Biological and Analytical Perspectives on D-Amino Acids in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
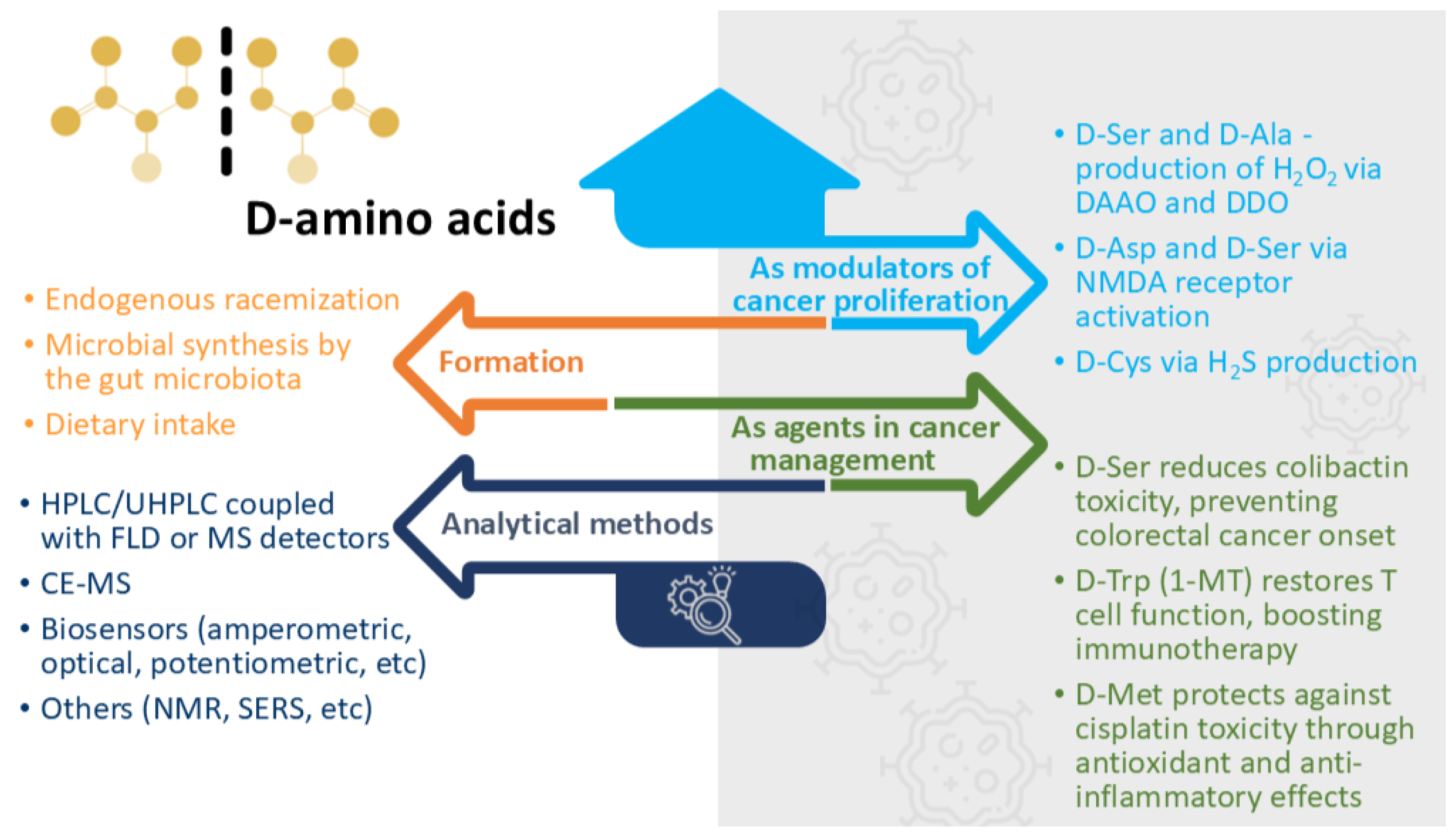
2. D-Amino Acid Synthesis
2.1. Endogenous Racemization
2.2. Microbial Synthesis by the Gut Microbiota
2.3. Dietary Intake
3. D-Amino Acid Detection and Quantification Methods
3.1. Separative Methods
3.2. Biosensors
3.3. Analytical Perspectives
4. D-Amino Acids in Tumours
5. Implications of D-Amino Acids in Cancer
5.1. The Manipulation of D-Amino Acid Levels as a Tool for Regulating Cell Proliferation
5.2. D-Amino Acids as Modulators of Cancer Proliferation Pathways
5.3. Specific D-Amino Acids as Functional Agents in Cancer Management
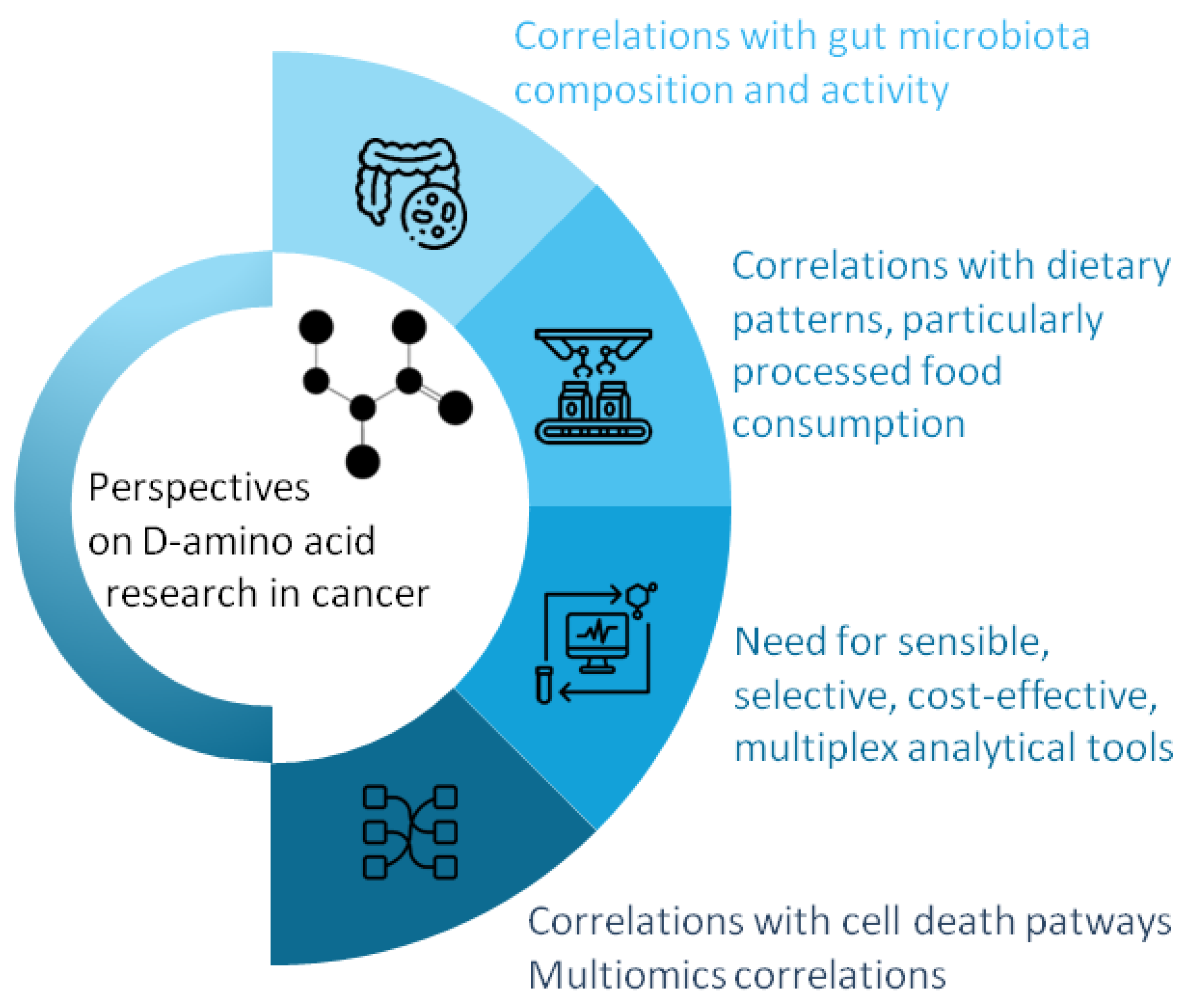
6. Future Research Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, S.; Wey, M.; Armstrong, D.W. D-Amino Acids in Biological Systems. Chirality 2023, 35, 508–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, N.; Saito, T. Homochirality and Life. Chem. Rec. 2004, 4, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, N.; Takata, T.; Fujii, N.; Aki, K.; Sakaue, H. D-Amino Acids in Protein: The Mirror of Life as a Molecular Index of Aging. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Proteins Proteom. 2018, 1866, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögl, F.; Erxleben, H. The Glutamic Acid of Tumour Proteins. Nature 1939, 144, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Kim, I.; Takata, T.; Kinouchi, T.; Isoyama, M.; Suzuki, M.; Fujii, N. Identification of D-Amino Acid-Containing Peptides in Human Serum. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulbagi, M.; Wang, L.; Siddig, O.; Di, B.; Li, B. D-Amino Acids and d-Amino Acid-Containing Peptides: Potential Disease Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.-X.; Wang, H.-F.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Chen, F.-E. Natural Occurrence, Biological Functions, and Analysis of D-Amino Acids. Pharmaceut. Fronts 2020, 2, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Armstrong, D.W.; Wolosker, H.; Zheng, Y. Detection and Analysis of Chiral Molecules as Disease Biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2023, 7, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzylowski, M.; Fujiwara, E.; Mousseau, D.D.; Baker, G.B. An Overview of the Involvement of D-Serine in Cognitive Impairment in Normal Aging and Dementia. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 754032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtas, G.; Pollegioni, L. D-Amino Acids as Novel Blood-Based Biomarkers. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 4202–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, S.; Sharma, V. D-Amino Acids in Antimicrobial Peptides: A Potential Approach to Treat and Combat Antimicrobial Resistance. Can. J. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; Lee, D.K.; Wei, I.A.; Qiu, T.A.; Rubakhin, S.S.; Roper, M.G.; Sweedler, J.V. Relations between Glucose and D-Amino Acids in the Modulation of Biochemical and Functional Properties of Rodent Islets of Langerhans. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 47723–47734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Balaram, H.; Sanyal, K. Amino Acid Chirality: Stereospecific Conversion and Physiological Implications. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 5084–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, T.; Lee, C.J.; Huang, C.; Lee, D.K.; Rubakhin, S.S.; Romanova, E.V.; Sweedler, J.V. Biodistribution and Racemization of Gut-Absorbed l/d-Alanine in Germ-Free Mice. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luykx, J.J.; Bakker, S.C.; Van Boxmeer, L.; Vinkers, C.H.; Smeenk, H.E.; Visser, W.F.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; Strengman, E.; Buizer-Voskamp, J.E.; De Groene, L.; et al. D-Amino Acid Aberrations in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma of Smokers. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Hamase, K.; Miyoshi, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Yasuda, K.; Mita, M.; Rakugi, H.; Hayashi, T.; Isaka, Y. Chiral Amino Acid Metabolomics for Novel Biomarker Screening in the Prognosis of Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Sawamura, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Kitagishi, Y.; Matsuda, S. D-Amino Acids as a Biomarker in Schizophrenia. Diseases 2022, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, I.N.d.O.; Roychaudhuri, R.; de Belleroche, J.; Mothet, J.P. D-Amino Acids: New Clinical Pathways for Brain Diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastings, J.J.A.J.; van Eijk, H.M.; Damink, S.W.O.; Rensen, S.S. D-Amino Acids in Health and Disease: A Focus on Cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Ye, C.; Wang, W.; Huang, R.; Guo, C.; Pan, Y.; Sun, C. LC-MS Analysis of Chiral Amino Acids in Human Urine Reveals D-Amino Acids as Potential Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2024, 1245, 124270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.L.; Beio, M.L.; Nelson, D.L.; Berkowitz, D.B. Human Serine Racemase: Key Residues/Active Site Motifs and Their Relation to Enzyme Function. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 435803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balu, D.T.; Takagi, S.; Puhl, M.D.; Benneyworth, M.A.; Coyle, J.T. D-Serine and Serine Racemase Are Localized to Neurons in the Adult Mouse and Human Forebrain. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Han, H.; Yin, J.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Role of D-Aspartate on Biosynthesis, Racemization, and Potential Functions: A Mini-Review. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katane, M.; Homma, H. Biosynthesis and Degradation of Free D-Amino Acids and Their Physiological Roles in the Periphery and Endocrine Glands. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 47, 562–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Origin, Microbiology, Nutrition, and Pharmacology of D-Amino Acids. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 1491–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, S.B.; Cava, F. Environmental Roles of Microbial Amino Acid Racemases. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1673–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanauchi, M.; Matsumoto, N. Characteristics of Alanine Racemase in Lactobacillus Sakei ZH-2 Strain. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 4745–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, H.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X.; Xu, Z.; Xia, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; et al. Brucella Proline Racemase Protein A Targets Tpl2 to Promote IL-10 Secretion for Establishment of Chronic Infection. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, L.L.; Thomas, A.M. Broad Spectrum Amino Acid Racemases (Bsrs): A Potential Target in Microbial Research. In Microbial Biodiversity, Biotechnology and Ecosystem Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 449–460. [Google Scholar]
- Roskjær, A.B.; Roager, H.M.; Dragsted, L.O. D-Amino Acids from Foods and Gut Microbiota and Their Effects in Health and Disease. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 3196–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Qiu, T.A.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Min, Y.; Zhang, L.; Dai, L.; Zhao, H.; Si, T.; Sweedler, J.V. Profiling of D-Alanine Production by the Microbial Isolates of Rat Gut Microbiota. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepert, I.; Fonseca, J.; Müller, C.; Milger, K.; Hochwind, K.; Kostric, M.; Fedoseeva, M.; Ohnmacht, C.; Dehmel, S.; Nathan, P.; et al. D-Tryptophan from Probiotic Bacteria Influences the Gut Microbiome and Allergic Airway Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.J.; Hariri, B.M.; McMahon, D.B.; Chen, B.; Doghramji, L.; Adappa, N.D.; Palmer, J.N.; Kennedy, D.W.; Jiang, P.; Margolskee, R.F.; et al. Bacterial D-Amino Acids Suppress Sinonasal Innate Immunity Through Sweet Taste Receptors in Solitary Chemosensory Cells. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaam7703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliashkevich, A.; Alvarez, L.; Cava, F. New Insights into the Mechanisms and Biological Roles of D-Amino Acids in Complex Eco-Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 359971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasabe, J.; Miyoshi, Y.; Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Zhang, T.; Mita, M.; Davis, B.M.; Hamase, K.; Waldor, M.K. Interplay between Microbial D-Amino Acids and Host d-Amino Acid Oxidase Modifies Murine Mucosal Defence and Gut Microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Sawamura, H.; Tsuji, A.; Matsuda, S. Promising Role of D-Amino Acids in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, S.; Sujino, T.; Miyamoto, K.; Yoshimatsu, Y.; Harada, Y.; Nishiyama, K.; Aoto, Y.; Adachi, K.; Hayashi, N.; Amafuji, K.; et al. D-Amino Acids Ameliorate Experimental Colitis and Cholangitis by Inhibiting Growth of Proteobacteria: Potential Therapeutic Role in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 16, 1011–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarovaya, O.; Borisevich, S.S.; Zarubaev, V.V.; Ikeda, Y.; Matsuda, S. Gut Protective Effect from D-Methionine or Butyric Acid against DSS and Carrageenan-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. Molecules 2023, 28, 4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, G.L.; Rosini, E.; Crespi, E.; Pollegioni, L. D-Amino Acids in Foods. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 104, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartus, A.T. D-Amino Acids and Cross-Linked Amino Acids as Food Contaminants. In Chemical Contaminants and Residues in Food; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 286–319. [Google Scholar]
