Cytokine and Metabolomic Signatures of Mepolizumab Response Across Upper and Lower Airway Compartments in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: An Exploratory Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Impact of Mepolizumab on Functional, Inflammatory, and Patient-Reported Outcomes
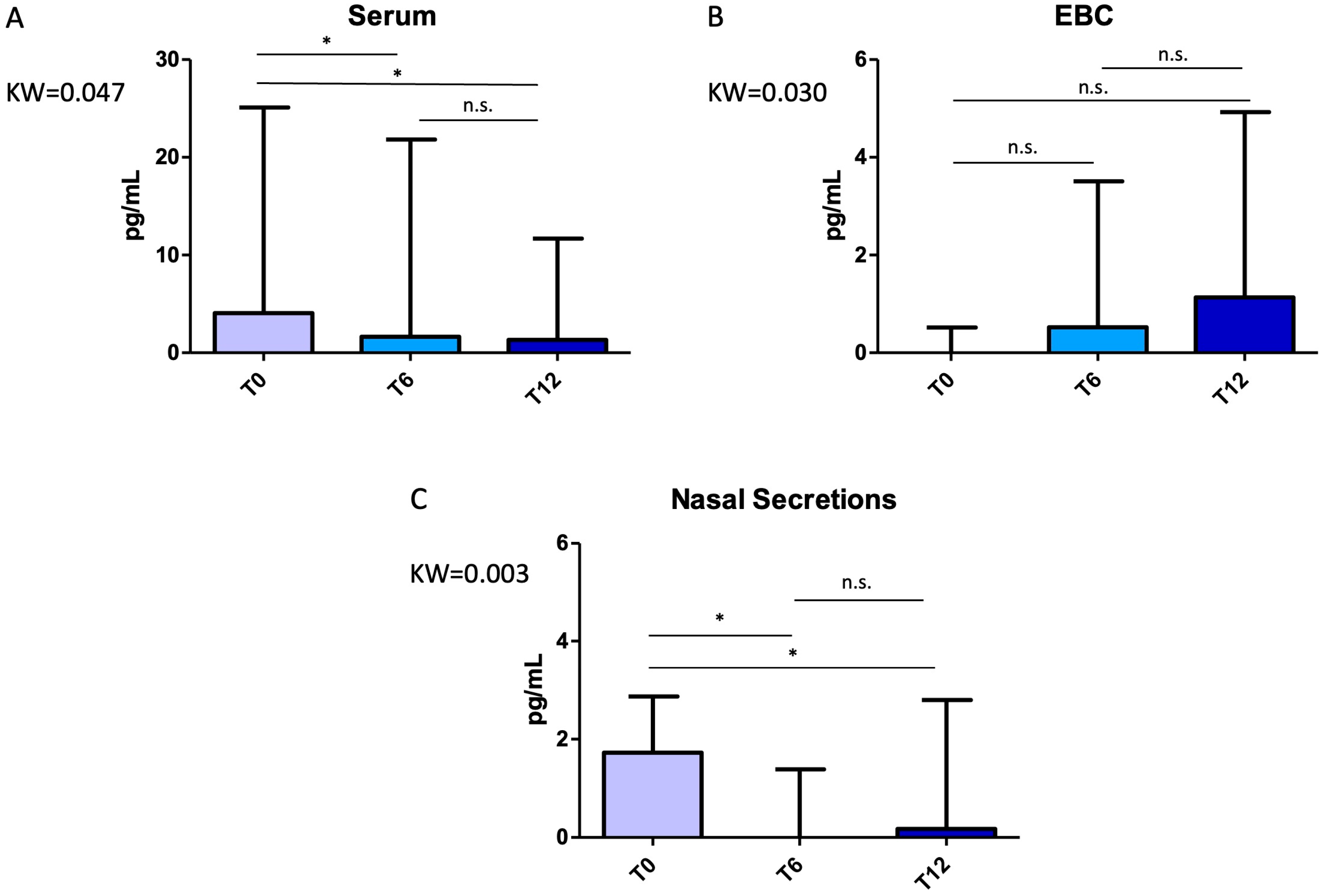
2.2. Impact of Mepolizumab on Cytokine Expression Across Biological Compartments
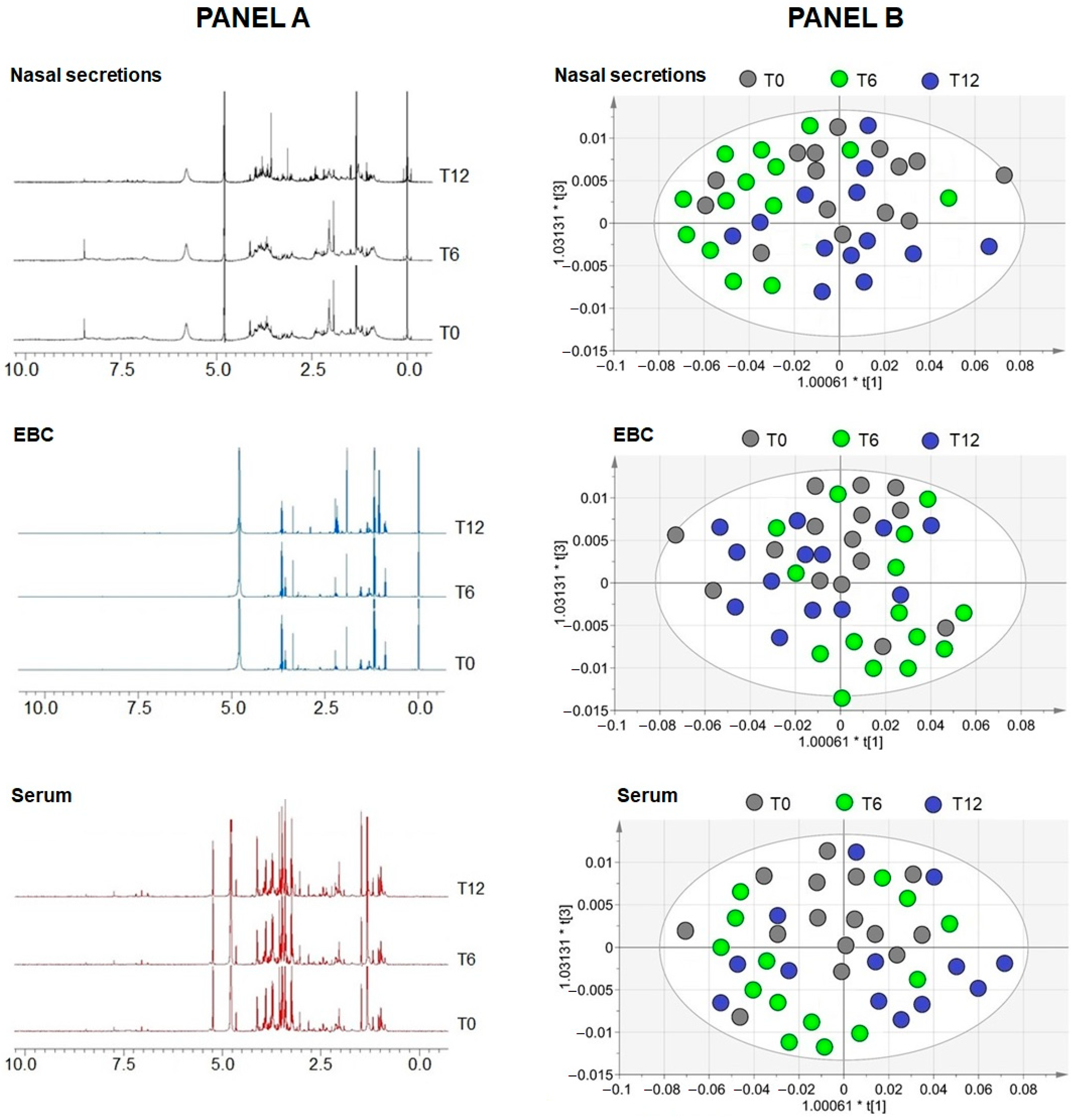
2.3. Metabolomics
2.4. Correlations
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Population
4.2. Ethics, Registration, and Reporting Standards
4.3. Study Protocol
4.4. Measurements
4.5. Sample Collection
4.6. NMR Sample Preparation and Acquisition
4.7. Statistical Analysis
4.8. Multivariate Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2025 GINA Main Report. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/2025-gina-strategy-report/ (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- McDonald, V.M.; Gibson, P.G. Exacerbations of severe asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Have, L.; Meulmeester, F.L.; de Jong, K.; Ten Brinke, A. Patient-centred outcomes in severe asthma: Fatigue, sleep, physical activity and work. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2025, 34, 240122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, M.D.; Yelin, E.H.; Katz, P.P.; Lactao, G.; Iribarren, C.; Blanc, P.D. Risk factors for work disability in severe adult asthma. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampogna, E.; Oliva, F.M.; Del Furia, M.J.; Cordani, C.; Lazzarini, S.G.; Arienti, C. Effectiveness of Rehabilitation Interventions in Adults With Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2025, 104, e28–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salandi, J.; Hayden, M.C.; Heinrichs, K.; Limbach, M.; Schultz, K.; Schwarzl, G.; Neumeister, W.; Loerbroks, A. Can an educational intervention in the context of inpatient pulmonary rehabilitation improve asthma self-management at work? A study protocol of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosch, I.; Schneeberger, T.; Holtdirk, A.; Gloeckl, R.; Kroll, D.; Buhl, R.; Hamelmann, E.; Idzko, M.; Taube, C.; Milger, K.; et al. Which people with severe asthma attend pulmonary rehabilitation? Insights from the German Asthma Net. ERJ Open Res. 2025, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gephine, S.; Fry, S.; Margoline, E.; Gicquello, A.; Chenivesse, C.; Grosbois, J.M. Home-based pulmonary rehabilitation for adults with severe asthma exposed to psychosocial chronic stressors. Respir. Med. 2023, 217, 107349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.J.; Wechsler, M.E.; Brusselle, G.; Buhl, R. Targeting the IL-5 pathway in eosinophilic asthma: A comparison of anti-IL-5 versus anti-IL-5 receptor agents. Allergy 2024, 79, 