Cell Culture Evaluation Hints Widely Available HIV Drugs Are Primed for Success if Repurposed for HTLV-1 Prevention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
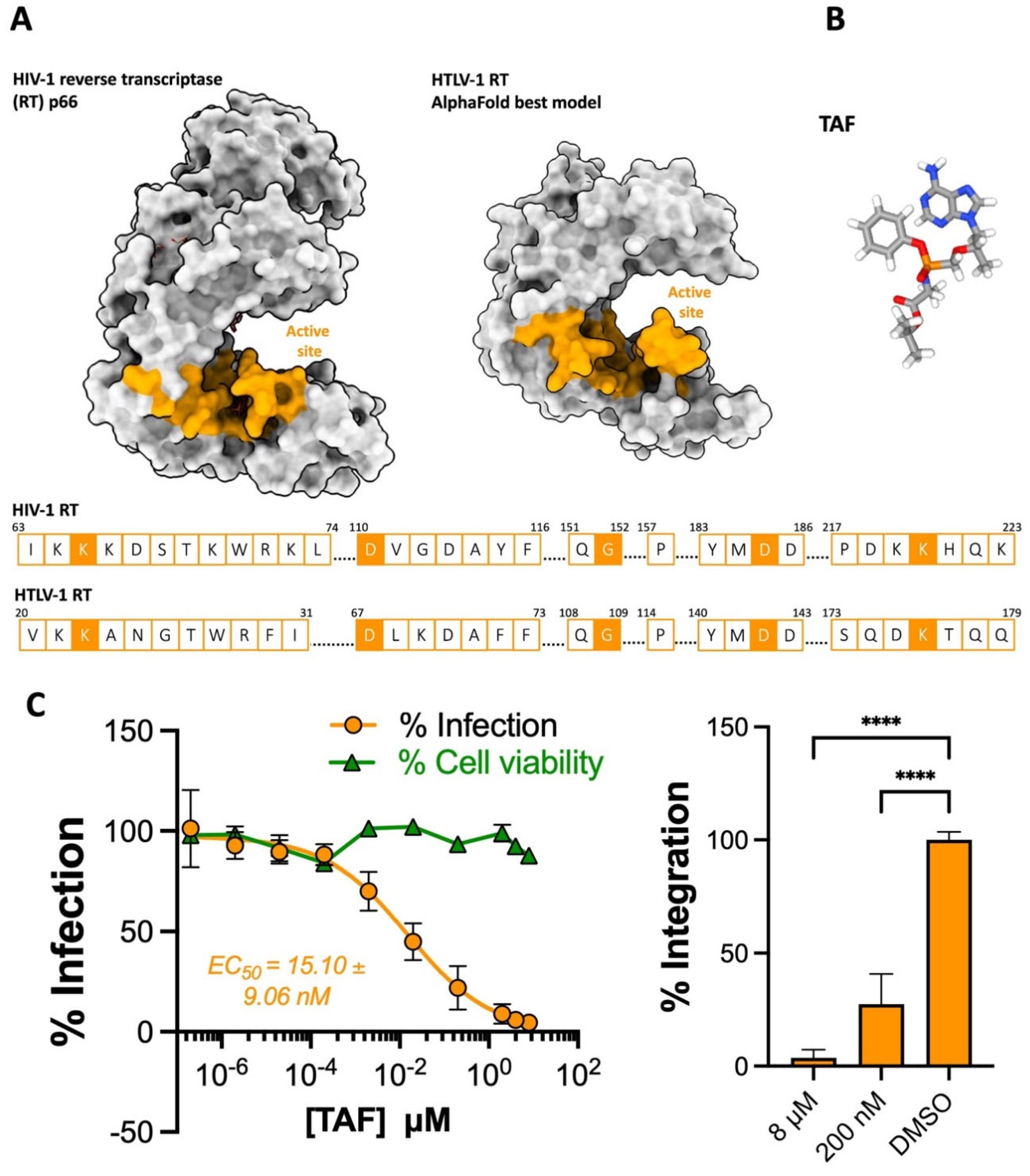
2.1. The NRTI Prodrug Tenofovir Alafenamide Inhibits HTLV-1 Transmission
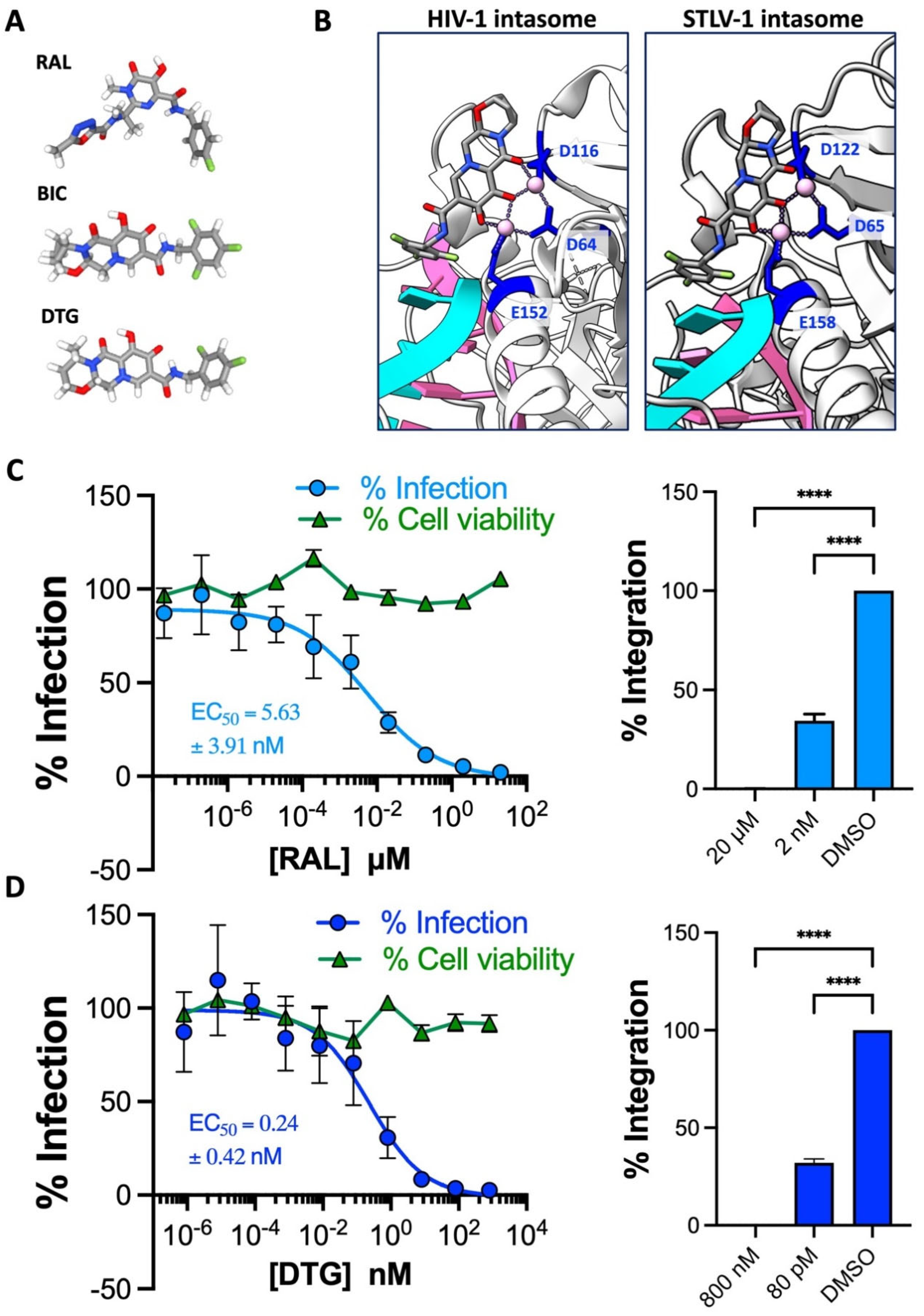
2.2. The 2nd Generation INSTI Dolutegravir Potently Inhibits HTLV-1 Transmission
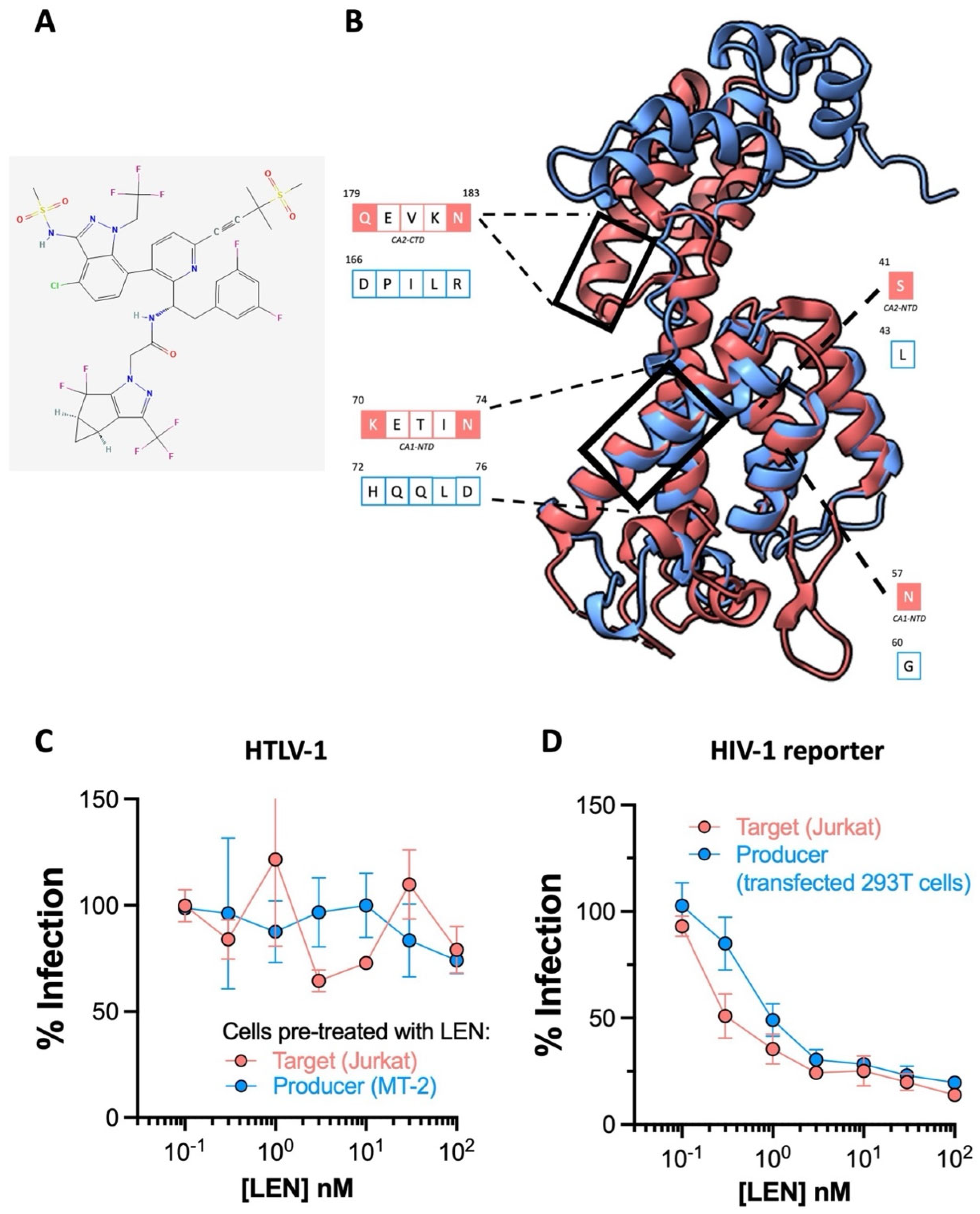
2.3. The HIV-1 Capsid Inhibitor Lenacapavir Is Inactive against HTLV-1
2.4. TAF-, RAL- and DTG-Treated Primary CD4+ T Cells Resist HTLV-1 Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Structure Visualisation and Homology Modelling
4.3. Cell Treatment and Cell-to-Cell Infection of HTLV-1
4.4. Quantifying the HTLV-1 Proviral Load and Integration
4.5. Production and Infection with HIV GFP Reporter Virus
4.6. HTLV-1 Infection of Primary CD4+ T Cells by Co-Culture with MT2 Cells
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutchings, M.; Truman, A.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, M.C.; Mellors, J.W. The transformation of HIV therapy: One pill once a day. Antivir. Ther. 2022, 27, 13596535211062396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futsch, N.; Mahieux, R.; Dutartre, H. HTLV-1, the Other Pathogenic Yet Neglected Human Retrovirus: From Transmission to Therapeutic Treatment. Viruses 2017, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, C.R.M.; Araujo, A.; Yamano, Y.; Taylor, G.P. HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie Skalka, A. The Retroviral Enzymes. Artic. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994, 63, 133–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maertens, G.N.; Engelman, A.N.; Cherepanov, P. Structure and function of retroviral integrase. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herschhorn, A.; Hizi, A. Retroviral reverse transcriptases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2717–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockbaum, G.J.; Henes, M.; Talledge, N.; Rusere, L.N.; Kosovrasti, K.; Nalivaika, E.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Ali, A.; Mansky, L.M.; Kurt Yilmaz, N.; et al. Inhibiting HTLV-1 Protease: A Viable Antiviral Target. ACS Chem. Biol. 2021, 16, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barski, M.S.; Minnell, J.J.; Maertens, G.N. Inhibition of HTLV-1 infection by HIV-1 first-and second-generation integrase strand transfer inhibitors. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 475549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barski, M.S.; Vanzo, T.; Zhao, X.Z.; Smith, S.J.; Ballandras-Colas, A.; Cronin, N.B.; Pye, V.E.; Hughes, S.H.; Burke, T.R.; Cherepanov, P.; et al. Structural basis for the inhibition of HTLV-1 integration inferred from cryo-EM deltaretroviral intasome structures. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneiderman, B.S.; Barski, M.S.; Maertens, G.N. Cabotegravir, the Long-Acting Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitor, Potently Inhibits Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 Transmission in vitro. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 889621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegulam, M.E.; Ratner, L. Integrase inhibitors effective against human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.A.; Lloyd, P.A.; Mcdonald, S.; Wykoff, J.; Derse, D. Susceptibility of Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Type I to Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestrieri, E.; Sciortino, M.T.; Mastino, A.; Macchi, B. Protective effect of the acyclic nucleoside phosphonate tenofovir toward human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type 1 infection of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2005, 68, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockman, S.; Brummel, S.S.; Ziemba, L.; Stranix-Chibanda, L.; McCarthy, K.; Coletti, A.; Jean-Philippe, P.; Johnston, B.; Krotje, C.; Fairlie, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dolutegravir with emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide fumarate or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, and efavirenz, emtricitabine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate HIV antiretroviral therapy regimens started in pregnancy (IMPAACT 2010/VESTED): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 1276–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Paik, J. Lenacapavir: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prather, C.; Lee, A.; Yen, C. Lenacapavir: A first-in-class capsid inhibitor for the treatment of highly treatment-resistant HIV. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2022, 82, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuske, S.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Clark, A.D.; Ding, J.; Naeger, L.K.; White, K.L.; Miller, M.D.; Gibbs, C.S.; Boyer, P.L.; Clark, P.; et al. Structures of HIV-1 RT–DNA complexes before and after incorporation of the anti-AIDS drug tenofovir. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, J.M.; Fan, H. The Discovery of Reverse Transcriptase. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, N. The efficacy and safety of tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in antiretroviral regimens for HIV-1 therapy: Meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callebaut, C.; Stepan, G.; Tian, Y.; Miller, M.D. In Vitro Virology Profile of Tenofovir Alafenamide, a Novel Oral Prodrug of Tenofovir with Improved Antiviral Activity Compared to That of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherepanov, P.; Maertens, G.N.; Hare, S. Structural insights into the retroviral DNA integration apparatus. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hare, S.; Gupta, S.S.; Valkov, E.; Engelman, A.; Cherepanov, P. Retroviral intasome assembly and inhibition of DNA strand transfer. Nature 2010, 464, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, D.O.; Li, M.; Craigie, R.; Lyumkis, D. Retroviral integrase: Structure, mechanism, and inhibition. Enzymes 2021, 50, 249–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Passos, D.O.; Li, M.; Jóźwik, I.K.; Zhao, X.Z.; Santos-Martins, D.; Yang, R.; Smith, S.J.; Jeon, Y.; Forli, S.; Hughes, S.H.; et al. Structural basis for strand-transfer inhibitor binding to HIV intasomes. Science 2020, 367, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazuda, D.; Blau, C.U.; Felock, P.; Hastings, J.; Pramanik, B.; Wolfe, A.; Bushman, F.; Farnet, C.; Goetz, M.; Williams, M.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Novel Human Immunodeficiency Virus Integrase Inhibitors from Fungal Metabolites. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 1999, 10, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espeseth, A.S.; Felock, P.; Wolfe, A.; Witmer, M.; Grobler, J.; Anthony, N.; Egbertson, M.; Melamed, J.Y.; Young, S.; Hamill, T.; et al. HIV-1 integrase inhibitors that compete with the target DNA substrate define a unique strand transfer conformation for integrase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11244–11249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summa, V.; Petrocchi, A.; Bonelli, F.; Crescenzi, B.; Donghi, M.; Ferrara, M.; Fiore, F.; Gardelli, C.; Paz, O.G.; Hazuda, D.J.; et al. Discovery of raltegravir, a potent, selective orally bioavailable HIV-integrase inhibitor for the treatment of HIV-AIDS infection. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5843–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zash, R.; Makhema, J.; Shapiro, R.L. Neural-Tube Defects with Dolutegravir Treatment from the Time of Conception. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchana, L.; Pariente, A.; Pannier, E.; Tsatsaris, V.; Treluyer, J.-M. Dolutegravir and neural tube defects: A new insight. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 405–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saladini, F.; Giannini, A.; Boccuto, A.; Dragoni, F.; Appendino, A.; Albanesi, E.; Vicenti, I.; Zazzi, M. Comparable in vitro activities of second-generation HIV-1 integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) on HIV-1 clinical isolates with INSTI resistance mutations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temereanca, A.; Ruta, S. Strategies to overcome HIV drug resistance-current