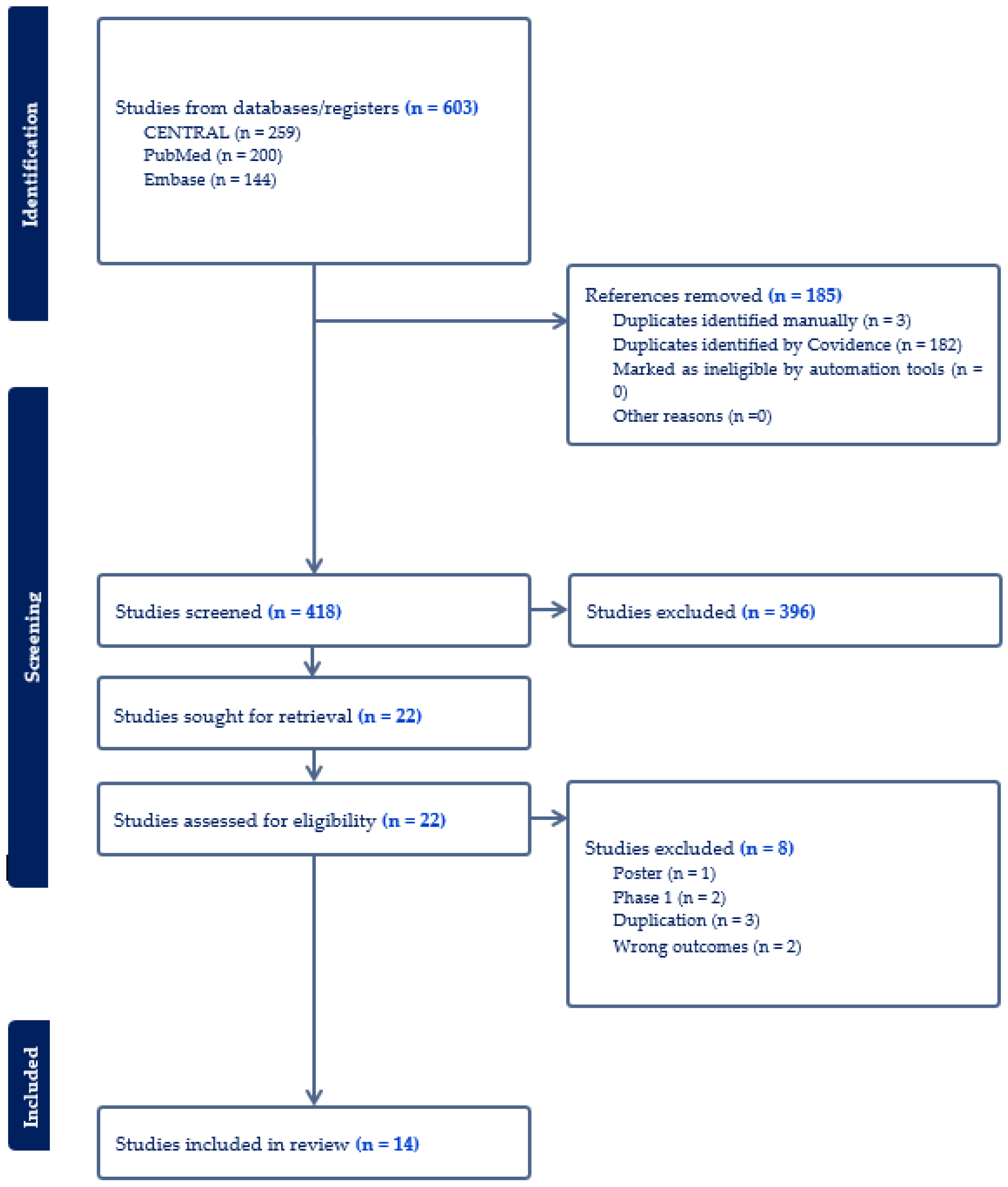
The Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Patients with Diabetes and/or Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Proportion of Patients Achieving Body Weight Targets of 5%, 10%, 15%
2.2. Change in Body Weight
2.3. Change in Waist Circumference
2.4. Change in HbA1c
2.5. Change in SBP
2.6. Change in DBP
2.7. Safety of Tirzepatide
2.7.1. Any Adverse Events
2.7.2. Serious Adverse Events
2.7.3. Treatment Discontinuation Due to Adverse Events
2.7.4. Gastrointestinal Adverse Events
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Search Strategy
4.2. Eligibility Criteria and Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
4.4. Outcomes
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Quality and Risk-of-Bias Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruze, R.; Liu, T.; Zou, X.; Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, R.; Yin, X.; Xu, Q. Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1161521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seravalle, G.; Grassi, G. Obesity and hypertension. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 122, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutor, A.W.; Lavie, C.J.; Kachur, S.; Milani, R.V.; Ventura, H.O. Updates on obesity and the obesity paradox in cardiovascular diseases. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 78, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutari, C.; DeMarsilis, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Obesity and diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 202, 110773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Xia, P.F.; Ma, M.N.; Li, Y.; Geng, T.T.; Zhang, Y.B.; Tu, Z.Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, L.R.; Zhang, B.F.; et al. Trends in the Prevalence of Metabolically Healthy Obesity Among US Adults, 1999–2018. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e232145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y.; Huang, W.J.; Hua, Y.; Qu, Q.; Cheng, C.; Liu, H.L.; Kong, X.Q.; Ma, Y.X.; Sun, W. Trends in general and abdominal obesity in US adults: Evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2001–2018). Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 925293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Sheng, H.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Q. Prevalence of diabetes in the USA from the perspective of demographic characteristics, physical indicators and living habits based on NHANES 2009–2018. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1088882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Gastaldelli, A.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Scherer, P.E. Why does obesity cause diabetes? Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagi, M.A.; Ahmed, H.; Rezq, M.A.A.; Sangroongruangsri, S.; Chaikledkaew, U.; Almalki, Z.; Thavorncharoensap, M. Economic costs of obesity: A systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.D.; Lin, J.; Mahoney, T.; Ume, N.; Yang, G.; Gabbay, R.A.; ElSayed, N.A.; Bannuru, R.R. Economic Costs of Diabetes in the U.S. in 2022. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, S.; Lau, D.C.W.; Vallis, M.; Sharma, A.M.; Biertho, L.; Campbell-Scherer, D.; Adamo, K.; Alberga, A.; Bell, R.; Boulé, N.; et al. Obesity in adults: A clinical practice guideline. CMAJ 2020, 192, E875–E891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; Khunti, K.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. 8. Obesity and Weight Management for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S145–S157. [Google Scholar]
- Mariam, Z.; Niazi, S.K. Glucagon-like peptide agonists: A prospective review. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2024, 7, e462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Müller, T.D. Incretin hormones and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1780–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaleh-Sachs, A.; Schwartz, J.L.; Bramante, C.T.; Nicklas, J.M.; Gudzune, K.A.; Jay, M. Obesity Management in Adults: A Review. JAMA 2023, 330, 2000–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, H.U.H.; Qazi, S.U.; Sajid, F.; Altaf, Z.; Ghazanfar, S.; Naveed, N.; Ashfaq, A.S.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Iqbal, H.; Qazi, S. Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Body Weight and Cardiometabolic Parameters in Individuals With Obesity and Without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Endocr. Pract. 2023, 30, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Block, C.; Bailey, C.; Wysham, C.; Hemmingway, A.; Allen, S.E.; Peleshok, J. Tirzepatide for the treatment of adults with type 2 diabetes: An endocrine perspective. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shi, H.; Xie, M.; Sun, Y.; Nahata, M.C. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide versus placebo in overweight or obese adults without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2024, 46, 1268–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, T.; Avgerinos, I.; Liakos, A.; Del Prato, S.; Matthews, D.R.; Tsapas, A.; Bekiari, E. Management of type 2 diabetes with the dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Guan, R.; Yan, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Cai, W.; Ma, G. Evaluation and comparison of efficacy and safety of tirzepatide and semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Bayesian network meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 199, 107031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhezi, O.S.; Alahmed, A.A.; Alfayez, O.M.; Alzuman, O.A.; Almutairi, A.R.; Almohammed, O.A. Comparative effectiveness of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the management of obesity in adults without diabetes: A network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohani, P.; Malekpour Alamdari, N.; Bagheri, S.E.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Sohouli, M.H. The effects of subcutaneous Tirzepatide on obesity and overweight: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1230206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronne, L.J.; Sattar, N.; Horn, D.B.; Bays, H.E.; Wharton, S.; Lin, W.Y.; Ahmad, N.N.; Zhang, S.; Liao, R.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Continued Treatment with Tirzepatide for Maintenance of Weight Reduction in Adults with Obesity: The SURMOUNT-4 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 331, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Chao, A.M.; Machineni, S.; Kushner, R.; Ard, J.; Srivastava, G.; Halpern, B.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide after intensive lifestyle intervention in adults with overweight or obesity: The SURMOUNT-3 phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2909–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; Frias, J.P.; Jastreboff, A.M.; le Roux, C.W.; Sattar, N.; Aizenberg, D.; Mao, H.; Zhang, S.; Ahmad, N.N.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity in people with type 2 diabetes (SURMOUNT-2): A double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Lee, B.W.; Chawla, M.; Kim, J.; Huo, L.; Du, L.; Huang, Y.; Ji, L. Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine as second-line or third-line therapy in type 2 diabetes in the Asia-Pacific region: The SURPASS-AP-Combo trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Frías, J.P.; Rodbard, H.W.; Tofé, S.; Sears, E.; Huh, R.; Fernández Landó, L.; Patel, H. Tirzepatide vs Insulin Lispro Added to Basal Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes: The SURPASS-6 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Oura, T.; Imaoka, T.; Seino, Y. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide monotherapy compared with dulaglutide in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS J-mono): A double-blind, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, J.P.; Davies, M.J.; Rosenstock, J.; Pérez Manghi, F.C.; Fernández Landó, L.; Bergman, B.K.; Liu, B.; Cui, X.; Brown, K. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prato, S.; Kahn, S.E.; Pavo, I.; Weerakkody, G.J.; Yang, Z.; Doupis, J.; Aizenberg, D.; Wynne, A.G.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Heine, R.J.; et al. Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes and increased cardiovascular risk (SURPASS-4): A randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvik, B.; Giorgino, F.; Jódar, E.; Frias, J.P.; Fernández Landó, L.; Brown, K.; Bray, R.; Rodríguez, Á. Once-weekly tirzepatide versus once-daily insulin degludec as add-on to metformin with or without SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3): A randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, J.P.; Nauck, M.A.; Van, J.; Kutner, M.E.; Cui, X.; Benson, C.; Urva, S.; Gimeno, R.E.; Milicevic, Z.; Robins, D.; et al. Efficacy and safety of LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, placebo-controlled and active comparator-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 2180–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.; Nauck, M.A.; Van, J.; Benson, C.; Bray, R.; Cui, X.; Milicevic, Z.; Urva, S.; Haupt, A.; Robins, D.A. Efficacy and tolerability of tirzepatide, a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate different dose-escalation regimens. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 938–946. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstock, J.; Wysham, C.; Frías, J.P.; Kaneko, S.; Lee, C.J.; Fernández Landó, L.; Mao, H.; Cui, X.; Karanikas, C.A.; Thieu, V.T. Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, D.; Onishi, Y.; Norwood, P.; Huh, R.; Bray, R.; Patel, H.; Rodríguez, Á. Effect of Subcutaneous Tirzepatide vs Placebo Added to Titrated Insulin Glargine on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The SURPASS-5 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.J. Weight Management: Obesity to Diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondmkun, Y.T. Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes: Associations and Therapeutic Implications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, E.S.; Silberman, C.; Davis, K.L.; Berria, R. Weight loss, glycemic control, and changes in cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving incretin therapies or insulin in a large cohort database. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1759–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbury, S.; Oyebode, O.; van Rens, T.; Barber, T.M. Obesity Stigma: Causes, Consequences, and Potential Solutions. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.H.; Yockey, S.R. Weight Loss and Improvement in Comorbidity: Differences at 5%, 10%, 15%, and over. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permana, H.; Yanto, T.A.; Hariyanto, T.I. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide as novel treatment for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2022, 16, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mesquita, Y.L.L.; Pera Calvi, I.; Reis Marques, I.; Almeida Cruz, S.; Padrao, E.M.H.; Carvalho, P.E.P.; da Silva, C.H.A.; Cardoso, R.; Moura, F.A.; Rafalskiy, V.V. Efficacy and safety of the dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide for weight loss: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagavathula, A.S.; Vidyasagar, K.; Tesfaye, W. Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Phase II/III Trials. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumholz, H.M.; de Lemos, J.A.; Sattar, N.; Linetzky, B.; Sharma, P.; Mast, C.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Bunck, M.C.; Stefanski, A. Tirzepatide and blood pressure reduction: Stratified analyses of the SURMOUNT-1 randomised controlled trial. Heart 2024, 110, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbay, M.; Copur, S.; Siriopol, D.; Yildiz, A.B.; Gaipov, A.; van Raalte, D.H.; Tuttle, K.R. Effect of tirzepatide on blood pressure and lipids: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 3766–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Pan, X.H.; Chew, H.S.J.; Goh, R.S.J.; Lin, C.; Anand, V.V.; Lee, E.C.Z.; Chan, K.E.; Kong, G.; Ong, C.E.Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide for treatment of overweight or obesity. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Yang, M.; Wen, H.; Zhou, S.; Xiong, C.; Wang, Y. A systematic review of the safety of tirzepatide-a new dual GLP1 and GIP agonist—Is its safety profile acceptable? Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1121387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author (Year) | Trial Name | Design/Phase | Patient Population | Sample Size | BMI (kg/m2) | HbA1c (%) | Intervention | Comparator | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aronne, 2024 [24] | SURMOUNT-4 | Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | ≥18 years old, obesity or overweight without diabetes | 670 | 38.4 | 5.5 | The maximum tolerated dose of tirzepatide | Placebo | 88-week |