2943–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, K.M.; Shaw, D.; Chupp, G.; Lehtimaki, L.; Heffler, E.; Finney-Hayward, T.; Zangrilli, J.; Kwiatek, J.; Siddiqui, S.; Roufosse, F.; et al. Interleukin-5 as a pleiotropic cytokine orchestrating airway type 2 inflammation: Effects on and beyond eosinophils. Allergy 2024, 79, 2662–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleman, F.; Lim, H.F.; Nair, P. Eosinophilic Endotype of Asthma. Immunol. Allergy Clin. 2016, 36, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddighe, D.; Mathias, C.B.; Freyschmidt, E.J.; Kombe, D.; Caplan, B.; Marseglia, G.L.; Oettgen, H.C. Basophils are rapidly mobilized following initial aeroallergen encounter in naive mice and provide a priming source of IL-4 in adaptive immune responses. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2014, 28, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salter, B.M.; Aw, M.; Sehmi, R. The role of type 2 innate lymphoid cells in eosinophilic asthma. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusack, R.P.; Whetstone, C.E.; Xie, Y.; Ranjbar, M.; Gauvreau, G.M. Regulation of Eosinophilia in Asthma-New Therapeutic Approaches for Asthma Treatment. Cells 2021, 10, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaia, C.; Vatrella, A.; Busceti, M.T.; Gallelli, L.; Terracciano, R.; Savino, R.; Pelaia, G. Severe eosinophilic asthma: From the pathogenic role of interleukin-5 to the therapeutic action of mepolizumab. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnasco, D.; Nicola, S.; Testino, E.; Brussino, L.; Pini, L.; Caminati, M.; Piccardo, F.; Canevari, R.F.; Melissari, L.; Ioppi, A.; et al. Long-Term Efficacy of Mepolizumab at 3 Years in Patients with Severe Asthma: Comparison with Clinical Trials and Super Responders. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnasco, D.; Bondi, B.; Caminati, M.; Nicola, S.; Pini, L.; Milanese, M.; Brussino, L.; Senna, G.; Canonica, G.W.; Braido, F. Evaluation of Clinical Remission in Best-Performing Severe Asthmatic Patients Treated for Three Years with Mepolizumab. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, D.; Maniscalco, M.; Motta, A. Nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics in respiratory medicine. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1801107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, M.; Motta, A. Metabolomics of exhaled breath condensate: A means for phenotyping respiratory diseases? Biomark. Med. 2017, 11, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, M.; Fuschillo, S.; Paris, D.; Cutignano, A.; Sanduzzi, A.; Motta, A. Clinical metabolomics of exhaled breath condensate in chronic respiratory diseases. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2019, 88, 121–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Laurentiis, G.; Paris, D.; Melck, D.; Maniscalco, M.; Marsico, S.; Corso, G.; Motta, A.; Sofia, M. Metabonomic analysis of exhaled breath condensate in adults by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, M.; Paris, D.; Melck, D.J.; Molino, A.; Carone, M.; Ruggeri, P.; Caramori, G.; Motta, A. Differential diagnosis between newly diagnosed asthma and COPD using exhaled breath condensate metabolomics: A pilot study. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1701825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, A.; Paris, D.; Melck, D.; de Laurentiis, G.; Maniscalco, M.; Sofia, M.; Montuschi, P. Nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics of exhaled breath condensate: Methodological aspects. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 39, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Liu, S.; Mao, S.; Ling, Y.; Liu, D.; He, X.; Wang, X. Metabonomic profiling of serum and urine by (1)H NMR-based spectroscopy discriminates patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and healthy individuals. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuschi, P.; Paris, D.; Melck, D.; Lucidi, V.; Ciabattoni, G.; Raia, V.; Calabrese, C.; Bush, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Motta, A. NMR spectroscopy metabolomic profiling of exhaled breath condensate in patients with stable and unstable cystic fibrosis. Thorax 2012, 67, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristan, A.I.; Jimenez-Luna, C.; Abreu, A.C.; Arrabal-Campos, F.M.; Salmeron, A.D.M.; Rodriguez, F.I.; Maresca, M.A.R.; Garcia, A.B.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J.; et al. Metabolomic profiling of COVID-19 using serum and urine samples in intensive care and medical ward cohorts. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos, C.; Papadopoulou, E.; Potonos, D.; Exarchos, K.; Beris, E.; Aggelopoulou, C.; Tryfon, S.; Gogali, A.; Kostikas, K. Effectiveness of anti-IL-5/5Ralpha biologics in severe asthma in real-world studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. ERJ Open Res. 2025, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavord, I.D.; Korn, S.; Howarth, P.; Bleecker, E.R.; Buhl, R.; Keene, O.N.; Ortega, H.; Chanez, P. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): A multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, H.G.; Liu, M.C.; Pavord, I.D.; Brusselle, G.G.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Chetta, A.; Humbert, M.; Katz, L.E.; Keene, O.N.; Yancey, S.W.; et al. Mepolizumab treatment in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chupp, G.L.; Bradford, E.S.; Albers, F.C.; Bratton, D.J.; Wang-Jairaj, J.; Nelsen, L.M.; Trevor, J.L.; Magnan, A.; Ten Brinke, A. Efficacy of mepolizumab add-on therapy on health-related quality of life and markers of asthma control in severe eosinophilic asthma (MUSCA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilette, C.; Canonica, G.W.; Chaudhuri, R.; Chupp, G.; Lee, F.E.; Lee, J.K.; Almonacid, C.; Welte, T.; Alfonso-Cristancho, R.; Jakes, R.W.; et al. REALITI-A Study: Real-World Oral Corticosteroid-Sparing Effect of Mepolizumab in