Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Insights into Virulence, Antibiotic Resistance, and Fight Strategies Against a Superbug
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Difference Between Classic and Hypervirulent K. peumoniae
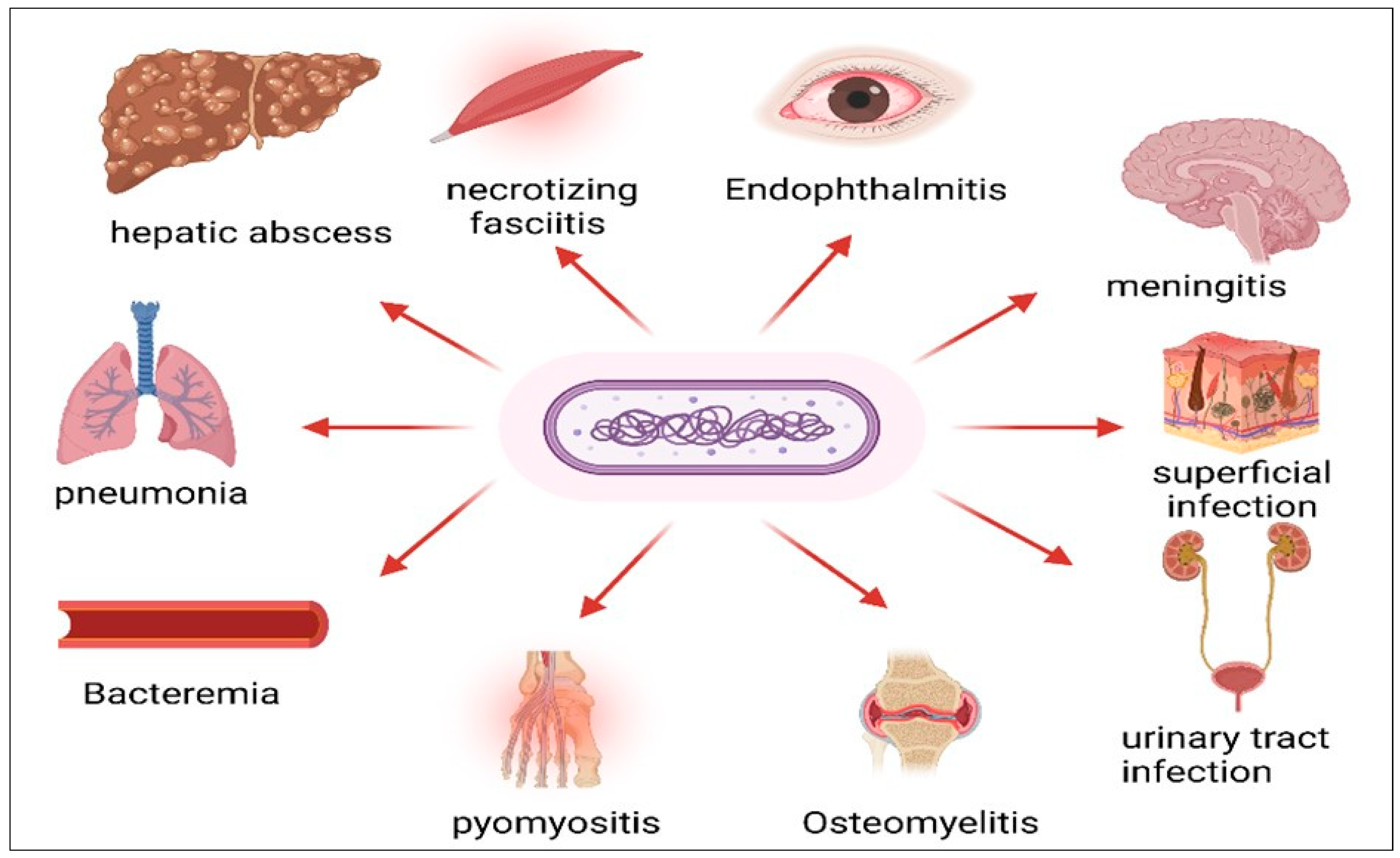
3. Diseases Caused by hvKP
4. Discovery and Epidemiology of hvKP
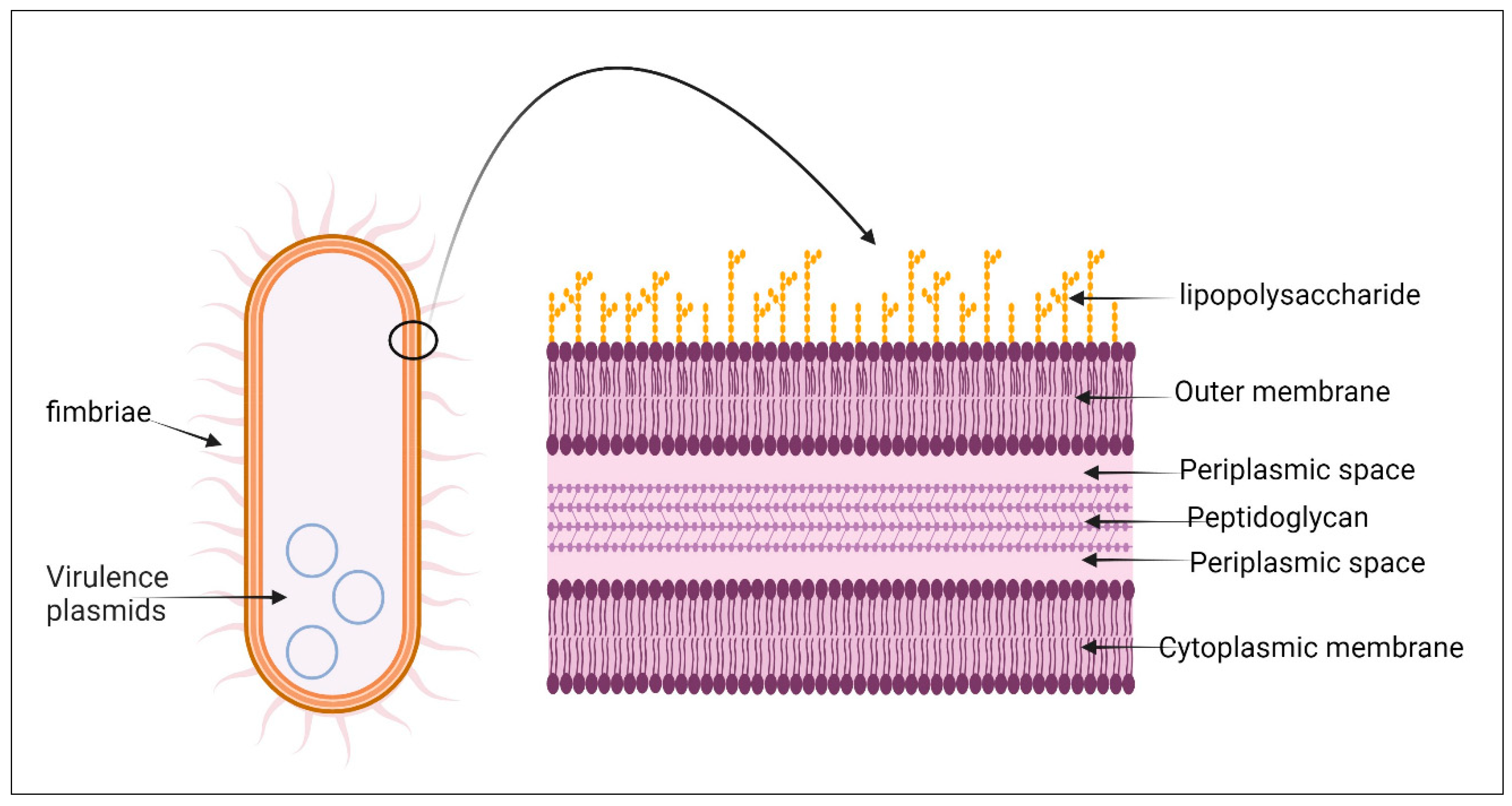
5. Bacterial Structure
6. Pathogenesis of hvKP
7. Virulence Factors and Genes
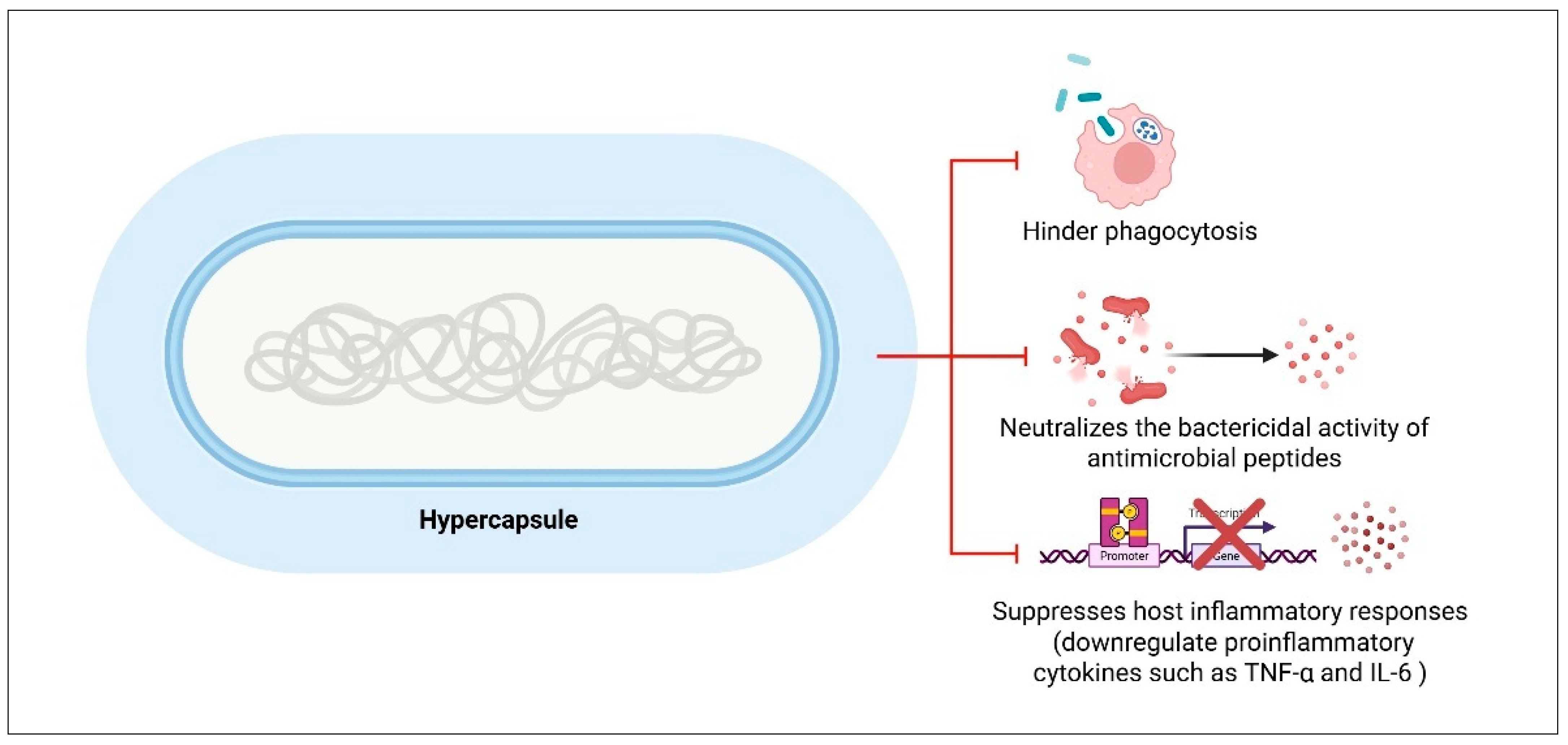
7.1. Capsule
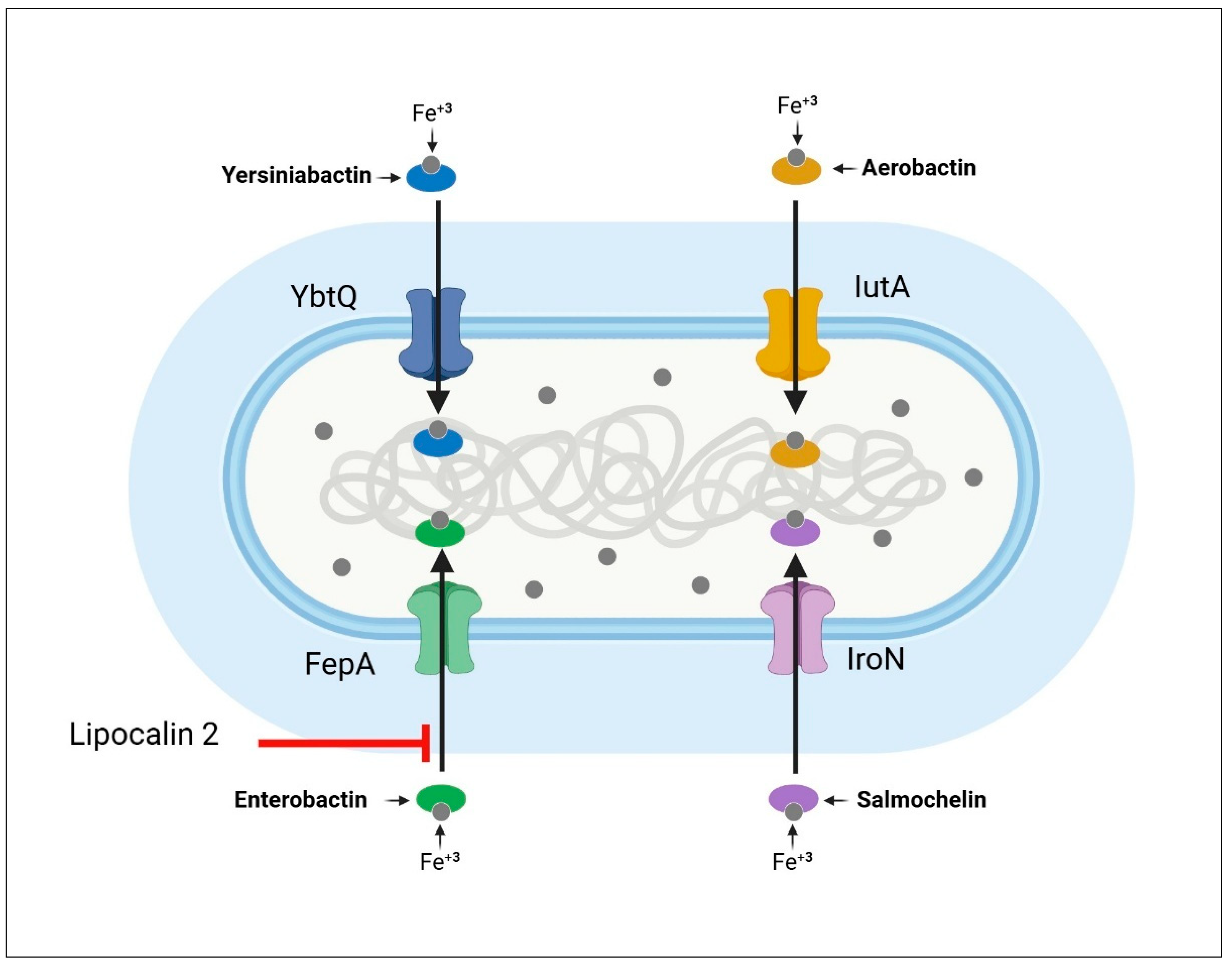
7.2. Siderophores
7.3. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
7.4. Fimbriae
7.5. Allantoin Metabolism
7.6. Colibactin
7.7. Peg-344
7.8. Type 6 Secretion System (T6SS)
8. Convergence of Hypervirulence and MDR in K. peumoniae
9. The Growing Threat of Antibiotic Resistance in hvKP
10. Clinical and Epidemiological Risk Factors
11. Association with Malignancy
12. Clinical Challenges with HVKP Infection
12.1. Diagnostic Challenges
12.2. Antibiotic Resistance and Treatment Challenges
13. Controlling the hvKP Infection: Recommendations
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magill, S.S.; Edwards, J.R.; Bamberg, W.; Beldavs, Z.G.; Dumyati, G.; Kainer, M.A.; Lynfield, R.; Maloney, M.; McAllister-Hollod, L.; Nadle, J. Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care–associated infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the Offense with a Strong Defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makharita, R.R.; El-Kholy, I.; Hetta, H.F.; Abdelaziz, M.H.; Hagagy, F.I.; Ahmed, A.A.; Algammal, A.M. Antibiogram and genetic characterization of carbapenem-resistant gram-negative pathogens incriminated in healthcare-associated infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3991–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, A.S.; Bajwa, R.P.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: A new and dangerous breed. Virulence 2013, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazili, T.; Sharngoe, C.; Endy, T.; Kiska, D.; Javaid, W.; Polhemus, M. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: An emerging disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 351, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Siu, L.K.; Lin, J.-C.; Chen, T.-L.; Tseng, C.-P.; Yeh, K.-M.; Chang, F.-Y.; Fung, C.-P. Seroepidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae colonizing the intestinal tract of healthy Chinese and overseas Chinese adults in Asian countries. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadasy, K.A.; Domiati-Saad, R.; Tribble, M.A. Invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae syndrome in North America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, e25–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ismail, D.; Campos-Madueno, E.I.; Donà, V.; Endimiani, A. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp): Overview, Epidemiology, and Laboratory Detection. Pathog. Immun. 2024, 10, 80–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, S.M.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Kazaal, S.S.; Mohammed Ali, A.N.; Aziz, S.N.; Makharita, R.R.; Algammal, A.M.; Al-Rejaie, S.; Behl, T.; Batiha, G.E.-S. Detection of gyrA and parC mutations and prevalence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.-T.; Chuang, Y.-P.; Shun, C.-T.; Chang, S.-C.; Wang, J.-T. A novel virulence gene in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains causing primary liver abscess and septic metastatic complications. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00001–e00019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, D.; Wu, A.; Li, R.; Cai, D.; Tong, H.; Wang, N.; Tan, J. Identification of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae based on biomarkers and Galleria mellonella infection model. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannini, E.C.; Lahitte, M.; Scapellato, P.; Nemirosvky, C.; Zylberman, M.; Vila, A.; Rodríguez, V.; Zucchi, R.; Mykietiuk, A.; David, V.; et al. Diversity of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clones causing cryptogenic liver abscesses and metastatic complications in Argentina. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2025. Online Ahead of Print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, D.; Zhao, J.; Chang, K.; Zhuo, X.; Cao, B. “Superbugs” with hypervirulence and carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae: The rise of such emerging nosocomial pathogens in China. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 2658–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ying, L.; Xiong, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, P.; Wang, Y.; Shen, P.; Xiao, Y. Understanding carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Key virulence factors and evolutionary convergence. hLife 2024, 2, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cobos, S.; Oteo-Iglesias, J.; Pérez-Vázquez, M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology outside Asian countries, antibiotic resistance association, methods of detection and clinical management. Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. Clín. 2025, 43, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.; Hetta, H.F.; Mabrok, M.; Behzadi, P. Editorial: Emerging multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens “superbugs”: A rising public health threat. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1135614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.L.; Lin, R.T.; Teo, J.W. Klebsiella pneumoniae in Singapore: Hypervirulent infections and the carbapenemase threat. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán-Nájera, J.C.; Garza-Ramos, U.; Barrios-Camacho, H. Hypervirulence and hypermucoviscosity: Two different but complementary Klebsiella spp. phenotypes? Virulence 2017, 8, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, L.; Du, H. Virulence factors in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Olson, R.; Fang, C.-T.; Stoesser, N.; Miller, M.; MacDonald, U.; Hutson, A.; Barker, J.H.; La Hoz, R.M.; Johnson, J.R. Identification of biomarkers for differentiation of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae from classical K. pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00776-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.