Abstract
Parkinson’s disease is associated with the loss of more than 40% of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. One of the therapeutic options for restoring striatal dopamine levels is the administration of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-Dopa). However, Parkinson’s disease patients on long-term L-Dopa therapy often experience motor complications, such as dyskinesias. L-Dopa-induced dyskinesias (LIDs) manifest as abnormal involuntary movements and are produced by elevated striatal dopamine levels, which lead to increased activity of the basal ganglia direct striato-nigral pathway. Dopamine D1 receptors are more than 95% confined to neurons of the direct pathway, where they colocalize with histamine H3 receptors. There is evidence of functional interactions between D1 and H3 receptors, and here we review the consequences of these interactions on LIDs.
1. Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is one of the most common neurodegenerative disorders worldwide, only second to Alzheimer’s disease. PD has a prevalence of more than 6 million people [1,2] and is originated by the progressive loss of the dopaminergic neurons located in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) [1,3]. The administration of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-Dopa) is one of the most effective treatments for PD motor symptoms [2,4]. However, in the long term, L-Dopa administration induces abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs), known as L-Dopa-induced dyskinesias (LIDs) [5].
LIDs are associated with elevated dopamine (DA) levels in the nucleus striatum, which lead to molecular and cellular alterations in the function of the basal ganglia (BG) direct pathway (see below and Figure 1C) [4,6,7,8]. The post-synaptic changes include cellular redistribution of DA D1-like receptors (D1Rs), sensitization of D1R intracellular signaling, and abnormal gene expression in D1R-expressing neurons [4,9,10].
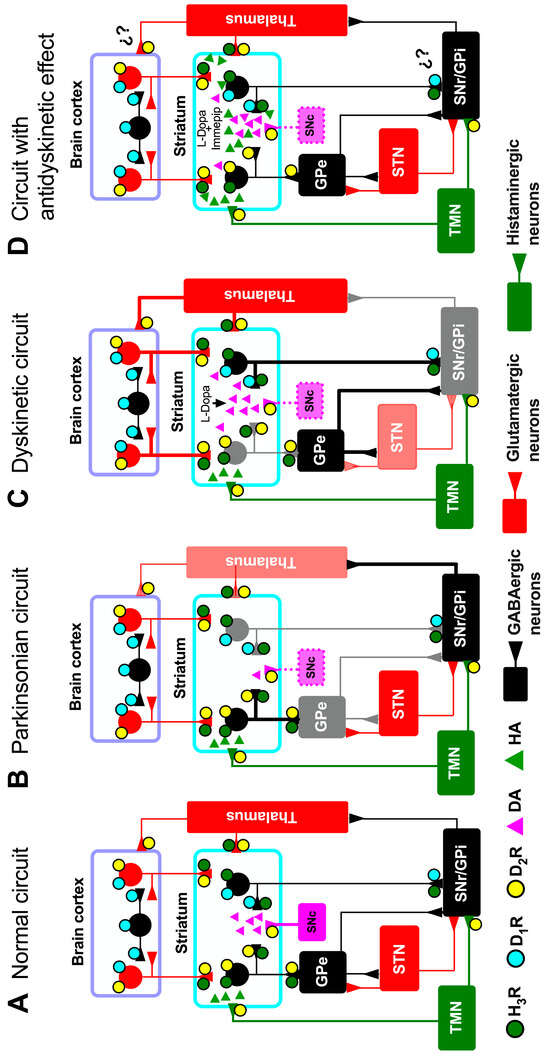
Figure 1.
Schematic view of the basal ganglia synaptic circuitry. (A) Normal circuit; (B) parkinsonian circuit; (C) dyskinetic circuit, and (D) circuit with the antidyskinetic effect of the chronic administration of the H3R agonist immepip. Black lines represent inhibitory neuronal pathways, while red lines represent excitatory projections. The thickness of the lines and the color intensity or lightness indicate the degree of activation of each projection. The grey tone in the external segment of the globus pallidus (GPe; 1B), the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr; 1C), the internal segment of the globus pallidus (GPi; 1C), thalamus (1B), and the subthalamic nucleus (STN; 1C) reflect differences in activation compared to other regions shown in black. Dotted pink lines indicate dopaminergic depletion in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc). MSN axons project to the SNr and the GPi through a direct pathway and to the GPe, which in turn projects to the STN, forming the indirect pathway that projects to the SNr and GPi. The legends ‘L-Dopa’ and ‘L-Dopa + immepip’ for the striatum in panels C and D indicate the systemic administration of L-Dopa alone or in conjunction with the H3R agonist immepip, respectively. ¿?, unconfirmed effect. DA, dopamine; HA, histamine; TMN, tuberomammillary nucleus.
In LIDs, the hyperactivity of the direct BG pathway is critical for the observed hypoactivity of the GABAergic pallido/nigro-thalamic projections, resulting from increased activity of the glutamatergic thalamo-cortical pathway (Figure 1C) [11,12]. Amantadine is highly effective for treating LIDs by antagonizing glutamate receptors and reducing excitatory neurotransmission [2,13,14]. However, the withdrawal of amantadine aggravates LIDs after ~7 days, indicating action reversibility and a rebound effect [15].