and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1133407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, J.O.; Rhee, M.S.; Tse, W.C.; Zheng, J.; Somoza, J.R.; Rowe, W.; Begley, R.; Chiu, A.; Mulato, A.; Hansen, D.; et al. Clinical targeting of HIV capsid protein with a long-acting small molecule. Nature 2020, 584, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bester, S.M.; Wei, G.; Zhao, H.; Adu-Ampratwum, D.; Iqbal, N.; Courouble, V.V.; Francis, A.C.; Annamalai, A.S.; Singh, P.K.; Shkriabai, N.; et al. Structural and mechanistic bases for a potent HIV-1 capsid inhibitor. Science 2020, 370, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.E.; Le Sage, V.; Lakdawala, S.S. Viral and host heterogeneity and their effects on the viral life cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 19, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouse, B.T.; Sehrawat, S. Immunity and immunopathology to viruses: What decides the outcome? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.M.; Shreffler, W.G.; Christopher Love, J. Revealing the heterogeneity of CD4 1 T cells through single-cell transcriptomics. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, A.K.; Aristodemou, A.; Giang, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Bangham, C.R.; Taylor, G.P.; Dominguez-Villar, M. HTLV-1 induces an inflammatory CD4+CD8+ T cell population in HTLV-1–associated myelopathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 9, e173738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnell, D.; Baeten, J.M.; Bumpus, N.N.; Brantley, J.; Bangsberg, D.R.; Haberer, J.E.; Mujugira, A.; Mugo, N.; Ndase, P.; Hendrix, C.; et al. HIV protective efficacy and correlates of tenofovir blood concentrations in a clinical trial of PrEP for HIV prevention. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2014, 66, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podany, A.T.; Scarsi, K.K.; Pham, M.M.; Fletcher, C.V. Comparative Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of HIV-1 Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors: An Updated Review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 59, 1085–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierhout, G.; McGregor, S.; Gessain, A.; Einsiedel, L.; Martinello, M.; Kaldor, J. Association between HTLV-1 infection and adverse health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosadas, C.; Assone, T.; Yamashita, M.; Adonis, A.; Puccioni-Sohler, M.; Santos, M.; Paiva, A.; Casseb, J.; Oliveira, A.C.; Taylor, G.P. Health state utility values in people living with HTLV-1 and in patients with HAM/TSP: The impact of a neglected disease on the quality of life. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P.S.; Harrington, W., Jr.; Kaplan, M.H.