Integration of Untargeted Metabolomics, Network Pharmacology, Single-Cell RNA Sequencing, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Reveals GOT1, CYP1A2, and CA2 as Potential Targets of Huang Qin Decoction Preventing Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
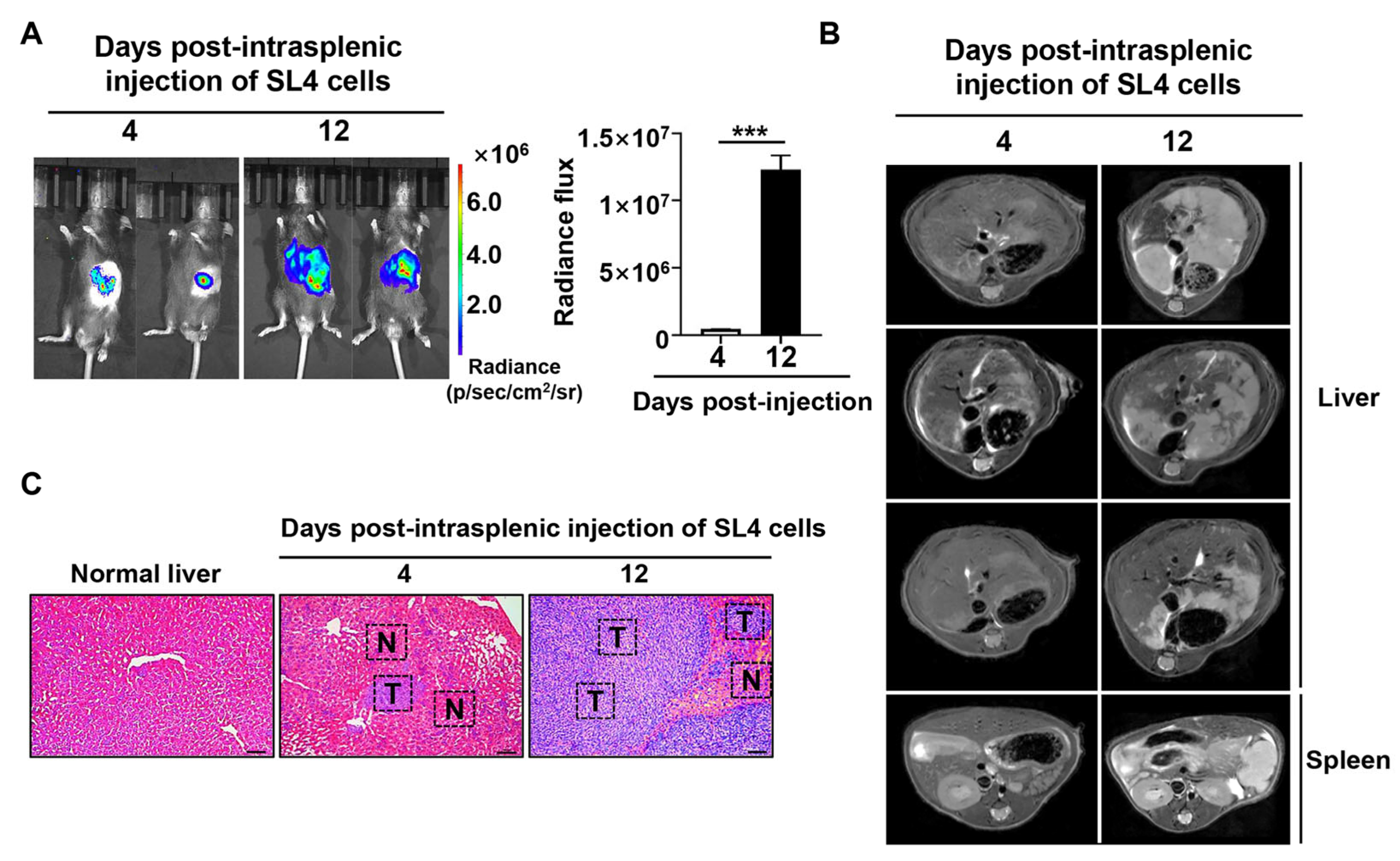
2.1. In Vivo Multimodal Imaging to Monitor Liver Metastasis of CRC
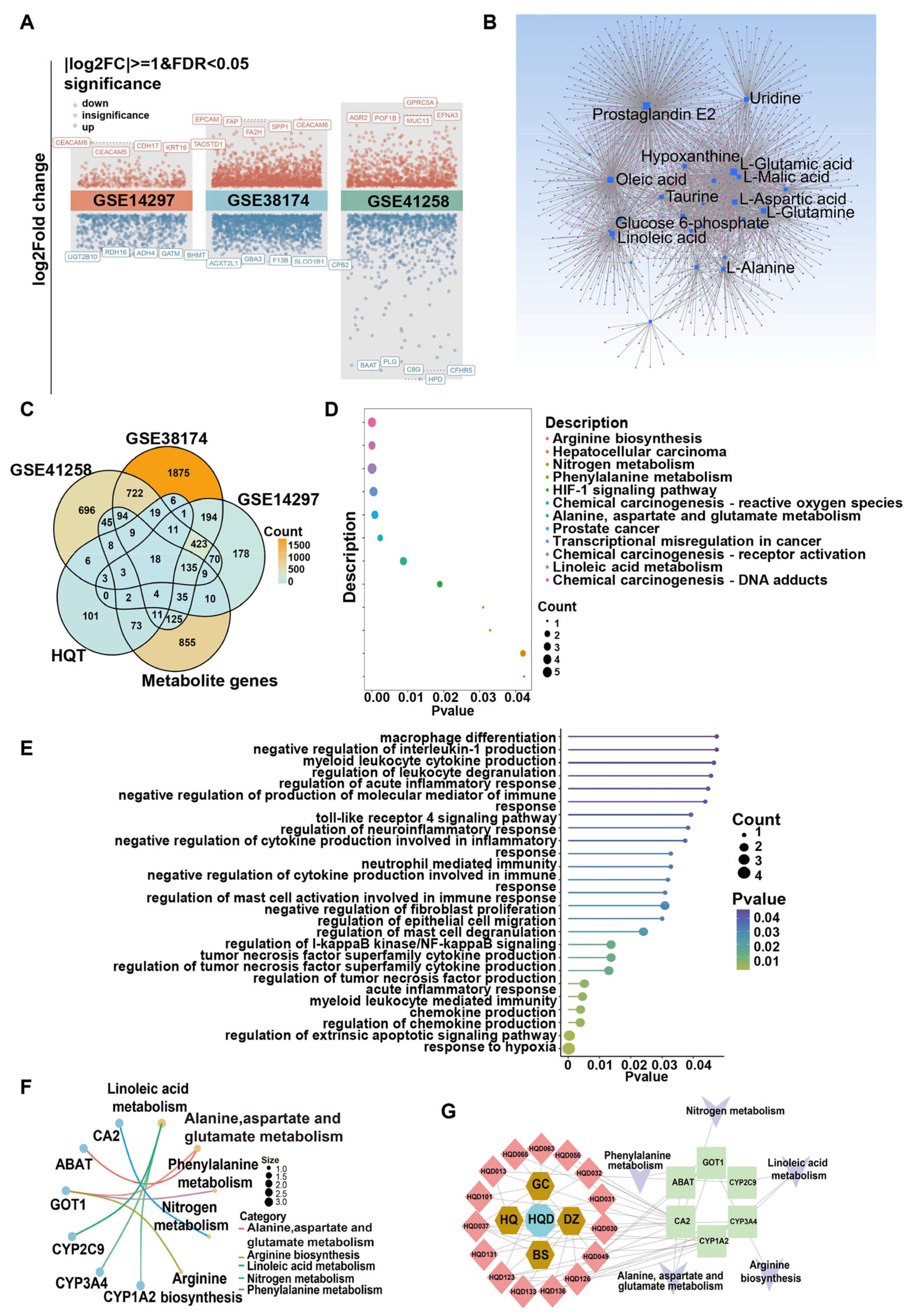
2.2. Metabolism Rewiring in Malignant Progression of CRC Liver Metastases
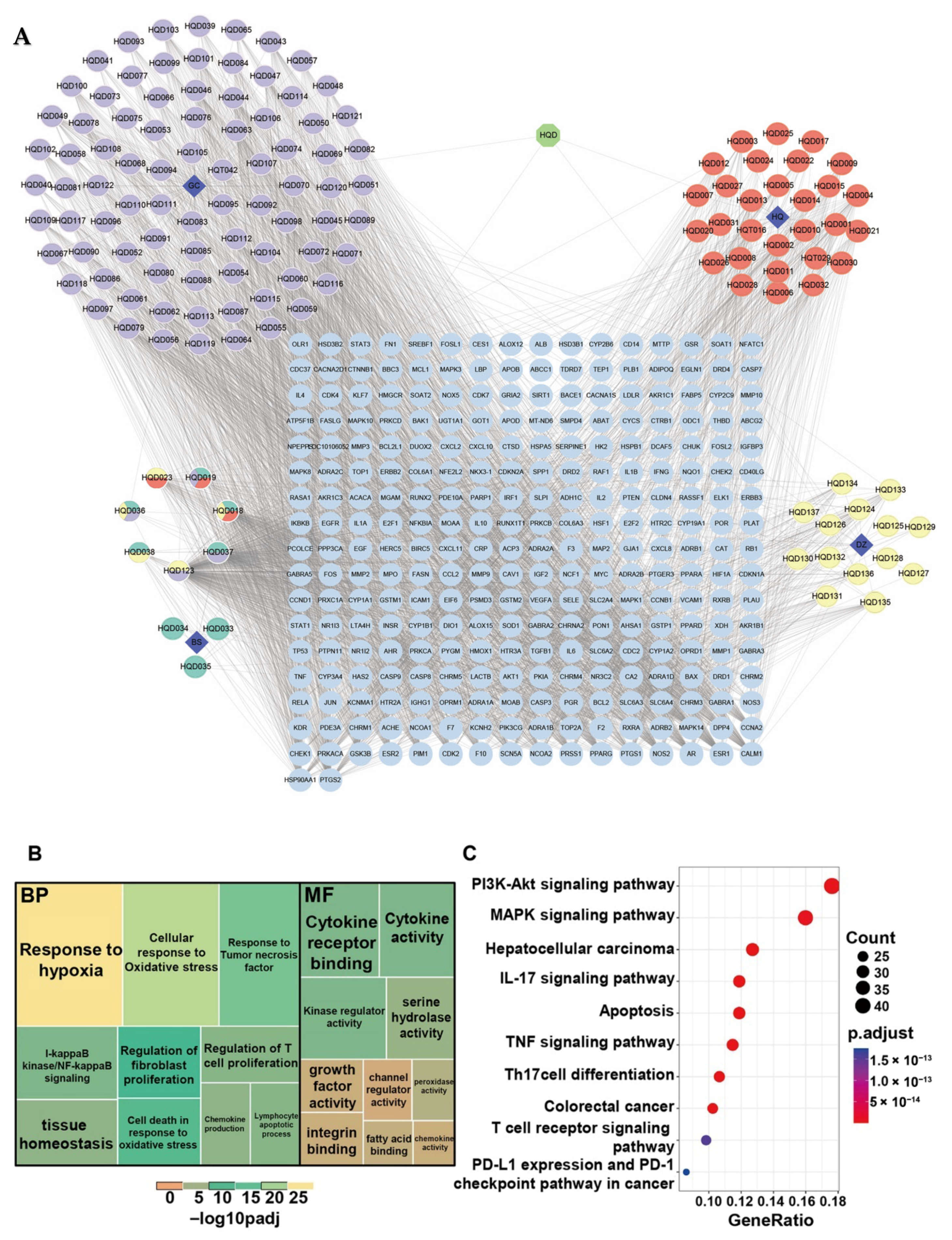
2.3. Elucidation of the Therapeutic Effects of HQD via Network Pharmacology
2.4. Integrated Metabolomic, Transcriptomic, and Network Pharmacology Analysis to Unveil the Mechanism of HQD Against CRC Liver Metastasis
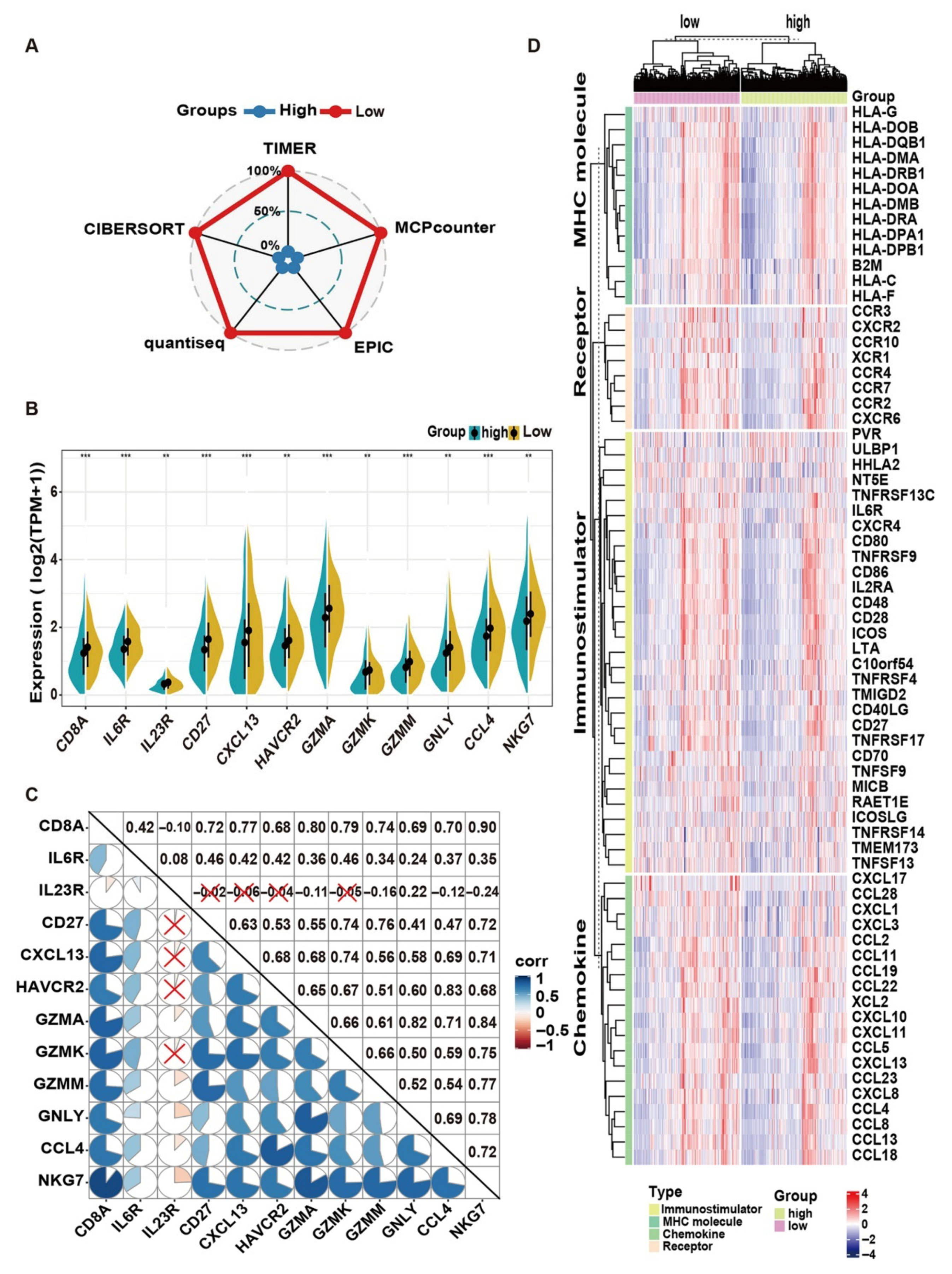
2.5. Bulk Transcriptome Data Implying That HQD May Prevent Liver Metastasis of CRC by Regulating the Tumor Immune Microenvironment
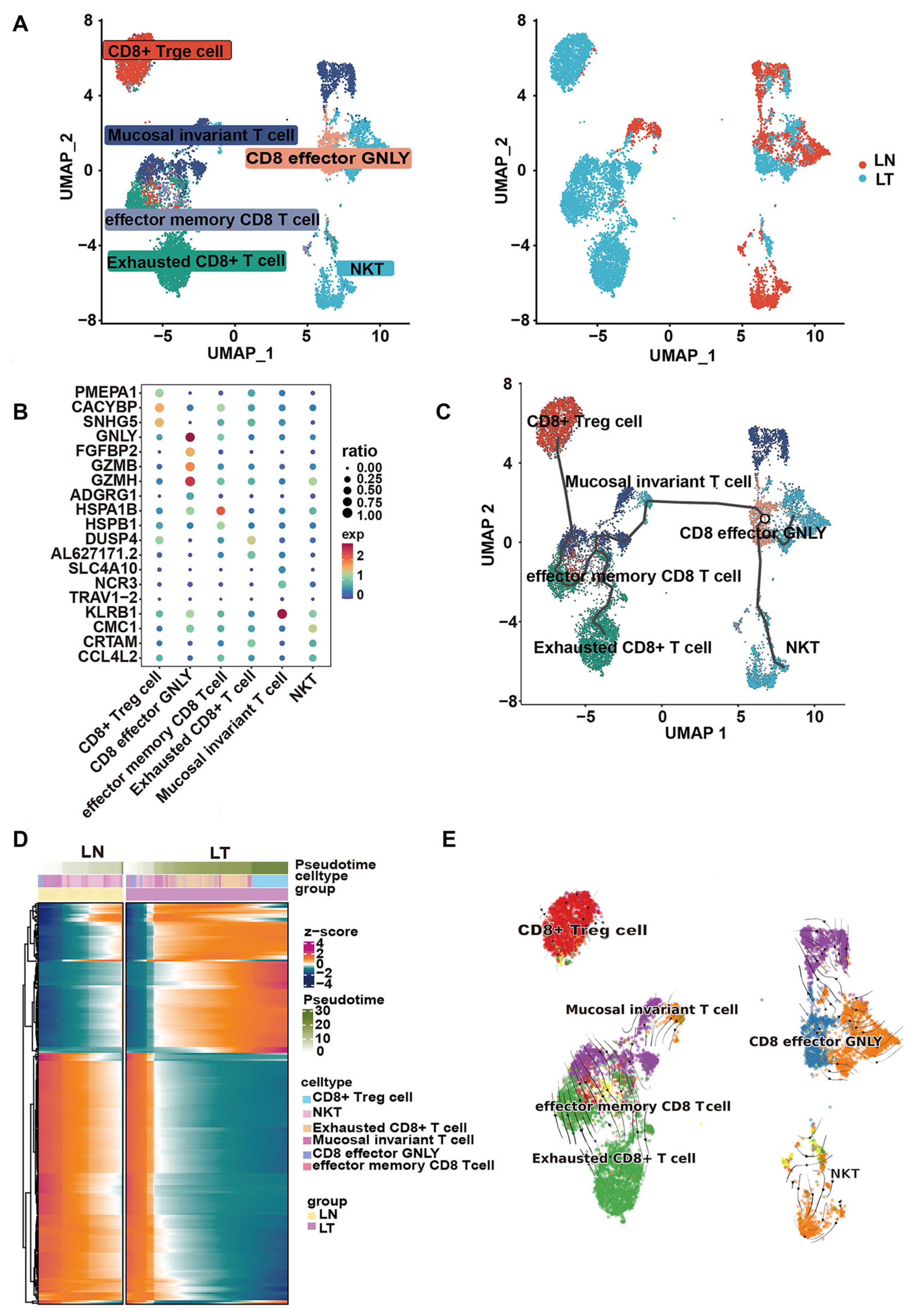
2.6. Single-Cell Sequencing Analysis Confirms the Anti-Tumor Immune Activity of HQD
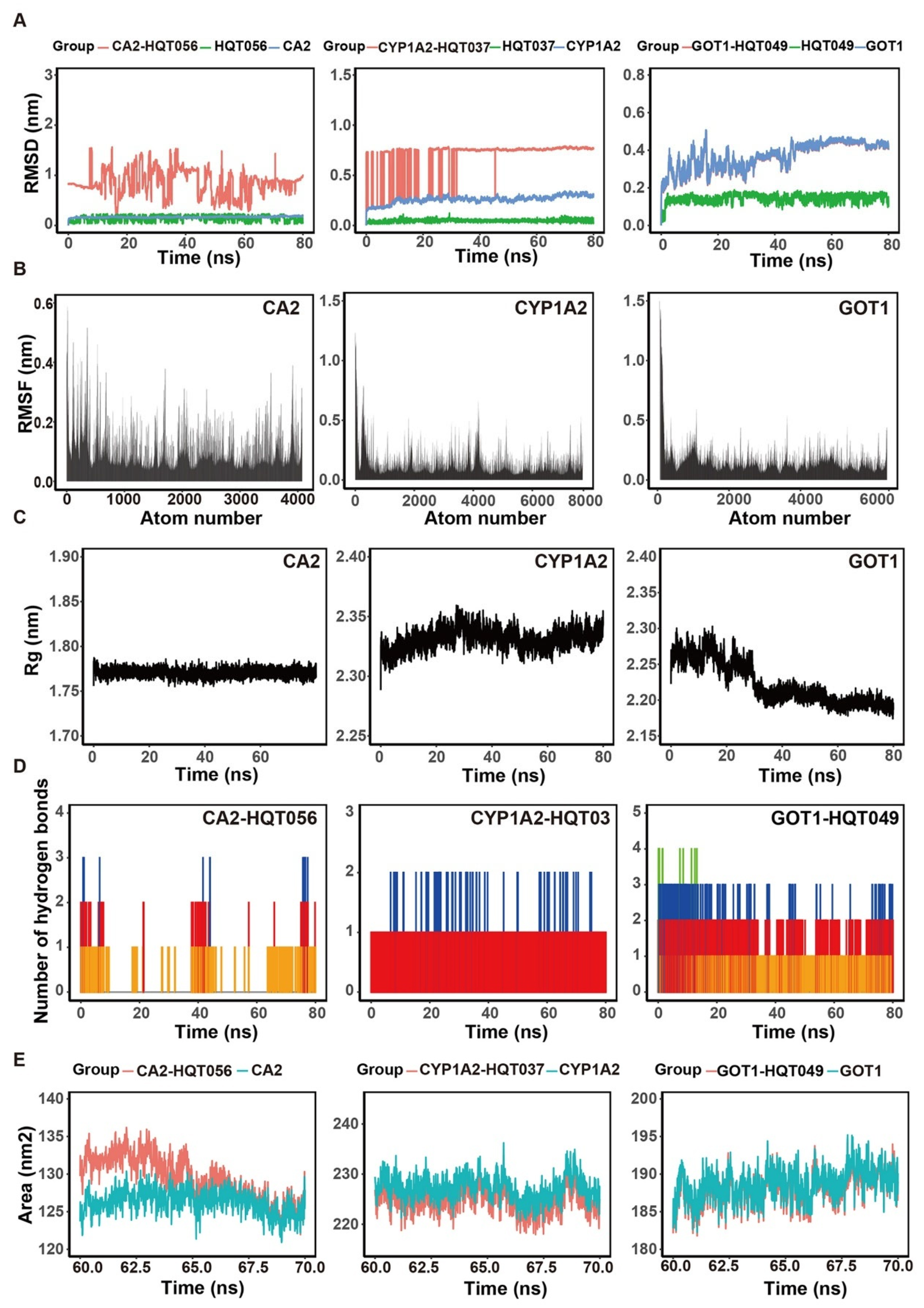
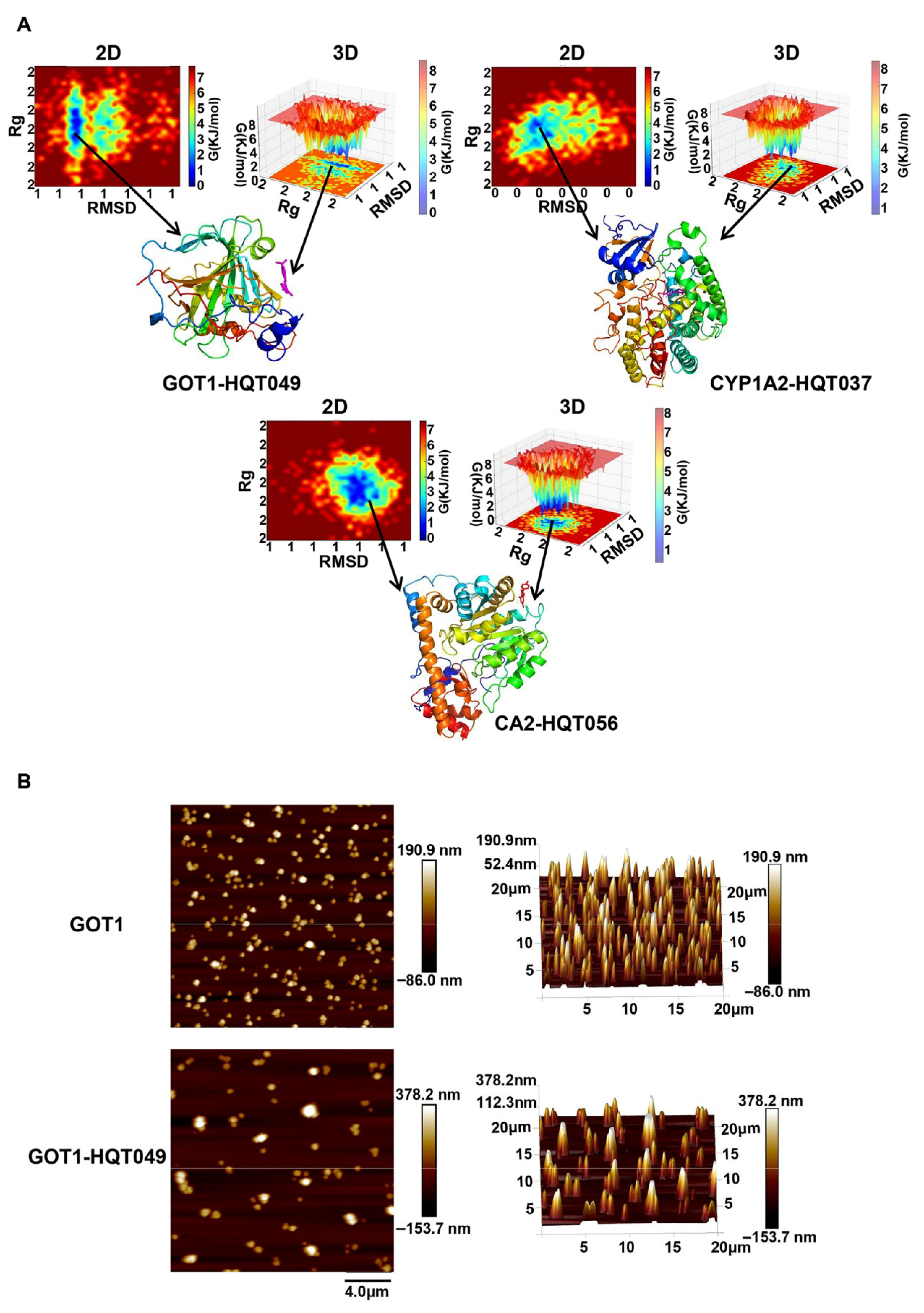
2.7. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulation
2.8. Molecular Surface Topography Analysis by AFM
2.9. Validation of the Anti-CRC Effect of Naringenin In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Development of CRC Liver Metastasis Animal Tumor Model and Multimodal In Vivo Imaging Evaluation
4.2. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis
4.3. Network Pharmacology Research on the Anti-Tumor Effect and Mechanism of HQD
4.3.1. Active Components Collection and Potential Targets Prediction of HQD
4.3.2. Identification of Therapeutic Targets Related to CRC Liver Metastasis
4.3.3. Integrated Analysis of Metabolome, Transcriptome, and Network Pharmacology to Screen the Key Targets for HQD Against CRC Liver Metastasis
4.3.4. Functional and Pathway Enrichment Analyses
4.3.5. Hub Targets and Core Ingredients Screening as Well as the Construction of Prescription–Herbs–Compounds–Targets–Pathways Network
4.4. Verification of the Mechanism of HQD in Hampering CRC Liver Metastasis
4.4.1. Molecular Docking
4.4.2. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
4.4.3. Molecular Morphology Assay by Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)
4.4.4. Bioinformatics Analysis for TCGA Datasets of CRC
Construction of Risk Score Model
Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Screening Between the Two Subtypes and Functional Enrichment Analysis
The Tumor Immune Microenvironment (TIME) Analysis
4.4.5. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data Analysis to Solidify Immunomodulatory Action of HQD
4.4.6. In Vitro Cellular Experimental Validation
Cell Viability Assay
Cell Migration and Invasion Experiments
Glutamine Detection
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GOT1 | Vesicle transport protein GOT1A |
| CYP1A2 | Cytochrome P450 1A2 |
| CA2 | Carbonic anhydrase 2 |