The BG direct and indirect pathways are initiated by the projecting axons of the striatal GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSNs), which constitute 95% of the striatal neuronal population [16]. The striatum is innervated by axons of dopaminergic and histaminergic neurons located in the SNc and the hypothalamus tuberomammillary nucleus, respectively [16]. Histamine H3 receptors (H3Rs) are co-expressed with D1Rs in the MSNs of the BG striato-nigral or direct pathway and with D2-like receptors (D2Rs) in striato-pallidal MSNs that originate from the first segment of the indirect pathway [17].
D1Rs comprise the D1 and D5 subtypes, both coupled to Gαs proteins and thus to the activation of the cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) signaling pathway. D2Rs include the D2, D3, and D4 subtypes, all coupled to Gαi/o proteins. The D2R main signaling mechanisms include the inhibition of the cAMP/PKA pathway and reduction in calcium entry through voltage-activated Ca2+ channels involved in neurotransmitter release [18].
H3Rs couple to Gαi/o proteins, and both the Gαi/o subunits and the Gβγ dimers mediate G protein-dependent signaling. The actions reported are: (a) inhibition of cAMP formation; (b) inhibition of the Na+/H+ exchanger; (c) inhibition of N- and P/Q-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels; (d) activation of G protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channels (GIRKs); (e) phospholipase C (PLC) activation; (f) activation of the mitogen-activated kinase (MAPK) pathway; (g) activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway; and h) phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activation [19].
As indicated above, MSNs of the BG direct pathway co-express H3Rs and D1Rs [17], and in slices of rat substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) and striatum H3R activation inhibits D1R-stimulated cAMP accumulation and GABA release [20,21,22], indicating an opposite functional interaction. However, there is still limited information on whether this functional interaction affects LIDs, originating from molecular and cellular changes in the BG circuitry, with D1R overstimulation playing a causative role. In this review, we examine the reported effects of co-activating D1Rs and H3Rs on BG function and their potential influence on LIDs.
2. Striatal Synaptic Circuitry
The striatum is the main target of the BG synaptic afferents and receives two major glutamatergic inputs, the first from all areas of the cerebral cortex [23,24] and the second from the thalamus [25] (see Figure 1A). The number of synaptic contacts of cortical afferents with MSNs nearly equals that of the thalamic inputs [23,25]; however, in terms of synaptic interactions and functional properties, the cortico-striatal projections are highly dominant [25,26,27]. The striatum also receives glutamatergic inputs from other brain regions, namely the subthalamic nucleus (STN), the pedunculopontine nucleus, the amygdala, and the hippocampus [28,29,30,31,32].
The external segment of the external globus pallidus (GPe) is a GABAergic nucleus that receives massive synaptic inputs from the striatal MSNs and provides GABAergic projections to the STN and back to the striatum [16,33]. Other neurons in the striatal circuit include GABAergic and cholinergic interneurons, which represent almost 5% of all striatal neurons in rodents and up to 23% in primates [16].
The striatum thus integrates diverse synaptic inputs, predominantly glutamatergic information from the cerebral cortex and thalamus and dopaminergic input from the SNc. In turn, through the direct and indirect pathways, the striatum modulates the function of the BG output nuclei, namely SNr and the globus pallidus internal segment (GPi) in primates and humans or entopeduncular nucleus in rodents. In recent decades, it has been clear that histaminergic innervation (see Figure 1A) [16,34,35] also plays a relevant role in modulating the striatal function, thus contributing to the intricate regulatory mechanisms involved in motor control, cognition, and neuropsychiatric conditions [34,36,37,38].
3. Distribution of D1Rs and H3Rs in the Striatum
H3Rs are localized on histaminergic terminals as autoreceptors controlling histamine synthesis and release [19]. In the striatum, H3Rs are co-expressed by D1Rs in the MSNs of the direct BG pathway [17,39] and with D2 receptors (D2Rs) in MSNs of the indirect pathway [40,41]. In both MSN subpopulations, H3Rs are located in the somato-dendritic region and in axons that project to the GPe for the indirect pathway, and for the direct pathway on the soma and nerve terminals of MSNs that project to the output nuclei of the BG (SNr and GPi) [42]. They are also present in MSN collateral axons that innervate MSNs of the same or different subpopulations (see Figure 1A) [43].
In addition, H3Rs are located on striatal glutamatergic and dopaminergic afferents from the cerebral cortex and SNc, respectively, as well as in intrinsic interneurons [17]. For cholinergic interneurons, the expression of H3R mRNA was confirmed in both the ventral (nucleus accumbens) and dorsal striatum [44]. However, H3R activation hyperpolarizes the resting membrane potential and decreases the spontaneous firing rate of cholinergic interneurons in the nucleus accumbens but not in the striatum. Furthermore, the lack of effect of H3R activation on acetylcholine release from nucleus accumbens synaptosomes suggests a trans-synaptic mechanism involving reduced acetylcholine release, mediated by somatodendritic H3Rs, which leads to decreased activation of nicotinic receptors located on dopaminergic terminals [44].
Striatal interneurons also express dopamine receptors. Functionally, D1R activation depolarizes GABAergic low-threshold spike (LTS) interneurons and results in excitatory post-synaptic currents (EPSCs) in cholinergic and fast-spiking (FSI) GABAergic interneurons. D2R activation induces inhibitory post-synaptic currents (IPSCs) in cholinergic interneurons [45,46,47]. Thus, a functional interaction between H3Rs and D1Rs can also occur in striatal cholinergic and GABAergic interneurons.
