Novel Potent and Selective Dopamine D4 Receptor Piperidine Antagonists as Potential Alternatives for the Treatment of Glioblastoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Compounds 9–20
2.2. Binding Studies
2.3. Functional Studies
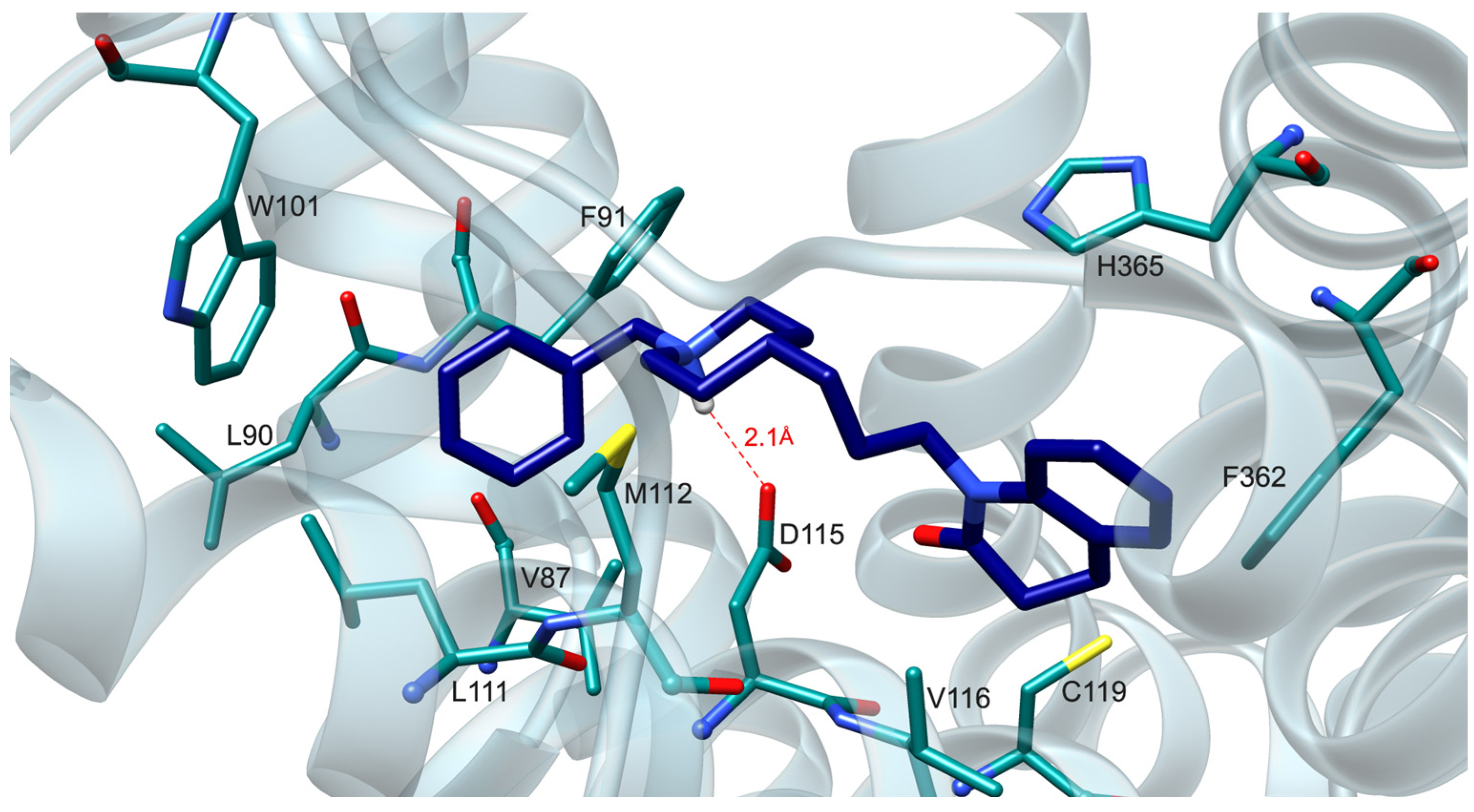
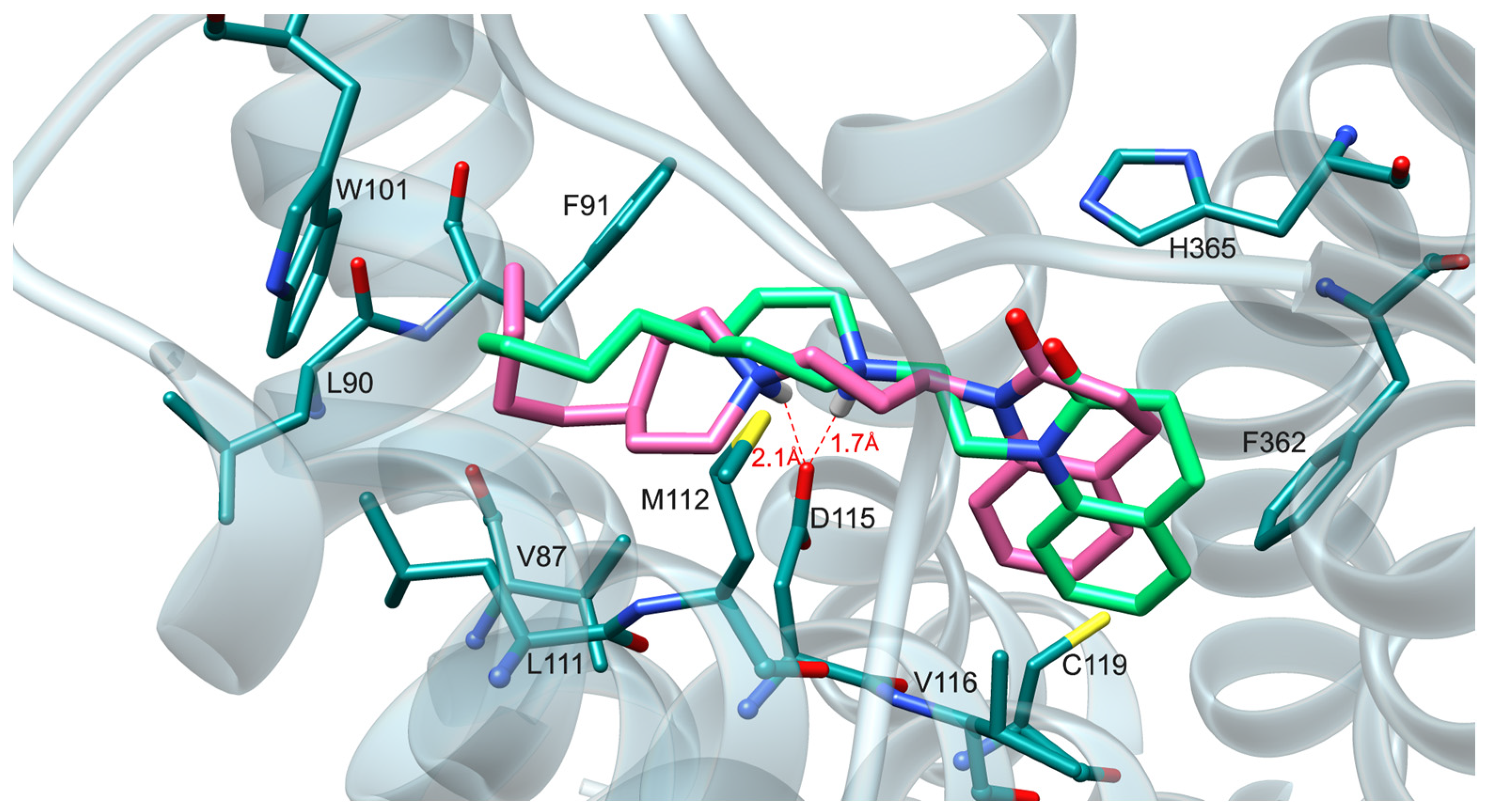
2.4. Molecular Modeling Studies
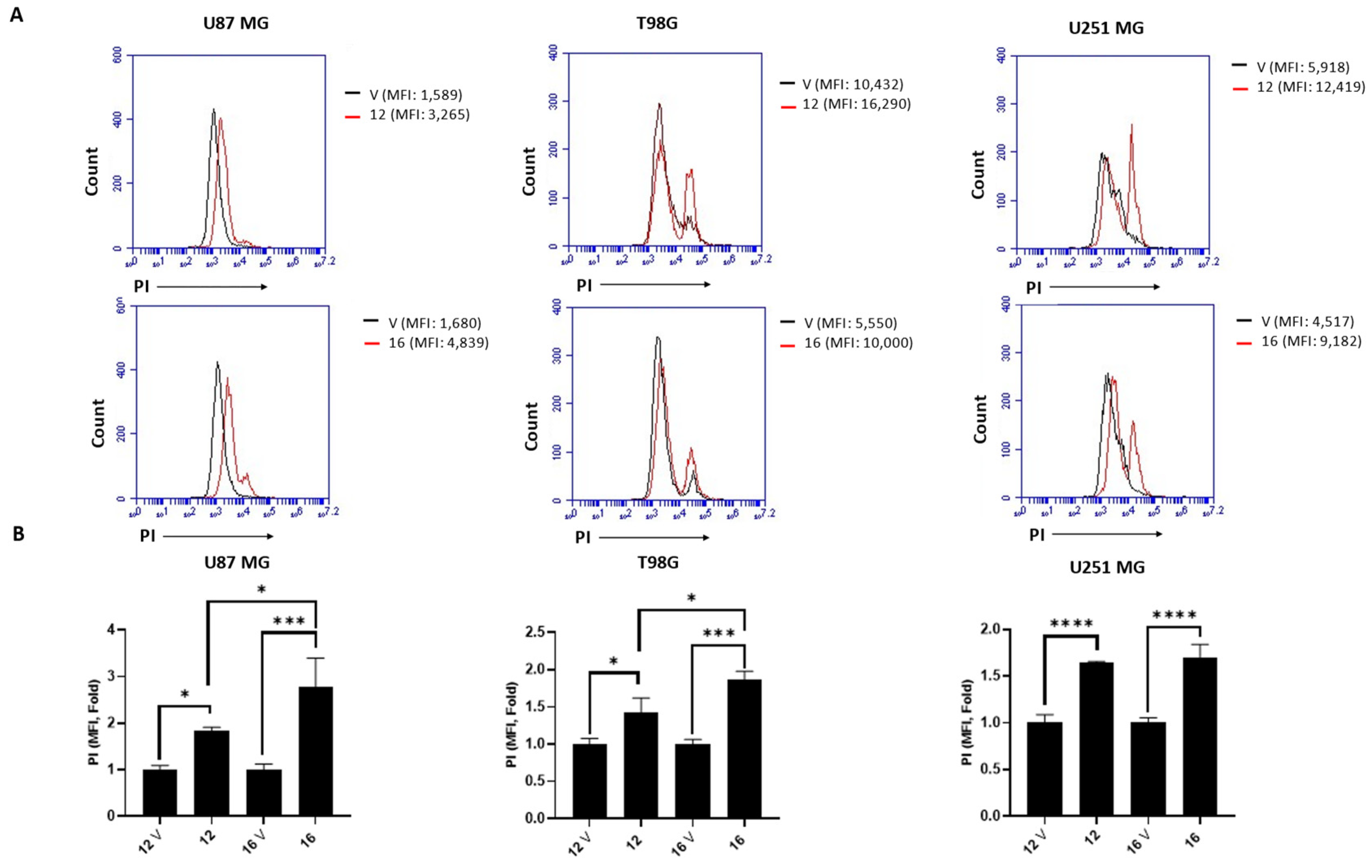
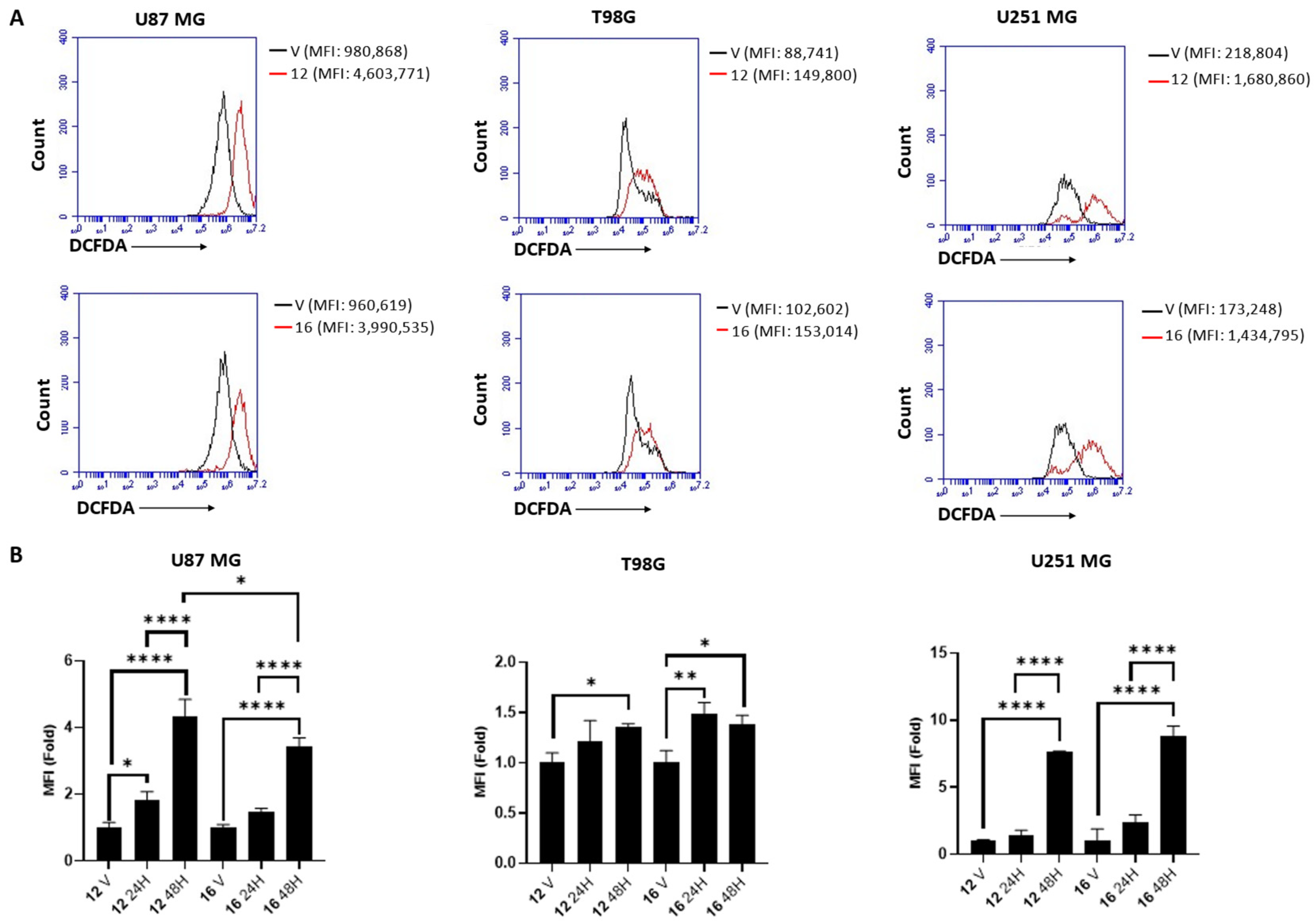
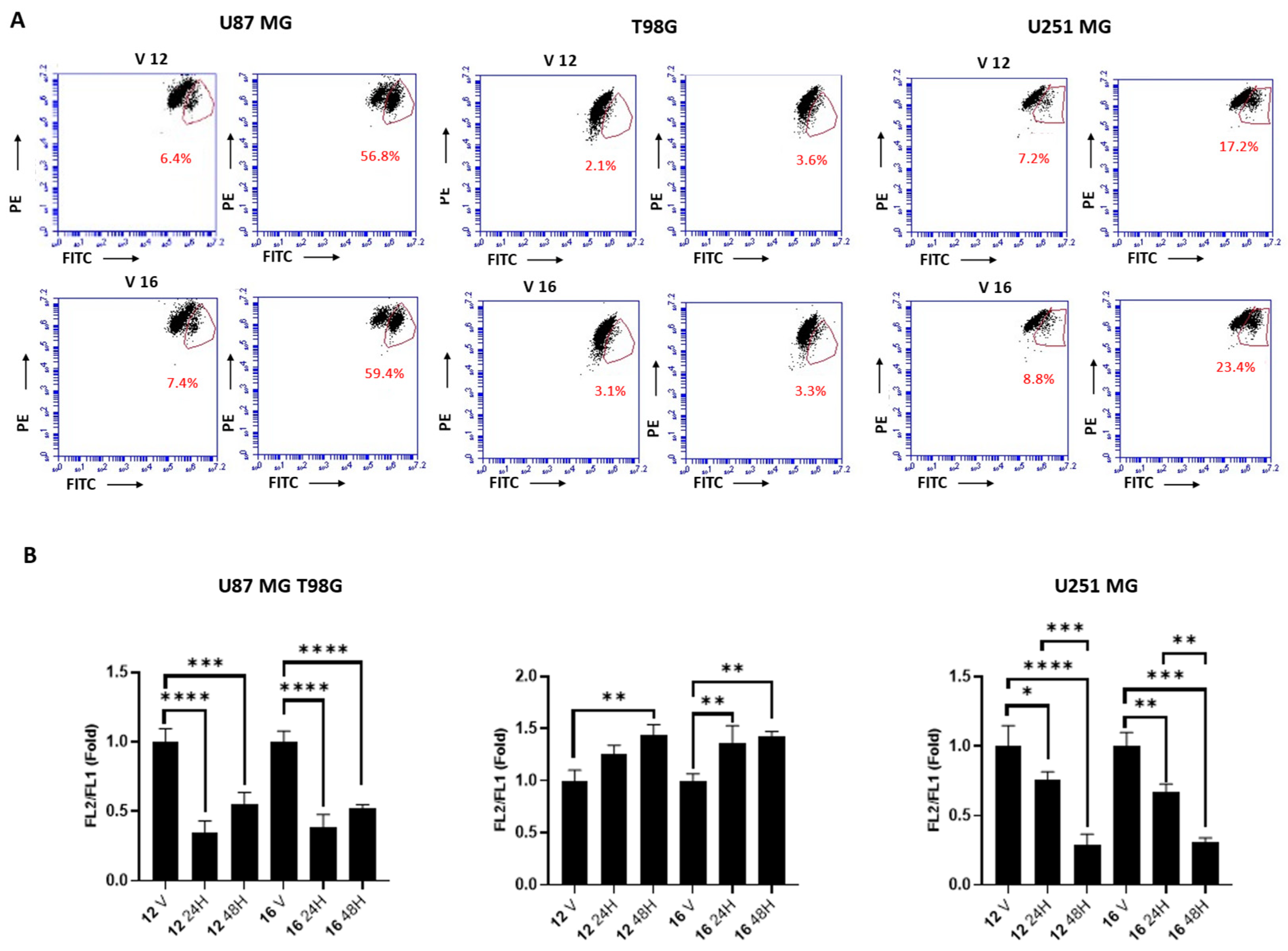
2.5. Biological Studies in GBM Cell Lines
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. 1-(2-(4-Butylpiperidin-1-yl)ethyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (9)
3.1.2. 1-(4-(4-Butylpiperidin-1-yl)butyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (10)
3.1.3. 1-(5-(4-Butylpiperidin-1-yl)pentyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (11)
3.1.4. 1-(2-(4-Benzylpiperidin-1-yl)ethyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (12)
3.1.5. 1-(4-(4-Benzylpiperidin-1-yl)butyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (13)
3.1.6. 1-(5-(4-Benzylpiperidin-1-yl)pentyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (14)
3.1.7. 1-(3-(1-Butylpiperidin-4-yl)propyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (15)
3.1.8. 1-(3-(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)propyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (16)
3.1.9. 1-(2-(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)ethyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (17)
3.1.10. 1-((1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (18)
3.1.11. 1-(3-(4-Phenyl-3,6-dihydropyridin-1(2H)-yl)propyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (19)
3.1.12. 1-(3-(3,4-Dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)propyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (20)
3.1.13. 4-Butylpyridine (21)
3.1.14. 4-Butylpiperidine (22)
3.1.15. 2-(4-Butylpiperidin-1-yl)ethan-1-ol (24)
3.1.16. 2-(4-Benzylpiperidin-1-yl)ethan-1-ol (25)
3.1.17. 4-(3-Hydroxypropyl)piperidine (26)
3.1.18. Ethyl 2-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-ylidene)acetate (27)
3.1.19. 3-(1-Butylpiperidin-4-yl)propan-1-ol (28)
3.1.20. 3-(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)propan-1-ol (29)
3.1.21. 2-(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)ethan-1-ol (30)
3.1.22. 1-(3-Bromopropyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (32)
3.1.23. 1-(4-Bromobutyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (33)
3.1.24. 1-(5-Bromopentyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one (34)
3.2. D2-like Radioligand Binding Assays