| HQD | Huang Qin Decoction |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| scRNA-seq | Single-cell RNA sequence |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| CAM | Complementary and alternative medicine |
| D4 | Day 4 |
| D12 | Day 12 |
| BLI | Bioluminescence imaging |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| QC | Quality control |
| TCMSP | Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform |
| OB | Oral bioavailability |
| DL | Drug-likeness |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| PPI | protein-protein interaction |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| EM | Energy minimization |
| NVT | Isothermal and isovolume |
| NPT | Isothermal and isobaric |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
| RMSF | Root mean square fluctuation |
| Rg | Radius of gyration |
| SASA | Solvent accessible surface area |
| MM/GBSA | Molecular Mechanics with Generalized Born and Surface Area |
| MM/PBSA | Molecular Mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area |
| FEL | Gibbs free energy landscape |
| AFM | Atomic force microscope |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas Program |
| COAD | Colon adenocarcinomas |
| READ | Rectal adenocarcinoma |
| TPM | Transcript per million |
| LASSO | Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator |
| KM | Kaplan–Meier |
| DEGs | Differential expressed genes |
| TIME | Tumor immune microenvironment |
| TIMER | Tumor Immune Estimation Resource |
| EPIC | Estimating the Proportion of Immune and Cancer Cells |
| CIBERSORT | Cell-type Identification by Estimating Relative Subsets of RNA Transcripts |
| UMI | Unique molecular identifier |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valderrama-Treviño, A.I.; Barrera-Mera, B.; Ceballos-Villalva, J.C.; Montalvo-Javé, E.E. Hepatic Metastasis from Colorectal Cancer. Euroasian J. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2017, 7, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.F.; Zhao, F.; Chen, D.; Liu, F.L. Current landscape of preoperative neoadjuvant therapies for initial resectable colorectal cancer liver metastasis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegiel, E.; Piotrowska, M.; Ptasznik, M.; Baran, A.; Lenart, J.; Podrażka, M.; Mazurek, J.; Stachowicz, H.; Bartos, W.; Adamczyk, M. Review of the effects of sodium butyrate on obesity, inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy and colorectal cancer. Prospect. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 22, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Deshmukh, R.; Majumder, R. A Comprehensive Review on the Use of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Cancer Treatment. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2024, 11, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwińska, M.; Kuśnierek, M. Lycium barbarum fruits–phytochemistry and activity of goji berries—from tradition to clinical studies. Prospect. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 22, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shi, K.; Wang, Y.; Zou, D.; Guo, S.; Li, T.; Xu, H.; Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Song, H.; et al. Effect of Huangqin Tang on Colonic Gene Expression in Rats with Ulcerative Colitis. Int. J. Genom. 2020, 2020, 4238757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, L.; Liu, H.; Feng, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Liu, B.; Liu, L.; Sun, J.; Chang, H.; et al. Huangqin tang alleviates colitis-associated colorectal cancer via amino acids homeostasisand PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway modulation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 334, 118597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Lin, J.; Li, W.; Wu, Z.; He, Z.; Huang, G.; Wang, J.; Ye, C.; Cheng, X.; Ding, C.; et al. Huangqin-tang ameliorates dextran sodium sulphate-induced colitis by regulating intestinal epithelial cell homeostasis, inflammation and immune response. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Li, W.Y.; Wan, Z.; Zhao, B.; He, Z.W.; Wu, Z.G.; Huang, G.L.; Wang, J.; Li, B.B.; Lu, Y.J.; et al. Huangqin-Tang Ameliorates TNBS-Induced Colitis by Regulating Effector and Regulatory CD4+ T Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 102021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Tang, D.X.; Yan, H.T.; Yang, B.; Yang, Z.; Long, F.X. Network pharmacology and molecular docking-based analyses to predict the potential mechanism of Huangqin decoction in treating colorectal cancer. World J. Clin. Cases 2023, 11, 4553–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Yang, L.J.; Fang, Z.; Fu, R.; Chen, J.B.; Liu, S.; Fei, B.Y. Anti-tumour effect of Huangqin Decoction on colorectal cancer mice through microbial butyrate mediated PI3K/Akt pathway suppression. J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Pan, S.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C.; Liang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. Huang Qin Decoction inhibits the initiation of experimental colitis associated carcinogenesis by controlling the PAD4 dependent NETs. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2022, 107, 154454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.; Bussom, S.; Guan, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Gullen, E.A.; Liu, S.H.; Cheng, Y.C. The four-herb Chinese medicine PHY906 reduces chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal toxicity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 45ra59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; He, X.; Man, V.H.; Ji, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. New application of in silico methods in identifying mechanisms of action and key components of anti-cancer herbal formulation YIV-906 (PHY906). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2019, 21, 23501–23513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.; Ren, Y.; Guan, F.