-L.; Ko, W.-C.; Cheng, K.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Lai, C.-C.; Chuang, Y.-C. Comparison of prevalence of virulence factors for Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscesses between isolates with capsular K1/K2 and non-K1/K2 serotypes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, T.A.; Olson, R.; MacDonald, U.; Beanan, J.; Davidson, B.A. Aerobactin, but not yersiniabactin, salmochelin, or enterobactin, enables the growth/survival of hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae ex vivo and in vivo. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3325–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, D.; Wu, H.; Ma, Y. Resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae to both intracellular and extracellular killing of neutrophils. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, K.A.; Treat, L.P.; Sepúlveda, V.E.; Miller, V.L. The small protein RmpD drives hypermucoviscosity in Klebsiella pneumoniae. MBio 2020, 11, e01750-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Cheng, D.-L.; Lin, C.-L. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess associated with septic endophthalmitis. Arch. Intern. Med. 1986, 146, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Yen, M.-Y.; Wang, R.-S. Septic metastatic lesions of pyogenic liver abscess: Their association with Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia in diabetic patients. Arch. Intern. Med. 1991, 151, 1557–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Lee, S.S.-J.; Yen, M.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S.; Wang, J.-H.; Wann, S.-R.; Lin, H.-H. Primary liver abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 1434–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Yu, F.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of pyogenic liver abscess in a tertiary hospital in East China. Medicine 2017, 96, e8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, K.G.; Aye, M. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: A case series of six Asian patients. Am. J. Case Rep. 2017, 18, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, H. High Prevalence of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in China: Geographic Distribution, Clinical Characteristics, and Antimicrobial Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6115–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrie, T.J.; Durant, H.; Yates, L. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization: 5-year prospective study. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1989, 11, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.L. Klebsiella pulmonary infections: Occurrence at one medical center and review. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1990, 12, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergis, E.N.; Indorf, A.; File, T.M.; Phillips, J.; Bates, J.; Tan, J.; Sarosi, G.A.; Grayston, J.T.; Summersgill, J.; Victor, L.Y. Azithromycin vs cefuroxime plus erythromycin for empirical treatment of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalized patients: A prospective, randomized, multicenter trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, W.-C.; Paterson, D.L.; Sagnimeni, A.J.; Hansen, D.S.; Von Gottberg, A.; Mohapatra, S.; Casellas, J.M.; Goossens, H.; Mulazimoglu, L.; Trenholme, G. Community-acquired Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia: Global differences in clinical patterns. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Yu, W.L.; Lee, N.Y.; Chang, C.M.; Ko, N.Y.; Wang, L.R.; Ko, W.C. Clinical implications of hypermucoviscosity phenotype in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates: Association with invasive syndrome in patients with community-acquired bacteraemia. J. Intern. Med. 2006, 259, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishibe, S.; Okubo, Y.; Morino, S.; Hirotaki, S.; Tame, T.; Aoki, K.; Ishii, Y.; Ota, N.; Shimomura, S.; Sakakibara, H. Pediatric hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae septic arthritis. Pediatr. Int. 2016, 58, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.-N.; Huang, C.-R.; Lu, C.-H.; Chien, C.-C. Adult Klebsiella pneumoniae meningitis in Taiwan: An overview. Acta Neurol Taiwan 2012, 21, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.-M.; Chen, S.-T.; Hsu, W.-C.; Chen, C.-M. Klebsiella meningitis in Taiwan: An overview. Epidemiol. Infect. 1997, 119, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, T.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Yu, K.; Liu, C. Gram-negative bacillary meningitis in adults: A recent six-year experience. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. = Taiwan Yi Zhi 1993, 92, 540–546. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Chang, S.-C.; Hsueh, P.; Chen, Y.; Sau, W.; Luh, K. Microbiologic features of adult community-acquired bacterial meningitis in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. = Taiwan Yi Zhi 2000, 99, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Durand, M.L.; Calderwood, S.B.; Weber, D.J.; Miller, S.I.; Southwick, F.S.; Caviness Jr, V.S.; Swartz, M.N. Acute bacterial meningitis in adults--A review of 493 episodes. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Liu, C.-J.; Chen, T.-J.; Fung, C.-P. Long-term mortality of patients with septic ocular or central nervous system complications from pyogenic liver abscess: A population-based study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.-T.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chang, S.-C.; Sau, W.-Y.; Luh, K.-T. Klebsiella pneumoniae meningitis: Timing of antimicrobial therapy and prognosis. Qjm 2000, 93, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, W. A rare presentation of brain abscess and ventriculitis/INS; caused by Klebsiella pneumonia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 333, e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzien, M.; Rosman, J.; Decré, D.; Brenkle, K.; Mendes-Martins, L.; Mateu, P. Seven hypervirulent ST380 Klebsiella pneumoniae septic localizations. Med. Mal. Infect. 