- Grishin, D.V.; Zhdanov, D.D.; Pokrovskaya, M.V.; Sokolov, N.N. D-Amino Acids in Nature, Agriculture and Biomedicine. Front. Life Sci. 2020, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón, C.; Lämmerhofer, M. Enantioselective Metabolomics by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 207, 114430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogos, L.G.; Pralea, I.E.; Moldovan, R.C.; Iuga, C.A. Indirect Enantioseparations: Recent Advances in Chiral Metabolomics for Biomedical Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lella, C.; Nestor, L.; De Bundel, D.; Vander Heyden, Y.; Van Eeckhaut, A. Targeted Chiral Metabolomics of D-Amino Acids: Their Emerging Role as Potential Biomarkers in Neurological Diseases with a Focus on Their Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis upon Chiral Derivatization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Koga, R.; Oyama, T.; Han, H.; Ueno, K.; Masuyama, K.; Itoh, Y.; Hamase, K. HPLC Analysis of Naturally Occurring Free D-Amino Acids in Mammals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 69, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, Y.; Sato, T.; Enomoto, N.; Ishii, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Yamada, T. High Concentrations of D-Amino Acids in Human Gastric Juice. Amino Acids 2007, 32, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Wu, H.; Wu, S.; Luo, R. Determination of Hepatoma-Associated DL-Amino Acids Enantiomers by RP-HPLC with Fluorescence Detector: Application in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 48, 490–495. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, C.; Fonseca, J.R.; Rock, T.M.; Krauss-Etschmann, S.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Enantioseparation and Selective Detection of D-Amino Acids by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry in Analysis of Complex Biological Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1324, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xing, Y.; Guo, X.; Cui, Y. Development of an UPLC–MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Quantitation of 11 d-Amino Acids in Different Regions of Rat Brain: Application to a Study on the Associations of d-Amino Acid Concentration Changes and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1058, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Huang, R.; Pan, Y.; Sun, C. Dynamic Profiling of Intra- and Extra-Cellular L/D-Amino Acids Metabolism in Colorectal Cell and Intestinal Epithelial Cell. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 255, 116622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Shen, K.; He, Q.; Hu, Y.; Sun, C.; Guo, C.; Pan, Y. Metabolic Profiling of Urinary Chiral Amino-Containing Biomarkers for Gastric Cancer Using a Sensitive Chiral Chlorine-Labeled Probe by HPLC-MS/MS. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 3952–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Hamase, K.; Tojo, Y.; Mita, M.; Konno, R.; Zaitsu, K. Determination of D-Serine and d-Alanine in the Tissues and Physiological Fluids of Mice with Various d-Amino-Acid Oxidase Activities Using Two-Dimensional High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 2506–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusho, A.; Ikejiri, K.A.; Ishii, C.; Akita, T.; Mita, M.; Nagano, M.; Ide, T.; Hamase, K. Two-Dimensional High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Chiral Amino Acids in Food Samples and Human Physiological Fluids Using Fluorescence Derivatization with 4-(N,N-Dimethylaminosulfonyl)-7-fluoro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole. Chromatography 2022, 43, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karongo, R.; Horak, J.; Lämmerhofer, M. Comprehensive Reversed-Phase×chiral Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Post-First Dimension Flow Splitting for Untargeted Enantioselective Amino Acid Analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, 2300351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, C.; Hamase, K. Two-Dimensional LC-MS/MS and Three-Dimensional LC Analysis of Chiral Amino Acids and Related Compounds in Real-World Matrices. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 235, 115627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, C.; Hamase, K. Development of Two-Dimensional LC-MS/MS Methods for Highly-Selective Analysis of Chiral Amino Acids and the Evaluation of Their Intrinsic Amounts in Mammals and Stereoinversion in Proteins. Chromatography 2024, 45, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakade, Y.; Kinoshita, M.; Nakada, M.; Sabit, H.; Ichinose, T.; Mita, M.; Yuno, T.; Noguchi-Shinohara, M.; Ono, K.; Iwata, Y.; et al. Urinary D-Asparagine Level Is Decreased by the Presence of Glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2024, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugaru, K.; Sujino, T.; Mita, M.; Sasabe, J.; Chida, A.; Harada, Y.; Hirata, K.; Sukawa, Y.; Kato, M.; Kawakubo, H.; et al. Clinical Significance of D-Amino Acid Profile for Cancer Detection in Early Stage and Prediction of Efficacy of Nivolumab in Gastric Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydoğan, C.; Çakan, B.B.; Ali, A. A Review on the Analysis of Chiral Molecules as Disease Biomarkers by LC/MS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2025, 39, e6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.; Westley, J.W. Optical Resolution of D,L Amino Acids by Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1965, 20, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner, H.; Haasmann, S.; Friedrich, A. Quantification