Treatment with Manganese Porphyrin, MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+, Suppressed the Activation of Macrophages in a Mouse Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
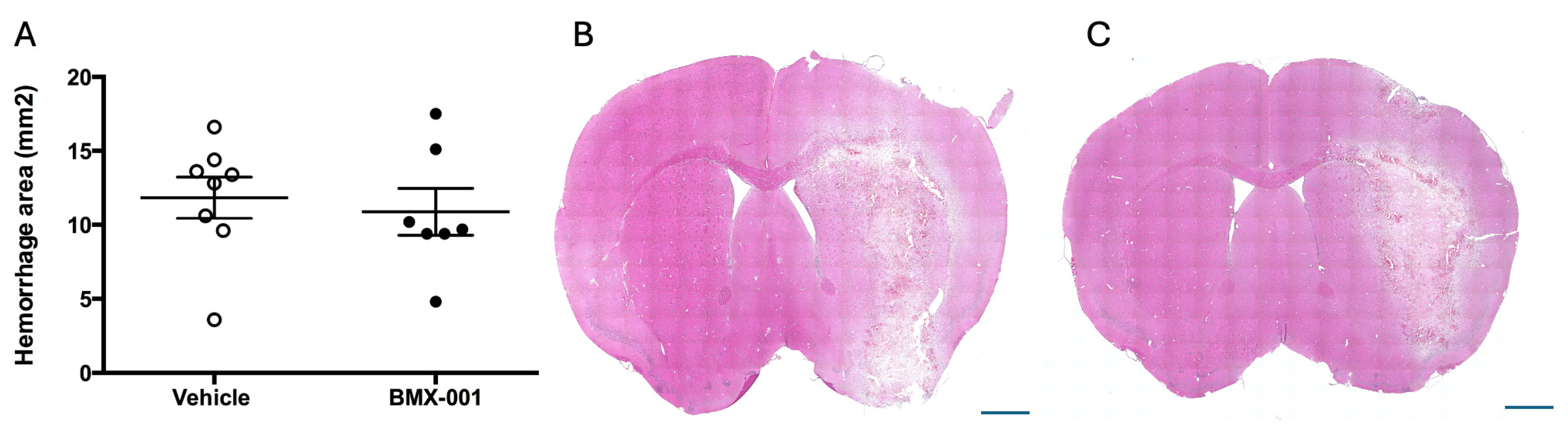
2.1. BMX-001 Does Not Worsen the Clinical Outcome in a Mouse Intracerebral Hemorrhage
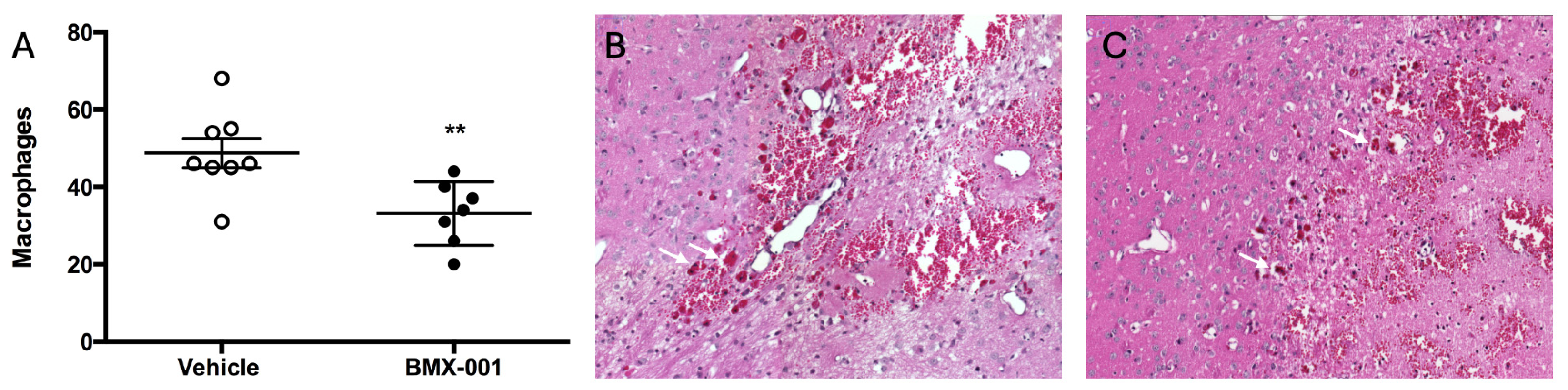
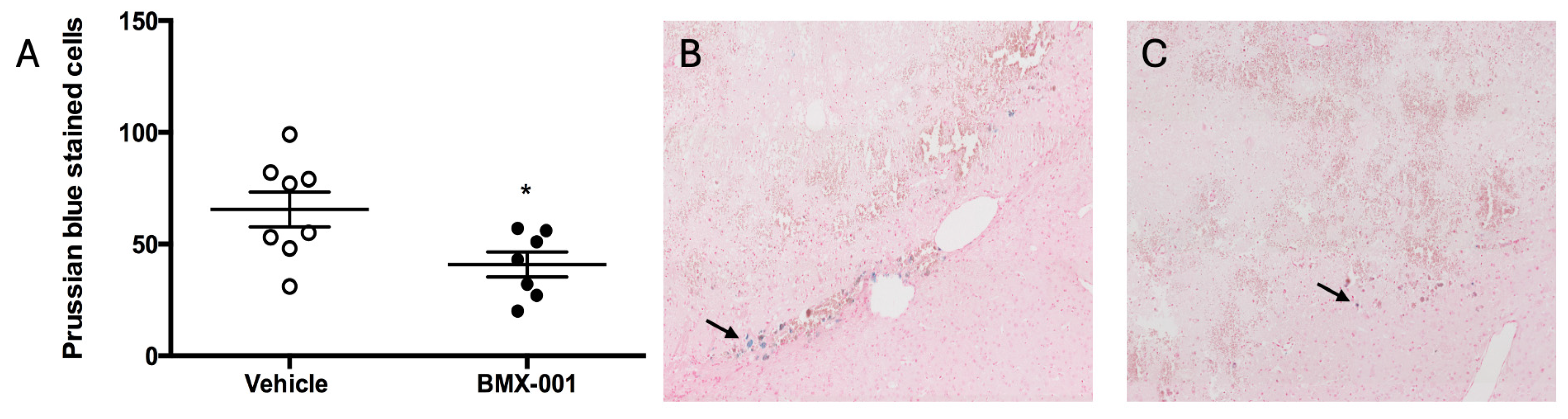
2.2. BMX-001 Treatment Reduces Level of Macrophages in Mouse Intracerebral Hemorrhage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Model and Housing
4.2. Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) Model and Drug Treatment
4.3. Neurological Functional Assessment
4.4. Histological Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICH | Intracerebral hemorrhage |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| tPA | Tissue plasminogen activator |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| Mn | Manganese |
| BMX-001 | MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+, Mn(III) meso-tetrakis(N-(2′-n-butoxyethyl)pyridinium-2-yl)por-phyrin |
| BMX-010 | MnTE-2-PyP5+, Mn (III) meso-tetrakis (N-ethylpyridinium-2-yl)porphyrin |
| AELO10150 | MnTDE-2-ImP5+, Mn(III)meso-tetrakis(N,N′-diethylimidazolium-2-yl)porphyrin |
References
- Ramphul, K.; Ramphul, Y.; Sombans, S.; Lohana, P.; Verma, R.; Kumar, N.; Joynauth, J. Incidence and mortality rates of acute ischemic stroke in hospitalized patients in the United States. Arch. Med. Sci. Atheroscler. Dis. 2021, 6, e132–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, Y.; Han, L. Projected Global Trends in Ischemic Stroke Incidence, Deaths and Disability-Adjusted Life Years From 2020 to 2030. Stroke 2023, 54, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, Y.Z.; Chandra, P.; Singh, R.; Hakeem, I.; Al Sirhan, S.; Kotob, M.; Akhtar, N.; Kamran, S.; Al Jerdi, S.; Muhammad, A.; et al. Incidence, clinical features, and outcomes of posterior circulation ischemic stroke: Insights from a large multiethnic stroke database. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1302298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Lim, M.; Nguyen, D.; Bowe, S.; MacKay, M.T.; Stojanovski, B.; Moodie, M. The incidence of pediatric ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Stroke 2023, 18, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, M.; Iosa, M.; Abbruzzese, L.; Matano, A.; Coccia, M.; Baudo, S.; Benedetti, A.; Gambarelli, C.; Spaccavento, S.; Ambiveri, G.; et al. The impact of cognitive function deficits and their recovery on functional outcome in subjects affected by ischemic subacute stroke: Results from the Italian multicenter longitudinal study CogniReMo. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2023, 59, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, D.; Wrona, P.; Homa, T.; Jakobschy, K.; Wrona, G.; Sawczyńska, K.; Giełczyński, M.; Popiela, T.; Słowik, A.; Turaj, W. Sex Alters the Effect of Perfusion Deficits on Functional Outcome in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Mechanical Thrombectomy. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2024, 54, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlemm, E.; Cheng, B.; Thomalla, G.; Kessner, S.S. Functional Lesion Network Mapping of Sensory Deficits After Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2023, 54, 2918–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.M.; Wissman, S.; Albers, G.W.; Jhamandas, J.H.; Madden, K.P.; Hamilton, S. Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (Alteplase) for ischemic stroke 3 to 5 h after symptom onset. The ATLANTIS Study: A randomized controlled trial. Alteplase Thrombolysis for Acute Noninterventional Therapy in Ischemic Stroke. JAMA 1999, 282, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Bluhmki, E.; Brozman, M.; Dávalos, A.; Guidetti, D.; Larrue, V.; Lees, K.R.; Medeghri, Z.; Machnig, T.; et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 h after acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.S.; Robinson, T.; Lindley, R.I.; Arima, H.; Lavados, P.M.; Lee, T.-H.; Broderick, J.P.; Chen, X.; Chen, G.; Sharma, V.K.; et al. Low-Dose versus Standard-Dose Intravenous Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Robinson, T.G.; Lee, T.H.; Li, Q.; Arima, H.; Bath, P.M.; Billot, L.; Broderick, J.; Demchuk, A.M.; Donnan, G.; et al. Low-Dose vs Standard-Dose Alteplase for Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: Secondary Analysis of the ENCHANTED Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Li, S.; Dai, H.; Lu, G.; Wang, W.; Che, F.; Geng, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, X.; Li, H.; et al. Tenecteplase vs Alteplase for Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: The ORIGINAL Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Jin, A.; Pan, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Tenecteplase Versus Alteplase in Treating Acute Ischemic Stroke With Diabetes and Admission Hyperglycemia. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e036393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.-B.; Chien, C.; Chang, F.-C.; Lin, C.-J.; Lee, I.-H.; Hsu, L.-C.; Chung, C.-P.; Liu, H.-Y.; Chi, N.-F.; How, C.-K.; et al. Better endovascular mechanical thrombectomy outcome in atrial fibrillation patients with acute ischemic stroke: A single-center experience. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Su, R.; Feng, X.; Mao, A.; Nguyen, T.N.; Cai, L.; Li, Q.; Guo, Q.; Yang, Q.; Sang, H.; et al. Long-term outcome of endovascular thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2025, 272, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullberg, T.; von Euler, M.; Wassélius, J.; Wester, P.; Arnberg, F. Survival and functional outcome following endovascular thrombectomy for anterior circulation acute ischemic stroke caused by large vessel occlusion in Sweden 2017–2019-a nationwide, prospective, observational study. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2023, 29, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Gerschenfeld, G.; Liegey, J.-S.; Laborne, F.