Severe Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 2646–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, P.; Marcuccio, G.; Raffio, G.; Formisano, R.; Candia, C.; Manzo, F.; Guerra, G.; Lubrano, E.; Mancusi, C.; Maniscalco, M. Endotyping Chronic Respiratory Diseases: T2 Inflammation in the United Airways Model. Life 2024, 14, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Woo, S.D.; Lee, Y.; Kim, C.K.; Shin, Y.S.; Ye, Y.M.; Park, H.S. Changes in Type 2 Biomarkers After Anti-IL5 Treatment in Patients With Severe Eosinophilic Asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2021, 13, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, M.; Candia, C.; Visca, D.; D’Amato, M.; Calabrese, C.; Ambrosino, P.; Molino, A.; Fuschillo, S. Revealing the gap: Fractional exhaled nitric oxide and clinical responsiveness to biological therapy in severe asthma—A retrospective study. ERJ Open Res. 2024, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scelo, G.; Tran, T.N.; Le, T.T.; Fageras, M.; Dorscheid, D.; Busby, J.; Al-Ahmad, M.; Al-Lehebi, R.; Altraja, A.; Beastall, A.; et al. Exploring Definitions and Predictors of Response to Biologics for Severe Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2024, 12, 2347–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosz, K.; Batko, J.; Blazejewska, M.; Gawor, A.; Sleziak, J.; Gomulka, K. Insight into IL-5 as a Potential Target for the Treatment of Allergic Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.E.; Gautam, S.; Chupp, G.L. Does Eosinophil Heterogeneity Translate into Functional Diversity? A Review of the Evolving Paradigm of Eosinophil Heterogeneity in Asthma. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacionyte, J.; Januskevicius, A.; Vasyle, E.; Rimkunas, A.; Miliauskas, S.; Malakauskas, K. Clinical Remission Criteria and Serum Levels of Type 2 Inflammation Mediators during 24 Weeks of Treatment with the Anti-IL-5 Drug Mepolizumab in Patients with T2-High Severe Asthma. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, M.; Koenderman, L. Immunological and hematological effects of IL-5(Ralpha)-targeted therapy: An overview. Allergy 2018, 73, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.L.; Villanueva, J.M.; Buckmeier, B.K.; Yamada, Y.; Filipovich, A.H.; Assa’ad, A.H.; Rothenberg, M.E. Anti-IL-5 (mepolizumab) therapy reduces eosinophil activation ex vivo and increases IL-5 and IL-5 receptor levels. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1473–1483.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, C.; Berti, A.; Cottini, M. The emerging roles of eosinophils: Implications for the targeted treatment of eosinophilic-associated inflammatory conditions. Curr. Res. Immunol. 2022, 3, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Dong, J. Baseline type 2 biomarker levels and clinical remission predictors in children with asthma. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1492644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.N.; Boca, S.M.; Shu, X.O.