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Bennett, J.M.; Liebman, H.A.; Bernstein-Singer, M.; Espina, B.M.; Cabral, L.; Allen, S.; et al. Treatment of Adult T-Cell Leukemia–Lymphoma with a Combination of Interferon Alfa and Zidovudine. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1744–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livier Ermine, O.H.; Idier Ouscary, D.B.; Ntoine Essain, A.G.; Ascal Urlure, P.T.; Eronique Eblond, V.L.; Athalie Ranck, N.F.; Gnes Uzyn -v Eil, A.B.; Ernard Io, B.R.; Lisabeth Acintyre, E.M.; Rançois Reyfus, F.D.; et al. Treatment of Adult T-Cell Leukemia-Lymphoma with Zidovudine and Interferon Alfa. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1749–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, A.; Bangham, C.R.M.; Casseb, J.; Gotuzzo, E.; Jacobson, S.; Martin, F.; Penalva De Oliveira, A.; Puccioni-Sohler, M.; Taylor, G.P.; Yamano, Y. Management of HAM/TSP. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, D.; Taylor, G.P. HTLV-1 Transmission and HIV Pre-exposure Prophylaxis: A Scoping Review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 881547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, P.V.; Cassar, O.; Gessain, A. Molecular epidemiology, genetic variability and evolution of HTLV-1 with special emphasis on African genotypes. Retrovirology 2019, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deodhar, S.; Sillman, B.; Bade, A.N.; Avedissian, S.N.; Podany, A.T.; McMillan, J.E.M.; Gautam, N.; Hanson, B.; Dyavar Shetty, B.L.; Szlachetka, A.; et al. Transformation of dolutegravir into an ultra-long-acting parenteral prodrug formulation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro-Proietti, A.B.F.; Amaranto-Damasio, M.S.; Leal-Horiguchi, C.F.; Bastos, R.H.C.; Seabra-Freitas, G.; Borowiak, D.R.; Ribeiro, M.A.; Proietti, F.A.; Ferreira, A.S.D.; Martins, M.L. Mother-to-Child Transmission of Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Viruses-1/2: What We Know, and What Are the Gaps in Understanding and Preventing This Route of Infection. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2014, 3, S24–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, A.; Hashemy, I.; Avval, F.Z.; Soleimani, A.; Rafatpanah, H.; Rezaee, S.A.; Griffith, R.; Mashkani, B. Molecular targeting for treatment of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 infection. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 109, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millen, S.; Thoma-Kress, A.K. Milk Transmission of HTLV-1 and the Need for Innovative Prevention Strategies. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 867147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, K.A.; Wang, H.; Slaughter, A.; Feng, L.; Kessl, J.J.; Koh, Y.; Wang, W. Allosteric integrase inhibitor potency is determined through the inhibition of HIV-1 particle maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8690–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.R.; Dinh, T.; Levintov, L.; Annamalai, A.S.; Rey, J.S.; Briganti, L.; Cook, N.J.; Pye, V.E.; Taylor, I.A.; Kim, K.; et al. The Drug-Induced Interface That Drives HIV-1 Integrase Hypermultimerization and Loss of Function. mBio 2023, 14, e0356022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardiota, N.; Jaberolansar, N.; Lackenby, J.A.; Chappell, K.J.; O’Donnell, J.S. HTLV-1 reverse transcriptase homology model provides structural basis for sensitivity to existing nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, A.G.; Witkover, A.; Melamed, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Cook, L.B.M.; Fields, P.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R.M. T Cell Receptor Vβ Staining Identifies the Malignant Clone in Adult T cell Leukemia and Reveals Killing of Leukemia Cells by Autologous CD8 + T cells. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1006030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lairmore, M.; Jason, J.; Hartley, T.; Khabbaz, R.; De, B.; Evatt, B. Absence of Human T-Cell Lymphotropic Virus Type I Coinfection in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Hemophilic Men. Blood 1989, 74, 2596–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alais, S.; Mahieux, R.; Dutartre, H. Viral Source-Independent High Susceptibility of Dendritic Cells to Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Infection Compared to That of T Lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 10580–10590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Maele, B.; De Rijck, J.; De Clercq, E.; Debyser, Z. Impact of the Central Polypurine Tract on the Kinetics of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Vector Transduction. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 4685–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulm, J.W.; Perron, M.; Sodroski, J.C.; Mulligan, R. Complex determinants within the Moloney murine leukemia virus capsid modulate susceptibility of the virus to Fv1 and Ref1-mediated restriction. Virology 2007, 363, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Tanaka, Y.; Tozawa, H. Monoclonal Antibody Defining Tax1 Protein of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type-I. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1989, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Public Health Impact and Implications for Future Actions: Who Global Consultation on The Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiang, M.; Jones, G.S.; Goldsmith, J.; Mulato, A.; Hansen, D.; Kan, E.; Tsai, L.; Bam, R.A.; Stepan, G.; Stray, K.M.; et al. Antiviral activity of bictegravir (GS-9883), a novel potent HIV-1 integrase strand transfer inhibitor with an improved resistance profile. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 7086–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.A.; Raugi, D.N.; Wu, V.H.; Zavala, C.G.; Song, J.; Diallo, K.M.; Seydi, M.; Gottlieb, G.S. Comparison of the antiviral activity of bictegravir against HIV-1 and HIV-2 isolates and integrase inhibitor-resistant HIV-2 mutants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.A.; He, G.X.; Eisenberg, E.; Cihlar, T.; Swaminathan, S.; Mulato, A.; Cundy, K.C. Selective intracellular activation of a novel prodrug of the human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase inhibitor tenofovir leads to preferential distribution and accumulation in lymphatic tissue. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margot, N.; Ram, R.; Abram, M.; Haubrich, R.; Callebaut, C. Antiviral activity of tenofovir alafenamide against HIV-1 with thymidine analog-associated mutations and M184V. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ANTIRETROVIRAL | HTLV-1 EC50 (nM) | HIV-1 EC50 (nM) |
|---|---|---|
| INSTI: | ||
| Raltegravir | 6.42 ± 4.24 [9] | 9.4 ± 1.4 [64] |
| Elvitegravir | 9.57 ± 5.54 [9] | 2.4 ± 0.9 [64] |
| Dolutegravir | 0.25 ± 0.42 | 1.4 ± 0.3 [64] |
| Bictegravir | 0.30 ± 0.17 [9] | 1.6 ± 0.4 [64] |
| Cabotegravir | 0.56 ± 0.26 [11] | 1.5 ± 0.3 [65] |
| NRTI: | ||
| Tenofovir disproxil fumarate | 17.78 ± 7.16 [9] | 50 ± 30 [66] |
| Tenofovir alafenamide | 15.10 ± 9.06 | 5.1 ± 2 [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalemera, M.D.; Maher, A.K.; Dominguez-Villar, M.; Maertens, G.N. Cell Culture Evaluation Hints Widely Available HIV Drugs Are Primed for Success if Repurposed for HTLV-1 Prevention. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060730
Kalemera MD, Maher AK, Dominguez-Villar M, Maertens GN. Cell Culture Evaluation Hints Widely Available HIV Drugs Are Primed for Success if Repurposed for HTLV-1 Prevention. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(6):730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060730
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalemera, Mphatso D., Allison K. Maher, Margarita Dominguez-Villar, and Goedele N. Maertens. 2024. "Cell Culture Evaluation Hints Widely Available HIV Drugs Are Primed for Success if Repurposed for HTLV-1 Prevention" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 6: 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060730
APA StyleKalemera, M. D., Maher, A. K., Dominguez-Villar, M., & Maertens, G. N. (2024). Cell Culture Evaluation Hints Widely Available HIV Drugs Are Primed for Success if Repurposed for HTLV-1 Prevention. Pharmaceuticals, 17(6), 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17060730







