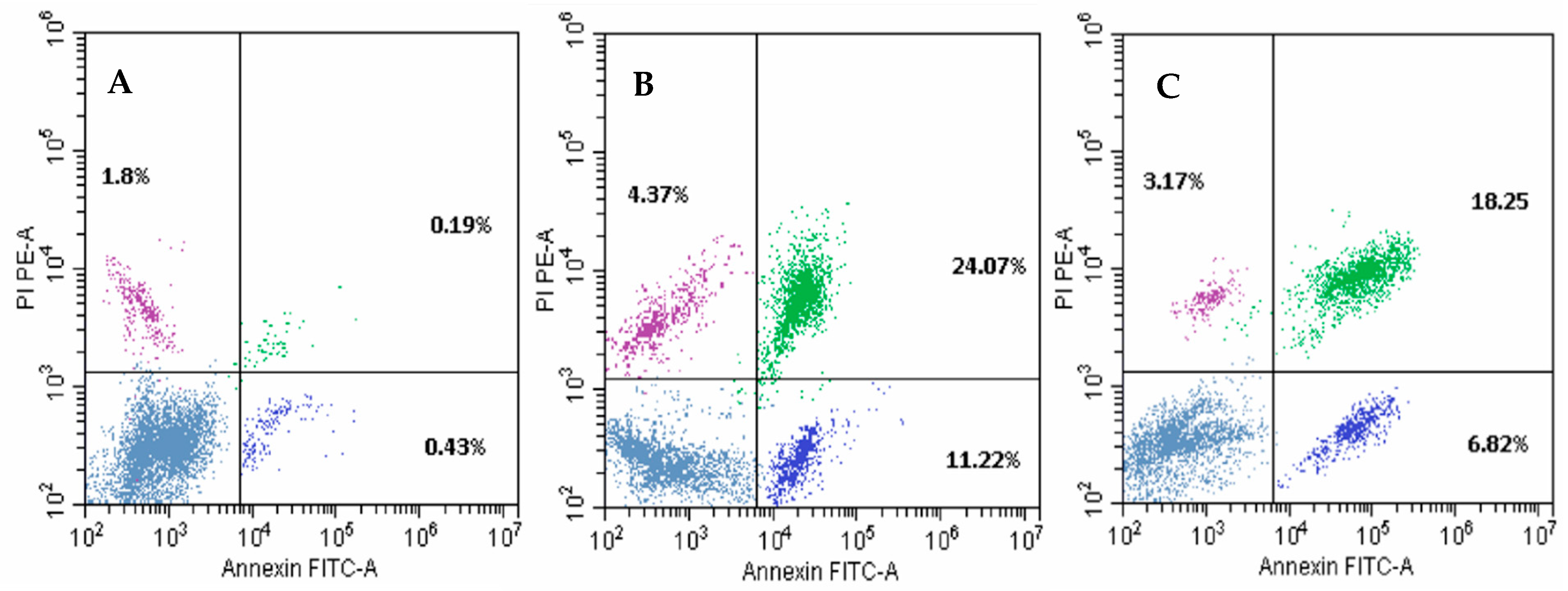
2.6. Apoptosis Analysis of Compounds 19a and 22b
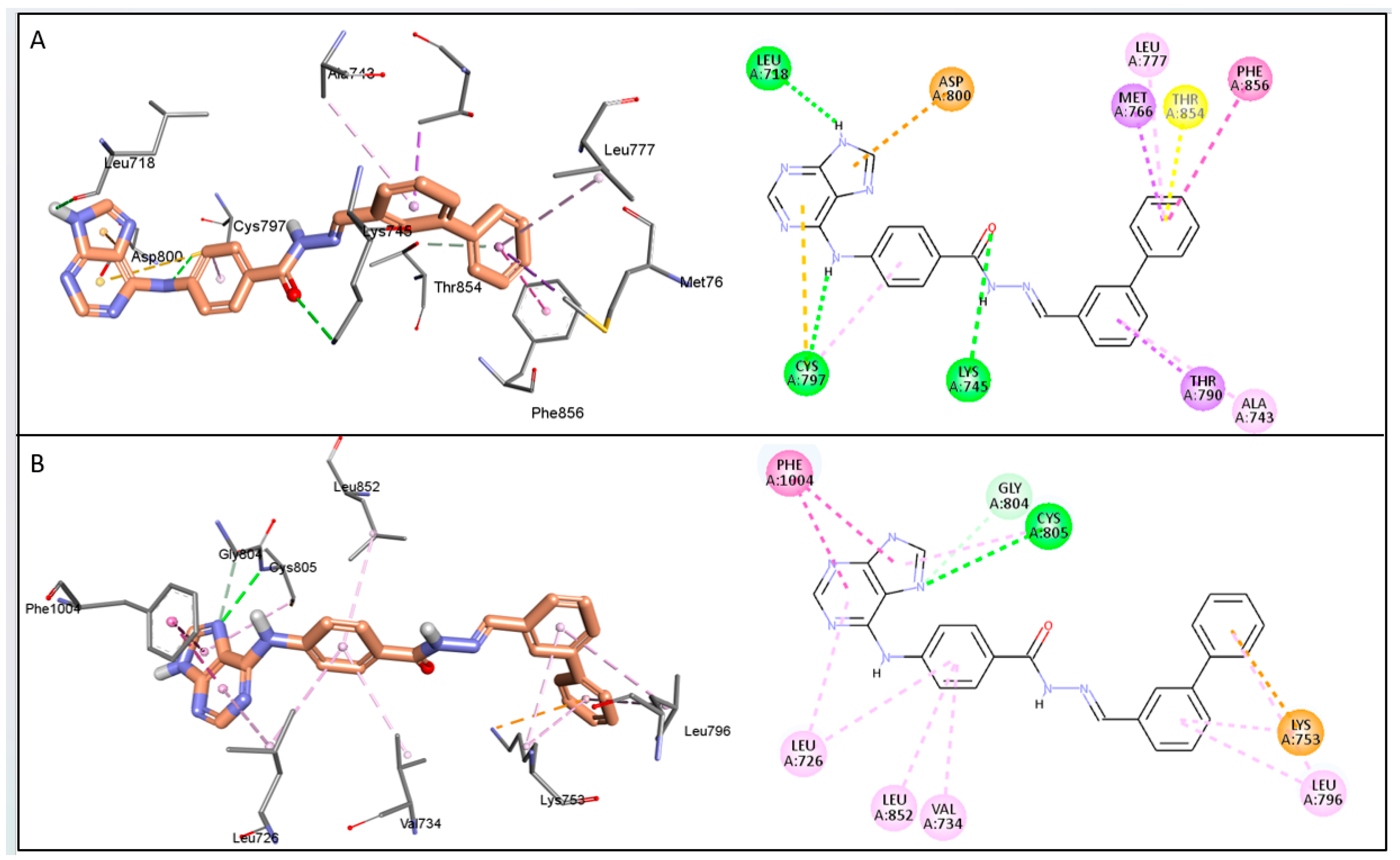
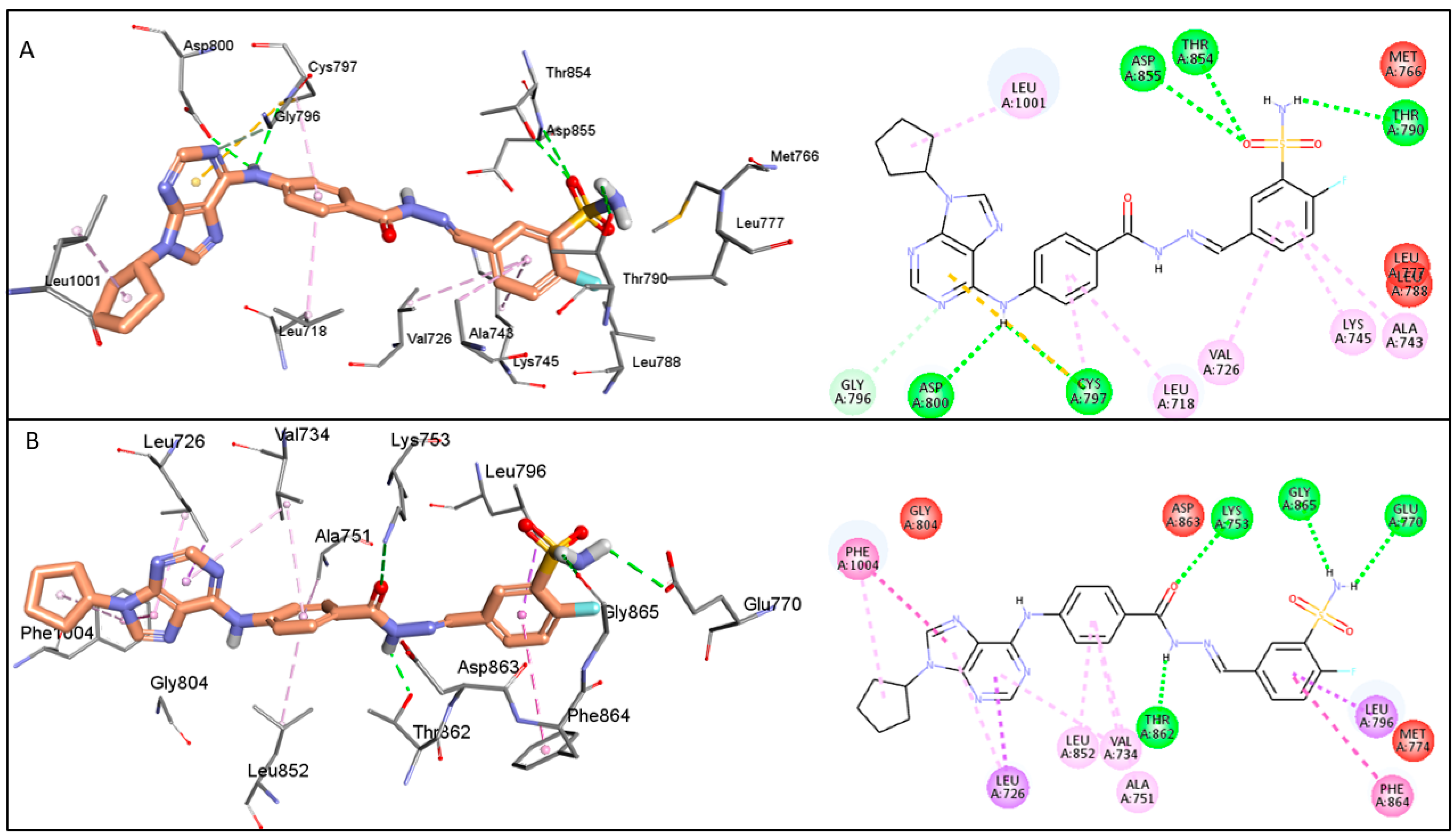
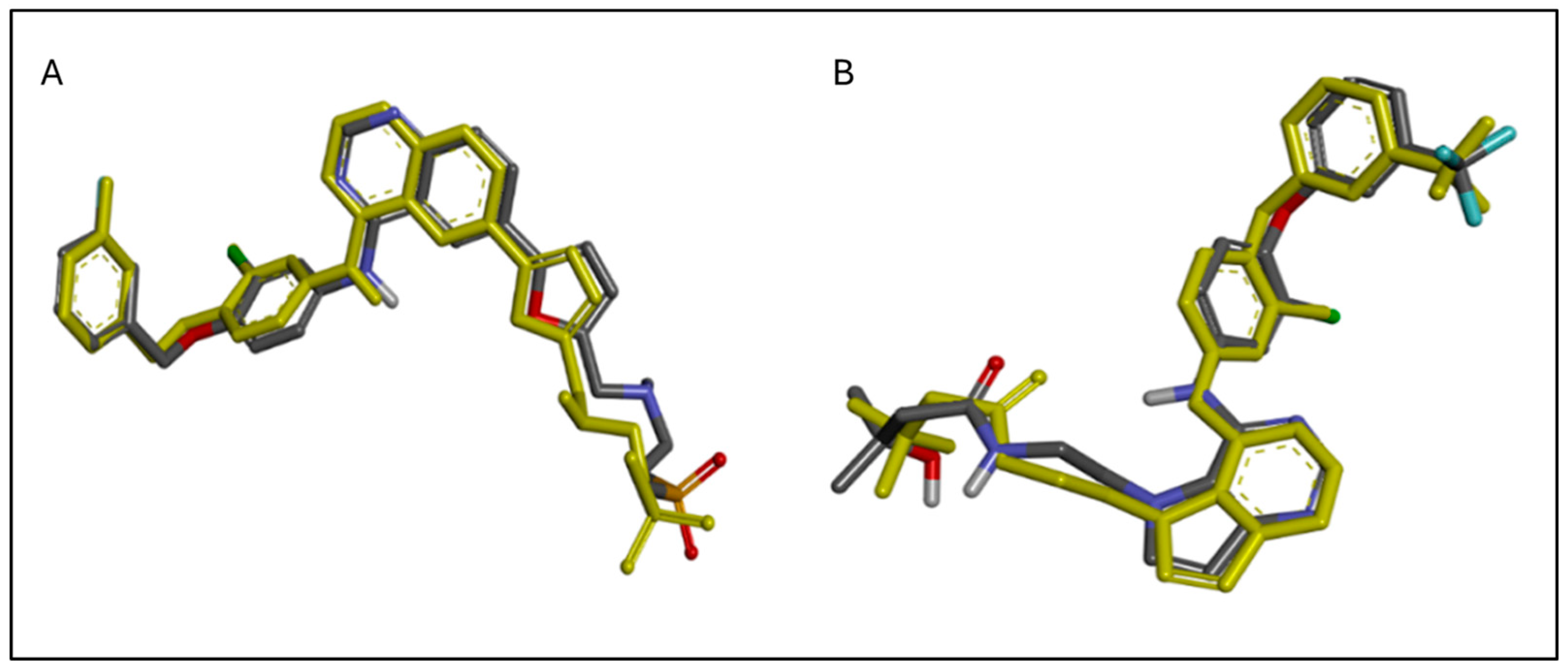
2.7. The Predicted Mode of Interaction of 19a and 22b Within the Active Site of EGFR and HER2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Silico Molecular Docking Studies
4.2. Chemistry
4.3. Biological Evaluation
4.3.1. Materials and Consumables
4.3.2. Cell Maintenance
4.3.3. Instrumentation and Data Processing
4.3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay (MTT)
4.3.5. In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay
4.3.6. Cell Cycle Assay
4.3.7. Apoptosis Analysis
4.3.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zugazagoitia, J.; Guedes, C.; Ponce, S.; Ferrer, I.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; Paz-Ares, L. Current Challenges in Cancer Treatment. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Davudian, S.; Shirjang, S.; Baradaran, B. The different mechanisms of cancer drug resistance: A brief review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Baek, M.; Kim, D.J. Protein Tyrosine Signaling and Its Potential Therapeutic Implications in Carcinogenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 4226–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S. Review of epidermal growth factor receptor biology. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 59, S21–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, D.S.; Brandt, R.; Ciardiello, F.; Normanno, N. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 1995, 19, 183–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor cell proliferation signaling pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesnelle, K.M.; Boehm, A.L.; Grandis, J.R. STAT-mediated EGFR signaling in cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 102, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alroy, I.; Yarden, Y. The ErbB signaling network in embryogenesis and oncogenesis: Signal diversification through combinatorial ligand-receptor interactions. FEBS Lett. 1997, 410, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, N.; Iqbal, N. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) in Cancers: Overexpression and Therapeutic Implications. Mol. Biol. Int. 2014, 2014, 852748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbah, D.A.; Hajjo, R.; Sweidan, K. Review on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Structure, Signaling Pathways, Interactions, and Recent Updates of EGFR Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, M.L.; Marrocco, I.; Yarden, Y. EGFR in cancer: Signaling mechanisms, drugs, and acquired resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Langer, C.J. Epidermal growth factor receptors as a target for cancer treatment: The emerging role of IMC-C225 in the treatment of lung and head and neck cancers. Semin. Oncol. 2002, 29, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Fang, W.; Mu, L.; Tang, Y.; Gao, L.; Ren, S.; Cao, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, A.; Liu, D.; et al. Overexpression of wildtype EGFR is tumorigenic and denotes a therapeutic target in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3884–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, P.R.; Maity, A. Cellular responses to EGFR inhibitors and their relevance to cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2007, 254, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, P.L.; Gray, N.S. Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, D.A.; Ashton, S.E.; Ghiorghiu, S.; Eberlein, C.; Nebhan, C.A.; Spitzler, P.J.; Orme, J.P.; Finlay, M.R.V.; Ward, R.A.; Mellor, M.J.; et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, V.A.; Hirsh, V.; Cadranel, J.; Chen, Y.-M.; Park, K.; Kim, S.-W.; Zhou, C.; Su, W.-C.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; et al. Afatinib versus placebo for patients with advanced, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of erlotinib, gefitinib, or both, and one or two lines of chemotherapy (LUX-Lung 1): A phase 2b/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hu, P.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y. Therapeutic effect of gefitinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer and its effect on the EGFR level in peripheral blood. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2017, 22, 1404–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Slamon, D.J.; Clark, G.M.; Wong, S.G.; Levin, W.J.; Ullrich, A.; McGuire, W.L. Human breast cancer: Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 1987, 235, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus-Porta, D.; Beerli, R.R.; Daly, J.M.; Hynes, N.E. ErbB-2, the preferred heterodimerization partner of all ErbB receptors, is a mediator of lateral signaling. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenferink, A.E.; Pinkas-Kramarski, R.; van de Poll, M.L.; van Vugt, M.J.; Klapper, L.N.; Tzahar, E.; Waterman, H.; Sela, M.; van Zoelen, E.J.; Yarden, Y. Differential endocytic routing of homo- and hetero-dimeric ErbB tyrosine kinases confers signaling superiority to receptor heterodimers. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3385–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemurro, F.; Valabrega, G.; Aglietta, M. Lapatinib: A dual inhibitor of EGFR and HER2 tyrosine kinase activity. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2007, 7, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban, N.; Kamashev, D.; Emelianova, A.; Buzdin, A. Targeted Inhibitors of EGFR: Structure, Biology, Biomarkers, and Clinical Applications. Cells 2024, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, A.; Pluta, K.; Latocha, M. Synthesis and anticancer activity of multisubstituted purines and xanthines with one or two propynylthio and aminobutynylthio groups. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, J.; Ojha, R.; Singh, H.; Kaur, M.; Bedi, P.; Nepali, K. Design strategies, structure activity relationship and mechanistic insights for purines as kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 112, 298–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peifer, C.; Bühler, S.; Hauser, D.; Kinkel, K.; Totzke, F.; Schächtele, C.; Laufer, S. Design, synthesis and characterization of N9/N7-substituted 6-aminopurines as VEGF-R and EGF-R inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, X.; Wan, G.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Yu, L. Discovery of 3-(((9H-purin-6-yl)amino)methyl)-4,6-dimethylpyridin-2(1H)-one derivatives as novel tubulin polymerization inhibitors for treatment of cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 184, 111728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, L.-J.; Liu, J.-J.; Zhong, L.; Zheng, R.-L.; Xu, Y.; Ji, P.; Zhang, C.-H.; Wang, W.-J.; Lin, X.-D.; et al. Structural optimization and structure–Activity relationships of N2-(4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl)-N8-phenyl-9H-purine-2,8-diamine derivatives, a new class of reversible kinase inhibitors targeting both EGFR-activating and resistance mutations. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10685–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayya, C.; Manda, S. Design and synthesis of new series 6, 7-disubstituted-7H-purine analogues induce G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer SKBR3 cells via selective EGFR/HER2 dual kinase inhibition. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug Res. 2022, 14, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.-J.; Hei, Y.-Y.; Zhang, J.-J.; Zheng, A.-Q.; Xin, M.; Zhang, S.-Q. Discovery of novel 9-heterocyclyl substituted 9H-purines as L858R/T790M/C797S mutant EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 186, 111888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, C.O.; Zarate, A.M.; Kryštof, V.; Mella, J.; Faundez, M.; Brea, J.; Loza, M.I.; Brito, I.; Hendrychová, D.; Jorda, R.; et al. Promising 2,6,9-trisubstituted purine derivatives for anticancer compounds: Synthesis, 3D-QSAR, and preliminary biological assays. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayya, C.; Dokala, A.; Manda, S. Novel 6, 7-disubstituted 7H-purine analogues as potential EGFR/HER2 dual kinase inhibitors overcome lapatinib resistance: Design, synthesis, in-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-N.; Bheemanaboina, R.R.Y.; Cai, G.-X.; Zhou, C.-H. Novel purine benzimidazoles as antimicrobial agents by regulating ROS generation and targeting clinically resistant Staphylococcus aureus DNA groove. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legraverend, M.; Grierson, D.S. The purines: Potent and versatile small molecule inhibitors and modulators of key biological targets. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 3987–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, Z.; Guven, E.B.; Ozbey, S.; Kazak, C.; Atalay, R.C.; Tuncbilek, M. Synthesis of novel substituted purine derivatives and identification of the cell death mechanism. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, T.; Boehme, R. Antiviral activity and mechanism of action of ganciclovir. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, S490–S494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, F.; Jafariyan, M.; Khatami, S.; Mortazavi, Y.; Azad, M. Assessment of Thiopurine–based drugs according to Thiopurine S-methyltransferase genotype in patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Iran. J. Ped. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 4, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Vipan Kumar, C. Hydrazone: A promising pharmacophore in medicinal chemistry. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Katariya, K.D.; Shah, S.R.; Reddy, D. Anticancer, antimicrobial activities of quinoline based hydrazone analogues: Synthesis, characterization and molecular docking. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 94, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, E.E.; Youssef, M.F.; Aboelmagd, A.; Boraei, A.T.A.; Nafie, M.S.; Haukka, M.; Barakat, A.; Sarhan, A.A.M. Discovery of Potent Indolyl-Hydrazones as Kinase Inhibitors for Breast Cancer: Synthesis, X-ray Single-Crystal Analysis, and In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Cancer Activity Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şenkardeş, S.; Han, M.I.; Gürboğa, M.; Özakpinar, Ö.B.; Küçükgüzel, Ş.G. Synthesis and anticancer activity of novel hydrazone linkage-based aryl sulfonate derivatives as apoptosis inducers. Med. Chem. Res. 2022, 31, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghaly, T.A.; Abbas, E.M.; Al-Soliemy, A.M.; Sabour, R.; Shaaban, M.R. Novel sulfonyl thiazolyl-hydrazone derivatives as EGFR inhibitors: Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking studies. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 121, 105684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labib, M.B.; Philoppes, J.N.; Lamie, P.F.; Ahmed, E.R. Azole-hydrazone derivatives: Design, synthesis, in vitro biological evaluation, dual EGFR/HER2 inhibitory activity, cell cycle analysis and molecular docking study as anticancer agents. Bioorganic Chem. 2018, 76, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milik, S.N.; Lasheen, D.S.; Serya, R.A.; Abouzid, K.A. How to train your inhibitor: Design strategies to overcome resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 142, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gureasko, J.; Shen, K.; Cole, P.A.; Kuriyan, J. An Allosteric Mechanism for Activation of the Kinase Domain of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Cell 2006, 125, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samir, E.M.; Mohareb, R.M. Novel synthesis of pyran-3-hydrazide derivatives and their uses to the synthesis hydrazide-hydrazone, pyrazole and thiazole derivatives with anticancer activities. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2021, 35, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.M.; Taher, F.A.; Abdel-Samad, M.R.; El-Gaby, M.S.; El-Adl, K.; Saleh, N.M. Design, synthesis, molecular docking, in silico ADMET profile and anticancer evaluations of sulfonamide endowed with hydrazone-coupled derivatives as VEGFR-2 inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 108, 104669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugappan, S.; Dastari, S.; Jungare, K.; Barve, N.M.; Shankaraiah, N. Hydrazide-hydrazone/hydrazone as enabling linkers in anti-cancer drug discovery: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1307, 138012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogyányi, T.; Kaplánek, R.; Kejík, Z.; Hosnedlová, B.; Antonyová, V.; Abramenko, N.; Veselá, K.; Martásek, P.; Vokurka, M.; Richardson, D.R.; et al. Azulene hydrazide-hydrazones for selective targeting of pancreatic cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, J.S.; Jayabalan, K.; Ragavendran, V.; Manoharan, M.T.; Shetty, A.N. Virtual and experimental high throughput screening of substituted hydrazones on β-Tubulin polymerization. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 114, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, A.A.-M.; El-Azab, A.S.; AlSaif, N.A.; Obaidullah, A.J.; Al-Obaid, A.M.; Al-Suwaidan, I.A. Synthesis, potential antitumor activity, cell cycle analysis, and multitarget mechanisms of novel hydrazones incorporating a 4-methylsulfonylbenzene scaffold: A molecular docking study. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 1520–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinuesa, A.; Viñas, M.; Jahani, D.; Ginard, J.; Mur, N.; Pujol, M.D. Regioselective alkylation reaction of purines under microwave irradiation. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2022, 59, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.H.M.; Sodero, A.C.R.; Jofily, P.; Silva, F.P., Jr. Key topics in molecular docking for drug design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plewczynski, D.; Łaźniewski, M.; Augustyniak, R.; Ginalski, K. Can we trust docking results? Evaluation of seven commonly used programs on PDBbind database. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camenisch, G.; Alsenz, J.; van de Waterbeemd, H.; Folkers, G. Estimation of permeability by passive diffusion through Caco-2 cell monolayers using the drugs’ lipophilicity and molecular weight. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 6, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, C.A.; Charman, W.N.; Porter, C.J. Computational prediction of formulation strategies for beyond-rule-of-5 compounds. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 101, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leckband, D.; Israelachvili, J. Intermolecular forces in biology. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2001, 34, 105–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, E.R.; Truesdale, A.T.; McDonald, O.B.; Yuan, D.; Hassell, A.; Dickerson, S.H.; Ellis, B.; Pennisi, C.; Horne, E.; Lackey, K.; et al. A Unique structure for epidermal growth factor receptor bound to GW572016 (Lapatinib): Relationships among protein conformation, inhibitor off-rate, and receptor activity in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6652–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, T.; Seto, M.; Banno, H.; Kawakita, Y.; Oorui, M.; Taniguchi, T.; Ohta, Y.; Tamura, T.; Nakayama, A.; Miki, H.; et al. Design and synthesis of novel human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) dual inhibitors bearing a pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine scaffold. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8030–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 | |||||
| Compound | Binding score (kcal/mol) | Compound | Binding score (kcal/mol) | ||
| EGFR | HER2 | EGFR | HER2 | ||
| 6a | −9.2 | −8.9 | 23a | −10.2 | −10.9 |
| 19a | −11.0 | −10.3 | Lapatinib | −11.1 | −10.3 |
 | |||||
| Compound | Binding score (kcal/mol) | Compound | Binding score (kcal/mol) | ||
| EGFR | HER2 | EGFR | HER2 | ||
| 6b | −9.8 | −9.6 | 19b | −11.7 | −10.6 |
| 16b | −10.6 | −10 | 22b | −11.0 | −10.8 |
| 17b | −11.0 | −10 | 23b | −10.3 | −10.9 |
| 18b | −9.9 | −9.9 | Lapatinib | −11.1 | −10.3 |
| Compound No. | Cytotoxicity (IC50) in µM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 (SI) ** | SKOV-3 (SI) ** | SKBR-3 (SI) ** | MRC-5 | |
| 19a | 0.810 ± 0.139 **** (64.6) | 2.192 ± 0.164 ** (23.88) | 1.414 ± 0.362 *** (37.03) | 52.360 ± 0.283 |
| 16b | 2.604 ± 0.351 *** (14.07) | 1.975 ± 0.07 ** (18.55) | 4.308 ± 0.948 ** (8.51) | 36.650 ± 0.200 |
| 22b | 3.950 ± 0.615 **** (15.34) | 1.541 ± 0.470 ** (39.32) | 3.801 ± 1.401 ** (15.94) | 60.590 ± 0.329 |
