Miraculin Can Contribute to a Reduction in Inflammatory Biomarkers and Cachexia in Malnourished Patients with Cancer and Taste Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
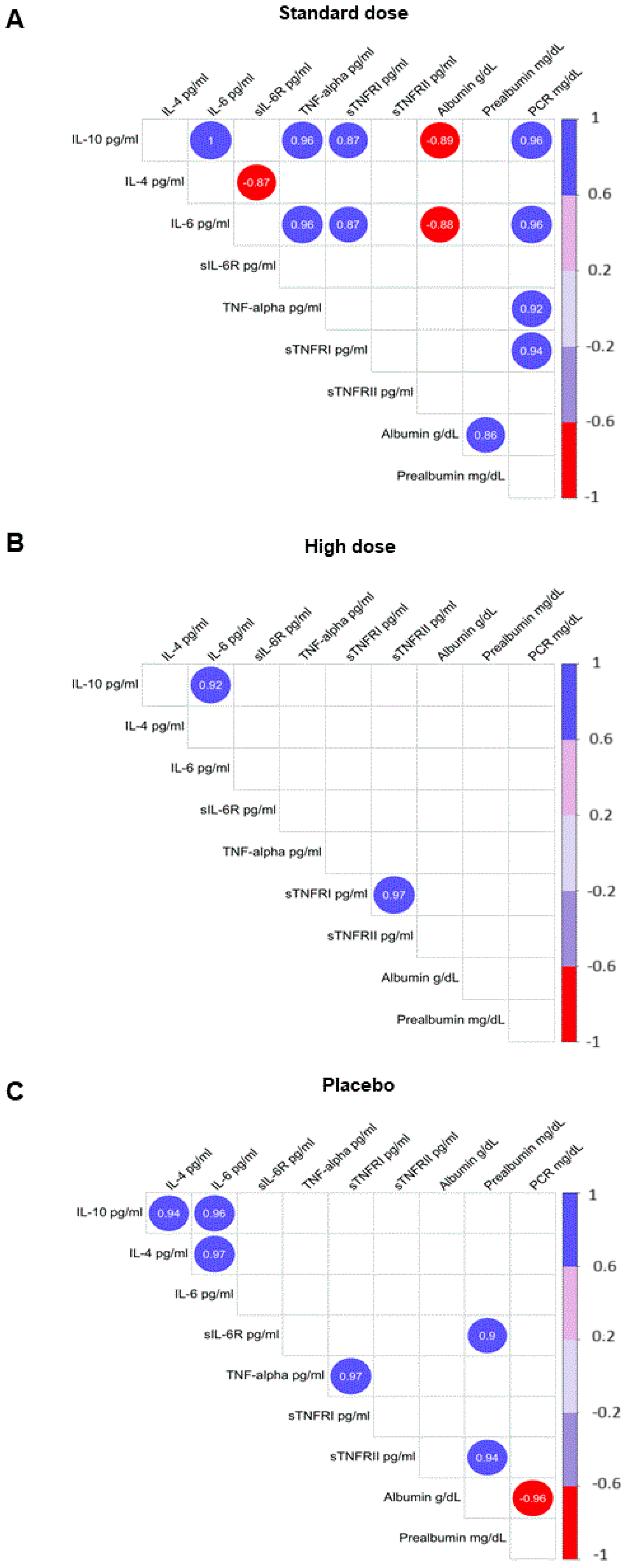
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Patients
4.2. Blood Samples
4.3. Determination of Plasma Cytokines, Tumor Cachexia Factors, and Biochemical Parameters
4.4. Taste Threshold
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization [Internet]. World Health Organization. Cited 21 May 2024. Available online: https://www.Who.Int/Health-Topics/Cancer#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Hovan, A.J.; Williams, P.M.; Stevenson-Moore, P.; Wahlin, Y.B.; Ohrn, K.E.O.; Elting, L.S.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Brennan, M.T.A. Systematic Review of Dysgeusia Induced by Cancer Therapies. Support. Care Cancer 2010, 18, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.L.; Dantas, J.B.d.L.; Melo, A.d.S.; Medrado, A.R.A.P.; Martins, G.B.; Lima, H.R.; Carrera, M. Dysgeusia in Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: Etiology, Diagnosis and Therapy. JORDI J. Oral Diagn. 2019, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.T.; Seniuk, N.A.; Richardson, P.M.; Gauldie, J.; Roder, J.C. Systemic Administration of Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Induces Cachexia in Rodents. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 2632–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Merlo, F.D.; Agnello, E.; Monge, T.; Devecchi, A.; Casalone, V.; Montemurro, F.; Ghigo, E.; Sapino, A.; Bo, S. Dysgeusia in Patients with Breast Cancer Treated with Chemotherapy—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghias, K.; Jiang, Y.; Gupta, A. The Impact of Treatment-Induced Dysgeusia on the Nutritional Status of Cancer Patients. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2023, 50, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Types of Cancer Treatment. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/radiation-therapy (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Geppert, J.; Rohm, M. Cancer Cachexia: Biomarkers and the Influence of Age. Mol. Oncol. 2024, 18, 2070–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, J.; von Haehling, S.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D.; Lainscak, M. Cachexia as a Major Public Health Problem: Frequent, Costly, and Deadly. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2013, 4, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, S.; Kir, S. The Role of Interleukin-6 Family Cytokines in Cancer Cachexia. FEBS J. 2024, 291, 4009–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matos-Neto, E.M.; Lima, J.D.C.C.; De Pereira, W.O.; Figuerêdo, R.G.; Riccardi, D.M.D.R.; Radloff, K.; Das Neves, R.X.; Camargo, R.G.; Maximiano, L.F.; Tokeshi, F.; et al. Systemic Inflammation in Cachexia—Is Tumor Cytokine Expression Profile the Culprit? Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Huang, X.; Huang, X.; Ju, D.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Ye, L. Research Progress of Interleukin-15 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1184703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, G.; Gotlieb, W.H. Interleukine-10 in Ovarian Cancer. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Zhao, K.; Jose, I.; Hoogenraad, N.J.; Osellame, L.D. Biomarkers for Cancer Cachexia: A Mini Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argilés, J.M. Cancer-Associated Malnutrition. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2005, 9, S39–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Plaza, B.; Álvarez-Mercado, A.I.; Arcos-Castellanos, L.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Brandimonte-Hernández, M.; Feliú-Batlle, J.; Hummel, T.; Gil, Á.; Palma-Milla, S. Efficacy and Safety of Habitual Consumption of a Food Supplement Containing Miraculin in Malnourished Cancer Patients: The CLINMIR Pilot Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, G.A.; Dodd, S.; Williamson, P.R. Design and Analysis of Pilot Studies: Recommendations for Good Practice. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2004, 10, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sánchez, H.; Guzmán-Facundo, F.R.; Herrera-Medina, D.; Sidani, S. Importancia Del Estudio Piloto En Un Proyecto de Intervención. Index Enferm. Digit. 2020, 32, e12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, P.; Parker, C.J.; Prchal, J.T. How Do Red Blood Cells Die? Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 655393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, K.C.H. The Mechanisms and Treatment of Weight Loss in Cancer. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1992, 51, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.D.; Fearon, K.C.H.; Tisdale, M.J.; McMillan, D.C.; Ross, J.A. Effect of a Fish Oil-Enriched Nutritional Supplement on Metabolic Mediators in Patients With Pancreatic Cancer Cachexia. Nutr. Cancer 2001, 40, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, K.C.H.; Glass, D.J.; Guttridge, D.C. Cancer Cachexia: Mediators, Signaling, and Metabolic Pathways. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, A.; Tsuchiya, A.; Nakajima, K.; Ito, K.; Terada, T.; Shimizu-Ibuka, A.; Briand, L.; Asakura, T.; Misaka, T.; Abe, K. Human Sweet Taste Receptor Mediates Acid-Induced Sweetness of Miraculin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16819–16824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, K.; Beidler, L.M. Mechanism of the Action of Taste-Modifying Protein. Nature 1969, 222, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Worp, W.R.P.H.; Schols, A.M.W.J.; Theys, J.; van Helvoort, A.; Langen, R.C.J. Nutritional Interventions in Cancer Cachexia: Evidence and Perspectives From Experimental Models. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 601329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.; Campos, M.M. Protective Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Cancer-Related Complications. Nutrients 2019, 11, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallima, H.; Ridi, R.E. Arachidonic Acid: Physiological Roles and Potential Health Benefits—A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 11, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppe, A.E.F.; Edelmann, M.J. Roles of Eicosanoids in Regulating Inflammation and Neutrophil Migration as an Innate Host Response to Bacterial Infections. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e0009521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacosa, A.; Rondanelli, M. Fish Oil and Treatment of Cancer Cachexia. Genes Nutr. 2008, 3, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onesti, J.K.; Guttridge, D.C. Inflammation-Based Regulation of Cancer Cachexia. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 168407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.