Diosmin Potentiates the Antidiabetic Effects of Linagliptin in Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects on Oral Glucose Tolerance (OGT)
2.2. Effects on Serum Insulin and C-Peptide Levels
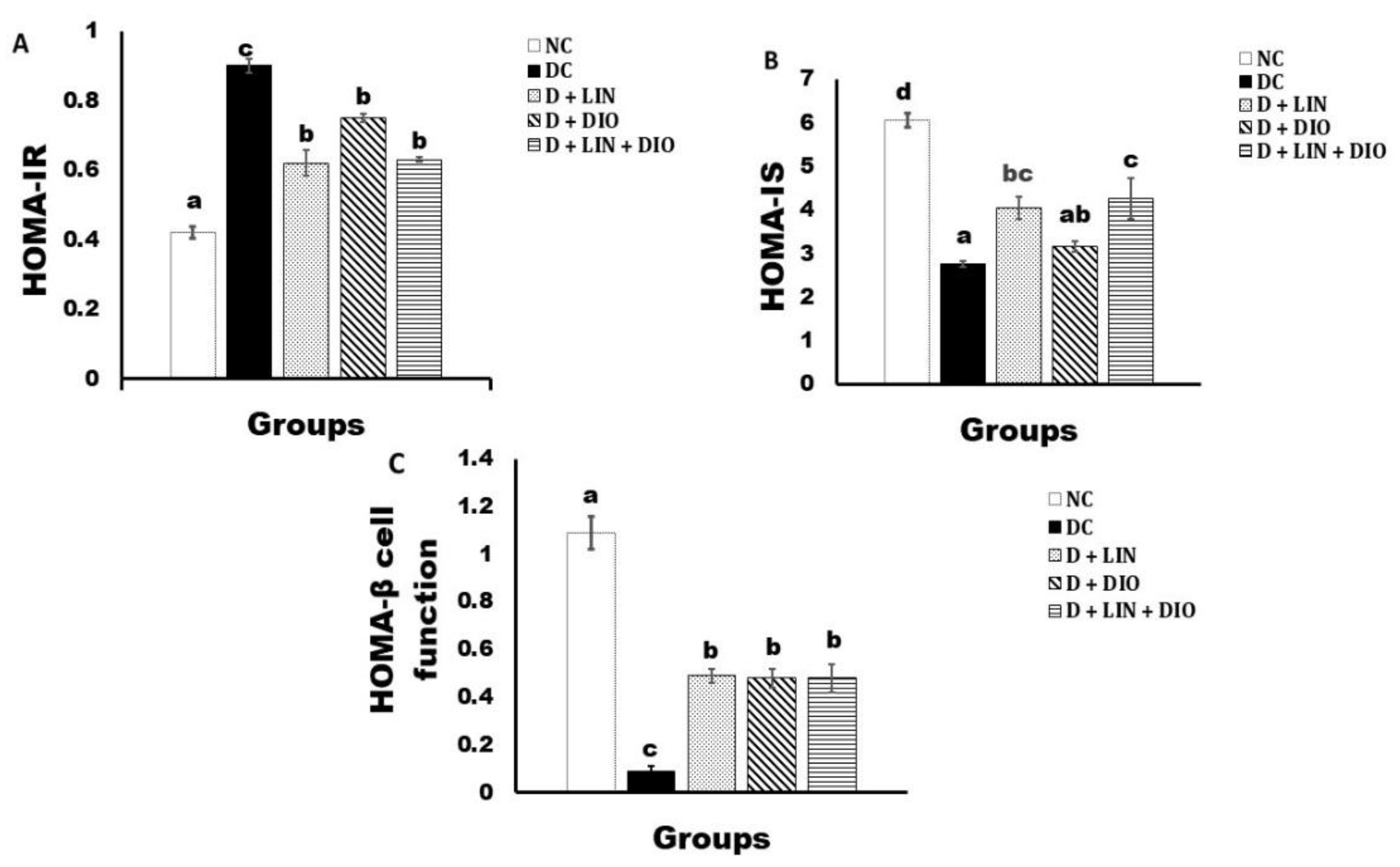
2.3. Effect on the HOMA-IR Cell Function, HOMA-IS, and HOMA-β Cell Function