| 19b | 1.844 ± 0.082 | 15.645 ± 1.475 | 3.197 ± 0.899 | ND |
| Lapatinib | 11.570 ± 0.249 (3.8) | 16.950 ± 2.570 (2.6) | 8.540 ± 0.640 (5.14) | 43.940 ± 0.420 |
| Erlotinib | 2.420 ± 0.784 (8.0) | 5.180 ± 1.200 (3.7) | 5.120 ± 0.879 (3.8) | 19.360 ± 0.138 |
| Compound No. | Protein Kinase Inhibition IC50 (µM) ± SEM | |
|---|---|---|
| EGFR | HER2 | |
| 19a | 0.081 ± 0.003 ** | 0.059 ± 0.002 |
| 16b | 0.062 ± 0.002 **** | 0.045 ± 0.010 |
| 22b | 0.074 ± 0.002 **** | 0.033 ± 0.015 |
| Lapatinib | 0.130 ± 0.002 | 0.037 ± 0.016 |
| Erlotinib | 0.038 ± 0.002 | 0.052 ± 0.004 |
| Compound/Cell Line | DNA Content (%) | Cell Cycle Distribution Index (CDI)/Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| %G0–G1 | %S | %G2/M | ||
| Cont. A549 | 54.23 ± 0.92 | 31.40 ± 1.12 | 14.36 ± 0.91 | 0.84 |
| 19a/A549 | 86.88 ± 0.95 **** | 9.21 ± 1.43 **** | 3.90 ± 1.22 *** | 0.15 Cell cycle arrest@G1 |
| 22b/A549 | 77.04 ± 1.85 *** | 18.60 ± 2.00 ** | 4.35 ± 0.29 *** | 0.29 Cell cycle arrest@G1 |
| Compound/Cell Line | Apoptosis | Necrosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Early | Late | ||
| Cont. A549 | 2.38 ± 0.31 | 0.48 ± 0.10 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 1.72 ± 0.23 |
| 19a/A549 | 37.70 ± 1.40 **** | 9.72 ± 1.06 *** | 23.13 ± 0.73 **** | 4.84 ± 0.34 |
| 22b/A549 | 27.48 ± 0.57 **** | 5.92 ± 0.74 *** | 18.21 ± 0.12 **** | 3.35 ± 0.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albalawi, F.S.; Bhat, M.A.; Bakheit, A.H.; Rahman, A.F.M.M.; Alsaif, N.A.; Jones, A.M.; Romero-Canelon, I. Purine–Hydrazone Scaffolds as Potential Dual EGFR/HER2 Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071051
Albalawi FS, Bhat MA, Bakheit AH, Rahman AFMM, Alsaif NA, Jones AM, Romero-Canelon I. Purine–Hydrazone Scaffolds as Potential Dual EGFR/HER2 Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071051
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbalawi, Fatemah S., Mashooq A. Bhat, Ahmed H. Bakheit, A. F. M. Motiur Rahman, Nawaf A. Alsaif, Alan M. Jones, and Isolda Romero-Canelon. 2025. "Purine–Hydrazone Scaffolds as Potential Dual EGFR/HER2 Inhibitors" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071051
APA StyleAlbalawi, F. S., Bhat, M. A., Bakheit, A. H., Rahman, A. F. M. M., Alsaif, N. A., Jones, A. M., & Romero-Canelon, I. (2025). Purine–Hydrazone Scaffolds as Potential Dual EGFR/HER2 Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071051