-X.; Yger, M.; Lyon, V.; Checkouri, T.; Tricard-Dessagne, B.; Marnat, G.; Clarençon, F.; Chausson, N.; et al. Treatment times, functional outcome, and hemorrhage rates after switching to tenecteplase for stroke thrombolysis: Insights from the TETRIS registry. Eur. Stroke J. 2022, 7, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, K.; Zhu, W.; Ye, L.; Li, Y. Effect of mechanical thrombectomy with and without intravenous thrombolysis on the functional outcome of patients with different degrees of thrombus perviousness. Neuroradiology 2023, 65, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackensen, G.B.; Patel, M.; Sheng, H.; Calvi, C.L.; Batinić-Haberle, I.; Day, B.J.; Liang, L.P.; Fridovich, I.; Crapo, J.D.; Pearlstein, R.D.; et al. Neuroprotection from delayed postischemic administration of a metalloporphyrin catalytic antioxidant. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 4582–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Yang, W.; Fukuda, S.; Tse, H.M.; Paschen, W.; Johnson, K.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Crapo, J.D.; Pearlstein, R.D.; Piganelli, J.; et al. Long-term neuroprotection from a potent redox-modulating metalloporphyrin in the rat. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sheng, H.; Spasojevic, I.; Tse, H.M.; Jung, J.Y.; Hong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Piganelli, J.D.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Warner, D.S. Neuroprotective efficacy from a lipophilic redox-modulating Mn(III) N-Hexylpyridylporphyrin, MnTnHex-2-PyP: Rodent models of ischemic stroke and subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batinic-Haberle, I.; Tovmasyan, A.; Spasojevic, I. Mn Porphyrin-Based Redox-Active Drugs: Differential Effects as Cancer Therapeutics and Protectors of Normal Tissue Against Oxidative Injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1691–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, W.; Du, L.; Chu, D.; Wang, P.; Yang, Z.; Qu, X.; Yang, Z.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Spasojevic, I.; et al. Intracarotid Infusion of Redox-Active Manganese Porphyrin, MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+, following Reperfusion Improves Long-Term, 28-Day Post-Stroke Outcomes in Rats. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, N.; Pandey, A.S.; Griauzde, J.; Gemmete, J.J.; Chenevert, T.L.; Keep, R.F.; Xi, G. Brain tissue iron quantification by MRI in intracerebral hemorrhage: Current translational evidence and pitfalls. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 39, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Hua, Y.; Keep, R.F.; Chaudhary, N.; Xi, G. Minocycline Effects on Intracerebral Hemorrhage-Induced Iron Overload in Aged Rats: Brain Iron Quantification With Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Stroke 2018, 49, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Hua, Y.; Keep, R.F.; Novakovic, N.; Fei, Z.; Xi, G. Minocycline attenuates brain injury and iron overload after intracerebral hemorrhage in aged female rats. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 126, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.Y.; Bai, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.Q.; Song, Y.X.; Qiang, R.R.; Zhang, N.; Zou, J.L.; Yang, Y.L.; et al. A new strategy for the treatment of intracerebral hemorrhage: Ferroptosis. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 382, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Jiang, N.; Wang, Y.; Song, G.; Li, P.; Fang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, W.; Xie, M. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor (TPPU) alleviates ferroptosis by regulating CCL5 after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 172, 116301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yan, D.; Nan, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhuo, Y.; Huo, H.; Jin, Q.; Yan, H.; Zhao, Z. Salvianolic acid A inhibits ferroptosis and protects against intracerebral hemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Qiu, L.; Cheng, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, C.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; et al. Alleviating Recombinant Tissue Plasminogen Activator-induced Hemorrhagic Transformation in Ischemic Stroke via Targeted Delivery of a Ferroptosis Inhibitor. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2309517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Carroll, D.W.; You, Y.; Chaiswing, L.; Wen, R.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Bondada, S.; Liang, Y.; St Clair, D.K. A novel redox regulator, MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+, enhances normal hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell function. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiswing, L.; Yarana, C.; Clair, W.S.; Tovmasyan, A.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Spasojevic, I.; Clair, D.S. A Redox-active Mn Porphyrin, MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+, Synergizes with Carboplatin in Treatment of Chemoresistant Ovarian Cell Line. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 9664636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangerle, A.; Kiechl, S.; Spiegel, M.; Furtner, M.; Knoflach, M.; Werner, P.; Mair, A.; Wille, G.; Schmidauer, C.; Gautsch, K.; et al. Recanalization after thrombolysis in stroke patients: Predictors and prognostic implications. Neurology 2007, 68, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Solomon, N.; Mac Grory, B.; Alhanti, B.; Saver, J.L.; Smith, E.E.; Xian, Y.; Bhatt, D.L.; Schwamm, L.H.; Uchino, K.; et al. Trends in Stroke Thrombolysis Care Metrics and Outcomes by Race and Ethnicity, 2003-2021. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2352927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Matsumaru, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Morimoto, M.; Kanazawa, R.; Takayama, Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Shigeta, K.; Okubo, S.; Hayakawa, M.; et al. Effect of Mechanical Thrombectomy Without vs With Intravenous Thrombolysis on Functional Outcome Among Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: The SKIP Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luff, M.K.; Khezri, N.; Miralbes, S.; Naravetla, B.; Spiotta, A.M.; Loehr, C.; Martínez-Galdámez, M.; A McTaggart, R.; Defreyne, L.; Vega, P.; et al. Hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke: Hemorrhagic subtypes and symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2025; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, R.H.; A Kent, T. Superoxide anion production during reperfusion is reduced by an antineutrophil antibody after prolonged cerebral ischemia. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Enghild, J.J.; Bowler, R.; Patel, M.; Batinić-Haberle, I.; Calvi, C.L.; Day, B.J.; Pearlstein, R.D.; Crapo, J.D.; Warner, D.S. Effects of metalloporphyrin catalytic antioxidants in experimental brain ischemia. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, J.; Homma, T.; Osaki, T. Superoxide Radicals in the Execution of Cell Death. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, M.; Wan, Y.; Hua, Y.; Keep, R.F.; Xi, G. Formation of Multinucleated Giant Cells after Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Characteristics and Role of Complement C3. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, M.; Jing, C.; Keep, R.F.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G. Multinucleated Giant Cells in Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, A.; Imai, T.; Jin, X.; Locascio, J.J.; Boisserand, L.; Herman, A.L.; Lamb, J.; Nagarkatti, K.; Diniz, M.A.; Kumskova, M.; et al. Biological and Procedural Predictors of Outcome in the Stroke Preclinical Assessment Network (SPAN) Trial. Circ. Res. 2024, 135, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, B.; Wang, H.; Jeong, S.; Hsieh, J.T.; Majeed, M.; Dawson, H.; Sheng, H.; Warner, D.S.; James, M.L. Progesterone Improves Neurobehavioral Outcome in Models of Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neuroendocrinology 2015, 103, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoo, N.; Sheng, H.; Mixco, J.; Homi, H.M.; Pearlstein, R.D.; Warner, D.S. Intraischemic nitrous oxide alters neither neurologic nor histologic outcome: A comparison with dizocilpine. Anesth. Analg. 2004, 99, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Cao, J.; Spasojevic, I.; Treggiari, M.; Sheng, H. Treatment with Manganese Porphyrin, MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+, Suppressed the Activation of Macrophages in a Mouse Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040547
Zhang S, Cao J, Spasojevic I, Treggiari M, Sheng H. Treatment with Manganese Porphyrin, MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+, Suppressed the Activation of Macrophages in a Mouse Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(4):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040547
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shasha, Jie Cao, Ivan Spasojevic, Miriam Treggiari, and Huaxin Sheng. 2025. "Treatment with Manganese Porphyrin, MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+, Suppressed the Activation of Macrophages in a Mouse Intracerebral Hemorrhage" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 4: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040547
APA StyleZhang, S., Cao, J., Spasojevic, I., Treggiari, M., & Sheng, H. (2025). Treatment with Manganese Porphyrin, MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+, Suppressed the Activation of Macrophages in a Mouse Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Pharmaceuticals, 18(4), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18040547