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, W.; Xu, C.H.; Liu, S.H.; Cheng, Y.C. Mechanism Based Quality Control (MBQC) of Herbal Products: A Case Study YIV-906 (PHY906). Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network pharmacology: The next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.T.; Lu, Y.; Yan, S.K.; Xiao, X.; Rong, X.L.; Guo, J. Network Pharmacology in Research of Chinese Medicine Formula: Methodology, Application and Prospective. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 26, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, B.; Chen, S.; Lin, M.; Chen, Y.; Jin, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y. Applications of Network Pharmacology in Traditional Chinese Medicine Research. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. eCAM 2020, 2020, 1646905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.; He, C.; He, Y.; Chen, L.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Li, P. Network pharmacology: A bright guiding light on the way to explore the personalized precise medication of traditional Chinese medicine. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, G. Integrated bioinformatics and network pharmacology to identify the therapeutic target and molecular mechanisms of Huangqin decoction on ulcerative Colitis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Recent Metabolomics Analysis in Tumor Metabolism Reprogramming. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 763902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, S.; Di Gennaro, E.; Capone, F.; De Stefano, A.; Nasti, G.; Vitagliano, C.; Setola, S.V.; Tatangelo, F.; Delrio, P.; Izzo, F.; et al. Plasma metabolomics, lipidomics and cytokinomics profiling predict disease recurrence in metastatic colorectal cancer patients undergoing liver resection. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1110104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Li, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, B.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Li, Y. Pharmacodynamic substances in Salvia miltiorrhiza for prevention and treatment of hyperlipidemia and coronary heart disease based on lipidomics technology and network pharmacology analysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Fan, S.; Yu, H.; Shu, L.; Li, Y. A New Strategy for the Rapid Identification and Validation of the Direct Targets of Aconitine-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 4649–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, C.; Huang, W.; Gu, K.; Yu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; et al. Stepwise rapid tracking strategy to identify active molecules from Ixeris sonchifolia Hance based on “’affinity mass spectrometry-atomic force microscopy imaging”’ technology. Talanta 2020, 217, 121031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Li, B.; Xu, M.; Yang, T.; Hao, X. Traditional Chinese medicine for precancerous lesions of gastric cancer: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Saif, M.W.; Dutschman, G.E.; Li, X.; Lam, W.; Bussom, S.; Jiang, Z.; Ye, M.; Chu, E.; Cheng, Y.C. Identification