2017, 47, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-J.; Lu, T.-C.; Ma, M.H.-M.; Wang, H.-P.; Chen, S.-C. Unrecognized cervical spinal epidural abscess associated with metastatic Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia and liver abscess in nondiabetic patients. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 65, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doud, M.S.; Grimes-Zeppegno, R.; Molina, E.; Miller, N.; Balachandar, D.; Schneper, L.; Poppiti, R.; Mathee, K. A k2A-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae causes liver and brain abscess in a Saint Kitt's man. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 6, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, G.; Takei, S.-i.; Sato, M.; Isokawa, O.; Takemae, T.; Takahashi, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess associated with septic spinal epidural abscess. Hepatol. Res. 2005, 31, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.-C.; Yu, Y.-C.; Tai, H.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Chang, S.-C.; Lai, S.-Y.; Yi, W.-C.; Fang, C.-T. Recent trend of necrotizing fasciitis in Taiwan: Focus on monomicrobial Klebsiella pneumoniae necrotizing fasciitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, G.L.; Brandt, P.B.; Gad, D.; Struve, C.; Justesen, U.S. Monomicrobial necrotizing fasciitis in a white male caused by hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1519–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Tu, J.; Jiang, J.; Bi, Y.; You, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhu, T.; Cao, Z.; Yu, Z. Clinical and genomic analysis of liver abscess-causing Klebsiella pneumoniae identifies new liver abscess-associated virulence genes. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, D.; Frazee, B. Necrotizing fasciitis caused by hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Filipino female in North America. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgbemena, O.; Serota, D.P.; Kumar, S.; Wozniak, J.E.; Weiss, D.S.; Kempker, R.R. Peculiar purulence: Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae causing pyomyositis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokesch, B.C.; TeKippe, M.; Kim, J.; Raj, P.; TeKippe, E.M.; Greenberg, D.E. Primary osteomyelitis caused by hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e190–e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazee, B.W.; Hansen, S.; Lambert, L. Invasive infection with hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae: Multiple cases presenting to a single emergency department in the United States. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2009, 53, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, R.; Lambert, L.; Frazee, B. Invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae infections, California, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschiv, F.; Popescu, G.A.; Borcan, A.M. Septic cutaneous emboli revealing a severe case of Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess syndrome. JMM Case Rep. 2018, 5, e005148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, K.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.-X.; Tian, F.; Wei, J.-C.; Tai, M.-H.; Zhou, L.; Meng, F.-D.; Wang, R.-T.; Xu, X.-S. Pyogenic liver abscesses associated with nonmetastatic colorectal cancers: An increasing problem in Eastern Asia. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2012, 18, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, A.; Gomez, E.; Alland, D.; Huang, D.B.; Chiang, T. K2 serotype Klebsiella pneumoniae causing a liver abscess associated with infective endocarditis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrino, D.; Ghigo, J.M.; Charbonnel, N.; Haagensen, J.A.; Forestier, C. The characterization of functions involved in the establishment and maturation of Klebsiella pneumoniae in vitro biofilm reveals dual roles for surface exopolysaccharides. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.; Wyres, K.L.; Judd, L.M.; Wick, R.R.; Jenney, A.; Brisse, S.; Holt, K.E. Tracking key virulence loci encoding aerobactin and salmochelin siderophore synthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, J.F.; Englender, H.; Gabriel, S.N.; Turton, S.E.; Kaufmann, M.E.; Pitt, T.L. Genetically similar isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K1 causing liver abscesses in three continents. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, M.; Stanton, R.A.; Ansari, U.; McAllister, G.; Chan, M.Y.; Sula, E.; Grass, J.E.; Duffy, N.; Anacker, M.L.; Witwer, M.L. Identification of a carbapenemase-producing hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate in the United States. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, M.J.W.; Reece, N.L.; Parry, C.M.; Rajahram, G.S.; Paterson, D.L.; Woolley, S.D. The rapid emergence of hypervirulent klebsiella species and burkholderia pseudomallei as major health threats in southeast Asia: The urgent need for recognition as neglected tropical diseases. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhan, L.; Jin, Y.; Duan, J.; Hao, Z.; Lv, J.; Qi, X.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; et al. Microbiological and clinical characteristics of hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates associated with invasive infections in China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, C.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Nabarro, L.E.B.; Ravi, R.; Ragupathi, N.K.D.; Rupali, P. Whole genome analysis of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from community and hospital acquired bloodstream infection. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Dong, N.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, D.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Shu, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R. A fatal outbreak of ST11 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese hospital: A molecular epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Kong, X.; Hao, J.; Liu, J. Epidemiological characteristics and formation mechanisms of multidrug-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance, Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae—Global Situation. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2024-DON527 (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Fang, C.-T.; Lai, S.-Y.; Yi, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R.; Liu, K.-L.; Chang, S.-C. Klebsiella pneumoniae genotype K1: An emerging pathogen that causes septic ocular or central nervous system complications from pyogenic liver abscess. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, P.-p.; Wang, L.-h.; Wei, D.-d.; Wan, L.-G.; Zhang, W. Capsular polysaccharide types and virulence-related traits of epidemic KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in a Chinese University Hospital. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Lv, J.; Niu, S.; Du, H.; Tang, Y.-W.; Bonomo, R.A.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Chen, L. In vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam against carbapenem-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01031-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Follador, R.; Heinz, E.; Wyres, K.L.; Ellington, M.J.; Kowarik, M.; Holt, K.E.; Thomson, N.R. The diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae surface polysaccharides. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Chang, H.; Lai, Y.; Peng, H.-L. RmpA regulation of capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 3144–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, P.F.; Zoumadakis, C.; Panopoulos, N.J.; Scoulica, E.V. Distribution of the putative type VI secretion system core genes in Klebsiella spp. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.T.; Liebenthal, D.; Tran, T.K.; Ngoc Thi Vu, B.; Ngoc Thi Nguyen, D.; Thi Tran, H.K.; Thi Nguyen, C.K.; Thi Vu, H.L.; Fox, A.; Horby, P. Klebsiella pneumoniae oropharyngeal carriage in rural and urban Vietnam and the effect of alcohol consumption. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadoni, I.; Zagato, E.; Bertocchi, A.; Paolinelli, R.; Hot, E.; Di Sabatino, A.; Caprioli, F.; Bottiglieri, L.; Oldani, A.; Viale, G. A gut-vascular barrier controls the systemic dissemination of bacteria. Science 2015, 350, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.; Wyres, K.L.; Duchêne, S.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gan, Y.-H.; Hoh, C.-H.; Archuleta, S.; Molton, J.S.; Kalimuddin, S. Population genomics of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal-group 23 reveals early emergence and rapid global dissemination. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struve, C.; Roe, C.C.; Stegger, M.; Stahlhut, S.G.; Hansen, D.S.; Engelthaler, D.M.; Andersen, P.S.; Driebe, E.M.; Keim, P.; Krogfelt, K.A. Mapping the evolution of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. MBio 2015, 6, e00630-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-C.; Lin, A.-C.; Chiang, M.-K.; Dai, Y.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Lu, M.-C.; Liau, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T. Genotoxic Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Lai, Y.-C.; Tan, M.-C.; Hsieh, L.-Y.; Wang, J.-T.; Shiau, Y.-R.; Wang, H.-Y.; Lin, A.-C.; Lai, J.-F.; Huang, I.-W. Prevalence and characteristics of pks genotoxin gene cluster-positive clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lorenzo, V. Isolation and characterization of microcin E 492 from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch. Microbiol. 1984, 139, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos, R.; Baeza, M.; Corsini, G.; Hetz, C.; Strahsburger, E.; Castillo, J.A.; Vergara, C.; Monasterio, O. Structure, organization and characterization of the gene cluster involved in the production of microcin E492, a channel-forming bacteriocin. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 42, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sá-Pessoa, J.; Przybyszewska, K.; Vasconcelos, F.N.; Dumigan, A.; Frank, C.G.; Hobley, L.; Bengoechea, J.A. Klebsiella pneumoniae reduces SUMOylation to limit host defense responses. Mbio 2020, 11, e01733-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.-C.; Chen, H.-W.; Wu, P.-K.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Wu, J.H. Mutation in fucose synthesis gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae affects capsule composition and virulence in mice. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Wu, A.M.; Tsai, C.G.; Chang, X.-Y.; Tsai, S.-F.; Wu, T.-S. Contribution of fucose-containing capsules in Klebsiella pneumoniae to bacterial virulence in mice. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.-F.; Lin, T.-L.; Lee, C.-Z.; Tsai, S.-F.; Wang, J.-T. Serum-induced iron-acquisition systems and TonB contribute to virulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae causing primary pyogenic liver abscess. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, M.S.; O'connor, C.; Miller, V.L. Yersiniabactin is a virulence factor for Klebsiella pneumoniae during pulmonary infection. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, X.; Sansonetti, P.J. Correlation of the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae K1 and K2 with the presence of a plasmid encoding aerobactin. Infect. Immun. 1986, 54, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.-C.; Fang, C.-T.; Lee, C.-Z.; Shun, C.-T.; Wang, J.-T. Genomic heterogeneity in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains is associated with primary pyogenic liver abscess and metastatic infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.-S.W.; Syu, W.-J.; Ho, W.-L.; Lin, C.-N.; Tsai, S.-F.; Wang, S.-H. SitA contributes to the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae in a mouse infection model. Microbes Infect. 