-J.; Lee, C.-W. Soluble Receptors in Cancer: Mechanisms, Clinical Significance, and Therapeutic Strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.A.; Horiuchi, S.; Topley, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Fuller, G.M. The Soluble Interleukin 6 Receptor: Mechanisms of Production and Implications in Disease. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Ruiz, A.; Tilz, G.P.; Zangerle, R.; Baier-Bitterlich, G.; Wachter, H.; Fuchs, D. Soluble Receptors for Tumour Necrosis Factor in Clinical Laboratory Diagnosis. Eur. J. Haematol. 1995, 54, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartikasari, A.E.R.; Cassar, E.; Razqan, M.A.M.; Szydzik, C.; Huertas, C.S.; Mitchell, A.; Plebanski, M. Elevation of Circulating TNF Receptor 2 in Cancer: A Systematic Meta-Analysis for Its Potential as a Diagnostic Cancer Biomarker. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 918254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlini, V.; Noonan, D.M.; Abdalalem, E.; Goletti, D.; Sansone, C.; Calabrone, L.; Albini, A. The Multifaceted Nature of IL-10: Regulation, Role in Immunological Homeostasis and Its Relevance to Cancer, COVID-19 and Post-COVID Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1161067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, T.; Koido, Y.; Aiboshi, J.; Yamashita, T.; Suzaki, S.; Kurokawa, A. The Ratio of Interleukin-6 to Interleukin-10 Correlates with Severity in Patients with Chest and Abdominal Trauma. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1999, 17, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulhaq, Z.S.; Soraya, G.V.; Hasan, Y.T.N.; Rachma, L.N.; Rachmawati, E.; Shodry, S.; Kusuma, M.A.S. Serum IL-6/IL-10 Ratio as a Biomarker for the Diagnosis and Severity Assessment of Primary-Open Angle Glaucoma. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 32, 2259–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Tang, C.; Li, X.; Feng, F. IL-6/IL-10 mRNA Expression Ratio in Tumor Tissues Predicts Prognosis in Gastric Cancer Patients without Distant Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Ma, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, R.; Zhao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Gao, G.; Liu, F.; et al. Profiling Serum Cytokines in COVID-19 Patients Reveals IL-6 and IL-10 Are Disease Severity Predictors. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, C.L.; Ventrucci, G.; Field, W.N.; Tisdale, M.J.; Gomes-Marcondes, M.C.C. Metabolic and Morphological Alterations Induced by Proteolysis-Inducing Factor from Walker Tumour-Bearing Rats in C2C12myotubes. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Li, F.; Qin, Z. TNF Receptor 2 Makes Tumor Necrosis Factor a Friend of Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocellin, M.C.; Camargo, C.Q.; Nunes, E.A.; Fiates, G.M.R.; Trindade, E.B.S.M. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Effects on Inflammatory Markers in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Dai, X.-Y.; Zhan, Z.-C.; Hao, Y.-K.; Tan, J.-L.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Hou, Y.; Xuan, W.-S.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.-Q.; et al. Triterpenoids from the Leaves of Synsepalum Dulcificum and Their Antitumor Activities against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 193, 116155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, K.B.; Hadi, S.A.; Sekaran, M.; Pichika, M.R. The Clinical Effects of Synsepalum dulcificum: A Review. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Plaza, B.; Gil, Á.; Menéndez-Rey, A.; Bensadon-Naeder, L.; Hummel, T.; Feliú-Batlle, J.; Palma-Milla, S. Effect of Regular Consumption of a Miraculin-Based Food Supplement on Taste Perception and Nutritional Status in Malnourished Cancer Patients: A Triple-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial-CLINMIR Pilot Protocol. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Brandimonte-Hernández, M.; López-Plaza, B.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Álvarez-Mercado, A.I.; Arcos-Castellanos, L.; Feliú-Batlle, J.; Hummel, T.; Palma-Milla, S.; Gil, A. Effect of a Novel Food Rich in Miraculin on the Intestinal Microbiome of Malnourished Patients with Cancer and Dysgeusia. Nutrients 2025, 17, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argilés, J.M.; López-Soriano, F.J.; Stemmler, B.; Busquets, S. Cancer-Associated Cachexia—Understanding the Tumour Macroenvironment and Microenvironment to Improve Management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argilés, J.M.; Busquets, S.; Stemmler, B.; López-Soriano, F.J. Cancer Cachexia: Understanding the Molecular Basis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, M.C.S.; Pimentel, G.D.; Costa, F.O.; Carvalheira, J.B.C. Molecular and Neuroendocrine Mechanisms of Cancer Cachexia. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 226, R29–R43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisdale, M.J. Are Tumoral Factors Responsible for Host Tissue Wasting in Cancer Cachexia? Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Migueles, J.; Esteban-Cornejo, I.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Pastor-Villaescusa, B.; Molina-García, P.; Rodriguez-Ayllon, M.; Rico, M.; Gil, A.; Aguilera, C.; et al. Sedentarism, Physical Activity, Steps, and Neurotrophic Factors in Obese Children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 2325–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walliczek-Dworschak, U.; Schöps, F.; Feron, G.; Brignot, H.; Hähner, A.; Hummel, T. Differences in the Density of Fungiform Papillae and Composition of Saliva in Patients With Taste Disorders Compared to Healthy Controls. Chem. Senses 2017, 42, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Graves, B.; Rosseel, Y.; Merkle, E.C. Computation and Application of Generalized Linear Mixed Model Derivatives Using Lme4. Psychometrika 2022, 87, 1173–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.S. Package Corrplot. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 2 June 2024).

| Variables | Standard-Dose DMB n = 10 | High-Dose DMB n = 11 | Placebo n = 10 | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 3 Months | Baseline | 3 Months | Baseline | 3 Months | Time (T) | Treatment (t) | T × t | |
| Cytokines (pg/mL) | |||||||||
| IL-6 | 4.7 ± 1.5 | 3.9 ± 2.1 | 5.0 ± 1.1 | 3.3 ± 1.4 | 5.9 ± 3.9 | 3.8 ± 2.0 | 0.142 | 0.896 | 0.900 |
| IL-1β | 5.6 ± 1.6 | 4.7 ± 0.8 | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 4.1 ± 1.3 | 4.5 ± 0.7 | 3.4 ± 0.3 * | 0.093 | 0.838 | 0.493 |
| TNF-α | 16.5 ± 2.2 | 16.4 ± 4.0 | 14.2 ± 2.5 | 9.3 ± 1.3 | 14.1 ± 1.6 | 12.6 ± 1.9 | 0.316 | 0.220 | 0.648 |
| INF-γ | 31.4 ± 8.9 | 25.3 ± 7.2 * | 18.1 ± 2.1 | 18.8 ± 4.7 | 20.0 ± 4.3 | 18.5 ± 3.5 | 0.229 | 0.530 | 0.206 |