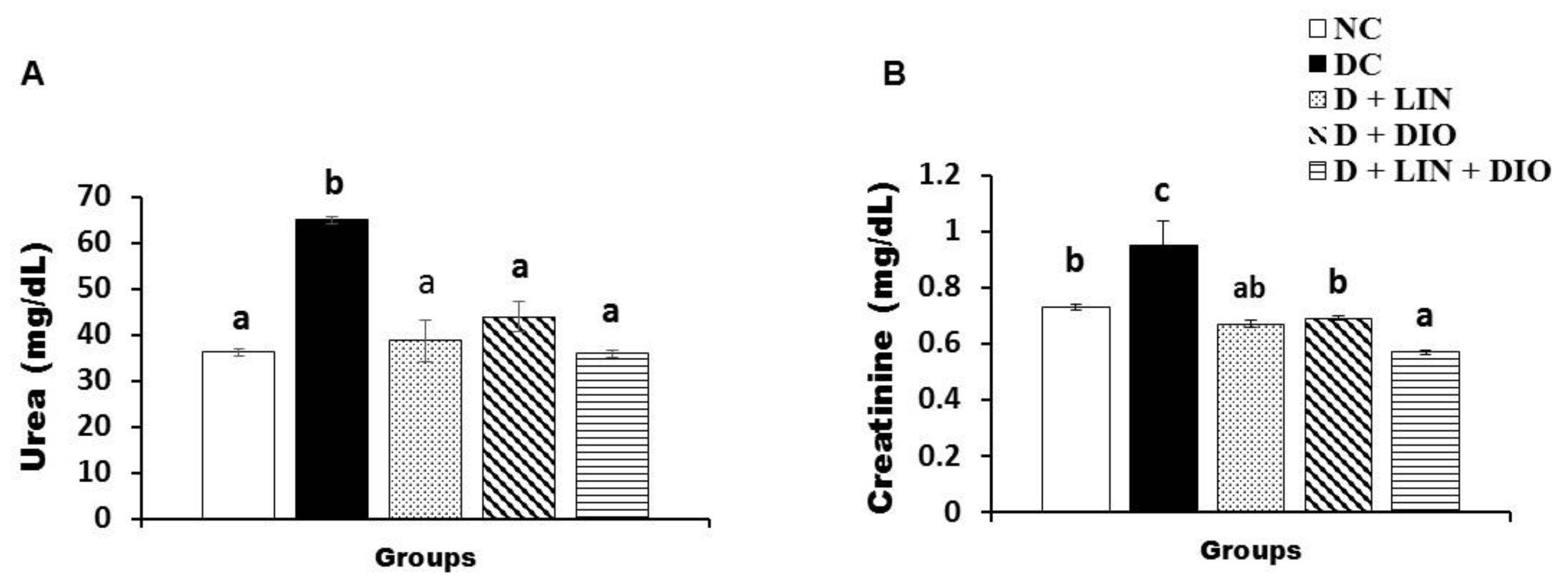
2.4. Effect on the Serum Urea and Creatinine Levels
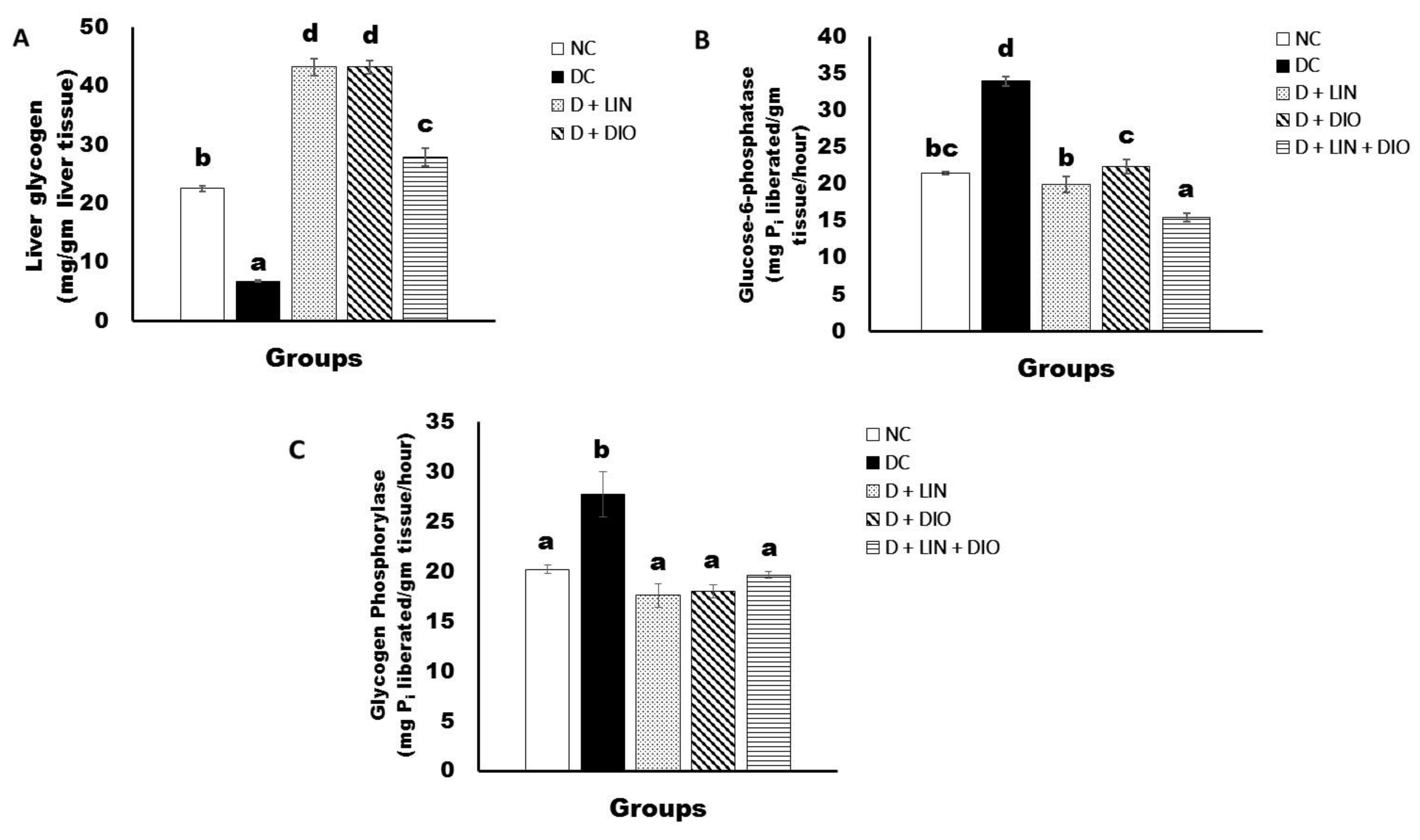
2.5. Effects on Liver Glycogen Content and Glucose-6-Phospatase and Glycogen Phosphorylase Activities
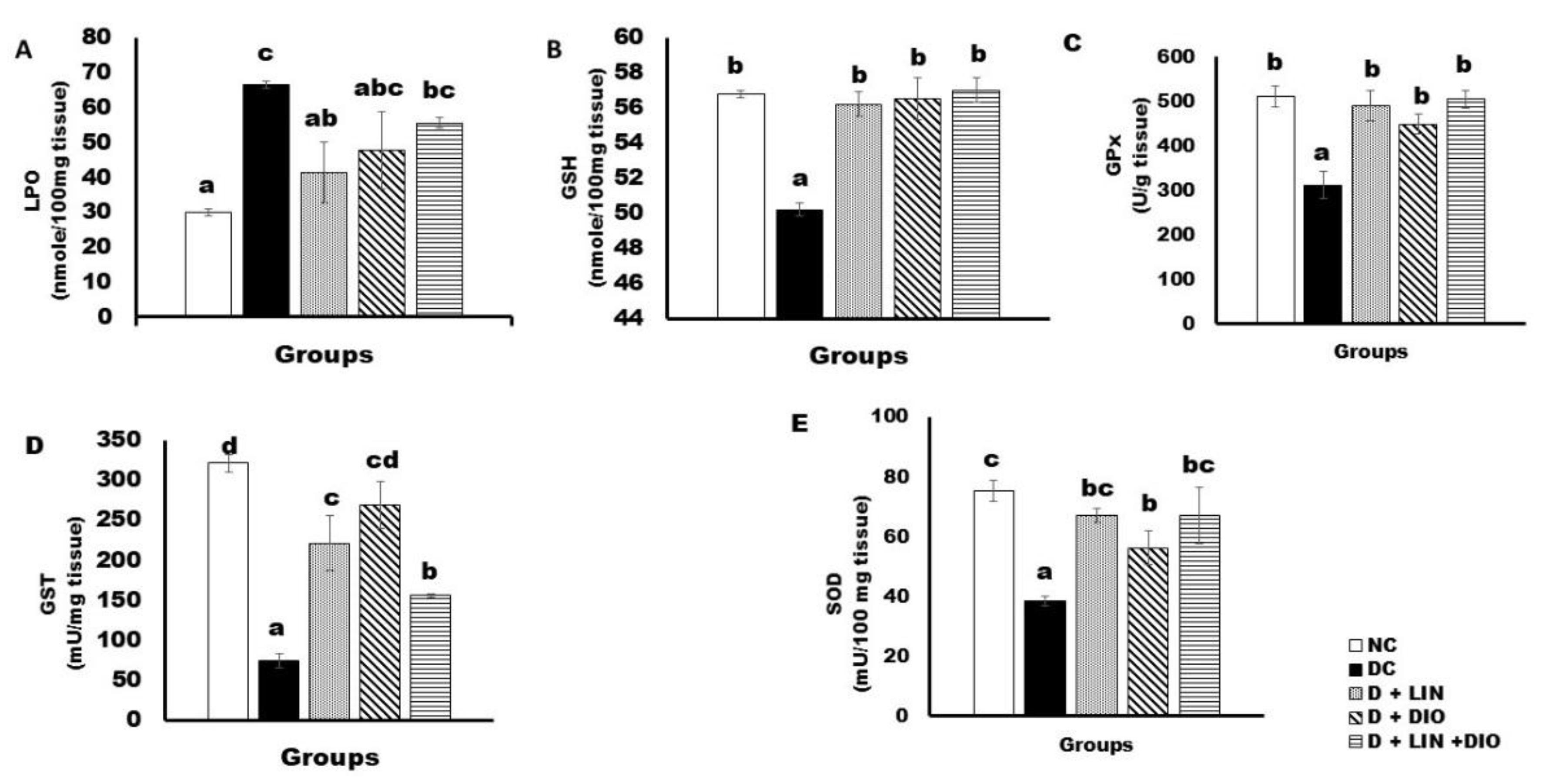