| Wadden, 2023 [25] | SURMOUNT-3 | Phase 3, randomized, parallel-arm, double-blind, placebo-controlled | ≥18 years old, obesity or overweight without diabetes | 579 | 35.9 | 5.4 | The maximum tolerated dose of tirzepatide | Placebo | 72-week |
| Garvey, 2023 [26] | SURMOUNT-2 | Phase 3, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled | ≥18 years old, with T2DM for at least 3 months, BMI ≥ 27 kg/m2 | 938 | 36·1 | 8·02 | Tirzepatide (10 mg or 15 mg) | Placebo | 72-week |
| Jastreboff, 2022 [29] | SURMOUNT-1 | Phase 3, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled | ≥18 years old, obesity or overweight without diabetes | 2539 | 38.0 | 5.6 | Tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg) | Placebo | 72-week |
| Gao, 2023 [27] | SURPASS-AP-Combo | Phase 3, randomized controlled, open label | ≥18 years old, with T2DM for at least 2 months, BMI ≥ 23 kg/m2 | 917 | 27.9 | 8.71 | Tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg) | Insulin glargine | 40-week |
| Inagaki, 2022 [30] | SURPASS J-mono | Phase 3, double-blinded, randomized, active-controlled | ≥20 years old, with T2DM for at least 8 months, BMI ≥ 23 kg/m2 | 636 | 28·1 | 8·2 | Tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg) | Dulaglutide 0.75 mg | 52-week |
| Rosenstock, 2023 [28] | SURPASS-6 | Phase 3b, randomized, open-label, parallel-group | ≥18 years old, with T2DM inadequately controlled with basal insulin, BMI 23–45 kg/m2 | 1428 | 33 | 8.8 | Tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg) | Insulin lispro | 52-week |
| Dahl, 2022 [37] | SURPASS-5 | Phase 3, randomized controlled, double-blind | With T2DM, BMI ≥ 23 kg/m2 | 475 | 33.4 | 8.3 | Tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg) | Placebo | 40-week |
| Del Prato, 2021 [32] | SURPASS-4 | Phase 3, randomized, open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group | ≥18 years old, with T2DM, BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 | 1995 | 32·6 | 8·5 | Tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg) | Insulin glargine 100 U/mL | 52-week |
| Ludvik, 2021 [33] | SURPASS-3 | Phase 3, randomized, active-controlled, open-label, parallel-group | ≥18 years old, with T2DM for at least 3 months, BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 | 1437 | 33.5 | 8.2 | Tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg) | Insulin degludec U100/mL | 52-week |
| Frías, 2021 [31] | SURPASS-2 | Phase 3, open-label, randomized, active-controlled | ≥18 years old, with T2DM, BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 | 1878 | 34.2 | 8.3 | Tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg) | Semaglutide 1 mg | 40-week |
| Rosenstock, 2021 [36] | SURPASS-1 | Phase 3, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled | ≥18 years old, with T2DM, BMI ≥ 23 kg/m2 | 705 | 31.9 | 7.9 | Tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg) | Placebo | 40-week |
| Frias, 2020 [35] | NCT03311724 | Phase 2, randomized, controlled, double-blind | With T2DM for at least 3 months, BMI 23–45 kg/m2 | 198 | 31.9 | 8.4 | Tirzepatide (12 mg or 15 mg) | Placebo | 12-week |
| Frias, 2018 [34] | NCT03131687 | Phase 2, double-blind, randomized | 18–75 years old, with T2DM for at least 3 months, BMI 23–50 kg/m2 | 318 | 32.4 | 8.1 | Tirzepatide (1 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg or 15 mg) | Placebo or 1.5 mg dulaglutide | 26-week |
| Trials | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | SURPASS-1 | SURPASS-2 | SURPASS-3 | SURPASS-4 | SURPASS-5 | SURPASS-6 | SURPASS-J-Mono | SURPASS-AP-Combo | NCT03131687 | NCT03311724 | SURMOUNT-1 | SURMOUNT-2 | SURMOUNT-3 | SURMOUNT-4 |
| Interventions | TZP 5 mg (121) vs. 10 mg (121) vs. 15 mg, (121) vs. placebo (115) | TZP 5 mg (470) vs. 10 mg (469) vs. 15 mg, (470) vs. semaglutide 1 mg (469) | TZP 5 mg (358) vs. 10 mg (360) vs. 15 mg, (359) vs. insulin degludec (360) | TZP 5 mg (329) vs. 10 mg (328) vs. 15 mg, (338) vs. insulin glargine (1000) | TZP 5 mg (116) vs. 10 mg (119) vs. 15 mg, (120) vs. placebo (120) | TZP 5 mg (243) vs. 10 mg (238) vs. 15 mg, (236) vs. insulin lispro (708) | TZP 5 mg (159) vs. 10 mg (158) vs. 15 mg, (160) vs. dulaglutide 0.75 mg (159) | TZP 5 mg (230) vs. 10 mg (228) vs. 15 mg, (229) vs. insulin glargine (230) | TZP 1 mg (52) vs. 5 mg (55) vs. 10 mg (51) vs. 15 mg, (53) vs. dulaglutide 1.5 mg (54) vs. placebo (51) | TZP 12 mg (29) vs. 15 mg, (28) vs. 15 mg (28) vs. placebo (26) | TZP 5 mg (630) vs. 10 mg (636) vs. 15 mg (630) vs. placebo (643) | TZP 10 mg (312) vs. 15 mg (311) vs. placebo (315) | MTD (287) vs. placebo (292) | MTD (335) vs. Placebo (335) |