Altogether, this information indicates that via H3R activation, histamine modulates key striatal synaptic pathways, influencing histaminergic, glutamatergic, and dopaminergic inputs to MSNs and striatal interneurons.
4. Functional Interaction Between H3Rs and D1Rs in the Striato-Nigral MSNs
There is information that supports the functional interaction between H3Rs and D1Rs in striato-nigral MSNs and, thus, in the direct BG pathway.
The first evidence for this interaction was the report that in slices of rat striatum and SNr, D1R activation facilitated depolarization-evoked GABA release, and H3R activation by the selective agonist immepip inhibited the component of release due to D1R stimulation [20,22]. Also in striatal slices, H3R activation inhibited D1R-induced cAMP accumulation, an action likely to take place in MSN bodies and their collaterals [21].
Further evaluation showed that the facilitatory action of D1Rs was mimicked by 8-bromo-cyclic AMP, prevented by PKA inhibition, and markedly reduced by ω-agatoxin TK, a blocker of P/Q-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, but not by ω-conotoxin MVIIA or nimodipine (blockers of N- or L-type Ca2+ channels, respectively). Moreover, the effect of 8-bromo-cyclic AMP was practically abolished by H3R activation [48]. Together, these data indicate that D1R-induced facilitation and H3R-mediated inhibition of GABA release from D1-MSN axon terminals converge at voltage-activated P-/Q-type Ca2+ channels present in the striato-nigral axons and the collaterals of D1R-expressing MSNs that remain in the striatum.
One heterodimeric configuration between D1Rs and H3Rs was confirmed on striato-nigral MSNs, where D1R activation facilitates the H3R-mediated stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in striatal slices [49,50]. This effect was not found in striato-pallidal MSNs [50]. Furthermore, H3Rs can form heteroreceptor complexes with D1Rs and glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. In the D1R/H3R dimer, H3R activation reduces D1R affinity for selective agonists and shifts D1R coupling from Gαs to Gαi/o proteins [49,51], and in the D1R/H3R/NMDA receptor complex, H3R activation prevents D1R-induced ERK-1/2 phosphorylation [52].
In the same line, by using microdialysis, we reported an in vivo functional interaction between H3Rs and D1Rs, in which striatal DA efflux is reduced by the intra-striatal infusion of the D1R agonist SKF-38393, an effect counteracted by the co-infusion of the H3R agonist immepip [53]. This result indicates that the histaminergic system participates in a negative feedback mechanism that controls dopaminergic transmission in the striatum and involves post-synaptic D1Rs and D2Rs as well as pre-synaptic D2Rs.
In conclusion, H3Rs and D1Rs interact in striato-nigral MSNs, modulating GABA release, the cAMP/PKA signaling pathway, and voltage-activated Ca2⁺ channels. The H3R-D1R functional interaction also contributes to a feedback mechanism that controls striatal neurotransmission, and through heteroreceptor complexes, H3Rs and D1Rs regulate dopaminergic signaling in the striatum.
5. Functional Interaction Between H3Rs and D1Rs and Its Effect on Movement
It is well established that the chronic administration of L-Dopa in PD patients and animals lesioned with neurotoxins (6-OHDA or MPTP) will lead to dyskinesias [4,7,9]. A causal factor of LIDs is the development of D1R sensitization in the striatum, with receptors responding atypically to the administration of dopaminergic drugs [4]. The experimental evidence previously reviewed suggested a role for the functional interaction between H3Rs and D1Rs in the control of movement. In this line, the pioneer study by Papathanou et al. [54] showed that the systemic administration of a single dose of the H3R agonist immepip at 1, 5, or 10 mg/kg did not affect LIDs in rats lesioned with 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) in the SNc [53]. However, the study was not concluded for marmosets lesioned with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and primed with L-Dopa because the administration of immepip or imetit, also H3R agonist, resulted in adverse effects that lead to interrupting the experiments. Nevertheless, partial data from the study showed that both agonists reduced the antiparkinsonian response induced by L-Dopa, thus appearing to decrease LIDs [54].
Our results showed that in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats, the chronic administration of the H3R agonist immepip in conjunction with L-Dopa reduced abnormal involuntary movement (AIM) scores and total AIMs for the three subtypes analyzed (axial, limb, and orolingual; see Figure 2) [37]. In contrast, the subacute and acute administration of a single dose (1 mg/kg, i.p.) of the H3R agonist did not affect LIDs, as previously reported by Papathanou et al. [54]. In both studies, at this dose, immepip did not produce any side effects [11,37]. Differences with the Papathanou et al. study [54] were the supplier of the H3R agonist and the administration route (subcutaneous in Papathanou et al. and intraperitoneal in our study).
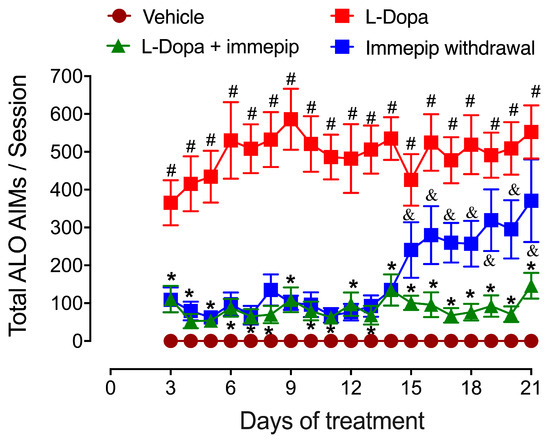
Figure 2.