2014, 16, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, G.; Borrell, N.; de Astorza, B.; Gómez, C.; Sauleda, J.; Albertí, S. Molecular analysis of the contribution of the capsular polysaccharide and the lipopolysaccharide O side chain to the virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae in a murine model of pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2583–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenico, P.; Salo, R.J.; Cross, A.S.; Cunha, B.A. Polysaccharide capsule-mediated resistance to opsonophagocytosis in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 4495–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Tateda, K.; Uchida, K.; Tsujimoto, S.; Yamaguchi, K. Role of bacterial capsule in local and systemic inflammatory responses of mice during pulmonary infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 49, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, X.; Chan, E.W.C.; Chen, S. The hypermucoviscosity of hypervirulent K. pneumoniae confers the ability to evade neutrophil-mediated phagocytosis. Virulence 2021, 12, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Q.; Yang, X.; Heng, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, G.; Peng, M.; Chan, E.-C.; Chen, S. Capsular polysaccharide enables Klebsiella pneumoniae to evade phagocytosis by blocking host-bacteria interactions. mBio 2025, 16, e0383824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Froumine, R.; Tokolyi, A.; Gorrie, C.L.; Lam, M.M.; Duchêne, S.; Jenney, A.; Holt, K.E. Distinct evolutionary dynamics of horizontal gene transfer in drug resistant and virulent clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.-J.; Lin, T.-L.; Chen, C.-T.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Hsieh, P.-F.; Hsu, C.-R.; Wu, M.-C.; Wang, J.-T. Genetic analysis of capsular polysaccharide synthesis gene clusters in 79 capsular types of Klebsiella spp. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.-J.; Fang, H.-C.; Yang, H.-C.; Lin, T.-L.; Hsieh, P.-F.; Tsai, F.-C.; Keynan, Y.; Wang, J.-T. Capsular polysaccharide synthesis regions in Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K57 and a new capsular serotype. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.R.; Molton, J.S.; Wyres, K.L.; Gorrie, C.; Wong, J.; Hoh, C.H.; Teo, J.; Kalimuddin, S.; Lye, D.C.; Archuleta, S. Differential host susceptibility and bacterial virulence factors driving Klebsiella liver abscess in an ethnically diverse population. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.-M.; Kurup, A.; Siu, L.; Koh, Y.; Fung, C.-P.; Lin, J.-C.; Chen, T.-L.; Chang, F.-Y.; Koh, T.-H. Capsular serotype K1 or K2, rather than magA and rmpA, is a major virulence determinant for Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess in Singapore and Taiwan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, C.; Chang, F.; Lee, S.; Hu, B.; Kuo, B.I.; Liu, C.; Ho, M.; Siu, L. A global emerging disease of Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: Is serotype K1 an important factor for complicated endophthalmitis? Gut 2002, 50, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athamna, A.; Ofek, I.; Keisari, Y.; Markowitz, S.; Dutton, G.; Sharon, N. Lectinophagocytosis of encapsulated Klebsiella pneumoniae mediated by surface lectins of guinea pig alveolar macrophages and human monocyte-derived macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Chuah, S.-K.; Chang, C.-C.; Chen, F.-J. The surface protein fructose-1, 6 bisphosphate aldolase of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K1: Role of interaction with Neutrophils. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Chang, C.-C.; Liu, J.-W.; Chen, R.-F.; Yang, K.D. Sialic acid involved in hypermucoviscosity phenotype of Klebsiella pneumoniae and associated with resistance to neutrophil phagocytosis. Virulence 2014, 5, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal, S.M. Significance of sialic acid in Klebsiella pneumoniae K1 capsules. Virulence 2014, 5, 648–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullen, J.; Rogers, H.J.; Griffiths, E. Iron binding proteins and infection. Br. J. Haematol. 1972, 23, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carniel, E. The Yersinia high-pathogenicity island: An iron-uptake island. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, V.I.; Bachman, M.A. Diverging roles of bacterial siderophores during infection. Metallomics 2015, 7, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miethke, M.; Marahiel, M.A. Siderophore-based iron acquisition and pathogen control. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 413–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, K.E.; Wertheim, H.; Zadoks, R.N.; Baker, S.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Dance, D.; Jenney, A.; Connor, T.R.; Hsu, L.Y.; Severin, J. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3574–E3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Gulick, A.M. Aerobactin synthesis proteins as antivirulence targets in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1052–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zsila, F.; Beke-Somfai, T. Human host-defense peptide LL-37 targets stealth siderophores. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flo, T.H.; Smith, K.D.; Sato, S.; Rodriguez, D.J.; Holmes, M.A.; Strong, R.K.; Akira, S.; Aderem, A. Lipocalin 2 mediates an innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating iron. Nature 2004, 432, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachman, M.A.; Lenio, S.; Schmidt, L.; Oyler, J.E.; Weiser, J.N. Interaction of lipocalin 2, transferrin, and siderophores determines the replicative niche of Klebsiella pneumoniae during pneumonia. MBio 2012, 3, e00224-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar-Sinha, S.; Valencia, G.A.; Janes, B.K.; Rosenberg, J.K.; Whitfield, C.; Bender, R.A.; Standiford, T.J.; Younger, J.G. The Klebsiella pneumoniae O antigen contributes to bacteremia and lethality during murine pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.S.; Mestre, F.; Albertí, S.n.; Hernández-Allés, S.; Álvarez, D.; Doménech-Sánchez, A.; Gil, J.; Merino, S.; Tomás, J.M.; Benedí, V.J. Klebsiella pneumoniae lipopolysaccharide O typing: Revision of prototype strains and O-group distribution among clinical isolates from different sources and countries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.-F.; Liu, J.-Y.; Pan, Y.-J.; Wu, M.-C.; Lin, T.-L. Klebsiella pneumoniae peptidoglycan-associated lipoprotein and murein lipoprotein. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, S.; Camprubi, S.; Alberti, S.; Benedi, V.-J.; Tomas, J. Mechanisms of Klebsiella pneumoniae resistance to complement-mediated killing. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroll, C.; Barken, K.B.