of chemicals and their metabolites from PHY906, a Chinese medicine formulation, in the plasma of a patient treated with irinotecan and PHY906 using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5785–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.X.; Li, M.Y.; Lei, J.X.; Wu, Y.Z.; Li, Z.H.; Chen, L.M.; Zhou, C.L.; Su, J.Y.; Huang, G.X.; Huang, X.Q.; et al. Huangqin decoction ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis: Role of gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism, mTOR pathway and intestinal epithelial barrier. Phytomedicine 2022, 100, 154052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Wu, Y.Z.; Qiu, J.G.; Lei, J.X.; Li, M.X.; Xu, N.; Liu, Y.H.; Jin, Z.; Su, Z.R.; Lee, S.M.; et al. Huangqin Decoction ameliorates ulcerative colitis by regulating fatty acid metabolism to mediate macrophage polarization via activating FFAR4-AMPK-PPARα pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 311, 116430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.H.; Cheng, Y.C. Old formula, new Rx: The journey of PHY906 as cancer adjuvant therapy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.; Jiang, Z.; Guan, F.; Huang, X.; Hu, R.; Wang, J.; Bussom, S.; Liu, S.H.; Zhao, H.; Yen, Y.; et al. PHY906(KD018), an adjuvant based on a 1800-year-old Chinese medicine, enhanced the anti-tumor activity of Sorafenib by changing the tumor microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changou, C.A.; Shiah, H.S.; Chen, L.T.; Liu, S.; Luh, F.; Liu, S.H.; Cheng, Y.C.; Yen, Y. A Phase II Clinical Trial on the Combination Therapy of PHY906 Plus Capecitabine in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncologist 2021, 26, e367–e373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Han, X.; Guan, F.; Cheng, W.; Liu, S.-H.; Chen, L.; Cheng, Y.-C. Abstract 2724: YIV906 (PHY906) enhanced the antitumor activity of immune checkpoint blockade therapy: Anti-PD1 against liver cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.C.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Vykoukal, J.V.; Dennison, J.B.; Hanash, S.M. Targeting metabolic vulnerabilities of cancer: Small molecule inhibitors in clinic. Cancer Rep. 2019, 2, e1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Li, T.; Wang, W.; Gan, W.; Lv, S.; Zeng, Z.; Hou, Y.; Yan, Z.; Yang, M. Indoleamine 2, 3-Dioxygenase 1 and CD8 Expression Profiling Revealed an Immunological Subtype of Colon Cancer With a Poor Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 594098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimian, J.; Hadi, A.; Salehi-Sahlabadi, A.; Kafeshani, M. The Effect of Arginine Intake on Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review of Literatures. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2019, 8, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Shen, Y.; Li, M.; Dan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J. Integration of Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveals the Antitumor Mechanism Underlying Tadalafil in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 793499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, S.; Chang, H.; Zhuang, F.; Shi, Y.; Chang, L.; Ai, W.; Du, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling Identified Serum Metabolite Biomarkers and Related Metabolic Pathways of Colorectal Cancer. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 6858809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, M. Nitric Oxide (NO) and NO Synthases (NOS)-Based Targeted Therapy for Colon Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirniö, P.; Väyrynen, J.P.; Klintrup, K.; Mäkelä, J.; Karhu, T.; Herzig, K.H.; Minkkinen, I.; Mäkinen, M.J.; Karttunen, T.J.; Tuomisto, A. Alterations in serum amino-acid profile in the progression of colorectal cancer: Associations with systemic inflammation, tumour stage and patient survival. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, R.; Mori, S.; Kishi, S.; Sasaki, R.; Iwata, N.; Ohmori, H.; Sasaki, T.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Nakashima, C.; Goto, K.; et al. Linoleic Acid Upregulates Microrna-494 to Induce Quiescence in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, R.; Xu, L.; Yang, N.; Dai, S.; Xu, X.; et al. Comprehensive Investigation on Associations between Dietary Intake and Blood Levels of Fatty Acids and Colorectal Cancer Risk. Nutrients 2023, 15, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Wang, D.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, W. Huangqin Tang Interference With Colitis Associated Colorectal Cancer Through Regulation of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition and Cell Cycle. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 837217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lu, N.; Lv, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Ke, L. Role of Huangqin Decoction in Intestinal Homeostasis and Colon Carcinogenesis Based on “SREBP1 Cholesterol Metabolism Treg Cell Differentiation”. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. eCAM 2023, 2023, 6715978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encarnación-Rosado, J.; Sohn, A.S.W.; Biancur, D.E.; Lin, E.Y.; Osorio-Vasquez, V.; Rodrick, T.; González-Baerga, D.; Zhao, E.; Yokoyama, Y.; Simeone, D.M.; et al. Targeting pancreatic cancer metabolic dependencies through glutamine antagonism. Nat. Cancer 2024, 5, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.; Zheng, J.; Li, X. Inhibition of GOT1 sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlaka, A.P.; Virko, S.V.; Burlaka, A.A.; Chernobai, V.; Yatsyna, O.I.; Ganusevich, I.I. Cytochrome P450 content in primary tumors and liver metastases of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Exp. Oncol. 2020, 42, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Huang, W.