Effect of the systemic administration of the H3R agonist immepip (1 mg/kg, i.p.) on total ALO (axial, limb, and orolingual) abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs) induced by L-Dopa (6.25 mg/kg; benserazide 15 mg/kg, i.p.). ALO AIMs were individually counted and then summed per session. The statistical analysis of total AIMs was conducted with repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test (8 animals per group). &,# p < 0.01, compared to the vehicle group; * p < 0.001, compared to the L-Dopa group.
Our results suggested thus that the H3R agonist helped prevent the development of LIDs but also that immepip is ineffective once dyskinesias are present [11]. This implication was supported by AIM reappearance after the withdrawal of the H3R agonist (see Figure 2) [11,37]. Also, the administration of the H3R agonist alone for 5 consecutive days prior to L-Dopa did not reduce AIMs [11], an effect possibly associated with H3R desensitization [55,56]. In this context, our data show that chronic H3R activation along with L-Dopa administration is necessary, in line with the information that a single dose of H3R agonists was not sufficient to inhibit LIDs in rats chronically treated with L-Dopa [54].
In summary, the evidence discussed indicates that H3R agonists modulate LIDs by reducing abnormal involuntary movements when chronically administered along L-Dopa. However, acute or subacute administration of H3R agonists is ineffective against established LIDs, likely due to H3R desensitization.
6. Functional Interaction Between H3Rs and D1Rs: A Potential Target to Reduce Dyskinesias
Together, the previously mentioned data raise the question of whether the functional interaction between H3Rs and D1Rs can be demonstrated in an altered striato-nigral circuit, such as in LIDs in PD.
As mentioned above, H3Rs and D1Rs couple to Gαi/o and Gαs proteins, respectively, and that H3R co-activation reduces D1R-induced GABA release and cAMP accumulation in striatal and SNr slices, indicating pre-synaptic and post-synaptic interactions taking place in the MSNs of the direct pathway [20,22,57].
In studies in which GABA release was analyzed in vivo by HPLC-coupled microdialysis in the rat striatum and total GABA content was determined post-mortem in striatal homogenates, our results showed that the systemic administration of L-Dopa to dyskinetic rats acutely increases GABA levels in striatal dialysates. The GABA/glutamate ratio is an indirect indicator of the fraction of glutamate converted to GABA before release into the synaptic cleft [58], and L-Dopa administration for 21 days augmented both GABA content and the GABA/glutamate ratio in the striatum ipsilateral to the lesioned SNc [11,37].
The reported changes in striatal GABAergic transmission suggest overactivity of the MSNs of the direct pathway, and in D1R knockout animals with 6-OHDA-induced nigro-striatal denervation, L-Dopa administration does not produce LIDs, ruling out the participation of the D2Rs in the genesis of the motor disorder [59,60]. Furthermore, L-Dopa administration for 21 days to parkinsonian animals increases glutamate and GABA levels in the ipsilateral and contralateral cerebral cortices [37]. Together, this information supports the theory that chronic L-Dopa administration to parkinsonian animals increases the activity of the cerebral cortex and striatal MSNs that express D1Rs and form the BG direct pathway.
In the striatum of parkinsonian rats treated with L-Dopa, the increase in both GABA and glutamate levels in dialysates was counteracted by the chronic co-administration of the H3R agonist immepip, but not by subchronic or acute administration [11]. For LIDs, the increase in striatal glutamate and GABA levels is consistent with the enhancement in glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission reported previously [61,62]. One likely explanation is the H3R-mediated inhibition of glutamate release from the cortico-striatal and thalamo-striatal terminals (see Figure 1D) [11,42,63], along with the decrease in striatal GABA content associated with the functional interaction between D1Rs and H3Rs [11,22].
H3R activation leads to the inhibition of adenylyl cyclases (ACs) and the subsequent reduction in cAMP formation (see Figure 3) [42], and H3R activation inhibits D1R-induced cAMP accumulation in striatal slices [21]. L-Dopa administration leads to the enhanced activation of the cAMP/PKA pathway, and in MSNs expressing D1Rs, PKA phosphorylates several substrates, including DARPP-32 (DA- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of 32 kDa), extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK-1/2), and proteins of the mTORC1 signaling pathway [4,64,65,66]. These molecular changes have been observed in MSNs of the striato-nigral direct pathway but not in MSNs of the indirect pathway [65]. In line with this, LIDs are reduced when L-Dopa administration is combined with drugs such as the PKA inhibitor Rp-cAMPS [66] or SL327, an ERK phosphorylation inhibitor [63,64]. Therefore, it is likely that the functional interaction between D1R and H3R explains the reduction in LIDs. However, molecular studies to corroborate this hypothesis are lacking.