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Struve, C. Role of type 1 and type 3 fimbriae in Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm formation. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Huang, Y.-J.; Fung, C.-P.; Peng, H.-L. Regulation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae Kpc fimbriae by the site-specific recombinase KpcI. Microbiology 2010, 156, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, H.-C.; Lee, C.-Z.; Ma, L.-C.; Fang, C.-T.; Chang, S.-C.; Wang, J.-T. Isolation of a chromosomal region of Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with allantoin metabolism and liver infection. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 3783–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusa, E.; Obradors, N.; Baldomà, L.; Badía, J.; Aguilar, J. Genetic analysis of a chromosomal region containing genes required for assimilation of allantoin nitrogen and linked glyoxylate metabolism in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 7479–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compain, F.; Babosan, A.; Brisse, S.; Genel, N.; Audo, J.; Ailloud, F.; Kassis-Chikhani, N.; Arlet, G.; Decré, D. Multiplex PCR for detection of seven virulence factors and K1/K2 capsular serotypes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4377–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faïs, T.; Delmas, J.; Barnich, N.; Bonnet, R.; Dalmasso, G. Colibactin: More than a new bacterial toxin. Toxins 2018, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; Zhou, M.; Jian, Z.; Yan, Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, W. Prevalence of pks gene cluster and characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced bloodstream infections. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulger, J.; MacDonald, U.; Olson, R.; Beanan, J.; Russo, T.A. Metabolite transporter PEG344 is required for full virulence of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strain hvKP1 after pulmonary but not subcutaneous challenge. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00093-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Duan, J.; Liu, L.; Shen, X.; Yu, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, F. Prevalence of community-acquired, hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in Wenzhou, China. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, C.; Jacob, J.J.; Vasudevan, K.; Biswas, R.; Manesh, A.; Sethuvel, D.P.M.; Varughese, S.; Biswas, I.; Veeraraghavan, B. Emergence of multidrug resistant hypervirulent ST23 Klebsiella pneumoniae: Multidrug resistant plasmid acquisition drives evolution. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 575289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Long, D.; Xiang, T.-X.; Du, F.-L.; Wei, D.D.; Wan, L.-G.; Deng, Q.; Cao, X.-W.; Zhang, W. Whole genome assembly and functional portrait of hypervirulent extensively drug-resistant NDM-1 and KPC-2 co-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae of capsular serotype K2 and ST86. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Long, D.; Huang, Q.; Wei, D.; Liu, X.; Wan, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y. Rapid detection to differentiate hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp) from classical K. pneumoniae by identifying peg-344 with loop-mediated isothermal amplication (LAMP). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asokan, G.V.; Ramadhan, T.; Ahmed, E.; Sanad, H. WHO global priority pathogens list: A bibliometric analysis of medline-pubmed for knowledge mobilization to infection prevention and control practices in Bahrain. Oman Med. J. 2019, 34, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance, to Guide Research, Development, and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Pendleton, J.N.; Gorman, S.P.; Gilmore, B.F. Clinical relevance of the ESKAPE pathogens. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2013, 11, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Klebsiella pneumoniae as a key trafficker of drug resistance genes from environmental to clinically important bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navon-Venezia, S.; Kondratyeva, K.; Carattoli, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.-J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, hypervirulence-associated determinants, and resistance mechanisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zong, Z. Carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae of sequence type 36. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02644-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lin, D.; Chan, E.W.-c.; Gu, D.; Chen, G.-X.; Chen, S. Emergence of carbapenem-resistant serotype K1 hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strains in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turton, J.F.; Payne, Z.; Coward, A.; Hopkins, K.L.; Turton, J.A.; Doumith, M.; Woodford, N. Virulence genes in isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae from the UK during 2016, including among carbapenemase gene-positive hypervirulent K1-ST23 and ‘non-hypervirulent’types ST147, ST15 and ST383. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Chen, S. Tracking microevolution events among ST11 carbapenemase-producing hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae outbreak strains. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Hetta, H.F. Ambulance vehicles as a source of multidrug-resistant infections: A multicenter study in Assiut City, Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, A.; Kong, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Fu, Y.; Fu, Y. Endogenous endophthalmitis caused by a multidrug-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strain belonging to a novel single locus variant of ST23: First case report in China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurieva, T.; Dautzenberg, M.J.; Gniadkowski, M.; Derde, L.P.; Bonten, M.J.; Bootsma, M.C. The transmissibility of antibiotic-resistant Enterobacteriaceae in intensive care units. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Tian, L.; Li, G.; Qu, H.; Sun, J.; Liang, W.