Phytochemicals Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease: A Mechanistic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Inflammation-Associated Signaling Pathways in ALD and Its Modulation by Phytochemicals
2.1. Alteration of Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Gut Microbiota
2.2. Hepatic Inflammation and the Role of Immune Cells in ALD
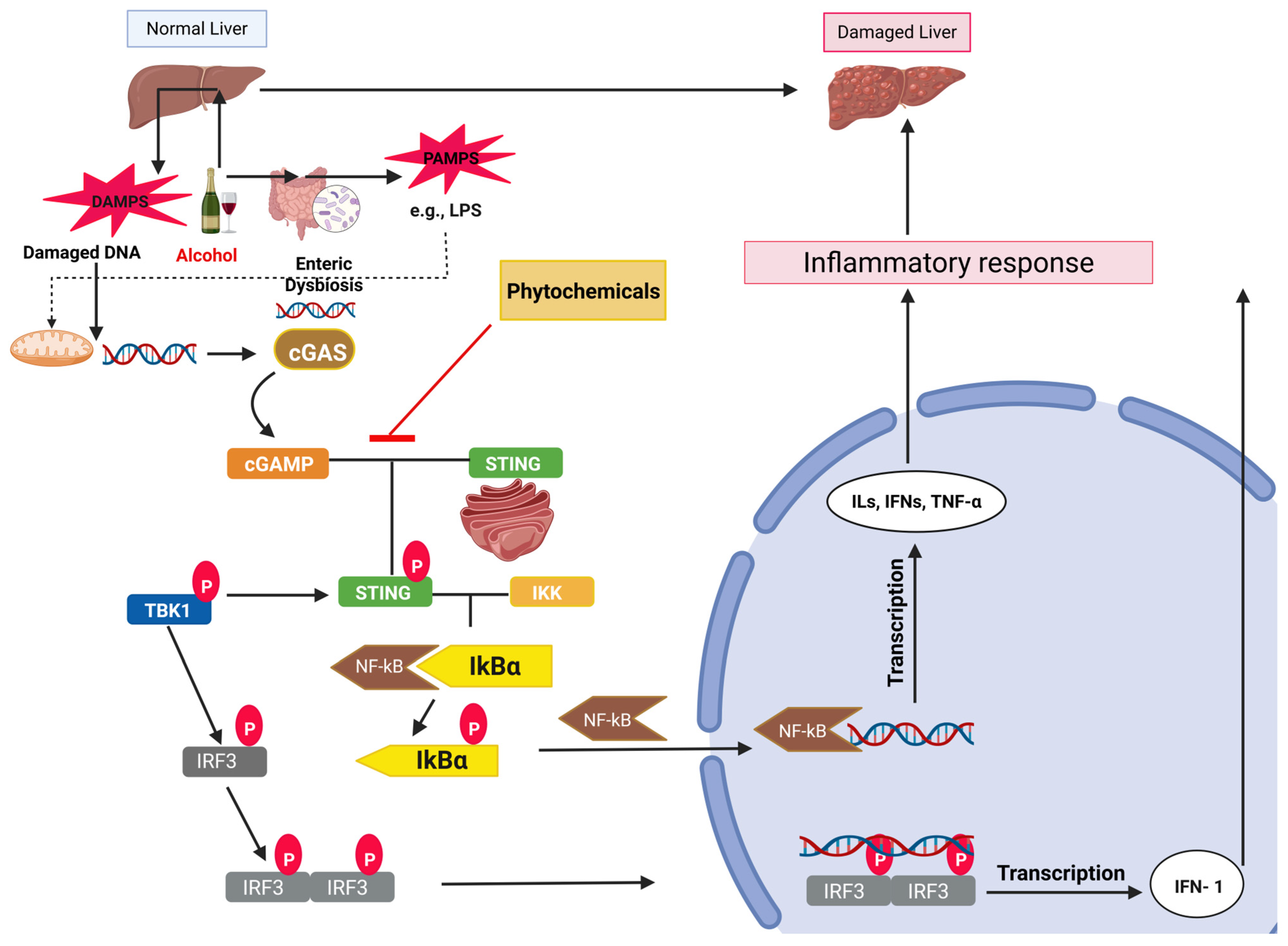
2.3. cGAS-STING Signaling in ALD
2.4. NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Axis in ALD
2.5. NF-кB Signaling Axis in ALD
2.6. MAPK Signaling Axis in ALD
2.7. JAK-STAT Signaling Axis in ALD
3. Conclusions and Future Perspective
4. Database Search
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFL | Alcoholic fatty liver |
| ALD | Alcohol-induced liver disease |
| APCs | Antigen-presenting cells |
| ASC | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein |
| cGAS | Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate (cGAMP) synthase |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| HSCs | Hepatic stellate cells |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IFR | Interferon regulatory factor |
| ILs | Interleukins |
| JAK-STAT | Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| NK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor–kappa B |
| NKT | Natural killer T cells |
| NLRP3 | NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| PAMPs | Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| PRR | Pattern recognition receptor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| STING | Stimulator of interferon gene |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-β |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Walsh, K.; Alexander, G. Alcoholic liver disease. Postgrad. Med. J. 2000, 76, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hernández-Évole, H.; Jiménez-Esquivel, N.; Pose, E.; Bataller, R. Alcohol-associated liver disease: Epidemiology and management. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torruellas, C.; French, S.W.; Medici, V. Diagnosis of alcoholic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11684–11699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, R.; Sinclair, J.M.A. Alcohol use disorder and the liver. Addiction 2021, 116, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, F.; Wong, N.K.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Chen, S.; Li, W.; Koike, K.; Liu, X.; et al. Epidemiological Realities of Alcoholic Liver Disease: Global Burden, Research Trends, and Therapeutic Promise. Gene Expr. 2020, 20, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, J.; Shield, K.D. Global burden of alcohol use disorders and alcohol liver disease. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H.K.; Bataller, R.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Gao, B.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Mueller, S.; Szabo, G.; Tsukamoto, H. Alcoholic liver disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2018, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’shea, R.S.; Dasarathy, S.; McCullough, A.J.; Practice Guideline Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Bala, S. Alcoholic liver disease and the gut-liver axis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangpunsakul, S.; Haber, P.; McCaughan, G.W. Alcoholic liver disease in Asia, Europe, and North America. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1786–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberg, F.; Byrne, C.D.; Pirola, C.J.; Mannisto, V.; Sookoian, S. Alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome: Clinical and epidemiological impact on liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Y.R.; Tian, Z. Roles of hepatic stellate cells in acute liver failure: From the perspective of inflammation and fibrosis. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mehal, W.; Nagy, L.E.; Rotman, Y. Immunological mechanisms and therapeutic targets of fatty liver diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamirano, J.; Lopez-Pelayo, H.; Michelena, J.; Jones, P.D.; Ortega, L.; Gines, P.; Caballeria, J.; Gual, A.; Bataller, R.; Lligona, A. Alcohol abstinence in patients surviving an episode of alcoholic hepatitis: Prediction and impact on long-term survival. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1842–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofair, A.N.; Barry, V.; Manos, M.M.; Thomas, A.; Zaman, A.; Terrault, N.A.; Murphy, R.C.; Stabach, N.; Huie, S.; Van Ness, G.; et al. The epidemiology and clinical characteristics of patients with newly diagnosed alcohol-related liver disease: Results from population-based surveillance. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.D.; Feng, B.; Gao, Y.; Wei, L. Effect of abstinence from alcohol on survival of patients with alcoholic cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Tsao, S.W.; Feng, Y. Current status of herbal medicines in chronic liver disease therapy: The biological effects, molecular targets and future prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28705–28745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osna, N.A.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Kharbanda, K.K. Alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenesis and current management. Alcohol Res. 2017, 38, 147–161. [Google Scholar]
- Akriviadis, E.; Botla, R.; Briggs, W.; Han, S.; Reynolds, T.; Shakil, O. Pentoxifylline improves short-term survival in severe acute alcoholic hepatitis: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Mathurin, P. Diagnosis and treatment of alcohol-associated liver disease: A review. JAMA 2021, 326, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, C.A. A comprehensive review of diagnosis and management of alcohol-associated hepatitis. SAGE Open Medicine 2024, 12, 20503121241297000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, N.T.; Maurice, J.B.; Nasralla, D.; Potts, J.; Westbrook, R. Recent advances in liver transplantation. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, N.S.; Bhangui, P.; Soin, A.S. Liver Transplant Outcomes in India. Clin. Liver Dis. 2022, 19, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Yan, N.; Wang, P.; Xia, Y.; Hao, H.; Wang, G.; Gonzalez, F.J. Herbal drug discovery for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laka, K.; Makgoo, L.; Mbita, Z. Cholesterol-lowering phytochemicals: Targeting the mevalonate pathway for anticancer interventions. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 841639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alum, E.U. Role of phytochemicals in cardiovascular disease management: Insights into mechanisms, efficacy, and clinical application. Phytomed. Plus 2025, 5, 100695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørkhaug, S.T.; Aanes, H.; Neupane, S.P.; Bramness, J.G.; Malvik, S.; Henriksen, C.; Skar, V.; Medhus, A.W.; Valeur, J. Characterization of gut microbiota composition and functions in patients with chronic alcohol overconsumption. Gut microbes 2019, 10, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G. Gut–liver axis in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fouts, D.E.; Starkel, P.; Hartmann, P.; Chen, P.; Llorente, C.; DePew, J.; Moncera, K.; Ho, S.B.; Brenner, D.A.; et al. Intestinal REG3 lectins protect against alcoholic steatohepatitis by reducing mucosa-associated microbiota and preventing bacterial translocation. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhong, W. Targeting the gut barrier for the treatment of alcoholic liver disease. Liver Res. 2017, 1, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, S.; Matamoros, S.; Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Jamar, F.; Starkel, P.; Windey, K.; Tremaroli, V.; Backhed, F.; Verbeke, K.; et al. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4485–E4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlesak, A.; Schafer, C.; Schutz, T.; Bode, J.C.; Bode, C. Increased intestinal permeability to macromolecules and endotoxemia in patients with chronic alcohol abuse in different stages of alcohol-induced liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, V.; Bode, J.C.; Bode, C.; Brenner, D.A.; Choudhry, M.A.; Hamilton, F.; Kang, Y.J.; Keshavarzian, A.; Rao, R.; Sartor, R.B.; et al. Alcohol, intestinal bacterial growth, intestinal permeability to endotoxin, and medical consequences: Summary of a symposium. Alcohol 2008, 42, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederbaum, A.I. Alcohol metabolism. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahadeeswaran, S.; Dasgupta, T.; Manickam, V.; Saraswathi, V.; Tamizhselvi, R. NLRP3: A new therapeutic target in alcoholic liver disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1215333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrier, L.; Berard, F.; Debrauwer, L.; Chabo, C.; Langella, P.; Bueno, L.; Fioramonti, J. Impairment of the intestinal barrier by ethanol involves enteric microflora and mast cell activation in rodents. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R. Endotoxemia and gut barrier dysfunction in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 50, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, S.; Toratani, S.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Kashiwabara, Y.; Vogel, S.N.; Metcalf, E.S. Pro- and anti-inflammatory gene expression in the murine small intestine and liver after chronic exposure to alcohol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 579–589. [Google Scholar]
- Fadl, A.A.; Sha, J.; Klimpel, G.R.; Olano, J.P.; Niesel, D.W.; Chopra, A.K. Murein lipoprotein is a critical outer membrane component involved in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium systemic infection. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1081–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, Y.; Bradford, B.U.; Gao, W.; Bojes, H.K.; Thurman, R.G. Inactivation of Kupffer cells prevents early alcohol-induced liver injury. Hepatology 1994, 20, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaa, A.; Thompson, K.J.; McKillop, I.H.; Clemens, M.G.; Schrum, L.W. S-adenosyl-L-methionine attenuates oxidative stress and hepatic stellate cell activation in an ethanol-LPS-induced fibrotic rat model. Shock 2008, 30, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.J.; Gong, Z.J.; Zhou, X.R.; Zhang, P.; Sun, X.M.; Li, X. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2006, 7, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, L.; Huang, F.; Deng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, M. Lychee (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) pulp phenolic extract provides protection against alcoholic liver injury in mice by alleviating intestinal microbiota dysbiosis, intestinal barrier dysfunction, and liver inflammation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9675–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Qiu, P.; Wang, J.; Niu, C.; Pan, S. Effects of compound Ginkgo biloba on intestinal permeability in rats with alcohol-induced liver injury. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Wu, C.; Jia, X.; Dong, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, M. Rice bran phenolic extract protects against alcoholic liver injury in mice by alleviating intestinal microbiota dysbiosis, barrier dysfunction, and liver inflammation mediated by the endotoxin–TLR4–NF-κB pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 68, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Yang, S.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Watanabe, Y.; Chen, J.R. Caulerpa lentillifera improves ethanol-induced liver injury and modulates the gut microbiota in rats. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Ahmad, M.F.; Nagy, L.E.; Tsukamoto, H. Inflammatory pathways in alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifnia, T.; Antoun, J.; Verriere, T.G.; Suarez, G.; Wattacheril, J.; Wilson, K.T.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Abumrad, N.N.; Flynn, C.R. Hepatic TLR4 signaling in obese NAFLD. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G270–G278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pone, E.J. Analysis by flow cytometry of B-cell activation and antibody responses induced by toll-like receptors. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1390, 229–248. [Google Scholar]
- Osna, N.A.; Rasineni, K.; Ganesan, M.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Kharbanda, K.K. Pathogenesis of alcohol-associated liver disease. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 1492–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, M.G. Cytokines—Central factors in alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Res. Health 2003, 27, 307. [Google Scholar]