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Matthews, C.E.; Hsing, A.W.; Tan, Y.T.; Ji, B.T.; Chow, W.H.; Cai, Q.; et al. Metabolomics in epidemiology: Sources of variability in metabolite measurements and implications. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2013, 22, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.H.; Roy, R.; McKay, R.T.; Ryan, D.; Brennan, L.; Tenori, L.; Luchinat, C.; Gao, X.; Zeri, A.C.; Gowda, G.A.; et al. Recommendations and Standardization of Biomarker Quantification Using NMR-Based Metabolomics with Particular Focus on Urinary Analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.A.; Sorkness, C.A.; Kosinski, M.; Schatz, M.; Li, J.T.; Marcus, P.; Murray, J.J.; Pendergraft, T.B. Development of the asthma control test: A survey for assessing asthma control. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juniper, E.F.; Bousquet, J.; Abetz, L.; Bateman, E.D.; Committee, G. Identifying ‘well-controlled’ and ‘not well-controlled’ asthma using the Asthma Control Questionnaire. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanger, J.; Clausen, J.L.; Coates, A.; Pedersen, O.F.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; et al. Standardisation of the measurement of lung volumes. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molino, A.; Fuschillo, S.; Mosella, M.; Accardo, M.; Guida, P.; Motta, A.; Maniscalco, M. Comparison of three different exhaled nitric oxide analyzers in chronic respiratory disorders. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, M.; Faraone, S.; Sofia, M.; Molino, A.; Vatrella, A.; Zedda, A. Extended analysis of exhaled and nasal nitric oxide for the evaluation of chronic cough. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, D.; Candia, C.; Molino, A.; D’Amato, M.; Motta, A.; Maniscalco, M. Benralizumab Affects Specific Compartments in Severe Asthma Patients With Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyposis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | T0 (n = 15) | T6 (n = 14) | T12 (n = 13) | T0 vs. T6 | T0 vs. T12 | T6 vs. T12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 53.0 ± 11.9 | - | - | - | - | - |
| AAO, years | 34.0 ± 19.8 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Males, n (%) | 4 (26.7) | - | - | - | - | - |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26.5 ± 6.6 | - | - | - | - | - |
| No. Exac. | 2.0 (2.0–3.0) | 0 (0–1.0) | 0 (0–1.0) | 0.001 | 0.003 | >0.999 |
| FEV1 (L) | 2.02 ± 0.68 | 2.29 ± 0.90 | 2.25 ± 0.80 | 0.032 | 0.043 | >0.999 |
| FEV1 (%) | 71.9 ± 19.3 | 78.4 ± 21.4 | 81.3 ± 18.2 | 0.128 | 0.056 | >0.999 |
| FeNO (ppb) | 69.0 (25.0–111.0) | 44.5 (25.8–94.8) | 31.0 (15.0–60.0) | >0.999 | 0.096 | 0.199 |
| ACT | 18.7 ± 4.7 | 23.0 ± 2.8 | 23.4 ± 3.3 | 0.026 | 0.032 | >0.999 |
| ACQ-5 | 1.23 ± 1.04 | 0.54 ± 0.86 | 0.45 ± 0.65 | 0.192 | 0.059 | >0.999 |