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J. Emergence of the third-generation cephalosporin-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae due to the acquisition of a self-transferable bla DHA-1-carrying plasmid by an ST23 strain. Virulence 2018, 9, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cejas, D.; Fernández Canigia, L.; Rincón Cruz, G.; Elena, A.X.; Maldonado, I.; Gutkind, G.O.; Radice, M.A. First isolate of KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumonaie sequence type 23 from the Americas. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3483–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Liu, W.; Zhao, F.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, H. Emergence of a hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate from clinical infections in China. J. Infect. 2015, 71, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.-d.; Wan, L.-G.; Deng, Q.; Liu, Y. Emergence of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae hypervirulent clone of capsular serotype K1 that belongs to sequence type 11 in Mainland China. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 85, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Chou, S.-H.; Liang, S.-W.; Ni, C.-E.; Lin, Y.-T.; Huang, Y.-W.; Yang, T.-C. Emergence of an XDR and carbapenemase-producing hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae strain in Taiwan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannatelli, A.; Giani, T.; D'Andrea, M.M.; Di Pilato, V.; Arena, F.; Conte, V.; Tryfinopoulou, K.; Vatopoulos, A.; Rossolini, G.M. MgrB inactivation is a common mechanism of colistin resistance in KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae of clinical origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5696–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Handigund, M.; Hwang, J.H.; Cho, Y.G.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, J. Clinical features and risk factors associated with 30-day mortality in patients with pneumonia caused by hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKP). Ann. Lab Med. 2020, 40, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, S.; Jacob, T.; Jacob, J.; AlSosowaa, A.A.; Cherian, T.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Vijayan, S. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A growing threat in the era of antimicrobial resistance. Microbe 2025, 7, 100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.; Dolin, R.; Blaser, M. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases: 2-Volume Set: Elsevier Health Sciences; Philadelphia, Saunders, Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Gu, G.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Li, J. Risk factors and clinical outcomes of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae induced bloodstream infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomakova, D.; Hsiao, C.; Beanan, J.; Olson, R.; MacDonald, U.; Keynan, Y.; Russo, T. Clinical and phenotypic differences between classic and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumonia: An emerging and under-recognized pathogenic variant. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobirk, S.K.; Struve, C.; Jacobsson, S.G. Primary Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess with metastatic spread to lung and eye, a North-European case report of an emerging syndrome. Open Microbiol. J. 2010, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, L.K.; Yeh, K.-M.; Lin, J.-C.; Fung, C.-P.; Chang, F.-Y. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: A new invasive syndrome. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederman, E.R.; Crum, N.F. Pyogenic liver abscess with a focus on Klebsiella pneumoniae as a primary pathogen: An emerging disease with unique clinical characteristics. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. | ACG 2005, 100, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastagia, M.; Arumugam, V. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscesses in a public hospital in Queens, New York. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2008, 6, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, D.; Lee, H.; Park, M.; Jung, S.-I.; Chang, H.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Son, J.; Moon, C.; Kwon, K.; Ryu, S. Fecal carriage of serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23 strains closely related to liver abscess isolates in Koreans living in Korea. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, W.Y.; Hwang, C.Y.; Chang, Y.T.; Su, C.W.; Hou, M.C.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, F.Y.; Lee, S.D.; Wu, J.C. Cancer risk in patients with pyogenic liver abscess: A nationwide cohort study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 36, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.K.; Chang, J.C.; See, L.C.; Tu, H.T.; Chen, J.S.; Liaw, C.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Yang, T.S. Higher rate of colorectal cancer among patients with pyogenic liver abscess with Klebsiella pneumoniae than those without: An 11-year follow-up study. Color. Dis. 2012, 14, e794–e801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltin, D.; Goldberg, E.; Bugaevsky, O.; Kelner, E.; Birkenfeld, S.; Gingold-Belfer, R.; Keller, N.; Niv, Y.; Dickman, R. Colonic carriage of Streptococcus bovis and colorectal neoplasia: A prospective 17-year longitudinal case–control study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, I.; Aldape, M.J.; Bryant, A.E.; Stevens, D.L. Spontaneous C. ásepticum gas gangrene: A literature review. Anaerobe 2017, 48, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Feng, J.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; Feng, Y.; Guo, R.; Zhou, M.; Hou, S.; Wang, G.; Hao, H.; et al. Epidemiology, environmental risks, virulence, and resistance determinants of Klebsiella pneumoniae from dairy cows in Hubei, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 858799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, S.; Doi, Y. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A call for consensus definition and international collaboration. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00959-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Guo, J. High prevalence of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in the genetic background of elderly patients in two teaching hospitals in China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetta, H.F.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.S. Editorial for special issue “antibiotic combination therapy: A strategy to overcome bacterial resistance”. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, S.M.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Mahran, K.M.; Hetta, H.F.; Abd El-Baky, R.M. Antimicrobial resistance pattern and molecular genetic distribution of metallo-β-lactamases producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from hospitals in Minia, Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Júnior, N.G.; Franco, O.L. Promising strategies for future treatment of Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms. Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.A.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Aziz, S.N.; Garallah, E.T.; Aziz, R.N.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Hetta, H.F. Bacterial dormancy: Strategies and molecular mechanisms for a sleeping beauty system. Rev. Res. Med. Microbiol. 2025, 10-1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-M.; Chung, A.Y.-F.; Chow, P.K.-H.; Cheow, P.-C.; Wong, W.-K.; Ooi, L.L.; Soo, K.-C. An appraisal of surgical and percutaneous drainage for pyogenic liver abscesses larger than 5 cm. Ann. Surg. 2005, 241, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, R.; Wang, G.; Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Guan, Y.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xi, H.; Zhao, R. Combination therapy of phage vB_KpnM_P-KP2 and gentamicin combats acute pneumonia caused by K47 serotype Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Rashed, Z.I.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Kassem, S.M.; Ata, H.S.; Nageeb, W.M. Phage therapy, a salvage treatment for multidrug-resistant bacteria causing infective endocarditis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurabov, F.; Zhilenkov, E. Characterization of four virulent Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteriophages, and evaluation of their potential use in complex phage preparation. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, M.F.; Bridwell, A.E.M.; Scott, N.E.; Vinogradov, E.; McKee, S.R.; Chavez, S.M.; Twentyman, J.; Stallings, C.L.; Rosen, D.A.; Harding, C.M. A promising bioconjugate vaccine against hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18655–18663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargaran, F.N.; Akya, A.; Rezaeian, S.; Ghadiri, K.; Lorestani, R.C.; Madanchi, H.; Safaei, S.; Rostamian, M. B cell epitopes of four fimbriae antigens of Klebsiella pneumoniae: A comprehensive in silico study for vaccine development. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diago-Navarro, E.; Calatayud-Baselga, I.; Sun, D.; Khairallah, C.; Mann, I.; Ulacia-Hernando, A.; Sheridan, B.; Shi, M.; Fries, B.C. Antibody-based immunotherapy to treat and prevent infection with hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2017, 24, e00456-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetta, H.F.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Khazaal, S.S.; Abbas, S.; Suhail, A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Ellah, N.H.A.; Ahmed, E.A.; Abd-Ellatief, R.B.; El-Masry, E.A. Antibiofilm and antivirulence potential of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Rashed, Z.I.; Alharbi, A.A.; Alsharef, S.; Alkindy, T.T.; Alkhamali, A.; Albalawi, A.S.; Battah, B.; Donadu, M.G. Quorum sensing inhibitors: An alternative strategy to win the battle against multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. Molecules 2024, 29, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Sirag, N.; Alsharif, S.M.; Alharbi, A.A.; Alkindy, T.T.; Alkhamali, A.; Albalawi, A.S.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Rashed, Z.I.; Alanazi, F.E. Antimicrobial peptides: The game-changer in the epic battle against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetta, H.F.; Ramadan, Y.N.; Al-Harbi, A.I.; Ahmed, E.A.; Battah, B.; Abd Ellah, N.H.; Zanetti, S.; Donadu, M.G. Nanotechnology as a promising approach to combat multidrug resistant bacteria: A comprehensive review and future perspectives. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Shama, U.H.; El-Gendy, H.; Mousa, W.S.; Hamouda, R.A.; Yousuf, W.E.; Hetta, H.F.; Abdeen, E.E. Synergistic and antagonistic effects of metal nanoparticles in combination with antibiotics against some reference strains of pathogenic microorganisms. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hetta, H.F.; Alanazi, F.E.; Ali, M.A.S.; Alatawi, A.D.; Aljohani, H.M.; Ahmed, R.; Alansari, N.A.; Alkhathami, F.M.; Albogmi, A.; Alharbi, B.M.; et al. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Insights into Virulence, Antibiotic Resistance, and Fight Strategies Against a Superbug. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050724
Hetta HF, Alanazi FE, Ali MAS, Alatawi AD, Aljohani HM, Ahmed R, Alansari NA, Alkhathami FM, Albogmi A, Alharbi BM, et al. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Insights into Virulence, Antibiotic Resistance, and Fight Strategies Against a Superbug. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050724
Chicago/Turabian StyleHetta, Helal F., Fawaz E. Alanazi, Mostafa A. Sayed Ali, Ahmed D. Alatawi, Hashim M. Aljohani, Rehab Ahmed, Nuha A. Alansari, Fahad M. Alkhathami, Alaa Albogmi, Bander M. Alharbi, and et al. 2025. "Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Insights into Virulence, Antibiotic Resistance, and Fight Strategies Against a Superbug" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050724
APA StyleHetta, H. F., Alanazi, F. E., Ali, M. A. S., Alatawi, A. D., Aljohani, H. M., Ahmed, R., Alansari, N. A., Alkhathami, F. M., Albogmi, A., Alharbi, B. M., Alanzi, H. S., Alaqyli, A. B., & Ramadan, Y. N. (2025). Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Insights into Virulence, Antibiotic Resistance, and Fight Strategies Against a Superbug. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050724