- Thurman, R.G. Alcoholic liver injury involves activation of Kupffer cells by endotoxin. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, G605–G611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClain, C.J.; Song, Z.; Barve, S.S.; Hill, D.B.; Deaciuc, I. Recent advances in alcoholic liver disease. IV. Dysregulated cytokine metabolism in alcoholic liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 287, G497–G502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Diehl, A.M. Cytokines in alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Medicine 2000, 343, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatano, E. Tumor necrosis factor signaling in hepatocyte apoptosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22 (Suppl. S1), S43–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Webber, E.M.; Kirillova, I.; Peschon, J.J.; Fausto, N. Analysis of liver regeneration in mice lacking type 1 or type 2 tumor necrosis factor receptor: Requirement for type 1 but not type 2 receptor. Hepatology 1998, 28, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, M.G.; Shear, N.H.; Bellentani, S.; Tiribelli, C. Role of cytokines in ethanol-induced cytotoxicity in vitro in Hep G2 cells. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.N.; Sun, R.; Jaruga, B.; Hong, F.; Kim, W.H.; Gao, B. Chronic ethanol consumption inhibits hepatic natural killer cell activity and accelerates murine cytomegalovirus-induced hepatitis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Yan, G.; Zheng, X.; Bai, L.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z. Suppression of Natural Killer cell activity by regulatory NKT10 cells aggravates alcoholic hepatosteatosis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Mahler, S.; Chervenak, R.; Wolcott, M. Alcohol affects the late differentiation of progenitor B cells. Alcohol Alcohol. 2011, 46, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Wang, F.; Wong, N.K.; Lv, Y.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Tipoe, G.L.; So, K.F.; Xu, A.; Chen, S.; et al. Divergent roles of Kupffer cell TLR2/3 signaling in alcoholic liver disease and the protective role of EGCG. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 9, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentek, R.; Molawi, K.; Sieweke, M.H. Tissue macrophage identity and self-renewal. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 262, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heide, D.; Weiskirchen, R.; Bansal, R. Therapeutic targeting of hepatic macrophages for the treatment of liver diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atri, C.; Guerfali, F.Z.; Laouini, D. Role of human macrophage polarization in inflammation during infectious diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voican, C.S.; Njike-Nakseu, M.; Boujedidi, H.; Barri-Ova, N.; Bouchet-Delbos, L.; Agostini, H.; Maitre, S.; Prevot, S.; Cassard-Doulcier, A.M.; Naveau, S.; et al. Alcohol withdrawal alleviates adipose tissue inflammation in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Benkdane, M.; Alons, E.; Lotersztajn, S.; Pavoine, C. M2 Kupffer cells promote hepatocyte senescence: An IL-6–dependent protective mechanism against alcoholic liver disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, R.; Wu, R.; Lee, S.; Zhu, N.L.; Chen, C.L.; French, S.W.; Xu, J.; Machida, K.; Tsukamoto, H. Osteopontin deficiency does not prevent but promotes alcoholic neutrophilic hepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2015, 61, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Kubes, P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2013, 13, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.S.; Lalor, P.F.; Thursz, M.; Newsome, P.N. The role of neutrophils in alcohol-related hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, K.L.; Cajigas-Du Ross, C.K.; Chaney, J.K.; Nagy, L.E. Role of the chemokine system in liver fibrosis: A narrative review. Dig. Med. Res. 2022, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Peiffer, B.; Feng, D.; Parra, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Shah, V.H.; Cameron, A.M.; Sun, Z.; Gao, B. IL-8+ neutrophils drive inexorable inflammation in severe alcohol-associated hepatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e178616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Feng, D.; Maccioni, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, B. New therapeutic target for alcohol-associated hepatitis (AH): AH-associated IL-8(+) neutrophils. eGastroenterology 2024, 2, e100166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, J.J. Rat hepatocytes and Kupffer cells interact to produce interleukin-8 (CINC) in the setting of ethanol. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 269, G518–G523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, H.; Dong, Z.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Zuo, L.; Wang, H. Platelets in alcohol-associated liver disease: Interaction with neutrophils. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 18, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.Z.; Chandimali, N.; Han, Y.H.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, T.D.; Jeong, D.K.; Sun, H.N.; Lee, D.S.; et al. Pathogenesis, early diagnosis, and therapeutic management of alcoholic liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Uchinami, H.; Qian, T.; Bennett, B.L.; Lemasters, J.J.; Brenner, D.A. Differential requirement for c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase in TNF-α-and Fas-mediated apoptosis in hepatocytes. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukić, M.; Radonjić, T.; Jovanović, I.; Zdravković, M.; Todorović, Z.; Kraišnik, N.; Aranđelović, B.; Mandić, O.; Popadić, V.; Nikolić, N. Alcohol, inflammation, and microbiota in alcoholic liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kong, L.; Shao, M.; Liu, J.; Sun, C.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Chai, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Protective effect of flavonoids extract of Hippophae rhamnoides L. on alcoholic fatty liver disease through regulating intestinal flora and inhibiting TAK1/p38MAPK/p65NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 292, 115225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamuta, M.; Higashi, N.; Kohjima, M.; Fukushima, M.; Ohta, S.; Kotoh, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Enjoji, M. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a polyphenol component of green tea, suppresses both collagen production and collagenase activity in hepatic stellate cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 677–681. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, L.; Liao, M.; Zheng, L.; He, M.; Huang, Q.; Wei, L.; Huang, R.; Zhang, S.; Lin, X. Combination therapy with taurine, epigallocatechin gallate and genistein for protection against hepatic fibrosis induced by alcohol in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1802–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Tan, Q.; Xv, S.