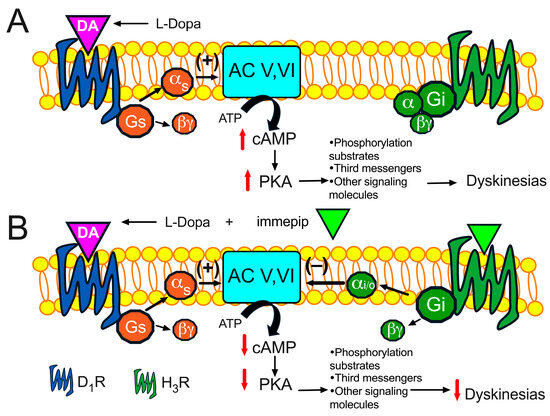
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of L-Dopa-induced intracellular signaling involving the cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) pathway (A). It is proposed that the co-administration of the H3R agonist immepip counteracts the effects of L-Dopa and reduces dyskinesias (B).
From the reviewed information, it can be inferred that the functional interaction between H3Rs and D1Rs modulates LIDs by reducing L-Dopa-induced increases in striatal GABA and glutamate levels through H3R-mediated inhibition of cAMP/PKA signaling. These findings highlight the potential role of H3R activation to counteract the overactivity of the striato-nigral-cortical circuit observed in PD, though molecular studies are required to further explore this mechanism.
7. Interaction Between H3Rs and D2Rs in the Striato-Pallidal MSNs
H3Rs and D2Rs are co-expressed by striato-pallidal MSNs, and a few studies suggest a functional interaction between H3Rs and D2Rs in the striatum [67,68].
H3Rs and D2Rs couple to Gαi/o proteins, and an additive action on [35S]-GTPγS binding to rat striatal membranes was observed following the co-activation of both receptors, a result that can be explained by only a fraction of the Gαi/o protein pool being activated by each of the two receptors or by the activation by each receptor of different Gαi/o subunit subtypes (αi1, αi2, αi3, αoA, or αoB) [67].
In reserpinized mice, H3R activation antagonizes locomotor behavior induced by D2R stimulation [68,69]. It was also reported that H3R activation reduces D2R affinity for the agonist quinpirole in sheep brain membranes and that the human H3R and D2R form a heterodimer as evidenced by BRET assays in transfected HEK-293 cells [69]. H3Rs co-immunoprecipitate with D2Rs in rat striatal lysates, and the proximity ligation assay (PLA) in mouse striatal sections supports the formation of an H3R/D2R complex. Furthermore, H3R co-activation modulated D2R-mediated Akt–GSK3β signaling in mouse D2R-expressing MSNs as visualized by immunohistochemistry and Western blot [68].
Together, this information indicates that H3Rs and D2Rs interact physically and functionally to modulate the activity of striato-pallidal neurons. However, as mentioned above, in D1R-knockout animals with 6-OHDA-induced lesions to striato-nigral neurons, the administration of L-Dopa does not result in dyskinesias, discarding a role for D2R in the pathogenesis of the disorder [57,58].
8. H3R/D1R Interaction in Huntington’s Disease (HD)
HD is a motor progressive neurodegenerative disorder caused by the expansion of a cytosine–adenine–guanine (CAG) trinucleotide repeat, coding a polyglutamine repeat within the N-terminal region of the protein huntingtin [70]. Like LIDs, dyskinesias in HD involve overactivity of the thalamo-cortical circuit. Dysfunction and death of striatal MSNs is a key HD neuropathological hallmark, and alterations in the striatal dopaminergic system may contribute to HD pathophysiology.
D1R over-activation occurs in the initial stages of HD, leading to abnormal dopaminergic neurotransmission and cell death [71]. In the study by Moreno-Delgado et al. [72], D1R/H3R heteromers were detected in immortalized striatal cells expressing mutant STHdhQ111 huntingtin, and D1R-induced ERK-1/2 phosphorylation, increase in intracellular Ca2+ levels and cell death were prevented by the H3R antagonist thioperamide via cross-antagonism. In the mutant HdhQ7/Q111 mouse, an HD model, thioperamide reduced motor and memory deficits. Furthermore, D1R/H3R heteromers were detected in the striatum (caudate-putamen) from control individuals and low-grade (0, 1, and 2 grades) HD patients but not in samples from high-grade (grades 3 or 4) patients, indicating that D1R/H3R heteromers are lost at late HD stages.
These data indicate that D1R/H3R heteromers participate in HD pathophysiology and may thus represent novel targets for the treatment of the disease.