2.6. Effects on the Liver Oxidative Stress and Anti-Oxidant Defense Parameters
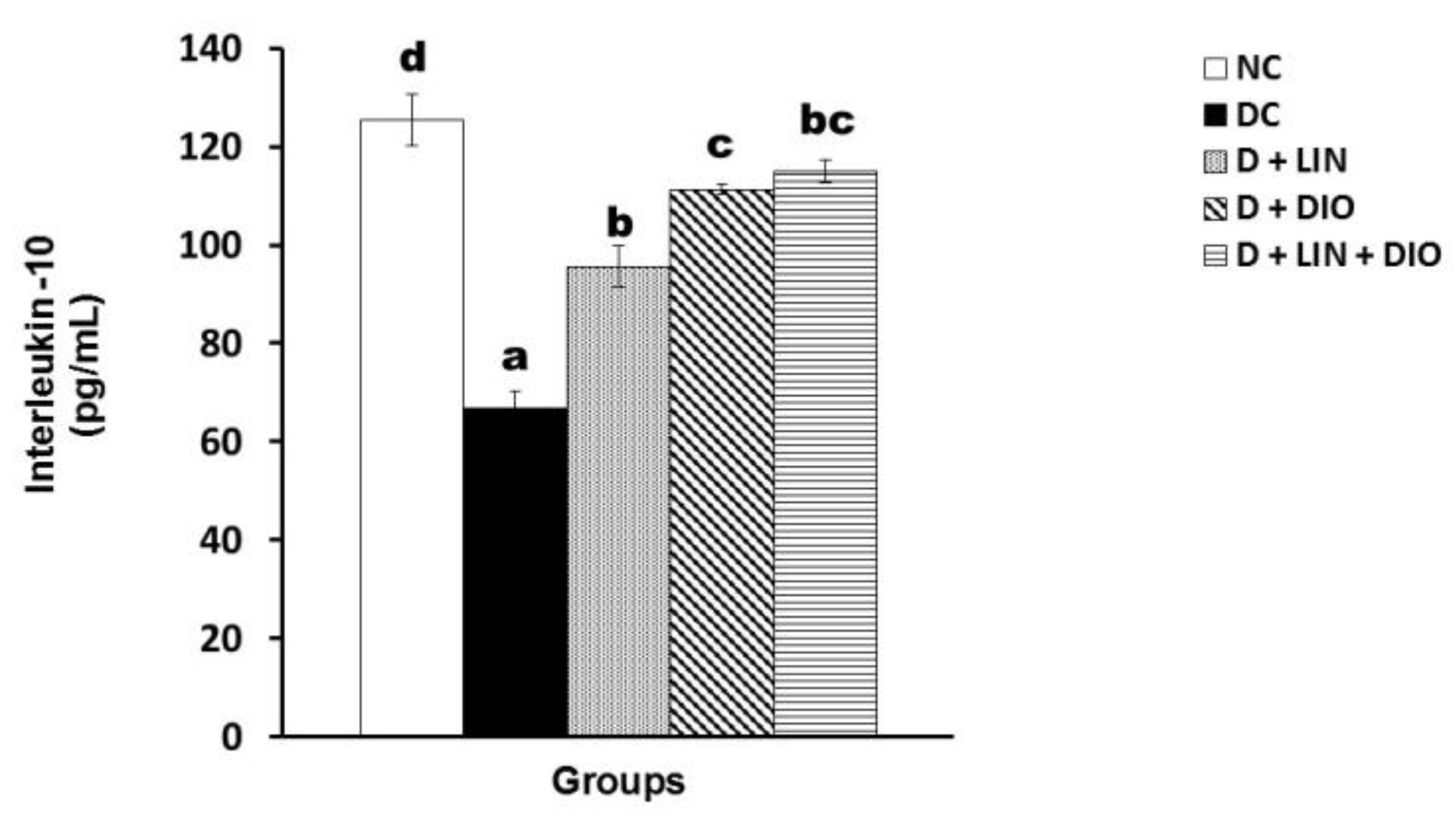
2.7. Effect on the Interleukin 10 (IL-10) Level
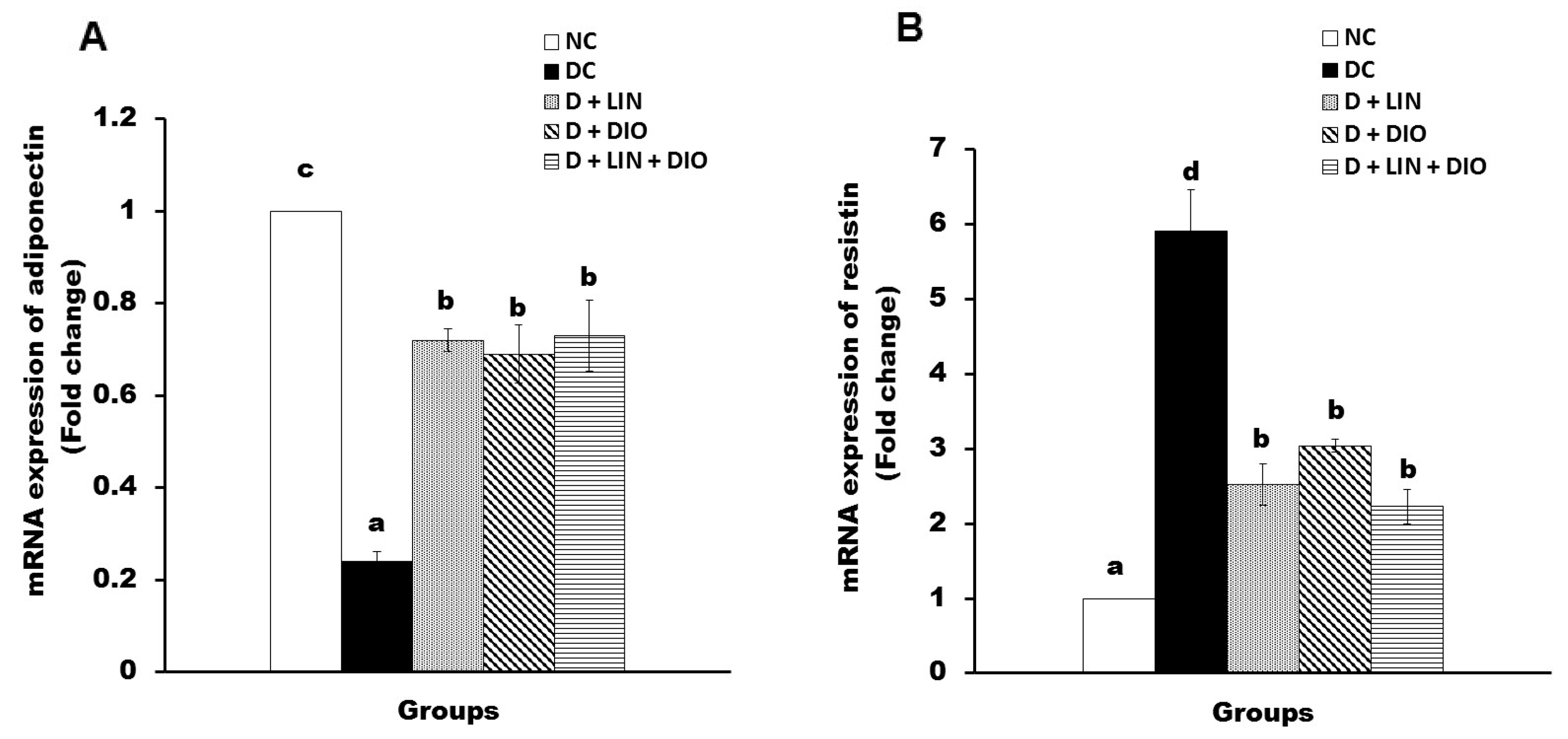
2.8. Effect on the mRNA Expression of Adiponectin and Resistin in Visceral Adipose Tissues