3.3. BRET Functional Assays
3.4. Experimental Details of Modeling Studies
3.5. Experimental Details of Biological Studies in GBM Cell Lines
3.5.1. Cell Lines
3.5.2. SRB Assay for Cell Viability
3.5.3. Measuring Cell Death by PI Staining
3.5.4. ROS Detection
3.5.5. Mitochondrial Transmembrane Potential (∆Ψm)
3.5.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
3.5.7. Colony Formation Assay
3.5.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DRs | Dopamine receptors |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| ICL3 | Third intracellular loop |
| GBM | Glioblastoma |
| BRET | Bioluminescence resonance energy transfer |
| SRB MD | Sulforhodamine B Molecular dynamics |
| TMZ | Temozolomide |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| MFI | Mean fluorescence intensity |
| DCFDA | 2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffer saline |
References
- Beaulieu, J.M.; Gainetdinov, R.R. The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 182–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, J.; Fan, T.; Guo, P.; Wang, J. Identification of functional divergence sites in dopamine receptors of vertebrates. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 83, 107140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulieu, J.M.; Espinoza, S.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Dopamine receptors—IUPHAR Review 13. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallone, D.; Picetti, R.; Borrelli, E. Structure and function of dopamine receptors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, R.M.; Chio, C.L.; Lajiness, M.E.; Goodman, L.V. Signal transduction pathways modulated by D2-like dopamine receptors. Adv. Pharmacol. 1998, 42, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgioni, G.; Del Bello, F.; Pavletić, P.; Quaglia, W.; Botticelli, L.; Cifani, C.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, E.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Piergentili, A. Recent findings leading to the discovery of selective dopamine D(4) receptor ligands for the treatment of widespread diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 212, 113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botticelli, L.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, E.; Del Bello, F.; Giorgioni, G.; Piergentili, A.; Romano, A.; Quaglia, W.; Cifani, C.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V. Underlying Susceptibility to Eating Disorders and Drug Abuse: Genetic and Pharmacological Aspects of Dopamine D4 Receptors. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boateng, C.A.; Nilson, A.N.; Placide, R.; Pham, M.L.; Jakobs, F.M.; Boldizsar, N.; McIntosh, S.; Stallings, L.S.; Korankyi, I.V.; Kelshikar, S.; et al. Pharmacology and Therapeutic Potential of Benzothiazole Analogues for Cocaine Use Disorder. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 12141–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsley, C.W.; Hopkins, C.R. Return of D(4) Dopamine Receptor Antagonists in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7233–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, V.; Sanyal, S.; Buchwaldt, S.; Paterson, A.; Jovanovic, V.; Van Tol, H.H.M. Modulation of Intracellular Cyclic AMP Levels by Different Human Dopamine D4 Receptor Variants. J. Neurochem. 1995, 65, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariano, M.A.; Wang, J.; Noblett, K.L.; Larson, E.R.; Sibley, D.R. Cellular distribution of the rat D4 dopamine receptor protein in the CNS using anti-receptor antisera. Brain Res. 1997, 752, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolma, S.; Selvadurai, H.J.; Lan, X.; Lee, L.; Kushida, M.; Voisin, V.; Whetstone, H.; So, M.; Aviv, T.; Park, N.; et al. Inhibition of Dopamine Receptor D4 Impedes Autophagic Flux, Proliferation, and Survival of Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavletić, P.; Semeano, A.; Yano, H.; Bonifazi, A.; Giorgioni, G.; Piergentili, A.; Quaglia, W.; Sabbieti, M.G.; Agas, D.; Santoni, G.; et al. Highly Potent and Selective Dopamine D4 Receptor Antagonists Potentially Useful for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 12124–12139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, N.; Neumeyer, J.L.; Baldessarini, R.J.; Zhen, X.; Zhang, A. Update 1 of: Recent progress in development of dopamine receptor subtype-selective agents: Potential therapeutics for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, Pr123–Pr178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wacker, D.; Levit, A.; Che, T.; Betz, R.M.; McCorvy, J.D.; Venkatakrishnan, A.J.; Huang, X.P.; Dror, R.O.; Shoichet, B.K.; et al. D(4) dopamine receptor high-resolution structures enable the discovery of selective agonists. Science 2017, 358, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cao, C.; He, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.C. Crystal structure of dopamine receptor D4 bound to the subtype selective ligand, L745870. eLife 2019, 8, e48822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Wang, S.; Balius, T.E.; Singh, I.; Levit, A.; Moroz, Y.S.; O’Meara, M.J.; Che, T.; Algaa, E.; Tolmachova, K.; et al. Ultra-large