| (number of participants) | ||||||||||||||
| Efficacy Outcomes | ||||||||||||||
| Change in A1c (%) | −1.87 vs. −1.89 vs. −2.07 vs. 0.04 | −2.01 vs. −2.24 vs. −2.30 vs. −1.86 | −1.93 vs. −2.20 vs. −2.37 vs. −1.34 | −2.24 vs. −2.43 vs. −2.58 vs. −1.44 | −2.11 vs. −2.40 vs. −2.34 vs. −0.86 | −1.92 vs. −2.15 vs. −2.27 vs. −1.13 | −2.4 vs. −2.6 vs. −2.8 vs. −1.3 | −2.24 vs. −2.44 vs. −2.49 vs. −0.95 | −0.7 vs. −1.6 vs. −2.0 vs. −2.4 vs. −1.1 vs. −0.1 | −1.7 vs. −2.0 vs. −1.8 vs. 0.2 | −0.40 vs. −0.49 vs. −0.51 vs. −0.07 | −2.1 vs. −2.1 vs. −0.5 | −0.5 vs. 0.0 | −0.57 vs. −0.22 |
| WL (kg) | −7.0 vs. −7.8 vs. −9.5 vs. −0.7 | −7.8 vs. −10.3 vs. −12.4 vs. −6.2 | −7.5 vs. −10.7 vs. −12.9 vs. 2.3 | −7.1 vs. −9.5 vs. −11.7 vs. 1.9 | −5.4 vs. −7.5 vs. −8.8 vs. 1.6 | −6.7 vs. −9.2 vs. −11.0 vs. 3.2 | −5.8 vs. −8.5 vs. −10.7 vs. −0.5 | −5.0 vs. −7.0 vs. −7.2 vs. 1.5 | −0.9 vs. −4.8 vs. −8.7 vs. −11.3 vs. −2.7 vs. −0.4 | −5.3 vs. −5.5 vs. −5.7 vs. −0.5 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| ≥5% WL, % | 67 vs. 78 vs. 77 vs. 14 | 65 vs. 76 vs. 80 vs. 54 | 66 vs. 84 vs. 88 vs. 6 | 63 vs. 78 vs. 85 vs. 8 | 47.9 vs. 57.9 vs. 71.6 vs. 6.0 | 64 vs. 79 vs. 83 vs. 6 | 61 vs. 82 vs. 89 vs. 11 | 55.7 vs. 71.6 vs. 74.1 vs. 5.6 | 13.5 vs. 47.3 vs. 70.6 vs. 62.3 vs. 22.2 vs. 0 | n/a | 85.1 vs. 88.9 vs. 90.9 vs. 34.5 | 79.2 vs. 82.8 vs. 32.5 | 87.5 vs. 16.5 | 98.5 vs. 69.0 |
| ≥10% WL, % | 31 vs. 40 vs. 47 vs. 1 | 34 vs. 47 vs. 57 vs. 24 | 37 vs. 56 vs. 69 vs. 3 | 36 vs. 53 vs. 66 vs. 2 | 20.7 vs. 41.6 vs. 40.7 vs. 0.8 | 33 vs. 52 vs. 61 vs. 2 | 34 vs. 50 vs. 67 vs. 3 | 26.8 vs. 41.9 vs. 45.1 vs. 0.5 | 5.8 vs. 16.4 vs. 39.2 vs. 37.7 vs. 9.3 vs. 0 | n/a | 73.4 vs. 85.9 vs. 90.1 vs. 13.5 | 63.4 vs. 69.6 vs. 8.7 | 88.0 vs. 4.8 | 94.0 vs. 44.4 |
| ≥15% WL, % | 13 vs. 17 vs. 27 vs. 0 | 15 vs. 24 vs. 36 vs. 8 | 13 vs. 28 vs. 43 vs. 0 | 14 vs. 24 vs. 37 vs. <1 | 6.9 vs. 23.7 vs. 22.9 vs. 0 | 14 vs. 30 vs. 41 vs. 0 | 16 vs. 26 vs. 45 vs. <1 | 10.1 vs. 17.1 vs. 17.9 vs. 0 | 0 vs. 5.5 vs. 21.6 vs. 24.5 vs. 1.9 vs. 0 | n/a | 50.2 vs. 73.6 vs. 78.2 vs. 6.0 | 41.4 vs. 51.8 vs. 2.6 | 73.9 vs. 2.1 | 87.1 vs. 24.0 |
| Change in WC, cm | −5.7 vs. −6.9 vs. −7.2 vs. −2.0 | −6.9 vs. −9.6 vs. −9.9 vs. −5.6 | n/a | n/a | −3.8 vs. −7.4 vs. −8.9 vs. +1.0 | −5.7 vs. −7.8 vs. −9.6 vs. 2.1 | n/a | n/a | −2.1 vs. −5.1 vs. −7.4 vs. −10.2 vs. −2.5 vs. −1.3 | −4.8 vs. −4.9 vs. −4.9 vs. −2.5 | −14.0 vs. −17.7 vs. −18.5 vs. −4.0 | −10.8 vs. −13.1 vs. −3.3 | −14.6 vs. 0.2 | −22.5 vs. −9.3 |
| Change in SBP, mmHg | −4.7 vs. −4.7 vs. −5.2 vs. −2.0 | −4.8 vs. −5.3 vs. −6.5 vs. −3.6 | −4.9 vs. −6.6 vs. −5.5 vs. 0.5 | n/a | −6.1 vs. −8.3 vs. −12.6 vs. −1.7 | −7.4 vs. −9.0 vs. −5.9 vs. −0.4 | n/a | −6.7 vs. −7.2 vs. −7.3 vs. 1.1 | 0 vs. −2.6 vs. −1.3 vs. −1.0 vs. −1.5 vs. 1.7 | n/a | −7.0 vs. −8.2 vs. −7.6 vs. −1.2 | −6.3 vs. −1.2 | −5.1 vs. 4.1 | −9.3 vs. −2.4 |
| Change in DBP, mmHg | −2.9 vs. −3.1 vs. −3.4 vs. −1.4 | −1.9 vs. −2.5 vs. −2.9 vs. −1.0 | −2.0 vs. −2.5 vs. −1.9 vs. 0.4 | n/a | −2.0 vs. −3.3 vs. −4.5 vs. −2.1 | −2.3 vs. −3.3 vs. −1.0 vs. −0.4 | n/a | −4.0 vs. −3.6 vs. −3.4 vs. 0.9 | −0.5 vs. −0.7 vs. −0.2 vs. −0.7 vs. −1.4 vs. 0.8 | n/a | −5.2 vs. −5.5 vs. −4.6 vs. −1.0 | n/a | −3.2 vs. 2.3 | −5.5 vs. −1.7 |
| Change in BMI (kg/m2) | −2.6 vs. −2.9 vs. −3.6 vs. −0.2 | −2.9 vs. −3.8 vs. −4.6 vs. −2.3 | n/a | n/a | −2.2 vs. −2.9 vs. −3.8 vs. +0.6 | −2.6 vs. −3.8 vs. −4.5 vs. 1.4 | n/a | n/a | −0.3 vs. −1.7 vs. −3.1 vs. −4.1 vs. −1.0 vs. −0.1 | n/a | n/a | −4.7 vs. −5.4 vs. −1.2 | −7.7 vs. 1.2 | −10.0 vs. −3.6 |
| Safety Outcomes | ||||||||||||||
| Overall AE (%) | 69 vs. 67 vs. 64 vs. 66 | 63.6 vs. 68.7 vs. 68.9 vs. 64.2 | 61 vs. 69 vs. 73 vs. 54 | 71 vs. 74 vs. 77 vs. 68 | 73.3 vs. 68.1 vs. 78.3 vs. 67.5 | 70.0 vs. 70.6 vs. 75 vs. 55.6 | 82 vs. 77 vs. 84 vs. 77 | 87 vs. 94.7 vs. 93 vs. 71.4 | 50 vs. 72.7 vs. 78.4 vs. 84.9 vs. 74.1 vs. 52.9 | 79.3 vs. 67.9 vs. 85.7 vs. 50.0 | 81.0 vs 81.8 vs 78.9 vs 72.0 | 78 vs 71 vs 76 | 87.1 vs 76.7 | 60.3 vs 55.8 |