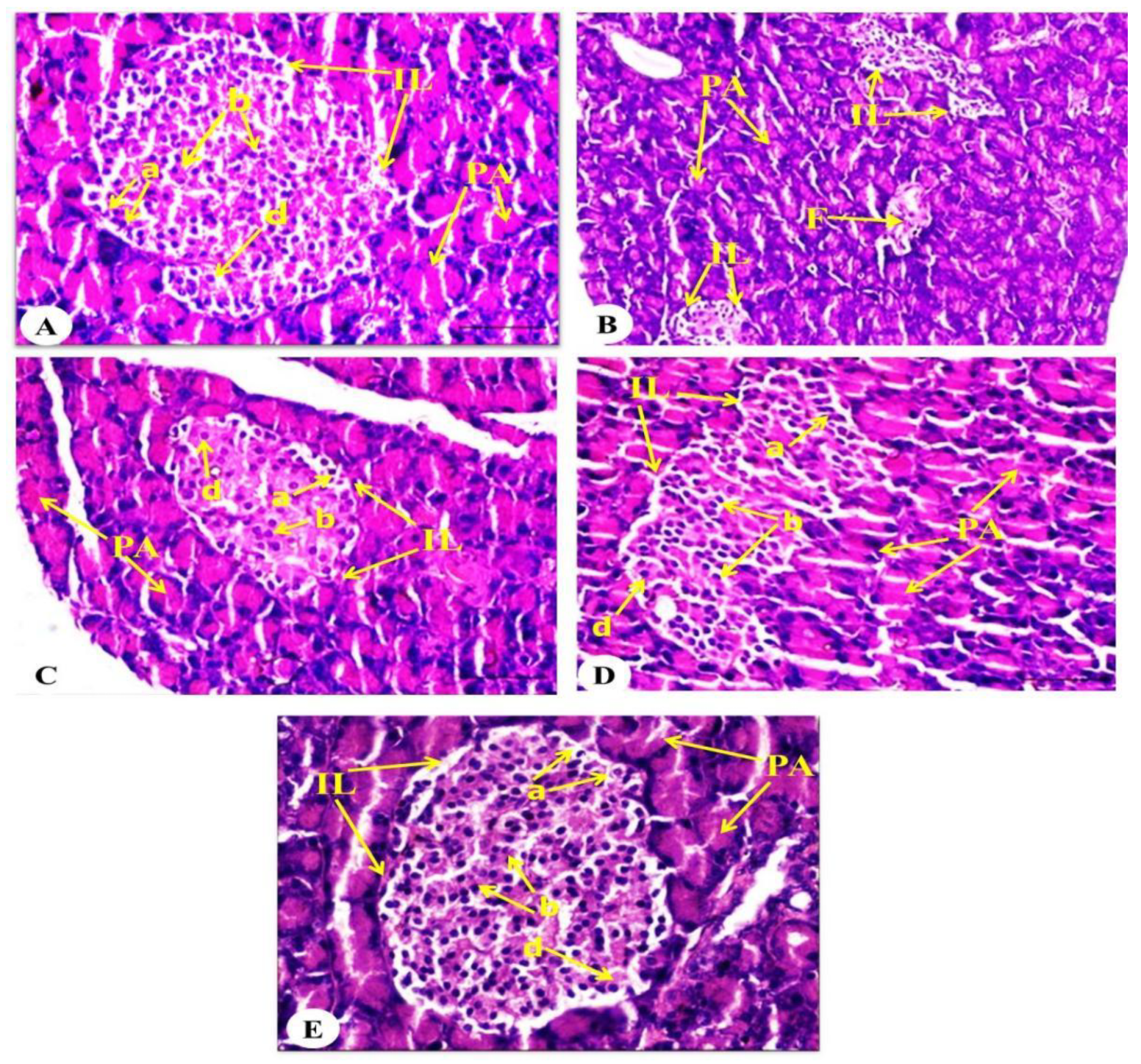
2.9. Effect on Pancreatic Histological Changes
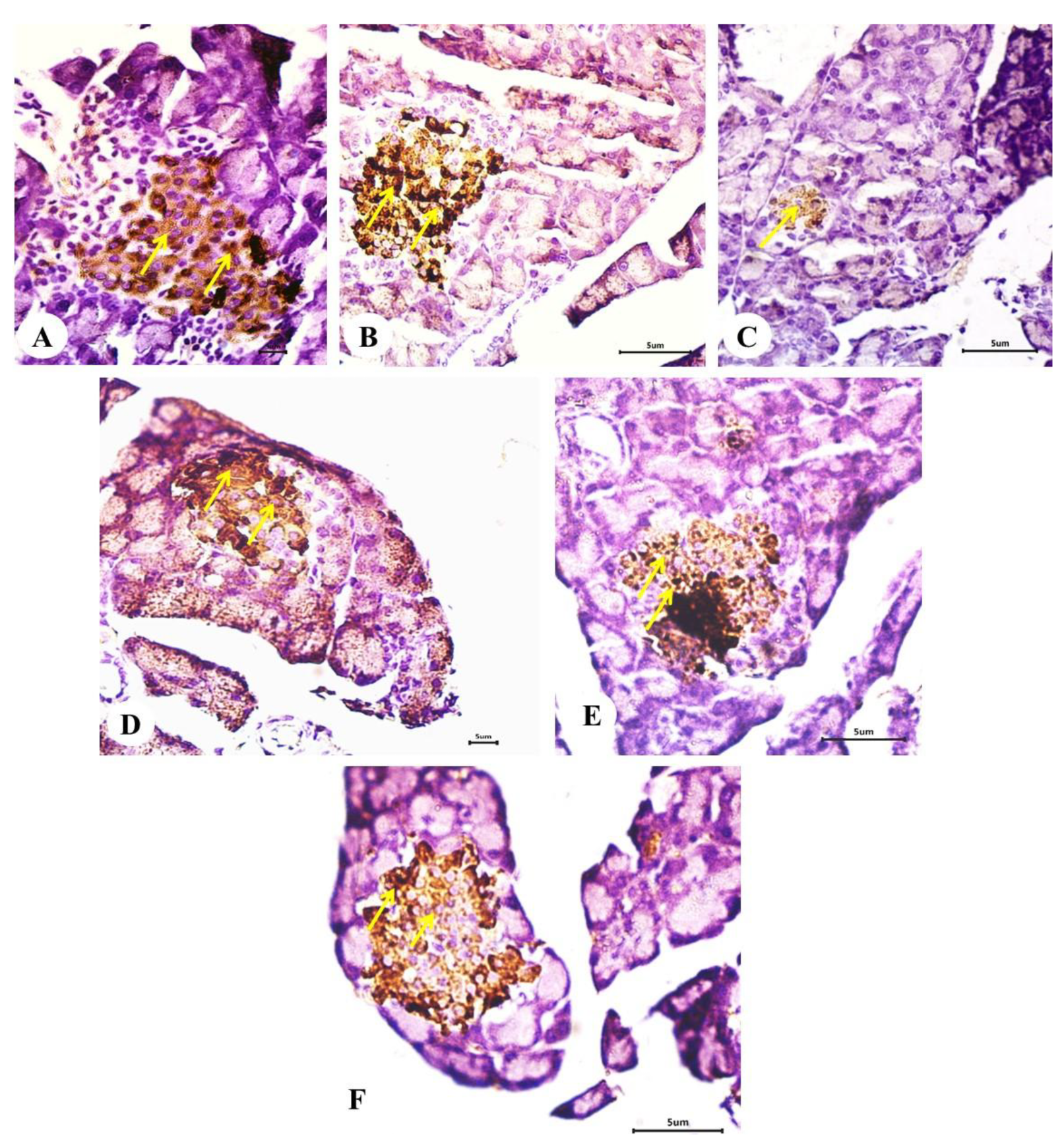
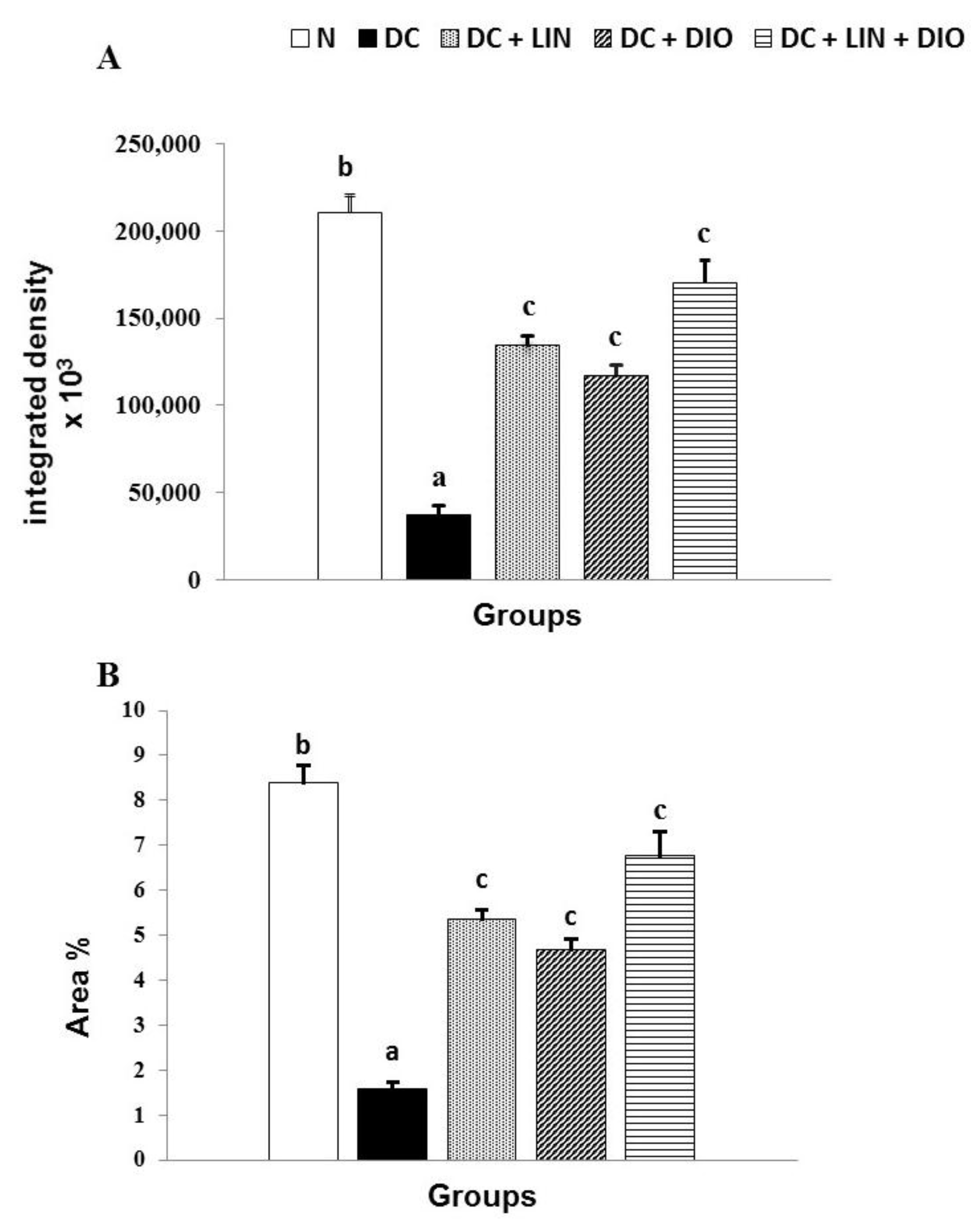
2.10. Effect on the Expression of Insulin in Pancreatic Islets (Immunohistochemical Investigations)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Experimental Animals
4.3. Induction of DM
4.4. Experimental Design and Blood and Tissue Sampling
- Normal control group (NC). These were healthy rats that were given an equivalent volume of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) (1% w/v) every other day for 28 days by oral gavage.