library docking for discovering new chemotypes. Nature 2019, 566, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graßl, F.; Bock, L.; Huete-Huerta González, Á.; Schiller, M.; Gmeiner, P.; König, J.; Fromm, M.F.; Hübner, H.; Heinrich, M.R. Exploring Structural Determinants of Bias among D4 Subtype-Selective Dopamine Receptor Agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 9710–9730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levoin, N.; Murthy, A.V.R.; Narendar, V.; Kumar, N.S.; Aparna, P.; Bhavani, A.K.D.; Reddy, C.R.; Mosset, P.; Grée, R. Discovery of potent dual ligands for dopamine D4 and σ1 receptors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2022, 69, 116851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, K.T.; Mashinson, V.; Vadukoot, A.K.; Hopkins, C.R. Discovery and characterization of benzyloxy piperidine based dopamine 4 receptor antagonists. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 61, 128615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bello, F.; Bonifazi, A.; Giorgioni, G.; Cifani, C.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Petrelli, R.; Piergentili, A.; Fontana, S.; Mammoli, V.; Yano, H. 1-[3-(4-Butylpiperidin-1-yl) propyl]-1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydroquinolin-2-one (77-LH-28-1) as a model for the rational design of a novel class of brain penetrant ligands with high affinity and selectivity for dopamine D4 receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3712–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, A.I.; Edwards, P.D.; Rieker, W.F.; Bailey, T.R. .alpha.-Amino carbanions via formamidines. Alkylation of pyrrolidines, piperidines, and related heterocycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 3270–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, N.; Besada, P.; Viña, D.; Sturlese, M.; Moro, S.; Terán, C. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling studies of phthalazin-1(2H)-one derivatives as novel cholinesterase inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 46170–46185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbertson, M.S.; Chang, C.T.C.; Duggan, M.E.; Gould, R.J.; Halczenko, W.; Hartman, G.D.; Laswell, W.L.; Lynch, J.J., Jr.; Lynch, R.J. Non-Peptide Fibrinogen Receptor Antagonists. 2. Optimization of a Tyrosine Template as a Mimic for Arg-Gly-Asp. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 2537–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, J.