| IL-15 | 11.7 ± 4.0 | 24.9 ± 13.5 | 42.1 ± 19.6 | 17.8 ± 7.4 | 10.4 ± 3.8 | 9.4 ± 1.1 | 0.555 | 0.233 | 0.347 |
| IL-4 | 36.9 ± 11.3 | 27.3 ± 4.9 | 38.2 ± 13.4 | 37.3 ± 19.7 | 71.1 ± 40.9 | 48.5 ± 24.6 | 0.042 | 0.499 | 0.379 |
| IL-10 | 9.3 ± 1.9 | 28.1 ± 18.8 | 12.8 ± 3.7 | 15.9 ± 6.6 | 17.1 ± 13.4 | 13.1 ± 6.6 | 0.386 | 0.826 | 0.454 |
| CNTF | 358.8 ± 122.7 | 300.0 ± 109.0 | 332.9 ± 115.5 | 413.3 ± 186.6 | 339.9 ± 169.6 | 378.3 ± 134.0 | 0.756 | 0.966 | 0.911 |
| Soluble receptors (μg/mL) | |||||||||
| sIL-6R | 11.0 ± 2.6 | 10.2 ± 1.7 | 9.7 ± 1.4 | 9.3 ± 2.7 | 8.6 ± 1.6 | 8.2 ± 2.0 | 0.624 | 0.530 | 0.979 |
| sTNFR-I | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.2 * | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.080 | 0.827 | 0.508 |
| sTNFR-II | 7.5 ± 1.9 | 4.6 ± 0.7 * | 6.8 ± 1.5 | 4.8 ± 1.1 | 5.1 ± 0.9 | 5.8 ± 1.6 | 0.011 | 0.615 | 0.279 |
| Tumor-derived factors (μg/mL) | |||||||||
| PIF | 14.8 ± 2.3 | 11.7 ± 2.3 * | 15.2 ± 2.3 | 10.6 ± 1.6 | 10.5 ± 0.3 | 10.0 ± 1.1 | 0.021 | 0.464 | 0.323 |
| Bead Panels or Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay | Analyte | Assay CV |
|---|---|---|
| HSTCMAG-28SK-06 (EMD Millipore Corporation, St. Louis, MO, USA) | TNF-α | 12.64 |
| IL-6 | 19.31 | |
| IL-1β | 7.86 | |
| IFN-γ | 7.14 | |
| IL-4 | 16.89 | |
| IL-10 | 8.87 | |
| HCYTA-60K (EMD Millipore Corporation, St. Louis, MO, USA) | IL-15 | 9.35 |
| HSCRMAG-32K-03 (EMD Millipore Corporation, St. Louis, MO, USA) | sIL-6R | 8.83 |
| sTNFR-I | 3.76 | |
| sTNFR-II | 5.65 | |
| CSB-E04527h (Cusabio, Wuhan, China) | CNTF | 5.97 |
| CSB-E13626h (Cusabio, Wuhan, China) | PIF | 8.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Álvarez-Mercado, A.I.; López-Plaza, B.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Arcos-Castellanos, L.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Brandimonte-Hernández, M.; Feliú-Batlle, J.; Hummel, T.; Palma-Milla, S.; Gil, Á. Miraculin Can Contribute to a Reduction in Inflammatory Biomarkers and Cachexia in Malnourished Patients with Cancer and Taste Disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050622
Álvarez-Mercado AI, López-Plaza B, Plaza-Diaz J, Arcos-Castellanos L, Ruiz-Ojeda FJ, Brandimonte-Hernández M, Feliú-Batlle J, Hummel T, Palma-Milla S, Gil Á. Miraculin Can Contribute to a Reduction in Inflammatory Biomarkers and Cachexia in Malnourished Patients with Cancer and Taste Disorders. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(5):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050622
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁlvarez-Mercado, Ana Isabel, Bricia López-Plaza, Julio Plaza-Diaz, Lucía Arcos-Castellanos, Francisco Javier Ruiz-Ojeda, Marco Brandimonte-Hernández, Jaime Feliú-Batlle, Thomas Hummel, Samara Palma-Milla, and Ángel Gil. 2025. "Miraculin Can Contribute to a Reduction in Inflammatory Biomarkers and Cachexia in Malnourished Patients with Cancer and Taste Disorders" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 5: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050622
APA StyleÁlvarez-Mercado, A. I., López-Plaza, B., Plaza-Diaz, J., Arcos-Castellanos, L., Ruiz-Ojeda, F. J., Brandimonte-Hernández, M., Feliú-Batlle, J., Hummel, T., Palma-Milla, S., & Gil, Á. (2025). Miraculin Can Contribute to a Reduction in Inflammatory Biomarkers and Cachexia in Malnourished Patients with Cancer and Taste Disorders. Pharmaceuticals, 18(5), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18050622