| SAE (%) | 4 vs. 2 vs. 1 vs. 3 | 7.0 vs. 5.3 vs. 5.7 vs. 2.8 | 8 vs. 6 vs. 7 vs. 6 | 15 vs. 17 vs. 12 vs. 19 | 7.8 vs. 10.9 vs. 7.5 vs. 8.3 | 6.2 vs. 5.9 vs. 6.4 vs. 10.9 | 5 vs. 6 vs. 4 vs. 9 | 6.5 vs. 6.1 vs. 6.6 vs. 9.1 | 3.8 vs. 1.8 vs. 5.9 vs. 3.8 vs. 5.6 vs. 3.9 | 3.4 vs. 0 vs. 0 vs. 0 | 6.3 vs 6.9 vs 5.1 vs 6.8 | 6 vs 9 vs 7 | 5.9 vs 4.8 | 3 vs 3 |
| AE leading to discontinuation (%) | 3 vs. 5 vs. 7 vs. 3 | 6.0 vs. 8.5 vs. 8.5 vs. 4.1 | 7 vs. 10 vs. 11 vs. 1 | 11 vs. 9 vs. 11 vs. 5 | 6.0 vs. 8.4 vs. 10.8 vs. 2.5 | 4.1 vs. 4.6 vs. 9.3 vs. 2.4 | 8 vs. 10 vs. 10 vs. 6 | 4.3 vs. 13.2 vs. 12.2 vs. 2.7 | 3.8 vs. 9.1 vs. 5.9 vs. 24.5 vs. 11.1 vs. 3.9 | 3.4 vs. 3.6 vs. 0 vs. 3.8 | 4.3 vs 7.1 vs 6.2 vs 2.6 | 4 vs 7 vs 4 | 10.5 vs 2.1 | 1.8 vs 0.9 |
| Nausea (%) | 12 vs. 13 vs. 18 vs. 6 | 17.4 vs. 19.2 vs. 22.1 vs. 17.9 | 12 vs. 23 vs. 24 vs. 2 | 12 vs. 16 vs. 23 vs. 2 | 12.9 vs. 17.6 vs. 18.3 vs. 2.5 | 13.6 vs. 20.6 vs. 25.8 vs. 1.1 | 12 vs. 20 vs. 20 vs. 8 | 20.0 vs. 32.9 vs. 31.9 vs. 2.3 | 3.8 vs. 20.0 vs. 21.6 vs. 39.6 vs. 29.6 vs. 5.9 | 24.1 vs. 39.3 vs. 35.7 vs. 7.7 | 24.6 vs 33.3 vs 31.0 vs 9.5 | 20 vs 22 vs 6 | 39.7 vs 14.0 | 8.1 vs 2.7 |
| Vomiting (%) | 3 vs. 2 vs. 6 vs. 2 | 5.7 vs. 8.5 vs. 9.8 vs. 8.3 | 6 vs. 9 vs. 10 vs. 1 | 5 vs. 8 vs. 9 vs. 2 | 6.9 vs. 7.6 vs. 12.5 vs. 2.5 | 4.5 vs. 8.8 vs. 12.7 vs. 0.6 | 8 vs. 5 vs. 12 vs. 1 | 9.1 vs. 14.9 vs. 12.7 vs. 1.4 | 3.8 vs. 7.3 vs. 15.7 vs. 26.4 vs. 9.3 vs. 2.0 | 17.2 vs. 17.9 vs. 17.9 vs. 3.8 | 8.3 vs 10.7 vs 12.2 vs 1.7 | 11 vs 13 vs 3 | 18.1 vs 1.4 | 5.7 vs 1.2 |
| Diarrhea (%) | 12 vs. 14 vs. 12 vs. 8 | 13.2 vs. 16.4 vs. 13.8 vs. 11.5 | 15 vs. 17 vs. 16 vs. 4 | 13 vs. 20 vs. 22 vs. 4 | 12.1 vs. 12.6 vs. 20.8 vs. 10.0 | 11.9 vs. 15.1 vs. 11.0 vs. 2.4 | 17 vs. 9 vs. 11 vs. 7 | 33.5 vs. 45.2 vs. 44.1 vs. 1.4 | 13.5 vs. 23.6 vs. 23.5 vs. 32.1 vs. 16.7 vs. 3.9 | 31.0 vs. 35.7 vs. 32.1 vs. 7.7 | 18.7 vs 21.2 vs 23.0 vs 7.3 | 20 vs 22 vs 9 | 31.0 vs 9.2 | 10.7 vs 4.8 |
| Constipation (%) | 6 vs. 5 vs. 7 vs. 1 | 6.8 vs. 4.5 vs. 4.5 vs. 5.8 | n/a | 5 vs. 4 vs. 4 vs. <1 | 6.0 vs. 6.7 vs. 6.7 vs. 1.7 | 2.5 vs. 3.4 vs. 5.9 vs. 0.6 | 15 vs. 18 vs. 14 vs. 11 | 5.2 vs. 7.5 vs. 10.0 vs. 1.4 | 1.9 vs. 3.6 vs. 11.8 vs. 3.8 vs. 5.6 vs. 0 | 3.4 vs. 10.7 vs. 17.9 vs. 0 | 16.8 vs 17.1 vs 11.7 vs 5.8 | 8 vs 9 vs 4 | 23.0 vs 6.8 | n/a |
| Intervention | Comparator | Odds Ratio or SMD (95% CI) | I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight loss ≥ 5% | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | 11.89 (9.36–15.11) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | 15.08 (9.26–24.57) | 73 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | 20.48 (13.38–31.34) | 71 |
| Weight loss ≥ 10% | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | 10.69 (8.29–13.79) | 27 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | 17.47 (13.90–21.96) | 33 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | 22.19 (18.27–26.96) | 50 |
| Weight loss ≥ 15% | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | 9.94 (7.30–13.54) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | 22.88 (17.06 –30.68) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | 25.61 (20.59–31.85) | 48 |
| Weight loss (kg) | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | −1.05 (−1.24–−0.87) | 22 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | −1.25 (−1.50–−1.00) | 77 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | −1.80 (−2.12–−1.49) | 93 |
| WC (cm) | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | −0.74 (−0.85–−0.63) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | −0.91 (−1.08–−0.73) | 63 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | −1.41 (−1.81–−1.02) | 96 |
| HbA1c (%) | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | −1.45 (−1.68–−1.21) | 69 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | −1.59 (−1.82–−1.37) | 62 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | −1.56 (−1.85–−1.27) | 91 |
| SBP (mmHg) | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | −0.38 (−0.53–−0.23) | 37 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | −0.44 (−0.63–−0.25) | 63 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | −0.55 (−0.74–−0.36) | 74 |
| DBP (mmHg) | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | −0.33 (−0.57–−0.09) | 70 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | −0.29 (−0.51–−0.07) | 77 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | −0.42 (−0.54–−0.29) | 55 |