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, T.; Mo, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates alcohol-induced liver injury by inhibiting steatosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 616409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.B.; Rashid, S.M.; Wali, A.F.; Ali, S.; Rehman, M.U.; Maqbool, M.T.; Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, S.F.; Siddiqui, N. Myricetin (3,3(‘),4(‘),5,5(‘),7-hexahydroxyflavone) prevents ethanol-induced biochemical and inflammatory damage in the liver of Wistar rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 9603271211066843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Mehmood, A.; Yuan, D.; Usman, M.; Murtaza, M.A.; Yaqoob, S.; Wang, C. Protective mechanism of edible food plants against alcoholic liver disease with special mention to polyphenolic compounds. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, G.N. STING: Infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2015, 15, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Du, J.; Zhu, H.; Ling, Q. The role of cGAS-STING signalling in liver diseases. JHEP Reports 2021, 3, 100324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, J.; Khan, S.; Gala, M.K.; Kedrin, D.; Sridharan, G.; Goodman, R.P.; Garber, J.J.; Masia, R.; Diagacomo, E.; Adams, D.; et al. Hepatic gap junctions amplify alcohol liver injury by propagating cGAS-mediated IRF3 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11667–11673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bai, X.C.; Chen, Z.J. Structures and mechanisms in the cGAS-STING innate immunity pathway. Immunity 2020, 53, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shu, C.; Yi, G.; Chaton, C.T.; Shelton, C.L.; Diao, J.; Zuo, X.; Kao, C.C.; Herr, A.B.; Li, P. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is activated by double-stranded DNA-induced oligomerization. Immunity 2013, 39, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, E.J.; Burdette, D.L.; Wilson, S.C.; Monroe, K.M.; Kellenberger, C.A.; Hyodo, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Hammond, M.C.; Vance, R.E. The innate immune DNA sensor cGAS produces a noncanonical cyclic dinucleotide that activates human STING. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablasser, A.; Goldeck, M.; Cavlar, T.; Deimling, T.; Witte, G.; Röhl, I.; Hopfner, K.-P.; Ludwig, J.; Hornung, V. cGAS produces a 2′-5′-linked cyclic dinucleotide second messenger that activates STING. Nature 2013, 498, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.J.; Bai, X.-c.; Zhang, X. Cryo-EM structures of STING reveal its mechanism of activation by cyclic GMP–AMP. Nature 2019, 567, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdette, D.L.; Monroe, K.M.; Sotelo-Troha, K.; Iwig, J.S.; Eckert, B.; Hyodo, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Vance, R.E. STING is a direct innate immune sensor of cyclic di-GMP. Nature 2011, 478, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, S.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Ru, H.; Shaw, N.; Jiang, Y.; Niu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Qiu, W.; Parvatiyar, K.; et al. Structural analysis of the STING adaptor protein reveals a hydrophobic dimer interface and mode of cyclic di-GMP binding. Immunity 2012, 36, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Barber, G.N. STING is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune signalling. Nature 2008, 455, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikanth, S.; Woo, J.S.; Wu, B.; El-Sherbiny, Y.M.; Leung, J.; Chupradit, K.; Rice, L.; Seo, G.J.; Calmettes, G.; Ramakrishna, C.; et al. The Ca(2+) sensor STIM1 regulates the type I interferon response by retaining the signaling adaptor STING at the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Du, F.; Xu, P.; Shu, C.; Sankaran, B.; Bell, S.L.; Liu, M.; Lei, Y.; Gao, X.; Fu, X.; et al. A conserved PLPLRT/SD motif of STING mediates the recruitment and activation of TBK1. Nature 2019, 569, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shang, G.; Gui, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.C.; Chen, Z.J. Structural basis of STING binding with and phosphorylation by TBK1. Nature 2019, 567, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Z.; Barber, G.N. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature 2009, 461, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Barber, G.N. Cytosolic-DNA-mediated, STING-dependent proinflammatory gene induction necessitates canonical NF-κB activation through TBK1. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5328–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ka, F. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 491–496. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Weng, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Shao, J.; Zheng, S. Oroxylin A activates ferritinophagy to induce hepatic stellate cell senescence against hepatic fibrosis by regulating cGAS-STING pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Antoine, D.J.; Lu, Y.; Arriazu, E.; Leung, T.M.; Klepper, A.L.; Branch, A.D.; Fiel, M.I.; Nieto, N. High mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) participates in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease (ALD). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22672–22691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjumaki, R.; Pridgeon, C.S.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. CYP2E1 in alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver injury. Roles of ROS, reactive intermediates and lipid overload. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McVicker, B.L.; Tuma, P.L.; Kharbanda, K.K.; Lee, S.M.; Tuma, D.J. Relationship between oxidative stress and hepatic glutathione levels in ethanol-mediated apoptosis of polarized hepatic cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2609–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: An overview of mechanisms of activation and regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehlen, N.; Crouchet, E.; Baumert, T.F. Liver fibrosis: Mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives. Cells 2020, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minutoli, L.; Puzzolo, D.; Rinaldi, M.; Irrera, N.; Marini, H.; Arcoraci, V.; Bitto, A.; Crea, G.; Pisani, A.; Squadrito, F.; et al. ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in brain, heart, kidney, and testis ischemia/reperfusion injury. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 2183026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Crother, T.R.; Karlin, J.; Dagvadorj, J.; Chiba, N.; Chen, S.; Ramanujan, V.K.; Wolf, A.J.; Vergnes, L.; Ojcius, D.M.; et al. Oxidized mitochondrial DNA activates the NLRP3 inflammasome during apoptosis. Immunity 2012, 36, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C.; Liu, P.F.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Shu, C.W. The interplay of autophagy and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis and therapy of retinal degenerative diseases. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Cai, T.; Wang, F.; Shao, F. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 2015, 526, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; She, Y.; Sun, Q.; Shi, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.-C.; Shao, F. Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature 2016, 535, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, T.; Xiao, J.; Xu, C.; Alippe, Y.; Sun, K.; Kanneganti, T.-D.; Monahan, J.B.; Abu-Amer, Y.; Lieberman, J. NLRP3 inflammasome activation triggers gasdermin D–independent inflammation. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabj3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evavold, C.L.; Ruan, J.; Tan, Y.; Xia, S.; Wu, H.; Kagan, J.C. The pore-forming protein gasdermin D regulates interleukin-1 secretion from living macrophages. Immunity 2018, 48, 35–44 e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Li, N.; Ren, R.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Lu, F.; Zong, R.; Yang, L.; Ma, X. Progress in the medicinal value, bioactive compounds, and pharmacological activities of Gynostemma pentaphyllum. Molecules 2021, 26, 6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Chen, Y.J.; Feng, Y.R.; Tang, Z.P. LanGui tea, an herbal medicine formula, protects against binge alcohol-induced acute liver injury by activating AMPK-NLRP3 signaling. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tian, L.; Chai, G.; Wen, B.; Wang, B. Targeting heme oxygenase-1 by quercetin ameliorates alcohol-induced acute liver injury via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4184–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pang, N.; Luo, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L. CBD alleviates liver injuries in alcoholics with high-fat high-cholesterol diet through regulating NLRP3 inflammasome–pyroptosis pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 724747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Li, X.; Jiang, M.; Cui, B.-W.; Xia, K.-L.; Wu, Y.-L.; Lian, L.-H.; Nan, J.-X. Amelioration of alcoholic liver steatosis by dihydroquercetin through the modulation of AMPK-dependent lipogenesis mediated by P2X7R–NLRP3-inflammasome activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4862–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Huang, X.; Liao, T.; Li, G.; Yu, X.; You, Y.; Huang, Y. Daucosterol induces autophagic-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer via JNK activation. Biosci. Trends 2019, 13, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, S.M.; El-Haddad, A.E.; El-Raey, M.A.; Abd El-Khalik, S.M.; Koheil, M.A.; Wink, M. A new octadecenoic acid derivative from Caesalpinia gilliesii flowers with potent hepatoprotective activity. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, S332–S336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, M.; Zha, Y.; Zhou, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, S. Daucosterol alleviates alcohol−induced hepatic injury and inflammation through P38/NF−ΚB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Nutrients 2023, 15, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, N.H.; Quang, T.H.; Son, J.H.; Koo, J.E.; Hong, H.J.; Koh, Y.S.; Song, G.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Inhibitory effect of ginsenosides from steamed ginseng-leaves and flowers on the LPS-stimulated IL-12 production in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2011, 34, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Yang, R.; Feng, R.; Liu, J.; Wan, J.B. Ginsenoside Rk2, a dehydroprotopanaxadiol saponin, alleviates alcoholic liver disease via regulating NLRP3 and NLRP6 inflammasome signaling pathways in mice. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Q. Clinical benefits and pharmacology of scutellarin: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 190, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, Z.; Fan, H.; Yang, Q.; Yu, G.; Pan, E.; He, N.; Li, X.; Zhao, P.; Fu, M. Scutellarin prevents acute alcohol-induced liver injury via inhibiting oxidative stress by regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibiting inflammation by regulating the AKT, p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathways. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B 2023, 24, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxford, T.; Ghosh, G. A structural guide to proteins of the NF-κB signaling module. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Bai, L.; Chen, W.; Xu, S. The NF-κB activation pathways, emerging molecular targets for cancer prevention and therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.J.; Relja, B. The impact of acute or chronic alcohol intake on the NF-Kappab signaling pathway in alcohol-related liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turvey, S.E.; Broide, D.H. Innate immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S24–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Regulation of inducible gene expression by the transcription factor NF-κB. Immunol. Res. 1999, 19, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, P.; Szabo, G. Signalling pathways in alcohol-induced liver inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czauderna, C.; Castven, D.; Mahn, F.L.; Marquardt, J.U. Context-dependent role of NF-κB signaling in primary liver cancer—From tumor development to therapeutic implications. Cancers 2019, 11, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdi, W.A.; AlGhamdi, S.A.; Alghamdi, A.M.; Imam, S.S.; Alshehri, S.; Almaniea, M.A.; Hajjar, B.M.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Sayyed, N.; Kazmi, I. Effect of Europinidin against alcohol-induced liver damage in rats by inhibiting the TNF-α/TGF-β/IFN-γ/NF-kB/Caspase-3 signaling pathway. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 22656–22664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyan, V.; Lubau, N.S.A.; Mukerjee, N.; Kumarasamy, V. Alcohol-induced liver injury in signalling pathways and curcumin’s therapeutic potential. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 11, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. Protective effect of artemisinin on chronic alcohol induced-liver damage in mice. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 52, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amen, Y.; Sherif, A.E.; Shawky, N.M.; Abdelrahman, R.S.; Wink, M.; Sobeh, M. Grape-leaf extract attenuates alcohol-induced liver injury via interference with NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, J.; Gong, K.; Chen, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, M.; Duan, Y.; Liao, C.; Han, J. Glabridin ameliorates alcohol-caused liver damage by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation via p38 MAPK/Nrf2/NF-κB pathway. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, R.; Zhang, S.; Lin, J.; Wei, L.; He, M.; Zhuo, L.; Lin, X. Protective effect of genistein isolated from Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides on hepatic injury and fibrosis induced by chronic alcohol in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 217, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.-C.; Zhou, R.-J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, M.; Ye, H.; Xie, M.-L. Apigenin protects against alcohol-induced liver injury in mice by regulating hepatic CYP2E1-mediated oxidative stress and PPARα-mediated lipogenic gene expression. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 275, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchetti, T.; Morresi, C.; Bellachioma, L.; Ferretti, G. Antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties of carthamus tinctorius, hydroxy safflor yellow A, and safflor yellow A. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Yuan, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of hydroxyl safflower yellow a in diabetic nephropathy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 929169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Fu, X.; Qi, M.; Zhu, F.; Fan, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chu, S. Hydroxysafflor yellow A ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury through PI3K/Akt and STAT3/NF-κB signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Hu, S.; Wu, X.; Ma, A.; Ma, Y. Lutein prevents liver injury and intestinal barrier dysfunction in rats subjected to chronic alcohol intake. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, T.G.; Scheel-Toellner, D.; Henriquez, N.V.; Deacon, E.; Salmon, M.; Lord, J.M. Serine/threonine protein kinases and apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 256, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Beers Gibson, T.; Xu, B.E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar]
- Kishore, R.; Hill, J.R.; McMullen, M.R.; Frenkel, J.; Nagy, L.E. ERK1/2 and Egr-1 contribute to increased TNF-alpha production in rat Kupffer cells after chronic ethanol feeding. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 282, G6–G15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Kishore, R.; McMullen, M.R.; Nagy, L.E. Chronic ethanol increases lipopolysaccharide-stimulated Egr-1 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages: Contribution to enhanced tumor necrosis factor alpha production. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14777–14785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroor, A.R.; Shukla, S.D. MAP kinase signaling in diverse effects of ethanol. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2339–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabitha, R.; Nishi, K.; Gunasekaran, V.P.; Agilan, B.; David, E.; Annamalai, G.; Vinothkumar, R.; Perumal, M.; Subbiah, L.; Ganeshan, M. p-Coumaric acid attenuates alcohol exposed hepatic injury through MAPKs, apoptosis and Nrf2 signaling in experimental models. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 321, 109044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.H.; Makki, H.M.M.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, H.J.; Jung, J. Narirutin ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury by targeting MAPK14 in zebrafish larvae. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Zhong, B.; Liao, Q.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; He, X. Review on the diverse biological effects of glabridin. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2023, 17, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmler, C.; Pauli, G.F.; Chen, S.N. Phytochemistry and biological properties of glabridin. Fitoterapia 2013, 90, 160–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Lami, M.S.; Uddin, T.M.; Das, R.; Islam, F.; Anjum, J.; Hossain, M.J.; Emran, T.B. Prospective multifunctional roles and pharmacological potential of dietary flavonoid narirutin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 112932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Wang, X.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Ma, J.; He, Y.; Seo, W.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Feng, D.; Gao, B. Protective and Detrimental Roles of p38α Mitogen-activated protein kinase in different stages of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2020, 72, 873–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatiani, S.S.; Baker, S.J.; Silverman, L.R.; Reddy, E.P. Jak/STAT pathways in cytokine signaling and myeloproliferative disorders: Approaches for targeted therapies. Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, J.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. The role of STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular function. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2468–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, J.F.; Wrzeszczynska, M.H.; Devgan, G.; Zhao, Y.; Pestell, R.G.; Albanese, C.; Darnell, J.E. Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 1999, 98, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, U.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Robinson, P.; Tweardy, D.J. Targeting Janus Kinases and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 to Treat Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Cancer: Rationale, Progress, and Caution. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 486–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Clemens, D.L.; Cederbaum, A.I.; Gao, B. Ethanol inhibits the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in freshly isolated rat hepatocytes but not in cultured hepatocytes or HepG2 cells: Evidence for a lack of involvement of ethanol metabolism. Clin. Biochem. 