- Diabetic control group (DC). This group consisted of diabetic rats that were given the equivalent volume of CMC (1% w/v) by oral gavage every other day for 28 days.
- Diabetic group treated with linagliptin (D + LIN). This group consisted of diabetic rats, but they were treated with linagliptin at a dose of 1 mg/kg (dissolved in 1% CMC) every other day for 28 days by oral gavage [59].
- Diabetic group treated with diosmin (D + DIO). In this group, diabetic rats were treated with diosmin at a dose of 10 mg/kg (dissolved in 1% CMC) every other day for 28 days by oral gavage [60].
- Diabetic group treated with both linagliptin and diosmin (D + LIN + DIO). The rats in this group were diabetic rats that were treated with linagliptin at a dose of 1 mg/kg and diosmin at a dose of 10 mg/kg every other day for 28 days by oral gavage.
4.5. Blood Sampling and Tissue Sampling
4.6. Biochemical Analysis
4.7. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.8. Determination of Oxidative Stress and Anti-Oxidant Defense Parameters
4.9. Histological and Immunohistochemical Investigations
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- ADA Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S14–S31. [CrossRef]
- Jalili, R.B.; Moeen Rezakhanlou, A.; Hosseini-Tabatabaei, A.; Ao, Z.; Warnock, G.L.; Ghahary, A. Fibroblast populated collagen matrix promotes islet survival and reduces the number of islets required for diabetes reversal. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersmann, A.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Müller, U.A.; Landgraf, R.; Nauck, M.; Freckmann, G.; Heinemann, L.; Schleicher, E. Definition, Classification and Diagnosis. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2019, 127, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiello, P.; Broca, C.; Gross, R.; Roye, M.; Manteghetti, M.; Hillaire-Buys, D.; Novelli, M.; Ribes, G. Experimental NIDDM: Development of a new model in adult rats administered streptozotocin and nicotinamide. Diabetes 1998, 47, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolzán, A.D.; Bianchi, M.S. Genotoxicity of Streptozotocin. Mutat. Res. Mutat. Res. 2002, 512, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhuria, R.S.; Singh, G.; Kaur, A.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, T. Current status and patent prospective of animal models in diabetic research. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2015, 4, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Asrafuzzaman, M.; Cao, Y.; Afroz, R.; Kamato, D.; Gray, S.; Little, P.J. Animal models for assessing the impact of natural products on the aetiology and metabolic pathophysiology of Type 2 diabetes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemann, C.; Wagner, L.; Stephan, M.; von Hörsten, S. Cut to the chase: A review of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase-4’s (DPP4) entanglement in the immune system. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 185, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prato, S.; Barnett, A.H.; Huisman, H.; Neubacher, D.; Woerle, H.J.; Dugi, K.A. Effect of linagliptin monotherapy on glycaemic control and markers of β-cell function in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, T.; Graefe-Mody, E.U.; Hüttner, S.; Ring, S.; Trommeshauser, D.; Dugi, K.A. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability of multiple oral doses of linagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in male type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009, 11, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines on Safety Monitoring of Herbal Medicines in Pharmacovigilance Systems; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/43034/9241592214_eng.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2004).
- Campanero, M.A.; Escolar, M.; Garcia-Quetglas, E.P.; Sadaba, B.; Azanza, J.R. Simultaneous determination of diosmin and diosmetin in human plasma by ion trap liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogucka-Kockaa, A.; Wozniaka, M.; Feldob, M.; Kockic, J.; Szewczyk, K. Diosmin -isolation techniques, determination in plant material and pharmaceutical formulations, and clinical use. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanapongsathorn, W.; Vajrabukka, T. Clinical trial of oral diosmin (Daflon®) in the treatment of hemorrhoids. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 1992, 35, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouZid, S.F.; Ahmed, O.M.; Ahmed, R.R.; Mahmoud, A.; Abdella, E.; Ashour, M.B. Antihyperglycemic Effect of Crude Extracts of Some Egyptian Plants and Algae. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, H.M.; Awaad, A.S.; Abdel Rahman, F.E.Z.S.; Al-Dossari, M.; Abd El-Gawaad, N.S.; Ahmed, O.M. Combinatory Effect and Modes of Action of Chrysin and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Streptozotocin/Nicotinamide-Induced Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, O.M.; Saleh, A.S.; Ahmed, E.A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Ebrahim, H.A.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Abdel-Gabbar, M. Efficiency of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Hesperetin in the Treatment of Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetes in Wistar Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Gabbar, M.A.; Abdel-Twab, S.M.; Fahmy, E.M.; Ebaid, H.; Alhazza, I.M.; Ahmed, O.M. Antidiabetic Potency, Antioxidant Effects, and Mode of Actions of Citrus reticulata Fruit Peel Hydroethanolic Extract, Hesperidin, and Quercetin in Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin-Induced Wistar Diabetic Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1730492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Akhani, S.P.; Vishwakarma, S.L.; Goyal, R.K. Anti-diabetic activity of Zingiber officinale in streptozotocin-induced type I diabetic rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.; Abdel Moneim, A.; Yazid, I.; Mahmoud, A. Antihyperglycemic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects and the probable mechanisms of action of Ruta graveolens infusion and rutin in nicotinamide-streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetol. Croat. 2010, 39, 15–35. [Google Scholar]