-M.; Parrot, I.; Sippl, W.; Rival, Y.M.; Wermuth, C.G. Design, Synthesis, and Structure–Activity Relationships of a Series of 3-[2-(1-Benzylpiperidin-4-yl)ethylamino]pyridazine Derivatives as Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 2707–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifazi, A.; Newman, A.H.; Keck, T.M.; Gervasoni, S.; Vistoli, G.; Del Bello, F.; Giorgioni, G.; Pavletić, P.; Quaglia, W.; Piergentili, A. Scaffold Hybridization Strategy Leads to the Discovery of Dopamine D(3) Receptor-Selective or Multitarget Bitopic Ligands Potentially Useful for Central Nervous System Disorders. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 3638–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bello, F.; Ambrosini, D.; Bonifazi, A.; Newman, A.H.; Keck, T.M.; Giannella, M.; Giorgioni, G.; Piergentili, A.; Cappellacci, L.; Cilia, A.; et al. Multitarget 1,4-Dioxane Compounds Combining Favorable D(2)-like and 5-HT(1A) Receptor Interactions with Potential for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease or Schizophrenia. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2222–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazonova, E.V.; Chesnokov, M.S.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Kopeina, G.S. Drug toxicity assessment: Cell proliferation versus cell death. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.G.; Fine, H.A. Diffuse Glioma Heterogeneity and Its Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, C.; Lu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Liu, K.; Luo, T.; Zhu, D.; et al. Pristimerin triggers AIF-dependent programmed necrosis in glioma cells via activation of JNK. Cancer Lett. 2016, 374, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, G.; Han, G.; Feng, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; Jin, F. Emodin induced necroptosis in the glioma cell line U251 via the TNF-α/RIP1/RIP3 pathway. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, C.; Navarra, G.; Coppola, L.; Avilia, G.; Pastorino, O.; Della Monica, R.; Buonaiuto, M.; Torelli, G.; Caiazzo, P.; Bifulco, M.; et al. N6-isopentenyladenosine induces cell death through necroptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, A.; Marinelli, O.; Morelli, M.B.; Iannarelli, R.; Amantini, C.; Russotti, D.; Santoni, G.; Maggi, F.; Nabissi, M. Isofuranodiene synergizes with temozolomide in inducing glioma cells death. Phytomedicine 2019, 52, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, C. The promise of mitochondria in the treatment of glioblastoma: A brief review. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Xu, Y.; Peng, S.; Qian, S.; Zhang, X.; Shen, S.; Yang, J.; Ye, J. Sodium butyrate opens mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) to induce a proton leak in induction of cell apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, H.M.; Shen, K. Intracellular and microenvironmental regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential in cancer cells. WIREs Mech. Dis. 2023, 15, e1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, G.; Das, S.; Bola Sadashiva, S.R. Berberine, a natural alkaloid sensitizes human hepatocarcinoma to ionizing radiation by blocking autophagy and cell cycle arrest resulting in senescence. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.P.; Huang, W.W.; Tsai, K.F.; Shiao, L.R.; Yang, Z.H.; Tseng, S.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Chan, P.; Leung, Y.M. CDN1163, a SERCA activator, causes intracellular Ca(2+) leak, mitochondrial hyperpolarization and cell cycle arrest in mouse neuronal N2A cells. Neurotoxicology 2023, 98, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Swargiary, G.; Singh, K.K. Natural Agents Targeting Mitochondria in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, F.; Pavletić, P.; Bonifazi, A.; Del Bello, F.; Giorgioni, G.; Piergentili, A.; Amantini, C.; Zeppa, L.; Sabato, E.; Vistoli, G.; et al. New Arylpiperazines as Potent and Selective Dopamine D4 Receptor Ligands Potentially Useful to Treat Glioblastoma. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 7441–7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bello, F.; Bonifazi, A.; Giorgioni, G.; Piergentili, A.; Sabbieti, M.G.; Agas, D.; Dell’Aera, M.; Matucci, R.; Górecki, M.; Pescitelli, G.; et al. Novel Potent Muscarinic Receptor Antagonists: Investigation on the Nature of Lipophilic Substituents in the 5- and/or 6-Positions of the 1,4-Dioxane Nucleus. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 5763–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedretti, A.; Mazzolari, A.; Gervasoni, S.; Fumagalli, L.; Vistoli, G. The VEGA suite of programs: An versatile platform for cheminformatics and drug design projects. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 1174–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.J. Optimization of parameters for semiempirical methods VI: More modifications to the NDDO approximations and re-optimization of parameters. J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korb, O.; Stützle, T.; Exner, T.E. Empirical scoring functions for advanced protein-ligand docking with PLANTS. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz, K.M., Jr.