| Intervention | Comparator | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight loss ≥ 5% | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 3.89 (1.10–13.77) | 95 |
| Basal insulin | 19.94 (16.25–24.47) | 36 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 10.63 (0.90–125.99) | 98 |
| Basal insulin | 40.62 (28.28–58.32) | 64 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 16.82 (1.07–263.37) | 98 |
| Basal insulin | 54.77 (33.35–89.95) | 79 | |
| Weight loss ≥ 10% | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 3.59 (0.85–15.14) | 90 |
| Basal insulin | 21.81 (10.09– 47.15) | 82 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 8.15 (2.15–30.96) | 90 |
| Basal insulin | 43.70 (20.44– 93.41) | 82 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 12.20 (2.60–57.27) | 91 |
| Basal insulin | 68.64 (29.50–159.68) | 86 | |
| Weight loss ≥ 15% | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 4.72 (0.86 –25.85) | 73 |
| Basal insulin | 56.38 (24.19–131.42) | 0 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 11.43 (2.31–56.54) | 74 |
| Basal insulin | 126.42 (54.73–292.04) | 2 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 20.25 (3.64–112.56) | 76 |
| Basal insulin | 208.36 (90.58–479.32) | 0 | |
| Weight loss (kg) | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −0.55 (−1.07–−0.04) | 93 |
| Basal insulin | −1.51 (−1.74–−1.29) | 87 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −1.06 (−1.66– −0.46) | 96 |
| Basal insulin | −1.96 (−2.24–−1.69) | 89 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −1.42 (−2.10–−0.74) | 97 |
| Basal insulin | −2.23 (−2.58–−1.89) | 94 | |
| WC (cm) | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −0.71 (−1.27–−0.16) | 84 |
| Basal insulin | NA | 0 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −1.01 (−1.41–−0.61) | 67 |
| Basal insulin | NA | 31 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −1.43 (−1.97–−0.88) | 81 |
| Basal insulin | NA | 33 | |
| HbA1c (%) | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −0.60 (−1.13–−0.06) | 95 |
| Basal insulin | −0.78 (−1.11–−0.44) | 93 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −0.84 (−1.29–−0.39) | 93 |
| Basal insulin | −0.98 (−1.33–−0.63) | 94 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −1.05 (−1.60–−0.50) | 95 |
| Basal insulin | −1.09 (−1.44–−0.74) | 94 | |
| SBP (mmHg) | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −0.28 (−0.60–0.04) | 55 |
| Basal insulin | −0.43 (−0.59–−0.27) | 76 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −0.31 (−0.91–0.29) | 86 |
| Basal insulin | −0.54 (−0.74–−0.34) | 83 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −0.38 (−1.18–0.41) | 92 |
| Basal insulin | −0.46 (−0.54–−0.38) | 0 | |
| DBP (mmHg) | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −0.18 (−0.65–0.28) | 78 |
| Basal insulin | −0.25 (−0.33–−0.17) | 0 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −0.20 (−0.81–0.42) | 87 |
| Basal insulin | −0.30 (−0.42–−0.17) | 59 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | −0.32 (−1.06–0.43) | 91 |
| Basal insulin | −0.19 (−0.32–−0.07) | 56 | |
| Intervention | Comparator | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse events lead to treatment discontinuation | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | 1.75 (1.06–2.90) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | 2.00 (1.15–3.47) | 17 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | 2.84 (1.99–4.05) | 23 |
| Serious adverse events | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | 0.94 (0.64–1.38) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | 0.98 (0.71–1.35) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | 0.94 (0.70–1.24) | 0 |
| Any adverse events | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | 1.53 (1.23–1.90) | 12 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | 1.36 (0.98–1.89) | 63 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | 1.53 (1.06–2.21) | 74 |
| Nausea | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | 3.12 (2.34–4.16) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | 4.38 (3.42–5.61) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | 4.27 (3.49–5.23) | 0 |