2001, 34, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norkina, O.; Dolganiuc, A.; Catalano, D.; Kodys, K.; Mandrekar, P.; Syed, A.; Efros, M.; Szabo, G. Acute alcohol intake induces SOCS1 and SOCS3 and inhibits cytokine-induced STAT1 and STAT3 signaling in human monocytes. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.K.; Chava, S.; Perumal, S.K.; Paal, M.C.; Rasineni, K.; Ganesan, M.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Osna, N.A.; Kharbanda, K.K. Acute ethanol-induced liver injury is prevented by betaine administration. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 940148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X. Inula britannica ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury by modulating SIRT1-AMPK/Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathway. Chin. Herb. Med. 2024, 16, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Cao, J.; Tao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, L. Hydroxytyrosol attenuates ethanol-induced liver injury by ameliorating steatosis, oxidative stress and hepatic inflammation by interfering STAT3/iNOS pathway. Redox Rep. 2023, 28, 2187564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Mehmood, A.; Soliman, M.M.; Iftikhar, A.; Iftikhar, M.; Aboelenin, S.M.; Wang, C. Protective effects of ellagic acid against alcoholic liver disease in mice. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 744520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, K.; Wang, P.; Xia, Y.; Yan, N.; Takahashi, S.; Krausz, K.W.; Hao, H.; Yan, T.; Gonzalez, F.J. Withaferin A alleviates ethanol-induced liver injury by inhibiting hepatic lipogenesis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 160, 112807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Huang, A.; Tong, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Yu, X. Nobiletin protects against alcohol-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and liver injury by regulating the hepatic NRF1-TFAM signaling pathway. Redox Rep. 2024, 29, 2395779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.B.; Gao, J.; Chai, Y.H.; Li, W.; Luo, Y.F.; Chen, Y.Z. Astragaloside alleviates alcoholic fatty liver disease by suppressing oxidative stress. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Xu, F.; Niu, J.; Wang, Z. Diammonium glycyrrhizinate ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury by reducing oxidative stress, steatosis, and inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, M.J.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, I.Y.; Sim, S.J.; Heo, H.J. Hepatoprotective effect of allium ochotense extracts on chronic alcohol-induced fatty liver and hepatic inflammation in C57BL/6 mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yang, K.; Li, T.; Tang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, P.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; et al. The protective effects of aqueous extract of Schisandra sphenanthera against alcoholic liver disease partly through the PI3K-AKT-IKK signaling pathway. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Name of Phytochemicals/Herbal Products | Preclinical Model | Mechanisms of Hepatoprotection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Betaine (Dietary sources) | Short-term ethanol-fed C57BL/6J mice | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓lipid accumulation, and ↑SAM: SAH ratio | [164] |
| Caulerpa lentillifera (edible green seaweed) (green algae) | Chronic and binge alcohol-fed Wistar rats | ↑AST, ↓AST, ↓GGT, ↓TLR4 pathway, and ↓ Gut dysbiosis | [47] |
| Inula Britannica (Asteraceae) | Chronic ethanol-fed C57BL/6J female mice | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓liver TG, ↓TC Interferes SIRT1-AMPK/Nrf2/NF-κB axis, ↓ hepatic lipid buildup, ↑antioxidant action, and ↓hepatic inflammation | [165] |
| Hydroxytyrosol | Chronic binge ethanol-fed male C57BL/6J mice | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓liver TG, ↓TC, ↓LDL-C, interfere with STAT3/iNOS pathway and p-AKT/SREBP-1c pathway, and ↓hepatic inflammation | [166] |
| Daucosterol (Sanchezia spesiosa) (Acanthaceae) | Short-term chronic and binge ethanol-fed male C57BL/6J mice | ↓ALT, ↓FFA, ↓liver TG, ↓p38/NF-κB/NLRP3, ↓hepatic lipid buildup, ↑antioxidant action, and ↓hepatic inflammation | [122] |
| Ellagic acid (polyphenol) | Chronic alcohol-fed ICR mice | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓ASP, ↓liver FFA, ↓liver TG, ↑antioxidant action, ↓hepatic inflammation, improves gut microbiota | [167] |
| Withaferin A | Chronic binge ethanol-fed wild-type mice based on C57BL/6J | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓liver TG ↓hepatic lipogenesis, and ↓hepatic lipid buildup | [168] |
| Glabiridin (Isoflavone) (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.) | Short-term chronic ethanol-fed C57BL/6J female mice. | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓liver FFA, ↓liver TG, interfere with the p38 MAPK/Nrf2/NF-kB pathway, ↓ oxidative stress, and ↓hepatic inflammation | [139] |
| Nobiletin (Polymethoxylated flavone) (from citrus fruit peels) | Male C57BL/6N wild-type (WT) mice | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓liver FFA, ↓liver cholesterol, interferes with NRF1-TFAM pathway, ↓hepatic inflammation, ↓oxidative stress, ↓ER stress, and ↓ apoptosis | [169] |
| Narirutin | EtOH-fed wild-type zebrafish larvae | ↓ALT, ↓AST, interfere with p38-MAPK pathway, ↓hepatic inflammation, ↓oxidative stress, ↓ER stress, and ↓lipid accumulation | [152] |
| Hydroxysafflor yellow A | Chronic and binge alcohol-fed C57BL/6J male mice. | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓LDL, ↑HDL, ↓liver TG, interfere with STAT3/NF-kB and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways, ↓hepatic inflammation, ↓oxidative stress, ↓ER stress, ↓lipid accumulation, and ↓hepatocyte apoptosis | [144] |
| Ginsenoside Rk1 | Alcohol-fed wild-type zebrafish | ↓liver lipid content, ↓liver TG Interferes with NF-kB pathway, and ↓hepatic inflammation | [82] |
| Ginsenoside Rk2 (Panax notoginseng) (Araliaceae) | Ethanol-fed C57BL/6J male mice | ↓ALT, ↓AST, interfere with Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, ↓oxidative stress, block the NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway, and ↓hepatic inflammation | [124] |