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Shao, B.; Zhong, J.; Tang, M.; Liang, S.; Zhao, X.; et al. CA II, a potential biomarker by proteomic analysis, exerts significant inhibitory effect on the growth of colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Cai, G.; Zhou, B.; Li, D.; Zhao, A.; Xie, G.; Li, H.; Cai, S.; Xie, D.; Huang, C.; et al. A distinct metabolic signature of human colorectal cancer with prognostic potential. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamanian, M.Y.; Golmohammadi, M.; Abdullaev, B.; García, M.O.; Alazbjee, A.A.A.; Kumar, A.; Mohaamed, S.S.; Hussien, B.M.; Khalaj, F.; Hodaei, S.M.; et al. A narrative review on therapeutic potential of naringenin in colorectal cancer: Focusing on molecular and biochemical processes. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Hua, L.; Hu, M.; Zhu, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. The role of the natural compound naringenin in AMPK-mitochondria modulation and colorectal cancer inhibition. Phytomedicine 2024, 131, 155786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Byun, J.K.; Choi, Y.K.; Park, K.G. Targeting glutamine metabolism as a therapeutic strategy for cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S.; Valdés-Tresanco, M.E.; Valiente, P.A.; Moreno, E. AMDock: A versatile graphical tool for assisting molecular docking with Autodock Vina and Autodock4. Biol. Direct 2020, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.; Olson, A.J.; Goodsell, D.S. Automated prediction of ligand-binding sites in proteins. Proteins 2008, 70, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S.; Valdés-Tresanco, M.E.; Valiente, P.A.; Moreno, E. gmx_MMPBSA: A New Tool to Perform End-State Free Energy Calculations with GROMACS. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 6281–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.H.; LaBella, K.A.; Lin, Y.; Xu, P.; Lee, R.; Hsieh, C.E.; Yang, L.; Zhou, A.; Blecher, J.M.; Wu, C.J.; et al. Oncogenic KRAS Drives Lipofibrogenesis to Promote Angiogenesis and Colon Cancer Progression. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 2652–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; He, J.; Wang, Z.; Zang, Q.; Wei, J.; Song, X.; Abliz, Z. Optimization and Evaluation Strategy of Esophageal Tissue Preparation Protocols for Metabolomics by LC-MS. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3459–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; Hatcher, E.; Acharya, C.; Kundu, S.; Zhong, S.; Shim, J.; Darian, E.; Guvench, O.; Lopes, P.; Vorobyov, I.; et al. CHARMM general force field: A force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the CHARMM all-atom additive biological force fields. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Qian, Q.; Zhu, T.; Zong, W.; Shang, Y.; Jin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, Z.; Chu, Y.; et al. Cell Taxonomy: A curated repository of cell types with multifaceted characterization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D853–D860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Li, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Bai, J.; Chen, J.; Jiang, W.; Yang, K.; Ou, Q.; et al. CellMarker 2.0: An updated database of manually curated cell markers in human/mouse and web tools based on scRNA-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D870–D876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, S.; Ma, J.; Chen, Z.; Song, G.; Rao, D.