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1668–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, E.L.; Cheng, X.; Jo, S.; Rui, H.; Song, K.C.; Dávila-Contreras, E.M.; Qi, Y.; Lee, J.; Monje-Galvan, V.; Venable, R.M.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Membrane Builder toward realistic biological membrane simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, C.J.; Walker, R.C.; Gould, I.R. Lipid21: Complex Lipid Membrane Simulations with AMBER. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2022, 18, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Man, V.H.; Yang, W.; Lee, T.S.; Wang, J. A fast and high-quality charge model for the next generation general AMBER force field. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM database and PPM web server: Resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D370–D376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterlini, M.G.; Ferguson, D.M. Constant temperature simulations using the Langevin equation with velocity Verlet integration. Chem. Phys. 1998, 236, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kräutler, V.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Hünenberger, P.H. A fast SHAKE algorithm to solve distance constraint equations for small molecules in molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for Processing and Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Trajectory Data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Compound | Structure | pKi | D2R/ D4R | D3R/ D4R | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2R | D3R | D4R | ||||
| 7 | 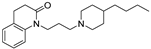 | 6.17 ± 0.16 | 6.21 ± 0.13 | 9.01 ± 0.04 | 691 | 631 |
| 8 | 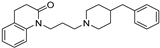 | 6.04 ± 0.06 | 5.74 ± 0.28 | 8.90 ± 0.19 | 724 | 1445 |
| 9 |  | 5.05 ± 0.08 | 4.88 ± 0.05 | 7.76 ± 0.11 | 512 | 758 |
| 10 | 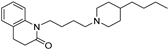 | 5.87 ± 0.04 | 6.51 ± 0.10 | 7.63 ± 0.08 | 58 | 13 |
| 11 | 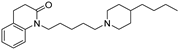 | 6.52 ± 0.09 | 6.54 ± 0.07 | 7.28 ± 0.04 | 5.8 | 5.5 |
| 12 | 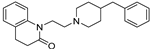 | 6.18 ± 0.12 | 6.03 ± 0.04 | 9.18 ± 0.08 | 1000 | 1413 |
| 13 | 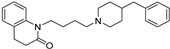 | 5.97 ± 0.08 | 6.52 ± 0.03 | 7.65 ± 0.13 | 48 | 13 |
| 14 | 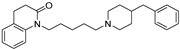 | 6.09 ± 0.09 | 6.39 ± 0.12 | 7.34 ± 0.06 | 18 | 8.9 |
| 15 | 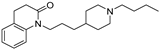 | 4.99 ± 0.06 | 5.97 ± 0.07 | 6.12 ± 0.06 | 13 | 1.4 |
| 16 | 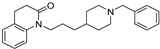 | 5.44 ± 0.03 | 5.70 ± 0.12 | 8.79 ± 0.15 | 2239 | 1230 |
| 17 |  | 4.90 ± 0.08 | 5.09 ± 0.05 | 6.52 ± 0.10 | 42 | 27 |