of D-Amino Acids in Human Urine Using GC-MS and HPLC. Amino Acids 1994, 6, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, M.P.; Dudzik, D.; Varas, E.; Gibellini, M.; Skotnicki, M.; Zorawski, M.; Zarzycki, W.; Pellati, F.; García, A. Optimization and Validation of a Chiral GC–MS Method for the Determination of Free d-Amino Acids Ratio in Human Urine: Application to a Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldhier, M.C.; Almstetter, M.F.; Nürnberger, N.; Gruber, M.A.; Dettmer, K.; Oefner, P.J. Improved Enantiomer Resolution and Quantification of Free D-Amino Acids in Serum and Urine by Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography–Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4537–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yu, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhao, S. Determination of D,L-Serine in Midbrain of Parkinson’s Disease Mouse by Capillary Electrophoresis with in-Column Light-Emitting Diode Induced Fluorescence Detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yuan, H.; Xiao, D. Detection of D-Serine in Rat Brain by Capillary Electrophoresis with Laser Induced Fluorescence Detection. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 822, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, A.; Moldovan, R.C.; Crommen, J.; Servais, A.C.; Fillet, M.; de Jong, G.J.; Somsen, G.W. Enantioselective Capillary Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry of Amino Acids in Cerebrospinal Fluid Using a Chiral Derivatizing Agent and Volatile Surfactant. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 940, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosini, E.; D’antona, P.; Pollegioni, L. Biosensors for D-Amino Acids: Detection Methods and Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Yang, L.; Jiang, X.; Luo, D.; Yang, D. Non-Invasive Detection of Gastric Cancer Relevant d-Amino Acids with Luminescent DNA/Silver Nanoclusters. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 19367–19373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie-Mihai, R.M.; Stefan-van Staden, R.I.; Magerusan, L.; Coros, M.; Pruneanu, S. Enantioanalysis of Tryptophan in Whole Blood Samples Using Stochastic Sensors—A Screening Test for Gastric Cancer. Chirality 2020, 32, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Ni, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B.; Duan, G.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, Y. Carbon Dots Confined in N-Doped Carbon as Peroxidase-like Nanozyme for Detection of Gastric Cancer Relevant D-Amino Acids. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; Lin, J.; Hu, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, J. Tuning the Peroxidase-Mimic Activity of CuX-Trithiocyanuric Acid Complexes for Colorimetric Detection of Gastric Cancer-Associated D-Amino Acids. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 424, 136871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. Detection of Gastric Cancer-Associated d-Amino Acids and Carcinoembryonic Antigen by Colorimetric and Immuno ECL Sensing Platform Based on the Catalysis of N/S-Doped Carbon Dots @ N-Rich Porous Carbon Nanoenzyme. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 17787–17794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, T.; Yang, J.; Liang, Q.; Shi, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, G. Enantiospecific Profiling of D-Amino Acid for Gastric Cancer Diagnosis by Using a Biocatalytic MHOF Nanoreactor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 423, 136716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreisewerd, L.; Aspers, R.L.E.G.; Feiters, M.C.; Rutjes, F.P.J.T.; Tessari, M. NMR Discrimination of D- and l-α-Amino Acids at Submicromolar Concentration via Parahydrogen-Induced Hyperpolarization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riskin, M.; Tel-Vered, R.; Frasconi, M.; Yavo, N.; Willner, I. Stereoselective and Chiroselective Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Analysis of Amino Acids by Molecularly Imprinted Au-Nanoparticle Composites. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 7114–7120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, L.; Kong, P.F.; Yang, H.; Liu, X. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Enantioselective Detection of Gastric Cancer-Related d-Amino Acids in Saliva Based on Enzyme-Mediated Cascade Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 13029–13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Zhang, D.; Yin, H.; Lu, B.; Hua, Z.; Tan, M.; Qian, Y. A Magnetically Embedded Pump-Free LoC-SERS Device Based on Enzyme-Mediated Cascade Reaction for Gastric Cancer-Related D-Amino Acids Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 409, 135615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaag, S.J.; Valadbeigi, Y.; Causon, T.; Gross, H.; Lämmerhofer, M. Three-Minute Enantioselective Amino Acid Analysis by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Drift Tube Ion Mobility-Mass Spectrometry Using a Chiral Core-Shell Tandem Column Approach. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 2666–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Míguez, R.; Bruyneel, B.; Castro-Puyana, M.; Marina, M.L.; Somsen, G.W.; Domínguez-Vega, E. Chiral Discrimination of DL-Amino Acids by Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry after Derivatization with (+)-1-(9-Fluorenyl)Ethyl Chloroformate. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3277–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, W.F.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; Ophoff, R.; Bakker, S.; Klomp, L.W.; Berger, R.; De Koning, T.J. A Sensitive and Simple Ultra-High-Performance-Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Based Method for the Quantification of d-Amino Acids in Body Fluids. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 7130–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, R.C.; Bodoki, E.; Servais, A.C.; Chankvetadze, B.; Crommen, J.; Oprean, R.; Fillet, M. Capillary Electrophoresis-Mass Spectrometry of Derivatized Amino Acids for Targeted Neurometabolomics—PH Mediated Reversal of Diastereomer Migration Order. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1564, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögl, F.; Erxleben, H. Zur Ätiologie Der Malignen Tumoren. Z. Physiol. Chem. 1939, 258, 59–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipmann, F.; Behrens, O.K.; Kabit, E.A.; Burk, D. The Determination of the Total D-Amino Acid Content of Human Tumors and Normal Tissues by Means of d-Amino Acid Oxidase. Science 1940, 91, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.M. Glutamic Acid from Normal and Cancerous Tissue. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1940, 1, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.A. Do Tumor Proteins Contain D-Amino Acids? A Review of the Controversy. Cancer Res. 1950, 10, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamemasa, O.; Goto, R.; Takeda, A.; Maruo, K. High Uptake of 14C-Labeled D-Amino Acids by Various Tumors. Gann Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1982, 1, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, G.H. Appearance of D-Amino Acids during Aging: D-Amino Acids in Tumor Proteins. EXS 1998, 85, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, G.H.; Torres, D.; Bruna, J.; Cerwinski, S.; Martin, T.; Bergljung, C.; Gruneiro, A.; Chou, S.; Man, E.; Pappatheodorou, S. Presence of D-Aspartate and D-Glutamate in Tumor Proteins. Cancer Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 15, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guan, L.; Wang, J.; Yin, S.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, M.M.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Structure-Based Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a Novel d-Amino Acid-Containing Peptide Inhibitor by Blocking the RAD51-BRCA2 Interaction for the Treatment of Kidney Cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 287, 117372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Wang, Y.; Alatrash, N.; Weatherly, C.A.; Roy, D.; MacDonnell, F.M.; Armstrong, D.W. Altered Profiles and Metabolism of L- and D-Amino Acids in Cultured Human Breast Cancer Cells vs. Non-Tumorigenic Human Breast Epithelial Cells. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan-van Staden, R.I.; Ilie-Mihai, R.M.; Magerusan, L.; Coros, M.; Pruneanu, S. Enantioanalysis of Glutamine—A Key Factor in Establishing the Metabolomics Process in Gastric Cancer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 3199–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Xie, M.; Han, J.; Yuan, D.; Yang, T.; Xie, Y. Development and Validation of a Rapid, Selective, and Sensitive LC–MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of d- and l-Amino Acids in Human Serum: Application to the Study of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2517–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krall, A.S.; Xu, S.; Graeber, T.G.; Braas, D.; Christofk, H.R. Asparagine Promotes Cancer Cell Proliferation through Use as an Amino Acid Exchange Factor. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Alonso, J.J.; López-Lázaro, M. Dietary Manipulation of Amino Acids for Cancer Therapy. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Cui, L.; Lu, S.; Xu, S. Amino Acid Metabolism in Tumor Biology and Therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercal, N.; Luo, X.; Matthews, R.H.; Armstrong, D.W. In Vitro Study of the Metabolic Effects of D-Amino Acids. Chirality 1996, 8, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, T.; Osaki, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Sato, H.; Fujii, J. D-Cysteine Supplementation Partially Protects against Ferroptosis Induced by XCT Dysfunction via Increasing the Availability of Glutathione. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2022, 71, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, S.H.; Lee, C.S.; Zulkifli, N.D.; Suresh, D.; Hamase, K.; Das, K.T.; Rajasuriar, R.; Leong, K.H. D-Amino Acids Differentially Trigger an Inflammatory Environment In Vitro. Amino Acids 2024, 56, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarangelo, G.; Spinelli, J.B.; Perez, E.M.; Baker, G.J.; Kurmi, K.; Elia, I.; Stopka, S.A.; Baquer, G.; Lin, J.