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; et al. Spatiotemporal Immune Landscape of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis at Single-Cell Level. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Chang, I.; Ramos, R.; Kuan, C.-H.; Myung, P.; Plikus, M.V.; Nie, Q. Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, J.S.; Zhu, Q.; Huynh, C.; Sivaramakrishnan, P.; Preston, E.; Dueck, H.; Stefanik, D.; Tan, K.; Trapnell, C.; Kim, J.; et al. A lineage-resolved molecular atlas of C. elegans embryogenesis at single-cell resolution. Science 2019, 365, eaax1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Manno, G.; Soldatov, R.; Zeisel, A.; Braun, E.; Hochgerner, H.; Petukhov, V.; Lidschreiber, K.; Kastriti, M.E.; Lönnerberg, P.; Furlan, A.; et al. RNA velocity of single cells. Nature 2018, 560, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, F.; Lv, S.; Hou, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Integration of Untargeted Metabolomics, Network Pharmacology, Single-Cell RNA Sequencing, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Reveals GOT1, CYP1A2, and CA2 as Potential Targets of Huang Qin Decoction Preventing Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071052
Li T, Yan Z, Zhou M, Zhao W, Zhang F, Lv S, Hou Y, Zeng Z, Yang L, Zhou Y, et al. Integration of Untargeted Metabolomics, Network Pharmacology, Single-Cell RNA Sequencing, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Reveals GOT1, CYP1A2, and CA2 as Potential Targets of Huang Qin Decoction Preventing Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(7):1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071052
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tiegang, Zheng Yan, Mingxuan Zhou, Wenyi Zhao, Fang Zhang, Silin Lv, Yufang Hou, Zifan Zeng, Liu Yang, Yixin Zhou, and et al. 2025. "Integration of Untargeted Metabolomics, Network Pharmacology, Single-Cell RNA Sequencing, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Reveals GOT1, CYP1A2, and CA2 as Potential Targets of Huang Qin Decoction Preventing Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 7: 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071052
APA StyleLi, T., Yan, Z., Zhou, M., Zhao, W., Zhang, F., Lv, S., Hou, Y., Zeng, Z., Yang, L., Zhou, Y., Zhu, Z., Ren, X., & Yang, M. (2025). Integration of Untargeted Metabolomics, Network Pharmacology, Single-Cell RNA Sequencing, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Reveals GOT1, CYP1A2, and CA2 as Potential Targets of Huang Qin Decoction Preventing Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(7), 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18071052