| Eosinophils, cells/μL | 450.0 (350.0–560.0) | 65.0 (50.0–87.5) | 50.0 (35.0–160.0) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.695 |
| Metabolites | Moieties | δ 1H (ppm) and Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|
| Aspartate | αCH | 3.85 (dd) |
| βCH | 2.67 (dd) | |
| β’CH3 | 2.82 (dd) | |
| Acetate | βCH3 | 1.90 (s) |
| Acetoin | CH | 4.42 (q) |
| CH3 | 2.21 (s) | |
| CH3 | 1.38 (d) | |
| Alanine | βCH3 | 1.46 (d) |
| CH | 3.77 (m) | |
| Ethanol | CH3 | 1.17 (t) |
| CH2 | 3.64 (q) | |
| Glutamate | αCH | 3.79 (t) |
| β,β’CH | 2.03 (dt) | |
| γCH2 | 2.30 (t) | |
| Glutamine | αCH | 3.77 (t) |
| βCH2 | 2.10 (c) | |
| γCH2 | 2.40 (c) | |
| Isoleucine | αCH | 3.68 (m) |
| βCH | 1.95 (m) | |
| γ’CH3 | 1.00 (m) | |
| δCH3 | 0.92 (t) | |
| Isopropanol | CH | 4.02 (m) |
| (CH3)2 | 1.18 (d) | |
| Lactate | βCH3 | 1.34 (d) |
| αCH | 4.11 (q) | |
| Leucine | αCH | 3.60 (t) |
| βCH2 | 1.70 (m) | |
| δ,δ’CH3 | 0.95 (d) | |
| Propionate | αCH2 | 2.19 (q) |
| βCH3 | 1.06 (t) | |
| Pyruvate | CH3 | 2.36 (s) |
| Threonine | αCH | 3.62 (d) |
| βCH | 4.22 (m) | |
| γCH3 | 1.33 (d) | |
| Tyrosine | C3,5H, Ring | 6.88 (d) |
| C2,6H, Ring | 7.17 (d) | |
| Valine | αCH | 3.60 (d) |
| βCH | 2.26 (m) | |
| γCH3 | 0.98 (d) | |
| γ’CH3 | 1.03 (d) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maniscalco, M.; Ambrosino, P.; Candia, C.; Di Stefano, A.; Gnemmi, I.; Zappa, M.; Ambrosino, N.; Visca, D.; Motta, A. Cytokine and Metabolomic Signatures of Mepolizumab Response Across Upper and Lower Airway Compartments in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: An Exploratory Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111704
Maniscalco M, Ambrosino P, Candia C, Di Stefano A, Gnemmi I, Zappa M, Ambrosino N, Visca D, Motta A. Cytokine and Metabolomic Signatures of Mepolizumab Response Across Upper and Lower Airway Compartments in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: An Exploratory Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2025; 18(11):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111704
Chicago/Turabian StyleManiscalco, Mauro, Pasquale Ambrosino, Claudio Candia, Antonino Di Stefano, Isabella Gnemmi, Martina Zappa, Nicolino Ambrosino, Dina Visca, and Andrea Motta. 2025. "Cytokine and Metabolomic Signatures of Mepolizumab Response Across Upper and Lower Airway Compartments in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: An Exploratory Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 18, no. 11: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111704
APA StyleManiscalco, M., Ambrosino, P., Candia, C., Di Stefano, A., Gnemmi, I., Zappa, M., Ambrosino, N., Visca, D., & Motta, A. (2025). Cytokine and Metabolomic Signatures of Mepolizumab Response Across Upper and Lower Airway Compartments in Severe Eosinophilic Asthma: An Exploratory Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 18(11), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18111704