9. Conclusions
The functional interaction between D1Rs and H3Rs most likely explains the H3R-induced reduction of LIDs in parkinsonism models, and may be the basis for novel pharmacological approaches to preventing or treating LIDs in PD patients. However, molecular and pharmacological studies are still required to elucidate in detail the signaling pathways involved in the D1R/H3R interaction. These findings will contribute to the understanding of the role of D1Rs and H3Rs in BG dysfunction occurring in hyperkinetic disorders and involving alterations of the dopaminergic system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.-L., J.-A.A.-M., and A.B.-N.; software, A.V.-M., J.L.C.-A., and A.B.-N.; formal analysis, A.V.-M.; data curation, A.V.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.-L., A.V.-M., J.-A.A.-M., and A.B.-N.; writing—review and editing, A.O.-H., J.L.C.-A., A.A.-R., and J.-A.A.-M.; visualization, A.V.-M.; supervision, J.-A.A.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Alexander Aguirre Pérez for his technical support in the preparation of the figure related to the behavioral study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| 6-OHDA | 6-Hydroxy-dopamine |
| AC | Adenylyl cyclase |
| AIMs | Abnormal involuntary movements |
| BG | Basal ganglia |
| D1Rs | Dopamine D1 receptors |
| D2Rs | Dopamine D2 receptors |
| DA | Dopamine |
| DARPP-32 | DA- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of 32 kDa |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| GPe | External segment of the globus pallidus |
| GPi | Internal segment of the globus pallidus |
| H3Rs | Histamine H3 receptors |
| L-Dopa | L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| LIDs | L-Dopa-induced dyskinesias |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| MPTP | 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine |
| MSNs | Medium spiny neurons |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| SNc | Substantia nigra pars compacta |
| SNr | Substantia nigra pars reticulata |
| STN | Subthalamic nucleus |
References
- Tolosa, E.; Garrido, A.; Scholz, S.W.; Poewe, W. Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Darweesh, S.; Llibre-Guerra, J.; Marras, C.; San Luciano, M.; Tanner, C. The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2024, 403, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spigolon, G.; Fisone, G. Signal transduction in l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia: From receptor sensitization to abnormal gene expression. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1171–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, G.; Yousaf, T.; Politis, M. PET Molecular Imaging Research of Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2017, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, G.; De Deurwaerdere, P.; Li, Q.; Marti, M.; Morgenstern, R.; Sohr, R.; Bezard, E.; Morari, M.; Meissner, W.G. L-dopa-induced dyskinesia: Beyond an excessive dopamine tone in the striatum. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabresi, P.; Picconi, B.; Tozzi, A.; Ghiglieri, V.; Di Filippo, M. Direct and indirect pathways of basal ganglia: A critical reappraisal. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastide, M.F.; Meissner, W.G.; Picconi, B.; Fasano, S.; Fernagut, P.O.; Feyder, M.; Francardo, V.; Alcacer, C.; Ding, Y.M.; Brambilla, R.; et al. Pathophysiology of L-dopa-induced motor and non-motor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 132, 96–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, A.; Porras, G.; Doudnikoff, E.; Stark, H.; Cador, M.; Bezard, E.; Bloch, B. Pharmacological Analysis Demonstrates Dramatic Alteration of D-1 Dopamine Receptor Neuronal Distribution in the Rat Analog of L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4829–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Luna, A.; Ríos, C.; Gálvez-Rosas, A.; Montes, S.; Arias-Montaño, J.-A.; Bueno-Nava, A. Chronic administration of the histamine H3 receptor agonist immepip decreases l-Dopa-induced dyskinesias in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1937–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Urbieta, H.; Gago, B.; de la Riva, P.; Delgado-Alvarado, M.; Marin, C.; Rodriguez-Oroz, M.C. Dyskinesias and impulse control disorders in Parkinson’s disease: From pathogenesis to potential therapeutic approaches. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 56, 294–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascol, O.; Fabbri, M.; Poewe, W. Amantadine in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and other movement disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.-Z.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Luo, X.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Wang, X.-P. An Update on Nondopaminergic Treatments for Motor and Non-motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2023, 21, 1806–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolam, J.P.; Ellender, T.J. Histamine and the striatum. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sepúlveda, M.; Rosell, S.; Hoffmann, H.M.; Castillo-Ruiz, M.d.M.; Mignon, V.; Moreno-Delgado, D.; Michel, V.; Díaz, J.; Sabriá, J.; Ortiz, J. Cellular distribution of the histamine H3 receptor in the basal ganglia: Functional modulation of dopamine and glutamate neurotransmission. Basal Ganglia 2013, 3, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.M.; Espinoza, S.; Gainetdinov, R.R. Dopamine receptors—IUPHAR Review 13. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Alamilla, G.; Márquez-Gómez, R.; García-Gálvez, A.-M.; Morales-Figueroa, G.-E.; Arias-Montaño, J.-A. The Histamine H3 Receptor: Structure, Pharmacology, and Function. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 649–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Floran, B.; Arias-Montaño, J.A.; Young, J.M.; Aceves, J. Histamine H3 receptor activation selectively inhibits dopamine D1 receptor-dependent [3H]GABA release from depolarization-stimulated slices of rat substantia nigra pars reticulata. Neuroscience 1997, 80, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lemus, E.; Arias-Montaño, J.A. Histamine H3 receptor activation inhibits dopamine D1 receptor-induced cAMP accumulation in rat striatal slices. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 364, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Montaño, J.A.; Floran, B.; Garcia, M.; Aceves, J.; Young, J.M. Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of depolarization-induced, dopamine D1 receptor-dependent release of 3H-gamma-aminobutryic acid from rat striatal slices. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerfen, C.R.; Surmeier, D.J. Modulation of Striatal Projection Systems by Dopamine. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 441–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolam, J.P.; Hanley, J.J.; Booth, P.A.; Bevan, M.D. Synaptic organisation of the basal ganglia. J. Anat. 2000, 196 Pt 4, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Peterson, J.D.; Surmeier, D.J. Corticostriatal and thalamostriatal synapses have distinctive properties. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 6483–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberberg, G.; Bolam, J.P. Local and afferent synaptic pathways in the striatal microcircuitry. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2015, 33, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Y.; Raju, D.V.; Pare, J.F.; Sidibe, M. The thalamostriatal system: A highly specific network of the basal ganglia circuitry. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Y.; Parent, A. Differential connections of caudate nucleus and putamen in the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). Neuroscience 1986, 18, 347–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doig, N.M.; Moss, J.; Bolam, J.P. Cortical and Thalamic Innervation of Direct and Indirect Pathway Medium-Sized Spiny Neurons in Mouse Striatum. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 14610–14618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodge, D.J.; Grace, A.A. Hippocampal dysregulation of dopamine system function and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshimizu, Y.; Fujiyama, F.; Nakamura, K.C.; Furuta, T.; Kaneko, T. Quantitative analysis of axon bouton distribution of subthalamic nucleus neurons in the rat by single neuron visualization with a viral vector. J. Comp. Neurol. 2013, 521, 2125–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouterlood, F.G.; van Oort, S.; Bloemhard, L.; Flierman, N.A.; Spijkerman, J.; Wright, C.I.; Beliën, J.A.M.; Groenewegen, H.J. Neurochemical fingerprinting of amygdalostriatal and intra-amygdaloid projections: A tracing–immunofluorescence study in the rat. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2018, 94, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, H. Globus pallidus external segment. In Progress in Brain Research; Tepper, J.M., Abercrombie, E.D., Bolam, J.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 160, pp. 111–133. [Google Scholar]
- Panula, P.; Nuutinen, S. The histaminergic network in the brain: Basic organization and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 472–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillot, C.; Heron, A.; Cochois, V.; Tardivel-Lacombe, J.; Ligneau, X.; Schwartz, J.C.; Arrang, J.M. A detailed mapping of the histamine H-3 receptor and its gene transcripts in rat brain. Neuroscience 2002, 114, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, B.; Saad, A.; Sadeq, A.; Jalal, F.; Stark, H. Histamine H3 receptor as a potential target for cognitive symptoms in neuropsychiatric diseases. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 312, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Luna, A.; Gálvez-Rosas, A.; Aguirre-Pérez, A.; Hidalgo-Bravo, A.; Alfaro-Rodriguez, A.; Ríos, C.; Arias-Montaño, J.-A.; Bueno-Nava, A. Chronic H3R activation reduces L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia, normalizes cortical GABA and glutamate levels, and increases striatal dopamine D1R mRNA expression in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned male rats. Psychopharmacology 2023, 240, 1221–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapanelli, M.; Pittenger, C. Histamine and histamine receptors in Tourette syndrome and other neuropsychiatric conditions. Neuropharmacology 2016, 106, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Yanai, K.; Iwata, R.; Ido, T.; Watanabe, T. Heterogeneous distributions of histamine H3, dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in rat-brain. Neuroreport 1994, 5, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerfen, C.R.; Engber, T.M.; Mahan, L.C.; Susel, Z.; Chase, T.N.; Monsma, F.J.; Sibley, D.R. D1 and D2 Dopamine Receptor-regulated Gene Expression of Striatonigral and Striatopallidal Neurons. Science 1990, 250, 1429–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmeier, D.J.; Ding, J.; Day, M.; Wang, Z.; Shen, W. D1 and D2 dopamine-receptor modulation of striatal glutamatergic signaling in striatal medium spiny neurons. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapanelli, M. The magnificent two: Histamine and the H3 receptor as key modulators of striatal circuitry. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 73, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taverna, S.; Ilijic, E.; Surmeier, D.J. Recurrent collateral connections of striatal medium spiny neurons are disrupted in models of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 5504–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varaschin, R.K.; Osterstock, G.; Ducrot, C.; Leino, S.; Bourque, M.-J.; Prado, M.A.M.; Prado, V.F.; Salminen, O.; Rannanpää, S.; Trudeau, L.-E. Histamine H3 Receptors Decrease Dopamine Release in the Ventral Striatum by Reducing the Activity of Striatal Cholinergic Interneurons. Neuroscience 2018, 376, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitzer, A.C.; Malenka, R.C. Striatal Plasticity and Basal Ganglia Circuit Function. Neuron 2008, 60, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuhma, N.; Oh, S.J.; Rayport, S. The dopamine neuron synaptic map in the striatum. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centonze, D.; Bracci, E.; Pisani, A.; Gubellini, P.; Bernardi, G.; Calabresi, P. Activation of dopamine D1-like receptors excites LTS interneurons of the striatum. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 2049–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Montaño, J.A.; Floran, B.; Floran, L.; Aceves, J.; Young, J.M. Dopamine D1 receptor facilitation of depolarization-induced release of γ-amino-butyric acid in rat striatum is mediated by the cAMP/PKA pathway and involves P/Q-type calcium channels. Synapse 2007, 61, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E.; Hoffmann, H.; Gonzalez-Sepulveda, M.; Navarro, G.; Casado, V.; Cortes, A.; Mallol, J.; Vignes, M.; McCormick, P.J.; Canela, E.I.; et al. Dopamine D-1-histamine H-3 Receptor Heteromers Provide a Selective Link to MAPK Signaling in GABAergic Neurons of the Direct Striatal Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5846–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapanelli, M.; Frick, L.R.; Horn, K.D.; Schwarcz, R.C.; Pogorelov, V.; Nairn, A.C.; Pittenger, C. The Histamine H3 Receptor Differentially Modulates Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) and Akt Signaling in Striatonigral and Striatopallidal Neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 21042–21052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrada, C.; Moreno, E.; Casado, V.; Bongers, G.; Cortes, A.; Mallol, J.; Canela, E.I.; Leurs, R.; Ferre, S.; Lluis, C.; et al. Marked changes in signal transduction upon heteromerization of dopamine D1 and histamine H3 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.; Moreno, E.; Moreno-Delgado, D.; Navarro, G.; Mallol, J.; Cortes, A.; Lluis, C.; Canela, E.I.; Casado, V.; McCormick, P.J.; et al. Heteroreceptor Complexes Formed by Dopamine D1, Histamine H3, and N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Glutamate Receptors as Targets to Prevent Neuronal Death in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4537–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Rodríguez, A.; Alonso-Spilsbury, M.; Arch-Tirado, E.; Gonzalez-Pina, R.; Arias-Montano, J.-A.; Bueno-Nava, A. Histamine H3 receptor activation prevents dopamine D1 receptor-mediated inhibition of dopamine release in the rat striatum: A microdialysis study. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 552, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanou, M.; Jenner, P.; Iravani, M.; Jackson, M.; Stockwell, K.; Strang, I.; Zeng, B.-Y.; McCreary, A.C.; Rose, S. The H3 receptor agonist immepip does not affect L-dopa-induced abnormal involuntary movements in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 741, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Galvez, A.M.; Escamilla-Sanchez, J.; Flores-Maldonado, C.; Contreras, R.G.; Arias, J.M.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Differential homologous desensitization of the human histamine H3 receptors of 445 and 365 amino acids expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 112, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio-Espinoza, A.; Escamilla-Sanchez, J.; Aquino-Jarquin, G.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Homologous desensitization of human histamine H3 receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Neuropharmacology 2014, 77, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lemus, E.; Arias-Montaño, J.-A. M1 Muscarinic Receptors Contribute to, whereas M4 Receptors Inhibit, Dopamine D1 Receptor-Induced [3H]-Cyclic AMP Accumulation in Rat Striatal Slices. Neurochem. Res. 2006, 31, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez-Rosas, A.; Avila-Luna, A.; Valdés-Flores, M.; Montes, S.; Bueno-Nava, A. GABAergic imbalance is normalized by dopamine D1 receptor activation in the striatum contralateral to the cortical injury in motor deficit-recovered rats. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 2211–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murer, M.G.; Moratalla, R. Striatal signaling in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia: Common mechanisms with drug abuse and long term memory involving D1 dopamine receptor stimulation. Front. Neuroanat. 2011, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmopil, S.; Martin, A.B.; De Diego, I.R.; Ares, S.; Moratalla, R. Genetic Inactivation of Dopamine D1 but Not D2 Receptors Inhibits L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia and Histone Activation. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Barajas, C.; Silva, I.; Lopez-Santiago, L.M.; Aceves, J.; Erlij, D.; Floran, B. L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemiparkinsonian rats is associated with up-regulation of adenylyl cyclase type V/VI and increased GABA release in the substantia nigra reticulata. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, P.; Johnston, T.H.; Koprich, J.B.; Fox, S.H.; Brotchie, J.M. The Pharmacology of L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 171–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Hernandez, A.; Nunez, A.; Sierra, J.J.; Arias-Montano, J.A. Histamine H3 receptor activation inhibits glutamate release from rat striatal synaptosomes. Neuropharmacology 2001, 41, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, E.; Valjent, E.; Usiello, A.; Carta, M.; Borgkvist, A.; Girault, J.A.; Herve, D.; Greengard, P.; Fisone, G. Critical involvement of cAMP/DARPP-32 and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase signaling in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 6995–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, E.; Alcacer, C.; Cacciatore, S.; Heiman, M.; Herve, D.; Greengard, P.; Girault, J.A.; Valjent, E.; Fisone, G. L-DOPA activates ERK signaling and phosphorylates histone H3 in the striatonigral medium spiny neurons of hemiparkinsonian mice. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakansson, K.; Lindskog, M.; Pozzi, L.; Usiello, A.; Fisone, G. DARPP-32 and modulation of cAMP signaling: Involvement in motor control and levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Park. Relat. Disord. 2004, 10, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert-Claude, M.; Morisset, S.; Gbahou, F.; Arrang, J.M. Histamine H3 and doparnine D2 receptor-mediated [35S]GTPγ[S] binding in rat striatum: Evidence for additive effects but lack of interactions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Pittenger, C. The histamine H3 receptor modulates dopamine D2 receptor–dependent signaling pathways and mouse behaviors. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrada, C.; Ferre, S.; Casado, V.; Cortes, A.; Justinova, Z.; Barnes, C.; Canela, E.I.; Goldberg, S.R.; Leurs, R.; Lluis, C.; et al. Interactions between histamine H3 and dopamine D2 receptors and the implications for striatal function. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, R.A.C. Huntington’s disease: A clinical review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, E.; Cepeda, C.; Levine, M. Dopamine imbalance in Huntington’s disease: A mechanism for the lack of behavioral flexibility. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Delgado, D.; Puigdellívol, M.; Moreno, E.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.; Botta, J.; Gasperini, P.; Chiarlone, A.; Howell, L.A.; Scarselli, M.; Casadó, V.; et al. Modulation of dopamine D1 receptors via histamine H3 receptors is a novel therapeutic target for Huntington’s disease. eLife 2020, 9, e51093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).