| 18 |  | 4.88 ± 0.07 | 5.12 ± 0.10 | 6.56 ± 0.05 | 48 | 28 |
| 19 |  | 6.24 ± 0.07 | 6.61 ± 0.11 | 8.82 ± 0.04 | 380 | 162 |
| 20 | 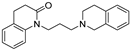 | 6.35 ± 0.03 | 6.64 ± 0.08 | 7.55 ± 0.13 | 16 | 8.1 |
| Dopamine | L745,870 | 12 | 16 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pEC50 (pIC50 for antagonists) | Go | 8.29 ± 0.05 | (7.08 ± 0.16) | N.D. (6.67 ± 0.08) | 8.36 ± 0.37 (7.21 ± 0.15) |
| Gi | 8.05 ± 0.10 | (6.83 ± 0.21) | 10.37 ± 1.64 (6.90 ± 0.29) | 10.53 ± 2.1 (7.41 ± 0.23) | |
| βArr2 | 7.57 ± 0.17 | (7.97 ± 0.23) | N.D. (6.89 ± 0.31) | 7.51 ± 0.64 (8.74 ± 0.45) | |
| Emax (Imax for antagonists) | Go | 100.0 ± 1.4 | (−74.4 ± 4.1) | N.D. (−68.9 ± 2.4) | 23.4 ± 2.5 (−46.7 ± 2.6) |
| Gi | 100.0 ± 2.9 | (−76.9 ± 5.5) | 15.6 ± 3.8 (−67.9 ± 8.3) | 15.5 ± 3.7 (−69.9 ± 5.5) | |
| βArr2 | 100.0 ± 4.9 | (−90.9 ± 6.0) | N.D. (−46.6 ± 6.0) | 17.9 ± 3.9 (−43.1 ± 5.2) |
| U87 MG (GI50, µM) | T98G (GI50, µM) | U251 MG (GI50, µM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 52.9 ± 0.6 | 25.7 ± 1.9 | 87.5 ± 1.0 |
| 16 | 65.5 ± 1.3 | 23.0 ± 4.8 | 90.4 ± 3.3 |
| TMZ | >200 | >200 | >200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matteucci, F.; Pavletić, P.; Bonifazi, A.; Garland, R.; Yano, H.; Amantini, C.; Zeppa, L.; Sabato, E.; Vistoli, G.; Mammoli, V.; et al. Novel Potent and Selective Dopamine D4 Receptor Piperidine Antagonists as Potential Alternatives for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050739
Matteucci F, Pavletić P, Bonifazi A, Garland R, Yano H, Amantini C, Zeppa L, Sabato E, Vistoli G, Mammoli V, et al. Novel Potent and Selective Dopamine D4 Receptor Piperidine Antagonists as Potential Alternatives for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050739
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatteucci, Federica, Pegi Pavletić, Alessandro Bonifazi, Rian Garland, Hideaki Yano, Consuelo Amantini, Laura Zeppa, Emanuela Sabato, Giulio Vistoli, Valerio Mammoli, and et al. 2025. "Novel Potent and Selective Dopamine D4 Receptor Piperidine Antagonists as Potential Alternatives for the Treatment of Glioblastoma" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050739
APA StyleMatteucci, F., Pavletić, P., Bonifazi, A., Garland, R., Yano, H., Amantini, C., Zeppa, L., Sabato, E., Vistoli, G., Mammoli, V., Cappellacci, L., Del Bello, F., Giorgioni, G., Petrelli, R., Piergentili, A., Quaglia, W., & Piergentili, A. (2025). Novel Potent and Selective Dopamine D4 Receptor Piperidine Antagonists as Potential Alternatives for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050739