-R.; Golby, A.J.; et al. Oncometabolite D-2HG Alters T Cell Metabolism to Impair CD8 + T Cell Function. Science 2022, 377, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasamura, T.; Matsuda, A.; Kokuba, Y. Tumor Growth Inhibition and Nutritional Effect of D-Amino Acid Solution in AH109A Hepatoma-Bearing Rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1998, 44, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasamura, T.; Matsuda, A.; Kokuba, Y. Effects of D-Methionine-Containing Solution on Tumor Cell Growth in Vitro. Arzneimittelforschung 1999, 49, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shennan, D.B.; Thomson, J. Inhibition of System L (LAT1/CD98hc) Reduces the Growth of Cultured Human Breast Cancer Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 20, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulos, F.; Michel, T. D-Amino Acid Oxidase-Derived Chemogenetic Oxidative Stress: Unraveling the Multi-Omic Responses to in Vivo Redox Stress. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2024, 79, 102438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Deng, D.; Nakamura, H.; Akuta, T.; Qin, H.; Iyer, A.K.; Greish, K.; Maeda, H. Oxystress Inducing Antitumor Therapeutics via Tumor-Targeted Delivery of PEG-Conjugated D-Amino Acid Oxidase. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardaweel, S.K.; Rana, A.D.; Almomani, N.F. An in Vitro Based Investigation into the Cytotoxic Effects of D-Amino Acids. Acta Pharm. 2013, 63, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, S.; Vitacolonna, A.; Crepaldi, T. NMDA Receptor and Its Emerging Role in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cota, A.L.; Martínez-Flores, D.; Rosendo-Pineda, M.J.; Vaca, L. NMDA Receptor-Mediated Ca2+ Signaling: Impact on Cell Cycle Regulation and the Development of Neurodegenerative Diseases and Cancer. Cell Calcium 2024, 119, 102856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, W.G.; Liu, F.; Lin, L.Z.; Tian, R.; Akerman, B. NMDA Receptors Are Important Regulators of Pancreatic Cancer and Are Potential Targets for Treatment. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 9, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, W.G.; Gao, G.; Memoli, V.A.; Pang, R.H.; Lynch, L. Breast Cancer Expresses Functional NMDA Receptors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 122, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, S.; Hu, J.; Ju, X.; Sun, G.; Shao, S.; Tang, R.X.; Zheng, K.Y.; Yan, J. The Role of Glutamate Receptors in the Regulation of the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1123841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckler, J.M.; Lewis, S.J. Advances in D-Amino Acids in Neurological Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Sung, Y.S.; Wey, M.; Wang, Y.; Alatrash, N.; Berthod, A.; MacDonnell, F.M.; Armstrong, D.W. Roles of N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptors and d-Amino Acids in Cancer Cell Viability. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6749–6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.Q.; Yuan, H.; Liang, X.Y.; Ji, X.Y.; Jiang, Q.Y.; Wu, D.D. The Potential Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Cancer Cell Apoptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Huang, D.; An, N.; Chen, D.; Zhao, D. A Novel Pathway for the Production of H2S by DAO in Rat Jejunum. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, N.; Koike, S.; Tanaka, M.; Ishigami-Yuasa, M.; Kimura, Y.; Ogasawara, Y.; Fukui, K.; Nagahara, N.; Kimura, H. A Novel Pathway for the Production of Hydrogen Sulfide from D-Cysteine in Mammalian Cells. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, C. Hydrogen Sulfide, an Endogenous Stimulator of Mitochondrial Function in Cancer Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libiad, M.; Vitvitsky, V.; Bostelaar, T.; Bak, D.W.; Lee, H.J.; Sakamoto, N.; Fearon, E.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Weerapana, E.; Banerjee, R. Hydrogen Sulfide Perturbs Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and Triggers Metabolic Reprogramming in Colon Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.H.; Wang, D.; Wang, W.; Shahid, M.; Khattak, S.; Ngowi, E.E.; Sarfraz, M.; Ji, X.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wu, D.D. Pharmacological Inhibition of Endogenous Hydrogen Sulfide Attenuates Breast Cancer Progression. Molecules 2022, 27, 4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Zuo, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, S. Hydrogen Sulfide Creates a Favorable Immune Microenvironment for Colon Cancer. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.K.M.; Araújo, T.S.L.; Sousa, N.A.; Sousa, F.B.M.; Nogueira, K.M.; Nicolau, L.A.D.; Medeiros, J.V.R. Evidence That D-Cysteine Protects Mice from Gastric Damage via Hydrogen Sulfide Produced by d-Amino Acid Oxidase. Nitric Oxide 2017, 64, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, E.; Ohta, T.; Konno, A.; Hirai, H.; Kurauchi, Y.; Katsuki, H.; Seki, T. D-Cysteine Activates Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells via the Generation of Hydrogen Sulfide and Nrf2 Activation. Cells 2022, 11, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, N.; Kimura, H. Production of Hydrogen Sulfide from D-Cysteine and Its Therapeutic Potential. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychaudhuri, R. Mammalian D-Cysteine: A New Addition to the Growing Family of Biologically Relevant D-Amino Acids. Chirality 2023, 35, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardaweel, S.K. D-Amino Acids: Prospects for New Therapeutic Agents. J. Med. Bioeng. 2014, 3, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxian, T.; Gerlitz, L.; Riedl, S.; Rinner, B.; Zweytick, D. Effect of L- to D-amino Acid Substitution on Stability and Activity of Antitumor Peptide Rdp215 against Human Melanoma and Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Sylvestre, M.; Song, K.; Pun, S.H. Development of D-Melittin Polymeric Nanoparticles for Anti-Cancer Treatment. Biomaterials 2021, 277, 121076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Guan, L.; Niu, M.M.; Xu, C.; Yang, L.; Liang, S. Discovery of a Highly Potent, Selective, and Stable d-Amino Acid-Containing Peptide Inhibitor of CDK9/Cyclin T1 Interaction for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 285, 117248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrez, M.V. Peptide Agents for Cancer Therapy. U.S. Patent 9,403,877B2, 2 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, W.J.; Goldenberg, D.M. D-Amino Acid Peptides. U.S. Patent 7,521,416B2, 15 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hallam, J.C.; Sandalli, S.; Floria, I.; Turner, N.C.A.; Tang-Fichaux, M.; Oswald, E.; O’Boyle, N.; Roe, A.J. D-Serine Reduces the Expression of the Cytopathic Genotoxin Colibactin. Microb. Cell 2023, 10, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Du, R.; Shang, Y. Biological Function of D-Tryptophan: A Bibliometric Analysis and Review. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1455540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q. Prognostic Role of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 Expression in Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 954495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.W.; Hajjar, J.; Hwu, P.; Naing, A. Targeting the Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Pathway in Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2015, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, L.; Bai, L.; Tong, R.; Yang, H.; Zhong, L. Targeting Indoleamine Dioxygenase and Tryptophan Dioxygenase in Cancer Immunotherapy: Clinical Progress and Challenges. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 2639–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.M.; Büsselberg, D. Cisplatin as an Anti-Tumor Drug: Cellular Mechanisms of Activity, Drug Resistance and Induced Side Effects. Cancers 2011, 3, 1351–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.C.M.; Rybak, L.P.; Meech, R.P.; Hughes, L. D-Methionine Provides Excellent Protection from Cisplatin Ototoxicity in the Rat. Hear. Res. 1996, 102, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.C.; Rehemtulla, A.; Sunkara, P.; Hamstra, D.; Buhnerkempe, M.; Ross, B. Oral D-Methionine Protects against Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss in Humans: Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial in India. Int. J. Audiol. 2022, 61, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.W.; Liu, S.H.; Young, Y.H.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y. D-Methionine Attenuated Cisplatin-Induced Vestibulotoxicity through Altering ATPase Activities and Oxidative Stress in Guinea Pigs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 215, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.S.; Lin, M.Y.; Liu, P.F.; Ko, J.L.; Huang, G.T.; Tu, D.G.; Ou, C.C. D-Methionine Improves Cisplatin-Induced Anorexia and Dyspepsia Syndrome by Attenuating Intestinal Tryptophan Hydroxylase 1 Activity and Increasing Plasma Leptin Concentration. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.T.; Ko, J.L.; Liu, T.C.; Chao, P.T.; Ou, C.C. Protective Effect of D-Methionine on Body Weight Loss, Anorexia, and Nephrotoxicity in Cisplatin-Induced Chronic Toxicity in Rats. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.T.; Liao, J.M.; Ko, J.L.; Lee, Y.L.; Chang, H.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Ou, C.C. D-Methionine Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Muscle Atrophy via Inhibition of Muscle Degradation Pathway. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1534735419828832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Ko, J.L.; Liao, J.M.; Huang, S.S.; Lin, M.Y.; Lee, L.H.; Chang, L.Y.; Ou, C.C. D-Methionine Alleviates Cisplatin-Induced Mucositis by Restoring the Gut Microbiota Structure and Improving Intestinal Inflammation. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835918821021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, W.M.; Daifalla, N.S.; Essawy, A.E. L-Methionine Protects against Nephrotoxicity Induced by Methotrexate through Modulation of Redox Status and Inflammation. Redox Rep. 2023, 28, 2270886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hussain, Z.; Zhao, Y. Promising Application of D-Amino Acids toward Clinical Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, N.; Khan, N.A.; Muhammad, J.S.; Siddiqui, R. The Role of Gut Microbiome in Cancer Genesis and Cancer Prevention. Health Sci. Rev. 2022, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağagündüz, D.; Cocozza, E.; Cemali, Ö.; Bayazıt, A.D.; Nanì, M.F.; Cerqua, I.; Morgillo, F.; Saygılı, S.K.; Berni Canani, R.; Amero, P.; et al. Understanding the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1130562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardi, F.; Khasraghi, L.B.; Shahbakhti, N.; Salami Naseriyan, A.; Najafi, S.; Sanaaee, S.; Alipourfard, I.; Zamany, M.; Karamipour, S.; Jahani, M.; et al. An Interplay between Non-Coding RNAs and Gut Microbiota in Human Health. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 201, 110739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Wang, G.P.; Chen, G.Q.; Chen, H.N.; Zhang, G.Y. Association between Ultra-Processed Foods and Risk of Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1175994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaksen, I.M.; Dankel, S.N. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lai, M.-C.; Zhong, Y.-M.; Chen, Y.-L.; Wu, N.; Chen, W.; Peng, H.-P. Hydrogen Peroxide Regulated Split-Type Electrochemiluminescence Sensing Platform for Non-Invasive Detection of Gastric Cancer-Associated D-Amino Acids. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1355, 344010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtas, G.; Pollegioni, L. D-Amino Acids and Cancer: Friends or Foes? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Type | Analytical Method | D-Amino Acids Studied | Main Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric cancer (GC) | ||||
| Gastric juice from GC patients and controls (+/− infection with H. pylori) | Derivatization followed by RP-HPLC-UV separation | D-Ser, D-Ala, D-Pro, D-Asp, D-Glu |
| [46] |
| Urine from GC patients and controls | RP-HPLC-MS/MS in combination with chiral chlorine-labelled probes | D-Asn, D-Cit, D-Gln, D-Thr, D-Ser, D-Ala, D-Tyr, D- Val, D-Met, D-Trp, D-Leu, D-Ile, D-Phe, D-AABA |
| [51] |
| Whole-blood samples from GC patients and controls | Enantioselective stochastic sensors | D-Glu |
| [91] |
| Enantioselective stochastic sensors | D-Try |
| [69] | |
| Plasma from GC patients before treatment and healthy controls Plasma from advanced GC patients before nivolumab | 2D HPLC-MS/MS | D-Ser, D-Asn, D-Ala, D-Pro |
| [58] |
| Saliva from GC patients and controls | Non-invasive biosensing system with luminescent DNA/silver nanoclusters | D-Ala, D-Pro |
| [68] |
| Carbon dots confined in N-doped carbon nanozyme with peroxidase-like activity (with colorimetric detection) | D-Pro, D-Ala |
| [70] | |
| CuX-trithiocyanuric acid complexes with peroxidase-like activity (with colorimetric detection) | D-Pro, D-Ala |
| [71] | |
| SERS coupled with a DAAO-mediated cascade reaction | D-Pro, D-Ala |
| [76] | |
| Biocatalytic nanoreactor based on mesoporous hydrogen-bonded organic framework | D-Phe, D-Ser, D-Ala, D-His, D-Arg, D-Orn, D-Asp |
| [73] | |
| Hepatic cancer (HC) | ||||
| Serum from HC patients and healthy controls | HPLC–MS/MS | D-Arg, D-Ile, D-Asp, D-Trp, D-Ala, D-Glu, D-Tyr, D-His, D-Asn, D-Met, D-Ser, D-Gln, D-Cys, D-Val, D-Leu, D-Phe, D-Thr |
| [92] |
| Plasma from HC patients and healthy controls | HPLC-FLD | D-Thr, D-Ala, D-Tyr, D-Val, total Met |
| [47] |
| Colorectal cancer (CRC) | ||||
| Urine from CRC patients and healthy controls | HPLC-MS/MS method based on D-BPCl probe | D-2-AABA, D-Ala, D-Asn, D-Gln, D-Ile, D-Leu, D-Met, D-Phe, D-Ser, D-Thr, D-Trp, D-Tyr, D-Val, D-Cit |
| [20] |
| HCT116 colorectal cancer cells and NCM460 normal intestinal epithelial cells | HPLC-MS/MS method based on D-BPCl probe | D-Ala, D-Gln, D-Leu, D-Met, D-Phe, D-Ser, D-Trp, D-Tyr |
| [50] |
| Glioblastoma (GBM) | ||||
| Resected tumour and non-tumour tissues, blood, and urine from patients with primary gliomas and healthy controls | 2D-HPLC-FLD | D-Ser, D-Ala, D-Asn, D-Pro |
| [57] |
| Breast cancer (BC) | ||||
| MCF-7 breast cancer cells and MCF-10A non-tumorigenic breast cells | HPLC-MS/MS with chiral separation | D-Asp, D-Ser |
| [90] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uifălean, A.; Iacobescu, M.; Salanță, L.C.; Hegheş, S.C.; Moldovan, R.-C.; Iuga, C.-A. Biological and Analytical Perspectives on D-Amino Acids in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050705
Uifălean A, Iacobescu M, Salanță LC, Hegheş SC, Moldovan R-C, Iuga C-A. Biological and Analytical Perspectives on D-Amino Acids in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050705
Chicago/Turabian StyleUifălean, Alina, Maria Iacobescu, Liana Claudia Salanță, Simona Codruța Hegheş, Radu-Cristian Moldovan, and Cristina-Adela Iuga. 2025. "Biological and Analytical Perspectives on D-Amino Acids in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050705
APA StyleUifălean, A., Iacobescu, M., Salanță, L. C., Hegheş, S. C., Moldovan, R.-C., & Iuga, C.-A. (2025). Biological and Analytical Perspectives on D-Amino Acids in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050705