| Astragaloside (Astragalus membranaceus) | Chronic and binge alcohol-fed SD rats | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓LDL, ↑HDL, ↓liver lipid content, ↓NF-kB pathway, ↓hepatic inflammation, ↓oxidative stress, ↓ER stress, ↓lipid peroxidation, and ↓hepatocyte apoptosis | [170] |
| Diammonium glycyrrhizinate | Chronic and binge alcohol-fed C57BL/6J male mice | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓liver TG, ↓serum TG, ↓DDX5/STAT1 axis, ↓hepatic lipid buildup, ↑antioxidant action, and ↓hepatic inflammation | [171] |
| Scutellarin (Erigeron breviscapus) (Asteraceae) | Binge alcohol-fed C57BL/6J male mice | ↓ALT, ↓AST, interfere Nrf2/HO-1 pathway & AKT, p38 MAPK/NF-kB pathway, and ↓hepatic inflammation | [126] |
| Lutein | Chronic and binge alcohol-fed male Wistar rats | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓GGT, ↓serum TG, ↑Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, ↓TLR4/NF-kB pathway, ↓hepatic inflammation, and ↓ oxidative stress | [145] |
| Myricetin | Chronic and binge alcohol-fed male Wistar rats | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓LDH, ↓lipid peroxidation, interfere with the NF-kB pathway, and ↓hepatic inflammation | [83] |
| Allium ochotense (Amaryllidaceae) | Alcohol-fed C57BL/6J mice | ↓CHL, ↓TG, ↓LDL, and ↓lipid peroxidation | [172] |
| Schisandra sphenanthera (Magnoliaceae) | Chronic alcohol-fed male Sprague Dawley rats | ↓ALT, ↓AST, ↓ADH, ↓ALDH, interfere with the PI3K-AKT pathway, ↓hepatic inflammation, and ↓oxidative stress | [173] |
| Oroxylin A, obtained from Scutellaria biacalensis, is a flavonoid compound. | CCl-4 induced mice model, 8 weeks | Oroxylin A inhibits the cGAS-STING pathway and induces the ferritinophagy of HSC | [102] |
| Extract of LanGui tea, a flavonoid-rich formulation containing Gynostemma pentaphyllum, Cinnamomum cassia, and Ampelopsis grossedentata. | Alcohol-induced male C57BL/6 mice model | Inhibits NLRP3 signaling and decreases the generation of IL-1β | [116] |
| Quercetin, a polyphenol | Alcohol-induced male Wistar rat model | It enhances the occurrence of HO-1 and IL-10 and, thus, inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation | [117] |
| Cannabidiol, extracted from marijuana plants | Ethanol plus high-fat diet male C57B/6J mice model | Inhibits the recruitment of macrophages, and thus, it leads to the inhibition of the NLRP3-pyroptosis pathway | [118] |
| Taxifolin, a dihydroflavone found in onions and milk thistle | Alcohol-induced male C57BL/6 mice model | Inhibits P2X7R-signaling IL-1β secretion by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway | [119] |
| p-coumaric acid, a hydroxycinnamic acid family | Ethanol-induced male Wistar rat model, 28 days | Inhibits phosphorylation of JNK, p38 MAP kinase, and ERK. | [151] |
| Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) | Male pathogen-free KM mice model | Reduces the expression of MAPK p38 protein and inflammatory cytokines | [79] |
| Narirutin, a flavone type flavonoid | Alcohol-induced zebrafish larvae model | Modulated the p38 MAPK signaling via binding to the MAPK14 and also suppressed the mRNA level of mapk14 | [152] |
| Europinidin, obtained from Plumbago europea | Ethanol-induced male Wistar rat model | Inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines and genes via inhibiting NF-kB initiation | [135] |
| Curcumin, obtained from Curcuma longa | Alcohol-induced rat, mouse model | It regulates the IkBα-NF-kB pathway to further decrease inflammation | [136] |
| Artemisinin, isolated from Artemisia annua, is a sesquiterpene lactone | Alcohol-induced male KM mice model | Inhibits NF-кB activation and reduces the expression of the inflammatory cytokines | [137] |
| Grape leaf extract, a phenolic compound isolated from leaves of the plant Vitis vinifera | Ethanol-induced male Sprague Dawley rat model | Suppress ethanol-induced NF-кB p65 subunit and TNF-α | [138] |
| Glabridin, an isoflavone obtained from licorice root | Ethanol-induced C57BL/6 female mice model | Decreases the nuclear translocation of NF-кB | [139] |
| Genistein, isolated from Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides Lam. | Alcohol-induced male SPF-Wistar rat model, 24 weeks | Reduces the DNA binding activity of NF-кB and downregulates its activity | [140] |
| Apigenin (4′, 5, 7-trihydroxyflavone), a flavonoid compound | Alcohol-induced male KM-mice model, 30 days | Increases expression of PPARα, downregulates the NF-kB signaling | [141] |
| Combination of epigallocatechin-3-gallate, taurine, and genistein | Alcohol-induced rat liver fibrosis model, 24 weeks | Restricted the production and secretion of the inflammatory cytokines like IL-6, TNF-α | [81] |
| Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a phenolic compound | Alcohol-induced female Sprague-Dawley rat model, 5 or more weeks | Inhibits gut leakiness and reduces endotoxemia | [43] |
| Lychee (Litchi chinensis Sonn) | Alcohol-induced male C57Bl/6 mice model, 8 weeks | Lychee pulp extract increases the production of mucus-protecting proteins and intestinal tight junction proteins and lowers the number of endotoxins in the blood. | [44] |
| A mixture of Ginkgo biloba and Rosa roxburghii | Alcohol-induced male Sprague Dawley rat model, 8 weeks | They restore tight junctions, hence protecting the intestinal barrier dysfunction | [45] |
| Rice bran phenolic extract | Alcohol-induced C57BL/6 mice model, 8 weeks | Its supplementation decreases pathogenic bacteria in the gut and protects the intestinal barrier, function, and permeability from alcohol. | [46] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Achary, S.T.; Gupta, P.; Rajput, A.; Sohkhia, W.; Bonam, S.R.; Sahu, B.D. Phytochemicals Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease: A Mechanistic Review. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050710
Achary ST, Gupta P, Rajput A, Sohkhia W, Bonam SR, Sahu BD. Phytochemicals Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease: A Mechanistic Review. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050710
Chicago/Turabian StyleAchary, Swati Tirunal, Prerna Gupta, Apoorva Rajput, Wanphidabet Sohkhia, Srinivasa Reddy Bonam, and Bidya Dhar Sahu. 2025. "Phytochemicals Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease: A Mechanistic Review" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050710
APA StyleAchary, S. T., Gupta, P., Rajput, A., Sohkhia, W., Bonam, S. R., & Sahu, B. D. (2025). Phytochemicals Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease: A Mechanistic Review. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050710