- Schaalan, M.; El-Abhar, H.S.; Barakat, M.; El-Denshary, E.S. Westernized-like-diet-fed rats: Effect on glucose homeostasis, lipid profile, and adipocyte hormones and their modulation by rosiglitazone and glimepiride. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2009, 23, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.M.; Abo-Salem, O.M.; El Esawy, B.H.; El Askary, A. The Potential Protective Effects of Diosmin on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Cardiomyopathy in Rats. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 359, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeage, K. Linagliptin: An update of its use in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 2014, 74, 1927–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahren, J.; Ekberg, K.; Samnegård, B.; Johansson, B.L. C-peptide: A new potential in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2001, 1, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D.F. The Proinsulin C-peptide—A Multirole Model. J. Diabetes Res. 2004, 5, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, T.; Graefe-Mody, U.; Deacon, C.F.; Ring, A.; Holst, J.J.; Woerle, H.J.; Dugi, K.A.; Heise, T. Linagliptin increases incretin levels, lowers glucagon, and improves glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2012, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pari, L.; Srinivasan, S. Antihyperglycemic effect of diosmin on hepatic key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraki, A.; Oyama, J.; Shimizu, T.; Node, N. The DPP4 inhibitor linagliptin exacerbated heart failure due to energy deficiency via downregulation of glucose absorption and utilization in mice. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, ehac544-2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enes, P.; Panserat, S.; Kaushik, S.; Oliva-Teles, A. Nutritional regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in fish. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Ahmed, O.M.; Ashour, M.B.; Abdel-Moneim, A. In vivo and in vitro antidiabetic effects of citrus flavonoids; a study on the mechanism of action. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2015, 35, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Shi, W.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, L. Metabolism and pharmacological activities of the natural health-benefiting compound diosmin. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8472–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrivel Venkatasamy, V.; Pericherla, S.; Manthuruthil, S.; Mishra, S.; Hanno, R. Effect of Physical activity on Insulin Resistance, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 1764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Coskun, O.; Kanter, M.; Korkmaz, A.; Oter, S. Quercetin, a flavonoid antioxidant, prevents and protects streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress and β-cell damage in rat pancreas. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 51, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.M.; Whalin, M.K.; Harrison, D.G.; Taylor, W.R.; Griendling, K.K. Oxidative stress and diabetic vascular complications. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2004, 4, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoopkumar-Dukie, S.; Walker, R.B.; Daya, S. A sensitive and reliable method for the detection of lipid peroxidation in biological tissues. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 53, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Hussein, M.M.; Ahmed, O.M.; Al-Jameel, S.S.; Al-Muzafar, H.M.; Amin, K.A.; Abdou, H.M. Oleuropein ameliorates hyperlipidemia, oxidative stress, inflammatory and liver dysfunction biomarkers, in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 14, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, Y.A.; Mansour, D.F.; Nada, S.A.; Abd El-Rahman, S.S.; Abdelsalam, R.M.; Attia, A.S.; El-Tanbouly, D.M. Linagliptin attenuates thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in rats: Modulation of C/EBP-β and CX3CL1/Fractalkine, neuro-inflammation, oxidative stress and behavioral defects. Life Sci. 2022, 295, 120378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ağır, M.S.; Eraslan, G. The effect of diosmin against liver damage caused by cadmium in rats. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, T.; Alruwaili, M.N.; Alshahrani, S.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Jali, A.; Ahmed, R.A.; Alam, M.F.; Moni, S.S. Hepatoprotective potential of diosmin against hepatotoxic effect of isoniazid and rifampin in wistar rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2023, 42, 09603271221149199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Ni, H.; Wu, M.; Tang, Z.; Halim, M.; Shi, D. ROS-mediated glucose metabolic reprogram induces insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 476, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Y.; Liou, S.S.; Hong, T.Y.; Liu, I.M. The benefits of the citrus flavonoid diosmin on human retinal pigment epithelial cells under high-glucose conditions. Molecules 2017, 22, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacco, F.; Brownlee, M. Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Pari, L. Ameliorative effect of diosmin, a citrus flavonoid against streptozotocin-nicotinamide generated oxidative stress induced diabetic rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2012, 195, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Salama, S.A.; Omar, H.A.; Arafa, E.S.A.; Maghrabi, I.A. Diosmin Protects against Ethanol-Induced Gastric Injury in Rats: Novel Anti-Ulcer Actions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Husseny, M.W.A.; Mamdouh, M.; Shaban, S.; Ibrahim Abushouk, A.; Zaki, M.M.M.; Ahmed, O.M.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Adipokines: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Vascular Dysfunction in Type II Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 8095926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, H.A.; Kahn, C.R. New mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance: Make no bones about it. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3854–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, T.; Tanaka, A.; Yoshida, H.; Oyama, J.-I.; Toyoda, S.; Sakuma, M.; Inoue, T.; Otsuka, Y.; Node, K. Comparison of the effects of linagliptin and voglibose on endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease: A prospective, randomized, pilot study (EFFORT). Heart Vessels 2018, 33, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerges, S.H.; Wahdan, S.A.; Elsherbiny, D.A.; El-Demerdash, E. Diosmin ameliorates inflammation, insulin resistance, and fibrosis in an experimental model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 401, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, M.W.; Qi, Y.; Patel, H.R.; Takahashi, N.; Banerjee, R.; Pajvani, U.B.; Sinha, M.K.; Gingerich, R.L.; Scherer, P.E.; Ahima, R.S. Regulation of Resistin Expression and Circulating Levels in Obesity, Diabetes, and Fasting. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stofkova, A. Resistin and visfatin: Regulators of insulin sensitivity, inflammation and immunity. Endocr. Regul. 2010, 44, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.A. Resistin- and obesity-associated metabolic diseases. Horm. Metab. Res. 2007, 39, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, H.B.; Hu, X.; Tyler, K.X.; Dalal, C.K.; Lazar, M.A. Mechanisms regulating adipocyte expression of resistin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19754–19761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, O.M.; Ali, T.M.; Abdel Gaid, M.A.; Elberry, A.A. Effects of enalapril and paricalcitol treatment on diabetic nephropathy and renal expressions of TNF-α, p53, caspase-3 and Bcl-2 in STZ-induced diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmed, O.M.; Mosa, N.M.; Abou-Seif, H.S. Therapeutic role of Arabic gum against nicotinamide/streptozotocin-induced diabetes and nephropathy in Wistar rats. Egypt. Pharm. J. 2024, 23, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.J. The Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin Rodent Model of Type 2 Diabetes: Renal Pathophysiology and Redox Imbalance Features. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmed, O.M.; Abdel Fattah, A.A.; Abdul-Hamid, M.; Abdel-Aziz, A.M.; Sakr, H.I.; Damanhory, A.A.; Abdel-Kawi, S.H.; Ghaboura, N.; Awad, M.M.Y. Antidiabetic and liver histological and ultrastructural effects of Cynara scolymus leaf and flower head hydroethanolic extracts in nicotinamide/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2023, 2023, 4223026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, A.S.; Kandeil, M.; Abdel-Gabbar, M.; Fahmy, E.M.; Almehmadi, M.M.; Ali, T.M.; Ahmed, O.M. The Antidiabetic Effects and Modes of Action of the Balanites aegyptiaca Fruit and Seed Aqueous Extracts in NA/STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Mohamed, B.M.; Ibraheem, I.B.M.; Soliman, H.A.; Ahmed, O.M. Characterization of Ulva fasciata ethanolic extract-mediated biosynthesized silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their nephrocadiopreventive effects in doxorubicin-injected wistar rats. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2020, 8 (Suppl. S2), 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.B.; Vickers, S.B.; Cheetham, S.C.; Headland, K.R.; Mark, M.; Klein, T. Effect of linagliptin, alone and in combination with voglibose or exendin-4, on glucose control in male ZDF rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 729, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, K.; Abuelsaad, A.; Abdelaziz, M.; Sakr, H.; Abdel-Aziz, A.; Ahmed, O. The preventive effects of diosmin alone or combined with irinotecan on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon cancer in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 4003–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, G.M.; Ahmed, O.M.; Abbas, N.H.; El Fateh, M.M. Evaluation of the anti-diabetic effects of epicatechin and/or gallic acid in STZ/NA- induced diabetic Wister rats. Res. J. Appl. Biotechnol. 2018, 4, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifter, S.; Dayton, S.; Novic, B.; Muntwyler, E. The estimation of glycogen with the anthrone reagent. Arch. Biochem. 1950, 25, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kabir, S.M.H.; Begum, R. Toxicity of three organophosphorus insecticides to shinghi fish, Heteropneustes fossilis (Block). Dacca Univ. Stud. (Bangladesh) Part B 1978, 26, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans, W.; Hers, H.-G. The stimulation of liver phosphorylase b by AMP, fluoride and sulfate. A technical note on the specific determination of the a and b forms of liver glycogen phosphorylase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1975, 54, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, A.W.; Gao, Y.-T.; Chua, S.; Deng, J.; Stanczyk, F.Z. Insulin Resistance and Prostate Cancer Risk. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, A.B.M.; Ahmed, O.M.; Ali, L.A.; Semmler, M. Maternal rat diabetes mellitus deleteriously affects insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in the offspring. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 429154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Bong, H.Y.; Jeong, H.I.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, O. Postprandial hypoglycemic effect of mulberry leaf in Goto-Kakizaki rats and counterpart control Wistar rats. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2009, 3, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, C.J.; Crouch, S.R. Spectrophotometric and Kinetics Investigation of the Berthelot Reaction for the Determination of Ammonia. Anal. Chem. 1977, 49, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, H.; Böhmer, M.; Heierli, C. Serum creatinine determination without protein precipitation. Clin. Chim. Acta 1972, 37, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminos, J.E.; Nogueiras, R.; Gallego, R.; Bravo, S.; Tovar, S.; García-Caballero, T.; Casanueva, F.F.; Diéguez, C. Expression and Regulation of Adiponectin and Receptor in Human and Rat Placenta. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4276–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.R.; Davenport, B.; Clore, J.N.; Stevens, W. Lipid metabolism and resistin gene expression in insulin-resistant Fischer 344 rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, E626–E633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Marklund, S.; Marklund, G. Involvement of the Superoxide Anion Radical in the Autoxidation of Pyrogallol and a Convenient Assay for Superoxide Dismutase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1974, 47, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preuss, H.G.; Jarrell, S.T.; Scheckenbach, R.; Lieberman, S.; Anderson, R.A. Comparative Effects of Chromium, Vanadium and Gymnema Sylvestre on Sugar-Induced Blood Pressure Elevations in SHR. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1998, 17, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutler, E.; Duron, O.; Kelly, B.M. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1963, 61, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matkovics, B.; Kotorman, M.; Sz Varga, I.; Quy Hai, D.; Varga, C. Oxidative stress in experimental diabetes induced by streptozotocin. Acta Physiol. Hung. 1997, 85, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, O.M.; Abd El-Twab, S.M.; Al-Muzafar, H.M.; Adel Amin, K.; Abdel Aziz, S.M.; Abdel-Gabbar, M. Musa paradisiaca L. leaf and fruit peel hydroethanolic extracts improved the lipid profile, glycemic index and oxidative stress in nicotinamide/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Gamble, M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 6th Edition. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, H.; Moustafa, N.; Ahmed, R.R.; El-Shahawy, A.A.G.; Eldin, Z.E.; Al-Jameel, S.S.; Amin, K.A.; Ahmed, O.M.; Abdul-Hamid, M. Therapeutic effect of oral insulin-chitosan nanobeads pectin-dextrin shell on streptozotocin-diabetic male albino rats. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Time (Min) | 0 min | 60 min | 120 min | 180 min | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | |||||
| NC | 77.125 ± 5.21 a | 127.88 ± 19.75 a | 111.5 ± 5.68 a | 81.00 ± 7.89 a | |
| DC | 438.70± 36.21 c | 598 ± 46.47 d | 560 ± 80.67 d | 498.00 ± 49.83 c | |
| D + LIN | 242.25 ± 65.8 ab | 377.5 ± 88.18 bc | 287 ± 62.09 bc | 319.00 ± 76.40 b | |
| D + DIO | 366.75 ± 76.49 bc | 502.25 ± 65.54 cd | 405.25 ± 56.05 c | 418.67 ± 87.07 bc | |
| D + LIN + DIO | 141.25 ± 35.15 a | 255 ± 55.6 ab | 169.75 ± 56.83 ab | 161.25 ± 30.99 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, E.B.; El-Kalaawy, A.M.; Ahmed, N.A.; Shams, A.; Khaliefa, A.K.; Ahmed, O.M. Diosmin Potentiates the Antidiabetic Effects of Linagliptin in Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050656
Abbas EB, El-Kalaawy AM, Ahmed NA, Shams A, Khaliefa AK, Ahmed OM. Diosmin Potentiates the Antidiabetic Effects of Linagliptin in Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050656
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Eman B., Asmaa M. El-Kalaawy, Noha A. Ahmed, Anwar Shams, Amal K. Khaliefa, and Osama M. Ahmed. 2025. "Diosmin Potentiates the Antidiabetic Effects of Linagliptin in Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050656
APA StyleAbbas, E. B., El-Kalaawy, A. M., Ahmed, N. A., Shams, A., Khaliefa, A. K., & Ahmed, O. M. (2025). Diosmin Potentiates the Antidiabetic Effects of Linagliptin in Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050656