| Vomiting | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | 4.19 (2.43–7.21) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | 4.61 (2.83–7.49) | 4 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | 6.76 (4.71–9.70) | 0 |
| Diarrhea | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | 2.25 (1.28–3.97) | 56 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | 2.59 (1.79–3.76) | 45 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | 3.26 (2.57–4.14) | 33 |
| Decreased appetite | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | Placebo | 3.45 (2.18–5.48) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | Placebo | 4.60 (3.09–6.84) | 0 |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | Placebo | 4.00 (2.49–6.41) | 23 |
| Intervention | Comparator | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse events lead to treatment discontinuation | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.34 (0.85–2.13) | 0 |
| Basal insulin | 2.28 (1.63–3.20) | 21 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.73 (1.00–2.99) | 44 |
| Basal insulin | 3.22 (1.50–6.88) | 76 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 2.17 (1.41–3.32) | 0 |
| Basal insulin | 4.00 (2.19–7.32) | 68 | |
| Serious adverse events | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 0.96 (0.26–3.50) | 79 |
| Basal insulin | 0.77 (0.54–1.10) | 45 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.20 (0.56–2.57) | 44 |
| Basal insulin | 0.75 (0.59–0.96) | 0 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 0.97 (0.33–2.81) | 71 |
| Basal insulin | 0.70 (0.49–0.98) | 38 | |
| Any adverse events | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.03 (0.82–1.30) | 0 |
| Basal insulin | 1.61 (1.14–2.27) | 75 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.17 (0.93–1.47) | 0 |
| Basal insulin | 2.32 (1.18–4.56) | 87 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.32 (1.04–1.67) | 0 |
| Basal insulin | 2.50 (1.58–3.94) | 80 | |
| Nausea | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.00 (0.73–1.36) | 35 |
| Basal insulin | 8.32 (5.33–12.99) | 20 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.30 (0.58–2.95) | 77 |
| Basal insulin | 14.92 (8.67–25.69) | 55 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.73 (1.03–2.91) | 57 |
| Basal insulin | 17.99 (11.52–28.10) | 28 | |
| Vomiting | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.37 (0.34–5.56) | 76 |
| Basal insulin | 4.92 (2.89–8.36) | 0 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.51 (0.72–3.17) | 40 |
| Basal insulin | 9.00 (5.11–15.86) | 22 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 3.03 (0.88–10.42) | 80 |
| Basal insulin | 10.23 (5.27–19.88) | 49 | |
| Diarrhea | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.60 (0.93–2.77) | 51 |
| Basal insulin | 6.53 (2.53–16.86) | 80 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.48 (1.07–2.04) | 0 |
| Basal insulin | 9.36 (3.37–25.98) | 81 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 1.44 (1.01–2.06) | 0 |
| Basal insulin | 8.60 (3.03–24.46) | 80 | |
| Decreased appetite | |||
| Tirzepatide 5 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 2.38 (1.15–4.94) | 53 |
| Basal insulin | 23.25 (11.34–47.70) | 31 | |
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 2.57 (1.12–5.89) | 64 |
| Basal insulin | 38.06 (15.43–93.90) | 40 | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | GLP-1 RAs | 3.21 (1.37–7.48) | 70 |
| Basal insulin | 46.87 (15.57–141.07) | 46 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Shi, H.; Xie, M.; Sun, Y.; Nahata, M.C. The Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Patients with Diabetes and/or Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050668
Liu L, Shi H, Xie M, Sun Y, Nahata MC. The Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Patients with Diabetes and/or Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050668
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ligang, Hekai Shi, Merilyn Xie, Yuxiao Sun, and Milap C. Nahata. 2025. "The Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Patients with Diabetes and/or Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050668
APA StyleLiu, L., Shi, H., Xie, M., Sun, Y., & Nahata, M. C. (2025). The Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Patients with Diabetes and/or Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050668






